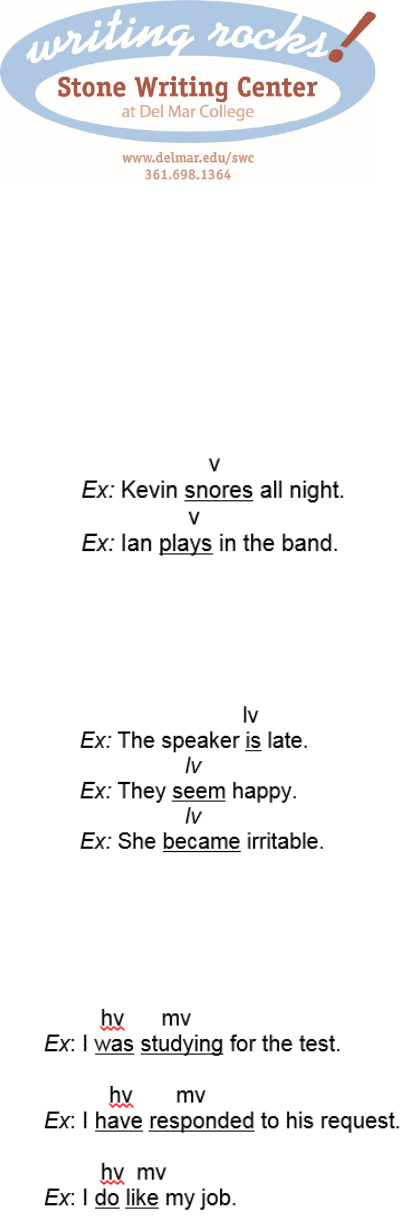
Verbs and Verb Tense
What is a Verb?
A verb is the word in a sentence that tells what the subject does, that links the subject to
another word that describes it, or that joins with another verb. There are three kinds of
verbs: action, linking, and helping.
Three Kinds of Verbs:
1. Action. These verbs tell what action the subject performs.
Linking. These verbs connect (link) the subject to another word or words that describe
the subject. Linking verbs show no action. Common linking verbs are am, are, is, was,
were, seem, and become.
2. Helping. These verbs join with another verb. The helping verb is often a form of be,
have, or do. Together, the helping verb and the main verb are called a complete
verb.

What is Verb Tense?
Verb tense tells when the action of a sentence occurred: in the present, in the past, or in
the future. Verbs change their forms or use helping verbs to indicate different tenses.
Ex. of present tense: Caitlin kicks the soccer ball.
Ex. of past tense: Caitlin kicked the soccer ball.
Ex. of future tense: Caitlin will kick the soccer ball.
Rules for Regular Verbs:
Many verbs in English are regular verbs; their forms follow standard rules.
1. Present Tense. This tense is used for actions that are currently happening. Use the
-s ending on the verb when the subject is he, she, or it. Use no ending on the verb
for all other subjects.
Ex: He/She/It jumps. (-s ending)
Ex: I/You/We/They jump. (no ending)
2. Past Tense. This tense is used for actions that have already happened. An -ed
ending is needed on the verb.
Ex: He jumped. (ed ending)
3. Future Tense. This tense is used for actions that have not happened yet. Add the
helping verb "will" before the main verb. The form of the main verb remains the
same, i.e., no ending.
Ex: She will jump. ("will" helping verb)
Rules for Irregular Verbs:
Irregular verbs do not follow the regular pattern for verb forms. Please refer to the
"Irregular Verbs" handout.
Remember:
A verb is the word in a sentence that tells what the subject does, that links the subject to
another word that describes it, or that joins with another verb. There are three kinds of
verbs: action, linking, and helping.
Verb tense tells when the action of a sentence occurred: in the present, in the past, or in
the future. Verbs change their form or use helping verbs to indicate different tenses.
