T H E S E C R E TA RY O F T H E N AVY
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
Department of the Navy
Correspondence
Manual
P u b l i s h e d B y
T H E S E C R E T A R Y O F T H E N A V Y

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
i
FOREWORD
This manual is issued to prescribe uniform standards for the management and preparation of
correspondence and is applicable to all commands and activities of the Department of the Navy.
The following directives and manuals are cancelled:
SECNAVINST 5216.5D of 29 Aug 96
Secretary of the Navy Writing Guide 14 Apr 06
Local supplements to amplify this manual may be issued and inserted as chapter 13. A local
supplement shall not contradict or repeat information contained in this manual.
Forward recommended changes to this manual to:
OFFICE OF THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
DIRECTOR OF ADMINISTRATION
1000 NAVY PENTAGON ROOM 4D652
WASHINGTON DC 20350-1000
Copies of this manual may be obtained through normal publications channels, Department of the
Navy IssuancesWeb site; or from the Marine Corps Publications Electronic Library Online Web
site. This manual is approved for authorized registered users and distribution is unlimited.
Authorized registered users may obtain copies of the publications from:
UNDER SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
PUBLICATIONS MANAGEMENT BRANCH
1000 NAVY PENTAGON ROOM 5D773
WASHINGTON DC 20350-1000
Robert O. Work
Under Secretary of the Navy
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
ii
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE
FOREWORD i
TABLE OF CONTENTS iii
REFERENCES ix
CHAPTER 1 – CORRESPONDENCE MANAGEMENT
1-1 – Objective and Responsibilities 1-1
1 Objective 1-1
2 Responsibilities 1-1
CHAPTER 2 – CORRESPONDENCE STANDARDS AND PROCEDURES
2-1 – Correspondence Standards and Procedures 2-1
1 General 2-1
2 North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) 2-1
2-2 – Procedures 2-1
1 Correspond Through Channels 2-1
2 Take Advantage of Correspondence Shortcuts 2-3
3 Coordination 2-4
4 Submit Finished Products for Signature 2-4
5 Signature Authority 2-4
6 Signature Stamps 2-5
7 Incoming Correspondence Controls 2-5
8 Replies to Correspondence 2-6
9 Outgoing Correspondence Controls 2-7
10 Limit Use of Social Security Numbers (SSN) 2-7
11 Identifying Navy and Marine Corps Personnel 2-7
12 Letterhead Stationery 2-8
13 Enclosures 2-9
14 Copies 2-10
15 Expressing Military Time 2-11
16 Expressing Dates 2-11
17 Abbreviations and Acronyms 2-11
18 Punctuating, Capitalizing, Spelling, Hyphenating, and Separating
Words
2-12
19 Proofreading 2-13
20 Typeface 2-12
21 Color of Ink 2-13

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
iv
TITLE PAGE
CHAPTER 3 - ELECTRONIC RECORDS
3-1 - General 3-1
3-2 - Procedures 3-1
1 Creation 3-1
2 Maintenance 3-2
3 Restrictions 3-2
4 Disposition 3-3
CHAPTER 4 - ELECTRONIC MAIL
4-1 - General 4-1
4-2 - Procedures 4-1
1 Managing E-Mail 4-1
2 Formal Correspondence 4-1
3 Informal Correspondence 4-2
4 Security and Privacy Issues 4-2
5 Records Management 4-2
6 Digital Signatures 4-2
CHAPTER 5 - FACSIMILE TRANSMISSION SERVICES
5-1 - General 5-1
5-2 - Procedures 5-1
1 Managing Facsimile Services 5-1
2 Security and Privacy Issues 5-1
3 Records Management 5-2
CHAPTER 6 – POSTAL STANDARDS
6-1 - General 6-1
6-2 - Procedures 6-1
1 Choosing the Right Size Envelope or Container 6-1
2 Sources of Address Information 6-1
3 Delivery and Return Address Formats 6-2
4 Mail Classifications 6-3
5 Mail Markings 6-3
Figure 6-1 Folding Techniques 6-4
Figure 6-2 Standard Address Abbreviations 6-5
Figure 6-3 State/Territory Abbreviations 6-6
Figure 6-4 Envelope Addressing Standards 6-7
CHAPTER 7 – CORRESPONDENCE FORMAT

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
v
TITLE PAGE
7-1 - Requirements 7-1
7-2 - Format 7-1
1 Margins 7-1
2 Sender’s Symbols 7-1
3 Classified Correspondence 7-2
4 For Official Use Only 7-3
5 “From:” Line 7-3
6 “To:” Line 7-4
7 “Via:” Line 7-5
8 Subject Line 7-5
9 Reference Line 7-6
10 Enclosure Line 7-10
11 Text 7-12
12 Paragraphs 7-12
13 Signature Line 7-13
14 “Copy To:” Line 7-14
15 Identifying Second and Later Pages 7-15
16 Page Numbering 7-15
17 Correspondence Package Assembly 7-15
18 Tabbing a Correspondence Package 7-15
Figure 7-1 Standard Letter – First Page 7-16
Figure 7-2 Standard Letter – Second Page 7-17
Figure 7-3 Standard Letter – Window – Envelope 7-18
Figure 7-4 Joint Letter 7-19
Figure 7-5 Standard Letter with Classification Markings – First Page 7-20
Figure 7-6 Standard Letter with Classification Markings – Second Page 7-21
Figure 7-7 Standard Letter with FOUO Markings 7-22
Figure 7-8 Paragraph Structure Format 7-23
Figure 7-9 Assembly of a Standard Correspondence Package Using Stacking
Method
7-24
Figure 7-10 Tabbing Correspondence Packages 7-25
CHAPTER 8 – MULTIPLE-ADDRESS LETTER
8-1 - General 8-1
8-2 - Listing Addressees 8-1
1 Using a “To:” Line Only 8-1
2 Using a “Distribution:” Line Only 8-1
3 Using Both a “To:” Line and “Distribution:” Line 8-1
8-3 - Preparing and Signing Copies 8-1
8-4 - Assembly of Multiple-Address Letters 8-1
Figure 8-1 Multiple-Address Letter Using “To: Line 8-2
Figure 8-2 Multiple-Address Letter Using “Distribution:” Line 8-3
Figure 8-3 Multiple-Address Letter Using a “To:” and “Distribution:” Line 8-4

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
vi
TITLE PAGE
Figure 8-4 Assembly of a Multiple-Address Letter 8-5
CHAPTER 9 – ENDORSEMENTS
9-1 - General 9-1
9-2 - Format 9-1
1 Endorsement Line 9-1
2 “Via:” Line 9-1
3 Adding References 9-1
4 Adding Enclosures 9-1
5 “Copy To:” Addressees 9-2
6 Forwarding Your Endorsement and Copies 9-2
7 Assembly of an Endorsement 9-2
Figure 9-1 New Page Endorsement 9-3
Figure 9-2 Assembly of an Endorsement 9-4
CHAPTER 10 – MEMORANDUMS
10-1 - General 10-1
10-2 - Formats 10-1
1 Memorandum For The Record 10-1
2 From-To Memorandum 10-1
3 Plain-Paper Memorandum 10-1
4 Letterhead Memorandum 10-1
5 Decision Memorandum 10-2
6 Memorandum of Agreement or Memorandum of Understanding 10-2
Figure 10-1 Memorandum For The Record 10-3
Figure 10-2 Printed “From-To” Memorandum 10-4
Figure 10-3 Plain-Paper Memorandum 10-5
Figure 10-4 Letterhead Memorandum 10-6
Figure 10-5 Memorandum of Agreement 10-7
Figure 10-6 Memorandum of Understanding – First Page 10-8
Figure 10-7 Memorandum of Understanding – Second Page 10-9
CHAPTER 11 – BUSINESS LETTERS
11-1 - General 11-1
11-2 - Parts of a Business Letter and Format 11-1
1 Identification Symbols 11-1
2 Inside Address 11-1
3 Attention Line 11-2
4 Salutation Line 11-2
5 Subject Line 11-2
6 Body of the Letter 11-2
7 References and Enclosures 11-3
8 Complimentary Close 11-3

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
vii
TITLE PAGE
9 Signature Line 11-3
10 Enclosure Line 11-3
11 Separate Mailing 11-3
12 “Copy To:” Line 11-4
13 Outgoing Copies 11-4
14 Identifying Second and Succeeding Pages 11-4
15 Numbering Pages 11-4
Figure 11-1 Business Letter Paragraph Formats 11-5
Figure 11-2 Business Letter – First Page 11-6
Figure 11-3 Business Letter – Second Page 11-7
Figure 11-4 Business Letter For Window Envelopes 11-8
Figure 11-5 Business Letter With An “Attention” Line 11-9
Figure 11-6 Short Business Letter 11-10
CHAPTER 12 - EXECUTIVE CORRESPONDENCE
12-1 - General 12-1
12-2 - Processes 12-1
1 Correspondence Management 12-1
2 Assigning Action to Incoming Correspondence 12-1
3 Routing Changes 12-2
4 Due Dates 12-2
5 Extensions 12-2
6 Interim 12-2
7 Distribution 12-3
12-3 - General Guidelines for Preparing a Letter 12-3
1 Stationery 12-3
2 Format 12-4
3 Date Line 12-5
4 Complimentary Closing 12-5
5 Page Numbering 12-6
6 Congressional Committees or Subcommittees Correspondence 12-6
12 -4 - General Guidelines for Preparing a Memorandum 12-6
1 Action or Information Memorandums 12-6
2 Package Assembly 12-7
Figure 12-1 SD Form 391 – DoD Correspondence Action Report 12-9
Figure 12-2 Sample Interim Response to Incoming Correspondence 12-10
Figure 12-3 Sample Interim Response for Congressional Correspondence 12-11
Figure 12-4 Congressional Response, One Chairperson 12-12
Figure 12-5 Congressional Response, Two Chairpersons 12-13
Figure 12-6 Congressional Response, to a Chairman of a Select Committee 12-14
Figure 12-7 Flag Stationery (8 ½ x 11), Secretary of the Navy 12-15
Figure 12-8 Flag Stationery (5x7), Chief of Naval Operations 12-16
Figure 12-9 Action Memorandum 12-17

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
viii
TITLE PAGE
Figure 12-10 Information Memorandum 12-18
Figure 12-11 Coordination Page 12-19
Figure 12-12 Standard Memorandum For 12-20
APPENDIX A – Military Models of Address A-1
APPENDIX B– Civilian Models of Address B-1
APPENDIX C – Stationary Requirements C-1
APPENDIX D – Forms and Envelops D-1
APPENDIX E – Index E-1
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
ix
REFERENCES
REFERENCE TITLE
NATO Standardization
Agreement (STANAG)
Number 2066
Format and Abbreviations in NATO Standardization Agreement
SNDL (OPNAVNOTE 5400) Standard Navy Distribution List
MCO 5216.19 Administration Action (AA) Form (NAVMC 10274, Rev. 3-86)
SECNAVINST 5730.5J Mission, Function, and Responsibilities of the Office of
Legislative Affairs and Procedures for Handling Legislative
Affairs and Congressional Relations
EO 9397 Executive Order 9397
MCO 5215.1K Marine Corps Directives Management Program
GPOStyle Manual U.S. Government Printing Office Style Manual
SECNAV M-5210.1 Department of the Navy Records Management Program
SECNAV M-5210.2 Department of the Navy Standard Subject Identification Code
(SSIC) Manual
SECNAV M-5510.36 Department of the Navy Information Security Program Manual
SECNAVINST 5720.42F Department of the Navy Freedom of Information Act (FOIA)
5 U.S.C. §552a Privacy Act of 1974
28 U.S.C.§1074 Federal Rules of Evidence
SECNAVINST 5000.37 Provision of the Department of the Navy Documentary Material
SECNAVINST5239.3B Department of the Navy Information Assurance Policy
USD P&R Memo Policy for Digital Signature Functionality and Acceptance, of 12
December 2006
OPNAVINST 5218.7B Navy Official Mail Management Instructions
DoD Manual 4000.25-6-M Department of Defense Activity Address Directory (DoDAAD)
SECNAVINST 5211.5E Department of the Navy Privacy Act (PA) Program
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
x
SECNAVINST 5430.7Q Assignment of Responsibilities and Authorities in the Office of
theSecretary of the Navy
MCO P5600.31G Marine Corps Publications and Printing Regulations
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
xi
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
1-1
CHAPTER 1
Correspondence Management
1-1 Objective and Responsibilities
1. Objective. To prescribe uniform standards for the management and preparation of
correspondence throughout the Department of the Navy (DON).
2. Responsibilities
a. The Secretary of the Navy (SECNAV) will administer the DON Correspondence
Management Program and coordinate proposed changes to this manual with the Chief of Naval
Operations (CNO) and the Commandant of the Marine Corps (CMC).
b. CNO and CMC will administer the Correspondence Management Program within the
Navy and Marine Corps, respectively.
c. Commanding Officers and Heads of Activities will establish a correspondence
management program based on the requirements and guidance of this manual and ensure that:
(1) Correspondence is screened, controlled, reviewed, and answered accordingly.
(2) Correspondence practices are reviewed periodically to improve products and
procedures.
(3) The most economical communications media and techniques available are used.
(4) Only essential correspondence is produced.
d. Administration Officers will:
(1) Screen incoming correspondence, assign action offices and due dates, and indicate
any required concurrences.
(2) Review outgoing correspondence for correct format and ensure prescribed
procedures are followed.
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
1-2
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
1-3

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-1
CHAPTER 2
Correspondence Standards and Procedures
2-1 Correspondence Standards
1. General. To a large degree, the image and effectiveness of the DON is portrayed by the tone,
quality, and responsiveness of correspondence. Properly written correspondence that clearly and
succinctly establishes a position, correctly and completely answers questions, and conveys the
right message, all aid in the effective management and operation of the DON. In order to
achieve this, correspondence must:
a. Be neat in appearance, correctly formatted, error free, and grammatically correct. With
the use of computers and advanced word processing software, the long-accepted practice of
allowing legible “pen and ink” changes to a piece of correspondence is no longer acceptable. All
correspondence shall be free of typographical errors and technically correctbefore it is signed.
b. Avoid stereotyping men and women based on gender. Use pronouns and titles that are
gender neutral.
c. Do not write unless you must. A conversation in person, by telephone, or by electronic
mail (e-mail) often saves two letters - the one you would have written and the other person’s
response. Conversations are often better than correspondence for working out details. Confirm
your conversation with a short memorandum (also referred to as “memo”) to the other person or
a “Memorandum For The Record” if issues of importance or policy are agreed upon during the
conversation.
d. Always include a point of contact, return telephone number, and e-mail address when
your correspondence might prompt a reply or inquiry.
2. North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). When writing to other NATO Forces use the
format and abbreviations in NATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG) Number 2066,
Layout for Military Correspondence. STANAG Number 2066 is stocked by the Naval Aviation
Supply Office (ASO), 5801 Tabor Avenue, Philadelphia, PA 19120-5099.
2-2 Procedures
1. Correspondence through Channels
a. Use the Chain of Command. Follow your chain of command when corresponding on
substantive matters such as command decisions, policy issues, and official recommendations.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-2
(1) Address communications directly to the top official of the organization concerned
by title. Show the action office by including the code or person’s title in parentheses
immediately after the activity’s name.
(2) Address correspondence concerning policy, management decisions, or other
important matters via the chain of command or those commands, activities, oroffices who have
cognizance over the subject matter. This keeps intermediate commands informed and allows
them to comment or approve as necessary.
(3) A “Via” addressee will always forward official correspondence with an
endorsement. The endorsement may be as simple as using the term “forwarded” when no
opinion or comment is needed. A “Via” addressee may elect to take final action, divert the
routing, or return the correspondence to the originator with appropriate explanation (chapter 9).
(4) When there is no time to send important correspondence “Via” the chain of
command and still meet a deadline, you may:
(a) Send correspondence via the chain of command, with an advance copy to the
“To” addressee. To alert all addressees to this unusual routing, repeat the action addressee by
Standard Navy Distribution List (SNDL) short title in a “Copy to:” line and include the term
“(advance)” after the short title.
EXAMPLE:
Copy to:
CNO (advance)
JAG
(b) Send correspondence directly to the “To” addressee with a concurrent copy to
each intermediate addressee. Include in the text a statement like this: “A copy of this
correspondence has been mailed directly to all addressees. Request “Via” addressees forward
your endorsements directly to....” Additionally, include the “Via” addressees by SNDL short
titles in the “Copy to:” line.
b. Variations to Corresponding Through the Chain of Command
(1) Authorized subordinates of different activities may correspond directly with each
other on routine matters.
(2) List any cognizant addressees in the “Via:” line when it is determined that they
should see a letter before it reaches the “to” addressee.
(3) Include intermediate commands as “Copy to” addressees instead of “Via”
addressees if you want them to see certain routine correspondence without having to endorse it.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-3
(4) Bypass intermediate commands that clearly have no interest in a letter’s content
and no requirement to comment or act.
c. Individuals Writing to Higher Authority
(1) Navy Personnel. When writing to higher authority on a personal matter affecting
the command, prepare your letter on plain bond paper in standard letter format. Examples
include requests for retirement or resignation. Address the letter to the higher authority and send
it “Via” your chain of command. Each “Via” addressee will prepare an endorsement and
forward the correspondence to the next addressee.
(2) Marine Corps Personnel. Use NAVMC 10274, Administrative Action (AA) Form,
as prescribed in Marine Corps Order 5216.19 (MCO 5216.19).
2. Take Advantage of Correspondence Shortcuts
a. Facsimile Machines. Facsimile machines provide a fast and reliable means for sending
official correspondence (chapter 5).
b. E-mail. You can use e-mail for formal and informal correspondence. See chapter 4 for
additional information.
c. Window Envelopes. Window envelopes eliminate the cost of addressing envelopes and
the risk of putting letters in the wrong envelopes. To format letters for use with window
envelopes see page 7-18. It should be noted that the window-envelope letter format has no
“From:” line, so every copy that goes outside your activity must be on letterhead to show its
origin. Do not use a window envelope for material that:
(1) Is classified.
(2) Involves national security.
(3) Is of a personal nature.
(4) Is sent to high-level officials.
d. Form and Guide Letters. Periodically review correspondence for recurring, routine
topics that can be addressed with a standard response. This standard response can be developed
into a form or format letter to save time. See“Form and Guide Letters, an Information
Resources Management Handbook by the General Services Administration (GSA).” This

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-4
handbook is available through the Military Standard Requisitioning and Issue Procedures
(MILSTRIP) system.
(1) Use form letters when possible for routine matters that require no personal touch.
Avoid form letters when expressing sympathy, apology, or appreciation.
(2) Guide letters are pre-drafted standard letters that contain paragraphs that you may
pick from to best fit the situation for which you are writing. Type or print them individually so
they seem personally composed.
3. Coordination. Coordination is a critical step in the processing of outgoing correspondence.
In order to ensure that a proper response or original letter is prepared, the originator will need to
decide who needs to concur before the letter is signed. The originator will obtain appropriate
concurrences, resolve major differences, and arrange for any needed retyping.
a. Always coordinate during the drafting stage, before the correspondence is put into final
form and submitted for signature. Ensure all coordination inputs are retained and filed with the
file copy of the signed correspondence.
b. Limit reviews to only those offices that have a substantial interest in the topic of the
correspondence.
c. In some cases, coordination can be done quickly and informally. Discussions by phone
or in person or coordination via e-mail are often more efficient than formal written coordination,
especially if a letter is brief and routine.
4. Submit Finished Products for Signature. Normally, submit correspondence for signature in
final form. Use double-spaced drafts only when changes are likely, perhaps because a subject is
controversial or a policy statement needs precise wording. Early guidance to writers about a
signer’s preferences will reduce the frequency of changes.
5. Signature Authority. Delegate signature authority to the lowest legal and practical level.
a. What the Commander/Commanding Officer/Officer in Charge Must Sign. The
commander/commanding officer/officer in charge must personally sign documents that:
(1) Establish policy.
(2) Center on the command’s mission or efficiency and are addressed to higher
authority.
(3) Deal with certain aspects of military justice.
(4) Are required by law or regulation.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-5
b. Delegation of Signature Authority
(1) Delegation of signature authority may be made to military and civilian subordinates.
All delegations of signature authority will be made in writing and signed by the person
delegating the authority. If the delegation of authority is provided for in a directive, indicate this
delegation in a generic reference to a billet or position title. For each individual that the
delegation of authority applies, a letter so delegating that authority to the individual, by name,
will be prepared. Include a brief outline of the scope of delegation, and if appropriate, authorize
the individual to further delegate or sub-delegate the authority. In the absence of specific sub-
delegation guidance, delegated signature authority shall not be sub-delegated.
(2) An individual who signs correspondence under delegated authority will use the
term “By direction” typed below their name when signing documents under this delegated
authority.
EXAMPLE: I. M. FRUSTER
By direction
c. Acting for the Commander/Commanding Officer/Officer in Charge. In the absence of
thecommander/commanding officer/officer in charge, and where specifically authorized by law
or regulation, an officer who temporarily succeeds to command shall sign official
correspondence with the term “Acting” typed below their name.
EXAMPLE: J. CANNON
Acting
d. Acting for an Official Who Signs by Title. When the signatory has been formally, but
temporarily, appointed to replace an official who signs correspondence by title rather than “By
direction,” the word “Acting” is typed below the typed name.
EXAMPLE: J. IVES
Deputy
Acting
e. Signing “For” an Absent Official. When a piece of correspondence is in final form and
the official that would normally sign the correspondence is unable to do so, it is permissible to
have the correspondence signed “for.” Rather than modifying the document to replace the
signature line, an individual already delegated signature authority may sign the correspondence
and hand write the term “for” before the typed name of the regular signing official. This method
should be used only when a delay would fail to meet a crucial deadline.
6. Signature Stamps/Electronic Signatures. Commanders/commanding officers/officers in
charge or civilian equivalents may authorize the use of a signature stamp or an electronic

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-6
signature that replicates his or her signature where personal signing of a piece of correspondence
is impractical or the correspondence is of a routine nature. Personnel authorized to use a
signature stamp of someone else’s signature shall pen their initials next to each signature they
stamp to authenticate the stamp. Safeguard signature stamps from unauthorized use.
7. Incoming Correspondence Controls. Controlled correspondence is correspondence that
requires some type of action, requires a response, or has long-term reference value.
a. Date Stamp. Date stamp all incoming controlled correspondence on the day it arrives at
the command. It is a good practice to date stamp all incoming correspondence, not just
controlled correspondence.
b. Restrict Assignment of Controls. Assign controls to only incoming mail that requires a
response or has long-term reference value. Incoming action correspondence should be routed
directly from the correspondence management office to the action office. If necessary, send
duplicate copies to intermediate or coordinating offices.
c. Track Correspondence. Use OPNAV 5211/7 Correspondence/Document Control Card
to track the status of controlled correspondence routed for action.
8. Replies to Correspondence
a. Controlled Correspondence. Take prompt action on incoming correspondence that
requires action or a response. Normally, correspondence should be answered within 10 working
days or as prescribed by the immediate superior in command or by the tasking authority for the
response.
b. Congressional Correspondence
(1) Reply directly to members of Congress if they contact your activity on routine and
non-policy matters. When doubt exists over whether to release certain information, contact the
Office of Legislative Affairs for guidance.
(2) Correspondence from Congress shall be answered within 5 workdays of receipt. If
a response cannot be provided within 5 days, send an interim response that acknowledges receipt
of the correspondence and provides an estimated date when a final response will be sent. Send
the original response plus an additional copy when responding to a Congressional inquiry. Also,
send a blind copy of your final reply and substantive interim replies to:
CHIEF OF LEGISLATIVE AFFAIRS
NAVY DEPARTMENT
WASHINGTON DC 20350-1000

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-7
(3) The opening line in the text of the response should read, “Thank you for your letter
of [date], concerning [issue].” NOTE: The date format is month day, year (i.e., June 19, 2009).
(4) When responding to a Congressional request, the closing line in the text of the
response should read, “If I may be of any further assistance, please let me know.”
(5) For more information on the handling of naval legislative affairs refer to
SECNAVINST 5730.5J, Mission, Function, and Responsibilities of the Office of Legislative
Affairs and Procedures for Handling Legislative Affairs and Congressional Relations.
c. Freedom of Information and Privacy Act Requests. Answer Freedom of Information
Act (FOIA) requests and Privacy Act requests within 10 workdays of receipt. If a response
cannot be provided within 10 days, send an interim response that acknowledges receipt of the
correspondence and provides an estimated date when a final response will be sent. Ensure all
responses for FOIA information and Privacy Act information is reviewed by the base or
command FOIA and Privacy Act coordinator or the base or command judge advocate general.
9. Outgoing Correspondence Controls
a. Impose Realistic Due Dates. When sending correspondence that requires a response or
has action for the recipient, put a “reply by” due date in your letter only when you have a
compelling reason to receive a response back by that date. When choosing the due date, allow
time for your letter to make its way up the chain of command to be signed, time for it to reach
the people who will take action, time for them to gather information and prepare a response, and
time for the response to make it back to you.
b. Sign and Mail. Correspondence should be signed at intervals throughout the day. This
method will keep signed correspondence from lingering overnight before it goes out. Arrange
for a special trip to the mailroom for important correspondence that is signed after the last
regular messenger and before the last mail dispatch. Alert the mailroom to the urgency.
c. Trace Late Replies. If a response is not received within a reasonable amount of time or
by the directed “reply by” date, follow up with the command that the correspondence was sent to.
There are two methods to follow up on late correspondence:
(1) Forward a copy of the original correspondence with the term “TRACER – [date]”
written or stamped in the top margin.
(2) Contact the command that the correspondence was originally sent to by phone or
via e-mail.
10. Limit Use of Social Security Numbers (SSN)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-8
a. Corresponding Within the Department of Defense (DoD). Limit the use of the SSN of a
Service member or civilian employee of the DoD unless essential for identification and
authorized for use by authority of Executive Order 9397.
b. Corresponding Outside of the DoD. Never use or provide the SSN of a Service member
or civilian employee of the DoD when corresponding with an individual or agency outside of the
DoD. The only exception to this policy is if the individual involved gives written permission to
release his or her SSN, or the incoming correspondence you are responding to includes the
individual’s SSN.
11. Identifying Navy and Marine Corps Personnel. This information is generally included in the
subject line of the standard letter and in the first paragraph of the business letter. Fully identify
the member when you first mention him or her. In later references to the member, simply use the
rank or rate and last name. Do not capitalize every letter of a member's last name, except in the
subject and signature lines. Capitalize the words "Sailor," "Marine" and “Service member” when
referring to members of the U.S. Navy or U.S. Marine Corps.
a. Navy Requirements
(1) Abbreviated rank for officers and rate and warfare designator for enlisted personnel
(e.g., AD1(AW), BM2(SW), CSSN(SS)) with no space between rank/rate and warfare designator,
(2) first name, middle initial if any, and last name,
(3) staff corps abbreviation (if any),
(4) branch of service,
(5) the last four digits of the SSN, and
(6) the designator for an officer.
EXAMPLE: RADM Michelle L. Howard, USN, XXX-XX-1234/1110
CDR Gilbert L. Williams, USN, XXX-XX-1234/6410
LCDR Sean L. Bartlett, SC, USNR, XXX-XX-1234/3100
MC2 Kevin O’Brien, USN, XXX-XX-1234
b. Marine Corps Requirements
(1) Unabbreviated grade,
(2) first name, middle initial if any, and last name,
(3) the last four digits of the SSN without hyphens,

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-9
(4) military occupational specialty, and
(5) branch of service.
EXAMPLES: Major Mary J. Smith XXX XX 1234/0430 USMC
Captain Brent R. Sowders XXX XX 1234/0202 USMCR
Sergeant Lauren M. Ferrell XXX XX 1234/0411 USMC
12. Letterhead Stationery. The standard size paper for all official letterhead stationery is 8-1/2
inches by 11 inches. Preprinted or computer generated letterhead is acceptable. Use white, plain
bond paper. Refer to appendix C for stationery usage guidelines.
a. Use of Letterhead Stationery
(1) Use command letterhead stationery only for official matters of the command.
Printing names of officials on letterhead stationery is prohibited. When using letterhead
stationery, the “From:” line will always contain the title of the activity head and command name.
The “From:” line will never contain the name of an individual.
(2) Use command letterhead stationery when corresponding as a member of a DON
approved board or committee. Indicate the letter is from the signing official by using the board
orcommittee title in the “From:” line.
(3) Do not use letterhead as personal stationery. For example, CDR Baker, captain of
the ship’s basketball team, may not use it for matters involving the team.
(4) The use of letterhead is authorized for commanders, commanding officers,officer’s
in charge and directors or those who have signature authority for commands that are represented
in theSNDL.
b. Letterhead Format
(1) Letterhead stationery of the DON shall bear a one-inch in diameter seal of the DoD.
Other seals, emblems, insignia, decorative or emblematic devices shall not be incorporated. See
appendix C for additional guidance.
(2) The letterhead begins with "DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY" centered on the
fourth line from the top of the page. Center the activity's name, address, and nine-digit zip code
on succeeding lines. Do not use abbreviations or punctuation in the address.
EXAMPLE:
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-10
CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS
2000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON DC 20350-2000
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
HEADQUARTERS UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS
3000 MARINE CORPS PENTAGON
WASHINGTON DC 20350-3000
(3) The address lines of letterhead for Navy activities shall conform to the SNDL
address for that activity. Marine Corps activities shall comply with current Marine Corps
Directives Management Program, MCO 5215.1K.
13. Enclosures. An enclosure can prevent a letter from becoming too detailed. Try to keep
letters short, down to one page whenever possible, and use enclosures for lengthy explanations
that cannot be avoided. An enclosure may include such things as manuals, publications,
photocopies of correspondence, charts, etc.
a. Marking Enclosures. Enclosures must be marked on the first page; however, you may
mark all pages. An enclosure marking goes in the lower right corner, whether the text is
arranged normally or lengthwise. Type “Enclosure” and its number in parentheses. You may
use pencil so an addressee can remove the marking easily should the enclosure be needed for
some later purpose. Arrange the typed pages lengthwise so they can be read from the right.
EXAMPLE: (First page. The enclosure line is right justified.)
Enclosure (1)
EXAMPLE: (Succeeding pages. The enclosure line is right justified and the page number is
centered and 2 lines below the enclosure line.
Enclosure (1)
2
b. Numbering Pages of Enclosures. Number only second and later pages. If you have
several different enclosures, number the pages of each independently.
c. Sending Enclosures Separately. When size, weight, or other factors prevent sending an
enclosure with a letter, send it separately and type “(sep cover)” after the enclosure’s description.
EXAMPLE: Encl: (1) SECNAV M-5216.5 (sep cover)
14. Copies. Keep in mind the following when reproducing paper copies:
a. Use two-sided photocopying whenever possible.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-11
b. If your letter must have “Copy to” addressees, include only those with a genuine need to
know. Be realistic.
c. Avoid “just in case” copies and whole batches of 10 or 15 copies when you can pinpoint
the quantity precisely.
d. Make the most of the “read, initial, and date” approach to information copies within
your command. Circulate a single copy among those who need to read the document, and have
them pass it on.
e. Distribute copies by e-mail or put information copies on your local area network. If
using either of these two methods, distribute the copy in approved FAM software application
format.
f. Avoid redundant file copies. Keep official command files in one central location to
simplify access. Retain one official file copy of all outgoing correspondence.
15. Expressing Military Time. Express military time in four digits based on the 24-hour clock.
The time range is 0001 to 2400. The first two digits are the hour after midnight and the last two
digits are the minutes. Do not use a colon to separate the hour from the minutes.
EXAMPLE: 6:30 am in civilian time is 0630 in military time
3:45 pm in civilian time is 1545 in military time
16. Expressing Dates. There are three date formats allowed for use in Navy correspondence.
The formats and their use are described below. In all date formats, the day is represented as one
ortwo digits (do not use a zero preceding the numerals 1 through 9when the day is single digit).
The abbreviated format and the standard format are used when corresponding with other military
organizations. The civilian format is used when corresponding with Congress, civilian agencies
and businesses, and individuals.
a. Abbreviated Format. The abbreviated format is only used as part of the sender’s
symbol, or in the absence of the sender’s symbol, as the date for the letter. The format consists
of a 1- or 2-digit day, the 3-letter abbreviation for the month, and the 2-digit abbreviated year.
EXAMPLE: 1 Feb 09
25 Mar 09
b. Standard Format. The standard format is only used in the text of correspondence. The
format consists of a 1- or 2-digit day, the spelled out month, and the 4-digit year.
EXAMPLE: 5 April 2009
17 November 2009

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-12
c. Civilian Format. The civilian format is used as both the date of the correspondence and
in the text. Do not use an abbreviated civilian format. The format consists of the spelled out
month, the 1- or 2-digit day, a comma, and the 4-digit year.
EXAMPLE: May 5, 2009
December 25, 2009
17. Abbreviations and Acronyms. Abbreviations and acronyms are one of the most misused
aspects of correspondence. When using abbreviations and acronyms the writer must consider the
audience. What is familiar to you may not be familiar to the reader. The use of abbreviations
and acronyms tends to detract from the content of the correspondence by causing the reader to
have to pause, remember what the abbreviation or acronym means, then continue reading.
a. Established abbreviations are acceptable in all but the most formal writing (e.g.,
directives). Some examples include “Mr.” (Mister), “Ms.” (Miss), “e.g”. (for example), “i.e.”
(that is), and “etc.” (et cetera),“sonar” (sound navigation and ranging), and “radar” (radio
detecting and ranging).
b. Do not abbreviate military titles in the text of press reports.
c. If you use an acronym, spell it out first and then define the acronym in parentheses.
After the initial definition, the acronym may be used without explanation.
EXAMPLE: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
SECOND USE: The NATO is holding a meeting in March.
18. Punctuating, Capitalizing, Spelling, Hyphenation, and Separating Words. For examples on
punctuating, capitalizing, and spelling, refer to the Government Printing Office (GPO) Style
Manual. Most word processors eliminate the need to divide words. If correspondence is
produced manually, use the Word Division Book, a supplement to the GPO Style Manual or your
dictionary for help with dividing words. Use hyphens sparingly; a slightly uneven right margin
is preferred over hyphenated words. Never hyphenate a word at the end of a page. Avoid
separating words in close association such as a person’s name, abbreviated titles, and dates. If a
full name must be split, do so after the first name, when there is no initial, or after the initial.
Never split the name of a ship.
19. Proofreading. Proofread correspondence several times and check it carefully to ensure it has
been correctly prepared. A recommended method of proofreading is:
a. Check format first. Do not read for substance until you are sure everything else is right.
b. Look at the framework of the correspondence:
(1) Is letterhead correct/straight?

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-13
(2) Are the margins 1 inch?
(3) Are page numbers centered 1/2 inch from the bottom of the page?
(4) Is there enough/too much room for the date?
(5) Are paragraphs aligned/indented properly?
(6) Are paragraphs sequentially numbered/lettered?
(7) Are enclosure markings correct?
(8) Are more than three lines hyphenated, and are successive lines hyphenated?
(9) Is there enough room for the signature line?
c. Next, look for typographical errors, misspelled words, improper punctuation, improper
spacing, and incorrect grammar:
(1) Read slowly. Look at each word separately.
(2) Look up all hyphenated words you are not sure of.
(3) When using a word processing program, use spell check and grammar check;
however, never solely depend on this method. Utilize spell check and grammar check as an
additional tool.
d. Lastly, read for content.
20. Typeface. For text, use 10 to 12 point font size. Courier New 12-point is the preferred font
style and size for official correspondence (e.g., directives), but fonts like Arial, Times New
Roman or CG Times may be used for informal correspondence. Bold, underline, script, and
italics may be used for occasional emphasis, but not for entire letters.
21. Color of Ink. Only use black or blue-black ink to sign correspondence. Photocopiers pick
up these colors well.
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-14
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
2-15
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
3-1
CHAPTER 3
Electronic Records
3-1 General. An electronic record is any information that is recorded in a form that only a
computer can process and that satisfies the definition of a Federal record (SECNAV M-5210.1
Department of the Navy Records Management Manual, part I, paragraph 17) -- information
made or received in connection with the transaction of public business and preserved or
appropriate for presentation as evidence of the organization, functions, policies, decisions,
operations, etc, or because of its information value. Electronic documents, including e-mails, are
Federal records to the same extent as their paper counterparts would be. In practice, there is no
difference between managing electronic and paper records.
3-2 Procedures
1. Creation. Before a document is created on an electronic records system that will maintain
the official file copy, each document must be identified sufficiently to enable authorized
personnel to retrieve, protect, and dispose of it. When feasible, create the electronic record
within a DoD certified electronic records management application (RMA), such as Hewlett
Packard Total Records Information Management (TRIM) Context, using procedures established
for record creation within the RMA.
a. Naming Files. Naming electronic files resembles labeling paper file folders. When
naming subdirectories or “folders,” use the Standard Subject Identification Code (SSIC)
(SECNAVM-5210.2, Department of the Navy Standard Subject Identification Code (SSIC)
Manual) and any logical combination of alphanumeric characters permitted by the operating
system and descriptive of the series. For example, a subdirectory labeled 5240 would show
“General Administration and Management” files containing correspondence on industrial
methods that are destroyed after5 years. Identifying information for each document may include
the office of origin, the SSIC, key words for retrieval, addressee (if any), signature, originator,
date, authorized disposition (coded or otherwise), and security classification (if applicable).
Ensure that electronically maintained records can be correlated with related records on paper,
microform, or other media. When creating within, or transferring to, an approved RMA, comply
with specific naming, identification and tracking requirements established for the RMA.
b. Labeling Disks or Tapes. Adhere to the following procedures when it is not practicable
to create or maintain an electronic record within an approved RMA (for example, none is
available to the activity). To prevent damage to the disk or tape, write the information on the
label before you put it on the disk. Never erase information on a label once it is in place. When
affixing a label to a disk, choose an area away from all holes. Be sure labels identify the
hardware and software that will read the information, security classification (if applicable), the
SSIC, description, and disposition instructions. Do not affix external labels to Compact Disk –
Read Only Memory disks.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
3-2
2. Maintenance
a. Electronic records that are not created within an approved RMA should be transferred
to one as soon as practicable within 6 months of the record creation date. However, electronic
records whose disposition schedule permits destruction within 6 months of the date the record
was created need not be transferred to, or maintained within, an approved RMA if destroyed
within that 6-month period. Once an electronic record is within an approved RMA, adhere to the
maintenance requirements established for that RMA. Pending transfer into an approved RMA,
or when an approved RMA is not available, adhere to the procedures in paragraphs 2b through
2d below to protect electronic records.
b. Make backup copies of files at least once a week. Do not use floppy disks for long-term
storage of permanent or unscheduled records because floppy disks are vulnerable to mishandling
and data loss is common. When disks are the only backup medium available, use them for
temporary storage only. If possible, store the backup media in a separate area from the source
data to provide additional insurance against data loss. As noted in the preceding paragraph, these
backup procedures are not required for an electronic record maintained in an approved RMA.
c. Equipment failure and power outages are additional causes of data loss. Save files
frequently. When using a word processing program, set the auto save feature to every 5 minutes.
d. Store frequently used files conveniently for immediate access. Store less frequently
used files on tape, disk, or other media.
e. Manage, use, and delete classified information under the guidelines contained in
SECNAV M-5510.36, Department of the Navy Information Security Program. Be sure the
records you maintain are necessary and pertinent. Appropriately destroy non-essential records.
3. Restrictions
a. FOIA. TheFOIA allows any person to seek access to records held by a Government
agency. See SECNAVINST 5720.42F, Department of the Navy Freedom of Information Act
(FOIA),, for information on processing requests.
b. Privacy Act. The purpose of the Privacy Act of 1974 (5 U.S.C. §552a) is to balance the
Government’s need to maintain information about individuals with the rights of individuals to be
protected against unwarranted invasion of their privacy stemming from Federal agencies’
collection, maintenance, use, and disclosure of personal information about them. As such, limit
access to personal data and other restricted documents.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
3-3
c. Electronic Records as Evidence. Under the Federal Rules of Evidence (28 U.S.C.
§1074), electronic records are acceptable to the courts as evidence; however, each judge is free
to dismiss evidence on the basis of the court’s independent evaluation.
4. Disposition
a. Identify and schedule electronic versions of official records for disposition. Refer to
SECNAV M-5210.1.
b. Erase electronic files used only as backup files or that only contain passing information
once a hard copy has been generated or when the data is no longer needed.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
4-1
CHAPTER 4
Electronic Mail
4-1 General. E-mail lets individuals and activities exchange information by computer. You
may use it for informal communications in place of telephone calls or to transmit formal
correspondence. The Defense Data Network must be used for long-haul data communications
support, unless the host system is waived. Whatever you send by e-mail must be for official
Government business or for authorized purposes (as defined by the Joint Ethics Regulations
section 2-301 (DoD 5500.7-R)). E-mails are subject to legal discovery , therefore, care should
be taken to ensure e-mails are created and managed appropriately per SECNAVINST 5000.37.
4-2 Procedures
1. Managing E-mail. Activities will establish procedures for accessing and managing e-mail.
Among other things, they must:
a. Prohibit users from sharing mailboxes or passwords.
b. Encourage users to check their mailboxes frequently, but at least twice a day.
c. If you are absent for more than 3 days, ensure you annotate that in your automated e-
mail response. Provide a point of contact for e-mails requiring immediate response.
d. Provide for periodic review of e-mail files to purge, retain, or file as appropriate.
2. Formal Correspondence. Activity heads may authorize the use of e-mail to correspond
formally. Your delegation of signature authority for correspondence is also your release
authority for e-mail. When corresponding formally:
a. Use standard DON correspondence formats including an SSIC, serial number, date, and
signature authority.
b. Type in your letterhead information to identify the originating organization.
c. Use “/s/” in place of the signature.
EXAMPLE: /s/
C. PALMERONE
By direction
d. Follow your chain of command.
e. Transmit only from your authorized e-mail address.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
4-2
f. Request acknowledgement of receipt in the original communication when it is required.
Acknowledgement may be via e-mail.
g. Keep a copy of any formal correspondence sent by e-mail as your activity’s file copy
(see paragraph 5 below).
3. Informal Correspondence. There are no specific guidelines for informal correspondence;
however, keep it brief, use good taste, and observe traditional customs and courtesies. Do not
use a complete signature line to identify the sender, but the sender must be fully identified. You
may omit the signature lineentirely if your computer automatically identifies the sender.
4. Security and Privacy Issues
a. Do not send classified information by e-mail unless the system, including the network,
is protected for the highest level of classified information you aresending. Refer to
SECNAVINST5239.3B,, Department of the Navy Information Assurance Policy, for additional
guidance on automated information system security.
b. Follow established guidelines and exercise good judgment in transmitting sensitive
information such as:
(1) Government information that would be of value to an adversary.
(2) Pre-award contractual information, budget information, or authorization data.
(3) Non-government information such as trade secrets the Government agreed to keep
confidential.
(4) “For Official Use Only” information.
(5) Information governed by the Privacy Act of 1974.
5. Records Management. E-mail lacks the built-in records management controls of the Naval
Computer and Telecommunications System (NCTS) and the Automatic Digital Network
(AUTODIN). An e-mail can be considered a record (see chapter 3, section 3-1, of this manual
for the definition of an electronic record). Activities will control the creation, use, maintenance,
and disposition of e-mail records. Follow chapter 3 of this manual and SECNAV M-5210.1.
6. Digital Signatures. DON policy for digital signatures continues to evolve. However, two
uses of digital signature have been established. In accordance with SECNAVINST 5239.3B,
commanders of DON organizations shall ensure e-mail messages requiring either message
integrity or non-repudiation are digitally signed using DoD Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). All
e-mail containing an attachment or embedded active content must be digitally signed. Per DoD
guidance (USD P&R Memo, Policy for Digital Signature Functionality and Acceptance, of 12
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
4-3
December 2006), digital signatures will be recognized and accepted as valid for all human
resource management documents.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
5-1
CHAPTER 5
Facsimile Transmission Services
5-1 General. Facsimile machines provide a rapid and reliable alternative to the various mail
systems for the transmission of documents. Whatever you send by facsimile must be for official
Government business or for authorized purposes (as defined by the Joint Ethics Regulations
section 2-301 (DoD 5500.7-R.)).
5-2 Procedures
1. Managing Facsimile Services
a. Limit transmissions requiring use of long distance services to time sensitive
communications only.
b. Send multiple documents that are going to the same location in batches rather than one
at a time.
c. Facsimile transmission cover sheets add to the cost of each transmission. Keep cover
sheets as simple and functional as possible with only essential information. Avoid graphics and
heavy gray or black areas because they slow transmissions and increase costs.
(1) Instead of using separate cover sheets when sending material via facsimile
transmission, commands are encouraged to procure a rubber stamp (1inch by 4 inches)
formatted as follows:
(2) Place the stamp at either the top, bottom, or side margin. This will eliminate the
need for an extra page and save money, material, labor, energy, and time.
2. Security and Privacy Issues
a. Do not transmit classified data via unsecured facsimile equipment. See SECNAV M-
5510.36 and SECNAVINST 5211.5E, Department of the Navy Privacy Act (PA) Program, for
more information regarding transmitting classified material via facsimile equipment.
b. Follow established guidelines and exercise good judgment in transmitting sensitive
information. See page 4-2, paragraph 4.
FROM:______________________
TO:________________________
ACTIVITY:___________________ ACTIVITY___________________
PHONE #:__________________ PHONE #:__________________
# OF PAGES:_______________ # OF PAGES:_______________
Replace thermal paper facsimiles that are records with photocopies.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
5-2
3. Records Management
a. Correspondence transmitted via a facsimile machine has the same authority as if it were
the original. Normally the original is retained by the sending activity. The sender determines
whether the correspondence is important enough to forward the original. If the original is
forwarded, the advance copy becomes non-record material and may be destroyed by the
receiving office once the original is received.
b. Activities that receive many official documents via facsimile may need to procure a
rubber stamp such as the one shown below to assist in identifying documents that are to be
retained for record purposes.
c. Some facsimile machines still use thermal paper, which can deteriorate in as little as 6
months. Because of this, thermal paper facsimiles that need to be retained for record purposes
should be photocopied.
ACTION COPY
DO NOT DESTROY

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-1
CHAPTER 6
Postal Standards
6-1 General. This chapter includes U.S. Postal Service (USPS) standards and Navy policies
pertaining to official mail. For additional information, refer to OPNAVINST 5218.7B, Navy
Official Mail Management Instructions.
6-2 Procedures
1. Choosing the Right Size Envelope or Container. Use envelopes or mailing containers only
slightly larger than the material being mailed and of sufficient strength to protect the contents
during the mail handling process. Envelopes should be no smaller than 3 1/2 inches by 5 inches
and no larger than 6 1/8 inches by 11 1/2 inches, if possible. Mail smaller than 3 1/2 inches by 5
inches cannot be mailed. You can send mail that is largerthan 6 1/8 inches by 11 1/2 inches;
however, it must bypass automated equipment and be processed through slower and less efficient
methods. Reduce mailing expenses by following these steps:
a. Use standard letter size (number 10) envelopes whenever possible. Generally,
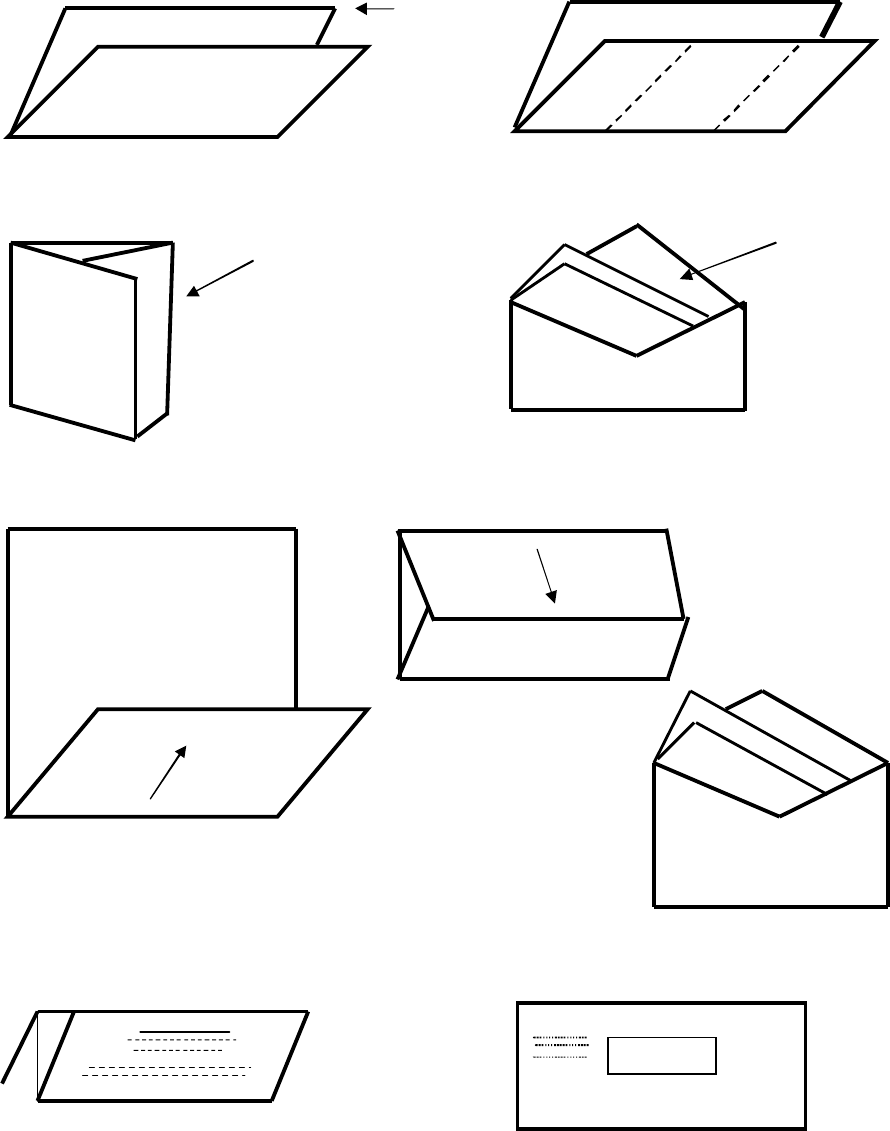
documents with four or less pages should be folded and mailed in a letter size envelope rather
than a larger size envelope. Seefigure 6-1. The USPS automated processing equipment cannot
handle envelopes thicker than 1/4 inch.
b. Use large envelopes for material that cannot be folded (photographs, diplomas,
negatives, and bulk material).
c. Consolidate by class, all mail generated on the same day and destined for the same
addressee.
d. Check with your mailroom for activities/agencies within the local area that are serviced
by couriers, as this requires no postage.
2. Sources of Address Information. Address official Navy mail to the command or activity
addresses in:
a. SNDL, parts 1 and 2.
b. Https://www.manpower.usmc.mil/portal/page?_pageid=278,1&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL
(Active Marine Link, Personal and Family Link, Military Personnel Services Link, Postal Link,
under reference).
c. Department of Defense Activity Address Directory (DoDAAD), DoD Manual 4000.25-
6-M.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-2
3. Delivery and Return Address Formats
a. Requirements
(1) Be sure you have the correct address and use organizational codes whenever
possible.
(2) Type, or print by other mechanical means, the delivery address in uppercase letters.
Use no punctuation except for the hyphen in the ZIP+4 code. Use black or blue-black ribbon or
ink. The return address may be preprinted, typewritten, or rubber stamped.
(3) If available, use the ZIP+4 code and USPS acceptable abbreviations. Figure 6-2 is
a listing of USPS acceptable abbreviations for streets and words that often appear in the names of
places. A listing of acceptable USPS two-letter State and territory abbreviations appears in
figure 6-3.
(4) Do not use print styles that:
(a) Incorporate proportional spacing,
(b) have characters that overlap,
(c) have highly styled characters such as script, italics, artistic, etc., or
(d) have dots that do not touch to form each letter (dot matrix styles).
(5) Limit official mail addresses (both delivery and return) to five lines. Format with a
uniform left margin and a maximum of 47 characters per line, including spaces.
(6) Center the address and single-space each line, blocked one below the other. Do not
indent lines. Leave at least a l-inch margin from the left and right edges of the envelope and at
least 5/8 inch from the bottom of the envelope. The last line of the address should be no lower
than 5/8 inch and no higher than 2 1/4 inches from the bottom of the envelope. Include all
required information within addressee and return addressee areas. Do not type in the margins or
clear area. Do not overlap the return address in the delivery address area. Be careful not to slant
the address. The lines must be parallel to the top and bottom edges of the envelope. Refer to
figure 6-4 for placement and format.
b. Mail Sent Within the DoD. Prepare the address as follows:
(1) Non-address Data Line - First Line (Optional). Use this to address official
correspondence to the official in charge, such as commanding officer, director, commander, etc.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-3
(2) Information/Attention Line - Second Line (Optional). If known, place the name of
the action officer, a specific individual, or section and code here.
(3) Name of Recipient Line - Third Line. Place the activity short title (less the city and
state) here.
(4) Delivery Address Line - Fourth Line. Place either a street address or post office
box number here. Use the word “SUITE” to designate locations within a building. Seefigure 6-
2for acceptable USPS street and places abbreviations.
(5) Post Office Line - Fifth Line. Place the city, state, and ZIP+4 code (in that order)
here. Use the standard two-letter abbreviations shown in figure 6-3.
4. Mail Classifications. Select the class of mail service that meets the security, accountability,
and delivery requirements of the material being shipped at the most economical cost. See
OPNAVINST 5218.7B for the definitions of classes of mail and special supplemental postal
services.
5. Mail Markings. Mark all mail, except first-class mail in a standard letter size (number 10)
envelope, with the class of mail service you desire. Place the marking, i.e., first-class, priority,
etc., in the upper right corner, about 1/4 inch below the postage meter imprint, mail stamp, or
permit imprint. Mailings without a class of mail marking, except those in a number 10 envelope,
will be assumed to contain no first-class material and will be sent as the lowest possible class of
service.
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-4
Number 6-3/4 Envelopes (3 5/8” X 6 ½”)
Number 10 Envelope (4 1/8” X 9 ½”)
Window Envelope
¼”
FIRST, FOLD LEAVING ¼” AT TOP
THEN, FOLD TWICE LEAVING ¼”
AT RIGHT
¼”
¼”

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-5
FIGURE 6-1. FOLDING TECHNIQUES
Academy ACAD Fork FRK Place PL
Agency AGNCY Fort FT Plain PLN
Airport ARPRT Freeway FWY Plains PLNS
Annex ANX Gardens GDNS Plaza PLZ
Arcade ARC Gateway GTWY Point PT
Avenue AVE Glen GLN Port PRT
Bayou BYU Green GRN Prairie PR
Beach BCH Grove GRV Radial RADL
Bend BND Harbor HBR Ranch RNCH
Bluff BLF Haven HVN Rapids RPDS
Bottom BTM Heights HTS Rest RST
Boulevard BLVD High HI Ridge RDG
Branch BR Highway HWY River RIV
Bridge BRG Hill HL Road RD
Brook BRK Hills HLS Row ROW
Burg BG Hollow HOLW Run RUN
Bypass BYP Hospital HOSP Rural R
Camp CP Inlet INLT Saint ST
Canyon CYN Institute INST School SCH
Cape CPE Island IS Shoal SHL
Causeway CSWY Islands ISS Shoals SHLS
Center CTR Isle ISLE Shore SHR
Circle CIR Junction JCT Shores SHRS
Cliffs CLFS Key KY South S
Club CLB Knolls KNLS Spring SPG
College CLG Lake LK Springs SPGS
Corner COR Lakes LKS Spur SPUR
Corners CORS Landing LNDG Square SQ
Court CT Lane LN Station STA
Courts CTS Light LGT Stravenue STRA
Cove CV Loaf LF Stream STRM
Creek CRK Locks LCKS Street ST
Crescent CRES Lodge LDG Summit SMT
Crossing XING Loop LOOP Terrace TER
Dale DL Lower LWR Trace TRCE
Dam DM Manor MNR Track TRAK
Deport DPO Meadows MDWS Trail TRL
Divide DV Mill ML Trailer TRLR
Drive DR Mills MLS Tunnel TUNL
East E Mission MSN Turnpike TPKE
Estates EST Mount MT Union UN
Expressway EXPY Mountain MTN University UNIV
Extension EXT National NAT Valley VLY
Fall FALL Neck NCK Viaduct VIA
Falls FLS North N View VW
Ferry FRY Orchard ORCH Village VLG
Field FLD Oval OVAL Ville VL
Fields FLDS Park PARK Vista VIS
Flats FLT Parkway PKY Walk WALK
Ford FRD Pass PASS Water WTR
Forest FRST Path PATH Way WAY

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-6
Forge FRG Pike PIKE Wells WLS
Pillar PLR Pines PNES West W
FIGURE 6-2. STANDARD ADDRESS ABBREVIATIONS
Alabama AL
Alaska AK
Arizona AZ
Arkansas AR
American Samoa AS
California CA
Colorado CO
Connecticut CT
Delaware DE
District of Columbia DC
Federated States of Micronesia FM
Florida FL
Georgia GA
Guam GU
Hawaii HI
Idaho ID
Illinois IL
Indiana IN
Iowa IA
Kansas KS
Kentucky KY
Louisiana LA
Maine ME
Marshall Island MH
Maryland MD
Massachusetts MA
Michigan MI
Minnesota MN
Mississippi MS
Missouri MO
Montana MT
Nebraska NE
Nevada NV
New Hampshire NH
New Jersey NJ
New Mexico NM
New York NY
North Carolina NC
North Dakota ND
Northern Mariana Island MP
Ohio OH
Oklahoma OK
Oregon OR
Palau PW
Pennsylvania PA
Puerto Rico PR
Rhode Island RI
South Carolina SC
South Dakota SD
Tennessee TN
Texas TX
Utah UT
Vermont VT
Virginia VA
Virgin Islands VI
Washington WA
West Virginia WV
Wisconsin WI
Wyoming WY

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-7
FIGURE 6-3. STATE/TERRITORY ABBREVIATIONS
EXAMPLES:
Ashore
COMMANDING OFFICER (Title of Official in Charge)
ATTN LT JAY BREWER (Action Officer, Organizational Code)
ACTIVITIY SHORT TITLE (Activity Short Title (less City & State)
STREET ADDRESS SUITE # (Street Address, Suite Number)
CITY STATE XXXXX-XXXX (City State ZIP+4)
Afloat
COMMANDING OFFICER (Title of Official in Charge)
ATTN ENS C D SUMMERHILL (Action Officer, Organizational Code)
USS BLUESAIL DDG 00 (Name of Ship or Squadron)
FPO AP 12345-0876 (Fleet Post Office and its number)
Naval Personnel
AMAA JAMES E. SCENNA (Addressee’s Name)
VFX 1 (Name of Ship or Squadron)
FPO AP 12345-0876 (Fleet Post Office and its number)
Personal/Business/Bldg Name
ATTN MR STEVEN HOOD (Personal Name)
AMERICAN AIRLINES CORP (Business Name)
SKYSCRAPER BLDG 2 (Building Name and Number)
12345 S RUNWAY ST (Street Address)
SKYLINE WA 54321-0123 (City State ZIP+4)
Standard Street Address
MR BERNARD G WATSON (Addressee’s Name)
112 45TH AVE E APT 3 (Street Address, Apartment Number)
SAVANNAH GA 23456-5431 (City State ZIP+4)
1 inch 1 inch
2 inch
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
ACTIVITY SHORT TITLE RETURN
ATTN ADDRESS
STREET ADDRESS AREA
CITY STATE XXXXX-XXXX
OFFICIAL BUSINESS
ADDRESS
AREA
COMMANDING OFFICER
ATTN MR SIMPSON CODE 10
ACTIVITY SHORT TITLE
STREET ADDRESS SUITE #
CITY STATE XXXXX-XXXX
POSTAGE
AREA
(a)
USPS USE ONLY
CLEAR AREA 4 ½”
5/8 inch

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
6-8
Foreign Addresses
MRS E BOATWRIGHT (Addressee’s Name)
101 INTERNATIONAL CIR (Street Address)
LONDON WIPGHQ (City, Postal Delivery Zone (If any)
ENGLAND (County Name)
FIGURE 6-4. ENVELOPE ADDRESSING STANDARDS
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-1
CHAPTER 7
Correspondence Formats
7-1 Requirements
1. Use the standard letter format or one of its variations to correspond officially within or
outside the DoD.
2. The format of the standard letter, with slight variations, sets the pattern for joint letters,
multiple-address letters, endorsements, directives, memoranda, etc. Refer to the two-page letter
illustrations at figures 7-1 and 7-2. Figure 7-3 contains the formatting techniques to use when
preparing a standard letter for use with a window envelope. Figure 7-4 is an example of a joint
letter for joint release by two commands.
3. The person whose title appears in the “To:” line is the action addressee. Aside from its one
action addressee, the standard letter may have any number of “Via” addressees, “Copy to”
addressees, or both. Seechapter 8 to prepare a letter with more than one action addressee.
7-2 Format
1. Margins. Allow l-inch top, bottom, left, and right margins on each page. On letterhead
paper, typing starts more than 1-inch from the top when the letterhead is printed. Do not right,
center, or full justify text or use proportional spacing. For directives, headers are 1 inch and
footers are .5 inches.
2. Sender’s Symbols. If “in reply refer to” is printed on your activity’s letterhead paper, type
the SSIC on the next line. If“in reply refer to” is not printed on your activity’s letterhead paper,
type the SSIC on the second line below the letterhead, starting 2 inches or more from the right
edge of the paper. The longest line of the sender’s symbol should end close to the right margin.
a. Authorized Sender’s Symbols. A sender’s symbol for a standard letter has three parts:
(1) Standard Subject Identification Code. An SSIC is a four- or five-digit number
which represent a document’s subject. They are used to categorize information by subject and
are required on all Navy and Marine Corps letters or messages, directives, memos, forms, and
reports. To find the SSIC that most closely represents the subject, refer to SECNAV M-5210.2,.
(2) Originator’s Code, By Itself Or In a Serial Number. The originator’s code, with or
without the serial number, is the originator's office symbol or the hull number of a ship. Each
command or activity will determine makeup of the originator’s code.
(a) Originator’s Code Without Serial Numbers. Start the originator’s code
immediately under the SSIC. Below are examples of two SSICs with only the originator’s code:

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-2
EXAMPLE: 5216 5800
Code 13 N00J
(b) Originator’s Code With Serial Numbers. All classified correspondence created
by your activity must be given a serial number. A serial number is not required on unclassified
correspondence. Whether unclassified correspondence is serialized or not depends on local
practice. Volume is the major criterion. An activity that produces little correspondence, and all
of it is unclassified, probably does not need to use serial numbers. The added control must be
weighed against the added complications of typing or stamping serial numbers. An activity that
uses serial numbers shall start a new sequence of numbers at the beginning of each calendar year
and assigns numbers consecutively beginning with 001.
(c) Classified Markings. Start the originator’s code immediately under the SSIC
followed by a forward slash with no spaces before or after the slash, the classification (if
classified) (C for Confidential, S for Secret, T for Top Secret), and then the next unused serial
number for the current calendar year. Below are two examples of a sender’s symbol using the
originator’s code and serial number:
EXAMPLE: 5216 5800
Ser Code 13/271 Ser N00J/C20
(3) Date. Date a letter on the same day it is signed. Do not type the date when
preparing correspondence that will be signed on a later date. Use the abbreviated date format
discussed in chapter 2, page 2-11.
EXAMPLE: 5216 5800
Ser Code 13/271 Ser N00J/S20
7 Sep 06 5 Jan 07
b. Exceptions to Requirements for Using Identification Symbols. Local practices
determine how to use identification symbols in the following cases:
(1) Letters to members of Congress or heads of Government agencies.
(2) Letters of praise or condolence.
c. Unauthorized Identification Symbols. Numbers assigned by word processing centers
and the initials of writers and typists are unauthorized as identification symbols; however, they
may be included on file copies as part of the drafter’s identification.
3. Classified Correspondence. You must have the right security clearance and know
marking/handling requirements to prepare classified correspondence. An example of a classified
letter is provided in figure 7-5. Refer to SECNAV M-5510.36 for additional information on
marking and handling classified correspondence.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-3
4. For Official Use Only
a. For Official Use Only (FOUO) applies to information that is not classified, but which
may be withheld from the public under the FOIA. Never use “For Official Use Only” as a
classification to protect national security.
b. To designate correspondence as FOUO, type “FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY” in capital
letters, centered at the bottom of the first and last page and any page that contains FOUO
information. See figure 7-7. For documents with cover or title pages, type, stamp, or print in
capital letters “FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY” centered at the bottom on the front cover and the
outside of the back cover. For additional information refer to SECNAV M-5510.36.
5. “From:” Line
a. General. Every standard letter must have a “From:” line, except a letter that will be
used with a window envelope. To prepare a letter for a window envelope, follow figure 7-3. As
a general rule, the “From:” line is composed of the activity head’s title and the activity’s name.
Refer to the three publications listed below for the correct names and mailing addresses for DON
and DoD activities.
(1) SNDL, Parts 1 and 2.
(2) Https://www.manpower.usmc.mil/portal/page?_pageid=278,1&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL
(Active Marine Link, Personal and Family Link, Military Personnel Services Link, PostalLink,
under reference).
(3) DoDAAD, DoD Manual 4000.25-6-M.
b. Converting an SNDL Address to a “From:” Line Address. The “From:” line gives more
than a title, but less than a full mailing address. Include enough information to distinguish your
activity from other activities that may have the same name, but are in a different city or country.
In some cases a one-of-kind title adequately identifies an activity and the location is unnecessary
(e.g., “Secretary of the Navy”). The below examples show various way of converting SNDL
addresses to “From:” line addresses.
EXAMPLE:
SNDL Entry From Line
COMMANDING OFFICER Commanding Officer, Naval Station Norfolk
NAVAL STATION

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-4
NORFOLK VA 23511-6000
COMMANDING OFFICER Commanding Officer, USS CHUNG-HOON (DDG 93)
USS CHUNG-HOON (DDG 93)
FPO AP 96662-1302
COMMANDING OFFICER Commanding Officer, Patrol Squadron 45
VP 45
UNIT 60172
FPO AA 34099-5918
c. Format. Type “From:” at the left margin on the second line below the date line. The
text begins two spaces after the colon. If the entry is longer than one line, start the second line
under the first word after the heading.
EXAMPLE:
From: Commanding Officer, USS BLUE RIDGE (LCC 19)
From: Commanding Officer, Naval Recruiting District Minneapolis,
212 3
rd
Avenue South, Minneapolis, MN 55401-2592
d. Avoid Multiple Titles. If your commanding officer has more than one title, choose the
title that corresponds with the content of the letter.
6. “To:” Line
a. General. Address all correspondence to the activity head of an activity. Include the
office code or person’s title that will act on your letter in parentheses, if known. If the office
code is composed of only numbers, add the word “Code” before the numbers. Do not add the
word “Code” before an office code that starts with a letter (e.g., “N” or “SUP”). Because
frequent turnover in personnel can result in misrouted mail, avoid using the name of an
individual in the “To:” line. You may use the complete mailing address and ZIP+4 code if you
want the address for a record. If you will be using a window envelope, follow figure 7-3.
b. Format. Type “To:” at the left margin on the first line under the “From:” line (do not
skip a line). Four spaces follow the colon.
EXAMPLE:
From: Chief of Naval Operations
To: Commanding Officer, USS JOHN C STENNIS (CVN 74)
From: Assistant Secretary of the Navy (Financial Management and
Comptroller)
To: Chief of Naval Reserve

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-5
From: Commanding Officer, Naval Station, San Diego (Code 10)
To: Officer in Charge, Personnel Support Activity Detachment,
China Lake, CA 93555-6001
7. “Via:” Line
a. General. Use a “Via:” line when one or more activities outside of your activity should
review a letter before it reaches the action addressee. The format for the “Via:” line is the same
as for the “From:” line and “To:” line discussed in paragraphs 5 and 6 above.
b. Format. Type “Via:” at the left margin on the first line below the “To:” line. Three
spaces follow the colon. If the entry is longer than one line, start the second line under the first
word after the heading.
EXAMPLE:
From: Chief of Naval Operations
To: Commander, U.S. Fleet Forces Command
Via: Commander, U.S. Pacific Fleet
c. Numbering Via Addressees. Number “Via” addressees if two or more are listed.
Follow the chain of command. Routing starts with the addressee listed first.
EXAMPLE:
From: Commander, Destroyer Squadron 23
To: Commander, U.S. Fleet Forces Command
Via: (1) Commander, Cruiser-Destroyer Group 1
(2) Commander, Naval Surface Force, U.S. Pacific Fleet
(3) Commander, U.S. Pacific Fleet
8. Subject Line
a. General. The subject line consists of a sentence fragment that tells readers what the
letter is about, usually in 10 words or less. Use normal word order and capitalize every letter
after the colon. In formal correspondence, do not use acronyms in the subject line. If the subject
appears elsewhere in the text of the letter, capitalize it using the “Title Case” format. When
replying to a letter, repeat the subject of the incoming correspondence in the subject line, unless a
change is essential for clarity.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-6
b. Format. Type “Subj:” at the left margin on the second line under the last line of the
previous heading. Two spaces follow the colon. If the entry is longer than one line, line the
second line under the first word after the heading.
EXAMPLE:
Subj: PROGRAM ACQUISITION PROCESS FOR THE ADVANCED SEA-BASED
TARGET PROFILING RADAR
9. Reference Line
a. General. Use only those references that bear directly on the subject at hand. Avoid
unnecessary or complicated references. Many letters may not need a reference, while others are
complete with a reference to only the latest communication in a series. List references in the
order they appear in the text. Always mention cited references in the text. Additionally, when
citing a reference it is not necessary to include the subject of the reference. However, the subject
may be included, following all other required elements, if it aids in clarifying or better
identifying the reference.
b. Avoiding Most NOTAL References. A not-to-all (NOTAL) reference is a document
that some addressees neither hold nor need. Avoid NOTAL references whenever possible. If a
NOTAL reference is unavoidable, follow the reference in the reference line with the term
“NOTAL” in parentheses. The following paragraphs discuss various referencing situations and
an appropriate action for each situation:
(1) If it is known that the action addressee does not have a reference listed in your
correspondence, include it as an enclosure to your correspondence or refer to it in the text.
Enclosing an existing document as an enclosure is not allowed in directives.
EXAMPLE: (Referencing a NOTAL reference in the text of the correspondence.)
“CNO WASHINGTON DC 121845Z Mar 07 directed all afloat Navy
activities to provide statistical data on fuel usage. Request
you provide the requested data by 1 June 2007.”
(2) If you would like to provide a copy of a reference listed in your correspondence to
a “Via” or “Copy to” addressee, annotate “w/ref (x)” in parentheses to the right of the addressee
you send it to. (Substitute the appropriate reference letter for x.) Only include this annotation on
the copy for the addressee you are sending the reference to. Do not include the distribution of a
reference to “Via” or “Copy to” addressees on the original letter.
EXAMPLE:

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-7
From: Chief of Naval Operations
To: Commander, U.S. Fleet Forces Command
Via: Commander, U.S. Pacific Fleet (w/ref (c))
Copy to:
COMNAVPERSCOM (w/ref (a))
c. Format. Type “Ref:” at the left margin on the second line below the subject line. Use a
lowercase letter in parentheses before the description of every reference. If you have only one
reference, list it as “Ref: (a)”. Three spaces follow the colon. References are listed in
alphabetical order, a through z. If you have more than 26 references, continue with (aa), (ab), etc.
If the entry is longer than one line, line the second line under the first word after the heading.
EXAMPLE:
Ref: (a) COMSUBGRU TWO ltr 7200 Ser N1/123 of 12 Mar 08
Ref: (ab) SECNAV M-5510.36
d. Citing Various Types of References
(1) Naval correspondence requires (a) the SNDL originator short title, (b) the type of
correspondence (“ltr” or “memo”), (c) the SSIC, (d) the originator’s code by itself or in a serial
number, and (e) the date. If the reference was not dated, type “(undated)” as illustrated below.
EXAMPLE:
USS SEAWOLF ltr 7200 Ser SSN 21/124 of 19 Apr 07
USS PORTER ltr 5216 Ser DDG 78/437 of 7 Mar 06 (NOTAL)
CNO memo 5216 Ser 09B33/6U317731 (undated)
(2) A business letter requires (a) the company name, (b) the term “ltr”, and (c) the date.
EXAMPLE:
Smith Widget Co. ltr of 14 Oct 05
(3) An e-mail requires (a) the SNDL originator's short title, (b) the term “e-mail,” (c)
the type of correspondence (“ltr” or “memo”), (d) the SSIC, (e) the originator’s code by itself or
in a serial number, and (f) the date.
EXAMPLE:
OPNAV e-mail ltr 5216 Ser N4/158 of 21 Sep 06

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-8
(4) A message requires (a) the originator's Plain Language Address as shown in the
“From:” line of the message (if listed, do not include the office code) and (b) the complete date-
time-group. When referencing general messages, include in parentheses the general message
type (All Navy (ALNAV), Naval Administrative (NAVADMIN), All Marine Corps (ALMAR),
etc.) and number/year.
EXAMPLE:
USS PORTER 071300Z Mar 04
NAS NORFOLK VA 101300Z Mar 06
CNO WASHINGTON DC 111300Z Mar 07 (NAVADMIN 123/09)
(5) Endorsements cite references depending on whether you want to mention them in
passing or highlight a particular one.
EXAMPLE:
ENS Joe J. Mainville, USNR, XXX-XX-6789/1105 ltr of 1 Apr 97
w/ends
CONNAVSURFPAC THIRD ENDORSEMENT 1070 Ser N1/3124 of 22 Apr 97 to
ENS Joe J. Mainville, USNR, XXX-XX-6789/1105 ltr of 1 Apr 97
(6) A telephone conversation or meeting requires (a) “PHONCON” or “Mtg”; (b) the
activity’s SNDL short title, the office code, the individual’s name, and (c) the date. Follow the
information for the first individual with a forward slash and repeat the information for the second
individual.
EXAMPLES:
PHONCON CNO (N09B2) Ms. Handy/COMNAVAIRLANT (N6) CDR Phillips of
17 Feb 09
Mtg COMSUBGRU TWO (N1) YNCS(SS) Foster/SECNAV YNCS(SW/AW)
Simpson of 9 Dec 09
(7) A Navy instruction requires (a) the SNDL short title combined with the term
“INST” and (b) the SSIC with the consecutive number and, if any, a revision letter. If
referencing a large instruction, do not call out the chapter, section, or paragraph in the reference
line, instead, identify them when using the reference in the text of the correspondence.
EXAMPLES:
NAVSUPINST 7510.1

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-9
SECNAV M-5216.5, Department of the Navy (DON) Correspondence
Manual
(identifying an enclosure, chapter, section or paragraph of a reference in the text)
“Reference (a), enclosure (3), paragraph 11a(2) requires …”
(8) A Navy notice requires (a) the SNDL short title of issuer combined with the term
“NOTE” and the SSIC, (b) the serial number, (c) the date, and (d) the cancellation date enclosed
in parenthesis (e.g., (Canc: Aug 08)). If referencing a large notice, do not call out the chapter,
section, orparagraph in the reference line, instead, identify them when using the reference in the
text of the correspondence.
EXAMPLE:
OPNAVNOTE 5216 Ser 09B/6U709210 of 21 May 08 (Canc: May 09)
(9) A DoD directive or instruction requires (a) the short title of issuer with either
Instruction or Directive, (b) the SSIC with consecutive number, and (c) the date with the month
spelled out. If referencing a large instruction or directive, do not call out the chapter, section, or
paragraph in the reference line, instead, identify them when using the reference in the text of the
correspondence.
EXAMPLE:
DoD Directive 2000.1 of 6 May 2006
DoD Instruction 1995.1 of 4 April 2008
(10) A DoD publication requires (a) the short title of issuer (b) the publication number,
(c) the publication type, (d) the title, and (e) the date.
EXAMPLE:
DoDD 4000.25-R-1, DoD Logistics Data Element Dictionary/
Directory, January 1990
DoD 5200.28-M, ADP Security Manual (C3I), January 1973
(11) A form requires (a) the issuer, (b) the form number, and (c) the issue or revision
date.
EXAMPLE:
NAVJAG 5800/15 (Rev. 7-1996)
(12) A report that has a Report Control Symbol requires (a) the report title, (b) the
issuer, and (c) the report number.
EXAMPLE:

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-10
Injury Report (NAVJAG 5800-19)
(13) A Navy publication requires (a) the issuer and (b) the publication number.
EXAMPLE:
NAVPERS 15018
(14) Code of Federal Regulations requires (a) the title number, (b) the term “CFR”, (c)
the part or chapter number, and (d) the section number (optional).
EXAMPLE:
41 CFR 201-45.000
(15) Federal Register (FR) requires (a) the volume number, (b) the term “FR”, and (c)
the page number.
EXAMPLE:
21 FR 623
(16) A United States Code requires (a) the title number, (b) the term “U.S.C.”, (c) the
section symbol(§), and (d) the section number. Do not include spaces in the term “U.S.C.”
EXAMPLE:
28 U.S.C. §1498
(17) An Executive Order requires (a) the term “E.O.” and (b) the order number.
EXAMPLE:
E.O. 12564
(18) “My” and “Your” Optional. To cite an earlier communication between your
activity and the action addressee, you may substitute a personal pronoun for the issuing activity.
To prevent confusion, avoid “my” and “your” in the reference line of a letter that has more than
one action addressee.
EXAMPLES:
My ltr 5216 Ser Code 10/049 of 2 Sep 09
Your msg 221501Z Aug 09

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-11
10. Enclosure Line
a. General. List enclosures in the enclosure line in the order they appear in the text.
Identify an enclosure using the same format as you would when identifying a reference. See
paragraph 9 above. When identifying a document, cite its subject or title exactly. Never list an
item in both the enclosure line and reference line of the same letter.
b. Format. Type “Encl:” at the left margin on the second line below the last line of the
previous heading. Two spaces follow the colon. Use a number in parentheses before the
description of every enclosure, even if you have only one. One space follows the closing
parenthesis. If the entry is longer than one line, start the second line under the first word after
the heading.
EXAMPLE:
Encl: (1) List of Reserve Officers Selected for Promotion to
Colonel
(2) CMC ltr 5216 Ser 00/451 of 5 Sep 09
(3) SECNAVINST 1400.1
c. Normal Distribution and When to Vary It. Normally, send one copy of the basic letter
plus any enclosures to all addressees. Do not use the term “w/encl” to indicate that all
addressees are being sent the enclosures. Avoid sending an enclosure if an addressee has it
already or if its bulk or other factors make furnishing it impractical.
d. Adding Copies of Enclosures for all Addressees. When sending more than one copy of
an enclosure to all addressees (“To,” “Via,” and “Copy to”), note the quantity in parentheses
after the enclosure's description.
EXAMPLE:
Encl: (1) OPNAV 5216/10 (10 Copies)
e. Variations Affecting Only Copy To Addressees. In certain circumstances, it may be
necessary to vary the normal distribution of enclosures to “Copy to” addressees. It is up to the
originator of the correspondence to make this determination. There are two basic methods of
varying distribution; all“Copy to” addressees are affected or only one or a few of the “Copy to”
addressees are affected.
(1) In these examples, all “Copy to” addressees are affected in the same way, so notes
appear beside the “Copy to” heading.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-12
EXAMPLE:
Copy to: (w/o encls)
Copy to: (w/o encls (2) and (3))
Copy to: (w/2 copies of encl (1))
(2) In this example, only some of the “Copy to” addressees are affected, so notes
appear beside the affected addressees.
EXAMPLE:
Copy to:
COMNAVSURFPAC (N1) (w/o encls)
USS MUSTIN (w/encl (2) only)
USS VANDERGRIFT
f. Variations Affecting Only Via Addressees. When varying the normal distribution of
enclosures to “Via” addressees, show the variation beside the affected addressee. One possible
variation appears below. Others may be adapted for the examples in paragraph 10e above.
EXAMPLE:
Via: Commanding Officer, Naval Technical Training Center,
Meridian (w/o encl)
g. Sending Enclosures Separately. When size, weight, or other factors prevent sending an
enclosure with a letter, send it separately and type the term “sep cover” in parentheses after the
enclosure's description.
EXAMPLE:
Encl: (1) SECNAV M-5216.5 (sep cover)
11. Text. Start the text on the second line down from the previous entry. The text shall be left
justified. Make the content clear by using plain English. Do not use slang or jargon. Refer to
chapter 12 for guidance on writing.
12. Paragraphs. Start all continuation lines at the left margin. All paragraphs are single spaced
and each paragraph or subparagraph begins on the second line below the previous paragraph or
subparagraph. When using a subparagraph, the first line is always indented the appropriate
number of spaces depending on the level of subparagraphing. All other lines of a subparagraph
continue at the left margin. Do not indent the continuation lines of a subparagraph. If there is a
paragraph 1a, there must be a paragraph 1b; if there is a paragraph 1a(1), there must be a
paragraph 1a(2), etc. It is acceptable for a paragraph to break across pages, but do not begin a

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-13
paragraph at the bottom of a page unless there is enough space for at least two lines of text on
that page and at least two lines of text are carried over to the next page. A signature page must
have at least two lines of text preceding the signature.
a. Identifying Paragraphs or Subparagraphs. Identify all paragraphs or subparagraphs with
a number or letter. See figure 7-8 for an example of paragraph and subparagraph structure and
identification.
b. Limit Subparagraphs. Documents rarely require subdividing to the extent shown in
figure 7-8. Do not subdivide past the second level until you have exhausted all re-paragraphing
alternatives first. Never subparagraph beyond the levels shown in figure 7-8.
c. Citing Paragraphs. When citing a paragraph or subparagraph, write the numbers and
letters without periods or spaces.
Example: 2b(4)(a)
d. Paragraph Headings. Use paragraph headings in long correspondence with widely
varying topics. Be brief but informative. Underline any heading and capitalize its key words
using the Title Case format. Be consistent across main paragraphs and subparagraphs. If
paragraph 1 has a heading, then paragraph 2 would need a heading; if paragraph 1a has a heading,
then paragraph 1b would need a heading.
13. Signature Line
a. General
(1) Only the original, which goes to the action addressee, must be signed; however, the
original and all copies must have typed or stamped signature line information below the
signature. The last name appears in all capital letters with the exception of a last name beginning
with a prefix.
EXAMPLE: (last name beginning with a prefix)
J. A. McBREARTY
(2) Start all lines of the signature line at the center of the page, beginning on the fourth
line below the text. The preferred way to identify the signatory is by typing their first initial,
middle initial, and last name. If the signatory does not have a middle name, use only their first
initial and last name. Signature lines can be changed based on the signers preference. Do not
include the signatory’s rank or a complimentary close. Add the signature line only when you are
sure who will sign the correspondence. If you use a stamp, remember to mark all copies and
avoid smeared or crooked impressions. Refer to chapter 2, page 2-4 for delegation of signature
authority guidance.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-14
b. Examples of Signature Lines
(1) When an activity head will sign the correspondence, the signature line is composed
of only their name.
EXAMPLE:
C. R. FIRMAN
(2) When a principal subordinate authorized to sign by title, such as the chief of staff
ordeputy in a major command will sign the correspondence, include their title as the second line
of the signature line.
EXAMPLE:
R. O. DAVIDSON, III
Deputy
(3) When an individual has been formally appointed to temporarily replace the
commanding officer or a subordinate who signs by title, include the term "Acting" as the last line
of the signature line.
EXAMPLES:
C. ESCOBAR H. T. MAC
Acting Deputy
Acting
(4) Put the term "By direction" under the name of a subordinate formally authorized to
sign official correspondence, but not by their title.
EXAMPLE:
L. AVALOS
By direction
(5) When the signatory is authorized to sign “by direction,” and the correspondence
will affect pay and allowances, the signature line will include the signatory’s (a) name, (b) title,
and (c) the phrase, “By direction of the [activity head].” (Insert the appropriate activity head
title).
EXAMPLE:
E. ESPINOSA
Executive Officer
By direction of the
Commanding Officer
14. “Copy To:” Line

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-15
a. General. Use this optional line to list addressees outside your activity who need to
know a letter's content but do not need to act on it. If you use the “Copy to:” line, keep the
number of activities to a minimum.
b. Format. Type "Copy to:" at the left margin on the second line below the signature line.
Identify addressees by their SNDL short title and/or SNDL numbers shown there. The SNDL
number is an alpha-numeric number that is used to group commands or activities by
classification. Do not list offices within the same activity individually, group them together in
parentheses after the entry.
c. Variations. “Copy to” addressees are normally listed in a single column at the left
margin and single spaced below the “Copy to:” line. A long list of copy to addressees can be
listed in columns, as a paragraph, or may be continued on the next page or placed entirely on a
new page. If the signature line of the correspondence is at the bottom of the page and the “Copy
to:” line will not fit on that page, type "Copy to: (see next page)" to indicate that the “Copy to:”
line is on the next page. Use this format for the “Distribution:” lines as well.
EXAMPLE: (Grouping of offices of an activity)
Copy to:
CNO (N1, N2, N3/5)
BUPERS (PERS 313C, PERS 49)
USS YORKTOWN (CG 48) (Code 01)
EXAMPLE: (Large list in column format)
Copy to:
CNO (N1, N2, N3/5) USS YORKTOWN (CG 48) (ADMIN)
BUPERS (PERS 313C) USS MUSTIN (DDG 89)
COMCARSTRKGRU ELEVEN USS BLUE RIDGE (LCC 19)
EXAMPLE: (Large list in paragraph format)
Copy to:
CNO (N1, N2, N3/5), BUPERS (PERS 313C), COMCARSTRKGRU ELEVEN,
USS YORKTOWN (CG 48) (ADMIN), USS MUSTIN (DDG 89)
EXAMPLE: (Continuation to a second page)
Copy to: (Cont'd)
COMCARSTRKGRU ELEVEN
USS YORKTOWN (CG 48) (ADMIN)
USS MUSTIN (DDG 89)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-16
15. Identifying Second and Later Pages. Repeat the subject line at the top of each page of the
basic letter. Start typing at the left margin on the sixth line from the top of the page. Continue
the text beginning on the second line below the subject.
16. Page Numbering. Do not number a single-page letter or the first page of a multiple-page
letter. Center page numbers 1/2 inch from the bottom edge, starting with the number 2. No
punctuation accompanies a page number. See figure 7-2. To number the pages of a TOP
SECRET document, see SECNAV M-5510.36.
17. Correspondence Package Assembly. The basic letter, the enclosures, and the background
material are assembled according to activity practices before they are presented for approval and
signature. Figure 7-9 illustrates an assembled correspondence package that is ready for signature
and mailing.
18. Tabbing a Correspondence Package. Tab the signature page (if not the first page),
enclosures, and background material. Label the tabs as appropriate. Figure 7-10 illustrates an
assembled correspondence package with tabs. Take care so tabs can be removed without
defacing the document.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-17
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAME OF ACTIVITY
ADDRESS
CITY STATE ZIP+4
SSIC
Code/Serial #
Date
%
From:**Activity head, name of activity, location when
*******needed
To:****Title, name of activity (Code), location when
*******needed
Via:***(1)*Title, name of activity (Code), location
***********when needed
*******(2)*Same as Via (1) above
%
Subj:**NORMAL WORD ORDER WITH ALL LETTERS CAPITALIZED
*******AND NO PUNCTUATION
%
Ref:***(a)*Communication or document that bears
***********directly on the subject at hand
%
Encl:**(1)*Title of Material – enclosed with letter
*******(2)*Title of Material (sep cover) – not
***********enclosed with letter
%
1.**This example shows the first page of a two-page
standard letter. Included are many of the elements that
might appear on a standard letter.
%
2.**Start the “From:” line on the second line below the
date line. The date may be typed or stamped.
%
3.**Arrange paragraphs as shown in figure 7-8.
%
****a.**Do not start a paragraph at the bottom of the page
unless at least two lines of text will remain on that page
and at least two lines of text will carry over to the next
page.
%
****b.**Do not number the first page, number only
succeeding pages.
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-18
FIGURE 7-1. STANDARD LETTER – FIRST PAGE
Subj:**REPEAT THE SUBJECT EXACTLY AS IT IS WRITTEN ON
*******THE FIRST PAGE OF THE LETTER
%
****c.**The second and succeeding pages of a standard
letter look like this:
%
********(1)*Start typing on the sixth line (1-inch top
margin). Repeat the subject line.
%
********(2)*Continue the text on the second line below the
subject line.
%
4.**”Copy to” addressees appear on all copies. “Blind
copy to” addressees, as well as the identity of the writer
and typist, appear on internal copies only.
5.**A standard letter uses no complimentary close.
%
%
%
NAME OF SIGNER
By direction
%
Copy to:
SNDL number and/or short title of information addressee
SNDL number and/or short title of 2
nd
information addressee
%
Blind copy to:
List blind copy addressees
2
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-19
FIGURE 7-2. STANDARD LETTER – SECOND PAGE
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAVY PERSONNEL COMMAND
5720 INTEGRITY DRIVE
MILLINGTON TN 38055-0130
5216
Ser 301/403
5 Oct 06
%
COMMANDER
NAVY PERSONNEL COMMAND (PERS-40)
5720 INTEGRITY DRIVE
MILLINGTON TN 38055-0130
%
%
%
%
Subj:**WINDOW-ENVELOPE FORMAT
%
1.**You may use a GSA general-purpose window envelope
(overall size 9-1/2 by 4-1/8 inches and window, 4-3/4 by 1-
1/4 inches, in lower left) if:
%
****a.**The address has no more than five lines, and does
not extend past the middle of the page. The complete
address must appear in the window with at least a 1/8-inch
margin, even if the letter shifts in the envelope.
%
****b.**The letter and enclosures are all unclassified.
%
****c.**Your letter does not have any “Via” addresses.
%
2.**Because this letter does not have a “From:” line, every
copy that goes to addressees outside your activity must be
on letterhead to show its origin.
%
3.**To fold the letter first turn up the bottom edge so it
just covers the subject, second, turn back the address
portion so the upper fold also falls along the top of the
subject.
%
%
%
A. J. ANGLIN
By direction
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-20
FIGURE 7-3. STANDARD LETTER – WINDOW – ENVELOPE

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-21
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAVAL SEA SYSTEMS COMMAND (20362-5101)
NAVAL SUPPLY SYSTEMS COMMAND (20376-5000)
WASHINGTON, DC
NAVSUP NAVSEA
5216 5216
Ser 02/318 Ser 07/207
9 Apr 06 17 Apr 06
%
JOINT LETTER
%
From:**Commander, Naval Sea Systems Command
*******Commander, Naval Supply Systems Command
%
To:****Chief of Naval Operations
%
Subj:**HOW TO PREPARE A JOINT LETTER
%
1.**A joint letter may be used to establish an agreement
between two or more activities or for other matters of mutual
concern. To prepare a Joint Memorandum, replace JOINT LETTER
with JOINT MEMORANDUM above the “From:” line.
%
2.**On plain bond paper, list the command titles in the
letterhead so the senior is at the top. If the activities are
in different cities or states, follow each title with its
Standard Navy Distribution List address.
%
3.**Arrange signature lines so the senior official is at the
right. Place the signature line of a third cosigner in the
middle of the page. The senior official signs the letter
last.
%
4.**If your activity is the last to sign, send copies of the
signed letter to all cosigners.
%
%
%
J. J. SMITH M. L. JONES
Acting Deputy
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-22
FIGURE 7-4. JOINT LETTER
SECRET
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
OFFICE OF THE CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS
2000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON DC 20350-2000
5216
Ser N09N/S391
11 May 06
%
From:**Vice Chief of Naval Operations
To:****Commander, U.S. Pacific Command
%
Subj:**CLASSIFICATION MARKINGS (U)
%
1.**(U)*This is an example of a classified letter. Each
paragraph shall be predicated with a portion marking.
%
****a.**(S)* Identify the classification of each paragraph.
This subparagraph is marked as SECRET as indicated by the (S)
portion marking.
%
****b.**(C)* Classification markings eliminate doubt as to
which portions of a document contain or reveal classified
information
%
2.**(U)*Stamp the letter’s highest classification in the center
of the top and bottom margins. Assign a serial number bearing
the initial of the highest classification.
%
3.**(U)*On the first page of a letter that contains classified
material, include associated markings. The example below is
for a derivatively classified document.
%
4.**(U)*There are numerous rules and requirements for properly
marking classified correspondence. This figure is a basic
example. Figure 2-6 briefly discusses how to correctly mark an
unclassified letter of transmittal that has classified
enclosures. Refer to SECNAV M-5510.36, chapter 6 for a
detailed description of how to properly mark classified
correspondence.
%
Derived from:**Multiple Sources
Declassify on:*10 Jun 15
SECRET
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-23
{Classified for illustration purposes only}
FIGURE 7-5. STANDARD LETTER WITH CLASSIFICATION MARKINGS - FIRST PAGE
SECRET
Subj:**CLASSIFICATION MARKINGS (U)
%
5.**(U)*When typing an unclassified letter that has a
classified enclosure, only these three steps are necessary.
%
****a.**(U) Type a classification statement on the second line
below the date line.
%
EXAMPLE:
SECRET—Unclassified upon removal of enclosure (1)
%
****b.**(U) Indicate that the subject or title of the enclosure
is unclassified.
%
EXAMPLE:
Encl: (1) Sample Classified Enclosure (U)
%
****c.**(U) Stamp the enclosure’s classification in the center
of the top and bottom margins of the letter of transmittal.
%
%
%
J. K. ELL
By direction
SECRET
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-24
2
{Classified for illustration purposes only}
FIGURE 7-6. STANDARD LETTER WITH CLASSIFICATION MARKINGS-SECOND PAGE
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAVY PERSONNEL COMMAND
5720 INTEGRITY DRIVE
MILLINGTON TN 38055-0130
5216
Ser N09L/729
25 Jun 98
%
From:**Commander, Navy Personnel Command
To:****Commander in Chief, U.S. Naval Forces, Europe
%
Subj:**FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY MARKINGS (FOUO)
%
1.**(FOUO) This illustrates a letter that has “For Official
Use Only” (FOUO) information. Mark the bottom front cover
(if any), interior pages of documents, and on the outside
back cover (if any) with “FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY”.
%
2.**(FOUO) Subjects, titles and each section part,
paragraph, and similar portion of an FOUO document requiring
protection shall be portion marked. Place the abbreviation
“(FOUO)” immediately following the portion letter or number,
or in the absence of letters or numbers, immediately before
the beginning of the portion. Unclassified letters of
transmittal with FOUO enclosures or attachments shall be
marked at the top left corner with “FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY
ATTACHMENT”.
%
3.**For more information on designating and marking material
FOUO, refer to SECNAV M-5510.36.
%
%
%
R. D. DAVIDSON
By direction
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-25
{Marking for illustration purposes only}
FOR OFFICIAL USE ONLY
FIGURE 7-7. STANDARD LETTER WITH FOUO MARKINGS
1.**Arrange paragraphs following the formats below. See
chapter 2, page 7-11 for additional guidelines.
%
2.**If subparagraphs are needed, use at least two; e.g., a
(1) must have a (2).
%
****a.**Indent each new subdivision four spaces and start
typing at the fifth space.
%
****b.**Text
%
********(1)*Documents rarely require subdividing to the
extent shown below.
%
********(2)*Text
%
************(a)*Do not subparagraph past this level until
you have exhausted all re-paragraphing alternatives.
%
************(b)*Text
%
****************1.**Text
%
********************a.**Text
%
************************(1)*Text
%
****************************(a)*Never subparagraph beyond
this level.
%
****************************(b)*Text
%
************************(2)*Text
%
********************b.**Text
%
****************2.**Text
10.**When using two digits, continue to indent each new
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-26
9. Background material
8. Official file copy (with
enclosure(s))
7. Envelope or mailing label (if
required)
6. Info addressee(s) copy(s) (with
enclosure(s))
5. Envelope or mailing label (if
required)
4 V
ia
addressee(s)
copy(s) (with
enclosure(s))
3
.
Courtesy copy (with
enclosure(s))
2. Original letter (with
enclosures) to be signed
1
Brief sheet if required
subdivision four spaces and start typing on the fifth space
(paragraphs will not line up).
%
****a.**Text
%
********(9)*Text
%
********(10)*Text
FIGURE 7-8. PARAGRAPH STRUCTURE FORMAT
Here is a suggested way to assemble a standard letter for
signature and mailing. If you use a folder rather than the
single stack of papers shown, clip items 1 and 9 to the
left side and 2 through 8 to the right side of the folder.
Tab signature page, enclosures, and background
material.
Check or arrow the intended addressee on
each copy.
Prepare envelopes or mailing
labels accordingto local practice.
Your activity might not require
them for addressees listed in the
SNDL.
BEFORE SIGNATURE AFTER SIGNATURE
1. Briefing sheet as prescribed locally, usually
omitted if letter is short or self-explanatory.
2. Original letter to be signed (signature tabbed
if not on first page), pages in normal order, with
enclosures.
3. Courtesy copy with enclosures, rarely used
except with responses to congressional inquiries.
4. Copies for via addressees, if any, each with
File
Mail
* - Space
% - Hard Return

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-27
3
2
1
enclosures.
5. Envelope or mailing label, if required.
6. Copies for “Copy to:” addressees, each with
enclosures.
7. Envelope or mailing label, if required.
8. Official file copy of letter with enclosures.
Expose the left margin so reviewers can initial
and date there.
9. Background material.
FIGURE 7-9. ASSEMBLY OF A STANDARD CORRESPONDENCE PACKAGE USING
STACKING METHOD
The example on theright illustrates tabbing
correspondence packages when correspondence is
in the natural order using the stacking method.
Tab 1 - Signature Tab
Tab 2 - Enclosure Tabs
Tab 3 - Background Material
File
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-28
FIGURE 7-10. TABBING CORRESPONDENCE PACKAGES
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
7-29

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
8-1
CHAPTER 8
Multiple-Address Letter
8-1 General. Use a multiple-address letter when you have more than one action addressee. The
multiple-address letter is the same as the standard letter, except in handling addresses. Separate
standard letters may be used in place of a multiple-address letter, but they require much more
work.
8-2 Listing Addresses. There are three ways to list addresses:
1. Using a “To:” Line Only. When you have four addresses or fewer, use the “To:” line by itself
as shown in figure 8-1.
2. Using a “Distribution:” Line Only. When you have more than four addresses, use the
“Distribution:” line by itself as shown in figure 8-2.
3. Using Both a “To:” Line and “Distribution:” Line. Use both the “To:” line and the
“Distribution:” line in the same letter when you show a group title whose distribution is
relatively unknown. Place the group title (“Area Records Officers,” for example) in the “To:”
line and identify each member in a “Distribution:” line. See figure 8-3.
8-3 Preparing and Signing Copies. Every action addressee must receive a letter that has a
letterhead and signature. The letterhead may be printed, typed, stamped, or photocopied. The
signature must be original or photocopied. To meet these requirements, make copies in one of
three ways.
1. Type original on letterhead paper. After the original has been signed, make the necessary
photocopies. Keep the original signed copy in the official file and send out photocopies.
2. Using letterhead carbons, type all the copies needed for addresses and for the file if a single
typing action will make them all. Then obtain an original signature on each action addressee’s
copy.
3. Using a word processor, type multiple originals on letterhead paper. Obtain an original
signature on each action addressee’s copy.
8-4 Assembly of Multiple-Address Letters. Figure 8-4 shows a suggested way to assemble a
multiple-address letter for signature and mailing.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
8-2
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
COMMANDER SUBMARINE GROUP TWO
NAVAL SUBMARINE BASE NEW LONDON
GROTON, CONNECTICUT 06349-5100
5216
Ser N3/258
25 Nov 09
From: Commander, Submarine Group TWO
To: Commander, Submarine Squadron TWO
Commander, Submarine Squadron FOUR
Commander, Submarine Squadron TWELVE
Subj: USING A “TO:” LINE ONLY
1. If you have four addressees or fewer, list all of them
in the “To:” line, starting one beneath the other. If you
have more than four addressees, list all of them in a
“Distribution:” lines as shown on the next page.
2. Use only long titles in the “To:” line.
M. D. FOSTER
By direction
Copy to:
COMNAVSEASYSCOM (SEA-06)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
8-3
FIGURE 8-1. MULTIPLE-ADDRESS LETTER USING “TO:” LINE
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
COMMANDER SUBMARINE GROUP TWO
NAVAL SUBMARINE BASE NEW LONDON
GROTON, CONNECTICUT 06349-5100
5216
Ser N3/260
28 Nov 08
From: Commander, Submarine Group TWO
Subj: USING A “DISTRIBUTION:” LINE ONLY
1. Omit the “To:” line and add a “Distribution:” line if
you have more than four action addressees or if you vary
the number of copies to any of the addressees. Addressees
shown in a “Distribution:” line are action addressees.
2. You may list addressees in the “Distribution:” line
by:
a. SNDL short titles
b. Collective titles, or
c. Both collective and SNDL short title.
3. Usually list “Distribution:” and “Copy to:” addressees
in single columns. Addressees may be listed in paragraphs
or columns to keep a letter from going to another page.
M. D. FOSTER
By direction
Distribution:
SNDL 28K1 (COMSUBFOR NORFOLK) (4 copies)
29B1 USS ENTERPRISE (CVN 65)
29N1 USS SCRANTON (SSN 756)
32DD2 USS FRANK CABLE (AS 40)
Copy to:
COMNAVSEASYSCOM (SEA-06)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
8-4
FIGURE 8-2. MULTIPLE-ADDRESS LETTER USING “DISTRIBUTION:” LINE
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
COMMANDER
NAVAL COMPUTER AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMMAND
4401 MASSACHUSETTS AVE, N W
WASHINGTON, DC 20394-5000
5216
Ser 00C/1760
18 Dec 09
From: Commander, Naval Computer and
Telecommunications Command
To: Standard of Conduct Coordinators
Subj: USING A “TO:” LINE AND “DISTRIBUTION:” LINE
1. Use both the “To:” line and “Distribution:” line in the
same letter when you show a group title whose distribution
is relatively unknown. Place the group title in the “To:”
line and identify each member in a “Distribution:” line.
R. HENDERSON
By direction
Distribution:
NAVCOMTELSTA WASHINGTON DC
NAVCOMTELSTA PENSACOLA
NAVCOMTELSTA SAN DIEGO
NAVCOMTELSTA SAN FRANCISCO

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
8-5
9. Background
material
8. Official file copy (with
enclosure(s))
7. Envelope or mailing label (if
required)
6. Info addressee(s) copy(s) (with
enclosure(s))
5. Envelope or mailing label (if
required)
4
S
econd letter (with enclosures) to
be signed
3
.
Envelope or mailing label (if
required)
2. Original letter (with enclosures)
to be signed
1
Brief sheet if required
FIGURE 8-3. MULTIPLE-ADDRESS LETTER USING A “TO:” LINE AND
“DISTRIBUTION:” LINE
Here is a suggested way to assemble a multiple-address
Letter for signature and mailing. If you use a folder
rather than the single stack of papers shown, clip
items 1 and 9 to the left side and 2 through 8 to
the right side of the folder.
Tab signature page, enclosures, and background material.
Check or arrow the intended addressee on each copy.
Prepare envelopes or mailing labels according to local practice.
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
8-6
Your activity might not require them for addressees listed in the SNDL.
BEFORE SIGNATURE AFTER SIGNATURE
1. Briefing sheet as prescribed locally, usually
omitted if letter is short or self-explanatory.
2. Original letter to be signed (signature tabbed
if not on first page), pages in normal order, with
enclosures.
3. Envelope or mailing label, if required.
4. Second letter to be signed (signature tabbed
if not on first page), pages in normal order, with Mail
enclosures.
5. Envelope or mailing label, if required.
6. Copies for “Copy to:” addressees, each with
enclosures.
7. Envelope or mailing label, if required.
8. Official file copy of letter with enclosures.
Expose the left margin so reviewers can initial
and date there.
9. Background material.
FIGURE 8-4. ASSEMBLY OF A MULTIPLE-ADDRESS LETTER
File
File

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
8-7
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
CHAPTER 9
Endorsements
9-1 General. When a letter is transmitted via your activity, use an endorsement to forward
comments, recommendations, or information. See figure 9-1. While an endorsement is mostly
used to transmit correspondence through the chain of command, you may also use it to redirect a
letter. Do not use an endorsement to reply to a routine letter. Additionally, a “Via” addressee
may alter the order of any remaining “Via” addressees or add others.
9-2 Format
1. Endorsement Line

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
9-2
a. Start the endorsement line at the left margin on the second line below the date line. If
the correspondence is classified, start the endorsement line on the second line below the
classification line.
b. Number each endorsement in the sequence in which it is added to the basic letter.
Indicate the numbers of the endorsement by using ordinal numbers such as FIRST, SECOND,
THIRD, etc. Following the number, type “ENDORSEMENT on” and identify the basic letter
using the same style as a reference line. When the heading exceeds one line, start the succeeding
line with the word on.
Example:
FIRST ENDORSEMENT on USS SCRANTON (SSN 756) ltr 3000 Ser SSN 756/001 of
5 May 96
2. “Via:” Line. When preparing your endorsement, include in the “Via:” line any remaining
“Via” addressees, if any. If there is only one via addressee remaining do not number it. If there
is more than one remaining,number the remaining addresses starting with the number (1) in
parenthesis and consecutively number the rest.
3. Adding References. Do not repeat a reference in the reference line of your endorsement that
has already been identified in thereference lines of the basic letter or a previous endorsement.
Identify only the references that you add. Assign a letter to all references you add by continuing
the sequence of letters from the basic letter and previous endorsements. For example, if the basic
letter and previous endorsements had references identified up to letter “f,” the first reference of
your endorsement would be letter “g.”
4. Adding Enclosures. Do not repeat an enclosure in your enclosure line that has already been
identified in theenclosure lines of the basic letter or prior endorsements. Identify only the
enclosures that you add. Assign a number to all enclosures that you add by continuing the
sequence of numbers from the basic letter and previous endorsements. For example, if the basic
letter and previous endorsements had enclosures identified up to number “5,” the first enclosure
of your endorsement would be number “6.”
5. “Copy To:” Addressees. If your endorsement is significant and not routine, each activity
that endorsed the basic letter before you and the originator of the basic letter shall be included as
a copy to addressee on your endorsement. Additionally, all copy to addressees from the basic
letter and previous endorsements shall be included as a copy to addressee. Significant
endorsements include “forwarded, recommending disapproval,” “readdressed and forwarded,”
and those with substantive comments. Routine endorsements include “forwarded,” “forwarded
for consideration,” and “forwarded, recommending approval.”
6. Forwarding Your Endorsement and Copies. When forwarding your endorsement to the next
via addressee or to the action addressee, you must also do the following:

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
9-3
a. Attach any enclosure you identified in your endorsement to the original for forwarding
to the action addressee.
b. Forward one copy of your endorsement to each remaining addressee.
c. Forward one copy of your endorsement to each copy to addressee. Include a copy of
any enclosure you added. If a copy to addressee will be receiving the basic letter and previous
endorsements for the first time from you, to the right of each of these addressees, type the word
“complete” in parentheses to show that your endorsement includes the basic letter, enclosures,
and prior endorsements.
7. Assembly of an Endorsement. Figure 9-2 shows a suggested way to assemble an
endorsement for signature and mailing.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
9-4
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAVAL AIR FORCE ATLANTIC
1279 FRANKLIN STREET
NORFOLK VA 23511-2494
5216
Ser N72/420
24 Jul 06
%
SECOND ENDORSEMENT on NAS Cecil Field ltr 5216 Ser 11/273
*******************of 9 Jul 06
%
From:**Commander, Naval Air Force, U.S. Atlantic Fleet
To:****Commander, U.S. Atlantic Fleet
%
Subj:**HOW TO PREPARE AN ENDORSEMENT
%
Encl:**(2)*SECNAV M-5216.5
%
1.**Start an endorsement on a new page. Number each page of
your endorsement and continue the sequence of numbers from the
previous endorsement or from the basic letter if you are the
first endorser.
%
2.**Every “new page” endorsement must repeat the basic
letter’s SSIC, identify the basic letter in the endorsement
line, and use the basic letter’s subject as its own.
%
%
%
J. H. KNIGHT
By direction
%
Copy to:
NAS Cecil Field (Code 11)
*COMSEABASEDASWWINGLANT (Code 019)
*Prior endorser included because second endorsement is
significant.
4
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
9-5
File
Mail to next
via addressee
or to the action
addressee
Mail
File
11. Background material
10. Official file copy with
enclosure(s)
9. Envelope(s) or mailing label(s)
for copy to addressee(s)
8. Copy(s) of your endorsement
7. Envelope or mailing label for
your endorsement (if required)
6. Copy(s) of endorsement for
additional Via addressees, if any
5. Enclosure(s) from previous
endorsements
4
. Basic letter
3
.
Previous endorsement(s) with
most recent on top
2. Endorsement (w
ith enclosures)
to be signed
1
Brief sheet
(
if required
)
FIGURE 9-1. NEW PAGE ENDORSEMENT
This is a suggested method to way to assemble an endorsement
for signature and mailing. If you use a folder rather than the
single stack of papers shown, clip items 1 and 11 to the
left side and 2 through 10 to the right side of the folder.
Tab signature page, enclosures, and background
material.
Check or arrow the intended addressee on
each copy.
Prepare envelopes or mailing labels
according to local practice. Your
activity might not require them
for addressees listed in the
SNDL.
BEFORE SIGNATURE AFTER SIGNATURE
1. Briefing sheet as prescribed locally, usually omitted if letter is
short or self explanatory.
2. Your endorsement.
3. Earlier endorsements, most recent on top.
4. Basic letter.
5. Earlier enclosures, plus any you added on top.
6. Copies of your endorsement for remainingVia addressees.
7. Envelope or mailing label, if required.
8. Copies of your endorsement for copy to addressees.
9. Envelope or mailing label, if required.
10. Official file copy of letter with enclosures. Left margin exposed
so reviewers can initial and date there.
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
9-6
11. Background material, such as incoming letter, referenced
documents.
FIGURE 9-2. ASSEMBLY OF AN ENDORSEMENT

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-1
CHAPTER 10
Memorandums
10-1 General. A memorandum provides a less formal way to correspond within an
activity/command. Subordinates within that activity or command may use a memorandum to
correspond directly with each other on routine official business or as an informal means of
communication.
10-2 Formats. There are several memorandum formats. All DON activities shall use the
appropriate memorandum that suits the subject, occasion, and audience. The following
paragraphs discuss the different types of memorandums:
1. Memorandum For The Record. Use a Memorandum for the Record (MFR) as an internal
document to record supporting information in the record that is not recorded elsewhere.
Examples include such things as documenting the results of a meeting, an important telephone
conversation, or an oral agreement. Type or handwrite these most informal memorandums. See
figure 10-1. A full signature line and identification symbols are not required; however, it should
be dated, signed, and show the organizational position of the signer. If it is only two or three
lines, include it on the file copy of your document. Leave out the subject line if you add your
MFR to the file copy.
2. From-To Memorandum. Use OPNAV 5215/144A DON Memo (8-1/2 X 11) or OPNAV
5215/144B DON Memo (8-1/5 X 5-1/2) for the “from—to” memorandum. Memorandum may
be directed to one or more addressees. If very informal, it may be handwritten. If the subject is
insignificant, a file copy is not required. See figure 10-2.
3. Plain-Paper Memorandum. Use plain-paper memorandums for informal communications
within your activity. It is no more formal than the memorandum form, but it is more flexible
when there are multiple addressees, via addressees, or both.
a. Identification Symbols. The only identification symbol you need is the date, unless
local practice calls for more.
b. Format. Prepare on white bond paper. Type the date on the sixth line so it ends flush
with the right margin unless it is used as part of the senders symbol. See figures 10-3 and 10-4.
4. Letterhead Memorandum. The letterhead memorandum may be used within your activity
and provides more formality than the printed form or plain-paper memorandum. When direct
liaison with individuals outside of your activity is authorized, the letterhead memorandum may
be used to correspond on routine matters that neither make a commitment nor take an official
stand. A full signature line is not required because the “From:” line identifies the signer. See
figure 10-4. For example: You have been appointed chairperson of a committee and need to
correspond with other members of the committee outside your activity.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-2
5. Decision Memorandum. When only requesting an approval/disapproval decision from a
single addressee, it is appropriate to type a decision block at the left margin, two lines below the
signature line in the following format:
COMMANDING OFFICER DECISION:
_____________________ Approved
_____________________ Disapproved
_____________________ Other
6. Memorandum of Agreement or Memorandum of Understanding
a. Use. The Memorandum of Agreement or Understanding may be used to document
mutual agreements of facts, intentions, procedures, limits on future actions, and areas of present
or future coordination, or commitments, etc. If a Memorandum of Agreement or Understanding
is initiated by a non-DoD activity, DON activities are authorized to use their format.
b. Format. Center “MEMORANDUM OF AGREEMENT” on the second line below the
date line. Center “BETWEEN” on the next line and follow with the names of the agreeing
activities (centered). To prepare a “Memorandum of Understanding,” substitute those words for
“Memorandum of Agreement,” and follow the same format as shown in figures 10-5 and 10-16.
Number and letter paragraphs and subparagraphs the same as other correspondence. The basic
text may contain, but is not limited to, the following titled paragraphs:
(1) Purpose. This paragraph defines or states in as few words as possible, the purpose
of the agreement.
(2) Problem. Present a clear, concise statement of the problem, to include a brief
background.
(3) Scope. Add a short statement specifying the area covered by the agreement.
(4) Agreement, Understanding. Spell out the agreement or understanding and
responsibilities of and between each of the parties involved.
(5) Effective Date. Enter the date the agreement will take effect.
c. Letterhead. On plain bond, type the command titles so the senior is at the top. If the
activities are in different cities or states, follow each title with its address.
d. Signatures. Arrange signature lines so the senior official is at the right. Place the
signature line of a third cosigner in the middle of the page. Precede all signature lines by over
scoring as shown in figures 10-5 and 10-7. The senior activity should sign the agreement after
the junior activity(ies).

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-3
e. Copies. The activity signing last should send copies of the agreement to all cosigners.
17 Jun 09
%
MEMORANDUM FOR THE RECORD
%
Subj:**MEMORANDUM FOR THE RECORD
%
1.**Use an MFR to record information in the record
that is not recorded elsewhere. Examples include such
things as results of a meeting, telephone
conversations, oral agreements, and other relevant
information.
%
2.**Type or handwrite these most informal memorandums.
If it is only two or three lines, include it on the
file copy of your document. Leave out the subject
line if you add your MFR to the file copy.
%
3.**A full signature line and identification symbols
are not required; however, it should be dated, signed,
and show the signer’s organizational code.
%
%
%
M. J. FORD
N11

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-4
FIGURE 10-1. MEMORANDUM FOR THE RECORD
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
Memorandum
DATE:
FROM:
TO:
SUBJ:
----------------The area above this line is preprinted. Fill in as appropriate.---------------
%
Ref:***(a)*SECNAV M-5216.1
%
Encl:**(1)*Printed Form
%
1.**This printed form is used for corresponding between
individuals and offices of the same activity. Very informal
memorandums may be hand written.
%
2.**The memorandum form comes in two sizes:
%
****a.**OPNAV 5216/144A (8-1/2 by 11 inches):
%
****b.**OPNAV 5216/144B (8-1/2 by 5-1/2 inches):
%
3.**The only identification symbol you need is the date, unless
local practice calls for more.
%
4.**Use names, titles, or codes in the “From:” and “To:” lines.
%
5.**Type reference and enclosure headings under the printed
headings. Note the headings for reference (a) and enclosure
(1). Allow a 1-inch left margin.
%
6.**The writer signs his or her name without the organizational
titles.
%
%
%
Signature
SAMPLE

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-5
OPNAV 5216/144A (Rev. AUG 1981)
FIGURE 10-2. PRINTED "FROM-TO" MEMORANDUM
%
%
%
%
%
8 Jul 09
%
MEMORANDUM
%
From:**Head, DON Records Management Branch (N161)
To:****Head, Technical Library Branch (N21)
*******Head, Mail and Files Branch (N13)
Via:***Head, Office Services Division (N1)
%
Subj:**PLAIN-PAPER MEMORANDUM
%
1.**The plain-paper “from-to” memorandum may be used within
your activity. It is no more formal than the memorandum
form, but it is more flexible when there are multiple
addressees, via addressees, or both.
%
2.**The only identification symbol you need is the date,
unless local practice calls for more. Start typing the date
on the sixth line, flush with the right margin.
%
3.**Prepare a plain-paper memorandum on white bond.
%
%
%
N. D. SOLAR

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-6
FIGURE 10-3. PLAIN-PAPER "FROM-TO" MEMORANDUM
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAVAL AIR FORCE
U.S. ATLANTIC FLEET
NORFOLK VA 22015-3421
5216
Memo 00/83
5 Jan 10
%
MEMORANDUM
%
From:**Head, Management Services Department, Naval
*******Air Facility, Detroit
To:****Operations Officer, Navy Regional Data
*******Automation Center, San Francisco
%
Subj:**LETTERHEAD MEMORANDUM
%
1.**When used within an activity, the letterhead memorandum
provides more formality than the printed memorandum form or
the plain-paper memorandum.
%
2.**A letterhead memorandum may be sent outside your
activity if:
%
****a.**Direct liaison is authorized,
%
****b.**The matter is routine, and
%
****c.**The memo neither makes a commitment nor takes an
official stand.
%
3.**Generally follow the standard letter format, but type
“MEMORANDUM” as shown here.
%
%
%
W. S. NELSON

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-7
FIGURE 10-4. LETTERHEAD MEMORANDUM
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAVAL AIR FORCE ATLANTIC
NORFOLK VA 23511-2494
%
MSC NAVINTCOM
5216 5216
Ser N02/234 Ser N7/702
18 Dec 09 20 Dec 09
%
MEMORANDUM OF AGREEMENT
BETWEEN
COMMANDER, MILITARY SEALIFT COMMAND
AND
COMMANDER, NAVAL INTELLIGENCE COMMAND
%
Subj:**MEMORANDUM OF AGREEMENT
%
1.**This example shows a one page “Memorandum of Agreement”
(MOA).
%
2.**On plain bond, type the command titles so the senior is
at the top. If the activities are in different cities or
states, follow each title with its address.
%
3.**Center “MEMORANDUM OF AGREEMENT” on the second line
below the date line. Center “BETWEEN” on the next line and
follow with the names of the agreeing activities. To
prepare a “Memorandum of Understanding” substitute those
words for “Memorandum of Agreement.” If your agreement is
two or more pages long, number and letter paragraphs and
subparagraphs the same as a standard letter.
%
4.**Arrange signature lines so the senior official is at the
right. Type a signature line above the signature lines.
%
5.**If your activity is the last to sign, send copies of the
signed agreement to all cosigners.
%

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-8
%
%
________________ __________________
M. L. SIMPSON B. D. WATSON
Acting Deputy
FIGURE 10-5. MEMORANDUM OF AGREEMENT
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
NAVAL AIR FORCE ATLANTIC
NORFOLK VA 23511-2494
%
NAVSEASYSCOM NAVAIRSYSCOM
5216 5216
Ser N02/234 Ser N7/702
12 Nov 09 15 Nov 09
%
MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING
BETWEEN
COMMANDER, NAVAL SEA SYSTEMS COMMAND
AND
COMMANDER, NAVAL AIR SYSTEMS COMMAND
%
Subj:**MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING
%
Ref:***(a) SECNAV M-5216.5
%
1.**Purpose. This example shows the first page of a two-
page “Memorandum of Understanding” (MOU). This paragraph
defines or states, in as few words as possible, the purpose
of the agreement or understanding. Use the MOU or MOA to
informally document mutual agreements of:
%
****a.**Facts.
%
****b.**Intentions.
%
****c.**Procedures.
%
****d.**Limits of future actions either or both will take.
%
****e.**Present or future coordination.
%

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-9
****f.**Present or future commitments.
%
2.**Problem.**Present a clear, concise statement of the
problem, to include a brief background. Mention reference
(a) and any other references in the text.
%
3.**Scope.**Add a short statement specifying the area
covered by the agreement.
FIGURE 10-6. MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING – FIRST PAGE
Subj:**MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING
%
4.**Agreement/Understanding. Spell out the agreement or
understanding and responsibilities of and between each of
the parties involved.
%
5.**Effective Date. Enter the date the agreement will take
effect.
%
%
%
_______________ _______________
W. T. DOOR T. CRUISE
Acting

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-10
2
FIGURE 10-7. MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING - SECOND PAGE
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
10-11

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-1
CHAPTER 11
Business Letters
11-1 General. Use the business letter to correspond with agencies, businesses, or individuals
outside DoD, who are unfamiliar with the standard letter. It alsomay be used for official
correspondence between individuals within DoD, when the occasion calls for a personal
approach. Before reading further, review figures 11-1, 11-2, and 11-3.
11-2 Parts of a Business Letter and Format
1. Identification Symbols. Include the following three identification symbols in the upper left
corner, blocked one below the other:
a. SSIC;
b. Originator’s code; and
c. Date. Write the date in month-day-year order. The month is written out in full,
followed by the day in Arabic numerals, a comma, and the full year also in Arabic numerals, e.g.,
May 25, 1967.
2. Inside Address. Place the inside address two to eight lines below the date, blocked flush
with the left margin. Placement of the inside address may be adjusted depending on the length of
the letter or local policy. Refer to figure 11-4 for proper placement of the inside address when
preparing a letter for use with a window envelope.
a. If your letter is directed to a particular individual, include the:
(1) Addressee’s courtesy title (Mr., Mrs., Ms.) and full name;
(2) business title (Vice President, Accounting), if appropriate;
(3) business name;
(4) street address; and
(5) the city, state, and ZIP+4 code on the last line. Note new requirement for only one
space between state and ZIP code vice two to five spaces.
b. If your letter is directed to a business in general, include the:
(1) Business name;
(2) full street address; and

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-2
(3) the city, state, and ZIP+4 code on the last line.
3. Attention Line. An attention line is optional. Use it to direct your letter to a business in
general and to also bring it to the attention of a particular person or department at the same time.
Start typing two lines below the last line of the inside address, blocked flush with the left margin,
and two lines above the salutation. See figure 11-5. Refer to figure 11-4 for proper placement of
theattention line when preparing a letter for use with a window envelope.
4. Salutation Line. Capitalize the first letter of the first word of the salutation as well as the
first letter of the addressee’s courtesy title and surname such as “Dear Mr. (or Ms., Mrs., Miss,
Dr., Captain, Lieutenant) Jones,” followed by a colon.
a. If your letter is addressed to:
(1) An all male organization, use a salutation such as “Gentlemen” or “Dear Sirs.”
(2) An all female organization, use a salutation such as “Ladies” or “Mesdames.”
(3) A mixed gender organization, or if you are not sure of the gender mix, use a
collective salutation such as “Ladies and Gentlemen” or “Dear Sir or Madam.”
(4) A business in general, but directed to the attention of a particular person or
department, use a collective salutation such as “Ladies and Gentlemen.”
b. If you cannot determine the gender of the addressee from previous communications,
omit the courtesy title (Mr., Mrs., Ms., etc.) and address the individual by first name or initial(s)
and last name such as “Dear Lee Doe” or “Dear L. Doe.”
c. Refer to appendices A and B for models of address and salutations. Start typing on the
second line below the last line of the inside address or attention line, flush with the left margin.
5. Subject Line. Use of a subject line is optional and may replace the salutation. The subject
line should be very brief, to the point, and not be more than one line in length if possible.
Capitalize every letter in the subject line. See figure 11-2.
a. If the subject line is replacing the salutation, start typing on the second line below the
last line of the inside address or attention line, flush with the left margin.
b. If the subject line is in addition to the salutation, start typing on the second line below
the salutation line.
6. Body of the Letter. Single-space within paragraphs and double space between paragraphs.
Indent main paragraphs four spaces and start typing on the fifth space. Do not number main

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-3
paragraphs. The first lines of subparagraphs should be indented, and lettered or numbered in
standard letter fashion. See figure 11-1. A business letter that is likely to run eight lines or less
may be double-spaced. Figure 11-6 is an illustration of a short business letter.
7. References and Enclosures. Refer to previous communications and enclosures in the body
of the letter only, without calling them references or enclosures.
8. Complimentary Close. Use “Sincerely” followed by a comma for the complimentary close
of a business letter starting at the center of the page on the second line below the text.
9. Signature Line
a. Start all lines of the signature line at the center of the page, beginning on the fourth line
below “Sincerely.” Type or stamp the following information:
(1) Signer’s name in all capital letters, with the exception of a last name starting with a
prefix, which would appear like this:
EXAMPLE:
J. A. McBREARTY
(2) Military grade (if any) spelled out,
(3) Functional title, and
(4) Authority line. The authority line may be omitted on a routine business letter that
neither makes a commitment nor takes an official stand.
b. Women’s names may begin with “Miss,” “Mrs.,” or “Ms.” One exception to this would
be when using “Mrs.” plus the writer’s husband’s name, which would appear like this: “MS.
ALBERT B. SEAY” or “MRS. A. B. SEAY.”
10. Enclosure Line
a. Type “Enclosure” on the second line below the signature line, number and describe
them briefly.
EXAMPLE:
Enclosures: 1. GPO Style Manual
2. Webster’s Dictionary
b. If the enclosures are insignificant, you do not have to describe them in the enclosure
line. Type “Enclosures” and the number of enclosures within parentheses: Enclosures (2).

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-4
11. Separate Mailing. When an enclosure is to be sent separately, type “Separate Mailing” and a
brief description like this:
EXAMPLE:
Separate Mailing: SECNAV M-5216.5
12. “Copy To:” Line. If everyone should know that a particular addressee will receive an
information copy, show that addressee by using a copy notation. Type “Copy to:” at the left
margin on the second line below the enclosure line, if any, or the signature line. List addressees
at the left margin or following “Copy to:”. Use long titles for activities listed in the SNDL:
EXAMPLE:
Copy to: Chief of Naval Operations (N86)
13. Outgoing Copies. Because the business letter does not have a “From:” line, every copy that
goes to addressees outside your activity must have a letterhead copy (printed, typed, stamped, or
reproduced from the original) to show its origin.
14. Identifying Second and Succeeding Pages. Repeat the identification symbols, from the first
page, on the sixth line from the top at the left margin. Continue the text beginning on the second
line below the identification symbols. See figure 11-3.
15. Numbering Pages. Do not number a single-page letter or the first page of a multiple-page
letter. Center page numbers 1/2 inch from the bottom edge, starting with the number 2. No
punctuation accompanies a page number. (To number the pages of a Top Secret document, see
SECNAV M-5510.36.)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-5
****Main paragraph format.
%
********a.**Indent each new subdivision eight spaces
and start typing at the ninth space.
%
********b.**Text.
%
************(l)*Documents rarely require subdividing to
the extent shown below.
%
************(2)*Text.
%
****************(a)*Text.
%
****************(b)*Text.
%
********************(1)*Text.
%
********************(2)*Text.
%
************************(a)*Text.
%
************************(b)*Never subparagraph beyond
this level.
%
****Text.
%
********a.**Indent each new subdivision eight spaces
and start typing at the ninth space.
%
********b.**Text.
%
************(9)*Text.
%
************(10)*When using two digits, continue to
indent each new subdivision (paragraphs will not line
up).

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-6
FIGURE 11-1. BUSINESS LETTER PARAGRAPH FORMATS
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
USS NEW HAMPSHIRE (SSN 778)
FPO AE 09579-2305
5216
Ser SSN 778/28
January 5, 2009
%
Mr. A. B. Seay
Vice President, Accounting
Widgets Unlimited, Inc.
1234 Any Street
Baltimore, MD 21085-1234
%
Dear Mr. Seay:
%
SUBJECT: PREPARATION OF A BUSINESS LETTER
%
****This example shows the first page of a two-page
business letter. A subject line is optional, but if used
will replace the salutation. Phrase the subject line in
normal word order. Make it very brief, to the point, and
not longer than one line. Capitalize every letter in the
subject line.
%
****Refer to previous communications and enclosures in the
body of the letter only, without calling them references or
enclosures. Do not number main paragraphs. Subparagraphs
are numbered and lettered the same as a standard letter.
%
****Start a paragraph near the end of a page only if that
page has room for two lines or more. Continue a paragraph
on the following page only if two lines or more can be
carried over. A signature page must have at least two
lines of text.
%
****Do not number the first page of a single page letter or
multiple page letter. The first page is assumed to be page
1. Center page numbers 1/2 inch from the bottom edge,
starting with the number 2. No punctuation accompanies a
page number.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-7
FIGURE 11-2. BUSINESS LETTER – FIRSTPAGE
5216
Ser SSN 778/28
January 5, 2009
%
****This example illustrates second and final page of a
business letter. Start typing on the sixth line flush with
the left margin. Repeat sender symbol from the first page.
Continue the text from the first page on the second line
below the date.
%
****Be sure to mention any enclosed documents in the body
of your letter and list them as enclosures on the second
line below the signature line. Type “Enclosures:” and
follow with a number and a brief description of the
enclosures (do not number when you have only one
enclosure). When the enclosures are of little importance,
instead of listing them with a description, you may
indicate the number of enclosures in parentheses without
the description; e.g., Enclosures (2). Materials, referred
to in the letter, that are being mailed separately should
be noted as shown below.
%
****To send an addressee an information copy or a courtesy
copy, type “Copy to:” flush with the left margin, two lines
below the signature line or two lines below any preceding
notation, such as the enclosure or separate mailing
notation.
%
Sincerely,
%
%
%
R. TREVOR KING
Executive Officer
By direction
of the Commander
%
Enclosures:**1.**Sample Business Letter
*************2.**SECNAVINST 5216.50
%
Separate Mailing:**Secretarial Handbook
%
Copy to:**Chief of Naval Operations (N61)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-8
2
FIGURE 11-3. BUSINESS LETTER - SECOND PAGE
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
USS MOMSEN (DDG 92)
FPO AP 99672--1307
5216
Ser 303/405
June 8, 2009
ATTN: RECORDS MANAGER
C & A TOOL COMPANY
505 FRANKLIN STREET
BELVIEW, VA 22812-1234
SUBJECT: SUBJECT LINE AND WINDOW-ENVELOPE FORMAT
[C & A Tool Company,] In this example the subject line
is used in place of the salutation. This is allowed on
routine administrative letters. The first sentence serves
as a greeting to the reader as shown above in [ ]. Start
typing the identification symbols on line 10, just below
the seal. Always start the address on line 16; the
salutation or subject line on line 25.
You may use a number 10 window envelope if the entire
address takes no more than five lines, it does not extend
past the middle of the page, and the letter and all
enclosures are unclassified. The full address must appear
in the window no matter how the letter may shift in the
envelope.
To fold the letter, turn up the bottom edge so it just
covers the subject and then turn back the address portion
so the upper fold falls along the top of the subject.
Sincerely,
Line 16
Line 25

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-9
ANN C. PHILLIPS
Commander, U.S. Navy
Executive Officer
By direction of the
Commanding Officer
FIGURE 11-4. BUSINESS LETTER FOR WINDOW ENVELOPES
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
USS ENTERPRISE (CVN 65)
FPO AE 09543-2810
5216
Ser 945/321
June 7, 2006
%
National Widget Company
6543 W. Hobson Street
New York, NY 12345-6789
%
Attention: H. Jones
%
Ladies and Gentlemen:
%
****When writing to a company, but directing your letter to a
particular person or office, use an attention line. The
attention line is placed two lines below the last line of the
inside address; type “Attention:” and then a name or title.
%
****The salutation must agree with the first line of the
address. It the first line is a business, division, or
organization collectively, a collective salutation such as
“Ladies and Gentlemen” is used even if the attention line
directs the letter to an individual. Note the inside address
and salutation in this letter.
Sincerely,
S. F. HANSON
Commander, U.S. Navy
Commanding Officer
Acting

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-10
FIGURE 11-5. BUSINESS LETTER WITH AN "ATTENTION" LINE
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
OFFICE OF THE CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS
2000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON DC 20350-2000
5216
Ser 301/789
April 7, 2006
%
Ms. Jane Ryan
J. M. Corporation
287 Duke Street
Newton, CA 93333-4321
%
Dear Ms. Ryan:
%
****This is an illustration of a short business letter.
There are several techniques you may use to balance the
appearance of a letter containing 100 words or less:
%
****a.**Start the inside address up to eight lines below
the date.
%
****b.**Use side margins of up to two inches.
%
****c.**In a letter containing eight lines or less, you
may double-space throughout the text.
{Note proper use of Ms. in parentheses in signature line.}
%
Sincerely,
%
%
%
(Ms.) F. E. ROBINSON
Head, Management Services

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
11-11
FIGURE 11-6. SHORT BUSINESS LETTER

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-1
CHAPTER 12
Executive Correspondence
12-1 General. This section provides specific guidance on the internal and external written
communication particular to the Headquarters, Department of the Navy (HqDON). When
forwarding correspondence to offices of flag/general officers and senior civilian officials within
HqDON, every effort should be made to strictly adhere to prescribed formats, as deviation could
unnecessarily delay processing for administrative action or complete restaffing.
12-2 Processes
1. Correspondence Management. HqDON correspondence is safeguarded and electronically
routed, reviewed, and edited through the Correspondence Management System – Taskers
Version 4.4. Taskers is a Web-based computer tracking system that is utilized as a contexts
manager for all official action and information correspondence (referred to as “taskers”) for
HqDON and selected echelon 2 commands. Refer to the Tasker User Guide 2006 for detailed
guidance on the Correspondence Management System.
2. Assigning Action to Incoming Correspondence. All action or information correspondence
received in HqDON is analyzed and routed to the appropriate office by the tasking authority for
chop, action, coordination or information.
a. Office of the Secretary and Under Secretary of the Navy. All action or information
correspondence for the Office of the Secretary of the Navy, Administrative Office (1000 Navy
Pentagon, Room 4E652, Washington, DC 20350) is controlled, routed and safeguarded.
(1) Incoming correspondence
(a) Upon receipt, general and Congressional correspondence shall be routed to an
executive civilian or staff assistant per SECNAVINST 5430.7Q, Assignment of Responsibilities
and Authorities in the Office of the Secretary of the Navy, and assigned as the action office to
facilitate coordination and review via SECNAV or Under Secretary of the Navy (UNSECNAV)
signature.
(b) Operational correspondence shall be assigned to the Director, Navy Staff or the
Director, Marine Corps Staff, as appropriate, for action or coordination to prepare proposed
responses for SECNAV or UNSECNAV signature.
(c) When coordination is required by both Navy and Marine Corps, the Office of
the Secretary of the Navy will determine who shall be the appropriate lead action office.
(2) Outgoing correspondence

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-2
b. Office of the Chief and Vice Chief of Naval Operations. All action or information
correspondence for the CNO and Vice Chief of Naval Operations (VCNO) signature is
controlled, routed and safeguarded by the Office of the Director, Navy Staff, Attn: Executive
Secretary (2000 Navy Pentagon, Room 4E563, Washington DC 20350).
(1) Incoming correspondence
(2) Outgoing correspondence
c. Office of the Commandant and Assistant Commandant of the Marine Corps. All action
or information correspondence for the CMC or Assistant Commandant of the Marine Corps
(ACMC) signature is controlled, routed and safeguarded by the Office of the Director, Marine
Corps Staff (3000 Marine Corps Pentagon, Room 4E448, Washington, DC 20350).
3. Routing Changes. Changes to action office assignment shall be made within 48 hours of
initial assignment. If the package requires transfer to another agency or office after that time, the
original action office shall coordinate with the receiving office. Prior to transferring action,
provide tasking authority with the name, organization, and telephone number of the new action
office.
4. Due Dates
a. General Correspondence. All general correspondence should be responded to within 20
working days of being entered into the Central Management System (CMS) for taskers. If
additional time is required, an interim letter and/or an approved extension are mandatory.
b. Congressional Correspondence. All Congressional correspondence should be
responded to within 7 working days of being entered into taskers. If additional time is required,
an interim letter will be sent. A copy of the interim letter shall be forwarded to the SECNAV
Congressional Liaison Office (CLO) for their files. All extensions must be coordinated with
SECNAV CLO.
5. Extensions. To request an extension of an OSD tasker, the action office must provide the
necessary information and prepare an official extension request with a SD Form 391 Secretary of
Defense Correspondence Action Report(see figure 12-1). The action office will also need to
provide a copy of the proposed interim that will be sent to the correspondent. All documents
shall be placed in the working documents area of the assigned tasker.
6. Interims
a. HqDON Correspondence
(1) An interim response shall be provided in the event the tasker cannot be answered
within the allotted time. It shall be used to acknowledge receipt of the tasker or letter, but more

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-3
importantly, to signal the desire to be responsive. The interim response will provide an overview
of the information available; the reason for the delay, along with a reasonable anticipated date
that the final reply shall be provided.
(2) It is the responsibility of the action office to ensure timely planning in the
preparation of interim responses. There shall be no extensions given in order to complete an
interim letter. The action office concerned shall forward a copy of all interim responses to
SECNAV Admin for retention. Subsequent interims shall be approved by the Administrative
Aide to the Secretary of the Navy (AASN).
b. OSD Correspondence. An interim response shall be prepared in accordance with
paragraph 6a. The interim response shall be signed out at the Assistant Secretary of the Navy
(ASN) level.
c. Congressional Correspondence. An interim response is required in the event the tasker
cannot be answered within the allotted time. It shall be used to acknowledge receipt of the tasker
or letter, but more importantly to signal the desire to be responsive (refer to figures 12-2, 12-3
and 12-4).
7. Distribution
a. A signed/dated copy of the correspondence with a copy of the action memo, references,
and background materials shall be returned to the action office. Only a signed copy of the
response shall be forwarded to the coordinating offices.
b. Envelopes and labels for all correspondence are the responsibility of the action office
and shall be included in all SECNAV/UNSECNAV or OSD signature packages. If packages are
missing labels, completed and signed correspondence shall be returned to the action office for
distribution.
12-3 General Guidelines for Preparing a Letter. Use letters for correspondence with
individuals outside the U.S. Government and for formal correspondence with officials of other
Federalagencies.
1. Stationery. Prepare all outgoing correspondence for SECNAV, CNO, or designated official
signature on the following letterhead:
a. Use SECNAV flag stationery (refer to figures 12-7 and 12-8) for personal
correspondence only (8 1/2 inches by 11 inches or 5 inches by 7 inches). Use plain bond for
successive pages.
b. Use SECNAV/UNSECNAV letterhead with DoD seal (refer tofigures 12-2 and 12-3)
for official correspondence (i.e., SECNAV addressed letters, business and personal, or official
responses to outside government officials) letters and memorandums requiring the SECNAV or

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-4
UNSECNAV signature). Use plain bond paper for successive pages. Additionally, use the DON,
Office of the Secretary of the Navy (refer to figure 12-6) when authorized to sign on behalf of
SECNAV (i.e., SECNAV instructions, notices and “reply direct” action responses).
c. CNO
d. VCNO
2. Format. Prepare all correspondence using 13 point, Times New Roman Font.
a. Salutations. All salutations shall be formal. The following guidance can be used to
prepare salutations, text for the body of the letter, closing lines, complimentary close and
signature line:
b. Opening Lines
(1) “Thank you for your letter of (date – November 6, 2005 – only use date if response
is timely) concerning...”
(2) “Thank you for your recent letter(s) concerning.........”
(3) “I am responding on behalf of...”
c. Body of the Letter
(1) Limit the use of “I" and "we."
(2) Indent each paragraph five spaces, start typing on the sixth space and do not
number the paragraphs.
(3) Limit response to one page whenever possible. Use enclosures if necessary.
(4) An acronym may be used after it is spelled out (be consistent throughout the
document).
(5) Spell out percent (instead of using the sign “%”).
(6) In replying to more than one member of Congress, you may use either:
(a) “A similar responsehas been sent to Senator (last name) and Senator (last
name), Congressman (last name) and Congressman (last name).”
(b) “A similar response has been sent to each of your colleagues who also
expressed an interest in this issue.”
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-5
d. Closing Lines (last paragraph)
(1) “Thank you for bringing this matter to my attention.”
(2) “I appreciate you taking the time to share your thoughts on this issue.”
(3) “As always, if I can be of any further assistance, please let me know.” (Preferred
on Congressional responses.)
e. Signature Lines
(1) Correspondence prepared for the signature of other officials should contain
standard closing and signature lines.
(2) The following is a sample of the signature line:
(a) Type the name at the center of the page on fourth line below the last line of
text or complimentary close.
(b) Type the official title on the line below his/her name commencing at the center
of the page as well.
f. Copy To. When writing a member of Congress in the capacity of Committee Chairman,
send a courtesy copy to the Committee ranking minority member (see figures 12-4, 12-5, and 12-
6). Indicate the “Copy to” addressee at the bottom left of the letter (two lines after signature
line).
EXAMPLES:
Senior Civilian Military
Ashley Godwin C. W. MARTOGLIO
Deputy Assistant Secretary of the Navy Rear Admiral, U.S. Navy
(Financial Management & Comptroller) Senior Military Assistant
to the Secretary of the Navy
NOTE: Title/position is not required if reflected in the letterhead.
EXAMPLE: Copy to:
The Honorable ________________
Ranking Minority Member

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-6
3. Date Line. Do not type the date on correspondence to be signed. Correspondence will be
dated by SECNAV Admin once the signature has been obtained.
4. Complimentary Closing. Use “Sincerely,” followed by comma for the complimentary close
for routine and congressional correspondence. Start the complimentary close at the center of the
page on the second line below the text. Also use “Sincerely,” for complimentary close of a flag
personal letter.
5. Page Numbering. Number second and succeeding pages at the bottom center of the page
allowing at least a double space below the last line of text and 1/2 inch from the bottom of the
page.
6. Congressional Committees or Subcommittees Correspondence. Responses addressed to
chairpersons of Congressional committees or subcommittees are of particular importance and
require additional guidance. Address the response to the chairperson with a courtesy copy to the
ranking minority member. The closing paragraph will specify other chairpersons receiving a
similar response. Examples of acceptable closing paragraphs are provided in this chapter.
SECNAV will sign all correspondence addressed to the chairpersons of Congressional
committees or subcommittees except for routine reports to Congress. Correspondence
addressing significant or high profile issues will also be signed by SECNAV. Deviation from
this policy must be requested and approved through the CLO.
12-4. General Guidelines for Preparing a Memorandum. Use memoranda for
correspondence within the Office of the Secretary of the Navy, DoD, the President and the White
House staff, and to send routine material to other Federalagencies. Standard memorandums are
used for routine correspondence within the DON.
1. Action or Information (“Info”) Memorandum
a. The following procedures shall be used for the preparation of SECNAV action (figure
12-9) or info memorandums (figure 12-10):
(1) Limit to one page, unless issue is complex and requires greater explanation.
(2) Use short, concise and clear bullet statements (use of black dot bullet preferred).
(3) Use 13 point, Times New Roman font.
(4) Page setup: 1-inch margins, top and bottom, right and left.
(5) Double space between headings.
(6) Double space between bullets.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-7
(7) Number pages at bottom center starting on page 2.
(8) If the document is classified, annotate the appropriate security classification
markings, with classification/declassified instructions, at the top and bottom of the document.
(9) Do not staple or use clam clips to assemble.
(10) An acronym may be used after it is spelled out the first time.
b. Lead offices must also prepare an action memo for the following types of
correspondence:
(1) Prepare reply for Secretary of Defense (SECDEF) signature (PRS).
(2) Prepare reply for Deputy Secretary of the Defense (DEPSECDEF) signature (PRD).
(3) Answer SECDEF note (ASN).
(4) Answer DEPSECDEF note (ADN).
(5) Answer military assistant note (AMAN).
(6) An action memo signed by a principal or deputy of the lead office must be prepared
for submission to the SECDEF, DEPSECDEF via SECNAV and UNSECNAV.
2. Package Assembly
a. The lead office will submit the proposed response to SECNAV Admin after assembling
the package for signature. The package will include an action memo or info memo and be set up
as follows:
(1) An action or info memo is required when forwarding documents to SECNAV. The
action/info memo shall be the top page on the right side of the package.
(2) All tabs must be identified in the action/info memo and shall be placed on the right
side of the folder under the memo. Use the following procedures to identify the contents of each
tab.
(a) TAB A. The action item (e.g., item for signature or approval). If a similar
letter is going to multiple addresses, all letters can go at TAB A. If there are different items for
signature or approval, they should be separated at TAB A-1, A-2, etc.
(b) TAB B. Incoming correspondence (if applicable).

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-8
(c) TAB C. Background information. If more than one tab is needed, tab
accordingly. If substantive or lengthy background information is forwarded, provide a one-page
executive summary of the information.
(d) TAB D (or last tab in package). Coordination information. Provide the
SECNAVa coordination page to identify a list of coordinating offices/activities (figure 12-11).
All coordination shall be provided or listed on one page and should be the last tab. Include
office/department, point of contact, phone number and date the package was processed or
coordinated. Concurrences must be obtained from heads of the SECNAV components involved,
or, in their absence, the principal deputy. List non-concurrence and provide comments at the
coordination tab. If the package did not require coordination, state “none” on the action or info
memo. When providing coordination, list principles, deputies or executive assistants as points of
contact for all correspondence to be signed by the SECNAV or UNSECNAV.
Approval/credibility of an action memo often depends on the coordination efforts.
b. Folder Assembly
(1) The package shall be assembled as follows:
Left side Left Side Right Side
Route Slip/Buck Slip
Incoming Letter
Drafts
Right Side
Action or Info Memo
TAB A (action)
TAB B (reference)
TAB C (summary/chops)
TAB D (coordination)
(2) Tabs are required to be typed and displayed in consecutive order on the far right
hand side on a separate plain tab paper. The reviewer should be able to see all tabs at once.
Copy of Tasker
TAB D
TAB C
TAB B
TAB A
Incoming Letter
Drafts
Actionor Info
Memo

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-9
FIGURE 12-1. SD FORM 391– DOD CORRESPONDENCE ACTION REPORT
SAMPLE

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-10
CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS
WASHINGTON, DC 20350-1000
April 7, 2009
Mr. or Ms. ( )
1234 Anywhere Street
Everywhere, NV 89701
Dear Mr. or Ms. ( ):
This is to acknowledge your letter of (April 2, 2007) (Use “recent” letter) to
(addressee) concerning (subject). (If not addressed to CNO then insert the
following: Your letter has been forwarded to the Chief of Naval Operations for
reply). Your letter has been referred to (lead office). I am responding on behalf of
(name).
We are gathering the information necessary to provide you a substantive
response and will reply further upon completion of our investigation into this
matter. You can expect a final response by (specify date) (up to 30 days from
original due date).
In the interim, if you require further assistance or have additional information
to provide, you may contact (name, phone number) who is coordinating the
response.
Sincerely,
G. ROUGHEAD
[Title/Position] (Not required when
replicated on letterhead)
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-11
FIGURE 12-2. SAMPLE INTERIM RESPONSE FOR INCOMINGCORRESPONDENCE

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-12
THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
WASHINGTON, DC 20350-1000
January 18, 2009
The Honorable ( )
(United States Senate) (House of Representatives)
Washington, DC (20510) (+ (4 digit code)
Dear (Senator or [Mr., Mrs., or Ms.]) (Last Name):
This is an interim response to your correspondence of (April 2, 2007) (Use
"recent" letter if response is not timely) on behalf of your constituent, (Full Name),
concerning (Subject).
We are currently gathering information necessary to provide you a
substantive response to address your inquiry. The issue(s) addressed in your letter
raised several questions concerning (Subject). You can expect our final reply by
(date – December 6, 2005).
If you should need any further assistance regarding this matter, please
contact (Action Officer, E-mail address, and Phone Number).
Sincerely,
Ray Mabus
[Title/Position] (Not required when
replicated on letterhead)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-13
FIGURE 12-3. SAMPLE INTERIM RESPONSE FOR CONGRESSIONAL
CORRESPONDENCE
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
OFFICE OF THE SECRETARY
1000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON, DC 20350-1000
January 15, 2009
The Honorable (Full Name)
Chairman, Committee on
Armed Services
House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20515
Dear Mr. or Madam Chairman:
Thank you for your letter of (July 31, 2007), concerning (Subject), I am
responding for the Secretary of the Navy.
(Response).
Again, I appreciate your taking the time to share your thoughts on this issue. If I
can be of further assistance, please let me know.
Sincerely,
Sean J. Stackley
Assistant Secretary of the Navy
(Research, Development and Acquisition)
[Title/Position] (required when not
replicated on letterhead)
Enclosure (if applicable)
Note: If a Senator or Congressman/woman uses letterhead paper
that lists him/her as Chairperson, the response should be in
the above format. Otherwise, address should be:
The Honorable (Full Name) The Honorable ( )
United States Senate House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20510 Washington, DC 20515
Dear Senator (Last Name): Dear Mr., Mrs., Ms.(Last Name):
A similar letter has been sent to Chairman ( ).
As always, if I can be of further assistance, please let me
know.
Copy to:
The Honorable ( )
Ranking Minority Member
Note
: This letterhead should be
used only by Principles who are
responding on behalf of The
Secretary of the Navy and have
been directed via Tasker, verbal, or
delegation.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-14
FIGURE 12-4. CONGRESSIONAL RESPONSE, ONE CHAIRPERSON
THE ASSISTANT SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
(RESEARCH, DEVELOPMENT AND ACQUISITION)
1000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON, DC 20350-1000
November 29, 2008
The Honorable (Full Name)
Chairman, Committee on
Armed Services
House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20515
Dear Mr. Chairman:
Thank you for your letter of (July 31, 2007), concerning (Subject).
(Response).
Again, I appreciate your taking the time to share your thoughts on this issue.
If I can be of further assistance, please let me know.
Sincerely,
Sean J. Stackley
[Title/Position] (Not required when
replicated on letterhead)
Enclosure (if applicable)
Note: If a Senator or Congressman/woman uses letterhead paper
that lists him/her as Chairperson, the response should be in the
above format. Otherwise, address should be:
The Honorable (Full Name) The Honorable ( )
United States Senate House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20510 Washington, DC 20515
Dear Senator (Last Name): Dear Mr., Mrs., Ms.(Last Name):
A similar letter has been sent to Chairman ( ).
As always, if I can be of further assistance, please let me know.
Copy to:
The Honorable ( )
Ranking Minority Member

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-15
FIGURE 12-5. CONGRESSIONAL RESPONSE, TWO CHAIRPERSONS
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
OFFICE OF THE SECRETARY
1000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON, DC 20350-1000
August 6, 2009
The Honorable (Full Name)
Chairman, Committee on
Armed Services
House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20515
Dear Mr. Chairman:
Thank you for your letter of (July31, 2007), concerning (Subject), I am
responding for the Secretary of the Navy.
(Response).
Again, I appreciate your taking the time to share your thoughts on this issue. If I
can be of further assistance, please let me know.
Sincerely,
Robert O. Work
Under Secretary of the Navy
[Title/Position] (Not required when
replicated on letterhead)
Enclosure (if applicable)
Note: If a Senator or Congressman/woman uses letterhead paper
that lists him/her as Chairperson, the response should be in
the above format. Otherwise, address should be:
The Honorable (Full Name) The Honorable ( )
United States Senate House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20510 Washington, DC 20515
Dear Senator (Last Name): Dear Mr., Mrs., Ms.(Last Name):
A similar letter has been sent to Chairman ( ).
As always, if I can be of further assistance, please let me
know.
Copy to:
The Honorable ( )
Ranking Minority Member
Note
: This letterhead should
be used only by Principles
who are responding on behalf
of The Secretary of the Navy
and have been directed via
Tasker, verbal, or delegation.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-16
FIGURE 12-6. CONGRESSIONAL RESPONSE, TO CHAIRMAN OF A SELECT
COMMITTEE
FIGURE 12-7. FLAG STATIONERY (8 1/2 X 11) – SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
12 December 2009
Chief of Naval Operations
2000 Navy Pentagon
Washington, DC 20350-2000
Dear Admiral Roughead,
Thank you for speaking on my behalf at this year’s Navy League
luncheon.
Your inspiring words received many compliments. Secretary
Gates expressed his appreciation and asked me to pass on many
thanks. I appreciate your valuable time.
Again, thank you.
Warmest Regards,
Ray Mabus

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-17
CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS
Vice Chief of Naval Operations
2000 Navy Pentagon
Washington, DC 20350-2000
Dear Admiral Greenert,
Thank you for hosting this years speaking on my behalf
at this year’s Navy League luncheon.
Your inspiring words received many compliments.
Secretary Gates expressed his appreciation and asked me to
pass on many thanks. I appreciate your valuable time.
Again, thank you and I appreciate your valuable time
spent and look forward to our next event.
Sincerely,
G. ROUGHEAD
Admiral, U.S. Navy
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-18
FIGURE 12-8. FLAG STATIONARY (5 x 7) – CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-19
[USE APPROPRIATE LETTERHEAD]
CLASSIFICATION (if required)
ACTION MEMO
February 21, 2009
FOR: SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
FROM: Anne Brennan, General Counsel of the Navy (Acting) (Full Name, Title)
SUBJECT: Action Memo Format (Use Title Case)
What the Secretary should do? This bullet explains what action is required. This is
different from the entry for recommendation (TAB A).
Due date for action. This bullet is used for incoming correspondence at TAB B.
Do not enter “I would like to have this done by” due date.
Why it is necessary and/or acceptable for the Secretary to approve or sign the
recommended action? This bullet identifies additional key points/contentious
issues and any problem areas (TAB C).
RECOMMENDATION: SECNAV approve or sign (TAB A).
NOTE: The recommendation supports the first bullet of the Action Memo. Use
this example if there is a document for signature. If no document for proposal/
signature at TAB A use below recommendation:
RECOMMENDATION: That SECNAV release funds by initialing as appropriate:
Approve_________ Disapprove_______
COORDINATION: [TAB D] (or as applicable – last tab) or [None]
ATTACHMENTS:
As stated
Classification/Declassification Authority and Instructions (if required)
Prepared By: Name, Organization, Phone (1 inch from the bottom)
CLASSIFICATION (if required)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-20
[USE APPROPRIATE LETTERHEAD]
CLASSIFICATION (if required)
INFO MEMO
December 6, 2009
FOR: SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
FROM: Roger Natsuhara, Assistant Secretary of the Navy (Installations and
Environment) (Full Name, Title)
SUBJECT: Info Memo Format
Reference: SECNAV M-5216.5
The first bullet will identify what information is being forwarded and why. If
forwarding a document, identify as TAB A.
The second and subsequent bullets will provide additional key points, as required:
background at TAB A.
When using a reference line, you would annotate it as shown above. A single
reference does not get assigned a letter. Multiple references are assigned (a), (b),
etc. The “R” in reference is the only letter capitalized. You would use the
reference line like this in all types of Executive Correspondence.
COORDINATION: [TAB D] (or as applicable – last tab) or [None]
ATTACHMENTS:
As stated
Prepared By: Name, Organization, Phone
FIGURE 12-9. ACTION MEMORANDUM
FIGURE 12-10. INFORMATION MEMORANDUM
**If there is more than one reference the reference line would look like the following:
References: (a) SECNAV M-5216.5
(b) SECNAV M-5510.36

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-21
[USE PLAIN BOND PAPER]
COORDINATION PAGE
Office/Dept Point of Contact/Title Phone Date
OPNAV (N44) RDML Jones (703) 555-1212 10 May 09
Director
OPNAV (N4B) Mrs. A. Whittemore (703) 556-1111 19 Mar 09
ADCNO
DMCS Col Jones (703) 697-1668 12 May 09
SGS
DNS VADM Fitzgerald (703) 555-1213 19 Apr 09
Director
ASN I&E Mr. B.J. Penn DSN 225-2222 22 May 09
ASN
DASN (I&E) Mr. Wayne Arny (703) 555-1215 22 May 09
DASN
FIGURE 12-11. COORDINATION PAGE

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-22
THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20350-1000
April 7, 2009
MEMORANDUM FOR SECRETARY OF DEFENSE
DEPUTY SECRETARY OF DEFENSE
SUBJECT: Preparing a Memorandum for the Office of the Secretary of Defense
Use memoranda for correspondence within the Department of Defense, to
the President and White House staff, and to send routine correspondence to other
Federal Agencies. Memos may be sent to multiple addresses, but do not address
them to someone through another office or person.
Prepare memos on letterhead appropriate to the signing official. Set a two-
inch top margin and one-inch side and bottom margin on first pages. Use plain
paper for succeeding pages with one-inch margins on all sides.
Single-space paragraphs and double–space paragraphs between them.
Indent paragraphs a half-inch from the left margin. Indent subparagraphs an
additional half- inch and identify them with bullets, numbers, and lower case
letters. Double space between subparagraphs
Do not date memos the Secretary or Deputy Secretary of Defense will sign.
The date shall be added when signed. Also omit the signature line on memos the
Secretary or Deputy Secretary of Defense will sign. For other officials, the
signature line may be typed or stamped leaving four blank lines below the text,
beginning at the center of the page. Run-over lines should be indented two
spaces. The title in the signature line may be omitted if the signer’s position is
reflected in the letterhead.
Normally attachments shall be identified in the text of the memo. When
this is the case the notation “Attachments: As stated” shall be typed at the left
margin a double space below the signature line. When attachments are not
identified, list all of them in the order they appear in the text.
Ray Mabus
Attachments:
As stated
cc:
General Counsel

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
12-23
FIGURE 12-12. STANDARD MEMORANDUM FOR
APPENDIX A
MILITARY MODELS OF ADDRESS
Addressee Letter and Envelope Salutation
Navy and Coast Guard Officers
Admiral ADM Dear Admiral (surname):
Vice Admiral VADM “
Rear Admiral (Upper Half) RADM “
Rear Admiral (Lower Half) RDML
Captain CAPT Dear Captain (surname):
Commander CDR Dear Commander (surname):
Lieutenant Commander LCDR “
Lieutenant LT Dear Lieutenant (surname):
Lieutenant Junior Grade LTJG “
Ensign ENS Dear Ensign (surname):
Chief Warrant Officer CWO5 Dear Chief Warrant Officer (surname):
CWO4 Dear Chief Warrant Officer (surname):
CWO3 Dear Chief Warrant Officer (surname):
CWO2 Dear Chief Warrant Officer (surname):
Warrant Officer WO Dear Warrant Officer (surname):
Marine Corps, Air Force, and Army Officers
Marines Air Force Army
General Gen Gen GEN Dear General (surname):
Lieutenant General LtGen Lt Gen LTG “
Major General MajGen Maj Gen MG “
Brigadier General BGen Brig Gen BG “
Colonel Col Col COL Dear Colonel (surname):
Lieutenant Colonel LtCol Lt Col LTC “
Major Maj Maj MAJ Dear Major (surname):
Captain Capt Capt CPT Dear Captain (surname):
First Lieutenant 1stLt 1st Lt 1LT Dear Lieutenant (surname):
Second Lieutenant 2ndLt 2nd Lt 2LT “
Chief Warrant Officer 5 CWO5 CW5 Dear Chief Warrant Officer (surname):
Chief Warrant Officer 4 CWO4 CW4 “
Chief Warrant Officer 3 CWO3 CW3 “
Chief Warrant Officer 2 CWO2 CW2 “
Warrant Officer WO WO1 Dear Warrant Officer (surname):
Navy and Coast Guard Enlisted
Master Chief Petty Officer of the Navy MCPON Dear Master Chief (surname):
Master Chief Petty Officer of the Coast Guard MCPOCG “
Master Chief Petty Officer MCPO “
Senior Chief Petty Officer SCPO Dear Senior Chief (surname):
Chief Petty Officer CPO Dear Chief (surname):

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
A-1
Addressee Letter and Envelope Salutation
Petty Officer First Class P01 Dear Petty Officer (surname):
Petty Officer Second Class P02
Petty Officer Third Class P03
Airman (includes Apprentice AN or AA or AR Dear Airman (surname):
and Recruit)
Constructionman (includes CN or CAor CR Dear Constructionman (surname):
Apprentice and Recruit)
Fireman (includes FN or FA or SR Dear Fireman (surname):
Apprentice and Recruit)
Hospitalman (includes HN or HA or HR Dear Hospitalman (surname):
Apprentice and Recruit)
Seaman (includes SN or SA or SR Dear Seaman (surname):
Apprentice and Recruit)
Ma
Marine Corps Enlisted
Sergeant Major of the Marine Corps SgtMaj Dear Sergeant Major (surname):
Sergeant Major SgtMaj “
Master Gunnery Sergeant MGySgt Dear Master Gunnery Sergeant (surname):
First Sergeant lstSgt Dear First Sergeant (surname):
Master Sergeant MSgt Dear Master Sergeant (surname):
Gunnery Sergeant GySgt Dear Gunnery Sergeant (surname):
Staff Sergeant SSgt Dear Staff Sergeant (surname):
Sergeant Sgt Dear Sergeant (surname):
Corporal Cpl Dear Corporal (surname):
Lance Corporal LCpl “
Private First Class PFC Dear Private First Class (surname):
Private Pvt Dear Private (surname):
Army Enlisted
Sergeant Major of the Army SMA Dear Sergeant Major (surname):
Command Sergeant Major CSM “
Sergeant Major SGM “
First Sergeant 1SG Dear First Sergeant (surname):
Master Sergeant MSG Dear Master Sergeant (surname):
Platoon Sergeant PSG Dear Sergeant (surname):
Sergeant First Class SFC “
Staff Sergeant SSG “
Sergeant SGT “
Corporal CPL Dear Corporal (surname):
Private First Class PFC Dear Private (surname):
Private PVT “
Specialists (all grades) SP7 Dear Specialist (surname):
SP6 “
(etc)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
A-2
Addressee Letter and Envelope Salutation
Air Force Enlisted
Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force CMSAF Dear Chief (surname):
Chief Master Sergeant CMSgt “
Senior Master Sergeant SMSgt Dear Sergeant (surname):
Master Sergeant MSgt “
Technical Sergeant TSgt “
Staff Sergeant SSgt “
Sergeant Sgt “
Senior Airman SrA Dear Airman (surname):
Airman First Class A1C “
Airman Azun “
Airman Basic AB “
Other Military
All retired military (rank) (full name), (USN, Dear (rank) (surname):
USMCR or other branch) (Ret)
Chaplain Chaplain (full name) (rank), Dear Chaplain (surname):
CHC, USN
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
A-3
APPENDIX B
CIVILIAN MODELS OF ADDRESS
1. The following examples of civilian models of address, salutation, and complimentary close
are used in the preparation of Navy business-format letters. They may be varied depending on
circumstances.
2. Use “The Honorable (Name)” in the address of Presidential appointees as well as Federal and
state elected officials. Avoid “The Honorable” in addresses of county and city officials, except
for mayors.
3. Use the title “Madam” in the salutation of a letter to a high-level woman diplomat or
government official, such as the United States Ambassador to the United Nations. Use the title
“Madam” in salutations of letters destined for women foreign heads of state and diplomats.
4. Use the title “Ms.” when addressing a woman by her surname (Ms. Jones). However, “Ms.,”
like “Mr.,” indicates nothing with regard to a person’s marital status. Therefore, use “Miss” or
“Mrs.” in the salutation when an incumbent or correspondent has indicated this preference.
Never use “Ms.” with a woman’s full married name; e.g., “Ms. John E. Doe” is incorrect. Use
“Mr.” with a position or surname if you don’t know the addressee’s gender and can’t find out
readily.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-1
MODELS OF ADDRESS AND SALUTATION
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
The White House
The President The President Dear Mr. (or Madam) President:
The White House Respectfully yours,
Washington, DC 20500-0001
Husband (or Wife) of the President Mr. (or Ms.) (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
The White House Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20500-0001
Assistant to the President The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Assistant to the President Sincerely,
The White House
Washington, DC 20500-000 1
Secretary to thePresident The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Secretary to the President Sincerely,
The White House
Washington, DC 20500-0001
Secretary to the President (full rank) (full name) Dear (rank) (surname):
(with military rank) Secretary to the President Sincerely,
The White House
Washington, DC 20500-0001
The Vice President
As Vice President The Vice President Dear Mr. (or Madam) Vice President:
The White House Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20500-0001
As Senate President The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) President:
President of the Senate Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20510-0001
The Judiciary
The Chief Justice The Chief Justice of the United States Dear Mr. (or Madam) Chief Justice:
The Supreme Court of the United States Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20543-0001
Associate Justice Mr. (or Madam) Justice (surname) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Justice:
The Supreme Court of the United States Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20543-0001
Retired Justice The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Justice:
(local address) Sincerely,
Presiding Justice The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Justice:
Presiding Justice Sincerely,
(name of the court)
(local address)
Judge of a Court The Honorable (full name) Dear Judge (surname):
Judge of the (name of court; Sincerely,
if a U.S. district court,
give district).
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-2
(local address)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-3
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
Clerk of a Court Mr. (or Ms.) (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Clerk of the (name of court; Sincerely,
if a U.S. district court, give district).
(local address)
Attorney Mr. (or Ms.) (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Attorney at Law Sincerely,
(local address)
The Senate
President pro Tempore The Honorable (full name) Dear Senator (surname):
of the Senate President pro Tempore Sincerely,
of the Senate
United States Senate
Washington, DC 20510-0000
Committee Chairman, The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam)
U.S. Senate Chairman, Committee on Sincerely,
(name of committee)
United States Senate
Washington, DC 20510-0000
Subcommittee Chairman The Honorable (full name) Dear Senator (surname):
U. S. Senate Chairman, Subcommittee on Sincerely,
(name of subcommittee) OR
(name of parent committee) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Chairman:
United States Senate Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20510-0000 (When incoming correspondence
is so signed and pertains to
subcommittee business)
United States Senator The Honorable (full name) Dear Senator (surname):
(Washington, DC office) United States Senate Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20510-0000
OR
(Away from Washington, DC) The Honorable (full name) Dear Senator (surname):
United States Senator Sincerely,
(local address)
Senator, Majority (or Minority) The Honorable (full name) Dear Senator (surname):
Leader Majority (or Minority) Leader Sincerely,
(Washington, DC office) United States Senate
Washington, DC 20510-0000
OR
(Away from Washington, DC) The Honorable (full name) Dear Senator (surname):
Majority (or Minority) Leader Sincerely,
United States Senate
(local address)
United States Senator-elect The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
(Washington, DC office) United States Senator-elect Sincerely,
United States Senate
Washington, DC 20510-0000
OR
(Away from Washington, DC) Mr. (or Ms.) (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-4
United States Senator-elect Sincerely,
(local address, if given)
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
Office of a deceased Senator Mr. (or Ms.) (Secretary’s full name, Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
if known) Sincerely,
Secretary to the Late Honorable (full name)
United States Senate
Washington, DC 20510-0000
Former Senator The Honorable (full name) Dear Senator (surname):
(local address) Sincerely,
Secretary of the Senate The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Secretary of the Senate Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20510-0000
Secretary or Administrative Mr. (or Ms.) (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Assistant to a Senator Secretary/Administrative Sincerely,
Assistant to the
Honorable (full name)
United States Senate
Washington, DC 20510-0000
House of Representatives
Speaker of the House The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Speaker:
of Representatives Speaker of the House of Representatives Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20515-0000
Committee Chairman The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Chairman:
Chairman, Committee on Sincerely,
(name of committee)
House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20515-0000
Subcommittee Chairman The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Chairman, Subcommittee on Sincerely,
(name of subcommittee) OR
(Name of parent committee) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Chairman:
House of Representatives Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20515-0000 (When incoming correspondence
is so signed and pertains to
subcommittee business)
United States Representative The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
(Washington, DC office) House of Representatives Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20515-0000
OR
(Away from Washington, DC) The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Member, United States House Sincerely,
of Representatives
(local address)
Representative-elect The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Representative-elect Sincerely,
House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20515-0000
OR
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-5
Mr. (or Ms.) (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Representative-elect Sincerely,
(local address, if given)

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-6
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
Office of a deceased Mr. (or Ms.) (Secretary’s full name, Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Representative if known) Sincerely,
Secretary to the LateHonorable (full name)
House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20515-0000
Former Representative The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
(local address) Sincerely,
Resident Commissioner The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Resident Commissioner Sincerely,
from (name of area)
House of Representatives
Washington, DC 20515-0000
Delegate of the District The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
of Columbia House of Representatives Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20515-0000
Legislative Agencies
Comptroller General The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
(Head of the General Comptroller General of Sincerely,
Accounting Office) the United States
Washington, DC 20548-0000
Public Printer (Head of The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
the U.S. Government U.S. Government Printing Office Sincerely,
Printing Office) Washington, DC 20401-0000
Librarian of Congress The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Librarian of Congress Sincerely,
Washington, DC 20540-0000
Executive Departments
Members of the Cabinet The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Secretary:
(if addressed as ‘Secretary”) Secretary of (name of department)* Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Attorney General (Head of The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Attorney General
the Department of Justice Attorney General Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Under Secretary The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
of a Department Under Secretary of (name of department) Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Deputy Secretary of a Department The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Deputy Secretary of (name of department) Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Assistant Secretary of a Department The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Assistant Secretary of (name of department) Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
*Titles for Cabinet Secretaries are: Secretary of Agriculture, Secretary of Commerce, Secretary of Defense, Secretary of

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-7
Education, Secretary of Energy, Secretary of Health and Human Services, Secretary of Housing and Urban Development, Secretary
of Interior, Secretary of Labor, Secretary of State, Secretary of Transportation, and Secretary of the Treasury.
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
Independent Organizations
Director, Office of Management Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
and Budget Director, Office of Management Sincerely,
and Budget
Washington, DC 20503-0000
Head of a Federal Agency, The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
(title), (name of agency) Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Head of a major organization The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
within an agency (if appointed (title ) (organization) Sincerely,
by the President) (name of agency)
Washington, DC 00000-0000
President of a Commission The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
President, (name of commission) Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Chairman of a Commission The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Chairman:
Chairman, (name of commission) Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Chairman of a Board The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Chairman:
Chairman, (name of board) Sincerely,
Washington, DC 00000-0000
Postmaster General The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam)
Postmaster General Postmaster General
Washington, DC 00000-0000 Sincerely,
American Missions
American Ambassador The Honorable (full name) Sir (or Madam): (formal)
American Ambassador Dear Mr. (or Madam) Ambassador:
American Embassy . (informal)
(city), (country) Sincerely,
American Ambassador (full rank) (full name) Sir (or Madam): (formal)
(with military rank) American Ambassador Dear (rank) (surname):
American Embassy (informal)
(city), (country) Sincerely,
American Minister The Honorable (full name) Sir (or Madam): (formal)
American Minister Dear Mr. (or Madam) Minister:
(city), (country) (informal)
Sincerely,
American Minister (full rank) (full name) Sir (or Madam): (formal)
(with military rank) American Minister Dear (rank) (surname):
(city), (country) (informal)
Sincerely,

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-8
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
Foreign Government Officials
Foreign Ambassador in His (or Her) Excellency (full name) Excellency: (formal)
the United States Ambassador of (country) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Ambassador:
(local address) 00000-0000 (informal)
Sincerely,
Foreign Minister in the The Honorable (full name) Sir (or Madam): (formal)
United States Minister of (country) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Minister:
(local address) 00000-0000 (informal)
Sincerely,
Foreign Charge d’Affaires Mr. (or Madam) (full name) Sir (or Madam): (formal)
in the United States Charge d’Affaires of (country) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Charge
(local address) 00000-0000 Affaires: (informal)
Sincerely,
State and Local Government
Governor of State The Honorable (full name) Dear Governor (surname):
Governor of (state) Sincerely,
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Acting Governor of a State The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Acting Governor of (state) Sincerely,
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Lieutenant Governor of a State The Honorable (full name) Dear Governor (surname):
Lieutenant Governor of (state) Sincerely,
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Secretary of state of a State The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Secretary of state of (state) Sincerely,
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Chief Justice of the Supreme The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Chief Justice:
Court of a State Chief Justice of the Sincerely,
Supreme Court of the
State of (state)
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Attorney General of a State The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Madam) Attorney General
Attorney General of the Sincerely,
State of (state)
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Treasurer, Comptroller, or The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Auditor of a State State Treasurer (Comptroller or Sincerely,
Auditor) of the State of
(state)
(city), (state) 00000-0000
President of the Senate The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
of a State President of the Senate Sincerely,
of the State of

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-9
(state)
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
State Senator The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
(state) Senate Sincerely,
(city), (state) 00000-0000
State Representative, The Honorable (full name) Dear Mr. (or Ms.) (surname):
Assemblyman or Delegate (state) House of Representatives Sincerely,
(Assembly or House of Delegates)
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Mayor The Honorable (full name) Dear Mayor (surname):
Mayor of (city) Sincerely,
(city), (state) 00000-0000
Ecclesiastical Organizations
Roman Catholic Church
Cardinal His Eminence (Christian name) Your Eminence: (formal)
Cardinal (surname) Dear Cardinal (surname):
Archbishop of (Archdiocese) (informal)
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
Archbishop The Most Reverend (full name) Your Excellency: (formal)
Archbishop of (Archdiocese) Dear Archbishop (surname):
(local address) 00000-0000 (informal)
Sincerely
Bishop The Most Reverend (full name) Your Excellency: (formal)
Bishop of (diocese) Dear Bishop (surname):
(local address) 00000-0000 (informal)
Sincerely,
Monsignor The Reverend Reverend Monsignor:
Monsignor (full name) (formal)
(local address) 00000-0000 Dear Monsignor (surname):
(informal) Sincerely,
Priest The Reverend (full name) Reverend Father: (formal)
(initials of the order, if any, Dear Father (surname):
after name) (informal)
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
Superior of a Sisterhood The Reverend Mother Dear Reverend Mother:
Superior (name of institution) (formal)
(local address) 00000-0000 Dear Mother (name):
(informal) Sincerely,
Sister Sister (full name) Dear Sister (full name):
(name of organization) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000
Superior of a Brotherhood Brother (name) Dear Brother:
Superior of (institution) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-10
Member of a Brotherhood Brother (full name) Dear Brother (full name):
(name of organization) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
Anglican/Episcopal Church
Bishop The Right Reverend (full name) Right Reverend: (formal)
(local address) 00000-0000 Dear Bishop (surname):
(informal) Sincerely,
Archdeacon The Venerable (full name) Venerable Sir (or Madam): (formal)
Archdeacon of (name) Dear Archdeacon
(local address) 00000-0000 (surname): (informal)
Sincerely,
Dean The Very Reverend (full name) Very Reverend: (formal)
Dean of (church) Dear Dean (surname):
(local address) 00000-0000 (informal)
Sincerely,
Canon The Very Reverend (full name) Very Reverend: (formal)
Canon of (church) Dear Canon (surname):
(local address) 00000-0000 (informal)
Sincerely,
Rector The Reverend (full name) Reverend: (formal)
The Rector of (name) Dear (Dr., Mr., or Ms.) (surname):
(local address) 00000-0000 (informal)
Sincerely,
Clergy of Other Denominations
Methodist Bishop The Reverend (full name) Reverend: (formal)
Methodist Bishop Dear Bishop (surname): (informal)
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
Mormon Elder Elder (or Brother) (full name) Dear Elder (surname):
Church of Jesus Christ of Sincerely,
Latter Day Saints
(local address) 00000-0000
Presbyterian Moderator The Moderator of (name) Dear Reverend:
(local address) 00000-0000 (formal)
OR Dear (Dr., Mr., or Ms.) (surname):
The Reverend (full name) (informal)
Moderator of (name) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000
Rabbi Rabbi (full name) Dear Rabbi (surname):
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
Seventh-Day Adventist Elder Elder (full name) Dear Elder (surname):
General Conference of Sincerely,
Seventh-day Adventists
(local address) 00000-0000

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-11
Minister, Pastor or Rector The Reverend (full name) Dear Dr. (surname):
(with doctorate) (title, name of church) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000
Salutation and
Addressee Letter and Envelope Complimentary Close
Minister, Pastor or Rector The Reverend (full name) Dear Reverend: (surname):
(without doctorate) (title, name of church)
(local address) 00000-0000
Eastern Orthodox Archbishop/ His Eminence (Christian Name) Your Eminence: (formal)
Metropolitan Archbishop of (city) Dear Archbishop (surname)
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
Eastern Orthodox Bishop The Right Reverend Your Grace: (formal)
(Christian name) Dear Bishop: (informal)
Bishop of (city) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000
Eastern Orthodox Priest The Reverend (name) Dear Reverend Father: (formal)
(local address) 00000-0000 Dear Father (Christian name):
(informal)
Sincerely,
Educational Institutions
President of a College Dr. (full name) Dear Dr. (surname):
or University President, (name of institution) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000
Dean of a University Dean (full name) Dear Dr. (surname):
or College School of (name) (“Dear Dean” if without
(name of institution) doctoral degree)
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
Professor Professor (full name) Dear Dr. (surname):
Department of (name) (“Dear Professor” if
(name of institution) without doctoral degree)
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
Other Addressees
An Unmarried Woman Ms. (or Miss) (full name) Dear Ms. (or Miss) (surname):
(local address) 00000-0000 Sincerely,
A Married Woman or Ms. (or Mrs.) (husband’s Dear Ms. (or Mrs.) (surname):
Widow full name) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000
Two or More Unmarried Mses. (surname) and Ladies (or Mesdames):
Women (surname) OR
(local address) 00000-0000 Dear Msess. (or Misses)
OR (surname)
Ms. (or Miss) (full name) and (surname):
and Ms. (or Miss) (full name) Sincerely,
(local address) 00000-0000

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
B-12
Two or More Men Messrs. (surname) and Gentlemen:
(surname) OR
(local address) 0000-0000 Dear Mr. (surname) and
OR Mr. (surname):
Mr. (full name) and Mr. Sincerely,
(full name)
(local address) 00000-0000
APPENDIX C
STATIONERY REQUIREMENTS
1. Preprinted Letterhead
a. Printing. Preprinted letterhead may be produced by letterpress, or offset lithography,
whichever is more economical. Embossing or engraving processes, including thermographic
processes are prohibited unless approved by the local Document Automation and Production
Service (DAPS).
b. Seal. All “official” letterhead stationery of the DON shall bear a 1-inch diameter of the
DoD seal 1/2 inch from the upper left and top edge of the sheet.
c. Other Emblematic Devices. Other seals, emblems, insignia, decorative, or emblematic
devices shall not be incorporated.
d. Preprinted Letterhead Language, Typography, and Printing. All components of the DON
and Headquarters United States Marine Corps shall comply with the following. (Other Marine
Corps activities refer to Marine Corps Publications and Printing Regulations, MCO P5600.31G).
(1) First Line. DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY centered horizontally 5/8 of an inch from
the top edge of the sheet in 10 to 12 point type. Try to match the following font styles:
Copperplate BT, Copperplate 32, Univers 55 (Roman) or Helvetica Roman.
(2) Individual Activity Name. Six to nine point matching font.
(3) Address and Zone Improvement Plan (Zip) Code. Six-point capital letters. Center
horizontally. Do not use building numbers as part of the zip code, i.e. 17055-0791.
(4) Leading. (space between lines) should be 13 points.
(5) Spacing. The bottom of the printing shall be 1 and 1/16 inch from the top of the
trimmed sheet.

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
C-1
(6) Color of Ink. Blue, Pantone Matching system (PMS) 288 or equivalent. Black ink is
an acceptable substitute but shall not be used for letterhead to be signed by the senior officials
identified in the following paragraph.
(7) Paper Stock. Letterhead stationery and continuation sheets for the SECDEF or
DEPSECDEF; the SECNAV, Deputy Secretary, UNSECNAV, and ASNs; the CNO and VCNO;
and the CMC and ACMC are not to exceed 20-pound basis weight (per 1000 sheets) 100 percent
white bond, JCP G80; all other official letterhead stationery is not to exceed 20-pound basis weight
(per 1000 sheets) 25 percent white bond, JCP G40.
(8) Trim Size. Eight and half inches by eleven inches.
2. Computer Generated Letterhead is an acceptable substitute for preprinted letterhead. The
format standards and specifications for preprinted letterhead shall be applied to computer generated
letterhead to the extent practicable. Digital or electronic signatures may be used to sign computer
generated letterhead. Adhere to the DON Chief Information Office guidance for use of digital
and/or electronic signatures (refer to paragraph 6 of chapter 4). The following font and format
guidance will assist in maintaining professional looking letterhead within the DON.
a. Font. Recommended fonts for computer generated letterhead are Times New Roman,
Century Schoolbook,Courier New, Helvetica or Univers (10 point bold for the DEPARTMENT
OF THE NAVY line and 8 point for the address lines). Try to match the layouts shown.
b. Spacing. The first line of the letterhead shall be centered on the fourth line from the top of
the page.
3. Optional Features
a. The phrase IN REPLY REFER TO may be printed in 5 point capital letters.
b. Marking to indicate address area for window envelopes.
c. Fold markings to indicate business letter folds.
d. A 1/2 point rule, 1 1/2 picas (approximately 3/4 inch long) placed 1 1/2 inches from the
bottom.
e. Slogans, when approved by the Office of the Secretary of the Navy, printed in the bottom
margin approximately 1/2 inch from the bottom of the page.
4. Letterhead Envelopes and Mailing Labels shall conform to USPS standards and OPNAVINST
5218.7B.
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
C-2
a. First Line. Navy activities and Headquarters, Marine Cops shall print DEPARTMENT OF
THE NAVY horizontally 3/8 inch from the top margin in 10 point capital letters. (Other Marine
Corps activities refer to MCO P5600.31G).
b. Individual Activity Name. Use 6 point capital letters.
c. Official Business. OFFICIAL BUSINESS is printed two lines below the last line of the
address text in 6 point capital letters.
d. Ancillary Services Endorsement. Endorsements such as “Forwarding Service Requested”
or “Return Service Requested” are optional. When added to the envelope or label it should be
placed two lines below the OFFICIAL BUSINESS phrase in 6 point capital letters.
e. Leading. Should be 13 points between each line. Center 3 pica hairline rules 6 points apart
under DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY and above OFFICIAL BUSINESS.
f. Borders, Markings, Slogans, or Designs. Shall not be imprinted or affixed.
g. Labels, Label size shall be no smaller than 5 inches by 3 inches. Margins for marginally
punched labels may be adjusted as required to allow necessary edge punching.
h. Colors ofInk. Labels shall be printed in black. Envelopes shall be printed in either black
or blue (PMS 288 or equivalent).
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
OFFICE OF THE SECRETARY
1000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON, DC 20350-1000
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
OFFICE OF THE CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS
2000 NAVY PENTAGON
WASHINGTON, DC 20350-2000
IN REPLY REFER TO
DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY
HEADQUARTERS, UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS
3000 MARINE CORPS PENTAGON
WASHINGTON, DC 20380-1775

SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
C-3
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS
COMMUNICATIONS COMPANY
HEADQUARTERS BATTALION
CAMP PENDLETON, CA 92055-5006
APPENDIX D
FORMS AND ENVELOPES
1. The following forms are available for download from GSA Forms Web site:
http://www.gsa.gov/Portal/gsa/ep/formsWelcome.do?pageTypeId=8199&channelId=-25201:
FORM STOCK NUMBER UI QTY
OF 363 PDF Format
Memorandum of Call
2. The following forms are available from Naval Forms Online (NFOL):
https://navalforms.daps.dla.mil/web/public/home:
OPNAV 5211/7 (Rev:Jun 1981) 0107-LF-052-1137 PG 100
Correspondence/Documents Control Card
OPNAV 5216/144A(Rev: Aug 1981) PDF Format
DON Memo (8-1/2 x 11)
OPNAV 5216/144B (Rev: Aug 1981) PDF Format
DON Memo (8-1/2 x 5-1/2)
OPNAV 5216/158 (Rev: Jul 1978) PDF Format
Routine Reply, Endorsement
Transmittal or Information Sheet
3. The following forms are available for purchase from GSA Global Supply: http://www.gsa.gov/glovalsupplyor
(800)525-8027, option 3:
FORM STOCK NUMBER UI QTY
OF 65A 7540-00-117-8424 BX 200
U.S. Government Messenger Envelope
(Large, 4-1/8 x 9-1/2)
OF 65B 7540-00-222-3467 BX 250
U.S. Government Messenger Envelope
SECNAV M-5216.5
March 2010
D-1
(Medium. 9-1/2 x 12)
OF 65C 7540-00-222-3468 BX 250
U.S. Government Messenger Envelope
(Small, 12 x 16)
OF 99 7540-01-317-7368 PD 50
Fax Transmittal
4. The following envelopes are available from GSA:
ENVELOPE STYLE NO. UI QTY
Plain, white #10 (4-1/8 x 9-1/2) 192 BX 500
Plain, brown (8-1/2 x 11-1/2) 68 BX 500
Plain, brown (12 x 9-1/2) 84 BX 500
Plain, brown (16 x 12) 104 BX 500

E-1
APPENDIX E
INDEX
Page Page
A
Abbreviations 6-5 Window-envelope format 11-8
Of addresses 6-5 Identification symbols 11-1
Of classified references 7-2 Outgoing copies 11-4
Of dates 2-11; 7-2 Page numbers 11-4
Of military ranks 2-8; A-1 References 11-3
Of NATO correspondence 2-1 Salutation 11-2
Of states 6-6 Second and succeeding pages 11-4
Overuse prohibited 2-11 Separate mailing 11-3
Acronyms 2-11 Signature 11-3
Acting 2-5; 7-14 Subject line optional 11-2
By direction letterAddressing Civilian Personnel
(See Models of Address – Civilian) Delegating authority for 2-4
In business letter 11-3Addressing Military Personnel
(See Models of Address – Military) In standard letter 7-14
Advance 2-2
Air Force Personnel
Enlisted models of address A-2
C
Office models of address A-1 Chain of command
Assembly for signature Corresponding through 2-1
Endorsement 9-2; 9-4 Rushed routing through 2-2
Multiple-address letter 8-1; 8-5 Classified correspondence
Standard letter 7-15; 7-24 Pagination if Top Secret 7-15
Tabbing correspondence 7-15 Security marking on 7-2; 7-20; 7-21
Serial number of 7-2
Coast Guard Personnel
B
Enlisted models of address A-1
“Blind copy to:“ line Officer models of address A-1
With congressional inquiries 2-6 Codes
Business letter As sender’s symbol 7-1
Address on 11-1 “To” address 7-4
Attention line 11-2; 11-8; 11-9 Complimentary close
Body of letter 11-2 In business letter 11-3
Complimentary close 11-3 Not in standard letter 7-13
“Copy to:” line 11-4 Congressional inquiries
Dates 2-11; 11-1 Blind copy to OLA 2-6
Enclosures 11-3 Courtesy copy to Congress 2-6
Examples of Reply deadlines 2-6
First page 11-6 Controls
Second page 11-7 Incoming correspondence 2-5
Paragraph formats 11-5 Outgoing correspondence 2-7
Short business letter 11-10 Reply deadlines 2-6
Tracking correspondence 2-6

E-2
Page Page
Coordinating efficiently 2-4 Enclosures
Copies In business letter 11-3
Coordination 2-4 In endorsement 9-1
Courtesy 2-6 In standard letter 7-10
Limit of 2-1 For copy-to addressees 7-11
Of multiple-address letter 8-1 Format for heading 7-10
“Copy to:” line For via addressees 7-12
In business letter 11-4 General 7-10
In standard letter 7-14 Increasing the quantity of 7-11
Correspondence Management 1-1 Marking on 2-10
Normal distribution of 7-11
Page numbers of 2-10D
Under separate cover 2-10; 7-12
Dates Endorsements
In business letter 11-1 Adding enclosures 9-1
In standard letter Basic-letter identification 9-1; 9-3
As sender’s symbol 7-2 Complete 9-2
In heading 2-11 Page number 9-1
2-11 Reference line 9-1In text
(see also due dates) Remaining addressees numbered 9-2
Digital signature 4-2 Sample of
“Distribution:” line 8-1; 8-3 Assembled endorsement 9-4
Drafter’s identification New-page endorsement 9-3
With WPC codes 7-2 Uses 9-1
Due dates Where to send copies 9-2
Normal time allowed for 2-7 Envelopes
Realistic setting of 2-7 Addressing of 6-1; 6-2; 6-7
Models of address A-1; B-1
Ordering D-1E
States abbreviated on 6-2; 6-6
Electronic Mail Window envelopes
Digital signature 4-2 Encouraged 2-3
Formal correspondence 4-1 Typing business letter for 11-8
General 4-1 Typing standard letter for 7-18
Informal correspondence 4-2 Executive Correspondence
Managing E-mail 4-1 12-1
Records management 4-2
Assigning action to incoming
correspondence
Security and privacy 4-2 12-1
Electronic records
Assigning action to outgoing
correspondence
As evidence 3-2 Complimentary close 12-5
Disposition 3-3 12-6
General 3-1
Congressional committees or
subcommittee correspondence
Identification of 3-1 12-9
Management of 3-1
Correspondence action report
(SD Form 391)
Restrictions/security/privacy issues 3-2 Correspondence management 12-1
Records management considerations 3-1; 3-2 Coordination 12-7; 12-19

E-3
Page Page
Date line 12-5 For official use only 7-3; 7-22
Distribution 12-3 2-7; 3-2
Due dates 12-2
Freedom of Information and Privacy
Act requests
Extensions 12-2 “From:” line
Format 12-4 In joint letter 7-1; 7-19
Body of letter 12-4 In standard letter
Closing lines 12-4 Format 7-4
Copy to 12-5 General 7-3
Opening line 12-4 Multiple title 7-4
Reference line 12-18
Salutation 12-4
Signature line 12-5
General 12-1
G
Interim responses 12-2 Guide and Form letters 2-3
Congressional correspondence 12-3
HqDON correspondence 12-2
OSD correspondence 12-3
H
Memoranda (preparation of) 12-6 Headings, paragraphs 7-13
Action or information memo 12-6
Package assembly 12-7; 12-8
Page numbering 12-6
I
Preparing a reply 12-3 Identification symbols
Routing changes 12-2 Authorized 7-1
Sample of Exceptions 7-2
Action memorandum 12-17 Unauthorized 7-2
Congressional response Identifying later pages
One Chairperson 12-12 Pages numbered 7-15
Two Chairpersons 12-13 Subject repeated 7-15
Chairman of a select committee 12-14 Identifying military personnel
Coordination page 12-19 Marine Corps 2-8
Flag stationery 12-16 Navy 2-8
Chief of Naval Operations 12-16 Indenting (see paragraphing)
Secretary of the Navy 12-15 Ink
Information memorandum 12-18 Color of 2-13; C-13
12-11Interim response for Congressional
correspondence
Memorandum for 12-20
J
Joint letter 7-19
Justifications, margins 7-1
F
Facsimile machines 2-3; 5-1
General 5-1
L
Records management 5-2 Letterhead 2-8; C-1
Security and privacy issues 5-1 Computer generated C-2
File copy In business letter 11-4
Samples of Preprinted requirements C-1
Form letters 2-3 Stationery requirements C-1
Forms used in correspondence D-1 6-1; 7-3
Font sizes and styles 2-13; C-2
List of Marine Corps Activities
information

E-4
Page Page
Models of address – Military
Air Force enlisted A-3
M
Air Force officers A-1
Margins Army enlisted A-2
In short business letter 11-10 Army officers A-1
In standard letter 7-1 Coast Guard enlisted A-1
Marine Corps Personnel Coast Guard officer A-1
Enlisted models of address A-2 Marine Corps enlisted A-2
How to fully identify 2-8 Marine Corps officers A-1
Officer models of address A-1 Navy enlisted A-1; A-2
Writing to higher authority 2-3 Navy officers A-1
Memorandum Other military A-3
Decision 10-2 Multiple-address letter
File copy 10-1 Copies 8-1
Format 10-1 How to assemble 8-1; 8-5
From/to 10-1 Listing of addressees 8-1
Letterhead memorandum 10-1 Normal use 8-1
Memorandum for the record 10-1 Normal used varied 8-1
Memorandum of agreement 10-2 Sample of letter assembled 8-1; 8-5
Memorandum of understanding 10-2 With “Distribution:” line 8-1; 8-3; 8-4
Plain-paper memorandum 10-1 With “To:” line 8-1
Sample of 8-1; 8-2; 8-4
Letterhead memorandum 10-6
With “To:” line and
“Distribution:” line
Memorandum for the record 10-3
Memorandum of agreement 10-7
Memorandum of understanding 10-8; 10-9
N
Plain-paper memorandum 10-5 Navy Personnel
Printed memorandum 10-4 Enlisted models of address A-1
Models of address – Civilian How to fully identify 2-8
Adjusting for gender B-1 Officer models of address A-1
American missions B-6 Writing to higher authority 2-3
Ecclesiastical B-8 NOTAL references discouraged 7-6
Educational institutions B-10
Executive departments B-5
Foreign government officials B-7
O
House of Representatives B-4 Organizer’s code
Independent organizations B-6 Exceptions 7-2
Judiciary B-2 Format 7-1
Legislative agencies B-5 In serial number 7-1
Missions, of U.S. B-6 Required 7-1
Other addressees B-10
Senate B-3
State and local governments B-7
The Honorable B-1
Vice President B-2
White House B-2

E-5
Page Page
Mail markings 6-3
P
Sources of address 6-1
Page numbers Within DoD 6-2
On enclosures 2-10 Privacy act requests 2-7
On endorsements 9-1; 9-3 Proofreading 2-12
On standard letters 7-15 2-12
Paperwork management
Punctuating, capitalizing, spelling,
hyphenation, and separating words
Coordinating efficiently 2-4
Due dates 2-7
Finished products for signing 2-4
R
Form and guide letters 2-3 References
General 2-1 In business letter 11-3
Limiting information copies 2-10 In endorsement 9-1
New office technology 2-3 In standard letter 7-7
Photo copies 2-10 Examples 7-7; 7-10
Prompt replies urged 2-6 Format 7-6
Prompt signing 2-7 General 7-6
Tracers 2-7 Mentioned in text if listed 7-6
Unnecessary file copies 2-10 My and your allowed in 7-10
Updating distribution lists 2-10 NOTAL discouraged 7-6
Window envelopes encouraged 2-3 Paragraphs 7-12
Writing discouraged 2-1 Replies
Paragraphing Due dates for 2-6
Headings encouraged 7-13 Promptness of 2-6
In business letter 11-2 Tracing late 2-7
In classified letter 7-2; 7-20
In standard letter 7-12; 7-23
Subparagraphing limited 7-12
S
Personal pronouns Salutation A-1 – A-3
Allowed in references 7-10 Civilian models of address B-1 – B-10
Personnel matters Military models of address A-1 – A-3
Congressional inquiries 2-6 Sample of
Military fully identified 2-8 Continuation pages 7-15
Social Security numbers 2-7 “Copyto:” line 7-15
Writing to higher authority 2-3 Dates 7-2
Photo copies Enclosures 7-10
Authorized 2-10 File copy 7-16
For multiple-address letters 8-1 Following channels 2-1
Limit copies 2-10 “From:” line 7-3
Postal standards Ink 2-13
Delivery and return address format 6-2 Joint letter 7-19
Folding techniques 6-4 Letter assembled 7-24
Mail classification 6-3 Margins 7-1

E-6
Page Page
Originator’s code 7-1; 7-2 Multiple-address letter 8-3
Page numbers 7-15 Standard letter 7-3
Paragraph format 7-23 Stationery 2-8; C-1
References 7-6 – 7-10
Security markings 7-20 – 7-22
Sender’s symbol 7-1
T
Serial number 7-1 Tabbing correspondence 7-25
Security markings 7-20 – 7-22 Telephone
Signature 7-13 For coordination 2-4
SSIC 7-1 Instead of writing letters 2-1
Standard letter 7-16 Text
Stationery 2-8; C-1 Of business letter 11-2
Subject 7-5 Of standard letter 7-12
Text 7-12 (also see paragraphing)
“To:” line 7-4 Time
Tabbing correspondence Expressing military time 2-11
Packages 7-25 “To:” line
Type 2-13 Codes encouraged 7-4
“Via:” line 7-5 Format 7-4
Window-envelope format 7-18 For window envelope 7-18
Sender’s symbols Top secret documents
Exceptions 7-2 Page numbering in 7-15
Required 7-1 Serial numbers required 7-1
Unauthorized 7-2 Tracers 2-7
Separate cover 2-10; 7-12 Typeface
Serial numbers 2-13; C-3
Format 7-1 2-13; C-2
Of classified references 7-2
When to use 7-1
Signature
U
Business letter 11-3 USPS – postal standards 6-1
Delegation of authority 2-4
Examples 2-5; 7-13 V
Electronic Signature 2-5; C-2
Facsimile stamps 2-5 “Via:” line 7-5
Signature line in general 2-4 Follow chain of command 2-2
Standard letter 7-12 Examples 7-5 – 7-10
Submitting for 2-4 Format 7-4
What commanding officers sign 2-4 Not with window envelopes 7-18
Sincerely 11-3 Numbering addresses in 7-5
Social security numbers 2-7 Routing when rushed 2-2
SSIC 7-1
Signature stamps 2-5
Standard letter 7-1
Standard Naval Distribution List 6-1
Z
Zip codes 6-2
Business letter 11-4
Converting “To:”/From:” lines 7-3
Table of Revisions/Changes
SECNAV Manual Basic Issuance Date
Change Number Revision Date

Brief of Revisions/Changes
1. Chapter _____, Page _____ , Paragraph ____ :
2. Chapter _____, Page _____ , Paragraph ____ :
3. Chapter _____, Page _____ , Paragraph ____ :
4. Chapter _____, Page _____ , Paragraph ____ :
The following are major changes in the policy and procedures
incorporated in the latest revision to this SECNAV Manual. A revised
Foreword and Table of Contents will be issued with each change.

S E C N A V M - 5 2 1 6 . 5
S t o c k N u m b e r
0516LP1100043
