Received via email on October 5, 2016
From: Robert Turesky,Universityof Minnesota
Comments:
I wanted to convey to theNTP our recent work, presented at the
Division of Chemical Toxicology Session, at the ACS Meetingin
Philadelphia (Aug 2016), where we showed that the cookedmeat
mutagen PhIP;but not other heterocyclic aromatic amines present
in cooked meat,forms DNA adducts in the prostate of a high
percentage of prostate cancer patients. There is littleto no
data in the published literature on unambiguous directphysical
evidence that mutagens in meat can cause DNA damage inhumans.
The missing link betweenthis evidence and the observational data
of epi studies on cooked meat diets andcancer risk very
compelling. Our DNA adduct biomarker data obtained by masss
spectrometry, is the missing link that is vital to performinga
useful evaluation chemicals formed in cooked meat cooked and
cancer risk. Our pilot work and, even more importantly,the
results from our continuing work with a larger sample size will
greatly aid in any such evaluation. Our preliminary datawill be
submitted for publication by the endof October. I am available
as a resource for further information about these dietary
genotoxicants
TITLE: Biomarkers of heterocyclic aromatic amines for molecular
epidemiology studies
AUTHORS: Robert J. Turesky1, Yi Wang1, Khyati Pathak1,Shun
Xiao1, Chirstopher Weight2, Michael Malfatti3, Kenneth
Turteltaub3, Kami White4, Lynne Wilkens4, Loic Le Marchand4
INSTITUTIONS (ALL):
1. Masonic Cancer Center, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
MN, United States.
2. Department of Urology, University of Minnesota MedicalSchool,
Minneapolis, MN, United States.
3. Biosciences and Biotechnology Division, Lawrence Livermore
National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, United States.
4. Epidemiology Program,University of Hawaii Cancer Center ,
Honolulu, HI, United States.

REVIEW
pubs.acs.org/crt
Metabolism and Biomarkers of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in Molecular
Epidemiology Studies: Lessons Learned from Aromatic Amines
Robert J. Turesky*
,†
and Loic Le Marchand*
,‡
†
Division of Environmental Health Sciences, Wadswort h Center, Albany, New York 12201, United States
‡
University of Hawaii Cancer Center, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, Hawaii 96813, United States
ABSTRACT: Aromatic amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines
(HAAs) are structurally related classes of carcinogens that are
formed during the combustion of tobacco or during the high-
temperature cooking of meats. Both classes of procarcinogens
undergo metabolic activation by N-hydroxylation of the exocyclic
aminegroup to produceacommonproposed intermediate, the
arylnitrenium ion, which is the cri tical metabolite implicated in
toxicity and DNA damage. However, the biochemistry and chemical
properties of these compounds are distinct, and different biomarkers
of aromatic amines and HAAs have been developed for human
biomonitoring studies. Hemoglobin adducts have been extensively
used as biomarkers to monitor occupational and environmental
exposures to a number of aromatic amines; however, HAAs do not form hemoglobin adducts at appreciable levels, and other biomarkers
have been sought. A number of epidemiologic studies that have investigated dietary consumption of well-done meat in relation to various
tumor sites reported a positive association between cancer risk and well-done meat consumption, although some studies have shown no
associations between well-done meat and cancer risk. A major limiting factor in most epidemiological studies is the uncertainty in quantitative
estimates of chronic exposure to HAAs, and thus, the association of HAAs formed in cooked meat and cancer risk has been difficult to
establish. There is a critical need t o establish long-term biomarkers of HAAs that can be implemented in molecular epidemioIogy studies. In
this review, we highlight and c ontrast the biochemistry of sev eral prototypical carcinogenic aromatic amines and HAAs to which humans are
chronically exposed. The biochemical properties and the impact of polymorphisms of the major xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes on the
biological effects of these chemicals are examined. Lastly, the analytical approaches that have been successfully employed to biomonitor
aromatic amines and HAAs, and emerging biomarkers of HAAs that may be implemen ted in molecular epidemiology studies are discussed.
’ CONTENTS
Introduction 1170
Aromatic Amine and HAA Exposure and 1172
Carcinogenesis
Enzymes of Metabolic Activation and Detoxication 1174
of Aromatic Amines and HAAs
Cytochrome P450s 1175
Peroxidases 1177
N-Acetyltransferases 1178
Sulfotransferases 1178
UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases 1179
Glutathione S-Transferases and Glutathione 1181
Conjugates
Biomonitoring Aromatic Amines, HAAs, and Their 1182
Metabolites in Human Urine
Aromatic Amine and HAA DNA Adducts 1184
Synthesis and Characterization of DNA Adducts 1184
Aromatic Amine and HAA DNA Adduct Formation 1186
DNA Adduct
Formation of Aromatic Amines and 1187
HAAs in Human Tissues
DNA Adducts of Aromatic Amines and HAAs in 1188
the Oral Cavity
Aromatic Amine and HAA Protein Adducts 1190
Hemoglobin Adducts 1190
Serum Albumin Adducts 1190
Biomonitoring of HAAs in Hair 1191
Epidemiology of Cooked Meats: Potential Role of 1193
HAAs in Human Cancer
Conclusions 1194
Author Information 1195
Acknowledgment 1195
Dedication 1195
Abbreviations 1195
References 1196
Received: March 31, 2011
Published: June 20, 2011
r
2011 American Chemical Society
1169 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s
|
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
in Vitro and in Experimental Animal Models
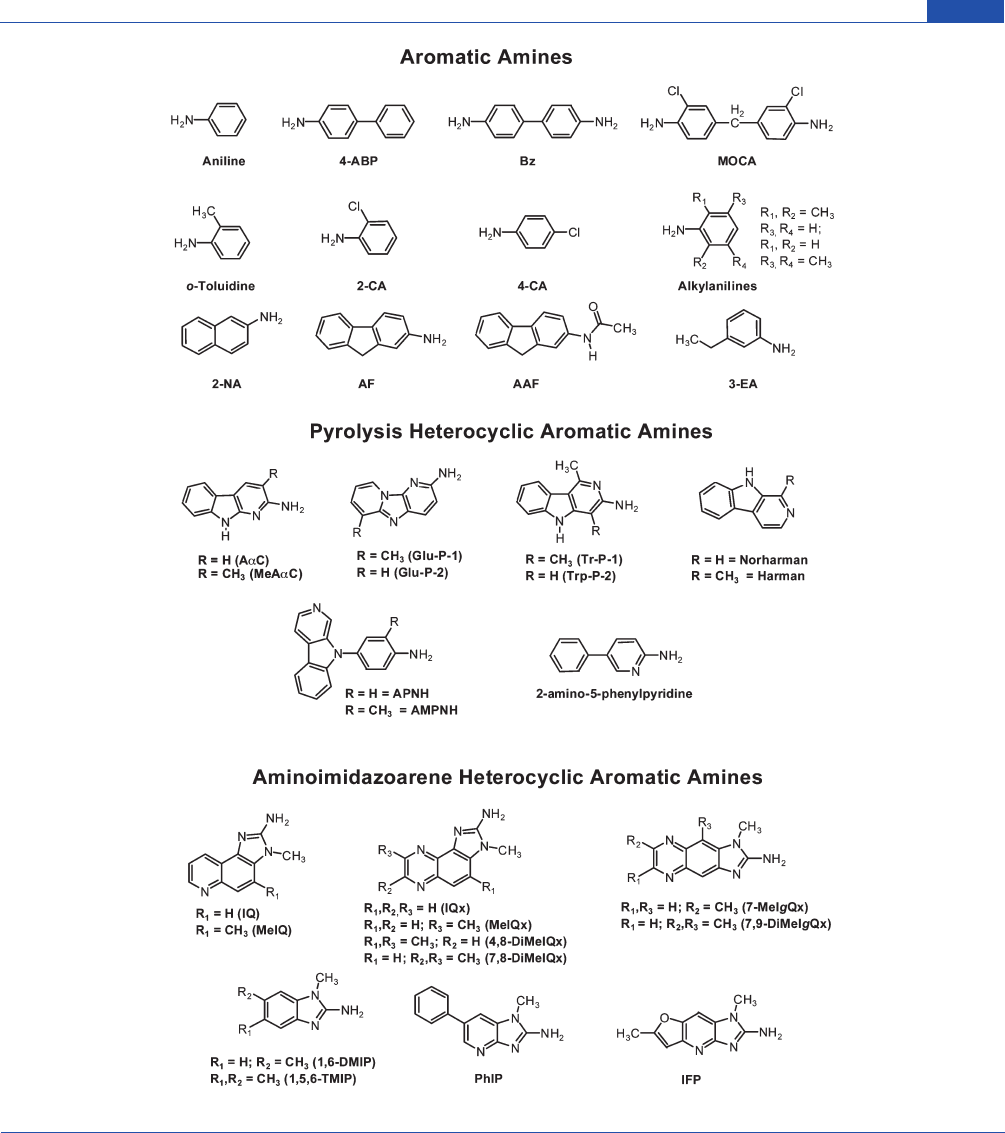
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 1. Chemical structures of prevalent aromatic amines and HAAs.
’ INTRODUCTION
Historically, the exposure to carcinogenic aromatic amines
occurred during the production of dyes and other complex
chemicals, and by their use as antioxidants in rubber-manufactur-
ing processes.
1,2
A number of aromatic amines arise during the
combustion of tobacco
3,4
and occur in the emissions of cooking oils.
5
Several heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs) are also produced
during the high-temperature burning of tobacco;
6,7
however, the
principal source of exposure to many HAAs occurs by the consump-
tion of well-done cooked meats.
8-10
HAAs are also present in pan-
fried residues used for gravies
11,12
and arise in fumes of cooking oils
13
and the airborne particulates generated by the frying or grilling of
meats.
14
Chemicals from both classes of compounds induce tumors
at multiple sites in experimental laboratory animals during long-term
carcinogen bioassays (see Figure 1 for chemical structures). Certain
aromatic amines are classified as human carcinogens (Group 1), and
several prevalent HAAs have been listed as probable or possible
human carcinogens (Group 2A and 2B), on the basis of toxicity data
reviewed by the International Agency for Research on Cancer.
3,15
The Report on Carcinogens, 11th edition, of the National Toxicology
Program, also concluded that prevalent HAAs are “reasonably
anticipated” to be human carcinogens.
16
Thus, there is much concern
1170 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
about the health risk associated with the exposure to these structurally
related classes of chemicals.
Aromatic amines and HAAs undergo metabolic activation by
N-hydroxylation of the exocyclic amine group, to form the
proposed arylnitrenium ion, which is the critical metabolite
implicated in toxicity and DNA damage.
17,18
However, the bio-
chemistry and chemical properties of aromatic amines and HAAs
and their metabolites are distinct and different biomarkers of these
carcinogens have been employed in human biomonitoring studies.
The term biomarker has varied meanings that comprise markers of
susceptibility; makers of the internal dose; markers of the biologi-
cally effective dose; markers of early biological effects; markers of
altered function; and markers of clinical disease.
19,20
In the context
used here, the biomarkers are defined as markers of exposure and
the biologically effective dose, and are representative early biomar-
kers of cancer risk. Some of the biomarkers include the unaltered
compounds or metabolites in bodily fluids or protein and DNA
adducts derived from the genotoxic metabolites. The characteriza-
tion of the urinary metabolic profiles of the genotoxi cant s can
provide an estimate of the relative extent of bioactivation, as
opposed to detoxification, undergone by the chemicals in vivo.
21
These measurements can also reveal interindividual differences in
metabolism due to polymorphisms that encode for enzymes
involved in xenobiotic metabolism; such differences can affect the
genotoxic potency of procarcinogens.
22
However, urinary biomar-
kers of many carcinogens, including HAAs, are transient and only
capture the last 24 h of exposure. For individuals who chronically but
intermittently consume g rilled meats, urinary HAA biomarkers may
go undetected. L onger-lived biomarkers of HAA exposure and
genetic damage are required for epidemiological investigations.
Certain drugs and carcinogens, including some HAAs, bind with
high affinity to proteins and pigme nts in the hair follicl e and become
entrapped in the hair-shaft during hair growth.
23-25
The biomoni-
toring of HAAs in hair may provide a more accurate estimate of
chronic exposure than the inferences obtained from food frequency
questionnaires that are often used in molecular epidemiology
studies.
19
However, the identification and measurement of chemical
specific DNA adducts in the target tissue are the most relevant
findings for risk assessment.
20,26
Unfortunately, DNA adduct mea-
surements in tissue are often precluded by the unavailability of
biopsy samples, which restricts the usage of this biomarker in large
scale human studies. Accessible biological fluids, such as blood,
27
urine,
21
exfoliated bladder epithelial cells in urine,
28
or exfoliated
mammary epithelial cells in milk of lactating women,
29,30
have
served as surrogate matrices in which to assess exposure to chemicals
or their metabolites or the formation of protein or DNA adducts.
The identi fication of protein or DNA carcinogen adducts clearly
demonstrates exposu re to the bio logically active metabolite, but th e
adduct must correlate with cancer risk, if it is considered valid as a
biomarker of health risk.
31,32
The levels of macromolecular carcino-
gen adduct formation also should be influenced by polymorphisms
in genes that encode enzymes involved in the bioactivation and/or
detoxication of these chemicals.
22
2-Aminofluorene (AF) and N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene (AAF)
are perhaps the most wel l-studied among the aromatic amines.
33
AF
and AAF were originally developed as pesticides but never used as
intended because they were discovered to be animal carcinogens.
34
The pioneering research conducted on the metabolic fate of AF,
AAF, and other prototypical arylamines, and the interactions of their
metabolites with nucleic acids and proteins
33,35,36
have served as a
foundation o f knowledge for the development of human biomarkers
toward aromatic amines as well as HAAs.
31,37,38
Many of the salient
studies on the metabolism and biochemical toxicology of aromatic
amines are summarized in review articles by Kiese;
39
Irving,
40
the
Millers,
35,36,41
Hoffmann and Fuchs;
42
Neumann;
43
Gorrod and
Manson;
44
and Kadlubar and Beland.
45
The impact of occuptational
and tobacco exposures to aromatic amines and cancer risk is
summarized by Clayson,
34
the Weisburgers,
46
and reviewed in the
IARC Monographs.
1-3, 47
The interested reader will find the histor-
ical perspectives of aromatic amine carcinogenesis and many citations
of the original research in these reviews. More recent reviews on the
implementation of biomarkers to monitor human exposure to
aromatic amines are highlighted in articles by Neu mann,
38,48
Skipper
and Tannenbaum,
31,49
Yu and colleagues,
50
Sabbioni and Jones,
51
Talaska and Al-Zoughool,
52
and Richter and Branner.
53
The research on HAAs commenced in 1977, when this class of
genotoxicants was discovered.
8
The identification of HAAs in cooked
foods is highlighted by Sugimura, Nagao, Wakabayashi, and
colleagues;
8
Felton, Knize, and colleagues;
10
and by othe rs;
54-57
mechanisms of HAA formation;
58,59
metabolism and genotox-
icity;
60-70
genetic changes involved tumor genes of HAA carcino-
genicity;
9,71,72
use of transgenic and mutant animal models for
investigations of HAA-induced mutagenesis and carcinogenesis;
73,74
earlier reviews on aproaches for human biomonitoring of HAAs and
their metabolites;
24,75
and the toxicological evaluation of HAAs by
IARC
15
and the National Toxicology Program
16
are also cited.
Arylamine-hemoglobin adducts have been extensively used
as biomarkers to monitor occupational and environmental expo-
sures to aromatic amines and to assess the risk of urinary bladder
cancer, a target organ of some aromatic amines.
34,46,76-78
The
biochemistry of arylamine-induced toxicity and methemoglobine-
mia are well documented.
39,79
The arylhydroxylamine metabolites,
produced by cytochrome P450s, can penetrate the erythrocyte and
undergo a co-oxidation reaction w ith oxy-hemoglobin (oxy-Hb), to
form the arylnitroso intermediates and methemoglobin (met-Hb).
The arylnitroso compounds can undergo enzymatic redox cycling
within the erythrocyte to reform the aryhydroxylamine and com-
mence another round of co-oxidation with oxy-Hb, ultimately
resulting in methemoglobinemia (Figure 2). The arylnitroso inter-
mediate can also react with the Cys
93
residue of the human β-Hb
chain to form a sulfinamide adduct.
79
Many aromatic amines
undergo the metabolic pathway of N-oxidation and form the
arylamine-Hb sulfinamide adduct.
38
In the case o f 4-aminobiphenyl
(4-ABP), thesiteofadduction at theHb-Cys
93β
chain was proven by
X-ray crystallography.
80,81
Arylamine-Hb sulfinamide adducts ap-
pear to be fairly stable in vivo,
80
but upon acid or base treatment, t he
adducts undergo hydrolysis to yield the parent amine and the Hb-
Cys
93β
sulfinic acid.
31,82
The released aromatic amine can be readily
measured by mass spectrometry (MS) methods.
31,83
HAAs undergo
metabolic activation by N-oxidation,
60
but the covalent binding of
the N-hydroxy-HAA metabolites to Hb in rodents
84-88
and in
humans
89-92
is very low, and the HAA-Hb sulfinamide adduct does
not appear to be a promising biomarker to assess human exposure.
Alternative biomarkers of HAAs have been sought: some of these
biomarkers include urinary metabolites, DNA adducts, serum
albumin (SA) adducts, and HAA residues in hair.
24,63,67,93-95
The measurement of HAA biomarkers in humans is a difficult
analytical task because usually only ∼1 μg to several micrograms of
each compound is consumed per day, for individuals eating well-
done cooked meat.
96
This level of exposure is considerably lower
than the levels of o ccupational e xposure to many arylamines. Thus,
the concentrations of HAA biomarkers in biological fluids or tissues
are often below the part per billion (ppb) level. Many HAA
biomarkers are polar and thermally labile molecules, which
1171 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
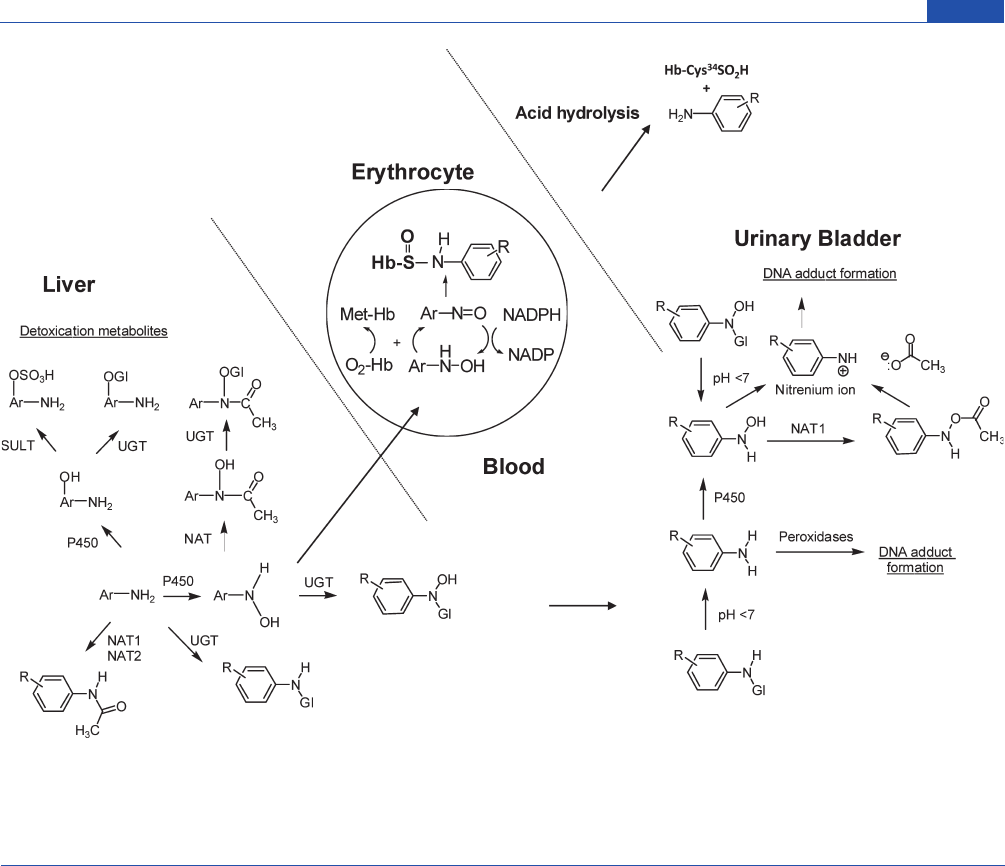
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 2. Mechanisms of arylamine-induced methemoglobinemia, arylamine-Hb sulfinamide adduct formation, and arylamine-DNA adduct formation
in the urinary bladder. The arylhydroxylamine metabolite can undergo oxidation to the arylnitroso intermediate within the erythrocyte and react with the
Hb-Cys
93β
to form an arylamine-Hb sulfinamide adduct. A portion of the arylhydroxylamine is excreted in urine in the unconjugated form or as an N-
glucuronide conjugate. Hydrolysis of the N-glucuronide conjugate by the mildly acidic pH conditions of urine regenerates the arylhydroxylamine, which
undergoes protonation to form the corresponding arylnitrenium ion and reacts with DNA in the urothelium.
precludes the employment of gas chromatography (GC) methods
for chemical analysis. During the past decade, highly sensitive
electrospray ionization (ESI) techniques
97
combined with liquid
chromatography (LC) have been developed to detect nonvolatile
and thermally labile compounds, including several different types of
HAA biomarkers.
98-103
The challenge remains to establish rapid and
robust analytical methods that can be used to measure HAA
biomarkers in large scale molecular epidemiological studies. Such
biomarkers would permit an accurate measure of HAA exposure and
their inter-relationships with metabolic phenotypes/genot ypes in-
volved in HAA genotoxicity and disease risk.
’ AROMATIC AMINE AND HAA EXPOSURE AND
CARCINOGENESIS
Some aromatic amines are known human urinary bladder
carcinogens.
1-3,34,47
The occurrence of urinary bladder tumors
among workers in dyestuff factories was first reported by Rehn in
1895,
104
who attributed these cancers to the patients’ occupation,
from which evolved t he term aniline cancer.
46
The textile dye,
chemical, and rubber-manufacturing industries were major sources
(MOCA) (Figure 1), up through much of the firsthalfofthe 20th
century.
1
During that time, epidemiological data emerged, which
demonstrated that workers occupationally exposed to these aro-
105,106
matic amines had elevated incidences of bladder cancer.
Aniline is a key intermediate in the manufacturing of dyes. Aniline,
however, was not carcinogenic in experimental animals, but 4-ABP,
2-NA, and Bz, contaminants in aniline dyes, were shown to be
carcinogenic.
1-3,34,46
Hueper established the first successful model
for human bladder cancer by demonstrating that dogs exposed to
2-NA de veloped bladder tumors.
107
Thereafter, Radomski and Brill
showed that N-oxidation of 2-NA played a critical role in the
initiation of bladder cancer in the same animal model.
108
The
urinary bladder, as well as the liver, intestine, and female mammary
gland are among the target organs of cancer development in rodents
exposedtoaromaticamines.
34,46,109
Historically, the levels of industrial exposure to some aromatic
amines were elevated in many manufacturing and chemical
plants. In one study, the airborne concentration of Bz in a
manufacturing plant, producing 3,000 pounds per shift, was
reported to range from <0.007 mg/m
3
to a maximum of
17.6 mg/m
3
, at various locations within the factory.
110
This ex-
of occupational exposure to AAs, such as aniline, 4-ABP, 2-naphthyl-
posure resulted in levels of Bz present in urine at concentrations
amine (2-NA), benzidine (Bz), and methylenebis-2-chloroaniline up to 159 μg/L, following the work shift.
110
In another chemical
1172 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
manufacturing plant, the concentrations of MOCA in urine from
postwork shift workers were detected at levels ranging from
70-1500 μg/L, and the urinary levels of o-toluidine reached up
to 132 μg/L from workers, following the work shift in another
chemical production plant.
111
In the United States and many
developed countries, strict federal regulations have drastically
diminished the industrial usage of many carcinogenic aromatic
amines. However, some aromatic amines, including 4-ABP and
Bz, are still found as contaminants at the ppb concentration in
color additives,
112,113
paints,
114
food colors,
115
leather and textile
dyes,
116,117
fumes from heated cooking oils,
5
and fuels.
118
Cigarette smoking
4
is a prominent source of exposure to
aromatic amines. 4-ABP and 2-NA occur in mainstream tobacco
smoke at levels ranging from 0.3-4 and 2-14 ng per cigarette,
respectively, whereas the amounts of o-toluidine range from 9 to
144 ng per cigarette.
4,119
Another potential source of exposure to
some aromatic amines is through the usage of commercial hair
dyes.
120,121
The exposure to a number of aromatic amines still
continues via their oxidized nitroarene derivatives that are
present in the atmosphere due to incomplete combustion of
organic materials.
51,122
There also appears to be considerable
nontobacco associated exposure to monocyclic alkylanilines; the
sources of exposure remain to be determined.
123
Carcinogenic HAAs were discovered nearly 35 years ago, when
Professor Takashi Sugimura at the National Cancer Center in Tokyo,
Japan, showed that the charred parts and smoke generated from
broiled fish and beef contained substances that exhibited potent
activities in Salmonella typhiumurium-based mutagenicity assays.
8
Since that hallmark study, more than 25 HAAs have been shown
to form in meats, fish, and poultry prepared under common house-
hold cooking practices.
10,57
The concentrations of HAAs can range
from less than 1 ppb to greater than 500 ppb.
9,10,124-126
The amounts
of HAAs formed in meats are dependent upon the type of meat and
the method of cooking; the HAA content generally increases as a
function of temperature and the duration of cooking.
125-127
There
are two major classes of HAAs (Figure 1). The “pyrolytic HAAs” arise
during the high-temperature pyrolysis (>250 °C) of some individual
amino acids, including glutamic acid and tryptophan, or during the
pyrolysis of proteins,
6,9,128
but pyrolytic HAAs also can form, at
the low ppb concentrations, in some cooked meats.
129
HAAs of the
second class, aminoimidazoarenes (AIAs), are formed in meats that
are cooked at lower temperatures (150-250 °C) more commonly
used in household kitchens. The Maillard reaction is thought to play
an important role in the formation of many AIAs.
10,58,130
The N-
methyl-imidazole-2-yl-amine portion of the mo lecule is derived
from creatine, and the remaining parts of the AIA skeleton are
assumed to arise from Strecker degradation products (for example,
pyridines or pyrazines), formed in the Maillard reaction between
hexoses and amino acids.
58,131
An aldol condensation is thought to
link the two molecules through an aldehyde or related Schiff base to
form 2-amino-3-me thylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ) and 2-amino-
3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (IQx)-ring-structured HAAs.
132
2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP) can
form in a model system containing phenylalanine, creatinine, and
glucose;
133
however, PhIP can also form in the absence of sugar.
10,132
PhIP is the most abundant of the carcinogenic AIAs formed in well-
done cooked meats and poultry, where the concentration can reach
up to 500 ppb.
10,125-127,129,130,134
Several of the pyrolytic HAAs also are produced during
the burning of tobacco. These HAAs induce lacI transgene muta-
tions and aberrant crypt foci in the colon of mice,
135,136
and cancer
of the liver and/or gastrointestinal tract of rodents.
9,137-139
2-Amin o-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole (ARC) occurs in mainstream
tobacco smoke at levels up to 258 ng/cig.
140-142
The amounts of
ARC formed in tobacco smoke are ∼25- to 100-fold higher than
those of 4-ABP
4
or benzo(a)pyrene,
143
and comparable to the levels
of the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methyl-nitrosamino)-1-(3-
pyridyl)-1-butanone;
144
these latter compounds are human carcino-
gens.
145
Other HAAs occur at lower quantities in tobacco smoke:
2-amino-3-methyl-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole (MeARC) forms at 10-
fold lower amounts than ARC,
6,7,140
the glutamic acid and pyrol-
ysate mutagens, 2-amino-6-methyldiprido[1,2-a:3
0
,2
0
-d]imidazole
(Glu-P-1) and 2-aminodiprido[1,2-a:3
0
,2
0
-d]imidazole (Glu-P-2),
and the tryptophan pyrolysate mutagens 2-amino-1,4-dimethyl-5H-
pyrido[4,3-b]indole (Trp-P-1) and 2-amino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido-
[4,3-b]indole (Trp-P-2) occur at <1 n g/cig.
146,147
Several AIAs also
arise in tobacco smoke: 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine (PhIP) occurs in mainstream smoke at levels up to 23 ng/
cig,
7,144
while IQ occurs at <1 ng/cig.
148
Creatine, a constituent of
muscle, is thought to be an essential precursor for the formation of
AIAs, on the basis of studies on AIA formation in model systems.
58
For that reason, the occurrence of AIAs in tobacco smoke is
surprising, although creatinine is present in the soil and in plants.
149
PhIP has also been identified in incineration ash and in airborne and
diesel-exhaust particles.
150
The mechanisms of AIA formation during
combustion remain to be determined. The possible causal role of
some HAAs in tobacco-associated cancers warrants investigation.
The β-carboline compounds 9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole
(norharman) and 1-methyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole (harman) are
formed at considerably higher levels in tobacco condensates and in
cooked foods than are other HAAs (Figure 1).
141,151
Norharman
and harman are not mutagenic in S. typhimurium in the presence or
absence of the liver S9 fraction mixture; however, a synergistic
mutagenic effect is observed when these compounds are coincu-
bated with aniline or o-toluidine.
152
This comutagenic effect is
attributed to the formation of novel, mutageni c HAAs.
153
The
structures of the compounds formed are 9-(4
0
-aminophenyl)-9H-
pyrido[3,4-b]indole (amino-phenylnorharman, APNH), 9-(4
0
-ami-
no-3-methylphenyl)-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole (amino-methyl-phe-
nylnorharman, AMPNH), and 9-(4
0
-aminophenyl)-1-methyl-9H-
pyrido[3,4-b]indole (amino-phenylharman, APH). APNH is a liver
and colon carcinogen in F344 rats.
154
The HAAs studied induce tumors at multiple sites in rodents
during long-term feeding studies. The target organs include the oral
cavity, liver, stomach, colon, pancreas, and the prostate gland in
males, and the mammary gland in females.
9,155
The total dose
required to induce tumor formation (TD
50
) varies for each HAA
and is host species-dependent. The TD
50
values of the individual
HAAs have been reported to range from 0.1 to 64.6 mg/kg/day in
rodents.
9
The dose concentrations of HAAs used in these carcino-
gen bioassays were large: up to several hundred parts per million of
HAA in the diet were given to rodents over a 2 year period.
9,156
However, the carcinogenic potency of some HAAs is ma rkedly
enhanced in experimental laboratory animals exposed to tumor
promoters or agent s that caus e cell proli ferati on.
9,157-159
Moreover,
only a fraction of the HAA doses employed during long-term feeding
studies can efficiently induce aberrant colonic crypt foci, large
intestinal tumors,
158,160,161
or mammary gland tumors,
157,162
when
adietthatishighinfat is incorporated into the feeding regimen. IQ is
also a powerful liver carcinogen in nonhuman primates, with a latent
period of just 27 to 37 months, making this compound one of the
most powerful carcinogens assayed in nonhuman primates.
163
Summaries of the genetic alterations of target genes of HAAs in
experimental animal carcinogenicity studies are available.
9,72,73
1173 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
The average dietary HAA intake can range from less than 2 to
>25 ng/kg per day.
96,164
This daily intake level is about one
million to 10
5
-fold lower than the TD
50
values of individual HAAs to
induce tumors in rodents during long-term carcinogen bioassays
with stand ard feeding protocols.
9
Thus, the amounts of HAAs
consumed may be too small to explain human carcinogenesis,
assuming that the susceptibility of humans to HAAs is the same
as that of rodents. However, the carcinogenic effects of chronic
exposure to multiple HAAs could be additive or possi bly synergistic
in humans.
165
A linear relationship between DNA adduct formation
and the HAA dose has been demonstrated in tissues of rodents
treated over a wide range with MeIQx,
166
IQ,
167
and PhIP.
168
Moreover, several HAA-DNA adducts have been detected in human
tissues,
90,169-178
demonstrating that even ppb concentrations of
HAAs in the die t can damage DNA. HAAs may be implicated in the
development of human cancer under conditions in which many
other mutagens-carcinogens, tumor promoters, and factors stimu-
lating tumor progression exist.
9,159
The colon, prostate, and female
mammary gland are common sites of cancer in Western countries in
which well-done cooked meats containing HAAs are frequently
consumed;
96,179
and the rates of cancer in these organs are
increasing in Japan and other countries that are adapting western
dietary habits.
9
These findings have raised suspicion that HAAs may
contribute to the incidences of these cancers and have led to a
multitude of epidemi ological studies guided by the understanding of
HAA exposure and metabolism generated by the laboratory data.
Although the focal point of this review is on the metabolism
and the implementation of biomarkers of HAAs for molecular
epidemiology studies, the cooking of foods results in the forma-
tion of other carcinogens, which include polycyclic aromatic
hydrocarbons, furan, acrylamide, among other chemicals that
may be harmful to human health. The fundamental question is
this: do individuals who eat small quantities of any of these
carcinogens over a lifetime have an increased cancer risk? There
has been debate about the relative level of concern regarding
exposure to HAAs as opposed to other genotoxicants in the diet,
such as acrylamide, which are present at higher levels than HAAs.
180
Risk assessment studies of dietary genotoxic carcinogens, including
HAAs and acrylamide, have been reported.
179,181-185
The risk
characterization of some genotoxic carcinogens has been conducted
by the method of margin of exposure (MOE), which is defined as the
ratio between a dose leading to tumor formation in experimental
animals and the human intake and can be used to indicate levels of
concern and also the ranking between various exposures to genotoxic
carcinogens.
184,186
The l arger the MOE, the smaller the risk posed by
exposure to the genotoxic carcinogen under consideration. The
international mean intake of acrylamide, which is formed in heated
starch-based foods, has been estimated to range from 0.3 to 2.0 μg/kg
bw per day for the general population.
187
This amount of acrylamide
is at least 10-fold greater than the daily HAA exposure. The MOE
value for acrylamide was determined to be ∼1000-fold lower than the
MOE value estimated for PhIP,
184
which is the most mass-abundant
HAA formed in cooked beef.
10
Recent risk assessment approaches
have incorporated human exposure data combined with physiologi-
cally based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PBPK/PD) mod-
eling, which are used to integrate rodent carcinogenicity data and
reduce the uncertain ty inherent in extrapolatin g toxicological findings
across species and dose by employing common exposure
biomarkers.
185
In one PBPK/PD modeling study, the risk estimates
of population-based lifetime excess cancer risks, based on the average
acrylamide consumption in the diet range, was estimated between
1-4 x 10
-4
.
185
The human cancer risk factor estimates reported for
HAAs have ranged widely.
179,181-183
An upper limit was estimated
as ∼1 cancer case per 10,000 individuals, when considering
exposure to multiple HAAs,
181
and a lower limit was calculated at
50 cases per 10
6
individuals.
182
HAA biomarkers were not employed
in these risk assessment studies. The wide spread among the risk
estimates can be attributed to interstudy differences in the assump-
tions used to calculate risk factors, including differing estimates
of daily individual HAA intake, which can vary by more than
100-fold,
10,125,126,134,188-190
different dose extrapolations from ani-
mal models using body weight versus surface area scalings, and the
usage of TD
50
values from various animal carcinogen bioassays, in
which differences are seen in the HAA carcinogenic potency.
9,163,191
Moreover, pro- and anticarcinogenic dietary factors can affect the
metabolism and biological potency of HAAs as well as other
procarcinogens in humans.
9,159,192
Taken together, the relative
importance of HAAs and other dietary genotoxicants to human
cancer risk are likely to vary considerably among individuals.
Biomarkers of early biological effects (i.e., macromolecular carcino-
gen adducts) that can be used in molecular epidemiology studies to
assess the dietary exposure, absorption, as well as interspecies and
interindividual differences in m etabolism of procarcinogens may aid
to advance our understanding of health risks posed by different
environmental or dietary genotoxicants.
’ ENZYMES OF METABOLIC ACTIVATION AND DE-
TOXICATION OF AROMATIC AMINES AND HAAs
The bioactivation of aromatic amines and HAAs, is largely carried
out by cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes.
35,36,60,193
Oxidation of
the exocyclic amine group produces genotoxic arylhydroxylamine
and N-hydroxy-HAA metabolites, whereas oxidation of the aromatic
and heterocylic aromatic ring systems produces detoxicated
metabolites.
34,41,44,45,194-198
There are important differences in the
biotransformation pathways of arylamines and HAAs, particularly by
N-a cetyltransferases (NAT1 and NAT2), which are discussed below.
The conversion of 2-acetylaminofluorene to N-hydroxy-2-acetylami-
nofluorene in the rat was the first unequivocal proof of N-hydro-
xylation of an aromatic amine in vivo.
199
The arylhydroxylamines,
arylhydroxamic acids, and N-hydroxy-HAA metabolites are esterified
by N-acetyltransferases (NATs), sulfotransferases (SULTs),
L-seryl-
tRNA and
L-prolyl-tRNA synthetases, and other ATP-dependent
45,60,68,200-206
enzymes. These esters are unstable and undergo
heterolytic cleavage to produce the reactive nitrenium ion that binds
to DNA
37,45,63,194
(Figure 3). In the case of monocyclic alkylanilines,
oxidation of the aromatic ring produces phenols, which can undergo
spontaneous or peroxidase-catalyzed oxidatio n, to form the quinone
imine, a highly reactive electrophile that can undergo redox cycling to
produce reactive oxygen species.
123
This chemical reaction pathway
may contribute to the DNA damage of monocyclic alkylanilines.
AIAs that contain the N-methyl-imidazole-2-yl-amine moiety,
such as IQ and MeIQx, can undergo nitrosation with nitric oxide,
under neutral pH conditions, to form 2-nitrosoamino-3-methyl-
imidazo[4,5-f]quinoline and 2-nitrosoamino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-
[4,5-f]quinoxaline. These N-nitroso-AIA compounds are converted
to reactive diazonium species that may form covalent DNA
adducts.
207,208
A mechanism for the NAT2-catalyzed bioactivation
of N-nitroso-MeIQx has been proposed (Figure 3).
209
The bioacti-
vation of AIAs via nitrosation may be an alternative mechanism to
P450-mediated N-oxidation of AIAs and contribute to their geno-
toxicity, under inflammatory conditions, during which elevated
levels of nitric oxide can arise.
209
1174 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
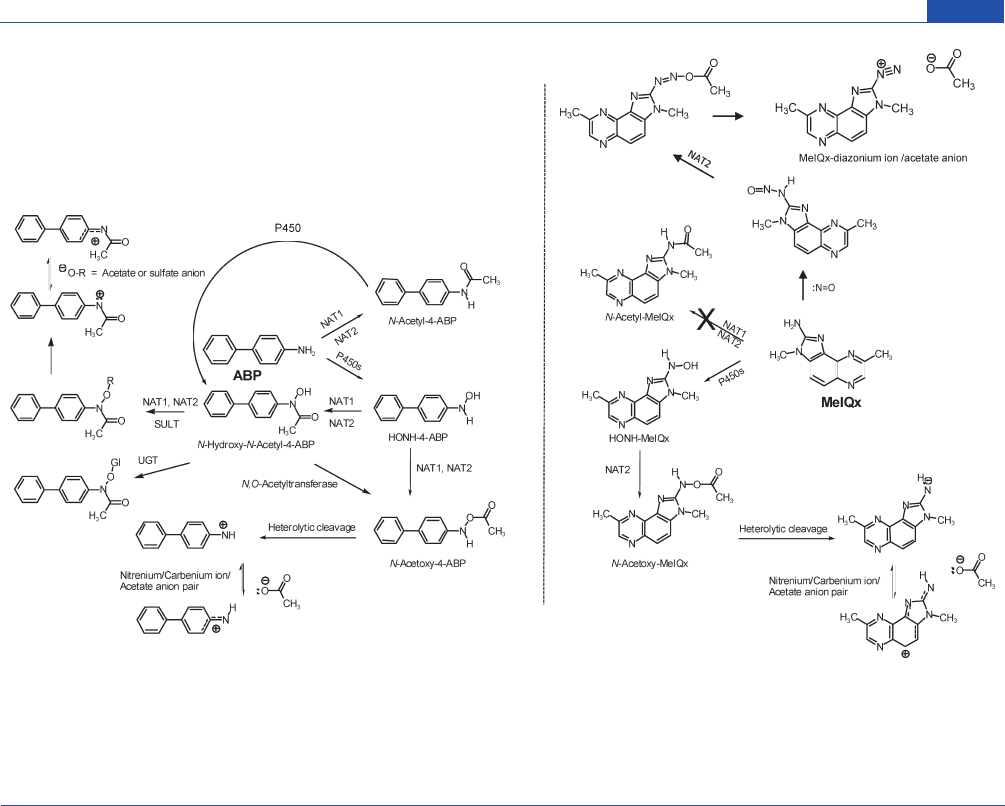
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 3. Metabolism of 4-ABP and MeIQx as prototypes of aromatic amines and HAAs. NAT enzymes effectively detoxicate arylamines, by N-
acetylation; however, many HAAs are poor substrates for NATs. NATs also catalyze the formation of N-arylhydroxamic acids, which can undergo
bioactivation by NAT1 and NAT2, or SULTs, or undergo detoxication by UGTs. NAT1 and NAT2 also serve as an N,O-acetyltransferase or O-
acetyltransferase and produce reactive N-acetoxy esters of the arylhyroxyalmines and N-hydroxy-HAAs, which are formed by P450s. N-Nitroso-MeIQx
formation can occur by reaction with nitric oxide under inflammatory conditions. The N-nitroso-MeIQx intermediate has been proposed to undergo
metabolic activation by NAT2 to produce a reactive diazonium ion of MeIQx that may damage DNA.
209
Cytochrome P450s. The mammalian CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and
CYP1B1 genes (http://drnelson.uthsc.edu/cytochromeP450.html),
encoding cytochromes P450 1A1, 1A2, and 1B1, respectively, and
several other xenobiotic metabolism enzyme genes, are regulated by
the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AHR).
210,211
These P450s are
responsible for the metabolic activation of many aromatic
amines, HAAs, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
212-223
Cyto-
chrome P450 1A2 accounts for approximately 15% of the P450
content in the human liver.
224
The P450 1A1 and 1B1 isoforms are
generally not expressed in the liver but are present at variable levels in
a number of extrahepatic tissues.
225-229
P450 1A2 catalyzes the
oxidation of many clinically used drugs and alkaloids at appreciable
levels including acetaminophen, imipramine, clozapine, caffeine, and
theophylliine.
230
The 3-N-demethylation of caffeine is catalyzed by
P450 1A2, and the urinary ratios a mong vari ous caffeine metabolites
following ingestion of this drug have been used to estimate individual
P450 1A2 activity and its inducibility in vivo.
231,232
P450 1A2
catalyzes the N-oxidation of planar aromatic amines such as
4-ABP, 2-NA, and AF, as well as many HAAs,
193,233
while P450
3A4, which is also prominently expressed in the liver, catalyzes the N-
oxidation of nonplanar aromatic amines such as MOCA.
234
P450
3A4 can activate other arylamines and HAAs,
235
but at considerably
lower rates than P450s 1A1, 1A2, or 1B1.
213,217,218
P450 2A6 was
identified as the m ajor P450 responsible f or the N-oxidation of
alkylanilines.
236
The rates of N-oxidation of 4-ABP, MOCA, 2-NA, and
HAAs are comparab le with human liver microsomes,
212,215,216,222,233
and comparable steady-state enzyme kinetic parameters have been
reported for the N-oxidat ion of 4-ABP and several HAAs with
recombinant human P450 1A2.
220-222,237
Human bladder micro-
somes also catalyze the N-oxidation of 4-ABP; some of this activity
may be attribu ted to P450 2A13.
238
In addition to N-oxidation, some
P450s catalyze the oxidation of the aromatic and heteroyclic aromatic
ring systems.
44,195,239
The liver is the most active organ in the metabolism and
bioactivation of many aromatic amines and HAAs.
60,66,197
The
constitutive P450 1A2 mRNA expression levels can vary by as much
as 15-fold in human liver,
240,241
and the expression of hepatic P450
1A2 protein ranges over 60-fold.
222,242
Varying levels of CpG
methylation
243
and genetic polymorphisms of the upstream 5
0
-
regulatory region of the P450 1A2 gene
244,245
alter the levels of
P450 1A2 mRNA exp ression. Chemicals in the environment,
246
tobacco,
247,248
and the diet, including constituents in cruciferous
vegetables
249,250
and grilled meat,
251,252
and medications
248,253
bind
to the AHR and increase the rate of transcription of the P450 1A2
gene, resulting in increased expression of the P450 1A2 protein and
210,211
other xenobiotic metabolism enzymes. The interindividual
variation in P450 1A2 activity is also observed in vivo for the
metabolism of caffeine, a substrate for P450 1A2:
233
more than a
70-fold range in P450 1A2 phenotype activity is observed in
humans.
231,248,254
Thegenotype(s) responsiblefor thelarge range
of interindividual differences in human hepatic P450 1A2 constitutive
expression is still not well understood.
255
The large interindividual
1175 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
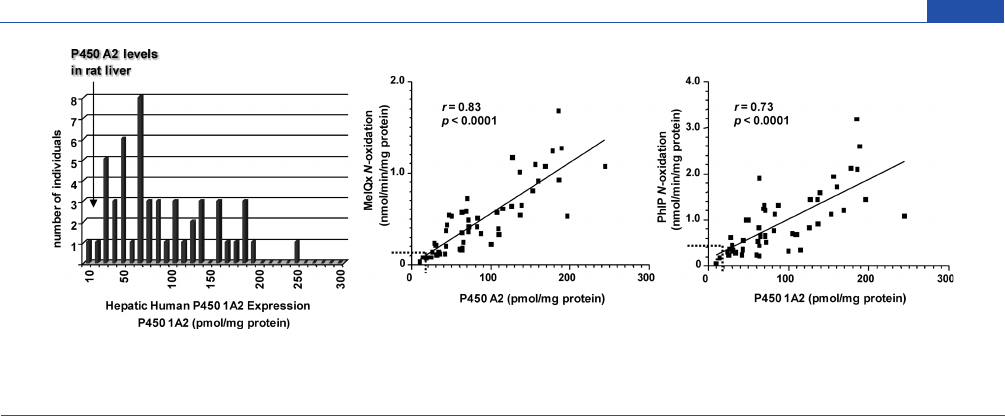
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 4. Levels of expression of P450 1A2 in human liver microsomes and correlation between P450 1A2 expression and rates of N-oxidation of MeIQx
and PhIP.
222
The checkered lines depicted in the correlation regression curves show the upper levels of P450 1A2 expression and rates of N-oxidation of
MeIQx and PhIP in rat liver microsomes.
variation in expression of P450 1A2 may be an important determi-
nant of individual susceptibility to aromatic amines and HAAs.
22,256
There are also large interspecies differences in the metabolism
of 4-ABP and HAA by P450s among mice, rats, and
humans,
214,222,257-259
which are attributed to different levels of
P450 expressi on, and differences in catalytic activities and
regioselectivities of P450s toward these substrates. These inter-
species distinctions in enzyme activities must be considered,
when human risk assessments of genotoxicants are conducted
from experimental animal toxicity data.
260
An example of the
range in the amount of P450 1A2 protein expressed in human
liver samples is shown in Figure 4. It is noteworthy that the
expression of P450 1A2 is significantly greater in humans than in
rodent strains that are used for carcinogen bioassays. Forty-three
out of the 51 human liver microsomal samples contain higher
P450 1A2 protein levels (5-250 pmol/mg microsomal protein,
median 71 pmol/mg, N = 51) than liver microsomal samples of
rats, where P450 1A2 content ranged from 5 to 35 pmol/mg
microsomal protein, depending upon the strain, source, and
diet.
222
The wide range in human P45 0 1A2 levels is paralleled by
a large variation in the rates of N-oxidation of MeIQx and PhIP,
which correlate well to the levels of P450 1A2. The rates of N-
oxidation of MeIQx and PhIP are much lower in liver microsomal
samples obtained from different strains of rats, which is reflective of
the lower amounts of P450 1A2 protein expressed in the rat liver.
There are important differences between human and rodent
P450s in terms of the catalytic activity and regioselectivity of HAA
oxidation; these characteristics affect the toxicological properties of
the molecules.
222,261
The catalytic efficiency of recombinant hu-
man P450 1A2 is superior to that of rat P450 1A2, in the N-
oxidation of PhIP and MeIQx. Recombinant human P450 1A2
shows about a 1.5-fold greater k
cat
(nmol product/nmol P450/
min) and 13-fold lower K
m
for PhIP N-oxidation compared to
those of rat P450 1A2. In the case of N-oxidation of MeIQx, the K
m
for recombinant human P450 1A2 and rat P450 1A2-mediated N-
oxidation of MeIQx are similar, but the k
cat
for recombinant
human P450 1A2 was 16-fold greater than that of rat P450 1A2.
The interspecies differences in the enzyme kinetic parameters for
N-oxidation of PhIP and MeIQx have also been observed with
human and rat liver microsomal samples.
222
However, the enzyme
kinetic parameters for the O-demethylation of methoxyresorufin
are similar for human and rat P450 1A2.
222
Important species differences also exist in the regioselectivity
of P450 1A2-mediated oxidation of HAAs. Human P450 1A2 is
regioselective for the N-oxidation (bioactivation) of HAAs, such
as IQ, MeIQx, and PhIP, and this enzyme does not appreciably
catalyze the ring-oxidation (detoxication) of the heteroaromatic
ring systems. However, the P450 1A2 orthologues of experi-
mental laboratory animals produce both N-oxidation and ring-
oxidation products at comparable levels.
103,214,222,262
Human P450
1A2 also catalyzes the oxidation of the C
8
-methyl group of MeIQx to
form the alcohol, 2-amino-(8-hydroxymethyl)-3-methylimidazo[4,5-
f]quinoxaline (8-CH
2
OH-IQx), which undergoes further oxidation
by P450 1A2 to form the carboxyli c acid, 2-amino-3-methylimi dazo-
[4,5-f]quinoxaline-8-carboxylic acid (IQx-8-COOH) (Figure 5).
262
IQx-8-COOH formation is the major pathway of metabolism and
detoxication of MeIQx in humans.
103
The rat P450 1A2 orthologue
catalyzes the detoxication of MeIQx through C-5 hydroxylation, but
it does not catalyze IQx- 8-COOH formation.
85,262-265
In the case of
PhIP, human P450 1A2 is highly selective for N-oxidation, whereas
rat P450 1A2 catalyzes both N-oxidation and 4
0
-hydroxylation of the
phenyl ring of PhIP to produce the detoxicated product, 2-amino-4
0
-
hydroxy-1-meth yl-6-phenyli mdazo[4,5-b]pyridine.
214,220-222
The metabolism of IQ, MeIQx , PhIP, and ARC (Figure 5)
has been studied with rodent and human liver micro-
60,197,214-216,222,257,266-273
somes, in experimental labora-
tory animals,
66,85,195,197,239,263,274,275, 275-281
rodent hepato-
195,265,282,283
cytes, human hepatocytes,
262,284
and HepG2
cells.
283
A number of metabolites of MeIQx and PhIP have also
been identified in human urine.
98,101,103,176,264,285-293
P450-medi-
ated ring-oxidation of MeIQx, IQ, and PhIP are major pathways of
in rodents
85,214,222,239,274
metabolism and detoxication and in
Cynomolgus monkeys.
196
P450 1A2 is not expressed in the liver
of Cynomolgus monkeys,
294
and other P450s, including P450 3A4
and/or P450 2C9/10, appear to contribute to the ring and exocyclic
N-oxidation of HAAs in this species.
196
These other P450s were
reported to N-hydroxylate IQ to an appreciable extent but did not
catalyze the N-oxidation of MeIQx; IQ is a carcinogen in Cyno-
molgus monkeys, but MeIQx is not.
196
The P450-mediated N-
demethylation of IQ and MeIQx is another importantbiotransfor-
mation pathway of IQ and MeIQx in rode nts a nd n onhuman
primates.
196,281
N-Demethylation of IQ is thought to be a det oxica-
tion pathway because the mutagenic potency of desmethyl-IQ is
more than 60-fold weaker than IQ.
295
However, the P450-mediated
N-demethylation of IQ or MeIQx is negligible with human liver
microsomes,
215,222,233
human hepatocytes,
272
or in humans.
103,264
The micro flora of the human colon catalyzes the oxidation of IQ and
1176 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 5. Major pathways of metabolism of ARC, IQ, MeIQx, and PhIP in experimental laboratory animals and humans.
MeIQx at the C-7 atom of the heterocyclic ring;
296
these oxidation
metabolites are not carcinogenic in rodents.
297
Numerous studies have shown that P450 1A2 plays a major
role in the metabolic activation of aromatic amines and HAAs
and in the formation of DNA adducts in rodents
63,298,299
(and
references cited therein). The pretreatment of human liver micro-
somes with various amounts of furafylline, a mechanism-based
inhibitor of P450 1A2,
300
led to a concentration-dependent inhibition
of HONH-MeIQx, 8-CH
2
OH-IQx, IQx-8-COOH, and HONH-
PhIP formationbyupto95%,
215,216,220,222 ,261
indicating the impor-
tant contribution of human P450 1A2 in the metabolism of these
carcinogens. The formation of 8-CH
2
OH-IQx and IQx-8-COOH,
and the glucuronide conjugates of HONH-MeIQx and HONH-
PhIP, was also inhibited to a similar degree in human hepatocytes
pretreated with furafylline.
262,284
In humans, the contribution of P450
1A2 to the metabolism of MeIQx and PhIP was demonstrated in a
pharmacokinetic study that used furafylline.
301
As much as 91% of the
MeIQx and 70% of the PhIP consumed in grilled meat were estimated
to undergo metabolism by P450 1A2.
301
Thus, P450 1A2 significantly
contributes to the metabolism of both MeIQx and PhIP in vivo in
humans but with marked differences in substrate specificity. Human
P450 1A2 primarily catalyzes the detoxification of MeIQx by oxida-
tion of the 8-methyl group, whereas it catalyzes the bioactivation of
PhIP by oxidation of the exocyclic amine group (Figure 5).
103,262
These metabolic studies support the notion that P450 1A2 is a major
enzyme involved in the metabolism of MeIQx and PhIP in humans.
Conversely, the results from several studies employing trans-
genic rodents have led investigators to propose that alternative
enzymes are involved in HAA- and arylamine-mediated toxicity and
that P450 1A2 may even be protective against these carcinogens in
animals.
211
The levels of DNA adducts of IQ and PhIP were found
to be lower in some organs of P4501A2-knockout mice than in
organs of wild-type mice; however, other P450s or enzyme path-
ways of activation also contributed to DNA adduct formation in
specificorgans.
302
In the neonatal mouse model, higher incidences
of lymphoma and hepatocellular adenoma occurred in female
P4501A2-knockout mice than in wild-type mice exposed to high
doses of PhIP (11 or 22 mg/kg),
258
indicating that PhIP-induced
carcinogenesis is independent of P450 1A2 expression. Methemo-
globin formation, a biomarker of exposure and toxicity to certain
aromatic amines, was higher in P450 1A2-knockout mice than in
wild-typemiceexposed to 4-ABP.
303
Furthermore, P450 1A2
expression in wild-type mice was not associated with 4-ABP-induced
hepatic oxidative stress or with 4-ABP-DNA adduct formation.
304
4-ABP-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in P4501A2-knockout mice
was also found to be independent of P450 1A2.
259
These paradox-
ical effects may lead us to question the importance of P450 1A2 in
HAA- and 4-ABP-mediated toxicity and malignancy.
211,305
We note
that very high concentrations of HAAs and 4-ABP were employed in
these transgenic rodent studies; the high doses may have triggered
metabolic pathways that lead to the formation of chemically reactive
metabolites, by other P450s or phase I enzymes, which may not arise
under low-dose treatments. Indeed, liver microsomes from P450
1A2-knockout mice displayed s igni ficant N-oxidation activity of
PhIP and 4-ABP.
258,259
TheroleofP4501A2 in theactivationas
opposed to the detoxication of HAAs or aromatic amines in the
intact animal is likely to depend on the extent of phase II
metabolism, the degree of coupling of N-oxidation with phase II
enzymes, and cell type- and tissue-specificcontext, aswellasthe
dose and pharmacokinetics of the compound under study.
211,305
Investigations in “humanized” mice containing the P450 1A2 allele
in place of th e orthol ogous mo use gene
280,306
can be used to assess
the role of human P450 1A2 in the DNA damage i nduced by HAAs
and aromatic amines, under realistic human exposure levels.
Peroxidases. Peroxidases, including prostaglandin H synthase
(PHS), an arachidonic acid-dependent peroxidase, may play a
significant role in the activation of aromatic amines and HAAs in
extrahepatic target tissues of experimental animals, such as
urinary bladder, colorectum, and mammary gland, where the
P450 content is low.
307-318
Much of the data are consistent with
a one-electron mechanism of arylamine or HAA oxidation by
PHS, and the N-hydroxy intermediates do not appe ar to be
involved in the metabolism by PHS.
310
However, a number of the
PHS oxidized products of arylamines and AIAs generate a DNA
1177 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
adduct profile that is similar to those generated by P450s,
suggesting a common DNA-reactive species, presumably an
arylnitrenium ion, produced by different pathways in these
cellular and enzyme model systems.
310,316,319-322
N-Acetyltransferases. N-Acetyltransferases (NATs) are critical
enzymes involved i n the genotoxicity of aromatic amines and HAAs.
There are two distinct N-acetyltransferase isoenzymes (designated
NAT1 and NAT2, http://louisville.edu/medschool/pharmacology/
consensus-human-arylamine-n-acetyltransferase-gene-nomencla-
ture/). NAT2 is expressed primarily in the liver, whereas NAT1
appears to be more prominently expressed in extrahepatic
tissues.
323,324
More than 25 genetic polymorphisms have been
identified for both NAT genes that can affect the catalytic activity
of NATs toward aromatic amines and HAAs.
323,325,326
NAT enzymes
have a dual role in the metabolism of aromatic amines and HAAs:
these enzymes can serve as mechanisms of bioactivation or detoxica-
tion. Some epidemiological studies suggest a role for NAT2 activity in
human susceptibilities to various cancers from tobacco smoke and
from the consumption of well-done meats, where the exposures to
aromatic amines and HAAs can be substantial.
327,328
N-Acetylation is an important mechanism of detoxication of
aromatic monoamines:
324
this biotransformation pathway is cata-
lyzedbybothNAT1and NAT2 andservesasacompetingpathway
of N-oxidation.
203
The resulting acetamides are generally viewed as
poor substrates for P450-mediated N-oxidation (Figure 3).
329
For
many aromatic amines, the catalytic efficiency (k
cat
/K
m
)of N-
acetylation by recombinant NAT1 is superior to that of recombinant
NAT2, but the relative affinity (K
m
) for each of the arylamine
substrates investigated was higher for recombinant N AT2.
203
Bz, an
aromatic diamine, is an exception. The N-acetylation of one
of the amine groups of Bz appears to facilitate P450-mediated
N-oxidation of the nonacetylated amine group, to form the
reactive N-4- hydroxyamino-N
0
-acetylbenzidine (HONH-N
0
-acetyl-
Bz) m etabolite.
318,330
Bz is preferentially N-acetylated by NAT1.
331,332
N-Acetylation of the arylhydroxylamines also occurs, to form
the arylhydroxamic acids, which can undergo bioactivation by N,
O-acetyltransferase or sulfotransferases (SULTs).
45
Direct acti-
vation of the arylhydroxylamines by O-acetylation also occurs
and results in formation of the reactive N-acetoxy intermediates that
readily bind to DNA.
60,194,3 33
NAT1 appears to function as an
O-acetyltransferase (OAT) and as an N,O-acetyltransferase, when
using acetyl coenzyme A or arylhydroxamic acids, respectively, as
acetyl donors. NAT2 appears to act preferentially as an OAT and
NAT (Figure 3). HAAs that contain the N-methyl-imidazo-
2-yl-amine moiety (AIAs) are poor substrates for NATs, and
N-acetylation is not an important pathway of detoxication in rodents
or humans. ARC and several other pyrolysate HAAs are substrates
for rodent NATs. Nonetheless, the catalytic rates are ∼1/1000 the
level observed for the N-acetylation of AF.
60
In contrast to the
parent HAAs, the HONH-AIA and HONH-HAA metabolites do
undergo O-acetylation, primarily by NAT2, to form the reactive
N-acetoxy species, whichbindtoDNA (Figure 2).
63,334,335
N-Hydroxy-ARC is an exception, and it undergoes O-acety lation
by both NAT1 and NAT2.
271
A mouse model deficient in both NAT1 and NAT2, Nat1/
2(-/-), was employed to examine the pharmacokinetics of
4-ABP, AF and PhIP.
336
The metabolism of AF was severely
affected, and the plasma clearance was increased by 4-fold in
Nat1/2(-/-) mice, whereas the clearance of 4-ABP was found
to be less dependent on N-acetylation, and no difference in
4-ABP plasma clearance rates was observed between wild-type
and knockout animals. PhIP did not undergo N-acetylation, nor
was its clearance affected by the NAT genotype.
336
In adult
female rapid and slow acetylator rats congenic at the NAT2 locus,
PhIP-DNA adduct formation was unaffected by NAT2 acetylator
status in the liver or any of the extrahepatic tissue examined,
whereas MeIQx-DNA adducts, particularly in the liver, were
significantly lower in slow acetylators.
337
Similar findings were
observed in congenic rapid and slow acetylator Syrian hamsters;
PhIP-DNA adduct formation was indep endent of N-acetylator
activity.
338
These data signify that PhIP genotoxicity in rodents is
not influenced by NAT enzymes.
HONH-PhIP, like many other HONH-HAAs, undergoes
activation by human NATs in subcelluar cytosolic assays,
339
and by recombinant NAT2,
335
to form the reactiv e N-acetoxy-
PhIP intermediate, which binds to DNA.
340,341
However, the
level of PhIP-induced mutation and DNA adduct formation in
Chinese hamster ovary cell lines cotransfected with NAT2*4
(rapid acetylator) or NAT2*5B (slow acetylator) alleles with
either P450 1A1 or P450 1A2 is comparable to cell lines only
transfected with the P450s.
342,343
A similar result was demon-
strated in Salmonella typhimurium bacterial strains expressing
NAT2,
68,344,345
human NAT1 or and PhIP appeared to be
activated by other phase II enzymes, including SULTs.
68,345,346
A much more potent effect of NAT2 phenotype was demon-
strated for the induction of mutagenicity and DNA adduct
IQ,
342
ARC.
348
formation of MeIQx,
347
and The findings
indicate that HONH-PhIP is a poor substrate for rodent and
human NATs. Thus, metabolic data obtained with subcelluar
fractions or isolated enzymes, particularly when high substrate
concentrations are employed, may not be reflective of enzyme
activity that occurs within cells. Therefore, the adverse biological
effects of NAT2 phenotype in the gene-environmental (cooked
red meat) studies may reflect exposure to other HAAs such as
MeIQx and ARC more so than PhIP. The identificatio n of
exposure to specific HAAs is very important in molecular
epidemiological investigations that seek to assess the significance
of HAAs and NAT2 genetic polymorphism in cancer risk.
The role of NAT2 genetic polymorphism in cancer risk has
been studied extensively, and the elevated risk of urinary bladder
cancer in cigarette smokers who are slow N-acetylators is well
documented.
50,77,78,349
This increased cancer risk has been attrib-
uted to the diminished capacity of slow N-acetylator individuals to
detoxicate aromatic amines present in tobacco; some of these
aromatic amines are bladder carcinogens
1-3,34 ,326
(Figure 3). How-
ever, the role of NAT2 phenotypes in cancer risk of HAAs is
unclear.
204,323
NAT2 does not efficiently detoxicate most HAAs, but
the N-hydroxylated HAA metabolites are substrates for O-acetyla-
tion by NAT2, and the resultant N-acetoxy intermediates readily
bind to DNA.
60,63,334,335,339,350,351
As a result, the increased cancer
risk maybemarkedlyelevatedinindividuals whoare both rapid
P450 1A2 N-oxidizers and rapid O-acetylators.
327,328
Sulfotransferases. The sulfotransferases (SULTs) are an-
other phase II enzyme involved in the metabolism of aromatic
amines and HAAs. The SULTs belong to a super family of genes
that are divided into two subfamilies: the phenol SULTs
(SULT1) and the hydroxysteroid SULTs (SULT2).
352-354
SULT1A1, 1A3, and 1B1 are expressed in all parts of the
gastrointestinal tract, often exceeding the protein levels that are
expressed in the liver.
355
In addition to the sulfating of phenolic
xenobiotics, steroids, and estrogens, the SULT enzymes can
serve to detoxicate or bioactivate HAAs or aromatic amines.
68,356
Rat SULT1A1 catalyzes the formation of sulfamates of IQ and
MeIQx
357-359
as detoxication products, but the sulfamation of
1178 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
PhIP does not occur in rats or other experimental laboratory
animals.
195
The sulfamate of MeIQx is excreted in the urine of
humans:
264,285
its formation is presumably catalyzed by
SULT1A1.
359
Boyland et al.
360
demonstrated that rats dosed
with aniline, 1-naphthylamine, or 2-NA excrete in the urine a very
small amount of these aromatic amines as the sulfamate deriva-
tives. The sulfamates of IQ and MeIQx are quite stable under the
range of pH conditions that exist in urine,
285,357,358
whereas the
sulfamates of many arylamines are labile.
360
Human SULT1A1 and SULT1A2 catalyze the binding of the
N-hydroxy metabolites of MOCA, AF, AAF, 4-ABP, PhIP, ARC,
and MeARC to DNA, although the N-hydroxy metabolites
of MeIQx and IQ are poor substrates for both SULT
isoforms.
68,202,205,345,356,361-363
The SULT-mediated metabolic
activation of arylhydroxylamines and N-hydroxy-HAAs has been
detected in human liver, colon, prostate, and female mammary
gland cytosols but not in the pancreas, larynx, or urinary bladder
epithelial cytosols.
361,364-366
SULT1E1, which is under hormo-
nal regulation, catalyzes the binding of HONH-PhIP to DNA in
cultured human mamm ary cells. Therefore, SULT1E1 was
proposed to play a role in the bioactivation of PhIP in breast
tissue.
367
However, a recent study failed to detect the SULT1E1
protein in breast tissue, and factors in the cell culture media may
have induced the expression of SULT1E1 protein in cultured
human mammary cells.
365
One common genetic polymorphism, an Arg213His poly-
morphism in the SULT1A1 gene, has a strong influence on the
level of enzyme protein and phenol sulfotransferase activity in
platelets, which has been used for metabolic phenotyping.
205
The
frequency of the variant SULT1A1*2 allele exceeds 10% in
Japanese,
368
African-Americans, and Caucasians.
369,370
The
SULT1A1*2 protein has low enzyme activity and stability
compared to the wild-type SULT1A1*1 protein.
361
DNA binding
studies using recombinant SULT1A1*1 and SULT1A1*2 have
shown that the SULT1A1*1 protein catalyzes HONH-4-ABP
and HONH-PhIP DNA adduct formation with much greater
efficiency than the SULT1A1*2 variant.
205
Several molecular epi-
demiological studies have explored the roles of SULT1A1*1 and
SULT1A1*2 genotypes and putative HAA exposure in breast,
371
colorectal,
370,372
and prostate cancer risk.
373
The expression of the
variant allele SULT1A1*2, with diminished capacity for bioactivation
of some HONH-HAAs, was associated with decreased risk of breast
cancer for women who often ate well-done cooked meat;
371
however, this genotype was not associated with a decreased risk
of colorectal
370,372
or prostate cancer.
373
The frequency of con-
sumption of grilled meats and the extent of exposure to HAAs are
uncertain in these subjects. In the absence of exposure to biologically
relevant levels of HAAs, a genetic polymorphism would not be
expected to be manifested as a risk factor.
374
Since SULTs are
involved in both the metabolic activation and detoxication of HAAs
and other dietary genotoxicants, as w ell as in maintaining hor-
monal homeostasis, it has been difficult to predict the impact of
SULT enzymes in individual susceptibilities following exposure to
cooked meat.
UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases. UDP-Glucuronosyltrans-
ferases (UGTs) catalyze the glucuronidation and elimination of
numerous classes of xeno biotics, steroids, and en dogenous com-
pounds, as well as the detoxication of various carcinogens
375-377
(http://www.pharmacogenomics.pha.ulaval.ca/sgc/ugt_alleles/).
The UGTs are present in the 1A, 2A, and 2B subfamilies and ex-
pressed in liver and extrahepatic tissues. Aromatic amines and HAAs
undergo metabolism by UGTs. The UGT1A family contributes
more to the metabolism of aromatic a mines than does the UGT2B
family.
378,379
4-ABP, Bz, and N-acetyl-Bz were reported to be cata-
lyzed most efficiently by UGT1A9, followed by UGT1A4,
UGT2B7, and last by UGT1A1.
379-382
Many of these isoforms
are also involved in the N-glucuronidati on of the respective
arylhydroxylamines or the O-glu curonidati on of N-arylhydroxamic
acids.
383-386
The N,O-glucuronide conjugates of N-arylhyd ro-
xamic acids are fairly stable and are viewed as detoxication pro-
ducts,
40,383,387,388
whereas the N,O-sulfonates of N-arylhydroxamic
acids are highly reactive species that bind to DNA and protein
(Figure 3).
389-391
Depending upon the structure of the HAA and the UGT
isoform, glucuronidation can occur at the exocyclic amine group or
the endocyclic N-imidazole atom of the AIAs and the N-hydroxy-
AIAs.
282,392-395
O-Glu curonide conjugates of ring-oxidized AIA
metabolites are also prominent metabolites that are excreted in urine
of rodents
195,239
and nonhuman primates
196
but not in the urine of
humans.
98,103,176,264,293
The human UGT1A family of enzymes is
principally involved in the N-glucuronidation of PhIP
396-398
and
most likely MeIQx as well.
262
On the basis of studies with
recombinant enzymes, the human UGT1A1 isoform followed by
UGT1A4, UGT1A8, and UGT1A9 are the most active enzymes
involved in N-glucuronidation of PhIP and HONH-PhIP;
397
other
studies reported that UGT1A9
399,400
or UGT1A10
401
were highly
active isoforms in the glucuronidation of HONH-PhIP. The N
2
atom of HONH-PhIP is the preferred site of conjugation for all of
the recombinant UGTs studied, except for UGT1A9, where the N3
imidazole atom is the preferential site of conjugation.
401,402
The
levels of formation of N
2
-(ß-1-glucosiduronyl-2-(hydroxyamino)-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (HON-PhIP-N
2
-Gl), the
principal metabolite of PhIP excreted in human urine,
98,101,103,176
showed a high interindividual variability in formation, up to 28-fold,
with human liver microsomes.
398
High and variable levels of UGT-
catalyzed glucuronidation of HONH-PhIP were also detected with
human colon microsomes, signifying that extrahepatic UGTs, such
as UGT1A10, may serve as an important enzyme of detoxication of
HONH-PhIP in colon.
401,402
The differential rates of UGT isoform activities reported for
aromatic amines, HAAs, and their N-hydroxylated substrates
should be viewed with caution. The discrepancy in enzyme
activities observed among the different UGTs may be in part
due to the different systems used for screening enzyme activity:
UGTs are membrane-bound, and recombinant UGT-overex-
pressing bacul osomes do not necessarily mimic activities that are
observed for UGT-overexpressing cell lines.
397,401
Moreover, the
complete activation of UGT activity in microsomal preparations
requires the presence of detergents or the membrane-permeabi-
lizing agent alamet hicin
394,402
to overcome the latency associated
with UGT-membrane bound enzymes; the assay conditions,
buffers, and cofactors were different in the studies cited above.
The N-glucuronidation of arylamines and arylhydroxylamines
is viewed as a mechanism of transport of the carcinogenic inter-
mediates, to the urinary bladder and colon (Figures 2 and 6), and
thought to contribute to the organotropism of aromatic amine
carcinogenesis. The N-glucuronide conjugates of arylamines, HAAs,
and their N-hydroxylated metabolites are eliminated in the urine and
bile of animal species and humans.
66,98,101,103,196,386,393,403,404
Aryl-
amine and arylhydroxylamine N-glucuronide conjugates can under-
go hydrolysis in the range of pH con ditions that exist in urine,
318,383
whereas AIA and HONH-AIA N-glucuronide conjugates are
stable.
103,275,358,393,394
The half-lives of the N-glucuronides of
4-ABP and HONH-4-ABP are 10.5 and 32 min, respectively,
1179 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
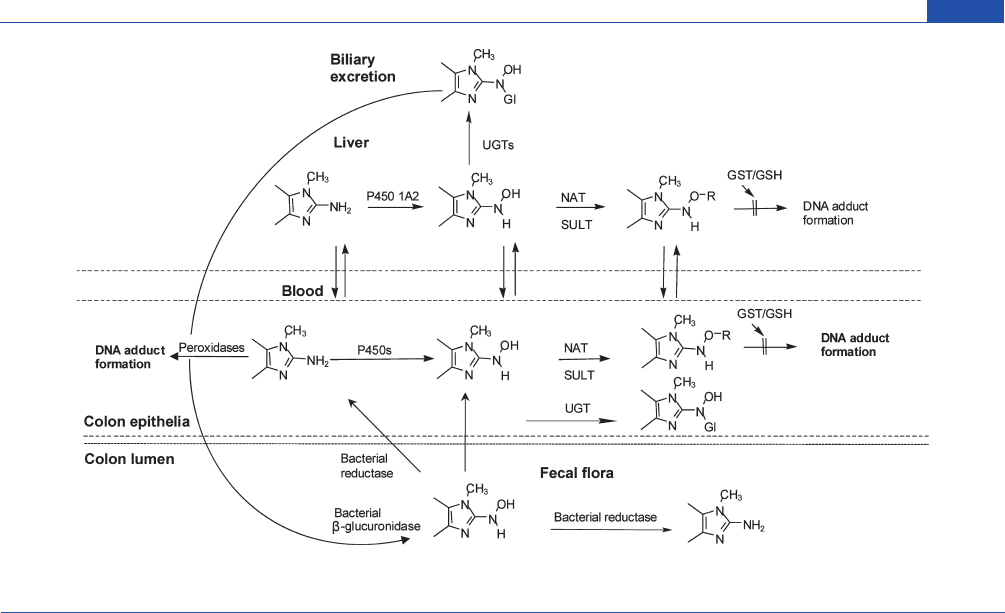
Figure 6. Metabolism of aromatic amines and HAAs by UGTs and the role of UGTs in transport of the genotoxic arylhydroxylamine and N-hydroxy-HAA
metabolites to the colon to form DNA adducts. Glutathione S-transferases, or GSH alone, can inactivate some N-oxidized arylamine or HAA metabolites.
at pH 5.5; the half-lives of N-glucuronide conjugates of Bz and the
N
0
-glucuronide of the HONH-N
0
-acetyl-Bz are 7.5 min and 3.5 h at
pH 5.5.
318,380,385
The regenerated arylamines can undergo bioacti-
vation by P450s or peroxidases in the bladder epithelium.
238,318
The
reactivity toward DNA of many arylhydroxylamines shows strong
pH dependence: the level of DNA adduct formation at pH 5.0 is 10-
to 50-fold higher than the level of adduct formed at pH 7.0.
45
This
enhanced reactivity at acidic pH is attributed to the formation of the
nitrenium ion.
76,405
Thus, arylhdroxylamines that are eliminated in
urine as the unconjugated metabolites or produced by hydrolysis of
the N-glucuronide conjugates undergo protonation in the acidic
bladder lumen to produce reactive species that readily b ind to DNA
of the urothelium
384,385
(Figure 3).
The pH of urine has also been reported to have a strong
influence on the levels of urinary Bz and its urothelial DNA
adducts formed in humans: A high urine pH was inversely
correlated with the proportions of free Bz, N-acetyl-Bz in urine
of postshift factory workers, and the average of each subject’s
urine pH was negatively associated with the urothelial addu ct
N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-N
0
-acetylbenzidine.
332,406
When the in-
ternal dose was controlled, subjects with a urine pH < 6 had 10-
fold higher DNA adduct levels than subjects with a urine pH >
7.
406
A more recent study has reported that urine pH is a risk
factor for bladder cancer, and a dose-response relationship in
bladder cancer risk was observed with increasing urinary acidity
among current smokers.
407
These findings are consistent with
the biochemical properties of aryalmines and support a caus al
role of arylamines in bladder cancer. The glucuronide conjugates
of HAAs, formed at either exocyclic or endocyclic nitrogen atoms
of the AIA and HONH-AIA imidazole moieties are stable in weak
acid,
103,275,358,393,394
and the reactivity of N-hydroxy-AIAs with
DNA is not appreciably enhanced by weak acid.
339,408
These
chemical properties may help to explain why AIAs are not
bladder carcinogens in experimental laboratory animals and
possibly in humans.
9
The UGT metabolism of arylamines is also thought to
contribute to the organotropism of aromatic amine-mediated large
intestinal carcinogenesis. Studies on aromatic amines in rodents
with surgically performed colostomies showed that tumors exclu-
sively appeared proximal to the colostomy, where the intestinal
segments were in actual contact with the fecal stream.
403,409-411
These experiments provided strong evidence that the induction of
tumors in the intestine was relate d to the transport of some form of
the carcinogen via the bile into the intestines rather than by the
bloodstream. The N-glucuronide conjugates of arylhydroxylamines
undergo hydrolysis by bacterial β-glucuronidases within the intes-
tines to release the arylhydroxylamine species,
66,412
which are
bioactvated by NATs or SULTs expressed in the intestines, to form
DNA adducts (Figure 6).
22,66,339,361,413
The N
2
- and N3-glucuronide conjugates of HONH-PhIP are
substrates for the β-glucuronidases of E. coli. from the fecal flora
of rodents and humans.
393
The liberated HONH-PhIP would be
expected to form DNA adducts in colorectal tissue. However, the
same level of PhIP-DNA adducts were reported to form in colon
and other extrahepatic tissues of sham- and bile duct-ligated
rats,
404
implying that the N-glucuronide conjugates of HONH-
PhIP eliminated in bile or the bloodstream are not involved in
PhIP-DNA adduct formation in the colon or other extrahepatic
tissues. Intestinal bacteria of rodents and humans have been
reported to catalyze the reduction of HONH-PhIP back to
PhIP.
393
Perhaps, this enzymatic reduction occurs before the
HONH-PhIP (or other HONH-AIAs) in the fecal stream can
reach the colonic crypt and damage DNA (Figure 6). In the rat,
the bioactivated PhIP metabolites appear to be either transported
from the liver through the blood circulation to extrahepatic
tissues or the direct occurrence of bioactivation of PhIP within
extrahepatic tissues.
404
The N
2
-glucuronide conjugates of IQ,
1180 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
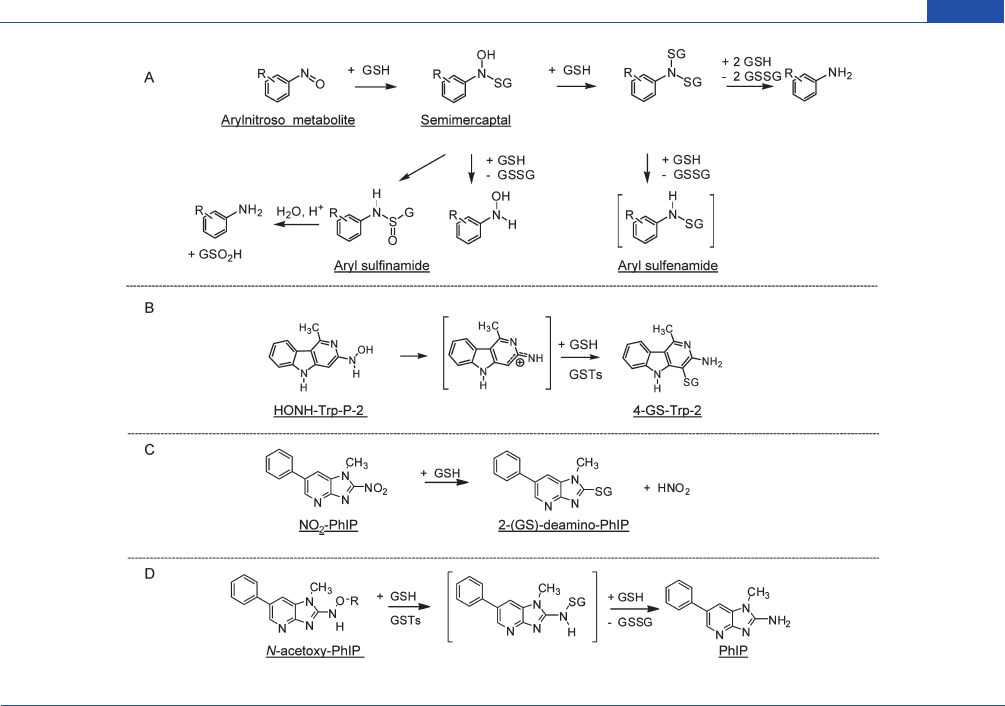
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 7. Reaction pathways of nitrosoarenes and nitroso-HAAs, N-hydroxy-HAAs, or nitro-HAA intermediates with GSH and GSTs.
393,419,420,429,430
MeIQx, and their N-hydroxylated metabolites are resistant
toward the hydrolytic action of β-glucuronidases.
103,275,358,394
The N3-methyl group of these AIAs appears to sterically hinder the
enzyme since t he N
2
-glucuronide conjugate of N-desmethyl-IQ i s a
substrate for bacterial β-glucuronidase.
275
Since significant inter-
individual variation in the N-glucuronidation of HAAs and HONH-
HAA occurs in vitro
398,402
and in vivo,
98,101,103,176,264,288,289
it is of
interest to further examine the interrelationshi p among genetic
polymorphisms in UGT1A isoforms, HAA exposure, and cancer
risk.
377,401,414-416
Glutathione S-Transferases and Glutathione Conjugates.
The glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are another important
class of enzymes involved in the detoxication of many endogen-
ous electrophi les and classes of xenobioti cs, i ncluding aromatic
amines and HAAs.
417
In humans, these enzymes are classified as
Alpha, Mu, Omega, Pi, Sigma, Theta, and Zeta.
418
The enzymes
occur as dimeric protein structures and are named according to their
subunit composition, for example, GST A1-2 is the enzyme
composed of subunits 1 and 2 in the Alpha class. The nonenzymatic
reactions of GSH or other thiols also can occur with arylhydrox-
ylamines, N-hydroxy-HAAs, their esterfied products, the oxidized
nitrosoderivatives,and,insomecases,oxidizednitro-AIAs. The
interaction of GSH or other thiols with arylni troso compounds has
been extensively examined. The reactions are complex and product
formation is dependent on thiol concentration, pH, and substituent
effects.
419-421
The initial product formed between the arylnitroso
derivatives and GSH is a labile semimercaptal. However, the
products formed by the reaction of 3-nitrosonitrobenzene and
4-nitrosonitrobenzene with GSH were sufficiently stable and char-
acterized by NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.
422
The
short-lived semimercaptals can react in several ways as depicted in
Figure 7A.
High exposures to 4-ABP result in the depletion of glutathione
(GSH) in the liver of mice.
303
The depletion of GSH in primary
hepatocytes, by
L-buthione sulfoximine, resulted in a 15-fold increase
in the formation of PhIP-DNA adducts,
423
and GSH depletion
in vivo in rats resulted in a 5-fold increase in hepatic PhIP-DNA
adducts.
404
An increase in the level of IQ bound to DNA also occurs
in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes, following the depletion of
cellular GSH.
424
These findings show that GSH is protective against
the genotoxicity of some aromatic amines and HAAs.
The peroxidatic activity of met-Hb and H
2
O
2
catalyzed the
oxidation of N-acetyl-Bz, presumably to the reactive nitroso inter-
mediate, whichwas trappedwithGSH to form astablesufinamide
adduct. The GSH conjugate was characterized by electrospray
ionization/mass spectrometry as N-(glutathion-S-yl)-N
0
-acetylben-
zidine S-oxide.
425
The nonenzymatic reaction of GSH with the
nitroso and N-hydroxy metabolites of AF produced the sulfinamide,
N-(glutathione-S-yl)-2-aminofluorene S-oxide, and the sulfenamide,
N-(glutathione-S-yl)-2-aminofluorene ; analogous GSH conjugates
were formed with the nitroso and N-hydroxy metabolites of
1-naphthylamine and 2-NA.
426
In rats treated with N-hydroxy-2-
acetylaminoflourene, the two biliary conjugates were identified as 1-
and 3-(glutathion-S-yl)-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene: no S-N-linked
conjugates were reported.
427
Sulfinamide and sulfonamide adducts were produced from the
nonenzymatic in vitro reaction of the nitroso metabolite of Glu-
P-1 with GSH.
428
Enzymatic reaction of GSTs from rat liver with
the N-hydroxylated metabolite of Trp-P-2 produced three GSH
conjugates.
429
One of the conjugates was found to be a more
1181 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
potent bacterial mutagen than HONH-Trp-P-2: the structure
may have been the semimercaptal conjugate, on the basis of mass
spectral data.
429
The structures of the two detoxicated products
appear to be, respectively, a sulfinamide adduct and a stable S-C
adduct that may have formed at the C-4 atom of Trp-P-2
(Figure 7B).
429
GSH reaction products with the oxidized nitro
derivatives of MeIQx and PhIP have been reported to form in
rodent hepatocy tes.
282,393
In these reactions, the thiol group of GSH
displaced the nitro moieties, by direct nucleophilic substitution, to
form 2-(glutathion-S-yl)-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-flquinoxaline
282
and 2-(glutath ion-S-yl)-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyri-
dine;
393
the GSH conjugate of NO
2
-PhIP was also detected in rat
bile and suggests that NO
2
-PhIP formation occurs in vivo.
393
The
S-C-linked GSHreactionproductswithNO
2
-MeIQx and NO
2
-
PhIP can form nonenzymatically (Figure 7C).
The effects of GSH and of purified human and rat GSTs on the
covalent DNA binding of the reactive N-acetoxy derivatives of PhIP,
IQ, and MeIQx were studied in vitro. GSH alone slightly inhibited
(10%) the binding of N-acetoxy-PhIP to DNA, but the bindin g was
strongly inhibited in the presence of both GSH and GSTs. Among
human GSTs, the isozyme A1-1 was most effective (90% in-
hibition), followed by A1-2 (40% inhibition) and P1-1 (30%
inhibition); other GSTs studied appeared to have little to no activity
toward N-acetoxy-PhIP.
430,431
Analysis of the incubation mixture
containing N-acetoxy-PhIP, GSH, and GST A1-1 revealed the
presence of oxidized GSH (GSSG) and reduced PhIP
(Figure 7D), but no GSH adducts were detected, suggesting that
a redox mechanism is involved in the deactivation of N-acetoxy-
PhIP. A short-lived GSH sulfenamide conjugate of PhIP may have
formed and undergone an ensuing reaction with GSH to produce
PhIP and GSSG.
430
GST P1-1 showed even higher substrate
specificity for the inhibition of DNA binding of ATP-dependent
metabolite(s) of HONH-PhIP than for N-acetoxy-PhIP.
432
The
binding of N-acetoxy-IQ or N-acetoxy-MeIQx to DNA was un-
affected by human or rat GSTs; however, GSH alone significantly
inhibited (40%) their binding to DNA.
430
The GST-dependent detoxication pathway may be an impor-
tant determinant for the organ specificity of PhIP-carcinogenesis
in rodents and possibly humans.
430,431
Human liver cytosol,
which contains high levels of GST A1-1, catalyzes the GST-
mediated detoxication of N-acetoxy-PhIP,
430
whereas the cytosol
of colon, which contains about 100-fold lower levels of the GST
A1-1 subunit than the liver,
433
does not display GST-mediated
inhibition of N-acetoxy-PhIP binding to DNA.
430
The high levels
of hepatic GST A1-1 activity may help to explain the lower levels
of PhIP-DNA adduct formation in the liver in comparison to that
in the pancreas or colorectal tissue of rats.
340,404
In humans, a
polymorphism in the 5
0
-regulatory region of the GSTA1 gene
results in the diminished expression of the GSTA1 and GSTA2
subunits.
434
In two case control studies, individuals who possess
the homozygous single nucleotide polymorphisms hGSTA1*B
(*B/*B) genotype and who would be predicted to have the
lowest levels of GSTA1 expression in liver were at a greater risk
for developing colorectal cancer, especially among consumers of
well-done cooked meat, than subjects with the homozygous
hGSTA1*A (*A/*A) genotype and express high levels of
GSTA1.
431,435
Individuals who are homozygous GSTA1*B could
be at risk of developing colorectal cancer, possibly as a result of
inefficient hepatic detoxication of N-oxidized derivatives of
PhIP.
431
However, a third case control study failed to detect an
elevated risk for colorectal cancer in subjects harboring the (*B/
*B) genotype.
436
Urinary mercapturic acid conjugates of PhIP, if
formed, could serve as biomarkers to assess the efficacy of
detoxication of PhIP by GSTs. Thus far, mercapturic acid
conjugates of PhIP or other HAAs have not been identified in
the urine of experimental laboratory animals or humans.
’ BIOMONITORING AROMATIC AMINES, HAAs, AND
THEIR METABOLITES IN HUMAN URINE
There are only a few reports on the direct chemical analyses of
carcinogenic arylamine metabolites in human urine.
406,437-440
On the
basis of metabolism studies in experimental laboratory animals,
44,441
in vitro with human liver slices,
318
andinvivoinhumans,
406,437-440
arylamine metabolites can be grouped according to (a) a substitution
on the amino group by acylation (acetylation or formylation) or by
conjugation with sul fate or glucuronic acid, (b) N-oxidation, (c) ring
oxidation, followed by sulfation or glucuronidation, and (d) in some
instances mercapturic acid formation. The analysis of carcinogenic
aromatic amines in human urine has been done primarily by gas
chromatography with electron capture detection or negative ion
chemical ionization mass spectrometry (GC-NICI-MS), following
chemical derivatization.
442-444
The procedures employed for the
isolation of aromatic amines from urine generally include acid or base
hydrolysis, followed by organic solvent extraction a nd/or solid p hase
extraction. Thus, the amount of a romatic amine measured represents
the unmetabolized compound plus the phase II conjugates. In one
study, smokers were reported to have 1.5- to 2-fold higher levels of
2-NA, 4-ABP and o-toluidine in their urine than nonsmokers: up to
204 ng o-toluidine, 21 ng of 2-NA, and 15 ng of 4-ABP present in
urine of smokers collected over 24 h.
445
There is one report on the detection of of N-acetyl-4-ABP and
the N-glucuronide of 4-ABP in urine of smokers by liquid chroma-
tography-electrospray ionization/tandem mass spectrometry (LC-
ESI/MS/MS) methods.
440
In that study, the geometric mean (95%
CI) of the total 4-ABP concentration was 1.64 pg/mg creatinine
(1.30-2.07) in nonsmokers (N = 41) and significantly greater, at
8.69 pg/mg creatinine (7.43-10.16) in smokers (N =89) (p <
0.001). Other studies reported no major differences in the excreted
levels of 2-ABP and 4-ABP in urine between smokers, passive
smokers, and nonsmokers
444
or in the levels of aniline and o-toluidine
in smokers as opposed to nonsmokers urine.
442
Significantly higher
concentrations of aniline, o-toluidine, m-toluidine, 2-NA, and
4-methyl-1,3-phenylenediamine were detected in the urine of factory
workers who smoked than in the urine of nonsmoking factory
workers, and there was a significant increase in the renal excretion
of unaltered 4-chloroa niline a nd m-toluidine in slow N-ace tylators as
opposed to rapid N-acetylators among the smoking workers, indicat-
ing NAT enzymes are involved in the detoxication of these
chemicals.
446
Aniline, p-toluidine, 2-NA, and 4-chloro-o-toluidine
were also detected in the urine of nonsmoking subjects who were
not occupationally exposed to aromatic amines.
446
Another study
reported up to 50-fold higher levels or o-toluidine in occupationally
exposed individuals than in nonoccupationally exposed subjects.
111
Certain aromatic amines have been observed to undergo decomposi-
tion in urine within a few hours and may explain why some arylamines
have been difficult to detect in urine.
444
In contrast to some aryl-
amines,MeIQx,PhIP, andARC are stable in the urine matrix.
447
Various analytical approaches have been devised to isolate HAAs
from human urine: such techniques have included solvent extrac-
tion,
24,301
solid-phase enrichment (SPE),
447
treatment of urinary
HAAs with blue cotton and ion exchange chromatography,
448
the
use of molecularly imprinted polymers,
292
and immunoaffinity
methods,
286
followed by quantification by GC-NICI-MS
24,301,449
1182 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
or LC-ESI/MS/MS,
292,447
or alternatively, followed by HPLC with
UV or fluorescence detection.
291,448
[
14
C]-MeIQx, [
14
C]-PhIP, and
their [
14
C]-radiolabeled metabolites have also been measured in
human urine by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS).
176,264,287
Urinary metabolites have also been detected by LC-ESI/MS/
MS
98,101,103,293
or indirectly, after chemical reduction or acid
hydrolysis of HONH-PhIP conjugates, with detection by LC-ESI/
MS/MS or GC-NICI-MS.
289,450
Most of the studies that have examined HAA biomarkers were
conducted with subjects on a controlled diet, eating well-done
cooked meat.
252,285,291,451-454
However, there are reports on the
identification of HAAs, including MeIQx, PhIP, APNH, ARC, in
the urine of subjects on a free-choice diet.
448,453,455-457
In the
case of ARC, urinary levels of this carcinogen were associated
with tobacco usage and not meat consumption.
456
Many of the
early biomonitoring studies focused on MeIQx and PhIP because
they are the two most mass-abundant HAAs formed in cooked
meat.
10
The metabolism pathways of pyrolytic HAAs in humans
are unknown.
458
The plasma half-life of MeIQx was estimated at
3.4 h, and the plasma half-life of PhIP was estimated at 4.6 h in
humans.
301
These short half-lives are consistent with the rapid
elimination of MeIQx and PhIP in urine after the consumption of
285,286,291,301,452,454,459
cooked meat. The metabolism of both
HAAs is extensive. The amounts of nonmetabolized MeIQx
range from about 1-6% of the dose, whereas the amount of
unaltered PhIP in 0-24 h postmeal urine ranges from about 0.5
to 2% of the dose.
93,285,291,452,454,459
In one study in Japan,
MeIQx, PhIP, and the tryptophan pyrolysate mutagens Trp-P-
1 and Trp-P-2 were detected in the urine of healthy volunteers on
a normal diet, but they were not found in the urine of hospitalized
patients receiving parenteral alimentation.
448
This finding shows
that the exposure to HAAs occurs from food and that these
compounds are not formed endogenously. However, APNH,
the reaction product formed from norharman and aniline in the
presence of P450 3A4 or 1A2,
460
was detected in 24-h urine
samples at levels ranging from 21 to 594 pg in subjects on a
nonrestricted diet; similar levels were measured in urine from
inpatients receiving parenteral alimentation.
457
These results
suggest that APNH is a novel endogenous mutagen/carcinogen;
the biological significance of this rodent carcinogen for human
cancer development requires further study.
Widely ranging concentrations of HAAs have been detected in
the urine of individuals on unrestricted diets evaluated world-
wide; such differences are probably attributable to the variabi lity
in the concentrations of HAAs in the diet.
448,453,455,456
Some
biomonitoring studies have examined the amount of MeIQx and
PhIP recovered in urine following acid hydrolysis. The hydrolysis
of urine provides an estimate of the contribution of phase II
conjugation to the metabolism of these AIAs.
103,285,455,461
Acid
treatment (1 N HCl, 80 °C for 8 h) increased the levels of MeIQx
in urine by as much as 18-fold,
103,285,453,454
while the amounts of
PhIP generally increased by only several fold or less.
103,285
The
increase in MeIQx content is attributed to the acid-labile MeIQx-
N
2
-SO
3
H and MeIQx-N
2
-Gl conjugates present in urine,
285
whereas the acid-labile N
2
- and N3-glucucuronide conjugates
of PhIP make up only a very minor percentage of the urinary
metabolites of PhIP and explain the modest increase in the
amounts of PhIP in urine, following acid treatment.
98,103,176
Interindividual differences in the urinary excretion of MeIQx
and PhIP have been reported in subjects on controlled diets.
452
Metabolic phenotypes may be expected to influence the leve ls of
HAAs excreted in urine. For example, higher P450 1A2 activity
was associated with significantly lower levels of unmetabolized
MeIQx in the urine of omnivores (P = 0.008), when adjusted for
the amount of meat eaten.
459
However, the levels of PhIP in urine
were not associated with P450 1A2 activity,
286
a finding that is
surprising since the contribution of P450 1A2 to the clearance of
PhIP was estimated to account for 70% of the elimination of PhIP
in a pharmacokinetic study.
301
The contribution of P450 1A2 to
the metabolism of PhIP may have been obscured since GSTs
reduce N-oxidized metabolites of PhIP back to the parent
amine.
430,434
N-Oxidation is an important biotransformati on pathway of
MeIQx and PhIP in humans. The levels of the urinary N
2
-
glucuronide conjugate of HONH-MeIQx were reported to range
from 2-17% of the ingested dose of MeIQx ,
288
but the major
urinary metabolite of MeIQx, the carboxylic acid, IQ-8-COOH,
which is also produced by P450 1A2,
261,262
ranged from 32 to
65% of the ingested dose.
103
The N
2
- and N3-glucuronide
metabolites of HONH-PhIP account for up to ∼24-54% of
the ingested dose of PhIP in urine within 24 h.
176,287,289
The large
variation in the urinary levels of IQx-8-COO H and HONH-MeIQ x
and HONH-PhIP N-glucuronide conjugates is likely due to the
wide range of P450 1A2 content expressed in the liver,
222,242
combined with varying levels of UGT activity, and o ther competing
pathways of metabolism.
264,287-289,402
The urinary level of the N
2
-glucuronide conjugate of HONH-
MeIQx did not correlate to P450 1A2 activity (N = 66 subjects),
whereas the level o f the N
2
-glucuronide conjugate of HONH-PhIP
did correlate to P450 1A2 acitivity, when caffeine was employed as
the metabolic probe for P450 1A2 phenotyping.
288,289
The pathway
of IQx-8-COOH formation,
261,262,264
which was discovered after
these metabolism studies were completed,
288,289
is a competing
reaction pathway of MeIQx-N-oxidation and may have obscured the
relationship between HON-MeIQx-N
2
-Gl and P450 1A2 activity.
The interindividual variability in enzymatic reduction of the
N-hydroxy-HAAs
430,462,463
is likely to contribute to the variability
of urinary excretion of N-glucuronide conjugates of HONH-MeIQx
and HOHN-PhIP and weaken the association between these HAA
urinary biomarkers and P450 1A2 activity. There was no evidence
for an inverse association between NAT2 phenotype activity and the
amounts of HON-MeIQx-N
2
-Gl or HON-PhIP-N
2
-Gl excreted
in urine,
288,289
a findin g that is consistent with the poor rates of
N-acetylation of MeIQx and Ph IP by NAT2.
335,339
In a pilot study,
individuals with a rapid P450 1A2 phenotype and who excreted high
levels of HONH-PhIP-N
2
-Gl urine had the lowest level of colon
PhIP-DNA adducts.
176
These data indicate that N-glucuronida-
tion plays an important role in the detoxication of HONH-
PhIP.
176,400,402,464
Definitive conclusions from a small data set
(N = 10 subjects) are tenuous, and further investigations using a
much larger study g roup should be pursued to confirm the protective
role of UGT enzymes and the usefulness of the HONH-PhIP- N
2
-Gl
urinary biomarker in HAA carcinogenesis studies.
The concurrent analysis of MeIQx and PhIP is impor tant since
the urinary excretion levels of either HAA by itself can serve only
as an approximate measure for the other, in assessing exposures
in humans consuming unrestricted diets.
455
The interrelation-
ship between the oxidative metabolism of MeIQx and that of
PhIP in urine samples from 10 volunteers on a controlled diet
was examined by calculation of the urinary metabolic ratio (MR)
(% dose of urinary metabolite/% dose of unmetabolized urinary
HAA) values for sever al of their P450 1A2-catalyzed oxidation
products.
103
The employme nt of MR values to assess enzyme
metabolizing activity must be done with caution because MR
1183 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
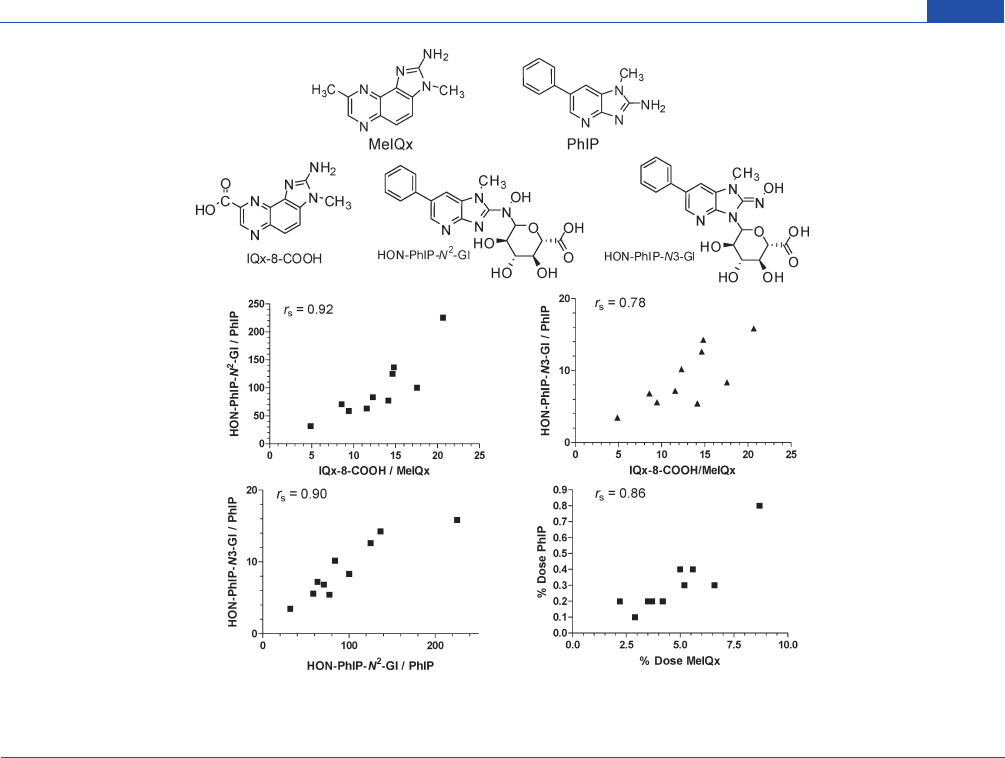
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 8. Scatter plots relating the percentage of the unmetabolized dose of MeIQx and PhIP, and relating the MR of P450 1A2-oxidized MeIQx and
PhIP metabolites (% of dose of metabolite/% of dose of unmetabolized MeIQx or PhIP) eliminated in urine collected for 10 h after meat
consumption.
103
values can be influenced by changes in urine flow rate.
465
The
extent of MeIQx and PhIP metabolism and the MR for IQx-8-
COOH and HON-PhIP-N
2
-Gl and HON-PhIP-N 3-Gl, the
major P450 1A2 oxidative urinary metabolites of MeIQx and
PhIP, were significantly correlated for a given subject (Figure 8).
The MR values were independent of urine flow rate and support
the notion that P450 1A2 is an important enzyme in the
metabolism of both procarcinoge ns in vivo.
103
A study on a
larger number of subjects will be required to firmly establish the
MR values and the inter-relationship between P450 1A2-mediated
metabolism of MeIQx and that of PhIP.
’ AROMATIC AMINE AND HAA DNA ADDUCTS
Some of the early structural characterization of arylhydroxyl-
amine DNA adducts were reported by Kriek
466
and by King and
Phillips,
467
who proposed that covalent linkage should occur
between the C8 atom of dG and the arylamine nitrogen of
N-hydroxyaminofluorene. The structural assignments were later
confirmed through the use of nuclear magnetic resonance spectro-
scopic techniques.
468
The characterization of m any other arylamine
DNA adducts followed these studies: both acetylated and nonace-
tylated adducts were identified in vitro and in vivo.
37,76,469,470
Synthesis and Characterization of DNA Adducts. The
structures of a number of the arylamine DNA adducts were
originally obtained by reacting the synthetic arylhydroxylamine
derivatives with DNA, followed by enzymatic digestion and spectro-
scopic characterizations.
37,76,469,470
The reactivity of many arylhy-
droxylamines toward DNA is enhanced under slightly acidic pH as
opposed to neutral pH; this increase in reactivity has been ascribed
to the formation of the aryl nitrenium ion.
76,405
In contrast to
arylhydroxylamines, the chemical reactivity of a number of
N-hydroxy-HAAs with DNA is only modestly enhanced under acidic
pH conditions, and alternative reaction conditions were employed
to produce the presumed nitrenium ion.
339,408,471
Many arylhydrox-
ylamines and N-hydroxy-HAAs primarily bind to dG at the C8 atom
of guanine. However, this site is only weakly nucleophilic, and the
dG-C8 adducts (and presumably dA-C8 adducts) have been
proposed to be rearrangement products that are preceded by
electrophilic substitution at the nucleophilic N7atomofdG. This
scheme has been postulated to be a general reaction for activated
aromatic amines and HAAs.
472,473
Minor reaction products of
arylhydroxylamines and N-hydroxy-HAAs are also formed at the
N
2
atom of dG and the C8 and N
6
atoms of dA.
37,474-476
The
structures of prominent arylamine and HAA adducts are shown in
Figure 9.
DNA adducts of HAAs have been synthesized by biomimetic
reactions of the N-hydroxy-HAA intermediates with deoxynu-
cleosides or DNA, in the presence of ketene gas, or acetic anhydride,
so as to produce the reactive N-acetoxy intermediate and facilitate
the formation of the nitrenium ion.
63,339-341,408,471,474,475,477,478
N-Acetoxy-IQ and N-acetoxy-MeIQx
339,408
have lifetimes of seconds
or less, but N-acetoxy-PhIP has been isolated and characterized by
mass spectrometry.
341
The imidazo moiety of AIAs may facilitate
the formation of the oxime tautomer and influence the chemical
reactivity of N-hydroxy-AIAs with DNA. The oxime structure favors
O-acetylation of the N-hydroxy-AIAs by acetic anhydride to produce
1184 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
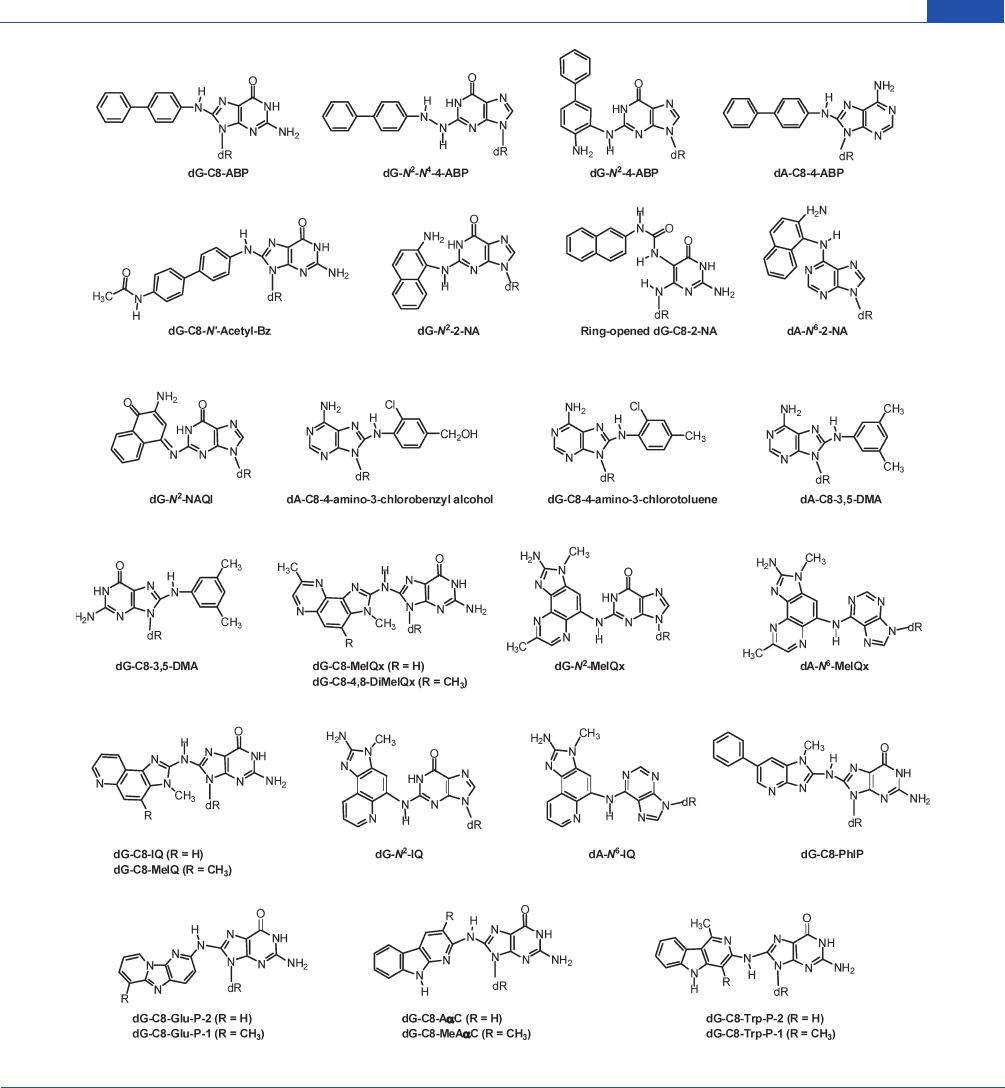
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 9. Structures of DNA adducts of aromatic amines and HAAs.
the N-acetoxy intermediates, instead of N-acetylation to form the
hydroxamic acids. The dG-C8 adducts of IQ,
408,474,479
MeIQ,
170
MeIQx,
474
2-amino-3,4,8-trimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline (4,8-
PhIP,
340,341,480
DiMeIQx),
477
ARC and 2-amino-3-methyl-9H-
pyrido[2,3-b]indole (MeARC),
478,481
and the glutamic acid and
tryptophan pyrolysate mutagens
471,482
are formed by biomimetic
reactions; these DNA adducts also occur in tissues of experimental
laboratory animals (see above citations and refs 63 and 100, and
references therein) (Figure 9).
Isomeric dG-N
2
-adducts of IQ and MeIQx are also formed in
vitro and in vivo; adduct formation occurs at the C-5 atoms of the
heteronuclei of these HAAs.
474,483-485
Recently, a hydrazine-linked
N7-dG adduct with IQ and a dA adduct of IQ formed in vitro by the
reaction of dG or dA with N-acetoxy-IQ were reported,
475
and a dA
adduct of MeIQx was also detected in the liver of rats.
476
Bond
formation within these dA adduct s is believed to occur between the
N
6
atom of adenine and the C-5 atom of the IQ or MeIQx
heteronucleus to form 5-(deoxyadenosin-N
6
-yl)-IQ (dA-N
6
-IQ)
or 5-(deoxyadenosin-N
6
-yl)-MeIQx (dA-N
6
-MeIQx). The forma-
tion of dG-N
2
and dA-N
6
adducts of IQ and MeIQx indicate that
both nitrenium and carbenium ion resonance forms exist for these
activated HAAs.
474,475
The overall yield of DNA adduct formation with deoxynucleo-
sides or DNA with arylhdroxylamines or N-hydroxy-HAAs are
generally several percent or lower. More recently, nonbiomimetic
approaches have been developed to synthesize aromatic amine- and
1185 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
HAA-DNA adducts in high yields, using the Buchwald-Hartwig
reaction of the cross-coupling of primary and secondary amines with
aryl halides. High-yield synthesis of dG and dA adducts of
arylamines,
486
dG-C8 and dG-N
2
adducts of IQ, and the dG-C8
adduct of PhIP (dG-C8-PhIP)
487-490
have been achieved wi th this
chemistry. The phosphoramidites of these adducts have been site-
specifically incorporated into oligonucleotides to explore the effect
of adducts in perturbations of DNA structure and the fidelity of
polymerases during translesional synthesis.
42,491-500
The resul ts
demonstrated that each arylamine-DNA or HAA-DNA adduct
structure and the location of the adduct within the sequence context
of the oligonucleotide affected the solution structure of the DNA
and the fidelity and the catalytic efficiency of the polymerases in a
unique manner.
Aromatic Amine and HAA DNA Adduct Formation in Vitro
and in Experimental Animal Models.
The early investigations
on the measurements of arylamine-DNA adducts in experimental
animals employed tritium-labeled carcinogens. Adduct identifi-
cation was achieved by HPLC with radiometric detection and by
cochromatography with unlabeled DNA adducts, which served
as UV standards.
37,76,469
More recent methods to detect and
quantitate arylamine- and HAA-DNA adducts include
32
P-
postlabeling;
501,502
immunohistochemistry (IHC);
503,504
GC-
NICI-MS of alkaline-treated DNA, a technique that cleaves the
bond between the guanyl C8 atom and the amino group of aromatic
amines or HAAs;
169,505
accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) for
the detection of tritiated or
14
C-labeled adducts;
89,166,506
and LC-
ESI-MS/MS methods.
100,480,507-513
Five DNA adducts of 4-ABP are formed, when HONH-ABP is
reacted with calf thymus DNA at pH 5.0
76
(Figure 9).
N-(Deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-4-ABP (dG-C8-4-ABP) is the principal
adduct and acco unts for 80% of the total adducts formed,
followed by dA-C8-ABP (15% of total adducts), and then
N-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-4-ABP (dG-N
2
-N
4
-4-ABP) (∼5% of
the total adducts). Two other minor dG adducts have been
identified: 3-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-4ABP (dG-N
2
-4-ABP) and
N-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-4-azobiphenyl.
514,515
In urothelial cells
of male Beagle dogs,
37
dG-C8-4-ABP accounted for 76% of the
total binding, followed by dG-N
2
-N
4
-4-ABP (15%), and then
followed by dA-C8-4-ABP (9%), 2 days after the oral administration
of [
3
H]-4-ABP.
37
DNA adducts of 4-ABP were quantified, by
32
P-
postlabeling and immunohistochemistry (IHC), in the liver and
bladder of male and female BALB/c mice, following treatment with
4-ABP at a range of concentrations (from 0, 7 up to 220 ppm) in
drinking water for 28 days.
516
The principal adduct in both tissues,
for both sexes, was dG-C8-4-ABP. The level of adduct formation
increased as a func tion of dose and correlated with the incid ence of
liver tumors in female mice. However, the relationship between
adducts and tumorigenesis was distinctly nonlinear in the bladders
of male mice, and tumor incidence rose rapidly at doses above the 50
ppm dose 4-ABP. Toxicity and cell proliferation may have increased
the tumor incidence in the bladder.
The reaction of N-hydroxy-2-aminonaphthalene (HONH-2-
NA) with DNA in vitro, at pH 5.0, results in the formation of
three DNA adducts (Figure 9).
76
The major adduct is an imidazole
ring-opened derivative of N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-NA (dG-C8-
NA, 50% of the total adducts), followed by lower levels of
1-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-2-NA (dG-N
2
-NA, 30% of total adducts)
and 1-(deoxyadenosin-N
6
-yl)-2-NA (dA-N
6
-NA, 15% of total
adducts). These same three DNA adducts were formed in target
(urothelium) and nontarget (liver) tissues of dogs 2 days after oral
administration of [
3
H]-2-NA.
37
A 4-fold higher binding level of
2-NA was found in the urothelial DNA than formed in liver DNA.
The major adduct in both tissues was the ring-opened dG-C8-NA,
followed by lower levels of dA-N
6
-NA and dG-N
2
-NA. The dG-N
2
adduct persisted in the liver, and this adduct and the ring-opened
dG-C8-NA adduct persisted in the bladder. The differential loss of
adducts indicates that active repair processes are present in both
tissues. The relative persistence o f the ring-opened dG-C8-NA
adduct in the target but not in the nontarget tissue suggests that this
adduct is a critical lesion for the initiation of urinary bladder cancer.
Peroxidative enzymes, such as PHS, catalyze both the
N-oxidation and ring-oxidation of 2-NA; 2-amino-1- naphthol is a
major ring-oxidation product.
319
PHS catalyzed the binding of 2-NA
to DNA and produced the same three adducts arising from
N-hydroxy-2-NA (vide supra). Three other adducts were also formed
from 2-imino-1-naphth oquinone, the oxidative product of 2-amino-
1-naphthol. The major adduct is N
4
-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-2-
amino-1,4-naphthoquinoneimine (dG-N
2
-NAQI) (Figure 9).
37,319
This adduct and two other minor adducts accounted for approxi-
mately 60% of the total DNA binding that was obtained by
incubation of 2-NA with PHS in vitro. The DNA adducts derived
from 2-imino-1-naphthoquinone were reported to account for
approximately 20% of the 2-NA bound to urothelial DNA in dogs,
but these peroxidative DNA adducts were not detected in liver
DNA.
319
The remaining adduction products in urothelium were
derived from HONH-2-NA. PHS expressed in the bladder could play
asignificant role in the bioactivation of2-NAdirectlyin the bladder
and could contribute to carcinogenesis of 2-NA and other ary lamines
that serve as substrates of PHS.
The reaction of calf thymus DNA with HONH-N
0
-acetylBz at
pH 5 gives rise to N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-N
0
-acetylbenzidine
(Figure 9).
517,518
The structural isomer, N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-
N-acetylbenzidi ne, and the nonacetylated derivative, N-(deoxy-
guanosin-8-yl)-benzidine, have not been identified in rat or mouse
liver DNA.
518
However, benzidine diimine, a reactive intermediate
formed during the enzymatic peroxi dation of Bz, can undergo
deprotonation of the cationic diimine to form its nitrenium ion,
whichreactswith dGtoform N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-benzidine.
This adduct was detected in vivo in the dog urothelium.
519
The reaction of HONH-MOCA in vitro, at pH 5 or 7, with
DNA produces N-(deoxyadenosin-8-yl)-4-amino-3-chloroben-
zyl alcohol and N-(deoxyadenosin-8-yl)-4-amino-3-chlorotoluene
as the m ajor adducts (Figure 9); these lesions are also formed in rat
liver
520
and in dog urinary bladder epithelium,
521
following treat-
ment with MOCA. The preferred reactivity of MOCA with dA is
atypical of most AAs and HAAs, which primarily react with
dG.
37,63,52 2
The chemistry of MOCA-DNA adduct formation is
also unusual: the adducts contain only a single ring derived
from MOCA. The incipient DNA adduct formed appears to
undergo fission at the methylene bridge of MOCA to form
N -(deoxyadenosin-8-yl)-4-amino-3-chlorobenzyl alcohol or
N-(deoxyadenosin-8-yl)-4-amino-3-chlorotoluene
520
(Figure 9).
dG-C8 adducts of monocyclic alkylanilines as well as 2- and
4-chloroaniline are also formed by reaction of the corresponding
N-(acyloxy)arylamines with dG and DNA.
523,524
A study with
3,5-DMA revealed that this arylamine forms a C8 adduct with dG
but also forms adducts at the N
6
and C8 ato ms of dA, and a
unique adduct with dC.
525,526
The formation of these DNA
adducts are consistent with the involvement of nitrenium ion
chemistry. It is noteworthy that several monocyclic arylamines
have been reported to form sulfinamide adducts with Hb in
rodents, but dG-C8 or other DNA adducts attributed to the
nitrenium ion were not detected in liver or extrahepatic
1186 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
tissues.
524,526
Therefore, biologically available N-hydroxy-AAs that
form Hb adducts do not necessarily produce DNA adducts.
524
The
quinone imine or quinone methide electrophiles may contribute to
the DNA damage and adduct formation of monocyclic
alkylanilines.
123
The doses of HAAs employed in many experimental labora-
tory animal studies exceeded daily human exposures by more
than a million-fold; many of these studies are reviewe d in refs 63
and 100. In early studies, several variants of the
32
P-postlabeling
method,
501,527
followed by DNA adduct separation by 2-dimen-
sional thin layer chromatography or HPLC,
63,479,528,529
were
used to discern HAA-DNA adducts. A myriad lesions were
detected in a number of these DNA binding studies; many of
the adduction products were subsequently shown to be incom-
pletely digested oligomers of the dG-C8-HAA adducts.
167,479,530
For many HAAs, DNA adduct formation is greatest in the liver of
rodents, a result perhaps attributable to the high levels of P450
1A2 expression.
63
However, DNA adducts are formed in all
tissues investigated, even in tissues that do not develop cancer,
indicating that other factors, such as tumor promotion, are
involved in tumorigenesis.
9,159
DNA adduct formation of MeIQx
166
and IQ
167
was found to
occur in a near linear dose-response relationship in the liver of
rodents over a wide range of doses. DNA adducts were formed at
dose levels approaching human exposures for both of these AIAs,
as well as for PhIP.
531
In contrast to many other HAAs, PhIP
shows levels of adduct formation in rodents that are lower in the
liver than in extrahepatic tissues; adduct levels are particul arly
elevated in the colon and pancreas,
340,404
in the prostate of male
rats,
155
and in mammary glands of female rats.
532
Both GSTs and
UGTs, which are expressed at high levels in the liver, catalyze the
metabolites,
397,402,430,464
detoxication of reactive PhIP thus
accounting for the relatively lower level of PhIP-DNA adduct
formation in the liver.
The isomeric dG-N
2
adducts of IQ and MeIQx are minor
adducts formed in vitro with the N-acetoxy-IQ and N-a cetoxy-
MeIQx (<10% of total adducts),
474
but their contribution to
the total amount of DNA adducts formed in rodents is
greater.
479,483,485,533
The dG-N
2
-IQ adduct became the promi-
nent lesion in slowly dividing tissues of nonhuman primates that
underwent chronic treatment with IQ,
483
suggesting preferential
repair of the dG-C8-IQ adduct. The contribution of dG-N
2
-
MeIQx to the total adducts in rats was significantly more
important than that observed in vitro when calf thymus DNA
was reacted with N-acetoxy-MeIQx.
485
dG-N
2
-MeIQx was the
major adduct detected in the liver of rats 24 h after gavage with a
0.5 mg/kg dose. Thus, isomeric dG-N
2
-AIA adducts are promi-
nent lesions formed in slowly dividing tissues of rodents and
nonhuman primates, particularly during chronic exposure.
DNA Adduct Formation of Aromatic Amines and HAAs in
Human Tissues.
The analyses of DNA adducts from human
tissues have often been conducted on biopsy samples of patients
that were obtained during clinical diagnosis of cancer.
27,534
The
DNA adducts formed are likely attributed to recent exposures;
however, the most relevant time to measure DNA adduct
formation is when tumor initiation is in progress and not many
years later when the cancer has been diagnosed.
27,32
Hence, the
assumption made is that current adduct levels are reflective of the
levels that existed during the time of cancer initiation. This
assumption may be valid for inviduals subjected to long-term
habitual exposure to genotoxic agen ts, such as those exposures that
occur through smoking or by frequently consuming well-done
cooked meats; however, only few studies have investigated the
variations in DNA adduct levels in individuals over time.
27,535
dG-C8-4-ABP was first dete cted by
32
P-postlabeling in human
urinary bladder tissue biopsy samples and exfoliated uorothelial
cells.
28,536
Subsequently, the adduct was detected by GC-NICI-
MS methods in lung and urinary bladder mucosa; dG-C8-4-ABP
was found at levels ranging from <0.32 to 49.5 adducts per 10
8
nucleotides in the lung and from <0.32 to 3.94 adducts per 10
8
nucleotides in bladder samples.
505
dG-C8-4-ABP has also been
detected, by IHC,
32
P-postlabeling, or GC-NICI-MS methods in
bladder and lung tissues from smokers and ex-smokers,
502
and by
IHC in the liver of Taiwanese subjects with hepatocelluar
carcinoma.
537
In pancreas tissue, a major adduct was observed
that was chromatographically identical to dG-C8-4-ABP in 8 of
29 organ donors, at levels ranging from 0.2 to 1.1 adducts per 10
8
nucleotides. Pancreas tissue displays low enzyme activities for
P450-mediated N-oxidation and prostaglandin hydroperoxida-
tion of 4-A BP, but high levels of 4-nitrobiphenyl reductase and
NAT1-mediated O-acetyltransferase activity are present.
538
The
dG-C8-4-ABP adduct levels in the pancreas did not correlate
with the number of cigarettes smoked per day or the length of
smoking history; other sources of environmental exposure to
4-ABP or the exposure to 4-nitrobiphenyl or other nitroarenes,
produced during combustion,
122
may contribute to arylamine-
DNA adduct formation in the pancreas.
The DNA present from the induced sputum of smokers,
representing DNA of the lower respiratory tract, was shown to
possess significantly higher levels of 4-ABP-DNA adducts than were
found in the sputum of nonsmokers, when assessed by IHC.
539
4-ABP-DNA adducts were also detected in female breast tissue
biopsy samples, when visualized by IHC;
504
the levels of 4-ABP-
DNA in tumor-adjacent normal tissues, but not in tumorigenic
tissue, were correlated to the frequency of women’ssmoking.
4-ABP-DNA adducts were also detected in laryngeal biopsies by
IHC,
540
and adduct levels were significantly higher in smokers than
were the levels measured in tissue from nonsmokers.
The putative dG-C8 adduct of 4-ABP, measured as 4-ABP
after acid treatment of DNA, was detected in biopsy samples
from 37 out of 75 bladder cancer patients, corresponding to 86 ( 22
adducts per 10
8
nucleotides (mean ( SE). The amount of 4-ABP-
DNA adducts in the bladder of current smokers was elevated in
subjects with more aggressive grade levels of bladder tumors.
541
In
another study, the putative dG-C8 adducts of 4-ABP and o-toluidine
were measured as the parent amines, after acid treatment of DNA
from epithelial and submucosal bladder tissue of bladder cancer
patients: 4 and 11 of 12 tumor samples contained adducts of 4-ABP
(1.9 ( 4.1 a dducts per 10
8
nucleotides) and o-toluidine (2.9 ( 1.5
adducts per 10
6
), respectively.
542
The levels of the putative dG-C8
adduct o-toluidin e, but not 4-ABP, were significantly higher in the
epithelium of smokers than in nonsmokers. The detection of high
levels o-toluidine-releasing DNA adducts is suggestive of a causal
role of o-toluidine in human bladder cancer.
LC-ESI-MS/MS methods have been employed to directly
quantitate dG-C8-4-ABP in human tissues. dG-C8-4-ABP was
detected in urinary bladder epithelium in 12 out of 27 subjects in
DNA extracted from tumor tissue or nontumor surrounding
tissue.
543
The levels of adducts ranged from 5 to 80 adducts per
10
9
bases, but a correlation was not observed between tobacco
smoking and adduct levels.
543
In another pilot study, dG-4-C8-ABP
was identified,byLC-ESI-MS/MS, in 6of12human pancreas
samples.
512
The levels ranged anywhere from 1 to 60 adduct per 10
8
nucleotides; again, there was no correlation observed between the
1187 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
level of adducts and smoking preference, age, or gender. The
prediction of the relationship between 4-ABP exposure from
tobacco smoke and adduct levels is not straightforward, being
confounded by environmental exposure to 4-nitrobiphenyl and a
variable persistence of dG-C8-4-ABP in the tissues. Because the
activation or detoxification processes of 4-ABP metabolism, as well
as DNA repair mechanisms, can be tissue-specific, a correlation
between tobacco usage and DNA adducts in different tissues may
not exist.
Another environmental source of exposure to 4-ABP is hair
dyes.
120,121
The relationship between 4-ABP-DNA adduct levels
and hair-dye usage has only been examined in one study, which
determined the levels of the putative 4-ABP-DNA adduct, by
32
P-
postlabeling, in exfoliated breast epithelial cells in milk from lactating
mothers.
544
The adduct levels were associated with the use of hair
coloring products (odds ratio 11.2), but not with tobacco usage, in a
statistically significant manner. Some commercial permanent hair
dyes are known to contain 4-ABP.
120,121
The presumed N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-N
0
-acetylbenzidine
adduct was identified by
32
P-postlabeling of DNA from exfoliated
urothelial cells of workers in factories manufacturing Bz in India.
332
This findin g supports the hypothesis that N-acetylation and the
ensuing formation of HONH-N
0
-acetyl-Bz is an important bioacti-
vation pathway for at least one Bz-related adduct in humans;
318
this
bioactivation pathway is analogous to the pathway proposed for Bz
activation in rodents.
518
Moreover, the same Bz adduct was
identified in white blood cells of exposed workers, and there was
asignificant correlation between WBC and exfoliated urothelial cell
Bz adduct levels.
545
This was the first study in humans to show a
relationship for a specific carcinogen adduct in a surrogate tissue and
in urothelial cells, the target for urinary bladder cancer of Bz.
The major DNA adduct isolated from exfoliated urothelial
cells collected from urine of a subject after an accidental acute
exposure to MOCA was detected as N-(deoxadenosin-8-yl)-4-
amino-3-chlorobenzyl alcohol by the
32
P-postlabeling method.
546
The adduct was found i n cell samples obtained betwe en 4 and 98 h
after initial exposure but not in samples collected at later times. The
level of DNA adducts 4 h after exposure was determined to be 516
adducts/10
8
nucleotides.
The putative dG-C8-MeIQx adduct was detected in the colon
and kidney of some individuals at levels of several adducts per 10
9
DNA bases, when assayed by
32
P-postlabeling.
547
A GC/MS
assay, following the hydrolysis of putative dG-C8-HAA adducts,
was employed to measure the levels of HAA adducts in DNA of
the colorectal mucosa
169
and lymphocytes from colorectal cancer
subjects;
175
the levels of the putative dG-C8-PhIP adduct were
found to be in the range of several adducts per 10
8
DNA bases. In
the latter study, the adduct was found in lymphocytes of about
30% of the subjects, and the adduct levels varied by a factor of 10-
fold between the lowest and the highest level. The level of
lymphocyte PhIP DNA adducts was no t significantly higher in
smokers or high meat consumers than that of individuals who ate
meat less frequently.
175
A subset of younger individuals carrying
two mutated GSTA1 alleles had higher adduct levels than
homozygous wild-type and heterozygous subjects. This finding
is consistent with the reported activity of the GSTA1 protein in
the detoxication of N-oxidized metabolites of PhIP.
430,548
In
another study, a PhIP-related DNA adduct (the presumed dG-
C8-PhIP adduct) was detected by the
32
P-postlabeling method in
106 of the 150 colorectal tissues analyzed: similar levels of
adducts were detected in tissues from controls, polyp patients,
or cancer patients.
549
Adducts attributed to dG-C8-PhIP were frequently detected,
by the
32
P-postlabeling method, in exfoliated breast epithelial
cells in milk of lactating mothers.
30
Thirty samples from the 64
subjects contain ed the presumed PhIP-DNA adduct, and the
mean level of adduct formation was 4.7 adducts/10
7
nucleotides.
In an ensuing study, PhIP-DNA adducts were detected, by IHC,
in mammary tissue of 82% of the women with breast cancer (N =
106) and also found in 71% of the tissue samples of the healthy
control patients (N = 49).
173
An interactive effect was observed
among well-done meat consumption and NAT2 genotype and the
level of PhIP-DNA adducts. This observed interactive effect is
surprising since HONH-PhIP does not appear to be bioactivated by
human NAT2 at appreciable levels.
342,343
Averyhighpercentageof
pancreas and prostate tissue biospecimens were also positive for
PhIP-DNA adducts, when assayed by IHC.
174,177
The mean l evel of
the PhIP-DNA adducts was g2.7 adducts/10
7
nucleotides, by IH C,
in both patients and the healthy control populations.
173,174,177
The
levels of PhIP-DNA adducts reported in breast, pancreas, and
prostate tissues of humans are comparable to the adduct levels
observed in these corresponding tissues of rodents treated with
either a single acute dose or chronic carcinogenic doses of PhIP
(10-50 mg/kg bw).
155,404,550
These findings imply that PhIP-DNA
adduct formation occurs with far greater efficiency in humans
exposed to ppb levels of dietary PhIP than the adducts which occur
in the rodents given high, carcinogenic doses of PhIP.
PhIP-DNA adducts were also measured, by AMS, in the breast
tissue of female cancer patients who had received a dose of
[
14
C]PhIP (20 μg PhIP/70 kg body weight) via oral adminis-
tration prior to surgery.
172
The estimates of PhIP-DNA adducts
obtained by AMS ranged from 26 to 480 adducts/10
12
nucleotides
172
or nearly 1,000- to 10,000-fold lower than the levels
of adducts reported by the IHC or
32
P-postlabeling techniques cited
above. The large discrepancy in e stimates of PhIP adducts in breast
tissue obtained by IHC
173
and
32
P-postlabeling,
30
as opposed to the
precise AMS method,
172
suggests that these biochemical assays are
detecting a variety of lesions in addition to or other than dG-C8-
PhIP. Moreover, the dG-C8-PhIP adduct is underestimated when
determined by
32
P-postlabeling in comparison to LC/MS
methods;
551,552
dG-C8-PhIP adduct measurements should be con-
ducted by quantitative LC/MS techniques.
DNA Adducts of Aromatic Amines and HAAs in the Oral
Cavity.
The oral cavity is the portal of entry for carcinogens that
are ingested in the diet or inhaled through smoking. The bioactiva-
tion of aromatic amines and HAAs can occur di rectly by P450s 1A1,
1A2, or 1B1 that are expressed in buccal cells of the oral cavity
553,554
or by P450 1A2 expressed in salivary glands.
555
The N-hydroxy
metabolites also can form by the action of P450 1A2 in the
liver
233,339
and reach the oral cavity through systemic circulation,
404
followed by phase II activation in cells of the oral cavity. Peroxidases
in saliva
556
may also catalyze the bioactivation of HAAs and
arylamines.
308,312,314,316,322,519
The potential of the oral microflora
to contribute to metabolism and DNA adduct formation of HAAs or
arylamines has not been investigated.
Both
32
P-postlabeling
557-560
and IHC techniques
561-563
were
employed to screen for DNA adducts in cells of the oral cavity.
Several of the studies reported differences in total DNA adduct
levels between smokers and nonsmokers; however, the complexity
of the adduct profiles and the inability to identify specificDNA
adducts precluded any interpretation on the principal DNA dama-
ging agents and their significance in the risk of development of oral
cancer or cancers of other organs.
557-563
Some of the lesions
detected were be lieved to be derived from polycyclic aromat ic
1188 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 10. LC/ESI/MS/MS
3
traces of dG-C8-4-ABP and dG-C8-PhIP adducts in saliva DNA, acquired with a linear quadrupole ion trap MS
178
for a
nonsmoker and a current smoker. The MS
3
product ion spectra of the aglycones of [BH
2
]
þ
and the [
13
C
10
]-dG-labeled internal standards, added to
DNA at a level of 1 adduct per 10
7
DNA bases, are presented in the lower panel. Adapted from ref 178. Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society.
hydrocarbons or aromatic amines.
557,561-563
As an extension of
those studi es, a selective LC/MS method was recently employed to
detect DNA adducts in saliva derived from carcinogens formed in
tobacco smoke and cooked meats. The dG-C8 adducts of 4-ABP,
PhIP, ARC, and MeIQx were identified in saliva samples from
volunteers on unrestricted diets, by LC-ESI/MS/MS
n
,atthe MS
3
scan stage mode with a linear quadrupole ion trap MS.
178
DNA
adducts of PhIP were found most frequently: dG-C8-PhIP was
identified in saliva samples from 13 of 29 ever-smokers and in saliva
samples from 2 of 8 never-smokers. dG-C8-ARCand dG-C8-
MeIQx were identified solely in saliva samples of 3 current smokers,
and dG-C8-4-ABP was detected in saliva from 2 current-smokers.
The levels of these different adducts ranged from 1 to 9 adducts
per 10
8
nucleotides. Moreover, the employment of the linear
quadrupole ion trap MS permitted the acquisition of product ion
spectra of the aglycone adducts [BH
2
]
þ
,atthe MS
3
scan stage, for
unambiguous identification of the carcinogen-DNA adducts
(Figure 10).
476,552,564
Some HAAs induce oral cancer in rodents
during long-term fee ding studies.
9
Moreover, an appreciable level of
metabolic activation of Trp-P-2 was observed in rat tongue,
565
and
elevated levels of salivary DNA adducts were reported in rats fed
with MeARC, resulting in severe atrophy of the salivary glands.
566
Thus, saliva may be a promising noninvasive fluid to m onitor
exposure and DNA damage of some HAAs and aromatic amines.
Exfoliated epithelial buccal cells and leukocytes are the princi-
pal mammalian cells present in saliva.
567,568
The time frame from
new cell production to exfoliation of the buccal cell from the
mucosal surface is estimated to be between 5 and 12 days,
569
and
the leukocytes, which originate mainly from the gingival crevice
and then migrate into the oral cavity, are predominantly short-
lived neutrophils and other granulocytes.
568,570
Given the short
life spans of both buccal and leukocyte cell types, the DNA
adducts present in saliva are likely to occur from recent exposures
to carcinogens. It is not known whether adducts are formed in
both cell-types and whether they preferentially form in one type.
Studies that examine kinetics of PhIP-DNA adduct formation in
cells of the oral cavity of humans exposed to defined amounts of
PhIP combined with studies that can unravel the myriad plausible
enzymes that contribute to PhIP adduct formation in oral cells
are required. Moreover, the level of adduct formation in the oral
1189 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
cavity must be shown to correlate to target tissues of cancer for
the validation of this biomarker.
’ AROMATIC AMINE AND HAA PROTEIN ADDUCTS
Carcinogen blood protein adducts have been used as an
alternative to DNA adducts for human biomarkers of several
different classes of carcinogens, including aromatic amines, poly-
cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and aflatoxin B
1
(AFB
1
).
31,49,571-574
The research on protein adducts originates from the pioneering
studies of the Millers and is based upon the paradigm of chemical
carcinogenesis in which electrophilic species or electrophilic meta-
bolites of carcinogenic compounds react with nucleophilic centers
on proteins as well as DNA.
35,36,575,576
The use of Hb as a dosimeter
for alkylation agents was introduced by Ehrenberg and his
collaborators.
577,578
The biomonitoring of carcinogen adducts with
serum albumin (SA) also has been examined for several different
classes of carcinogens.
31,49
The biomonitoring blood protein carci-
nogen adducts is advantageous because up to several hundre d
milligrams of Hb or SA, as opposed to ∼100 μgDNA,can be
obtained from a 10 mL blood sample. Moreover, stable carcinogen
protein adducts are expected to accumulate and follow the kinetics
of the lifetime of Hb or half-life of SA, during chronic exposure. In
humans, the lifetime of Hb is 120 days, and the half-life of SA is
between 20 and 25 days.
31
Thus, the steady state levels of Hb and SA
carcinogen adducts would be, respectively, about 60- and 29-fold
dose.
578,579
higher after chronic exposure than after a single
Carcinogen protein add ucts of aromat ic amines and HAAs are
formed through their N-oxidized metabolites and represent a
measure of the biologically effective dose.
31,38
However, there are
caveats in the application of blood protein adducts for human risk
assessment. The adduction of carcinogens to blood proteins does
not represent genetic damage, and adduct formation with Hb occurs
in the erythrocyte, which may not reflect the genetic damage that
occurs in the target organ. In the case of SA adducts, the adduct can
form in the hepatocyte, the cell where SA is biosynthesized
580
and
where metabolic activation of arylamines and HAAs occurs.
60
Hemoglobin Adducts. A number of aromatic amines form
adducts with Hb, via a sulfinamide linkage (Figure 2), in
experimental laboratory animals.
38,80,524
The existence of aryl-
amine Hb sulfinamide adducts for many arylamines demon-
strates that N-oxidation is a common metabolic pathway for this
class of genotoxicants. The percent of the arylamine dose bound to
Hb as a sulfinamide linkage ranges over 100-fold in rodents,
depending upon the structure of the chemical.
38,48,524
The highest
levels of arylamine-Hb adducts were reported for 4-ABP, where over
5% of the dose is bound to Hb in the form of the sulfinamide
adduct.
80
In a hallmark study, Hb sulfinamide adducts of 15
aromatic amines were determined in nonsmokers and smokers,
and significant differences between smokers and nonsmokers were
observed for Hb adducts of 4-ABP, 3-aminobiphenyl, 2-NA, o-and
p-tolui dine, 2,4-dimethylaniline, and 2-ethylaniline; some of these
arylamines are human bladder carcinogens.
581
In a study among
factory workers exposed to Bz and Bz-based dyes, the Hb-adduct
levels of N-acetyl-Bz, Bz, and 4-ABP correlated strongly with each
other.
111
The levels of N-acetyl-Bz adducts were 20-fold higher than
the levels of Bz-sulfinamide adducts, and the results are consistent
with P450 activation of N-acetyl-Bz to form HONH-N
0
-acetyl-Bz as
a major reactive metabolite in vivo.
318,582
The validation of a protein carcinogen adduct as a biomarker
requires that the biomarker correl ates to exposure, DNA damage,
and cancer risk. The Hb-sulfinamide adduct of 4-ABP fulfills
these requirements. The levels of 4-ABP-Hb sulfinamide adduct
formation were shown to correlate with the number of cigarettes
per day.
581,583,584
smoked Subjects with rapid N-acetylator
phenotypes have decreased levels of the 4-ABP-Hb adduct in
comparison to that in slow N-acetylator phenotypes.
583,584
Thus,
N-acetylation, a detoxication pathway and a competing metabolic
fate to N-hydroxylation, results in a decreased level of the
biologically effective dose of 4-ABP in rapid N-acetylator phe-
notypes. The levels of 4-ABP-Hb adducts were also shown to
correlate with the amount of dG-C8-4-ABP adduct present in
exfoliated urothelial cells.
536
Elevated levels of 4-ABP-Hb and
other arylamine-Hb sulfinamide adduct levels are associated
with increased bladder cancer risk, both in smokers as well as
nonsmokers.
50,77,78,584,585
HAAs also react with Hb and SA. However, the levels of IQ,
MeIQx, and PhIP bound to Hb are low in experimental
laboratory animals (∼0.01% of the dose), and the levels of
HAA-SA adducts are only several fold higher.
49,88,90,263,586-588
The low level of HAA-Hb sulfinamide formation does not seem to
be attributed to the poor reactivity of the N-hydroxy-HAA meta-
bolites with Hb. In the case of IQ, a metabolic study conducted in
vitro showed that the N-hydroxy-IQ metabolite penetrates the
human erythrocyte and induces methemoglobinemia and that a
portion of the IQ bound to Hb (∼10%) wasreleasedbyacidand
recovered as IQ.
586
Thus, N-hydroxy-IQ does appear to form a
sulfinamide adduct with Hb. The N-hydroxy and nitroso derivatives
of Glu-P-1 were also shown to modify the thiol groups of Hb.
589
The low levels of HAA-Hb sulfinamide formation with HAAs in
rodents suggest that there is little free N-hydroxy-HAA present in
the blood that is available to react with Hb. The inefficient binding of
HAAs to Hb will probably preclude the development of HAA-Hb
adductsasbiomarkers inhumans.
88,90
Serum Albumin Adducts. Aromatic amines also react with
SA. Human SA is 585 amino acids in length and is the most
abundant protein in plasma (∼45 mg/mL). Its roles include
maintenance of osmotic pressure and transport of endogenous
(i.e., fatty acids, bilirubin, and steroids) and exogenous (drugs)
chemicals.
590
The single tryptophan residue at position 214 of rat SA
is a selective si te of binding for several activated arylamines.
391
This
amino acid reacts with the N-sulfonyloxy ester of N-acetyl-4-
aminobiphenyl to form an adduct with a stable 4-ABP-trypto-
phan-linkage (Figure 11).
390
The same adduction product was
shown to form by a reaction of the synthetic sulfate ester of
N-hydroxy-N-acetyl-4-aminobiphenyl and the sulfate esters of
N-hydroxy-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene and HONH-N,N
0
-diacetyl-
benzidine with human SA in vitro (Kadlubar, F. F., personal
communication).
391
SULT enzymes play a critical role in the
formation of these adducts in hepatocytes.
391
To our knowledge,
an analytical method has not been established to biomonitor this
arylamine-tryptophan SA adduct in humans.
Some of the addu ct(s) of IQ, MeIQx and PhIP formed with SA
in rodents or produced in vitro with rat or human SA are acid-
labile.
88,586,587,591,592
An adduct formed between IQ and rat SA
adduct was characterized by MS,
1
H NMR, and amino acid
analysis and shown to contain a sulfinamide linkage formed through
the SA-Cys
34
: this adduct accounted for about 10% of the total SA
adducts formed in rats (Figure 11).
586
Cys
34
is one of 35 conserved
cysteine residues in SA across species.
590
Thirty-four of these
cysteines are involved in 17 disulfide bonds. Thesingleunpaired
Cys
34
is present either as a free thiol or in an oxidized form: this
residue is present partially as disulfide linkages with low molecular-
weight thiols.
593
SA-Cys
34
is thought to be responsible for many of
1190 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 11. Mechanism of formation of protein adducts of 4-ABP and IQ with rat SA. The of N-sulfonyloxy ester of N-hydroxy-4-acetylaminobiphenyl
reacts with the sole tryptophan residue of rat SA.
390
In the case of IQ, the HONH-IQ metabolite undergoes further oxidation, by either transition metals
or P450 1A2, to form the nitroso metabolite.
602
Nitroso-IQ reacts with the SA-Cys
34
residue to form the semimercaptal, which undergoes rearrangement
to the sulfinamide structure. A tetrapeptide containing N-acetyl-4-ABP adducted to Ala-Trp-Ala-Val and a tripeptide containing the IQ adduct at
Cys-Pro-Tyr are recovered upon digestion of SA with Pronase. In analogy to arylamine-Hb sulfinamide adduct chemistry (see Figure 2), acid treatment
of the IQ-SA sulfinamide adduct results in hydrolysis and the generation of IQ and the SA-Cys
34
sulfinic acid.
587
the antioxidant properties of SA and accounts for ∼80% of the net
free thiols in plasma.
594,595
The scavenging properties of this Cys
34
residue to reactive carcinogenic and to xic electrophiles are well
documented.
596
Adducts at Cys
34
have been identified with reactive
metabolites of various toxicants in rodent or human SA, including
MeIQx,
587
PhIP,
592,597
acrylamide,
598
sulfur mustard,
599
benzene,
600
and acetaminophen,
601
in addition to IQ.
586
Acid-labile adducts of
MeIQx and PhIP have been reported to form with SA; these adducts
may be sulfinami de linkages at the Cys
34
residue.
587,591
A plausible
scheme for HAA-SA sulfinamide adduct formation, based upon
studies with IQ,
586
is depicted in Figure 11. The N-hydroxy-HAA
metabolites can undergo further oxidation by P450 1A2 or by
transition metals to form the nitroso-HAA intermediates,
602
which
can react with the SA-Cys
34
to form HAA- SA-Cys
34
sulfinamide
adducts. There is one report in the literature on the measurement of
putative acid-labile MeIQx-SA-Cys
34
sulfinami de adducts in a pilot
human study. The le vel of t his adduct, if present, was reported to be
below the LOD of the GC/MS assay (29 attomol MeIQx/mg
SA).
587
It is unlikely that the sulfinamide adduct of MeIQx with
human SA can be used as a dosimeter for human AIA exposure.
The binding of
14
C-PhIP to SA was shown to be much greater
than the binding of
14
C-MeIQx to SA in humans, by AMS
measurements.
92,588
Moreover, PhIP-SA adduct formation was up
to 40-fold greater in humans than in rats, given comparable doses of
the chemic al.
92
The levels of PhIP adducts formed with human SA
90
may be sufficient to establish MS methods of biomonitoring toward
this adduct(s). An acid-labile PhIP-SA adducts(s) was (were)
detected in human subjects on a noncontrolled diet; levels were
10-fold higher in meat-eaters than in vegetarians (6.7 ( 1.6 vs 0.7 (
0.3fmolPhIP/mg protein; mean ( SE).
591
The structure(s) of the
adduct attributed to the acid-labile lesion has not been determined. It
seems likely that some portion of the acid-labile PhIP adduction
products were formed at the Cys
34
residue in human SA.
592,597
The
chemical stability of the adduct(s) is(are) unknown. Thesamestudy
revealed the presence of acid-labile PhIP-Hb adducts in human
subjects; the adduct levels were about 2-fold lower than the levels of
the acid-labile PhIP-SA adducts.
591
These findings suggest that
HONH-PhIP forms sulfinamide adducts with SA and Hb in humans.
The results contradict the data reported on PhIP blood protein
adduct formation in humans by AMS measurements, where the levels
of PhIP-Hb adducts were about 40- to 50-fold lower than that of
PhIP-SA adducts.
90
However, the PhIP blood protein adduct data
was obtained following a single dose, in the AMS study, whereas the
adduct levels in the population-based study represent an integral value
of chronic exposure over the lifespan of the blood proteins.
591
Further
investigati ons on the imp lementatio n of PhIP bloo d protein a dducts
in humanpopulationstudies arewarranted.
’ BIOMONITORING OF HAAs IN HAIR
Human hair and animal fur have served as matrices for
biomonitoring of chemicals such as nicotine, other drugs and
narcotics, and hormones.
23,25,603
Studies with experimental
laboratory animals have shown that
3
H-labeled PhIP accumulates
in melanin-rich tissues, including including fur.
24
The radio-
activity cleared from the body within several days but stayed in
the hair and was present in the cortex of the distal hair shafts 4
weeks after exposure. Follo wing digestion of the hair matrix,
chemical analyses showed that the radioactivity represented
unmetabolized PhIP.
24
However, the exposures in the animal
studies occurred at levels exceeding the levels of PhIP or other
HAAs in the human diet by at least 4 orders of magnitude.
Nevertheless, Alexander and co-workers established a method to
quantitate PhIP in mouse fur and then applied the technique to
measure PhIP in human hair by GC/NCI/MS.
24,604
Thereafter,
Kobayashi and collaborators established a method to quantitate
PhIP in human hair by LC-ESI/MS, employing the selected ion
monitoring mode.
605,606
Both methods require up to several
hundred milligrams of hair and entail lengthy extraction proce-
dures for chemical analysis. The prerinsing of the hair shaft prior
to digestion of the hair matrix is required in order to remove
HAAs that may have been deposited on the external surface of
the cuticle by exposures from the fumes of cooking oils or
airborne particulates generated by the frying or grilling of
meats.
13,14
The prerinsing procedure is essential to distinguish
dietary intake of PhIP from airborne exposure.
1191 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 12. Bioaccumulation of PhIP in the hair of omnivores and vegetarians. The melanin in the hair follicle has high affinity for PhIP, and sequesters
the carcinogen from the bloodstream, following first-pass metabolism.
24
The LC-ESI/MS/MS trace shows the presence of PhIP in the hair of an
omnivore but not in the hair sample of a vegetarian. The identity of PhIP was confirmed by its product ion spectrum.
607
A more recent study reported a simplified method for the
extraction and analysis of HAAs in hair, by employing base hydrolysis
to digest hair, followed by tandem solvent/solid phase extraction for a
cleanup method.
607
The quantification of PhIP was performed by
LC-ESI/MS/MS in the selected reaction monitoring mode: the
LOQ value was 50 pg of PhIP/g of hair when 50 mg of hair was
assayed.
607
The analytical method was employed to measure HAA
adducts in a pilot study of 12 human volunteers. PhIP was detected in
the hair of all six omnivores (nonhair dye users) at levels ranging from
290 to 890 pg/g hair, whereas PhIP was detected in the hair from one
outofsix vegetarians, andataleveljustabove theLOQ (65pg/g
hair).
607
These findings demonstrate that PhIP exposure occurs
primarily through meat consumption (Figure 12). MeIQx and ARC
were below the LOQ (50 pg/g hair) in hair samples from all of the
omnivoresaswellasthe sixvegetarians.
The levels of PhIP measured in the hair of subjects in the
United States (290 to 890 pg/g)
607
are within the same range of
the levels of PhIP detected in the hair of subjects in Norway
(60-7500 pg/g hair)
608
and in subjects in Japan (180-
3600 pg/g hair) on unrestricted diets.
606
The levels of PhIP in hair
samples from two omnivores in the United States were found to vary
by less than 24% over a 6 month interval.
607
A study on 20 Japanese
volunteers reported a reasonably good correlation after adjust-
ment for hair melanin content between intakes of PhIP, MeIQx, and
Trp-P-1 estimated with a Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) and
the mean PhIP cont ent of hair sampl es collected 1-3months
apart .
609
These findings signify that the exposure to PhIP and its
accumulation in hair are relatively constant over time.
The hair biomarker represents an integrated exposure to PhIP
over a time period of weeks to months and may be a superior
method to assess exp osure to PhIP than the FFQs, whi ch are
often used in molecular epidemiology studies.
19
PhIP levels in
hair appear to be a good biomarker of long-term exposure to
HAAs; however, this hair biomarker is not a predictor of DNA
1192 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
damage.
607
Moreover, levels of PhIP accumulated in the hair of
individuals are highly variable. This large variation in the levels of
PhIP in hair reflect in part the different concentrations of PhIP in
the diet.
10
The pharmacokinetics and metabolism of PhIP are
also likely to influence the levels of PhIP that accumulate in hair.
Because of the large interindividual differences in the hepatic
P450 1A2 protein content,
222,242
the amount of unmetabolized
PhIP in the bloodstream that reaches the hair follicle, following
first-pass metabolism, is expected to widely range and may affect
the levels of PhIP accrued in hair. The pigmentation of hair also
may affect the amount of PhIP incorporated into hair.
Eumelanin,
610
a pigment that is more predominant in black hair
than in lighter-colored hair,
611
has a high affinity for PhIP. Thus,
dark-haired individuals may sequester larger amounts of PhIP
than light-haired individuals, on the basis of findings from a study
that reported mice with dark pigmente d fur accrued more PhIP
in their fur than mice with light pigmented fur.
610
Approximately
25% of the male population and 42% of the female population
have been reported to use hair dyes in the United States, Europe,
and Japan
612
with permanent hair dye being the most commonly
used hair dye product. The oxidizing conditions used to develop
the desired hair dye colors are likely to produce oxidation
products of PhIP
120,612,613
during the dye development process
and would escape detection by current analytical methods. A
robust analytical method to measure PhIP in users of hair dyes
still requires development and validation.
’ EPIDEMIOLOGY OF COOKED MEATS: POTENTIAL
ROLE OF HAAs IN HUMAN CANCER
Many epidemiological investigations have examined the inter-
relationships among the consumption of cooked red meat, its
effect on human cancer risk of the digestive tract, prostate gland,
the mammary gland, and the potential causal role of HAAs in the
etiology of these cancers.
19,70,124
The 2007 WCRF/AICR report
on nutrition and cancer concluded that red meat and processed
meat are “convincing causes” of colorectal cancer and that there
is “limited evidence” that they also cause esophagus, stomach,
pancreas, lung, endometrial, and prostate cancers.
614
Although
several classes of car cinogens are present in red meat and
processed meat and multiple mechanisms of carcinogenesis are
likely to be at play,
615-617
the exposure and causal role of HAAs
in cancer development through eating meat cooked well-done
has been an area of great research interest. The majority of
epidemiologic studies that inves tigated dietary consumption of
well-done meat in relation to various tumor sites reported a
positive association between cancer risk and well-done meat
consumption (see reviews in refs 124 and 618 and references
therein). However, some studies have shown no associations
between well-done meat and cancer risk.
124,618
Fewer studies
have attempted to estimate the intake of specific HAAs. A
number of them have shown associations with cancer or color-
risk,
615,619-621 622
ectal adenoma whereas others have not
(reviewed in ref 618). Thus, overall, the dietary data have been
suggestive but inconsistent.
A similarly large number of studies have explored the associa-
tions of polymorphisms in genes or pathways involved in the
metabolism of HAAs (e.g., NAT2, P450 1A2, and P450 1B1) with
cancer risk, and their results have been qui te inconsistent.
324,623-625
However, whole-genome association studies have recently demon-
strated that common genetic variants only have small effects on
risk. In particular, it can be assumed that an effect of a genetic
polymorphism in a xenob iotic metaboli sm enzyme in volved in
carcinogen bioactivation (or detoxication) would be unlikely to
be manifested when there is a low, biologically insufficient level of
exposure to the carcinogen. Thus, it is probably important to
consider both the exposure and the genetic variants to be able to
detect an association with disease risk.
A smaller number of studies have examined the combined
effects of dose (e.g., well-done meat or HAA intake and smok ing)
and metabolic genotypes or phenotypes, and these studies were
mainly investigating colorectal cancer or adenoma. Interactions
were suggested between the intake of red meat, well-done meat,
626-630 631
or HAA and variants in NAT2;
NAT1, AHR,
632
CYP1B1,
632,633
and SULT1A1,
633
as well as in a combination of
metabolic genes (CYP1A2, CYP2E1, CYP1B1,and CYP2C9),
634
in
relation to colorectal cancer or adenoma risk. However, other
studies failed to replicate these associations.
627,635-637
Similar
interactions were found with NAT2 and meat intake for bladder
cancer.
638
Again, these data are suggestive, but they do not show a
high level of consistency across studies.
Because of its high interindividual variation, P450 1A2 activity
may be relevant for cancers associated with exposure to HAAs.
This enzyme, which is prominently expressed in the liver
224
and other
enzymes catalyzing the activation and/or detoxification of HAAs (and
aromatic amines) that are inducible by lifestyle factors or modulated
by genetic polymorphisms may account for interindividual differences
in susceptibility to these carcinogens.
256
Two case-control studies
support the concept that rapid P450 1A2 activity in combination with
rapid NAT2 activity is a risk factor for colorectal cancer in indivi-
duals eating well-done cooked meat, which is a rich source of
HAAs.
327,328,639
In one of the two studies, this association was limited
to smokers (Figure 13),
328
which makes biological sense since
smoking induces P450 1A2. These findings, if confirmed, would
support the hypothesis that individuals with high metabolic pheno-
types in P450 1A2 and NAT2 activities will have elevated levels of
some types of HAA-DNA adducts, which may lead to the develop-
ment of cancer. However, a third study failed to find any modifying
effect of NAT2 or P450 1A2 activity, also measured by urinary
caffeine metabolites, or an association of HAA with adenoma.
631
A critical limiting factor in most epidemiological studies is the
uncertainty in quantitative estimates of chronic exposure to HAAs
(or other carcinogens). For most molecular epidemiology studies,
the extent of HAA exposure is difficult to assess, and thus, the
association of HAAs formed in cooked meat and cancer risk has
been difficult to establish. The extent of exposure to HAAs from
meat in molecular epidemiology studies is often inferred by FFQ
often combined with pictures of meat cooked at different levels of
doneness.
19,134,190
Intake estimates for meats cooked at a specified
level of doneness and with various methods of high-temperature
cooking (pan-frying, broiling, and barbecuing/grilling) are based on
usual frequency and portion size. HAA intake estimates are then
derived using corresponding HAA meat content values.
615
There are
clear difficu lties in quantifying cooking doneness by such methods,
the day-to-day variation in diet can be large, and the conventional
FFQ
640
can be especially problematic when exposure to the com-
pound of interest spreads over a range of food items at varying levels
of concentrations. Moreover, the accuracy of the FFQ is particularly
challenging in the assessment of levels of HAA formation because
the levels of HAAs formed are highly dependent on the type of
meat cooked and, especially, the method, temperature , and durati on
of cooking. These variable parameters can lead to differences
of HAA concentrati ons by mor e than 100-fold.
10,125,126,134,189,641
Furthermore, a number of cooked meat samples assayed for HAAs
1193 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
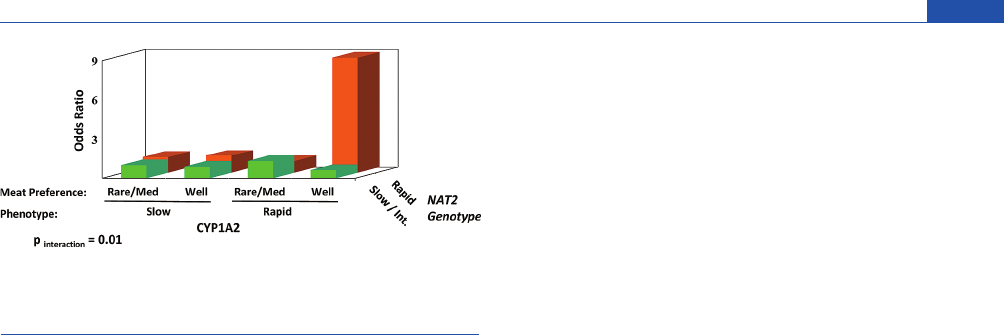
Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
Figure 13. Three-way interaction of red meat preference, NAT2 genotype,
and P450 1A2 phenotype on the risk of colorectal cancer among ever-
smokers (149 cases and 216 controls), p interaction = 0.01.
639
across all levels of doneness categories were reported to have no
detectable HAAs of any kind.
641
Clearly, the uncertainties in HAA
concentrations in daily staples can result in poor estimation of
chronic exposure to these compounds. The limitations of the
questionnaire-based exposure assessment methods are likely to be
a major reason for the inconsistency in the epidemiologic data. Thus,
the required data are not currently available to fully characterize the
relationship between HAAs and human cancer risk. Stable, long-lived
biomarkers of HAAs are required for any reliable assessment of HAA
exposure for use in population studies.
’ CONCLUSIONS
The demonstration of exposure and chemical-specific adducts
in target tissues, combined with the correlation of specific DNA
adducts with mutation spectra in tumor related genes, provides a
mechanistic understanding of the causal role for a chemical in the
development of cancer.
20,26,642
The laboratory research conducted
on AFB
1
, a fungal toxicant and a potent animal carcinogen that is
found as a contaminant in various crops,
15
is theprime exampleof
where biomarkers of carcinogen exposure have been employed to
identify and refine cancer risk estimates.
642,643
The positive associa-
tions observed betwe en dietary AFB
1
exposure and the incidence of
hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia and Africa were greatly strength-
ened by the application of validated biomarkers, which included
DNA and SA adducts, and a characteristic mutation spectrum in the
p53 tumor suppressor gene that is linked to a DNA adduct of
AFB
1
.
571,572,642,644,645
There is also promising biomarker data that
support a role of aristolo chic acid , a carci nogen present in the plan t
species of the genus Aristolochia, as a causal agent of urothelial cancer
in subjects of the Balkans
564,646
and Taiwan.
647
With regard to aromatic amines, the causal role of some these
compounds in human bladder cancer was revealed through epide-
miological studies conducted worldwide on factory workers occu-
pationally exposed to high levels of the procarcinogens.
1-3,105,106
Later, laboratory studies elucidated the biochemical mechanisms of
aromatic amine metabolism and adduction products with protein
and DNA,
45,76
which set the stage for the employment of arylamine-
Hb and DNA adducts a s biomarkers of exposure. The implementa-
tion of these biomarkers in human epidemiology studies has
strengthened the association of arylamines with cancer risk and
has also implicated aromatic amines in tobacco-associat ed bladder
28,31,50,52,536,581,583
cancer.
Such extensive biomarker data have yet to be established in
molecular epidemiology studies examining the potential cancer
causal role of HAAs or other genotoxicant s that are formed at the
ppb concentrations in cooked foods. The daily exposure to
numerous genotoxicants in cooked foods makes dietary hazard
assessment a challenging task , particularly when carcinogenesis
involves numerous steps,
71
and when dietary, environmental,
and genetic factors can impact the biological potency of the
procarcinogens.
9,22,157-159,413
Ultimately, the incorporation of
biomarkers in molecular epidemiology studies may help to
disentangle the uncertainty about the relative contributions of
various dietary genotoxicants to cancer risk.
24,185
Although a
causal link with cancer has not been established for HAAs, many
epidemiology studies have associated frequent consumption of
well-done cooked meat products to colorectal cancer, and less
124,618
consistently, prostate and breast cancer. Our current
knowledge about the biochemistry of HAAs indicates that the
underlying biochemi cal mechanisms of HAA metabolism, DNA
adduct formation, DNA repair, and mutations are compa rable to
those involved in aromatic amine carcinogenicity.
Even though aromatic amines and HAAs are structurally
related classes of chemicals and share some common pathways of
metabolism, the strategies employed for human bimonitoring of
these procarcinogens are different. The assessment of chronic
exposure to many arylamines has been successfully done through
the measurement of Hb sulfinamide adducts formed by a reaction of
the arylnitroso intermediates with the Hb-Cys
93β
residue. This
adductome approach has been employed to measure 15 aromatic
amine Hb sulfinamide adducts.
581
HAAs also undergo extensive
N-oxidation in humans, as demonstrated by the urinary metabolite
profiles of MeIQx and PhIP,
98,101,103,176,264,287-292
but the HAA-Hb
sulfinamide adducts appear to be formed at insufficient levels to
exploit this protei n adduct for human biomonitoring. An al ternative
potential adductome approach that can be applied to measure
reactive carcinogenic and toxic electro philes is through their add uc-
tion products formed at the Cys
34
residue of SA.
596
Human SA-
Cys
34
may bescreenedfor thesulfenamide or sulfinamide adducts of
PhIP
90,591,592
or adducts formed with N-oxidized intermediates of
other HAAs; however, the structures of these human SA-Cys
34
adducts have not yet been fully characterized by spectroscopic
techniques, and th e chemi cal stabi lity of th e adduct(s) is unknown.
Further studies on the characterization of PhIP-SA adducts are
required to validate this biomarker prior to its application in
population-based studies.
The N-glucuronide conjugates of many arylamines and aryl-
hydroxylamines undergo facile hydrolysis in the urinary bladder
and as a result are not readily measured,
76,318
whereas the
N-glucuronide conjugates of AIAs and HONH-AIAs are stable
in the mildly acidic pH conditions of urine.
103
Therefore, the
direct monitoring of urinary N-glucuronide metabolites of MeIQx
and PhIP and their N-hydroxylated metabolites may be used to
examine metabolic phenotypes for enzymes such as UGTs or
P450 1A2;
176,459
however, the short half-life of these metabolites
in urine reflects recent dietary intake only, making it unsuitable for
the assessment of chronic but intermittent exposures.
The biomonitoring of HAA levels in hair or macromolecular
HAA adducts has the potential to assess long-term exposure to these
carcinogens. On the basis of the current state of knowledge of HAA
exposure and the literature on HAA biomarkers, several biomarkers
of PhIP seem to be most promising for employment in molecular
epidemiology studies. A very high percentage of humans in different
parts of the world contain PhIP in their hair.
604,607,609
The
implementation of this hair biomarker in epidemio logy studi es
can confirm chronic exposure to PhIP, but it does not represent
DNA damage or necessarily represent cancer risk.
607
Putative PhIP-DNA adducts have been detected with very high
frequency in the human pancreas, prostate, and female mammary
1194 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
gland or in exfoliated epithelial cells from human milk samples
of women in the United States by IHC or
32
P-postlabeling
methods.
30,173,174,177
Surprisingly, the levels of PhIP-DNA adducts
formed in these tissues are comparable t o the adduct levels reported
in the corresponding tissues of rodents giv en a single acute dose or
chronic carcinogenic doses of PhIP, which exceeded human dietary
levels by a million-fold or more .
155,404,550
The frequent d etection of
PhIP-DNA adducts at such high levels in human tissues is alarming.
However, the proof of identity of PhIP-DNA adducts by IHC and
32
P-postlabeling detection methods is equivocal. If the high levels of
PhIP-DNA adducts in human tissues are confirmed by selective and
quantitative mass spectrometry methods, PhIP would be recognized
as a major dietary DNA-damaging agent.Furthermore,the inter-
pretation of the rodent bi ochemical and carcin ogenicity data
9,155,191
extrapolated across species to assess the human health risk of
PhIP and possibly other HAAs would require re-examina-
tion.
96,164,179,181-184
Currently available mass spectrometry instru-
ments have the requisite sensitivity to measure PhIP-DNA adducts
in human tissues and biologi cal fluids.
178,480
Thus, there is an urgent
need to corroborate the DNA adduct binding data obtained by
32
P-
postlabeling and IHC methods with quantitative mass spectrometry
techniques.
In conclusion, rapid through-put methods still need to be
developed for analyses of HAA biomarkers by mass spectrometry
methods in large scale human epidemiology studies. The em-
ployment of novel analytical approaches and mass spectrometry
techniques to measure HAA biomarkers in large prospective
studies with appropriate biospecimens presents the most poten-
tial to characterize better the health risks of dietary and tobacco-
associated HAAs in human cancers.
’ AUTHOR INFORMATION
Corresponding Author
*(R.J.T.) Tel: 518-474-4151. Fax: 518-473-2095. E-mail: Rturesky@
wadsworth.org. (L.L.M.) Tel: 808-586-2988. Fax: 808-586-2982.
Notes
We apologize for omissions made necessary by the space
requirements for this review. Many of the omitted studies are
of undoubted importance to the field of chemical carcinogenesis
and molecula r epidemiology.
Funding Sources
A portion of the data reported in this manuscript w as suppo rted by
grant R01 CA122320 (to R.J.T.), and by R01 CA60987 and
CA72520 (to L.L.M.) from the National Cancer Institute, by R21
ES014438 (to R.J.T.) from the National Institute of Environmental
Health Sciences, and by grant numbers 2007/58 (to R.J.T.) and
RFA09/149 (to L.L.M.) from the World Cancer Research Fund
International.
’ ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We are greatly appreciative of the critical comments of this
manuscript provided by the reviewers.
’ DEDICATION
This work is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Fred Kadlubar, a
mentor, collaborator, and dear friend, who greatly contributed to the
fields of chemical carcinogenesis and molecular epidemiology.
’ ABBREVIATIONS
AMS, accelerator mass spectrometry; AIAs, aminoimidazoarenes;
AAs, aromatic amines; FFQ, Food Frequency Questionnaire; GC-
NICI-MS, gas chromatography with negative ion chemical ioniza-
tion-mass spectrometry; GST, glutathione S-transferase; HAAs, het-
erocyclic aromatic amines; Hb, hemoglobin; IHC, immunohisto-
chemistry; LC-ESI/MS/MS, liquid chromatography-electrospray
ionization/tandem mass spectrometry; MOE, margin of exposure;
MR, metabolic ratio; NATs, N-acetyltransferases; OAT, O-acetyl-
transferase; PBPH/PD, physiologically based pharmacokinetic/
pharmacodynamic; PHS, prostaglandin H synthase; SA, serum albu-
min; SULTs, sulfotransferases; UGTs, uridine diphosphate-glucuro-
nosyltransferases; 4-ABP, 4-aminobiphenyl; HONH-4-ABP, N-
hydroxy-4-aminobiphenyl; IFP, 2-amino-1,6-dimethylfuro[3,2-e]-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine; AAF, N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene; AF, 2-ami-
nofluorene; HONH-AF, N-hydroxy-2-aminofluorene; Trp-P-1, 2-
amino-1,4-dimethyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole; Trp-P-2, 2-amino-1-
methyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole; Glu-P-2, 2-aminodiprido[1,2-
a:3
0
,2
0
-d]imidazole; Glu-P-1 , 2-amino-6-methyldiprido[1,2-
a:3
0
,2
0
-d]imidazole; APNH, 9-(4
0
-aminophenyl)-9H-pyri do[3,4-
b]indole; AMPNH, 9-(4
0
-amino-3-methylphenyl)-9H-pyrido[3,4-
b]indole; IQx, 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline; IgQx,
2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-g]quinoxaline; 7-MeIgQx, 2-amino-
3,7-dimethylimidazo[4,5-g]quinoxaline; 7,9-DiMeIgQx, 2-amino-
3,7,9-trimethylimidazo[4,5-g]quinoxaline; MeIQx, 2-amino-3,8-di-
methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline; HONH-MeIQx, N-hydroxy-2-
amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline; IQx-8-COOH, 2-
amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline-8-carboxylic acid; 8-CH
2
-
OH-IQx, 2-amino-8-(hydroxymethyl)-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quin-
oxaline; MeIQx-N
2
-Gl, N
2
-(ß-1-glucosiduronyl)-2-amino-3,8-dime-
thylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline; HON-MeIQx-N
2
-Gl, N
2
-(ß-1-gluco-
siduronyl)-2-(hydroxyamino)-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxa-
line; MeIQx-N
2
-SO
3
H, N
2
-(3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxa-
lin-2-yl-sulfamic acid; DMIP, 2-amino-1,7-dimethylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine; TMIP, 2-amino-1,5,6-trimethylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine;
4,8-DiMeIQx, 2-amino-3,4,8-trimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline;
7,8-DiMeIQx, 2-amino-3,7,8-trimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline;
MeIQ, 2-amino-3,4-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline; IQ, 2-amino-
3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline; HONH-IQ, N-hydroxy-2-amino-
3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline; PhIP, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenyl-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine; HONH-PhIP, N-hydroxy-2-amino-1-meth-
yl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine; PhIP, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phe-
nylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridin e; HONH-PhIP, HON-PhIP-N
2
-Gl, N
2
-
(ß-1-glucosiduronyl-2-(hydroxyamino)-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine; HON-PhIP-N3-Gl, N3-(ß-1-glucosiduronyl-2-(hy-
droxyamino)-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine; PhIP-N
2
-
Gl, N
2
-(ß-1-glucosiduronyl-2-amino-1-methyl-6- phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine; PhIP-N3-Gl, N3-(ß-1-glucosiduronyl-2-amino-1-methyl-
6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine; MeARC, 2-amino-3-methyl-9H-
pyrido[2,3-b]indole; ARC, 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b ]indole;
HONH-ARC, 2-hy droxyamino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole; Bz, benzi-
dine; N-acetyl-Bz, N-acetylbenzidine; HONH-N
0
-acetyl-Bz, N-4-hy-
droxyamino- N
0
-acetylbenzidine; 2-CA, 2-chloroaniline; 4-CA, 4-chlo-
roaniline; 3-EA, 3-ethylaniline; 2-NA, 2-naphthylamine; HONH-2-
NA, N-hydroxy-2-aminonaphthalene; 3,5-DMA, 3,5-dimethyaniline;
dG-C8-ABP, N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-ABP; dG-N
2
-N
4
-4-ABP,
N-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-ABP; dG-N
2
-ABP, 3-(deoxyguano-
sin-N
2
-yl)-4-ABP; dA-C8-4-ABP, N-(deoxyadenosin-8-yl)-4-
ABP; dG-C8-N
0
-acetyl-Bz,N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-N
0
-acetyl-
benzidine; dG-N
2
-2-NA, 1-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-2-NA; dG-
C8-2-NA , N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-NA; ring-opened-dG-C8-NA,
1195 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
ring-opened-N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-NA; dA-N
6
-2-NA, 1-(deoxy-
adenosin-N
6
-yl)-2-NA; dG-N
2
-NAQI, N
4
-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-
2-amino-1,4-naphthoquinoneimine; dG-C8-MeIQx, N-(deoxygua-
nosin-8-yl)-MeIQx; dG-C8-4,8-DiMeIQx, N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-
4,8-MeIQx; dG-N
2
-MeIQx, 5-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-MeIQx; dG-
C8-IQ, N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-IQ; dG-C8-MeIQ, N-(deoxygua-
nosin-8-yl)-MeIQ; dA-N
6
-IQ, 5-(deoxyadenosin-N
6
-yl)-IQ; dG-N
2
-
IQ, 5-(deoxyguanosin-N
2
-yl)-IQ; dG-C8-ARC, N-(deoxyguanosin-
8-yl)-ARC; dG-C8-MeARC, N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-MeARC; dG-
C8-PhIP, N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-PhIP.
’ REFERENCES
(1) International Agency for Resarch on Cancer (1987) Overall
Evaluation of Carcinogenicity: an Updating of IARC Monographs 1-42,
IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans 7
(Suppl), International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France.
(2) International Agency for Research on Cancer (2010) Some
Aromatic Amines, Organic Dyes, and Related Exposures, IARC Mono-
graphs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Vol. 99,
International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France.
(3) International Agency for Research on Cancer (1986) Tobacco
Smoking, IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to
Humans, Vol. 38, International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon,
France.
(4) Patrianakos, C., and Hoffmann, D. (1979) Chemical studies on
tobacco smoke LXIV. On the analysis of aromatic amines in cigarette
smoke. J. Assoc. Off Anal. Chem. 3, 150–154.
(5) Chiang, T. A., Pei-Fen, W., Ying, L. S., Wang, L. F., and Ko, Y. C.
(1999) Mutagenicity and aromatic amine content of fumes from heated
cooking oils produced in Taiwan. Food Chem. Toxicol. 37, 125–134.
(6) Matsumoto, T., Yoshida, D., and Tomita, H. (1981) Determina-
tion of mutagens, amino-alpha-carbolines in grilled foods and cigarette
smoke condensate. Cancer Lett. 12, 105–110.
(7) Manabe, S., Tohyama, K., Wada, O., and Aramaki, T. (1991)
Detection of a carcinogen, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyri-
dine, in cigarette smoke condensate. Carcinogenesis 12, 1945–1947.
(8) Sugimura, T., Nagao, N., Kawachi, T., Honda, M., Yahagi, T.,
Seino, Y., Stao, S., Matsukura, N., Matsushima, T., Shirai, A., Sawamura,
M., and Matsumoto, H. (1977) Mutagen-Carcinogens in Food, with
Special Reference to Highly Mutagenic Pyrolytic Products in Broiled
Foods, in Origins of Human Cancer, Book C (Hiatt, H. H., Watson, J. D.,
and Winstein, J. A., Eds.) pp 1561-1577, Cold Spring Harbor Labora-
tory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
(9) Sugimura, T., Wakabayashi, K., Nakagama, H., and Nagao, M.
(2004) Heterocyclic amines: Mutagens/carcinogens produced during
cooking of meat and fish. Cancer Sci. 95, 290–299.
(10) Felton, J. S., Jagerstad, M., Knize, M. G., Skog, K., and
Wakabayashi, K. (2000) Contents in Foods, Beverages and Tobacco,
in Food Borne Carcinogens Heterocyclic Amines (Nagao, M., and Sugimura, T.,
Eds.) pp 31-71, John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, England.
(11) Laser Reutersward, A., Skog, K., and Jagerstad, M. (1987)
Effects of creatine and creatinine content on the mutagenic activity of
meat extracts, bouillons and gravies from different sources. Food Chem.
Toxicol. 25, 747–754.
(12) Gross, G. A., Turesky, R. J., Fay, L. B., Stillwell, W. G., Skipper,
P. L., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (1993) Heterocyclic aromatic amine
formation in grilled bacon, beef and fish and in grill scrapings. Carcinogenesis
14, 2313–2318.
(13) Yang, C. C., Jenq, S. N., and Lee, H. (1998) Characterization of
the carcinogen 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f
]quinoxaline in cook-
ing aerosols under domestic conditions. Carcinogenesis 19, 359–363.
(14) Thiebaud, H. P., Knize, M. G., Kuzmicky, P. A., Hsieh, D. P.,
and Felton, J. S. (1995) Airborne mutagens produced by frying beef,
pork and a soy-based food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 33, 821–828.
(15) International Agency for Research on Cancer (1993) Some
Naturally Occurring Substances: Food Items and Constituents,
Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins, IARC Monographs on
the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans , Vol. 56, International
Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France.
(16) National Toxicology Program (2005) National Toxicology Pro-
gram. Report on Carcinogenesis, 11th ed., U.S. Department of Health and
Human Services, Public Health Service, Research Triangle Park, NC.
(17) Scribner, J. D., Fisk, S. R., and Scribner, N. K. (1979) Mechan-
isms of action of carcinogenic aromatic amines: an investigation using
mutagenesis in bacteria. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 26,11–25.
(18) Hatch, F. T., Knize, M. G., and Colvin, M. E. (2001) Extended
quantitative structure-activity relationships for 80 aromatic and hetero-
cyclic amines: structural, electronic, and hydropathic factors affecting
mutagenic potency. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 38, 268–291.
(19) Sinha, R. (2002) An epidemiologic approach to studying
heterocyclic amines. Mutat. Res. 506-507, 197–204.
(20) Jarabek, A. M., Pottenger, L. H., Andrews, L. S., Casciano, D.,
Embry, M. R.,Kim,J.H., Preston, R. J., Reddy,M.V., Schoeny,R., Shuker,
D., Skare, J., Swenberg, J., Williams, G. M., and Zeiger, E. (2009) Creating
context for the use of DNA adduct data in cancer risk assessment: I. Data
organization. Crit.Rev.Toxicol.39, 659–678.
(21) Hecht, S. S. (2002) Human urinary carcinogen metabolites:
biomarkers for investigating tobacco and cancer. Carcinogenesis
23, 907–922.
(22) Kadlubar, F. F., Butler, M. S., Kaderlik, K. R., Chou, H.-C., and
Lang, N. P. (1992) Polymorphisms for aromatic amines metabolism in
humans: relevance for human carcinogenesis. Environ. Health Perspect.
98,69–74.
(23) Nakahara, Y., Takahashi, K., and Kikura, R. (1995) Hair analysis
for drugs of abuse. X. Effect of physicochemical properties of drugs on
the incorporation rates into hair. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 18, 1223–1227.
(24) Alexander, J., Reistad, R., Hegstad, S., Frandsen, H., Ingebrigt-
sen, K., Paulsen, J. E., and Becher, G. (2002) Biomarkers of exposure to
heterocyclic amines: approaches to improve the exposure assessment.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 40, 1131–1137.
(25) Gratacos-Cubarsi, M., Castellari, M., Valero, A., and Garcia-
Regueiro, J. A. (2006) Hair analysis for veterinary drug monitoring in
livestock production. J. Chromatogr., B 834,14–25.
(26) Himmelstein, M. W., Boogaard, P. J., Cadet, J., Farmer, P. B.,
Kim, J. H., Martin, E. A., Persaud, R., and Shuker, D. E. (2009) Creating
context for the use of DNA adduct data in cancer risk assessment: II.
Overview of methods of identi
fication and quantitation of DNA damage.
Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 39, 679–694.
(27) Phillips, D. H. (2005) DNA adducts as markers of exposure and
risk. Mutat. Res. 577, 284–292.
(28) Talaska, G., al Juburi, A. Z., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1991) Smoking
related carcinogen-DNA adducts in biopsy samples of human urinary
bladder: identification of N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-4-aminobiphenyl as a
major adduct. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 , 5350–5354.
(29) Thompson, P. A., DeMarini, D. M., Kadlubar, F. F., McClure,
G. Y., Brooks, L. R., Green, B. L., Fares, M. Y., Stone, A., Josephy, P. D.,
and Ambrosone, C. B. (2002) Evidence for the presence of mutagenic
arylamines in human breast milk and DNA adducts in exfoliated breast
ductal epithelial cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 39, 134–142.
(30) Gorlewska-Roberts, K., Green, B., Fares, M., Ambrosone, C. B.,
and Kadlubar, F. F. (2002) Carcinogen-DNA adducts in human breast
epithelial cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 39, 184–192.
(31) Skipper, P. L., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (1990) Protein adducts
in the molecular dosimetry of chemical carcinogens. Carcinogenesis
11, 507–518.
(32) Rundle, A. (2006) Carcinogen-DNA adducts as a biomarker for
cancer risk. Mutat. Res. 600,23–36.
(33) Kriek, E. (1992) Fifty years of research on N-acetyl-2-amino-
fluorene, one of the most versatile compounds in experimental cancer
research. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 118, 481–489.
(34) Clayson, D. B. (1981) Specific aromatic amines as occupational
bladder carcinogens. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 15–19.
(35) Miller, J. A. (1970) Carcinogenesis by chemicals: an overview:
G. H. A. Clowes memorial lecture. Cancer Res. 30, 559–576.
1196 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(36) Miller, E. C. (1978) Some current perspectives on chemical
carcinogenesis in humans and experimental animals: Presidential ad-
dress. Cancer Res. 38, 1479–1496.
(37) Beland, F. A., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1985) Formation and
persistence of arylamine DNA adducts in vivo. Environ. Health Perspect.
62,19–30.
(38) Neumann, H. G. (1988) Biomonitoring of aromatic amines and
alkylating agents by measuring hemoglobin adducts. Int. Arch. Occup.
Environ. Health 60, 151–155.
(39) Kiese, M. (1966) The biochemical production of ferrihemo-
globin-forming derivatives from aromatic amines, and mechanisms of
ferrihemoglobin formation. Pharmacol. Rev. 18, 1091–1161.
(40) Irving, C. C. (1973) Conjugates of N-Hydroxy Compounds, in
Metabolic Conjugation and Metabolic Hydrolysis (Fishman, W. H., Ed.) pp
53-119, Academic Press, Inc., New York.
(41) Miller, J. A., and Miller, E. C. (1969) The metabolic activation
of carcinogenic aromatic amines and amides. Prog. Exp. Tumor Res.
11, 273–301.
(42) Hoffmann, G. R., and Fuchs, R. P. (1997) Mechanisms of
frameshift mutations: insight from aromatic amines. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
10, 347–359.
(43) Neumann, H. G. (2010) Aromatic amines: mechanisms of
carcinogenesis and implications for risk assessment. Front. Biosci.
15, 1119–1130.
(44) Gorrod, J. W., and Manson, D. (1986) The metabolism of
aromatic amines. Xenobiotica 16, 933–955.
(45) Kadlubar, F. F., and Beland, F. A. (1985) Chemical Properties
of Ultimate Carcinogenic Metabolites of Arylamines and Arylamides, in
Polycyclic Hydrocarbons and Carcinogenesis (Harvey, R. G., Ed.) pp
332-370, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
(46) Weisburger, J. H., and Weisburger, E. K. (1966) Chemicals as
causes of cancer. Chem. Eng. News 44, 124–142.
(47) International Agency for Research on Cancer (2004) Tobacco
Smoke and Involuntary Smoking, IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Vol. 83, International Agency for Research
on Cancer, Lyon, France.
(48) Neumann, H. G. (1984) Analysis of hemoglobin as a dose
monitor for alkylating and arylating agents. Arch. Toxicol. 56,1–6.
(49) Skipper, P. L., Peng, X., SooHoo, C. K., and Tannenbaum, S. R.
(1994) Protein adducts as biomarkers of human carcinogen exposure.
Drug Metab. Rev. 26, 111–124.
(50) Yu, M. C., Skipper, P. L., Tannenbaum, S. R., Chan, K. K., and
Ross, R. K. (2002) Arylamine exposures and bladder cancer risk. Mutat.
Res. 506-
507,21–28.
(51) Sabbioni, G., and Jones, C. R. (2002) Biomonitoring of
arylamines and nitroarenes. Biomarkers 7, 347–421.
(52) Talaska, G., and Al-Zoughool, M. (2003) Aromatic amines and
biomarkers of human exposure. J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part C: Environ.
Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 21, 133–164.
(53) Richter, E., and Branner, B. (2002) Biomonitoring of exposure
to aromatic amines: haemoglobin adducts in humans. J. Chromatogr., B
778,49–62.
(54) Kataoka, H. (1997) Methods for the determination of muta-
genic heterocyclic amines and their applications in environmental
analysis. J. Chromatogr., A 774, 121–142.
(55) Pais, P., and Knize, M. G. (2000) Chromatographic and related
techniques for the determination of aromatic heterocyclic amines in
foods. J. Chromatogr., B 747, 139–169.
(56) Busquets, R., Mitjans, D., Puignou, L., and Galceran, M. T.
(2008) Quantification of heterocyclic amines from thermally processed
meats selected from a small-scale population-based study. Mol. Nutr.
Food Res. 52 , 1408–1420.
(57) Alaejos, M. S., and Afonso, A. M. (2011) Factors that affect the
content of heterocyclic aromatic amines in foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci.
Food Saf. 10,52–108.
(58) Jagerstad, M., Skog, K., Grivas, S., and Olsson, K. (1991)
Formation of heterocyclic amines using model systems. Mutat. Res.
259, 219–233.
(59) Messner, C., and Murkovic, M. (2004) Evaluation of a new
model system for studying the formation of heterocyclic amines.
J. Chromatogr., B 802,19–26.
(60) Kato, R. (1986) Metabolic activation of mutagenic heterocyclic
aromatic amines from protein pyrolysates. CRC Crit. Rev. Toxicol
16, 307–348.
(61) Wakabayashi, K., Nagao, M., Esumi, H., and Sugimura, T. (1992)
Food-derived mutagens and carcinogens. Cancer Res. 52, 2092s–2098s.
(62) Eisenbrand, G., and Tang, W. (1993) Food-borne heterocyclic
amines. Chemistry, formation, occurrence and biological activities. A
literature review. Toxicology 84,1–82.
(63) Schut, H. A., and Snyderwine, E. G. (1999) DNA adducts of
heterocyclic amine food mutagens: implications for mutagenesis and
carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 20, 353–368.
(64) Gooderham, N. J., Murray, S., Lynch, A. M., Yadollahi-Farsani,
M., Zhao, K., Boobis, A. R., and Davies, D. S. (2001) Food-derived
heterocyclic amine mutagens: variable metabolism and significance to
humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 29, 529
–534.
(65) Felton, J. S., Knize, M. G., Bennett, L. M., Malfatti, M. A.,
Colvin, M. E., and Kulp, K. S. (2004) Impact of environmental exposures
on the mutagenicity/carcinogenicity of heterocyclic amines. Toxicology
198, 135–145.
(66) Kadlubar, F. F., Kaderlik, K. R., Mulder, G. J., Lin, D.-X., Butler,
M. A., Teitel, C. H., Minchin, R. F., Ilett, K. F., Friesen, M. D., Bartsch,
H., Nagao, M., Esumi, E., Sugimura, T., and Lang, N. P. (1995)
Metabolic Activation and DNA Adduct Detection of PhIP in Dogs,
Rats, And Humans in Relation to Urinary Bladder and Colon Carcino-
genesis, in Heterocyclic Amines in Cooked Foods: Possible Human Carcino-
gens (Adamson, R. H., Gustafsson, J.-A., Ito, N., Nagao, M., Sugimura, T.,
Wakabayashi, K., and Yamazoe, Y., Eds.) 23rd Proceedings of the
Princess Takamatusu Cancer Society, pp 207-213, Princeton Scientific
Publishing Co., Inc., Princeton, NJ.
(67) Airoldi, L., Magagnotti, C., Pastorelli, R., and Fanelli, R. (2004)
Enzyme polymorphisms influencing the metabolism of heterocyclic
aromatic amines. J. Chromatogr., B 802, 175–181.
(68) Glatt, H. (2006) Metabolic Factors Affecting the Mutagenicity
of Heteroyclic Amines, in Acrylamide and Other Hazardous Compounds
in Heat-Treated Foods (Skog, K., and Alexander, J., Eds.) pp 358-404,
Woodhead Publishing Ltd., Cambridge, England.
(69) Turesky, R. J. (2007) Formation and biochemistry of carcino-
genic heterocyclic aromatic amines in cooked meats. Toxicol. Lett.
168, 219–227.
(70) Alaejos, M. S., Gonzalez, V., and Afonso, A. M. (2008)
Exposure to heterocyclic aromatic amines from the consumption of
cooked red meat and its effect on human cancer risk: a review. Food
Addit. Contam., Part A 25,2–24.
(71) Sugimura, T. (1992) Multistep carcinogenesis: A 1992 per-
spective. Science 258, 603–607.
(72) Nagao, M., Ushijima, T., Toyota, M., Inoue, R., and Sugimura,
T. (1997) Genetic changes induced by heterocyclic amines. Mutat. Res.
376, 161–167.
(73) Nagao, M. (2000) Mutagenicity, in Food Borne Carcinogens
Heterocyclic Amines (Nagao, M., and Sugimura, T., Eds.) pp 163-195,
John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, England.
(74) Dashwood, R. H. (2003) Use of transgenic and mutant animal
models in the study of heterocyclic amine-induced mutagenesis and
carcinogenesis. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 36,35–42.
(75) Turesky, R. J., Fay, L. B., and Welti, D. H. (1995) Metabolism of
Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Strategies of Human Biomonitoring,
in Heterocyclic Amines in Cooked Foods: Possible Human Carcinogens
(Adamson, R. H., Gustafsson, J.-A., Ito, N., Nagao, M., Sugimura, T.,
Wakabayashi, K., and Yamazoe, Y., Eds.) 23rd Proceedings of the
Princess Takamatusu Cancer Society, pp 59-68, Princeton Scientific
Publishing Co., Inc., Princeton, NJ.
(76) Beland, F. A., Beranek, D. T., Dooley, K. L., Heflich, R. H., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1983) Arylamine-DNA adducts in vitro and in vivo:
their role in bacterial mutagenesis and urinary bladder carcinogenesis.
Environ. Health Perspect. 49, 125
–134.
1197 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(77) Castelao, J. E., Yuan, J. M., Skipper, P. L., Tannenbaum, S. R.,
Gago-Dominguez, M., Crowder, J. S., Ross, R. K., and Yu, M. C. (2001)
Gender- and smoking-related bladder cancer risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.
93, 538–545.
(78) Skipper, P. L., Tannenbaum, S. R., Ross, R. K., and Yu, M. C.
(2003) Nonsmoking-related arylamine exposure and bladder cancer
risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 12, 503–507.
(79) Kiese, M., and Taeger, K. (1976) The fate of phenylhydrox-
ylamine in human red cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.
292,59–66.
(80) Green, L. C., Skipper, P. L., Turesky, R. J., Bryant, M. S., and
Tannenbaum, S. R. (1984) In vivo dosimetry of 4-aminobiphenyl in rats
via a cysteine adduct in hemoglobin. Cancer Res. 44, 4254–4259.
(81) Ringe, D., Turesky, R. J., Skipper, P. L., and Tannenbaum, S. R.
(1988) Structure of the single stable hemoglobin adduct formed by
4-aminobiphenyl in vivo. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1,22–24.
(82) Skipper, P. L., and Stillwell, W. G. (1994) Aromatic amine-
hemoglobin adducts. Methods Enzymol. 231, 643–649.
(83) Bryant, M. S., Skipper, P. L., Tannenbaum, S. R., and Maclure,
M. (1987) Hemoglobin adducts of 4-aminobiphenyl in smokers and
nonsmokers. Cancer Res. 47, 602–608.
(84) Turesky, R. J., Markovic, J., Bracco-Hammer, I., and Fay, L. B.
(1991) The effect of dose and cytochrome P450 induction on the
metabolism and disposition of the food-borne carcinogen 2-amino-3,8-
dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline. Carcinogenesis 12, 1847–1855.
(85) Sj€odin, P., Wallin, H., Alexander, J., and Jagerstad, M. (1989)
Disposition and metabolism of the food mutagen 2-amino-3,8-dimethyl-
imidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline(MeIQx) in rats. Carcinogenesis 10, 1269–1275.
(86) Dragsted, L. O., Frandsen, H., Reistad, R., Alexander, J., and
Larsen, J. C. (1995) DNA-binding and disposition of 2-amino-1-methyl-
6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in the rat. Carcinogenesis
16, 2785–2793.
(87) Watkins, B. E., Suzuki, M., Wallin, H., Wakabayashi, K.,
Alexander, J., Vanderlaan, M., Sugimura, T., and Esumi, H. (1991)
The effect of dose and enzyme inducers on the metabolism of 2-amino-
1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in rats. Carcinogenesis
12, 2291–2295.
(88) Lynch, A. M., Murray, S., Boobis, A. R., Davies, D. S., and
Gooderham, N. J. (1991) The measurement of MeIQx adducts with
mouse haemoglobin in vitro and in vivo: implications for human
dosimetry. Carcinogenesis 12, 1067–1072.
(89) Turteltaub, K. W., Dingley, K. H., Curtis, K. D., Malfatti, M. A.,
Turesky, R. J., Garner, R. C., Felton, J. S., and Lang, N. P. (1999)
Macromolecular adduct formation and metabolism of heterocyclic
amines in humans and rodents at low doses. Cancer Lett. 143
, 149–155.
(90) Dingley, K. H., Curtis, K. D., Nowell, S., Felton, J. S., Lang,
N. P., and Turteltaub, K. W. (1999) DNA and protein adduct formation
in the colon and blood of humans after exposure to a dietary-relevant
dose of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine. Cancer Epi-
demiol. Biomarkers Prev. 8, 507–512.
(91) Mauthe, R. J., Dingley, K. H., Leveson, S. H., Freeman, S. P.,
Turesky, R. J., Garner, R. C., and Turteltaub, K. W. (1999) Comparison
of DNA-adduct and tissue-available dose levels of MeIQx in human and
rodent colon following administration of a very low dose. Int. J. Cancer
80, 539–545.
(92) Garner, R. C., Lightfoot, T. J., Cupid, B. C., Russell, D.,
Coxhead, J. M., Kutschera, W., Priller, A., Rom, W., Steier, P., Alexander,
D. J., Leveson, S. H., Dingley, K. H., Mauthe, R. J., and Turteltaub, K. W.
(1999) Comparative biotransformation studies of MeIQx and PhIP in
animal models and humans. Cancer Lett. 143, 161–165.
(93) Boobis, A. R., Gooderham, N., Edwards, R. J., Murray, S.,
Lynch, A. M., Yadollahi-Farsani, M., and Davies, D. S. (1996) Enzymic
and interindividual differences in the human metabolism of heterocyclic
amines. Arch. Toxicol.(Suppl.) 18, 286–302.
(94) Turesky, R. J. (2006) Genotoxicity, Metabolism, And Biomar-
kers of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines, in Acrylamide and Other Hazar-
dous Compounds in Heat-Treated Foods (Skog, K., and Alexander, J., Eds.)
pp 247-274, Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, England.
(95) Teunissen, S. F., Rosing, H., Schinkel, A. H., Schellens, J. H.,
and Beijnen, J. H. (2010) Review on the analysis of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine and its phase I and phase II metabolites in
biological matrices, foodstuff and beverages. J. Chromatogr., B
878, 3199–3216.
(96) Keating, G. A., and Bogen, K. T. (2004) Estimates of hetero-
cyclic amine intake in the US population. J. Chromatogr., B 802, 127–133.
(97) Fenn, J. B., Mann, M., Meng, C. K., Wong, S. F., and White-
house, C. M. (1989) Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of
large biomolecules. Science 246,64–71.
(98) Kulp, K. S., Knize, M. G., Fowler, N. D., Salmon, C. P., and
Felton, J. S. (2004) PhIP metabolites in human urine after consumption
of well-cooked chicken. J. Chromatogr., B 802, 143–153.
(99) Koc, H., and Swenberg, J. A. (2002) Applications of mass
spectrometry for quantitation of DNA adducts. J. Chromatogr., B
778, 323–343.
(100) Turesky, R. J., and Vouros, P. (2004) Formation and analysis
of heterocyclic aromatic amine-DNA adducts in vitro and in vivo.
J. Chromatogr., B 802, 155–166.
(101) Walters, D. G., Young, P. J., Agus, C., Knize, M. G., Boobis,
A. R., Gooderham, N. J., and Lake, B. G. (2004) Cruciferous vegetable
consumption alters the metabolism of the dietary carcinogen 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in humans. Carcinogen-
esis 25, 1659–
1669.
(102) Singh, R., and Farmer, P. B. (2006) Liquid chromatography-
electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry: the future of DNA adduct
detection. Carcinogenesis 27, 178–196.
(103) Gu, D., McNaughton, L., LeMaster, D., Lake, B. G., Gooderham,
N. J., Kadlubar, F. F., and Turesky, R. J. (2010) A comprehensive
approach to the profiling of the cooked meat carcinogens 2-amino-
3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimi-
dazo[4,5-b]pyridine, and their metabolites in human urine. Chem. Res.
Toxicol. 23,788–801.
(104) Rehn, L. (1895) Blasengeschwulste bei Fuchsinarbeitern.
Arch. Klin. Chir. 50, 588–600.
(105) Case, R. A., Hosker, M. E., McDonald, D. B., and Pearson, J. T.
(1954) Tumours of the urinary bladder in workmen engaged in the
manufacture and use of certain dyestuff intermediates in the British
chemical industry. I. The role of aniline, benzidine, alpha-naphthyla-
mine, and beta-naphthylamine. Br. J. Ind. Med. 11,75–104.
(106) Melick, W. F., Naryka, J. J., and Kelly, R. E. (1971) Bladder
cancer due to exposure to para-aminobiphenyl: a 17-year followup.
J. Urol. 106, 220–226.
(107) Hueper, W. C., Wiley, F. H., and Wolfe, H. D. (1938)
Experimental production of bladder tumors in dogs by administration
of beta-naphthylamine. J. Ind. Hyg. 20,46–84.
(108) Radomski, J. L., and Brill, E. (1970) Bladder cancer induction by
aromatic amines: role of N-hydroxy metabolites. Science 167, 992–993.
(109) Poirier, M. C., and Beland, F. A. (1992) DNA adduct measure-
ments and tumor incidence during chronic carcinogen exposure in animal
models: Implications for DNA adduct-based human cancer risk assessment.
Chem.Res.Toxicol.5, 749–7 55.
(110) Zavon, M. R., Hoegg, U., and Bingham, E. (1973) Benzidine
exposure as a cause of bladder tumors. Arch. Environ. Health 27,1–7.
(111) Ward, E. M., Sabbioni, G., DeBord, D. G., Teass, A. W., Brown,
K. K., Talaska, G. G., Roberts, D. R., Ruder, A. M., and Streicher, R. P. (1996)
Monitoring of aromatic amine exposures in workers at a chemical plant with a
known bladder cancer excess. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 88, 1046–1052.
(112) Stavric, B., Klassen, R., and Miles, W. (1979) Gas-liquid
chromatographic-mass spectrometric determination of alpha- and
beta-naphthylamines in FD&C Red No. 2(amaranth). J. Assoc. Off. Anal.
Chem. 62, 1020–1026.
(113) Davis, V. M., and Bailey, J. E., Jr. (1993) Chemical reduction of
FD&C yellow No. 5 to determine combined benzidine. J. Chromatogr.
635, 160–164.
(114) Garrigos, M. C., Reche, F., Marin, M. L., and Jimenez, A.
(2002) Determination of aromatic amines formed from azo colorants in
toy products. J. Chromatogr., A 976
, 309–317.
1198 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(115) Lancaster, F. E., and Lawrence, J. F. (1999) Determination of
benzidine in the food colours tartrazine and sunset yellow FCF, by
reduction and derivatization followed by high-performance liquid
chromatography. Food Addit. Contam. 16, 381–390.
(116) Oh, S. W., Kang, M. N., Cho, C. W., and Lee, M. W. (1997)
Detection of carcinogenic amines from dyestuffs or dyed substrates. Dyes
Pigm. 33, 119–135.
(117) Cioni, F., Bartolucci, G., Pieraccini, G., Meloni, S., and Moneti,
G. (1999) Development of a solid phase microextraction method for
detection of the use of banned azo dyes in coloured textiles and leather.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 13, 1833–1837.
(118) Tokiwa, H., Nakagawa, R., and Horikawa, K. (1985) Muta-
genic/carcinogenic agents in indoor pollutants; the dinitropyrenes
generated by kerosene heaters and fuel gas and liquefied petroleum
gas burners. Mutat. Res. 157,39–47.
(119) Stabbert, R., Schafer, K. H., Biefel, C., and Rustemeier, K.
(2003) Analysis of aromatic amines in cigarette smoke. Rapid Commun.
Mass Spectrom. 17, 2125–2132.
(120) Turesky, R. J., Freeman, J. P., Holland, R. D., Nestorick, D. M.,
Miller, D. W., Ratnasinghe, D. L., and Kadlubar, F. F. (2003) Identifica-
tion of aminobiphenyl derivatives in commercial hair dyes. Chem. Res.
Toxicol. 16, 1162–1173.
(121) Akyuz, M., and Ata, S. (2008) Determination of aromatic
amines in hair dye and henna samples by ion-pair extraction and gas
chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 47,68–80.
(122) Neumann, H. G. (2001) Health risk of combustion products:
toxicological considerations. Chemosphere 42, 473–479.
(123) Skipper, P. L., Kim, M. Y., Sun, H. L., Wogan, G. N., and
Tannenbaum, S. R. (2010) Monocyclic aromatic amines as potential
human carcinogens: old is new again. Carcinogenesis 31,50–58.
(124) Knize, M. G., and Felton, J. S. (2005) Formation and human
risk of carcinogenic heterocyclic amines formed from natural precursors
in meat. Nutr. Rev. 63, 158–165.
(125) Sinha, R., Rothman, N., Brown, E. D., Salmon, C. P., Knize,
M. G., Swanson, C. S., Rossi, S. C., Mark, S. D., Levander, O. A., and
Felton, J. S. (1995) High concentrations of the carcinogen 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) occur in chicken but are
dependent on the cooking method. Cancer Res. 55, 4516–4519.
(126) Ni, W., McNaughton, L., LeMaster, D. M., Sinha, R., and
Turesky, R. J. (2008) Quantitation of 13 heterocyclic aromatic amines in
cooked beef, pork, and chicken by liquid chromatography-electrospray
ionization/tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56,68–78.
(127) Knize, M. G., Dolbeare, F. A., Carroll, K. L., Moore, D. H., and
Felton, J. S. (1994) Effect of cooking time and temperature on the
heterocyclic amine content of fried beef patties. Food Chem. Toxicol.
32, 595–
603.
(128) Yoshida, D., Matsumoto, T., Yoshimura, R., and Matsuzaki, T.
(1978) Mutagenicity of amino-alpha-carbolines in pyrolysis products of
soybean globulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 83, 915–920.
(129) Skog, K., Solyakov, A., Arvidsson, P., and Jagerstad, M. (1998)
Analysis of nonpolar heterocyclic amines in cooked foods and meat
extracts using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr., A
803, 227–233.
(130) Skog, K. I., Johansson, M. A., and Jagerstad, M. I. (1998)
Carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in model systems and cooked foods: a
review on formation, occurrence and intake. Food Chem. Toxicol.
36, 879–896.
(131) Milic, B. L., Djilas, S. M., and Candadanoic-Brunet, J. M.
(1993) Synthesis of some heterocyclic aminoimidazoarenes. Food Chem.
46, 273–276.
(132) Murkovic, M. (2004) Formation of heterocyclic aromatic
amines in model systems. J. Chromatogr., B 802,3–10.
(133) Shioya, M., Wakabayashi, K., Sato, S., Nagao, M., and Sugimura, T.
(1987) Formation of a mutagen, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine(PhIP) in cooked beef, by heating a mixture containing creatinine,
phenylalanine and glucose. Mutat. Res. 191, 133–138.
(134) Sinha, R., Rothman, N., Salmon, C. P., Knize, M. G., Brown,
E. D., Swanson, C. A., Rhodes, D., Rossi, S., Felton, J. S., and Levander,
O. A. (1998) Heterocyclic amine content in beef cooked by different
methods to varying degrees of doneness and gravy made from meat
drippings. Food Chem. Toxicol. 36, 279–287.
(135) Okonogi, H., Ushijima, T., Shimizu, H., Sugimura, T., and
Nagao, M. (1997) Induction of aberrant crypt foci in C57BL/6N mice
by 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(AaC) and 2-amino-3,8-dimethy-
limidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline(MeIQx). Cancer Lett. 111, 105–109.
(136) Zhang, X. B., Felton, J. S., Tucker, J. D., Urlando, C., and
Heddle, J. A. (1996) Intestinal mutagenicity of two carcinogenic food
mutagens in transgenic mice: 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine and amino(alpha)carboline. Carcinogenesis 17, 2259–2265.
(137) Fujita, H., Nagano, K., Ochiai, M., Ushijima, T., Sugimura, T.,
Nagao, M., and Matsushima, T. (1999) Difference in target organs in
carcinogenesis with a heterocyclic amine, 2-amino-3,4-dimethylimidazo[4,5-
f]quinoline, in different strains of mice. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 90, 1203–1206.
(138) Nakagama, H., Ochiai, M., Ubagai, T., Tajima, R., Fujiwara, K.,
Sugimura, T., and Nagao, M. (2002) A rat colon cancer model induced
by 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, PhIP. Mutat.
Res. 506-
507, 137–144.
(139) Ochiai, M., Imai, H., Sugimura, T., Nagao, M., and Nakagama,
H. (2002) Induction of intestinal tumors and lymphomas in C57BL/6N
mice by a food-borne carcinogen, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 93, 478–483.
(140) Yoshida, D., and Matsumoto, T. (1980) Amino-alpha-carbo-
lines as mutagenic agents in cigarette smoke condensate. Cancer Lett.
10, 141–149.
(141) Smith, C. J., Qian, X., Zha, Q., and Moldoveanu, S. C. (2004)
Analysis of alpha- and beta-carbolines in mainstream smoke of reference
cigarettes by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr., A
1046, 211–216.
(142) Zhang, L., Ashley, D. L., and Watson, C. H. (2011) Quantitative
analysis of six heterocyclic aromatic amines in mainstream cigarette smoke
condensate using isotope dilution liquid chromatography-electrospray ioni-
zation tandem mass spectrometry. Nicotine.Tob.Res.13, 120–126.
(143) Zha, Q., Qian, N. X., and Moldoveanu, S. C. (2002) Analysis
of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the particulate phase of cigarette
smoke using a gas chromatographic-high-resolution mass spectrometric
technique. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 40, 403–408.
(144) Hoffmann, D. (1998) Letters to the editor: Tobacco smoke
components. Beitr€age zur Tabakforschung Int. 18,49–52.
(145) Hecht, S. S. (2003) Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers
and tobacco-induced cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 733–744.
(146) Kanai, Y., Wada, O., and Manabe, S. (1990) Detection of
carcinogenic glutamic acid pyrolysis products in cigarette smoke con-
densate. Carcinogenesis 11, 1001–1003.
(147) Manabe, S., Wada, O., and Kanai, Y. (1990) Simultaneous
determination of amino-alpha-carbolines and amino-gamma-carbolines
in cigarette smoke condensate by high-performance liquid chromatog-
raphy. J. Chromatogr. 529, 125–133.
(148) Yamashita, M., Wakabayashi, K., Nagao, M., Sato, S., Yamaizumi,
Z., Takahashi, M., Kinae , N., Tomita, I., and Sugimura, T. (1986) Detection
of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in cigarette smoke conden-
sate. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 77, 419–422.
(149) Sullivan, M. X. (1911) The origin of creatinine in soils. J. Am.
Chem. Soc. 33, 2035–2042.
(150) Manabe, S., Kurihara, N., Wada, O., Izumikawa, S., Asakuno,
K., and Morita, M. (1993) Detection of a carcinogen, 2-amino-1-methyl-
6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, in airborne particles and diesel-exhaust
particles. Environ. Pollut. 80, 281–
286.
(151) Totsuka, Y., Ushiyama, H., Ishihara, J., Sinha, R., Goto, S.,
Sugimura, T., and Wakabayashi, K. (1999) Quantification of the co-
mutagenic beta-carbolines, norharman and harman, in cigarette smoke
condensates and cooked foods. Cancer Lett. 143, 139–143.
(152) Totsuka, T., Nishigaki, R., Sugimura, T., and Wakabayashi, K.
(2006) The Possible Involvement of Mutagenic and Carcinogenic Hetero-
yclic Amines in Human Cancer, in Acrylamide and Other Hazardous
Compounds in Heat-Treated Foods (Skog, K., and Alexander, J., Eds.)
pp 296-515, Woodhead Publisher, Boca Raton, FL.
1199 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(153) Hada, N., Totsuka, Y., Enya, T., Tsurumaki, K., Nakazawa, M.,
Kawahara, N., Murakami, Y., Yokoyama, Y., Sugimura, T., and Wakabayashi,
K. (2001) Structures of mutagens produced by the co-mutagen norharman
with o- and m-toluidine isomers. Mutat. Res. 493, 115–126.
(154) Kawamori, T., Totsuka, Y., Uchiya, N., Kitamura, T., Shibata,
H., Sugimura, T., and Wakabayashi, K. (2004) Carcinogenicity of
aminophenylnorharman, a possible novel endogenous mutagen, formed
from norharman and aniline, in F344 rats. Carcinogenesis 25, 1967–1972.
(155) Shirai, T., Sano, M., Tamano, S., Takahashi, S., Hirose, M.,
Futakuchi, M., Hasegawa, R., Imaida, K., Matsumoto, K., Wakabayashi,
K., Sugimura, T., and Ito, N. (1997) The prostate: A target for
carcinogenicity of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-
(PhIP) derived from cooked foods. Cancer Res. 57, 195–198.
(156) Ohgaki, H., Hasegawa, H., Kato, T., Suenaga, M., Ubukata, M.,
Sato, S., Takayama, S., and Sugimura, T. (1986) Carcinogenicity in mice
and rats of heterocyclic amines in cooked foods. Environ. Health Perspect.
67, 129–134.
(157) Ghoshal, A., Preisegger, K. H., Takayama, S., Thorgeirsson,
S. S., and Snyderwine, E. G. (1994) Induction of mammary tumors in
female Sprague-Dawley rats by the food-derived carcinogen 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine and effect of dietary fat. Carci-
nogenesis 15, 2429–2433.
(158) Ubagai, T., Ochiai, M., Kawamori, T., Imai, H., Sugimura, T.,
Nagao, M., and Nakagama, H. (2002) Efficient induction of rat large
intestinal tumors with a new spectrum of mutations by intermittent
administration of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in
combination with a high fat diet. Carcinogenesis 23, 197–200.
(159) Sugimura, T. (1982) Mutagens, carcinogens, and tumor
promoters in our daily food. Cancer 49, 1970–1984.
(160) Nakagama, H., Nakanishi, M., and Ochiai, M. (2005) Model-
ing human colon cancer in rodents using a food-borne carcinogen, PhIP.
Cancer Sci. 96 , 627–636.
(161) Ochiai, M., Nakagama, H., Watanabe, M., Ishiguro, Y., Sugimura,
T., and Nagao, M. (1996) Efficient method for rapid induction of aberrant
crypt foci in rats with 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine.
Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 87, 1029–1033.
(162) Snyderwine, E. G. (2002) Mammary gland carcinogenesis by
food-derived heterocyclic amines: metabolism and additional factors
influencing carcinogenesis by 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine(PhIP). Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 39, 165–170.
(163) Adamson, R. H., Thorgeirsson, U. P., Snyderwine, E. G.,
Thorgeirsson, S. S., Reeves, J., Dalgard, D. W., Takayama, S., and
Sugimura, T. (1990) Carcinogenicity of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo-
[4,5-f]quinoline in nonhuman primates: induction of tumors in three
macaques. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 81,10–14.
(164) Bogen, K. T., and Keating, G. A. (2001) U.S. dietary exposures
to heterocyclic amines. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 11, 155–168.
(165) Hasegawa, R., Tanaka, H., Tamano, S., Shirai, T., Nagao, M.,
Sugimura, T., and Ito, N. (1994) Synergistic enhancement of small and
large intestinal carcinogenesis by combined treatment of rats with five
heterocyclic amines in a medium-term mutli-organ bioassay. Carcino-
genesis 15, 2567–2573.
(166) Turteltaub, K. W., Felton, J. S., Gledhill, B. L., Vogel, J. S.,
Southon, J. R., Caffee, M. W., Finkel, R. C., Nelson, D. E., Proctor, I. D.,
and Davis, J. C. (1990) Accelerator mass spectrometry in biomedical
dosimetry: relationship between low-level exposure and covalent bind-
ing of heterocyclic amine carcinogens to DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci U.S.
A. 87, 5288–5292.
(167) Turesky, R. J., Box, R. M., Markovic, J., Gremaud, E., and
Snyderwine, E. G. (1997) Formation and persistence of DNA adducts of
2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in the rat and nonhuman
primates. Mutat. Res. 376, 235–241.
(168) Fukushima, S., Wanibuchi, H., Morimura, K., Iwai, S., Nakae,
D., Kishida, H., Tsuda, H., Uehara, N., Imaida, K., Shirai, T., Tatematsu,
M., Tsukamoto, T., Hirose, M., and Furukawa, F. (2004) Existence of a
threshold for induction of aberrant crypt foci in the rat colon with low
doses of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenolimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine. Toxicol.
Sci. 80, 109 –114.
(169) Friesen, M. D., Kaderlik, K., Lin, D., Garren, L., Bartsch, H.,
Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1994) Analysis of DNA adducts of
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in rat and human
tissues by alkaline hydrolysis and gas chromatography/electron capture
mass spectrometry: validation by comparison with
32
P-postlabeling.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 7, 733–739.
(170) Tada, A., Ochiai, M., Wakabayashi, K., Nukaya, H., Sugimura,
T., and Nagao, M. (1994) Identification of N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-
amino-3,4-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(dG-C8-MeIQ) as a major
adduct formed by MeIQ with nucleotides in vitro with DNA in vivo.
Carcinogenesis 15, 1275–1278.
(171) Turteltaub, K. W., Mauthe, R. J., Dingley, K. H., Vogel, J. S.,
Frantz, C. E., Garner, R. C., and Shen, N. (1997) MeIQx-DNA adduct
formation in rodent and human tissues at low doses. Mutat. Res.
376, 243–252.
(172) Lightfoot, T. J., Coxhead, J. M., Cupid, B. C., Nicholson, S.,
and Garner, R. C. (2000) Analysis of DNA adducts by accelerator mass
spectrometry in human breast tissue after administration of 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine and benzo[a]pyrene. Mutat.
Res. 472, 119–127.
(173) Zhu, J., Chang, P., Bondy, M. L., Sahin, A. A., Singletary, S. E.,
Takahashi, S., Shirai, T., and Li, D. (2003) Detection of 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-DNA adducts in normal breast
tissues and risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev.
12, 830–837.
(174) Zhu, J., Rashid, A., Cleary, K., Abbruzzese, J. L., Friess, H.,
Takahashi, S., Shirai, T., and Li, D. (2006) Detection of 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP)-DNA adducts in human
pancreatic tissues. Biomarkers 11, 319–328.
(175) Magagnotti, C., Pastorelli, R., Pozzi, S., Andreoni, B., Fanelli,
R., and Airoldi, L. (2003) Genetic polymorphisms and modulation of
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP)-DNA adducts
in human lymphocytes. Int. J. Cancer 107,878–884.
(176) Malfatti, M. A., Dingley, K. H., Nowell-Kadlubar, S., Ubick,
E. A., Mulakken, N., Nelson, D., Lang, N. P., Felton, J. S., and Turteltaub,
K. W. (2006) The urinary metabolite profile of the dietary carcinogen
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine is predictive of co-
lon DNA adducts after a low-dose exposure in humans. Cancer Res.
66, 10541–10547.
(177) Tang, D., Liu, J. J., Rundle, A., Neslund-Dudas, C., Savera,
A. T., Bock, C. H., Nock, N. L., Yang, J. J., and Rybicki, B. A. (2007)
Grilled meat consumption and PhIP-DNA adducts in prostate carcino-
genesis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 16, 803–808.
(178) Bessette, E. E., Spivack, S. D., Goodenough, A. K., Wang, T.,
Pinto, S., Kadlubar, F. F., and Turesky, R. J. (2010) Identification of
carcinogen DNA adducts in human saliva by linear quadrupole ion
trap/multistage tandem mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23,
1234–1244.
(179) Layton, D. W., Bogen, K. T., Knize, M. G., Hatch, F. T.,
Johnson, V. M., and Felton, J. S. (1995) Cancer risk of heterocyclic
amines in cooked foods: an analysis and implications for research.
Carcinogenesis 16,39–52.
(180) Felton, J. S., and Knize, M. G. (2006) A meat and potato war:
implications for cancer etiology. Carcinogenesis 27, 2367–2370.
(181) Gaylor, D. W., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1991) Quantitative Risk
Assessments of Heterocyclic Amines in Cooked Foods, in Mutagens in
Foods: Detection and Prevention (Hayatsu, H., Ed.) pp 229-236, CRC
Press, Boca Raton, FL.
(182) Lutz, W. K., and Schlatter, J. (1992) Chemical carcinogens and
overnutrition in diet-related cancer. Carcinogenesis 13, 2211–2216.
(183) Adamson, R. H., Thorgeirsson, U. P., and Sugimura, T. (1996)
Extrapolation of heterocyclic amine carcinogenesis data from rodents
and nonhuman primates to humans. Arch. Toxicol. (Suppl 18), 303–318.
(184) Dybing, E., O’Brien, J., Renwick, A. G., and Sanner, T. (2008)
Risk assessment of dietary exposures to compounds that are genotoxic
and carcinogenic--an overview. Toxicol. Lett. 180, 110–117.
(185) Doerge, D. R., Young, J. F., Chen, J. J., Dinovi, M. J., and
Henry, S. H. (2008) Using dietary exposure and physiologically based
1200 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling in human risk extrapola-
tions for acrylamide toxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 6031–6038.
(186) Barlow, S., Renwick, A. G., Kleiner, J., Bridges, J. W., Busk, L.,
Dybing, E., Edler, L., Eisenbrand, G., Fink-Gremmels, J., Knaap, A.,
Kroes, R., Liem, D., Muller, D. J., Page, S., Rolland, V., Schlatter, J.,
Tritscher, A., Tueting, W., and Wurtzen, G. (2006) Risk assessment of
substances that are both genotoxic and carcinogenic report of an
International Conference organized by EFSA and WHO with support
of ILSI Europe. Food Chem. Toxicol. 44, 1636–1650.
(187) JEFCA (2011) http://www.who.int/foodsafety/chem/jecfa/
summaries/summary_report_64_final.pdf, Internet communication.
(188) Skog, K., Steineck, G., Augustsson, K., and Jagerstad, M.
(1995) Effect of cooking temperature on the formation of heterocyclic
amines in fried meat products and pan residues. Carcinogenesis 16, 861–867.
(189) Skog, K., and Solyakov, A. (2002) Heterocyclic amines in poultry
products: a literature review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 40, 1213–1221.
(190) Sinha, R., Knize, M. G., Salmon, C. P., Brown, E. D., Rhodes,
D., Felton, J. S., Levander, O. A., and Rothman, N. (1998) Heterocyclic
amine content of pork products cooked by different methods and to
varying degrees of doneness. Food Chem. Toxicol. 36, 289–297.
(191) Dooley, K. L., Von Tungelin, L. S., Bucci, T., and Kadlubar,
F. F. (1992) Comparative carcinogenicity of 4-aminobiphenyl and the
food pyrolysates, Glu-P-1, IQ, PhIP, and MeIQx in the neonatal B6C3F
1
male mouse. Cancer Lett. 62, 205–209.
(192) Schwab, C. E., Huber, W. W., Parzefall, W., Hietsch, G., Kassie,
F., Schulte-Hermann, R., and Knasmuller, S. (2000) Search for com-
pounds that inhibit the genotoxic and carcinogenic effects of hetero-
cyclic aromatic amines. Crit Rev. Toxicol. 30,1–69.
(193) Guengerich, F. P., and Shimada, T. (1991) Oxidation of toxic
and carcinogenic chemicals by human cytochrome P-450 enzymes.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 4, 391–407.
(194) Kato, R., and Yamazoe, Y. (1987) Metabolic activation and
covalent binding to nucleic acids of carcinogenic heterocyclic amines
from cooked foods and amino acid pyrolysates. Jpn. J. Cancer Res.
78, 297–311.
(195) Alexander, J., Heidenreich, B., Reistad, R., and Holme, J. A.
(1995) Metabolism of the Food Carcinogen 2-Amino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in the Rat and Other Rodents,
in Heterocyclic Amines in Cooked Foods: Possible Human Carcinogens
(Adamson, R. H., Gustafsson, J.-A., Ito, N., Nagao, M., Sugimura, T.,
Wakabayashi, K., and Yamazoe, Y., Eds.) 23rd Proceedings of the
Princess Takamatusu Cancer Society, pp 59-68, Princeton Scientific
Publishing Co., Inc., Princeton, NJ.
(196) Snyderwine, E. G., Turesky, R. J., Turteltaub, K. W., Davis,
C. D., Sadrieh, N., Schut, H. A., Nagao, M., Sugimura, T., Thorgeirsson,
U. P., Adamson, R. H., and Thorgeirsson, S. S. (1997) Metabolism of
food-derived heterocyclic amines in nonhuman primates. Mutat. Res.
376, 203–210.
(197) Yamazoe, Y., and Nagata, K. (2000) In Vitro Metabolism, in
Food Borne Carcinogens Heterocyclic Amines (Sugimura, T., and Nagao,
M., Eds.) pp 74-89, John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, England.
(198) Turesky, R. J. (2005) Interspecies metabolism of heterocyclic
aromatic amines and the uncertainties in extrapolation of animal toxicity
data for human risk assessment. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 49, 101–117.
(199) Cramer, J. W., Miller, J. A., and Miller, E. C. (1960) N-
Hydroxylation: A new metabolic reaction observed in the rat with the
carcinogen 2-acetylaminofluorene. J. Biol. Chem. 235, 885–888.
(200) Irving, C. C. (1971) Metabolic activation of N-hydroxy
compounds by conjugation. Xenobiotica 1, 387–398.
(201) Yamazoe, Y., Shimada, M., Shinohara, A., Saito, K., Kamataki,
T., and Kato, R. (1985) Catalysis of the covalent binding of 3-hydro-
xyamino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole to DNA by a L-proline- and
adenosine triphosphate-dependent enzyme in rat hepatic cytosol. Cancer
Res. 45, 2495–2500.
(202) Ozawa, S., Chou, H. C., Kadlubar, F. F., Nagata, K., Yamazoe,
Y., and Kato, R. (1994) Activation of 2-hydroxyamino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by cDNA-expressed human and rat ar-
ylsulfotransferases. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 85, 1220–1228.
(203) Hein, D. W., Doll, M. A., Rustan, T. D., Gray, K., Feng, Y.,
Ferguson, R. J., and Grant, D. M. (1993) Metabolic activation and
deactivation of arylamine carcinogens by recombinant human NAT1 and
polymorphi c NAT2 acetyltransferases. Carcinogenesis 14
, 1633–1638.
(204) Hein, D. W. (2000) N-Acetyltransferase genetics and their
role in predisposition to aromatic and heterocyclic amine-induced
carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Lett. 112-113, 349–356.
(205) Nowell, S., Ambrosone, C. B., Ozawa, S., MacLeod, S. L.,
Mrackova, G., Williams, S., Plaxco, J., Kadlubar, F. F., and Lang, N. P.
(2000) Relationship of phenol sulfotransferase activity(SULT1A1)
genotype to sulfotransferase phenotype in platelet cytosol. Pharmaco-
genetics 10, 789–797.
(206) Agus, C., Ilett, K. F., Kadlubar, F. F., and Minchin, R. F. (2000)
Characterization of an ATP-dependent pathway of activation for the
heterocyclic amine carcinogen N-hydroxy-2-amino-3-methylimidazo-
[4,5-f]quinoline. Carcinogenesis 21, 1213–1219.
(207) Lakshmi, V. M., Schut, H. A., and Zenser, T. V. (2005) 2-
Nitrosoamino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline activated by the inflamma-
tory response forms nucleotide adducts. Food Chem. Toxicol. 43, 1607–1617.
(208) Lakshmi, V. M., Clapper, M. L., Chang, W. C., and Zenser,
T. V. (2005) Hemin potentiates nitric oxide-mediated nitrosation of
2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(IQ) to 2-nitrosoamino-3-
methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 18, 528–535.
(209) Zenser, T. V., Lakshmi, V. M., Schut, H. A., Zhou, H. J., and
Josephy, P. D. (2009) Activation of aminoimidazole carcinogens by nitrosa-
tion: mutagenicity and nucleotide adducts. Mutat. Res. 673,109–115.
(210) Whitlock, J. P., Jr., Chichester, C. H., Bedgood, R. M., Okino, S. T.,
Ko,H. P., Ma,Q., Dong,L., Li,H., and Clarke-Katzenberg, R. (1997)
Induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes by dioxin. Drug Metab. Rev.
29,1107–1127.
(211) Nebert, D. W., Dalton, T. P., Okey, A. B., and Gonzalez, F. J.
(2004) Role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of the
CYP1 enzymes in environmental toxicity and cancer. J. Biol. Chem.
279, 23847–23850.
(212) Butler, M. A., Guengerich, F. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1989)
Metabolic oxidation of the carcinogens 4-aminobiphenyl and 4,4
0
-
methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) by human hepatic microsomes and by
purified rat hepatic cytochrome P-450 monooxygenases. Cancer Res.
49,25–31.
(213) Shimada, T., Iwasaki, M., Martin, M. V., and Guengerich, F. P.
(1989) Human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 enzymes involved
in the bioactivation of procarcinogens detected by umu gene response in
Salmonella typhimurium TA 1535/pSK1002. Cancer Res. 49, 3218–3228.
(214) Wallin, H., Mikalsen, A., Guengerich, F. P., Ingelman-Sundberg,
I., Solberg, K. E., Rossland, O. J., and Alexander, J. (1990) Di fferential rates
of metabolic activation and detoxification of the food mutagen 2-amino-
1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by different cytochrome P450
enzymes. Carcinogenesis 11, 489–492.
(215) Rich, K. J., Murray, B. P., Lewis, I., Rendell, N. B., Davies, D. S.,
Gooderham, N. J., and Boobis, A. R. (1992) N-Hydroxy-MeIQx is the
major microsomal oxidation product of the dietary carcinogen MeIQx
with human liver. Carcinogenesis 13, 2221–2226.
(216) Zhao, K., Murray, S., Davies, D. S., Boobis, A. R., and Gooderham,
N. J. (1994) Metabolism of the food derived mutagen and carcinogen
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) by human li-
ver microsomes. Carcinogenesis 15, 1285–1288.
(217) Shimada, T., and Guengerich, F. P. (1991) Activation of
amino-R-carboline, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine,
and a copper phthalocyanine cellulose extract of cigarette smoke
condensate by cytochrome P-450 enzymes in rat and human liver
microsomes. Cancer Res. 51, 5284–5291.
(218) Shimada, T., Hayes, C. L., Yamazaki, H., Amin, S., Hecht, S. S.,
Guengerich, F. P., and Sutter, T. R. (1996) Activation of chemically
diverse procarcinogens by human cytochrome P- 450 1B1. Cancer Res.
56,2979–2984.
(219) Frandsen, H., Nielsen, P. A., Grivas, S., and Larsen, J. C. (1994)
Microsomal metabolism of the food mutagen 2-amino-3,4,8-trimethyl-3H-
imidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline to mutagenic metabolites. Mutagenesis 9,59–65.
1201 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(220) Hammons, G. J., Milton, D., Stepps, K., Guengerich, F. P., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1997) Metabolism of carcinogenic heterocyclic and
aromatic amines by recombinant human cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Carcinogenesis 18, 851–854.
(221) Crofts, F. G., Sutter, T. R., and Strickland, P. T. (1998)
Metabolism of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by
human cytochrome P4501A1, P4501A2 and P4501B1. Carcinogenesis
19, 1969–1973.
(222) Turesky, R. J., Constable, A., Richoz, J., Varga, N., Markovic, J.,
Martin, M. V., and Guengerich, F. P. (1998) Activation of heterocyclic
aromatic amines by rat and human liver microsomes and by purified rat
and human cytochrome P450 1A2. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 11, 925–936.
(223) Frederiksen, H., and Frandsen, H. (2003) Impact of five
cytochrome P450 en zymes on the metabolism of two heter ocyclic aromatic
amines, 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(ARC) and 2-amino-3-methyl-
9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(MeARC). Pharmacol. Toxicol. 92, 246–248.
(224) Guengerich, F. P., and Turvy, C. G. (1991) Comparison of
levels of several human microsomal cytochrome P-450 enzymes and
epoxide hydrolase in normal and disease states using immunochemical
analysis of surgical liver samples. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 256, 1189–1194.
(225) Sutter, T. R., Tang, Y. M., Hayes, C. L., Wo, Y.-Y. P., Jabs,
E. W., Li, X., Yin, H., Cody, C. W., and Greenlee, W. F. (1994) Complete
cDNA sequence of a human dioxin-inducible mRNA identifies a new
gene subfamily of cytochrome P450 that maps to chromosome 2*. J. Biol.
Chem. 269, 13092–13099.
(226) Ding, X., and Kaminsky, L. S. (2003) Human extrahepatic
cytochromes P450: function in xenobiotic metabolism and tissue-
selective chemical toxicity in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts.
Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 43, 149–173.
(227) Kim, J. H., Sherman, M. E., Curriero, F. C., Guengerich, F. P.,
Strickland, P. T., and Sutter, T. R. (2004) Expression of cytochromes
P450 1A1 and 1B1 in human lung from smokers, non-smokers, and ex-
smokers. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 199 , 210–219.
(228) Martin, F. L., Patel, I. I., Sozeri, O., Singh, P. B., Ragavan, N.,
Nicholson, C. M., Frei, E., Meinl, W., Glatt, H., Phillips, D. H., and Arlt,
V. M. (2010) Constitutive expression of bioactivating enzymes in
normal human prostate suggests a capability to activate pro-carcinogens
to DNA-damaging metabolites. Prostate 70, 1586–1599.
(229) Williams, J. A., Stone, E. M., Millar, B. C., Gusterson, B. A.,
Grover, P. L., and Phillips, D. H. (1998) Determination of the enzymes res-
ponsible for activation of the heterocyclic amine 2-amino-3-methylimidazo-
[4,5-f]quinolineinthe humanbreast. Pharmacogenetics 8, 519–528.
(230) Bertz, R. J., and Granneman, G. R. (1997) Use of in vitro and
in vivo data to estimate the likelihood of metabolic pharmacokinetic
interactions.
Clin. Pharmacokinet. 32, 210–258.
(231) Butler, M. A., Lang, N. P., Young, J. F., Caporaso, N. E., Vineis,
P., Hayes, R. B., Teitel, C. H., Massengill, J. P., Lawsen, M. F., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1992) Determination of CYP1A2 and NAT2 pheno-
types in human populations by analysis of caffeine urinary metabolites.
Pharmacogenetics 2, 116–127.
(232) Kalow, W., and Tang, B. K. (1991) Use of caffeine metabolite
ratios to explore CYP1A2 and xanthine oxidase ratios. Clin. Pharmacol.
Ther. 50, 508–519.
(233) Butler, M. A., Iwasaki, M., Guengerich, F. P., and Kadlubar,
F. F. (1989) Human cytochrome P-450
PA
(P450IA2), the phenacetin
O-deethylase, is primarily responsible for the hepatic 3-demethylation of
caffeine and N-oxidation of carcinogenic arylamines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
U.S.A. 86, 7696 –7700.
(234) Yun, C. H., Shimada, T., and Guengerich, F. P. (1992) Contri-
butions of human liver cytochrome P450 enzymes to the N-oxidation of
4,4
0
-methylene-bis(2-chloroaniline). Carcinogenesis 13, 217–222.
(235) Yamazaki, H., Inui, Y., Wrighton, S. A., Guengerich, F. P., and
Shimada, T. (1995) Procarcinogen activation by cytochrome P450 3A4
and 3A5 expressed in Escherichia coli and by human liver microsomes.
Carcinogenesis 16, 2167–2170.
(236) Gan, J., Skipper, P. L., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (2001)
Oxidation of 2,6-dimethylaniline by recombinant human cytochrome
P450s and human liver microsomes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 14, 672–677.
(237) Crofts, F. G., Strickland, P. T., Hayes, C. L., and Sutter, T. R.
(1997) Metabolism of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyri-
dine(PhIP) by human cytochrome P4501B1. Carcinogenesis 18, 1793–1798.
(238) Nakajima, M., Itoh, M., Sakai, H., Fukami, T., Katoh, M.,
Yamazaki, H., Kadlubar, F. F., Imaoka, S., Funae, Y., and Yokoi, T.
(2006) CYP2A13 expressed in human bladder metabolically activates
4-aminobiphenyl. Int. J. Cancer 119, 2520–2526.
(239) King, R. S., Kadlubar, F. F., and Turesky, R. J. (2000) In Vivo
Metabolism of Heterocyclic Amines, in Food Borne Carcinogens: Hetero-
cyclic Amines (Nagao, M., and Sugimura, T., Eds.) pp 90-111, John
Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Chichester, England.
(240) Schweikl, H., Taylor, J. A., Kitareewan, S., Linko, P., Nagorney,
D., and Goldstein, J. A. (1993) Expression of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2
genes in human liver. Pharmacogenetics 3, 239–249.
(241) Eaton, D. L., Gallagher, E. P., Bammler, T. K., and Kunze, K. L.
(1995) Role of cytochrome P450 1A2 in chemical carcinogenesis:
implications for human variability in expression and enzyme activity.
Pharmacogenetics 5, 259–274.
(242) Belloc, C., Baird, S., Cosme, J., Lecoeur, S., Gautier, J.-C.,
Challine, D., de Waziers, I., Flinois, J.-P., and Beaune, P. H. (1996)
Human cytochrome P450 expressed in Escherichia coli: production of
specific antibodies. Toxicology 106, 207–219.
(243) Hammons, G. J., Yan-Sanders, Y., Jin, B., Blann, E., Kadlubar,
F. F., and Lyn-Cook, B. D. (2001) Specific site methylation in the 5
0
-
flanking region of CYP1A2 interindividual differences in human livers.
Life Sci. 69, 839–845.
(244) Nakajima, M., Yokoi, T., Mizutani, M., Kinoshita, M., Funayama,
M., and Kamataki, T. (1999) Genetic polymorphism in the 5
0
-flanking
region of human CYP1A2 gene: effect on the CYP1A2 inducibility in
humans. J. Biochem.(Tokyo) 125, 803–808.
(245) Sachse, C., Bhambra, U., Smith, G., Lightfoot, T. J., Barrett,
J. H., Scollay, J., Garner, R. C., Boobis, A. R., Wolf, C. R., and Good-
erham, N. J. (2003) Polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 CYP1A2
gene(CYP1A2) in colorectal cancer patients and controls: allele fre-
quencies, linkage disequilibrium and influence on caffeine metabolism.
Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 55,68–76.
(246) Conney, A. H. (1982) Induction of microsomal enzymes by
foreign chemicals and carcinogenesis by polycyclic aromatic hydrocar-
bons: G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Lecture. Cancer Res. 42, 4875–4917.
(247) Conney, A. H., Pantuck, E. J., Hsiao, K. C., Kuntzman, R.,
Alvares, A. P., and Kappas, A. (1977) Regulation of drug metabolism in
man by environmental chemicals and diet. Fed. Proc. 36, 1647–1652.
(248) Vistisen, K., Poulsen, H. E., and Loft, S. (1992) Foreign
compound metabolism capacity in man measured from metabolites of
dietary caffeine. Carcinogenesis 13, 1561–1568.
(249) Pantuck, E. J., Pantuck, C. B., Garland, W. A., Min, B. H.,
Wattenberg, L. W., Anderson, K. E., Kappas, A., and Conney, A. H.
(1979) Stimulatory effect of brussels sprouts and cabbage on human
drug metabolism. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 25,88–95.
(250) Bjeldanes, L. F., Kim, J. Y., Grose, K. R., Bartholomew, J. C.,
and Bradfield, C. A. (1991) Aromatic hydrocarbon responsiveness-
receptor agonists generated from indole-3-carbinol in vitro and
in vivo: comparisons with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Proc.
Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 9543–9547.
(251) Pantuck, E. J., Hsiao, K. C., Conney, A. H., Garland, W. A.,
Kappas, A., Anderson, K. E., and Alvares, A. P. (1976) Effect of charcoal-
broiled beef on phenacetin metabolism in man. Science 194, 1055–1057.
(252) Sinha, R., Rothman, N., Brown, E. D., Mark, S. D., Hoover,
R. N., Caporaso, N. E., Levander, O. A., Knize, M. G., Lang, N. P., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1994) Pan-fried meat containing high levels of hetero-
cyclic aromatic amines but low levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocar-
bons induces cytochrome P4501A2 activity in humans. Cancer Res.
54, 6154–6159.
(253) Diaz, D., Fabre, I., Daujat, M., Saint, A. B., Bories, P., Michel, H.,
and Maurel, P. (1990) Omeprazole is an aryl hydrocarbon-like inducer of
human hepatic cytochrome P450. Gastroenterology 99, 737–747.
(254) Le Marchand, L., Franke, A. A., Custer, L., Wilkens, L. R., and
Cooney, R. V. (1997) Lifestyle and nutritional correlates of cytochrome
1202 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
CYP1A2 activity: inverse associations with plasma lutein and alpha-
tocopherol. Pharmacogenetics 7,11–19.
(255) Jiang, Z., Dragin, N., Jorge-Nebert, L. F., Martin, M. V.,
Guengerich, F. P., Aklillu, E., Ingelman-Sundberg, M., Hammons, G. J .,
Lyn-Cook,B. D., Kadlubar, F.F., Saldana, S. N.,Sorter, M.,Vinks, A.A.,
Nassr, N., von, R. O., Jin, L., and Nebert, D. W. (2006) Search for an
association between the human CYP1A2 genotype and CYP1A2 metabolic
phenotype. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 16, 359–367.
(256) Turesky, R. J. (2004) The role of genetic polymorphisms in
metabolism of carcinogenic heterocyclic aromatic amines. Curr. Drug
Metab. 5, 169–180.
(257) Lin, D.-X., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1995) Species
differences in the biotransformation of the food-borne carcinogen
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by hepatic micro-
somes and cytosols from humans, rats, and mice. Drug Metab. Dispos.
23, 518–524.
(258) Kimura, S., Kawabe, M., Yu, A., Morishima, H., Fernandez-
Salguero, P., Hammons, G. J., Ward, J. M., Kadlubar, F. F., and Gonzalez,
F. J. (2003) Carcinogenesis of the food mutagen PhIP in mice is
independent of CYP1A2. Carcinogenesis 24, 583–587.
(259) Kimura, S., Kawabe, M., Ward, J. M., Morishima, H., Kadlubar,
F. F., Hammons, G. J., Fernandez-Salguero, P., and Gonzalez, F. J. (1999)
CYP1A2 is not the primary enzyme responsible for 4-aminobiphenyl-
induced hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Carcinogenesis 20, 1825–1830.
(260) Guengerich, F. P. (1997) Comparisons of catalytic selectivity
of cytochrome P450 subfamily members from differe nt species. Chem.-Biol.
Interact. 106, 161–182.
(261) Turesky, R. J., Parisod, V., Huynh-Ba, T., Langou€et, S., and
Guengerich, F. P. (2001) Regioselective differences in C(8)- and
N-oxidation of 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline by hu-
man and rat liver microsomes and cytochromes P450 1A2. Chem. Res.
Toxicol. 14, 901–911.
(262) Langou€et, S., Welti, D. H., Kerriguy, N., Fay, L. B., Huynh-Ba,
T., Markovic, J., Guengerich, F. P., Guillouzo, A., and Turesky, R. J.
(2001) Metabolism of 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline
in human hepatocytes: 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline-8-
carboxylic acid is a major detoxification pathway catalyzed by cyto-
chrome P450 1A2. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 14, 211–221.
(263) Turesky, R. J., Aeschbacher, H. U., W€urzner, H. P., Skipper,
P. L., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (1988) Major routes of metabolism of the
food-borne carcinogen 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline
in the rat. Carcinogenesis 9
, 1043–1048.
(264) Turesky, R. J., Garner, R. C., Welti, D. H., Richoz, J., Leveson,
S. H., Dingley, K. H., Turteltaub, K. W., and Fay, L. B. (1998)
Metabolism of the food-borne mutagen 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-
[4,5-f]quinoxaline in humans. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 11, 217–225.
(265) Wallin, H., Holme, J. A., Becher, G., and Alexander, J. (1989)
Metabolism of the food carcinogen 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]-
quinoxaline in isolated rat liver cells. Carcinogenesis 10, 1277–1 283.
(266) Niwa, T., Yamazoe, Y., and Kato, R. (1982) Metabolic
activation of 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole by rat-liver microsomes.
Mutat. Res. 95, 159–170.
(267) Yamazoe, Y., Kamataki, T., and Kato, R. (1981) Species
difference in N-hydroxylation of a tryptophan pyrolysis product in
relation to mutagenic activation. Cancer Res. 41, 4518–4522.
(268) Yamazoe, Y., Shimada, M., Kamataki, T., and Kato, R. (1983)
Microsomal activation of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline, a
pyrolysate of sardine and beef extracts, to a mutagenic intermediate.
Cancer Res. 43, 5768–5774.
(269) Yamazoe, Y., Abu-Zeid, M., Manabe, S., Toyama, S., and Kato,
R. (1988) Metabolic activation of a protein pyrolysate promutagen
2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline by rat liver microsomes
and purified cytochrome P-450. Carcinogenesis 9, 105–109.
(270) Raza, H., King, R. S., Squires, R. B., Guengerich, F. P., Miller,
D. W., Freeman, J. P., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1996)
Metabolism of 2-amino-alpha-carboline. A food-borne heterocyclic
amine mutagen and carcinogen by human and rodent liver microsomes
and by human cytochrome P4501A2. Drug Metab. Dispos. 24, 395–400.
(271) King, R. S., Teitel, C. H., and Kadlubar, F. F. (2000) In vitro
bioactivation of N-hydroxy-2-amino-alpha-carboline. Carcinogenesis
21, 1347–1354.
(272) Turesky, R. J., Guengerich, F. P., Guillouzo, A., and Langouet,
S. (2002) Metabolism of heterocyclic aromatic amines by human
hepatocytes and cytochrome P4501A2. Mutat. Res. 506-507, 187–195.
(273) Frederiksen, H., and Frandsen, H. (2002) In vitro metabolism of
two heterocyclic amines, 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(A(alpha)C)
and 2-amino-3-methyl-9H-pyridol2,3-b]indole(MeA(alpha)C) in human
and rat hepatic microsomes. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 90, 127
–134.
(274) Luks, H. J., Spratt, T. E., Vavrek, M. T., Roland, S. F., and
Weisburger, J. H. (1989) Identification of sulfate and glucuronic acid
conjugates of the 5-hydroxy derivative as major metabolites of 2-amino-
3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in rats. Cancer Res. 49, 4407–4411.
(275) Snyderwine, E. G., Welti, D. H., Fay, L. B., W€urzner, H. P., and
Turesky, R. J. (1992) Metabolism of the food-mutagen 2-amino-3-
methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in nonhuman primates undergoing car-
cinogen bioassay. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 5, 843–851.
(276) Snyderwine, E. G., Buonarati, M. H., Felton, J. S., and
Turteltaub, K. W. (1993) Metabolism of the food-derived mutagen/
carcinogen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP)
in nonhuman primates. Carcinogenesis 13, 2517–2522.
(277) Turesky, R. J., Gross, G. A., Stillwell, W. G., Skipper, P. L., and
Tannenbaum, S. R. (1994) Species diff erences in metabolism of
heterocyclic aromatic amines, human exposure, and biomonitoring.
Environ. Health Perspect. 102 (Suppl 6), 47–51.
(278) Malfatti, M. A., Buonarati, M. H., Turteltaub, K. W., Shen,
N. H., and Felton, J. S. (1994) The role of sulfation and/or acetylation in
the metabolism of the cooked-food mutagen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in Salmonela typhimurium and isolated
rat hepatocytes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 7, 139–147.
(279) Frederiksen, H., and Frandsen, H. (2004) Excretion of
metabolites in urine and faeces from rats dosed with the heterocyclic
amine, 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(ARC). Food Chem. Toxicol.
42, 879–885.
(280) Chen, C., Ma, X., Malfatti, M. A., Krausz, K. W., Kimura, S.,
Felton, J. S., Idle, J. R., and Gonzalez, F. J. (2007) A comprehensive
investigation of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-
(PhIP) metabolism in the mouse using a multivariate data analysis
approach. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 20, 531–542.
(281) Lakshmi, V. M., Hsu, F. F., and Zenser, T. V. (2008) N-
Demethylation is a major route of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-
f]quinoline metabolism in mouse. Drug Metab. Dispos. 36, 1143–1152.
(282) Turesky, R. J., Bracco-Hammer, I., Markovic, J., Richli, U.,
Kappeler, A.-M., and Welti, D. H. (1990) The contribution of N-oxida-
tion to the metabolism of the food-borne carcinogen 2-amino-3,8-
dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline in rat hepatocytes. Chem. Res. Tox-
icol. 3, 524–535.
(283) Yuan, Z. X., Jha, G., McGregor, M. A., and King, R. S. (2007)
Metabolites of the carcinogen 2-amino-alpha-carboline formed in male
Sprague-Dawley rats in vivo and in rat hepatocyte and human HepG2
cell incubates. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 20, 497–503.
(284) Langou€et, S., Paehler, A., Welti, D. H., Kerriguy, N., Guillouzo,
A., and Turesky, R. J. (2002) Differential metabolism of 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in rat and human hepatocytes.
Carcinogenesis 23, 115–122.
(285) Stillwell, W. G., Turesky, R. J., Gross, G. A., Skipper, P. L., and
Tannenbaum, S. R. (1994) Human urinary excretion of sulfamate and
glucuronde conjugates of 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimdazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline-
(MeIQx). Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 3, 399–405.
(286) Stillwell, W. G., Kidd, L.-C.K.S.-B., Wishnok, J. W., Tannenbaum,
S. R., and Sinha, R. (1997) Urinary excretion of unmetabolized and phase II
conjugates of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine and
2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline in humans: Relationship
to cytochrome P450 1A2 and N-acetyltransferase actvity. Cancer Res.
57, 3457–3464.
(287) Malfatti, M. A., Kulp, K. S., Knize, M. G., Davis, C., Massengill,
J. P., Williams, S., Nowell, S., MacLeod, S., Dingley, K. H., Turteltaub,
1203 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
K. W., Lang, N. P., and Felton, J. S. (1999) The identification of
[2-
14
C]2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine metabolites
in humans. Carcinogenesis 20, 705–713.
(288) Stillwell, W. G., Turesky, R. J., Sinha, R., and Tannenbaum,
S. R. (1999) N-oxidative metabolism of 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-
f]quinoxaline(MeIQx) in humans: excretion of the N
2
-glucuronide con-
jugate of 2-hydroxyamino-MeIQx in urine. Cancer Res. 59, 5154–5159.
(289) Stillwell, W. G., Sinha, R., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (2002)
Excretion of the N
2
-glucuronide co njugate o f 2-hy droxyam ino-1-me thyl-6 -
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in urine and its relationship to CYP1A2 and
NAT2 activity levels in humans. Carcinogenesis 23, 831–838.
(290) Kulp, K. S., Knize, M. G., Malfatti, M. A., Salmon, C. P., and
Felton, J. S. (2000) Identi fication of urine metabolites of 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine following consumption of a
single cooked chicken meal in humans. Carcinogenesis 21, 2065–2072.
(291) Strickland, P. T., Qian, Z., Friesen, M. D., Rothman, N., and
Sinha, R. (2002) Metabolites of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in human urine after consumption of charbroiled
or fried beef. Mutat. Res. 506-507, 163–173.
(292) Frandsen, H. (2008) Biomonitoring of urinary metabolites of
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) following human
consumption of cooked chicken. Food Chem. Toxicol. 46, 3200–3205.
(293) Fede, J. M., Thakur, A. P., Gooderham, N. J., and Turesky, R. J.
(2009) Biomonitoring of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine(PhIP) and its carcinogenic metabolites in urine. Chem. Res.
Toxicol. 22, 1096–1105.
(294) Edwards, R. J., Murray, B. P., Murray, S., Schulz, T., Neubert,
D., Gant, T. W., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Boobis, A. R., and Davies, D. S. (1994)
Contribution of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 to the activation of heterocyclic
amines in monkeys and humans. Carcinogenesis 15, 829–836.
(295) Barnes, W. S., Lovelette, C. A., Tong, C., Williams, G. M., and
Weisburger, J. H. (1985) Genotoxicity of the food mutagen 2-amino-3-
methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(IQ) a nd analogs. Carcinogenesis 6, 441–444.
(296) Van Tassell, R. L., Kingston, D. G., and Wilkins, T. D. (1990)
Metabolism of dietary genotoxins by the human colonic microflora; the
fecapentaenes and heterocyclic amines. Mutat. Res. 238, 209–221.
(297) Weisburger, J. H., Rivenson, A., Kingston, D. G., Wilkins,
T. D., Van Tassell, R. L., Nagao, M., Sugimura, T., and Hara, Y. (1995)
Dietary modulation of the carcinogenicity of the heterocyclic amines. Princess
Takamatsu Symp. 23, 240–250.
(298) Hammons, G. J., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1987) The Role of
Cytochrome P-450 in the Metabolism of Carcinogens, in Mammalian
Cytochromes P-450 (Guengerich, F. P., Ed.) pp 81- 130, CRC Press,
Boca Raton, FL.
(299) Hammons, G. J., Dooley, K. L., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1991) 4-
Aminobiphenyl-hemoglobin adduct formation as an index of in vivo N-oxi-
dation by hepatic cytochrome P-450IA2. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 4,144–147.
(300) Kunze, K. L., and Trager, W. F. (1993) Isoform-selective
mechanism-based inhibition of human cytochrome P450 1A2 by furafyl-
line. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 6
, 649–656.
(301) Boobis, A. R., Lynch, A. M., Murray, S., de la Torre, R., Solans, A.,
Farr ee, M.,Segura, J.,Gooderham, N. J.,and Davies,D.S.(1994)CYP1A2-
catalyzed conversion of dietary heterocyclic amines to their proximate car-
cinogens is their major route of metabolism in humans. Cancer Res. 54,89–94.
(302) Snyderwine, E. G., Yu, M., Schut, H. A., Knight-Jones, L., and
Kimura, S. (2002) Effect of CYP1A2 deficiency on heterocyclic amine
DNA adduct levels in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 40, 1529–1533.
(303) Shertzer, H. G., Dalton, T. P., Talaska, G., and Nebert, D. W.
(2002) Decrease in 4-aminobiphenyl-induced methemoglobinemia in
Cyp1a2(-/-) knockout mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 181,32–37.
(304) Tsuneoka, Y., Dalton, T. P., Miller, M. L., Clay, C. D., Shertzer,
H. G., Talaska, G., Medvedovic, M., and Nebert, D. W. (2003) 4-
aminobiphenyl-induced liver and urinary bladder DNA adduct forma-
tion in Cyp1a2(-/-) and Cyp1a2(þ/þ) mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.
95, 1227–1237.
(305) Ma, Q., and Lu, A. Y. (2007) CYP1A induction and human
risk assessment: an evolving tale of in vitro and in vivo studies. Drug
Metab. Dispos. 35, 1009–1016.
(306) Cheung, C., Ma, X., Krausz, K. W., Kimura, S., Feigenbaum, L.,
Dalton, T. P., Nebert, D. W., Idle, J. R., and Gonzalez, F. J. (2005)
Differential metabolism of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine(PhIP) in mice humanized for CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. Chem.
Res. Toxicol. 18, 1471–1478.
(307) Zenser, T. V., Mattammal, M. B., Armbrecht, H. J., and Davis,
B. B. (1980) Benzidine binding to nucleic acids mediated by the
peroxidative activity of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase. Cancer
Res. 40, 2839–2845.
(308) Kadlubar, F. F., Frederick, C. B., Weis, C. C., and Zenser, T. V.
(1982) Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase-mediated metabolism of
carcinogenic aromatic amines and their binding to DNA and protein.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 108, 253–258.
(309) Wise, R. W., Zenser, T. V., Kadlubar, F. F., and Davis, B. B.
(1984) Metabolic activation of carcinogenic aromatic amines by dog
bladder and kidney prostaglandin H synthase. Cancer Res.
44, 1893–1897.
(310) Boyd, J. A., and Eling, T. E. (1985) Metabolism of aromatic
amines by prostaglandin H synthase. Environ. Health Perspect. 64,45–51.
(311) Boyd, J. A., and Eling, T. E. (1987) Prostaglandin H synthase-
catalyzed metabolism and DNA binding of 2-naphthylamine. Cancer Res.
47, 4007–4014.
(312) Flammang, T. J., Yamazoe, Y., Benson, R. W., Roberts, D. W.,
Potter, D. W., Chu, D. Z., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1989)
Arachidonic acid-dependent peroxidative activation of carcinogenic
arylamines by extrahepatic human tissue microsomes. Cancer Res.
49, 1977–1982.
(313) Wolz, E., Wild, D., and Degen, G. H. (1995) Prostaglandin-H
synthase mediated metabolism and mutagenic activation of 2-amino-3-
methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(IQ). Arch. Toxicol. 69, 171–179.
(314) Josephy, P. D. (1996) The role of peroxidase-catalyzed
activation of aromatic amines in breast cancer. Mutagenesis 11,3–7.
(315) Degen, G. H., Wolz, E., Gerber, M., and Pfau, W. (1998)
Bioactivation of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(IQ) by
prostaglandin H synthase. Arch. Toxicol. 72, 183–186.
(316) Wolz, E., Pfau, W., and Degen, G. H. (2000) Bioactivation of
the food mutagen 2-amino-3-methyl-imidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(IQ) by
prostaglandin-H synthase and by monooxygenases: DNA adduct anal-
ysis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 38, 513–522.
(317) Wiese, F. W., Thompson, P. A., and Kadlubar, F. F. (2001)
Carcinogen substrate specificity of human COX-1 and COX-2. Carci-
nogenesis 22,5–10.
(318) Zenser, T. V., Lakshmi, V. M., Hsu, F. F., and Davis, B. B.
(2002) Metabolism of N-acetylbenzidine and initiation of bladder
cancer. Mutat. Res. 506-507,29–40.
(319) Yamazoe, Y., Miller, D. W., Weis, C. C., Dooley, K. L., Zenser,
T. V., Beland, F. A., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1985) DNA adducts formed by ring-
oxidation of the carcinogen 2-naphthylamine with prostaglandin H synthase
in vitro and in the dog urothelium in vivo. Carcinogenesis 6, 1379–1387.
(320) Lakshmi, V. M., Zenser, T. V., and Davis, B. B. (1998) N
0
-(3
0
-
monophospho-deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-N-acetylbenzidine formation by
peroxidative metabolism. Carcinogenesis 19, 911–917.
(321) Williams, J. A., Stone, E. M., Millar, B. C., Hewer, A., and
Phillips, D. H. (2000) Pathways of heterocyclic amine activation in the
breast: DNA adducts of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(IQ)
formed by peroxidases and in human mammary epithelial cells and
fibroblasts. Mutagenesis 15, 149–154.
(322) Gorlewska-Roberts, K. M., Teitel, C. H., Lay, J. O., Jr., Roberts,
D. W., and Kadlubar, F. F. (2004) Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed activation
of carcinogenic aromatic and heterocyclic amines. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
17, 1659–1666.
(323) Hein, D. W., Doll, M. A., Fretland, A. J., Leff, M. A., Webb, S. J.,
Xiao, G. H., Devanaboyina, U. S., Nangju, N. A., and Feng, Y. (2000)
Molecular genetics and epidemiology of the NAT1 and NAT2 acetyla-
tion polymorphisms. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 9,29–42.
(324) Hein, D. W. (2002) Molecular genetics and function of NAT1
and NAT2: role in aromatic amine metabolism and carcinogenesis.
Mutat. Res. 506-507,65–77.
1204 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(325) Blum, M., Demierre, A., Grant, D. M., Heim, M., and Meyer,
U. A. (1991) Molecular mechanism of slow acetylation of drugs and
carcinogens in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 5237–5241.
(326) Hein, D. W. (2006) N-acetyltransferase 2 genetic polymorph-
ism: effects of carcinogen and haplotype on urinary bladder cancer risk.
Oncogene 25, 1649–1658.
(327) Lang, N. P., Butler, M. A., Massengill, J. P., Lawson, M., Stotts,
R. C., Hauer-Jensen, M., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1994) Rapid metabolic
phenotypes for acetyltransferase and cytochrome P4501A2 and putative
exposure to food-borne heterocyclic amines increase the risk for color-
ectal cancer or polyps. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 3, 675–682.
(328) Le Marchand, L., Hankin, J. H., Pierce, L. M., Sinha, R.,
Nerurkar, P. V., Franke, A. A., Wilkens, L. R., Kolonel, L. N., Donlon, T.,
Seifried, A., Custer, L. J., Lum-Jones, A., and Chang, W. (2002) Well-
done red meat, metabolic phenotypes and colorectal cancer in Hawaii.
Mutat. Res. 506- 507, 205–214.
(329) Cohen, S. M., Boobis, A. R., Meek, M. E., Preston, R. J., and
McGregor, D. B. (2006) 4-Aminobiphenyl and DNA reactivity: case
study within the context of the 2006 IPCS Human Relevance Frame-
work for Analysis of a cancer mode of action for humans. Crit Rev.
Toxicol. 36, 803–819.
(330) Lakshmi, V. M., Zenser, T. V., and Davis, B. B. (1997) Rat liver
cytochrome P450 metabolism of N-acetylbenzidine and N,N
0
-diacetyl-
benzidine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 25, 481–488.
(331) Zenser, T. V., Lakshmi, V. M., Rustan, T. D., Doll, M. A., Deitz,
A. C., Davis, B. B., and Hein, D. W. (1996) Human N-acetylation of
benzidine: role of NAT1 and NAT2. Cancer Res. 56, 3941–3947.
(332) Rothman, N., Bhatnagar, V. K., Hayes, R. B., Zenser, T. V.,
Kashyap, S. K.,Butler, M. A.,Bell, D. A.,Lakshmi,V., Jaeger, M., Kashyap, R.,
Hirvonen, A., Schulte, P. A., Dosemeci, M., Hsu, F., Parikh, D. J., Davis, B. B.,
and Talaska, G. (1996) The impact of interindividual variation in NAT2
activity on benzidine urinary metabolites and urothelial DNA adducts in
exposed workers. Proc.Natl. Acad. Sci.U.S.A.93, 5084–5089.
(333) Flammang, T. J., Yamazoe, Y., Guengerich, F. P., and Kadlubar,
F. F. (1987) The S-acetyl coenzyme A-dependent metabolic activation of
the carcinogen N-hydroxy-2-aminofluorene by human liver cytosol and its
relationship to the aromatic amine N-acetyltransferase phenotype. Carcino-
genesis 8, 1967–1970.
(334) Hein, D. W., Rustan, T. D., Ferguson, R. J., Doll, M. A., and
Gray, K. (1994) Metabolic activation of aromatic and heterocylic
N-hydroxyarylamines by wild-type and mutant recombinant human
NAT1 and NAT2 acetyltransferases. Arch. Toxicol. 68, 129–133.
(335) Minchin, R. F., Reeves, P. T., Teitel, C. H., McManus, M. E.,
Mojarrabi, B., Ilett, K. F., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1992) N- and
O-acetylation of aromatic and hetercyclic amine carcinogens by human
monomorphic and polymorphic acetyltransferases expressed in COS-1
cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 185, 839–844.
(336) Sugamori, K. S., Brenneman, D., and Grant, D. M. (2006) In
vivo and in vitro metabolism of arylamine procarcinogens in acetyl-
transferase-deficient mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 34, 1697–1702.
(337) Metry, K. J., Neale, J. R., Bendaly, J., Smith, N. B., Pierce,
W. M., Jr., and Hein, D. W. (2009) Effect of N-acetyltransferase 2
polymorphism on tumor target tissue DNA adduct levels in rapid and
slow acetylator congenic rats administered 2-amino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine or 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-
f]quinoxaline. Drug Metab. Dispos. 37, 2123–2126.
(338) Steffensen, I. L., Fretland, A. J., Paulsen, J. E., Feng, Y., Eide,
T. J., Devanaboyina, U. S., Hein, D. W., and Alexander, J. (2000) DNA
adduct levels and intestinal lesions in congenic rapid and slow acetylator
Syrian hamsters administered food mutagens 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenyl-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) or 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quino-
line(IQ). Pharmacol. Toxicol. 86, 257–263.
(339) Turesky, R. J., Lang, N. P., Butler, M. A., Teitel, C. H., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1991) Metabolic activation of carcinogenic heterocyclic
aromatic amines by human liver and colon.
Carcinogenesis 12, 1839–1845.
(340) Lin, D., Kaderlik, K. R., Turesky, R. J., Miller, D. W., Lay, J. O.,
Jr., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1992) Identification of N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine as the major adduct
formed by the food-borne carcinogen, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenyl-
imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine, with DNA. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 5, 691–697.
(341) Frandsen, H., Grivas, S., Andersson, R., Dragsted, L., and
Larsen, J. C. (1992) Reaction of the N
2
-acetoxy derivative of 2-amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) with 2
0
-deoxyguanosine
and DNA. Synthesis and identification of N
2
-(2
0
-deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-
PhIP. Carcinogenesis 13, 629–635.
(342) Wu, R. W., Tucker, J. D., Sorensen, K. J., Thompson, L. H., and
Felton, J. S. (1997) Differential effect of acetyltransferase expression on
the genotoxicity of heterocyclic amines in CHO cells. Mutat. Res.
390,93–103.
(343) Metry, K. J., Zhao, S., Neale, J. R., Doll, M. A., States, J. C.,
McGregor, W. G., Pierce, W. M., Jr., and Hein, D. W. (2007) 2-Amino-1-
methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-induced DNA adducts and
genotoxicity in Chinese hamster ovary(CHO) cells expressing human
CYP1A2 and rapid or slow acetylator N-acetyltransferase 2. Mol.
Carcinog. 46, 553–563.
(344) Wild, D., Feser, W., Michel, S., Lord, H. L., and Josephy, P. D.
(1995) Metabolic activation of heterocyclic aromatic amines catalyzed
by human arylamine N-acetyltransferase isozymes(NAT1 and NAT2)
expressed in Salmonella typhimurium. Carcinogenesis 16, 643–648.
(345) Muckel, E., Frandsen, H., and Glatt, H. R. (2002) Hetero-
logous expression of human N-acetyltransferases 1 and 2 and sulfo-
transferase 1A1 in Salmonella typhimurium for mutagenicity testing of
heterocyclic amines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 40, 1063–1068.
(346) Wu, R. W., Panteleakos, F. N., Kadkhodayan, S., Bolton-Grob,
R., McManus, M. E., and Felton, J. S. (2000) Genetically modified
Chinese hamster ovary cells for investigating sulfotransferase-mediated
cytotoxicity and mutation by 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 35,57–65.
(347) Bendaly, J., Zhao, S., Neale, J. R., Metry, K. J., Doll, M. A.,
States, J. C., Pierce, W. M., Jr., and Hein, D. W. (2007) 2-Amino-3,8-
dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline-induced DNA adduct formation
and mutagenesis in DNA repair-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells
expressing human cytochrome P4501A1 and rapid or slow acetylator
N-acetyltransferase 2. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 16, 1503–1509.
(348) Turesky, R. J., Bendaly, J., Yasa, I., Doll, M. A., and Hein, D. W.
(2009) The impact of NAT2 acetylator genotype on mutagenesis and
DNA adducts from 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole. Chem. Res. Tox-
icol. 22, 726–733.
(349) Garcia-Closas, M., Malats, N., Silverman, D., Dosemeci, M.,
Kogevinas, M.,Hein, D. W.,Tardon,A., Serra,C., Carrato,A., Garcia-
Closas, R., Lloreta, J., Castano-Vinyals, G., Yeager, M., Welch, R., Chanock,
S.,Chatterjee,N., Wacholder, S.,Samanic,C., Tora,M., Fernandez, F.,Real,
F. X., and Rothman, N. (2005) NAT2 slow acetylation, GSTM1 null
genotype, and risk of bladder cancer: results from the Spanish Bladder
Cancer Study and meta-analyses. Lancet 366, 649–659.
(350) Shinohara, A., Yamazoe, Y., Saito, K., Kamataki, T., and Kato,
R. (1984) Species differences in the N-acetylation by liver cytosol of
mutagenic heterocyclic aromatic amines in protein pyrolysates. Carci-
nogenesis 5, 683–686.
(351) Shinohara, A., Saito, K., Yamazoe, Y., Kamataki, T., and Kato,
R. (1986) Acetyl coenzyme A dependent activation of N-hydroxy
derivatives of carcinogenic arylamines: Mechanism of activation, species
diff
rences, tissue distribution, and acetyl donor specificty. Cancer Res.
46, 4362–4367.
(352) Blanchard, R. L., Freimuth, R. R., Buck, J., Weinshilboum,
R. M., and Coughtrie, M. W. (2004) A proposed nomenclature system
for the cytosolic sulfotransferase(SULT) superfamily. Pharmacogenetics
14, 199–211.
(353) Nowell, S., and Falany, C. N. (2006) Pharmacogenetics of
human cytosolic sulfotransferases. Oncogene 25, 1673–1678.
(354) Hempel, N., Gamage, N., Martin, J. L., and McManus, M. E.
(2007) Human cytosolic sulfotransferase SULT1A1. Int. J. Biochem. Cell
Biol. 39, 685–689.
(355) Teubner, W., Meinl, W., Florian, S., Kretzschmar, M., and
Glatt, H. (2007) Identification and localization of soluble sulfotrans-
ferases in the human gastrointestinal tract. Biochem. J. 404, 207–215.
1205 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(356) Gamage, N., Ba rnett, A., Hempel, N., Duggleby, R. G .,
Windmill,K.F., Martin,J.L., andMcManus, M.E.(2006) Human
sulfotransferases and their role in chemical metabolism. Toxicol. Sci.
90,5–22.
(357) Turesky, R. J., Skipper, P. L., Tannenbaum, S. R., Coles, B., and
Ketterer, B. (1986) Sulfamate formation is a major route for detoxifica-
tion of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in the rat. Carcinogen-
esis 7, 1483–1485.
(358) Turesky, R. J., Aeschbacher, H. U., Malnoe, A., and W€urzner,
H. P. (1988) Metabolism of the food-borne mutagen/carcinogen
2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline in the rat: assessment
of biliary metabolties for genotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 26, 105–110.
(359) Ozawa, S., Nagata, K., Yamazoe, Y., and Kato, R. (1995)
Formation of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline- and 2-amino-
3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline-sulfamates by cDNA-expressed
mammalian phenol sulfotransferases. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 86, 264–269.
(360) Boyland, E., Manson, D., and Orr, S. F. (1957) The biochem-
istry of aromatic amines. II. The conversion of arylamines into arylsulphamic
acids and arylamine-N-glucosiduronic acids. Biochem. J. 65, 417–423.
(361) Chou, H. C., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1995)
Metabolic activation of N-hydroxy arylamines and N-hydroxy hetero-
cyclic amines by human sulfotransferase(s). Cancer Res. 55, 525–529.
(362) Yamazoe, Y., Nagata, K., Ozawa, S., Gong, D. W., and Kato, R.
(1995) Activation and detoxication of carcinogenic arylamines by
sulfation. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 23, 154–162.
(363) Abu-Zeid, M., Yamazoe, Y., and Kato, R. (1992) Sulfotrans-
ferase-mediated DNA binding of N-hydroxyarylamines(amide) in liver
cytosols from human and experimental animals. Carcinogenesis
13, 1307–1314.
(364) Di Paolo, O. A., Teitel, C. H., Nowell, S., Coles, B. F., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (2005) Expression of cytochromes P450 and glutathione
S-transferases in human prostate, and the potential for activation of
heterocyclic amine carcinogens via acetyl-coA-, PAPS- and ATP-depen-
dent pathways. Int. J. Cancer 117,8–13.
(365) Williams, J. A., Stone, E. M., Fakis, G., Johnson, N., Cordell,
J. A., Meinl, W., Glatt, H., Sim, E., and Phillips, D. H. (2001) N-
Acetyltransferases, sulfotransferases and heterocyclic amine activation in
the breast. Pharmacogenetics 11, 373–388.
(366) Williams, J. A. (2001) Single nucleotide polymorphisms,
metabolic activation and environmental carcinogenesis: why molecular
epidemiologists should think about enzyme expression. Carcinogenesis
22, 209–214.
(367) Lewis, A. J., Walle, U. K., King, R. S., Kadlubar, F. F., Falany,
C. N., and Walle, T. (1998) Bioactivation of the cooked food mutagen
N-hydroxy-2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by es-
trogen sulfotransferase in cultured human mammary epithelial cells.
Carcinogenesis 19, 2049
–2053.
(368) Ozawa, S., Shimizu, M., Katoh, T., Miyajima, A., Ohno, Y.,
Matsumoto, Y., Fukuoka, M., Tang, Y. M., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar,
F. F. (1999) Sulfating-activity and stability of cDNA-expressed allo-
zymes of human phenol sulfotransferase, ST1A3*1((213)Arg) and
ST1A3*2((213)His), both of which exist in Japanese as well as
Caucasians. J. Biochem.(Tokyo) 126, 271–277.
(369) Carlini, E. J., Raftogianis, R. B., Wood, T. C., Jin, F., Zheng, W.,
Rebbeck, T. R., and Weinshilboum, R. M. (2001) Sulfation pharmaco-
genetics: SULT1A1 and SULT1A2 allele frequencies in Caucasian,
Chinese and African-American subjects. Pharmacogenetics 11,57–68.
(370) Bamber, D. E., Fryer, A. A., Strange, R. C., Elder, J. B., Deakin,
M., Rajagopal, R., Fawole, A., Gilissen, R. A., Campbell, F. C., and
Coughtrie, M. W. (2001) Phenol sulphotransferase SULT1A1*1 geno-
type is associated with reduced risk of colorectal cancer. Pharmacoge-
netics 11, 679–685.
(371) Zheng, W., Xie, D., Cerhan, J. R., Sellers, T. A., Wen, W., and
Folsom, A. R. (2001) Sulfotransferase 1A1 polymorphism, endogenous
estrogen exposure, well-done meat intake, and breast cancer risk. Cancer
Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 10,89–94.
(372) Moreno, V., Glatt, H., Guino, E., Fisher, E., Meinl, W.,
Navarro, M., Badosa, J. M., and Boeing, H. (2005) Polymorphisms in
sulfotransferases SULT1A1 and SULT1A2 are not related to colorectal
cancer. Int. J. Cancer 113, 683–686.
(373) Steiner, M., Bastian, M., Schulz, W. A., Pulte, T., Franke, K. H.,
Rohring, A., Wolff, J. M., Seiter, H., and Schuff-Werner, P. (2000)
Phenol sulphotransferase SULT1A1 polymorphism in prostate cancer:
lack of association. Arch. Toxicol. 74, 222–225.
(374) Vineis, P., and McMichael, A. (1996) Interplay between
heterocyclic amines in cooked meat and metabolic phenotype in the
etiology of colon cancer. Cancer Causes Control 7, 479–486.
(375) Burchell, B. (2003) Genetic variation of human UDP-glucur-
onosyltransferase: implications in disease and drug glucuronidation. Am.
J. Pharmacogenomics. 3,37–52.
(376) Guillemette, C. (2003) Pharmacogenomics of human UDP-
glucuronosyltransferase enzymes. Pharmacogenomics J. 3, 136–158.
(377) Nagar, S., and Remmel, R. P. (2006) Uridine diphosphoglucur-
onosyltransferase pharmacogenetics and cancer. Oncogene 25, 1659–1672.
(378) Green, M. D., and Tephly, T. R. (1996) Glucuronidation of
amines and hydroxylated xenobiotics and endobiotics catalyzed by
expressed human UGT1.4 protein. Drug Metab. Dispos. 24, 356–363.
(379) Green, M. D., and Tephly, T. R. (1998) Glucuronidation of
amine substrates by purified and expressed UDP-glucuronosyltransfer-
ase proteins. Drug Metab. Dispos. 26, 860–867.
(380) Ciotti, M., Lakshmi, V. M., Basu, N., Davis, B. B., Owens, I. S.,
and Zenser, T. V. (1999) Glucuronidation of benzidine and its meta-
bolites by cDNA-expressed human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and
pH stability of glucuronides. Carcinogenesis 20, 1963–1969.
(381) Al-Zoughool, M., and Talaska, G. (2006) 4-Aminobiphenyl
N-glucuronidation by liver microsomes: optimization of the reaction
conditions and characterization of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
isoforms. J. Appl. Toxicol. 26, 524–532.
(382) Orzechowski, A., Schrenk, D., Bock-Hennig, B. S., and Bock,
K. W. (1994) Glucuronidation of carcinogenic arylamines and their
N-hydroxy derivatives by rat and human phenol UDP-glucuronosyl-
transferase of the UGT1 gene complex. Carcinogenesis 15, 1549–1553.
(383) Kadlubar, F. F., Miller, J. A., and Miller, E. C. (1977) Hepatic
microsomal N-glucuronidation and nucleic acid binding of N-hydroxy aryl-
amines in rela tion to urinary bladder carcinogenesi s. Cancer Res. 37,805–814.
(384) Babu, S. R., Lakshmi, V. M., Hsu, F. F., Zenser, T. V., and
Davis, B. B. (1995) Glucuronidation of N-hydroxy metabolites of
N-acetylbenzidine. Carcinogenesis 16, 3069–3074.
(385) Babu, S. R., Lakshmi, V. M., Huang, G. P., Zenser, T. V., and
Davis, B. B. (1996) Glucuronide conjugates of 4-aminobiphenyl and its
N-hydroxy metabolites. pH stability and synthesis by human and dog
liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 51, 1679–1685.
(386) Zenser, T. V., Lakshmi, V. M., and Davis, B. B. (1998) N-
glucuronidation of benzidine and its metabolites. Role in bladder cancer.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 26, 856–859.
(387) Irving, C. C. (1981) Glucuronide formation in the metabolism
of N-substituted aryl compounds. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr 58, 109–111.
(388) Radomski, J. L., Hearn, W. L., Radomski, T., Moreno, H., and
Scott, W. E. (1977) Isolation of the glucuronic acid conjugate of N-hydroxy-4-
aminobiphenyl from dog urine and its mutagenic activity. Cancer Res. 37,
1757–1762.
(389) Mulder, G. J., and Meerman, J. H. (1983) Sulfation and
glucuronidation as competing pathways in the metabolism of hydro-
xamic acids: the role of N,O-sulfonation in chemical carcinogenesis of
aromatic amines. Environ. Health Perspect. 49,27–32.
(390) Skipper, P. L., Obiedzinski, M. W., Tannenbaum, S. R., Miller,
D. W., Mitchum, R. K., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1985) Identification of the
major serum albumin adduct formed by 4-aminobiphenyl in vivo in rats.
Cancer Res. 45, 5122–5127.
(391) Tannenbaum, S. R., Skipper, P. L., Wishnok, J. S., Stillwell,
W. G., Day, B. W., and Taghizadeh, K. (1993) Characterization of
various classes of protein adducts. Environ. Health Perspect. 99,51–55.
(392) Styczynski, P. B., Blackmon, R. C., Groopman, J. D., and Kensler,
T. W. (1993) The direct glucuronidation of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) by human and rabbit liver microsomes.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 6,846–851.
1206 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(393) Alexander, J., Wallin, H., Rossland, O. J., Solberg, K. E.,
Holme, J. A., Becher, G., Andersson, R., and Grivas, S. (1991) Formation
of a glutathione conjugate and a semistable transportable glucuronide
conjugate of N
2
-oxidized species of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in rat liver. Carcinogenesis 12, 2239–2245.
(394) Kaderlik, K. R., Mulder, G. J., Turesky, R. J., Lang, N. P., Teitel,
C. H., Chiarelli, M. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1994) Glucuronidation of
N-hydroxy heterocyclic amines by human and rat liver microsomes.
Carcinogenesis 15, 1695–1701.
(395) Snyderwine, E. G., Welti, D. H., Davis, C. D., Fay, L. B., and
Turesky, R. J. (1995) Metabolism of the food-derived carcinogen
2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline(MeIQx) in nonhuman
primates. Carcinogenesis 16, 1377–1384.
(396) Malfatti, M. A., and Felton, J. S. (2001) N-glucuronidation of
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) and N-hy-
droxy-PhIP by specific human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Carcino-
genesis 22, 1087–1093.
(397) Malfatti, M. A., and Felton, J. S. (2004) Human UDP-
glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 is the primary enzyme responsible for the
N-glucuronidation of N-hydroxy-PhIP in vitro. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
17, 1137–1144.
(398) Girard, H., Thibaudeau, J., Court, M. H., Fortier, L. C.,
Villeneuve, L., Caron, P., Hao, Q., von Moltke, L. L., Greenblatt, D. J.,
and Guillemette, C. (2005) UGT1A1 polymorphisms are important
determinants of dietary carcinogen detoxification in the liver. Hepatology
42, 448–457.
(399) Strassburg, C. P., Strassburg, A., Nguyen, N., Li, Q., Manns,
M. P., and Tukey, R. H. (1999) Regulation and function of family 1 and
family 2 UDP-glucuronosyltransferase genes(UGT1A, UGT2B) in hu-
man oesophagus. Biochem. J. 338 (Pt 2), 489–498.
(400) Yueh, M. F., Nguyen, N., Famourzadeh, M., Strassburg, C. P.,
Oda, Y., Guengerich, F. P., and Tukey, R. H. (2001) The contribution of
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A9 on CYP1A2-mediated genotoxicity
by aromatic and heterocyclic amines. Carcinogenesis 22, 943–950.
(401) Dellinger, R. W., Chen, G., Blevins-Primeau, A. S., Krzeminski,
J., Amin, S., and Lazarus, P. (2007) Glucuronidation of PhIP and N-OH-
PhIP by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A10. Carcinogenesis 28, 2412–2418.
(402) Nowell, S. A., Massengill, J. S., Williams, S., Radominska-
Pandya, A., Tephly, T. R., Cheng, Z., Strassburg, C. P., Tukey, R. H.,
MacLeod, S. L., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1999) Glucuronidation
of 2-hydroxyamino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by hu-
man microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: identification of spe-
cific UGT1A family isoforms involved. Carcinogenesis 20, 1107–1114.
(403) Nussbaum, M., Fiala, E. S., Kulkarni, B., el-Bayoumy, K., and
Weisburger, J. H. (1983) In vivo metabolism of 3,2
0
-dimethyl-4-
aminobiphenyl(DMAB) bearing on its organotropism in the Syrian
golden hamster and the F344 rat. Environ. Health Perspect. 49, 223–231.
(404) Kaderlik, K. R., Minchin, R. F., Mulder, G. J., Ilett, K. F.,
Daugaard-Jenson, M., Teitel, C. H., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1994) Meta-
bolic activation pathway for the formation of DNA adducts of the
carcinogen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP)
in rat extrahepatic tissues. Carcinogenesis 15, 1703–1709.
(405) Heller, H. E., Hughes, E. E., and Ingold, C. K. (1951) A new
view of the arylhydroxylamine rearrangement. Nature 168, 909–910.
(406) Rothman, N., Talaska, G., Hayes, R. B., Bhatnagar, V. K., Bell,
D. A., Lakshmi, V. M., Kashyap, S. K., Dosemeci, M., Kashyap, R., Hsu,
F. F., Jaeger, M., Hirvonen, A., Parikh, D. J., Davis, B. B., and Zenser,
T. V. (1997) Acidic urine pH is associated with elevated levels of free
urinary benzidine and N-acetylbenzidine and urothelial cell DNA
adducts in exposed workers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev.
6, 1039–1042.
(407) Alguacil, J, Kogevinas, M, Silverman, D, Malats, N, Real, F. X.,
Garcia-Closas, M, Tardon, A, Rivas, M, Tora, M, Garcia-Closas, R, Serra,
C, Carrato, A, Pfeiffer, R, Fortuny, J, Samanic, C, and Rothman, N.
(2011) Urinary pH, cigarette smoking and bladder cancer risk. Carci-
nogenesis 32, 843–847.
(408) Snyderwine, E. G., Roller, P. P., Adamson, R. H., Sato, S., and
Thorgeirsson, S. S. (1988) Reaction of the N-hydroxylamine and
N-acetoxy derivatives of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline with
DNA. Synthesis and identification of N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-IQ. Car-
cinogenesis 9, 1061–1065.
(409) Walpole, A. L., Williams, M. H., and Roberts, D. C. (1952)
The carcinogenic action of 4-aminodiphenyl and 3:2
0
-dimethyl-4-ami-
no-diphenyl. Br. J. Ind. Med. 9, 255–263.
(410) Navarrete, A., and Spjut, H. J. (1967) Effect of colostomy on
experimentally produced neoplasms of the colon of the rat. Cancer
20, 1466–1472.
(411) Cleveland, J. C., Litvak, S. F., and Cole, J. W. (1967)
Identification of the route of action of the carcinogen 3:2-dimethyl-4-
aminobiphenyl in the induction of intestinal neoplasia. Cancer Res.
27, 708–714.
(412) Zenser, T. V., Lakshmi, V. M., and Davis, B. B. (1999) Human
and Escherichia coli beta-glucuronidase hydrolysis of glucuronide con-
jugates of benzidine and 4-aminobiphenyl, and their hydroxy metabo-
lites. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27, 1064–1067.
(413) Kaderlik, K. R., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1995) Metabolic poly-
morphisms and carcinogen-DNA adduct formation in human popula-
tions. Pharmacogenetics 5, S108–S117.
(414) Strassburg, C. P., Vogel, A., Kneip, S., Tukey, R. H., and
Manns, M. P. (2002) Polymorphisms of the human UDP-glucurono-
syltransferase(UGT) 1A7 gene in colorectal cancer. Gut 50, 851–856.
(415) Butler, L. M., Duguay, Y., Millikan, R. C., Sinha, R., Gagne,
J. F., Sandler, R. S., and Guillemette, C. (2005) Joint effects between
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A7 genotype and dietary carcinogen
exposure on risk of colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev.
14, 1626–1632.
(416) Girard, H., Butler, L. M., Villeneuve, L., Millikan, R. C., Sinha,
R., Sandler, R. S., and Guillemette, C. (2008) UGT1A1 and UGT1A9
functional variants, meat intake, and colon cancer, among Caucasians
and African-Americans. Mutat. Res. 644 ,56–63.
(417) Hayes, J. D., Flanagan, J. U., and Jowsey, I. R. (2005)
Glutathione transferases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 45,51–88.
(418) Mannervik, B., Board, P. G., Hayes, J. D., Listowsky, I., and
Pearson, W. R. (2005) Nomenclature for mammalian soluble glu-
tathione transferases. Methods Enzymol. 401,1–8.
(419) Eyer, P. (1994) Reactions of oxidatively activated arylamines
with thiols: reaction mechanisms and biologic implications. An over-
view. Environ. Health Perspect. 102 (Suppl 6), 123–132.
(420) Dolle, B., Topner, W., and Neumann, H. G. (1980) Reaction
of arylnitroso compounds with mercaptans. Xenobiotica 10, 527–536.
(421) Kazanis, S., and McClelland, R. A. (1992) Electrophilic
intermediate in the reaction of glutathione and nitrosoarenes. J. Am.
Chem. Soc. 114, 3052–3059.
(422) Ellis, M. K., Hill, S., and Foster, P. M. (1992) Reactions of
nitrosonitrobenzenes with biological thiols: identification and reactivity
of glutathion-S-yl conjugates. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 82
, 151–163.
(423) Kaderlik, K. R., Mulder, G. J., Shaddock, J. G., Casciano, D. A.,
Teitel, C. H., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1994) Effect of glutathione depletion
and inhibition of glucuronidation and sulfation on 2-amino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) metabolism, PhIP-DNA adduct
formation and unscheduled DNA synthesis in primary rat hepatocytes.
Carcinogenesis 15, 1711–1716.
(424) Loretz, L. J., and Pariza, M. W. (1984) Effect of glutathione
levels, sulfate levels, and metabolic inhibitors on covalent binding of
2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline and 2-acetylaminofluorene
to cell macromolecules in primary monolayer cultures of adult rat
hepatocytes. Carcinogenesis 5, 895–899.
(425) Zenser, T. V., Lakshmi, V. M., Hsu, F. F., and Davis, B. B.
(2001) Methemoglobin oxidation of N-acetylbenzidine to form a
sulfinamide. Drug Metab. Dispos. 29, 401–406.
(426) Mulder, G. J., Unruh, L. E., Evans, F. E., Ketterer, B., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1982) Formation and identification of glutathione
conjugates from 2-nitrosofluorene and N-hydroxy-2-aminofluorene.
Chem.-Biol. Interact. 39, 111–127.
(427) Meerman, J. H., Beland, F. A., Ketterer, B., Srai, S. K., Bruins,
A. P., and Mulder, G. J. (1982) Identification of glutathione conjugates
1207 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
formed from N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofl uorene in the rat. Chem.-Biol.
Interact. 39, 149–168.
(428) Umemoto, A., Grivas, S., Yamaizumi, Z., Sato, S., and Sugimura,
T. (1988) Non-enzymatic glutathione conjugation of 2-nitroso-6-methyl-
dipyrido [1,2-a:3
0
,2
0
-d] imidazole(NO-Glu-P-1) in vitro: N-hydroxy-
sulfonamide, a new binding form of arylnitroso compounds and thiols.
Chem.-Biol. Interact. 68,57–69.
(429) Saito, K., Yamazoe, Y., Kamataki, T., and Kato, R. (1983)
Activation and detoxication of N-hydroxy-Trp-P-2 by glutathione and
glutathione transferases. Carcinogenesis 4, 1551–1557.
(430) Lin, D.-X., Meyer, D. J., Ketterer, B., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar,
F. F. (1994) Effects of human and rat glutathione-S-transferase on the
covalent binding of the N-acetoxy derivatives of heterocyclic amine
carcinogens in vitro : a possible mechanism of organ specificity in their
carcinogensis. Cancer Res. 54, 4920–4926.
(431) Coles, B., Nowell, S. A., MacLeod, S. L., Sweeney, C., Lang,
N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (2001) The role of human glutathione
S-transferases(hGSTs) in the detoxification of the food-derived carcino-
gen metabolite N-acetoxy-PhIP, and the effect of a polymorphism in
hGSTA1 on colorectal cancer risk. Mutat. Res. 482,3–10.
(432) Nelson, C. P., Kidd, L. C., Sauvageot, J., Isaacs, W. B., De
Marzo, A. M., Groopman, J. D., Nelson, W. G., and Kensler, T. W.
(2001) Protection against 2-hydroxyamino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine cytotoxicity and DNA adduct formation in human
prostate by glutathione S-transferase P1. Cancer Res. 61, 103–109.
(433) Howie, A. F., Forrester, L. M., Glancey, M. J., Schlager, J. J.,
Powis, G., Beckett, G. J., Hayes, J. D., and Wolf, C. R. (1990) Glutathione
S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase expression in normal and
tumour human tissues. Carcinogenesis 11, 451–458.
(434) Coles, B. F., Morel, F., Rauch, C., Huber, W. W., Yang, M.,
Teitel, C. H., Green, B., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (2001) Effect of
polymorphism in the human glutathione S-transferase A1 promoter on
hepatic GSTA1 and GSTA2 expression. Pharmacogenetics 11, 663–669.
(435) Sweeney, C., Coles, B. F., Nowell, S., Lang, N. P., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (2002) Novel markers of susceptibility to carcinogens
in diet: associations with colorectal cancer. Toxicology 181-182,83–87.
(436) van der Logt, E. M., Bergevoet, S. M., Roelofs, H. M., van,
H. Z., te Morsche, R. H., Wobbes, T., de Kok, J. B., Nagengast, F. M., and
Peters, W. H. (2004) Genetic polymorphisms in UDP-glucuronosyl-
transferases and glutathione S-transferases and colorectal cancer risk.
Carcinogenesis 25, 2407–2415.
(437) Weisburger, J. H., Grantham., P. H., Steibigel, N. H., Dall,
D. P., and Weisburger, E. K. (1964) Activation and detoxication of N-2-
fluorenylacetamide in man. Cancer Res. 24, 475–479.
(438) Cocker, J., Boobis, A. R., Wilson, H. K., and Gompertz, D.
(1990) Evidence that a beta-N-glucuronide of 4,4
0
-methylenebis(2-
chloroaniline)(MOCA) is a major urinary metabolite in man: implica-
tions for biological monitoring. Br. J. Ind. Med. 47, 154–161.
(439) Cocker, J., Boobis, A. R., and Davies, D. S. (1988) Determina-
tion of the N-acetyl metabolites of 4,4
0
-methylene dianiline and 4,4
0
-
methylene-bis(2-chloroaniline) in urine. Biomed. Environ. Mass Spec-
trom. 17, 161–167.
(440) Seyler, T. H., and Bernert, J. T. (2011) Analysis of 4-amino-
biphenyl in smoker’ s and nonsmoker’s urine by tandem mass spectro-
metry. Biomarkers 16, 212–221.
(441) Boyland, E., and Manson, D. (1966) The biochemistry of
aromatic amines. The metabolism of 2-naphthylamine and 2-naphthyl-
hydroxylamine derivatives. Biochem. J. 101,84–102.
(442) el-Bayoumy, K., Donahue, J. M., Hecht, S. S., and Hoffmann,
D. (1986) Identification and quantitative determination of aniline and
toluidines in human urine. Cancer Res. 46, 6064–6067.
(443) Weiss, T., and Angerer, J. (2002) Simultaneous determination
of various aromatic amines and metabolites of aromatic nitro com-
pounds in urine for low level exposure using gas chromatography-mass
spectrometry. J. Chromatogr., B 778 , 179–192.
(444) Grimmer, G., Dettbarn, G., Seidel, A., and Jacob, J. (2000)
Detection of carcinogenic aromatic amines in the urine of non-smokers.
Sci. Total Environ. 247,81–90.
(445) Riedel, K., Scherer, G., Engl, J., Hagedorn, H. W., and Tricker,
A. R. (2006) Determination of three carcinogenic aromatic amines in
urine of smokers and nonsmokers. J. Anal. Toxicol. 30, 187–195.
(446) Riffelmann, M., Muller, G., Schmieding, W., Popp, W., and
Norpoth, K. (1995) Biomonitoring of urinary aromatic amines and
arylamine hemoglobin adducts in exposed workers and nonexposed
control persons. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 68,36–43.
(447) Holland, R. D., Taylor, J., Schoenbachler, L., Jones, R. C.,
Freeman, J. P., Miller, D. W., Lake, B. G., Gooderham, N. J., and Turesky,
R. J. (2004) Rapid biomonitoring of heterocyclic aromatic amines in
human urine by tandem solvent solid phase extraction liquid chroma-
tography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
17, 1121–1136.
(448) Ushiyama, H., Wakabayashi, K., Hirose, M., Itoh, H., Sugi-
mura, T., and Nagao, M. (1991) Presence of carcinogenic heterocyclic
amines in urine of healthy volunteers eating normal diet, but not
of inpatients receiving parenteral alimentation. Carcinogenesis 12,
1417–1422.
(449) Stillwell, W. G., Turesky, R. J., Sinha, R., Skipper, P. L., and
Tannenbaum, S. R. (1999) Biomonitoring of heterocyclic aromatic
amine metabolites in human urine. Cancer Lett. 143, 145–148.
(450) Frandsen, H. (2007) Deconjugation of N-glucuronide con-
jugated metabolites with hydrazine hydrate--biomarkers for exposure to
the food-borne carcinogen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine(PhIP). Food Chem. Toxicol. 45, 863–870.
(451) Murray, S., Gooderham, N. J., Boobis, A. R., and Davies, D. S.
(1989) Detection and measurement of MeIQx in human urine after
ingestion of a cooked meat meal. Carcinogenesis 10, 763–765.
(452) Lynch, A. M., Knize, M. G., Boobis, A. R., Gooderham, N.,
Davies, D. S., and Murray, S. (1992) Intra- and interindividual variability
in systemic exposure in humans to 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-
f]quinoxaline and 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine,
carcinogens present in food. Cancer Res. 52, 6216–6223.
(453) Ji, H., Yu, M. C., Stillwell, W. G., Skipper, P. L., Ross, R. K.,
Henderson, B. E., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (1994) Urinary excretion of
2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline in white, black, and
Asian men in Los Angeles County. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev.
3, 407–411.
(454) Reistad, R., Rossland, O. J., Latva-Kala, K. J., Rasmussen, T.,
Vikse, R., Becher, G., and Alexander, J. (1997) Heterocyclic aromatic
amines in human urine following a fried meat meal. Food Chem. Toxicol.
35, 945–955.
(455) Kidd, L. C., Stillwell, W. G., Yu, M. C., Wishnok, J. S., Skipper,
P. L.,Ross, R. K.,Henderson,B.E., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (1999) Urinary
excretion of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in
White, African-American, and Asian-American men in Los Angeles County.
Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 8, 439–445.
(456) Turesky, R. J., Yuan, J. M., Wang, R., Peterson, S., and Yu,
M. C. (2007) Tobacco smoking and urinary levels of 2-amino-9H-
pyrido[2,3-b]indole in men of Shanghai, China. Cancer Epidemiol.
Biomarkers Prev. 16, 1554–1560.
(457) Nishigaki, R., Totsuka, Y., Kataoka, H., Ushiyama, H., Goto, S.,
Akasu, T., Watanabe, T., Sugimura, T., and Wakabayashi, K. (2007)
Detection of aminophenylnorharman, a possible endogenous mutagenic
and carcinogenic compound, in human urine samples. Cancer Epidemiol.
Biomarkers Prev. 16, 151–156.
(458) Frederiksen, H. (2005) Two food-borne heterocyclic amines:
metabolism and DNA adduct formation of amino-alpha-carbolines. Mol.
Nutr. Food Res. 49, 263–273.
(459) Sinha, R., Rothman, N., Mark, S. D., Murray, S., Brown, E. D.,
Levander, O. A., Davies, D. S., Lang, N. P., Kadlubar, F. F., and Hoover,
R. N. (1995) Lower levels of urinary 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-
f]quinoxaline(MeIQx) in humans with higher CYP1A2 activity. Carci-
nogenesis 16, 2859–2861.
(460) Oda, Y., Totsuka, Y., Wakabayashi, K., Guengerich, F. P., and
Shimada, T. (2006) Activation of aminophenylnorharman, amino-
methylphenylnorharman and aminophenylharman to genotoxic meta-
bolites by human N-acetyltransferases and cytochrome P450 enzymes
1208 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
expressed in Salmonella typhimurium umu tester strains. Mutagenesis
21, 411–416.
(461) Strickland, P. T., Qian, Z., Friesen, M. D., Rothman, N., and
Sinha, R. (2001) Measurement of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in acid-hydrolyzed urine by high-performance
liquid chromatograpy with fluorescence detection. Biomarkers
6, 313–325.
(462) King, R. S., Teitel, C. H., Shaddock, J. G., Casciano, D. A., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1999) Detoxification of carcinogenic aromatic and
heterocyclic amines by enzymatic reduction of the N-hydroxy derivative.
Cancer Lett. 143, 167–171.
(463) Kurian, J. R., Chin, N. A., Longlais, B. J., Hayes, K. L., and
Trepanier, L. A. (2006) Reductive detoxification of arylhydroxylamine
carcinogens by human NADH cytochrome b5 reductase and cyto-
chrome b5. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 19, 1366–1373.
(464) Malfatti, M. A., Wu, R. W., and Felton, J. S. (2005) The effect
of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 expression on the mutagenicity
and metabolism of the cooked-food carcinogen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-
phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in CHO cells. Mutat. Res. 570, 205–214.
(465) Miners, J. O., Osborne, N. J., Tonkin, A. L., and Birkett, D. J.
(1992) Perturbation of paracetamol urinary metabolic ratios by urine
flow rate. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 34, 359–362.
(466) Kriek, E. (1965) On the interaction of N-2-fluorenylhydrox-
ylamine with nucleic acids in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.
20, 793–799.
(467) King, C. M., and Phillips, B. (1969) N-hydroxy-2-fluorenyla-
cetamide. Reaction of the carcinogen with guanosine, ribonucleic acid,
deoxyribonucleic acid, and protein following enzymatic deacetylation or
esterification. J. Biol. Chem. 244, 6209–6216.
(468) Beland, F. A., Allaben, W. T., and Evans, F. E. (1980)
Acyltransferase-mediated binding of N-hydroxyarylamides to nucleic
acids. Cancer Res. 40, 834–840.
(469) Kriek, E. (1972) Persistent binding of a new reaction product
of the carcinogen N-hydroxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene with guanine in
rat liver DNA in vivo. Cancer Res. 32, 2042–2048.
(470) Westra, J. G., Kriek, E., and Hittenhausen, H. (1976) Identifica -
tion of the persistently bound form of the carcinogen N-acetyl-2-amino-
fluorene to rat liver DNA in vivo. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 15, 149–164.
(471) Hashimoto, Y., and Shudo, K. (1985) Chemical modification
of DNA with muta-carcinogens. I. 3-Amino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-
b]indole and 2-amino-6-methyldipyrido[1,2-a:3
0
,2
0
-d]imidazole: meta-
bolic activation and structure of the DNA adducts. Environ. Health
Perspect. 62, 209–214.
(472) Humphreys, W. G., Kadlubar, F. F., and Guengerich, F. P.
(1992) Mechanism of C8 alkylation of guanine residues by activated
arylamines: evidence for initial adduct formation at the N7 position.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 8278–8282.
(473) Kennedy, S. A., Novak, M., and Kolb, B. A. (1997) Reactions
of ester derivatives of carcinogenic N-(4-biphenylyl)hydroxylamine and
the corresponding hydroxamic acid with purine nucleosides. J. Am.
Chem. Soc. 119, 7654–7664.
(474) Turesky, R. J., Rossi, S. C., Welti, D. H., Lay, J. O., Jr., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1992) Characterization of DNA adducts formed in vitro
by reaction of N-hydroxy-2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline
and N-hydroxy-2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline at the
C-8 and N
2
atoms of guanine. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 5, 479–490.
(475) Jamin, E. L., Arquier, D., Canlet, C., Rathahao, E., Tulliez, J.,
and Debrauwer, L. (2007) New insights in the formation of deoxynu-
cleoside adducts with the heterocyclic aromatic amines PhIP and IQ by
means of ion trap MSn and accurate mass measurement of fragment
ions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 18, 2107–2118.
(476) Bessette, E. E., Goodenough, A. K., Langouet, S., Yasa, I.,
Kozekov, I. D., Spivack, S. D., and Turesky, R. J. (2009) Screening for
DNA adducts by data-dependent constant neutral loss-triple stage mass
spectrometry with a linear quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometer. Anal.
Chem. 81, 809–819.
(477) Frandsen, H., Grivas, S., Turesky, R. J., Anndersson, R.,
Dragsted, L. O., and Larsen, J. C. (1994) Formation of DNA adducts
by the food mutagen 2-amino-3,4,8-trimethyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-
f]quinoxaline in vitro and in vivo. Identification of a N
2
-(2
0
-deoxygua-
nosin-8-yl)-4,8-DiMeIQx adduct. Carcinogenesis 15, 2553–2558.
(478) Frederiksen, H., Frandsen, H., and Pfau, W. (2004) Syntheses
of DNA-adducts of two heterocyclic amines, 2-amino-3-methyl-9H-
pyrido[2,3-b]indole(MeARC) and 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole-
(ARC) and identification of DNA-adducts in organs from rats dosed
with MeARC. Carcinogenesis 25, 1525–1533.
(479) Ochiai, M., Nakagama, H., Turesky, R. J., Sugimura, T., and
Nagao, M. (1999) A new modification of the
32
P-post-labeling method
to recover IQ-DNA adducts as mononucleotides. Mutagenesis
14, 239–242.
(480) Singh, R., Arlt, V. M., Henderson, C. J., Phillips, D. H., Farmer,
P. B., and Gamboa daCosta, G. (2010) Detection and quantitation of
N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine adducts in DNA using online column-switching liquid
chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr., B
878, 2155–2162.
(481) Pfau, W., Schulze, C., Shirai, T., Hasegawa, R., and Brockstedt,
U. (1997) Identification of the major hepatic DNA adduct formed by the
food mutagen 2-amino-9H-pyrido[2,3-b]indole(ARC). Chem. Res. Tox-
icol. 10, 1192–1197.
(482) Hashimoto, Y., Shudo, K., and Okamoto, T. (1982) Modifica-
tion of nucleic acids with muta-carcinogenic heteroaromatic amines
in vivo. Identification of modified bases in DNA extracted from rats
injected with 3-amino-1-methyl-5H-pyrido[4,3-b]indole and 2-amino-
6-methyldipyrido[1,2-a3:3
0
,2
0
-d]imidazole. Mutat. Res. 105,9–13.
(483) Turesky, R. J., Gremaud, E., Markovic, J., and Snyderwine,
E. G. (1996) DNA adduct formation of the food-derived mutagen
2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in nonhuman primates un-
dergoing carcinogen bioassay. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 9, 403–408.
(484) Turesky, R. J., and Markovic, J. (1995) DNA adduct formation
of the food carcinogen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline(IQ)
in liver, kidney and colorectum of rats. Carcinogenesis 16, 2275–2279.
(485) Paehler, A., Richoz, J., Soglia, J., Vouros, P., and Turesky, R. J.
(2002) Analysis and quantification of DNA adducts of 2-amino-3,8-
dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline in liver of rats by liquid chromatog-
raphy/electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
15, 551–561.
(486) Lakshman, M. K. (2005) Synthesis of biologically important
nucleoside analogs by palladium-catalyzed C-N bond formation. Cur.
Org. Synth. 2,83–112.
(487) Elmquist, C. E., Stover, J. S., Wang, Z., and Rizzo, C. J. (2004)
Site-specific synthesis and properties of oligonucleotides containing C8-
deoxyguanosine adducts of the dietary mutagen IQ. J. Am. Chem. Soc.
126, 11189–11201.
(488) Stover, J. S., and Rizzo, C. J. (2007) Synthesis of oligonucleo-
tides containing the N
2
-deoxyguanosine adduct of the dietary carcino-
gen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
20, 1972–1979.
(489) Bonala, R., Torres, M. C., Iden, C. R., and Johnson, F. (2006)
Synthesis of the PhIP adduct of 2
0
-deoxyguanosine and its incorporation
into oligomeric DNA. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 19, 734–738.
(490) Takamura-Enya, T., Ishikawa, S., Mochizuki, M., and Wakabayashi,
K. (2006) Chemical synthesis of 2
0
-deoxyguanosine-C8 adducts with
heterocyclic amines: an application to synthesis of oligo nucleotides site-speci-
fically adducted with 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 19,770–778.
(491) Patel, D. J., Mao, B., Gu, Z., Hingerty, B. E., Gorin, A., Basu,
A. K., and Broyde, S. (1998) Nuclear magnetic resonance solution
structures of covalent aromatic amine-DNA adducts and their mutagenic
relevance. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 11, 391–407.
(492) Shibutani, S., Suzuki, N., and Grollman, A. P. (1998) Muta-
genic specificity of(acetylamino)fluorene-derived DNA adducts in
mammalian cells. Biochemistry 37, 12034 –12041.
(493) Shibutani, S., Fernandes, A., Suzuki, N., Zhou, L., Johnson, F.,
and Grollman, A. P. (1999) Mutagenesis of the N-(deoxyguanosin-
8-yl)-2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine DNA adduct
1209 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
in mammalian cells. Sequence context effects. J. Biol. Chem.
274, 27433–27438.
(494) Brown, K., Hingerty, B. E., Guenther, E. A., Krishnan, V. V.,
Broyde, S., Turteltaub, K. W., and Cosman, M. (2001) Solution
structure of the 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine
C8-deoxyguanosine adduct in duplex DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.
A. 98, 8507–8512.
(495) Cho, B. P. (2004) Dynamic conformational heterogeneities of
carcinogen-DNA adducts and their mutagenic relevance. J. Environ. Sci.
Health, Part C: Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 22,57–90.
(496) Choi, J. Y., Stover, J. S., Angel, K. C., Chowdhury, G., Rizzo,
C. J., and Guengerich, F. P. (2006) Biochemical basis of genotoxicity of
heterocyclic arylamine food mutagens: Human DNA polymerase eta
selectively produces a two-base deletion in copying the N
2
-guanyl
adduct of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline but not the C8
adduct at the NarI G3 site. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 25297–25306.
(497) Stover, J. S., Chowdhury, G., Zang, H., Guengerich, F. P., and
Rizzo, C. J. (2006) Translesion synthesis past the C8- and N
2
-deox-
yguanosine adducts of the dietary mutagen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo-
[4,5-f]quinoline in the NarI recognition sequence by prokaryotic DNA
polymerases. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 19, 1506–1517.
(498) Wang, F., DeMuro, N. E., Elmquist, C. E., Stover, J. S., Rizzo,
C. J., and Stone, M. P. (2006) Base-displaced intercalated structure of
the food mutagen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in the
recognition sequence of the NarI restriction enzyme, a hotspot for -2
bp deletions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 10085–10095.
(499) Broyde, S., Wang, L., Zhang, L., Rechkoblit, O., Geacintov,
N. E., and Patel, D. J. (2008) DNA adduct structure-function relation-
ships: comparing solution with polymerase structures. Chem. Res.
Toxicol. 21,45–52.
(500) Delaney, J. C., and Essigmann, J. M. (2008) Biological proper-
ties of single chemical-DNA adducts: a twenty year perspective. Chem.
Res. Toxicol. 21, 232–252.
(501) Randerath, K., Randerath, E., Agrawal, H. P., Gupta, R. C.,
Schurda, M. E., and Reddy, M. V. (1985) Postlabeling methods for
carcinogen-DNA adduct analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 62,57–65.
(502) Culp, S. J., Roberts, D. W., Talaska, G., Lang, N. P., Fu, P. P.,
Lay, J. O., Jr., Teitel, C. H., Snawder, J. E., Von Tungeln, L. S., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1997) Immunochemical,
32
P-postlabeling, and GC/MS
detection of 4-aminobiphenyl-DNA adducts in human peripheral lung in
relation to metabolic activation pathways involving pulmonary N-oxida-
tion, conjugation, and peroxidation. Mutat. Res. 378,97–112.
(503) Poirier, M. C., Santella, R. M., and Weston, A. (2000)
Carcinogen macromolecular adducts and their measurement. Carcino-
genesis 21, 353–359.
(504) Faraglia, B., Chen, S. Y., Gammon, M. D., Zhang, Y., Teitelbaum,
S. L.,Neugut, A. I.,Ahsan,H., Garbowski, G. C.,Hibshoosh,H., Lin, D.,
Kadlubar, F. F., and Santella, R. M. (2003) Evaluation of 4-aminobiphenyl-
DNA adducts in human breast cancer: the influence of tobacco smoke.
Carcinogenesis 24, 719–725.
(505) Lin, D., Lay, J. O., Jr., Bryant, M. S., Malaveille, C., Friesen, M.,
Bartsch, H., Lang, N. P., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1994) Analysis of
4-aminobiphenyl-DNA adducts in human urinary bladder and lung by
alkaline hydrolysis and negative ion gas chromatography-mass spectro-
metry. Environ. Health Perspect. 102 (Suppl 6), 11–16.
(506) Dingley, K. H., Roberts, M. L., Velsko, C. A., and Turteltaub,
K. W. (1998) Attomole detection of
3
H in biological samples using
accelerator mass spectrometry: application in low-dose, dual-isotope
tracer studies in conjunction with
14
C accelerator mass spectrometry.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 11, 1217–1222.
(507) Doerge, D. R., Churchwell, M. I., Marques, M. M., and Beland,
F. A. (1999) Quantitative analysis of 4-aminobiphenyl-C8-deoxyguano-
syl DNA adducts produced in vitro and in vivo using HPLC-ES-MS.
Carcinogenesis 20, 1055–1061.
(508) Beland, F. A., Doerge, D. R., Churchwell, M. I., Poirier, M. C.,
Schoket, B., and Marques, M. M. (1999) Synthesis, characterization, and
quantitation of a 4-aminobiphenyl-DNA adduct standard. Chem. Res.
Toxicol. 12,68–77.
(509) Gangl, E. T., Turesky, R. J., and Vouros, P. (1999) Determina-
tion of in vitro- and in vivo-formed DNA adducts of 2-amino-3-
methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline by capillary liquid chromatography/mi-
croelectrospray mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 12, 1019–1027.
(510) Soglia, J. R., Turesky, R. J., Paehler, A., and Vouros, P. (2001)
Quantification of the heterocyclic aromatic amine DNA adduct
N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in
livers of rats using capillary liquid chromatography/microelectrospray
mass spectrometry: a dose-response study. Anal. Chem. 73, 2819–2827.
(511) Crosbie, S. J., Murray, S., Boobis, A. R., and Gooderham, N. J.
(2000) Mass spectrometric detection and measurement of N
2
-(2
0
-
deoxyguanosin-8-yl)PhIP adducts in DNA. J. Chromatogr., B 744 ,55–64.
(512) Ricicki, E. M., Soglia, J. R., Teitel, C., Kane, R., Kadlubar, F., and
Vouros, P. (2005) Detection and quantification of N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-
4-aminobiphenyl adducts in human pancreas tissue using capillary liquid
chromatography-microelectrospray mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
18, 692–699.
(513) Randall, K. L., Argoti, D., Paonessa, J. D., Ding, Y., Oaks, Z.,
Zhang, Y., and Vouros, P. (2010) An improved liquid chromatography-
tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of 4-amino-
biphenyl DNA adducts in urinary bladder cells and tissues. J. Chromatogr., A
1217,4135–4143.
(514) Hatcher, J. F., and Swaminathan, S. (2002) Identification of
N-(deoxyguanosin-8-yl)-4-azobiphenyl by(
32)
P-postlabeling analyses of
DNA in human uroepithelial cells exposed to proximate metabolites of
the environmental carcinogen 4-aminobiphenyl. Environ. Mol. Mutagen.
39, 314–322.
(515) Swaminathan, S., and Hatcher, J. F. (2002) Identification of
new DNA adducts in human bladder epithelia exposed to the proximate
metabolite of 4-aminobiphenyl using
32
P-postlabeling method.
Chem.-Biol. Interact. 139, 199–213.
(516) Poirier, M. C., Fullerton, N. F., Smith, B. A., and Beland, F. A.
(1995) DNA adduct formation and tumorigenesis in mice during the
chronic administration of 4-aminobiphenyl at multiple dose levels.
Carcinogenesis 16, 2917–2921.
(517) Martin, C. N., Beland, F. A., Roth, R. W., and Kadlubar, F. F.
(1982) Covalent binding of benzidine and N-acetylbenzidine to DNA at
the C-8 atom of deoxyguanosine in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res.
42, 2678–2686.
(518) Kennelly, J. C., Beland, F. A., Kadlubar, F. F., and Martin, C. N.
(1984) Binding of N-acetylbenzidine and N,N
0
-diacetylbenzidine to
hepatic DNA of rat and hamster in vivo and in vitro. Carcinogenesis
5, 407–412.
(519) Yamazoe, Y., Roth, R. W., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1986)
Reactivity of benzidine diimine with DNA to form N-(deoxyguanosin-
8-yl)-benzidine. Carcinogenesis 7, 179–182.
(520) Segerb€ack, D., and Kadlubar, F. F. (1992) Characterization of
4,4
0
-methylenebis(2-chloroaniline)--DNA adducts formed in vivo and
in vitro. Carcinogenesis 13, 1587–1592.
(521) Segerb€ack, D., Kaderlik, K. R., Talaska, G., Dooley, K. L., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1993)
32
P-postlabelling analysis of DNA adducts of 4,4
0
-
methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) in target and nontarget tissues in the dog
and their implications for human risk assessment. Carcinogenesis
14, 2143–2147.
(522) Turesky, R. J. (1994) DNA Adducts of Heterocyclic Aromatic
Amines, Arylazides and 4-Nitroquinoline 1-Oxide, in DNA Adducts:
Identification and Biological Significance (Hemminki, K., Dipple, A., Shuker,
D. E. G., Kadlubar, F. F., Segerb €ack, D.,and Bartsch, H.,Eds.) pp 217-228,
International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France.
(523) Marques, M. M., Mourato, L. L., Santos, M. A., and Beland,
F. A. (1996) Synthesis, characterization, and conformational analysis of
DNA adducts from methylated anilines present in tobacco smoke. Chem.
Res. Toxicol. 9,99–108.
(524) Jones, C. R., and Sabbioni, G. (2003) Identification of DNA
adducts using HPLC/MS/MS following in vitro and in vivo experiments
with arylamines and nitroarenes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 16, 1251–1263.
(525) Cui, L., Sun, H. L., Wishnok, J. S., Tannenbaum, S. R., and
Skipper, P. L. (2007) Identification of adducts formed by reaction of
1210 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
N-acetoxy-3,5-dimethylaniline with DNA. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
20, 1730–1736.
(526) Skipper, P. L., Trudel, L. J., Kensler, T. W., Groopman, J. D.,
Egner, P. A., Liberman, R. G., Wogan, G. N., and Tannenbaum, S. R.
(2006) DNA adduct formation by 2,6-dimethyl-, 3,5-dimethyl-, and
3-ethylaniline in vivo in mice. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 19, 1086–1090.
(527) Gupta, R. C., Reddy, M. V., and Randerath, K. (1982)
32
P-
postlabeling analysis of non-radioactive aromatic carcinogen--DNA
adducts. Carcinogenesis 3, 1081–1092.
(528) Pfau, W., Lecoq, S., Hughes, N. C., Seidel, A., Platt, K. L.,
Grover, P. L., and Phillips, D. H. (1993) Separation of
32
P-labelled
nucleoside 3
0
,5
0
-bisphosphate adducts by HPLC. IARC Sci. Publ.
233–242.
(529) Baranczewski, P., and Moller, L. (2004) Relationship between
content and activity of cytochrome P450 and induction of heterocyclic
amine DNA adducts in human liver samples in vivo and in vitro. Cancer
Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 13, 1071–1078.
(530) Pfau, W., Brockstedt, U., Sohren, K. D., and Marquardt, H.
(1994)
32
P-post-labelling analysis of DNA adducts formed by food-
derived heterocyclic amines: evidence for incomplete hydrolysis and a
procedure for adduct pattern simplification. Carcinogenesis 15, 877–882.
(531) Turteltaub, K. W., Vogel, J. S., Frantz, C. E., and Shen, N.
(1992) Fate and distribution of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine in mice at a human dietary equivalent dose. Cancer Res.
52, 4682–4687.
(532) Ghoshal, A., Davis, C. D., Schut, H. A. J., and Snyderwine,
E. G. (1995) Possible mechanisms for PhIP-DNA adduct fomation in
the mammary gland of female Sprague-Dawley rats. Carcinogenesis
16, 2725–2731.
(533) Turesky, R. J., Markovic, J., and Aeschlimann, J. M. (1996)
Formation and differential removal of C-8 and N
2
-guanine adducts of
the food carcinogen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline in the
liver, kidney, and colorectum of the rat. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 9, 397–402.
(534) Phillips, D. H. (2002) Smoking-related DNA and protein
adducts in human tissues. Carcinogenesis 23, 1979–2004.
(535) Mooney, L. A., Santella, R. M., Covey, L., Jeffrey, A. M.,
Bigbee, W., Randall, M. C., Cooper, T. B., Ottman, R., Tsai, W. Y., and
Wazneh, L. (1995) Decline of DNA damage and other biomarkers in
peripheral blood following smoking cessation. Cancer Epidemiol. Bio-
markers Prev. 4, 627–634.
(536) Talaska, G., Schamer, M., Skipper, P., Tannenbaum, S.,
Caporaso, N., Unruh, L., Kadlubar, F. F., Bartsch, H., Malaveille, C.,
and Vineis, P. (1991) Detection of carcinogen-DNA adducts in ex-
foliated urothelial cells of cigarette smokers: association with smoking,
hemoglobin adducts, and urinary mutagenicity. Cancer Epidemiol. Bio-
markers Prev. 1,61–66.
(537) Wang, L. Y., Chen, C. J., Zhang, Y. J., Tsai, W. Y., Lee, P. H.,
Feitelson, M. A., Lee, C. S., and Santella, R. M. (1998) 4-Aminobiphenyl
DNA damage in liver tissue of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and
controls. Am. J. Epidemiol. 147, 315–323.
(538) Anderson, K. E., Hammons, G. J., Kadlubar, F. F., Potter, J. D.,
Kaderlik, K. R., Ilett, K. F., Minchin, R. F., Teitel, C. H., Chou, H. C.,
Martin, M. V., Guengerich, F. P., Barone, G. W., Lang, N. P., and
Peterson, L. A. (1997) Metabolic activation of aromatic amines by
human pancreas. Carcinogenesis 18, 1085 –1092.
(539) Besaratinia, A., Van Straaten, H. W., Kleinjans, J. C., and Van
Schooten, F. J. (2000) Immunoperoxidase detection of 4-aminobiphe-
nyl- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-DNA adducts in induced
sputum of smokers and non-smokers. Mutat. Res. 468, 125–135.
(540) Flamini, G., Romano, G., Curigliano, G., Chiominto, A.,
Capelli, G., Boninsegna, A., Signorelli, C., Ventura, L., Santella, R. M.,
Sgambato, A., and Cittadini, A. (1998) 4-Aminobiphenyl-DNA adducts
in laryngeal tissue and smoking habits: an immunohistochemical study.
Carcinogenesis 19, 353–357.
(541) Airoldi, L., Orsi, F., Magagnotti, C., Coda, R., Randone, D.,
Casetta, G., Peluso, M., Hautefeuille, A., Malaveille, C., and Vineis, P.
(2002) Determinants of 4-aminobiphenyl-DNA adducts in bladder
cancer biopsies. Carcinogenesis 23, 861–866.
(542) Bohm, F., Schmid, D., Denzinger, S., Wieland, W. F., and
Richter, E. (2011) DNA adducts of ortho-toluidine in human bladder.
Biomarkers 16, 120–128.
(543) Zayas, B., Stillwell, S. W., Wishnok, J. S., Trudel, L. J., Skipper,
P., Yu, M. C., Tannenbaum, S. R., and Wogan, G. N. (2007) Detection
and quantification of 4-ABP adducts in DNA from bladder cancer
patients. Carcinogenesis 28, 342–349.
(544) Ambrosone, C. B., Abrams, S. M., Gorlewska-Roberts, K., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (2007) Hair dye use, meat intake, and tobacco exposure
and presence of carcinogen-DNA adducts in exfoliated breast ductal
epithelial cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 464, 169–175.
(545) Zhou, Q., Talaska, G., Jaeger, M., Bhatnagar, V. K., Hayes,
R. B., Zenzer, T. V., Kashyap, S. K., Lakshmi, V. M., Kashyap, R.,
Dosemeci, M., Hsu, F. F., Parikh, D. J., Davis, B., and Rothman, N.
(1997) Benzidine-DNA adduct levels in human peripheral white blood
cells signi fi cantly correlate with levels in exfoliated urothelial cells. Mutat.
Res. 393, 199–
205.
(546) Kaderlik, K. R., Talaska, G., DeBord, D. G., Osorio, A. M., and
Kadlubar, F. F. (1993) 4,4
0
-Methylene-bis(2-chloroaniline)-DNA ad-
duct analysis in human exfoliated urothelial cells by
32
P-postlabeling.
Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2,63–69.
(547) Totsuka, Y., Fukutome, K., Takahashi, M., Takashi, S., Tada,
A., Sugimura, T., and Wakabayashi, K. (1996) Presence of N
2
-(deoxy-
guanosin-8-y l)-2-amino-3,8-dimethyli midazo [4,5-f ]quino xaline(dG-
C8-MeIQx) in human tissues. Carcinogenesis 17, 1029–1034.
(548) Coles, B. F., and Kadlubar, F. F. (2003) Detoxification of
electrophilic compounds by glutathione S-transferase catalysis: Deter-
minants of individual response to chemical carcinogens and chemother-
apeutic drugs? Biofactors 17, 115–130.
(549) Jonsson, C., Stal, P., Sjoqvist, U., Akerlund, J. E., Lofberg, R.,
and M€oller, L. (2010) DNA adducts in normal colonic mucosa from
healthy controls and patients with colon polyps and colorectal carcino-
mas. Mutagenesis 25, 499–504.
(550) He, Y. H., Friesen, M. D., Ruch, R. J., and Schut, H. A. (2000)
Indole-3-carbinol as a chemopreventive agent in 2-amino-1-methyl-
6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) carcinogenesis: inhibition of
PhIP-DNA adduct formation, acceleration of PhIP metabolism, and
induction of cytochrome P450 in female F344 rats. Food Chem. Toxicol.
38,15–23.
(551) Phillips, D. H., and Castegnaro, M. (1999) Standardization
and validation of DNA adduct postlabelling methods: report of inter-
laboratory trials and production of recommended protocols. Mutagenesis
14, 301–315.
(552) Goodenough, A. K., Schut, H. A., and Turesky, R. J. (2007)
Novel LC-ESI/MS/MS
n
method for the characterization and quantifi-
cation of 2
0
-deoxyguanosine adducts of the dietary carcinogen 2-amino-
1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by 2-D linear quadrupole ion
trap mass spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 20, 263–276.
(553) Vondracek, M., Xi, Z., Larsson, P., Baker, V., Mace, K., Pfeifer,
A., Tjalve, H., Donato, M. T., Gomez-Lechon, M. J., and Grafstrom, R. C.
(2001) Cytochrome P450 expression and related metabolism in human
buccal mucosa. Carcinogenesis 22, 481–488.
(554) Spivack, S. D., Hurteau, G. J., Jain, R., Kumar, S. V., Aldous,
K. M., Gierthy, J. F., and Kaminsky, L. S. (2004) Gene-environment
interaction signatures by quantitative mRNA profiling in exfoliated
buccal mucosal cells. Cancer Res. 64, 6805–6813.
(555) Kragelund, C., Hansen, C., Torpet, L. A., Nauntofte, B.,
Brosen, K., Pedersen, A. M., Buchwald, C., Therkildsen, M. H., and
Reibel, J. (2008) Expression of two drug-metabolizing cytochrome
P450-enzymes in human salivary glands. Oral Dis. 14, 533–540.
(556) Ihalin, R., Loimaranta, V., and Tenovuo, J. (2006) Origin,
structure, and biological activities of peroxidases in human saliva. Arch.
Biochem. Biophys. 445, 261–268.
(557) Jones, N. J., McGregor, A. D., and Waters, R. (1993) Detec-
tion of DNA adducts in human oral tissue: correlation of adduct levels
with tobacco smoking and differential enhancement of adducts using the
butanol extraction and nuclease P1 versions of 32P postlabeling. Cancer
Res. 53, 1522–1528.
1211 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(558) Stone, J. G., Jones, N. J., McGregor, A. D., and Waters, R.
(1995) Development of a human biomonitoring assay using buccal
mucosa: comparison of smoking-related DNA adducts in mucosa versus
biopsies. Cancer Res. 55, 1267–1270.
(559) Foiles, P. G., Miglietta, L. M., Quart, A. M., Quart, E., Kabat,
G. C., and Hecht, S. S. (1989) Evaluation of
32
P-postlabeling analysis of
DNA from exfoliated oral mucosa cells as a means of monitoring
exposure of the oral cavity to genotoxic agents. Carcinogenesis
10, 1429–1434.
(560) Chacko, M., and Gupta, R. C. (1988) Evaluation of DNA
damage in the oral mucosa of tobacco users and non-users by
32
P-adduct
assay. Carcinogenesis 9, 2309–2313.
(561) Zhang, Y. J., Hsu, T. M., and Santella, R. M. (1995) Immu-
noperoxidase detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA ad-
ducts in oral mucosa cells of smokers and nonsmokers. Cancer Epidemiol.
Biomarkers Prev. 4, 133–138.
(562) Romano, G., Mancini, R., Fedele, P., Curigliano, G., Flamini,
G., Giovagnoli, M. R., Malara, N., Boninsegna, A., Vecchione, A.,
Santella, R. M., and Cittadini, A. (1997) Immunohistochemical analysis
of 4-aminobiphenyl-DNA adducts in oral mucosal cells of smokers and
nonsmokers. Anticancer Res. 17, 2827–2830.
(563) Besarati, N. A., Van Straaten, H. W., Godschalk, R. W., Van
Zandwijk, N., Balm, A. J., Kleinjans, J. C., and Van Schooten, F. J. (2000)
Immunoperoxidase detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA
adducts in mouth floor and buccal mucosa cells of smokers and
nonsmokers. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 36, 127–133.
(564) Grollman, A. P., Shibutani, S., Moriya, M., Miller, F., Wu, L.,
Moll, U., Suzuki, N., Fernandes, A., Rosenquist, T., Medverec, Z.,
Jakovina, K., Brdar, B., Slade, N., Turesky, R. J., Goodenough, A. K.,
Rieger, R., Vukelic, M., and Jelakovic, B. (2007) Aristolochic acid and the
etiology of endemic(Balkan) nephropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.
104, 12129–12134.
(565) Takiguchi, M., Darwish, W. S., Ikenaka, Y., Ohno, M., and
Ishizuka, M. (2010) Metabolic activation of heterocyclic amines and
expression of CYP1A1 in the tongue. Toxicol. Sci. 116,79–91.
(566) Takayama, S., Nakatsuru, Y., Ohgaki, H., Sato, S., and
Sugimura, T. (1985) Atrophy of salivary glands and pancreas of rats
fed on diet with 2-amino-3-methyl-R-carboline. Proc. Jpn. Acad. 61, Ser. B
277–280.
(567) Klinkhamer, J. M. (1963) Human oral leukocytes. J. Am. Soc.
Periodontists 1, 109–117.
(568) Osswald, K., Mittas, A., Glei, M., and Pool-Zobel, B. L. (2003)
New revival of an old biomarker: characterisation of buccal cells and
determination of genetic damage in the isolated fraction of viable
leucocytes. Mutat. Res. 544, 321–329.
(569) Squier, C. A., Johnson, N. W., and Hopps, R. M. (1976) In
Human Oral Mucosa: Development, Structure and Function pp 3-42,
Blackwell, Oxford, UK.
(570) Ashkenazi, M., and Dennison, D. K. (1989) A new method for
isolation of salivary neutrophils and determination of their functional
activity. J. Dent. Res. 68, 1256–1261.
(571) Gan, L. S., Skipper, P. L., Peng, X. C., Groopman, J. D., Chen,
J. S., Wogan, G. N., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (1988) Serum albumin
adducts in the molecular epidemiology of aflatoxin carcinogenesis:
correlation with aflatoxin B1 intake and urinary excretion of aflatoxin
M1. Carcinogenesis 9, 1323–1325.
(572) Wild, C. P., Hudson, G. J., Sabbioni, G., Chapot, B., Hall, A. J.,
Wogan, G. N., Whittle, H., Montesano, R., and Groopman, J. D. (1992)
Dietary intake of aflatoxins and the level of albumin-bound afl
atoxin in
peripheral blood in The Gambia, West Africa. Cancer Epidemiol.
Biomarkers Prev. 1, 229–234.
(573) Granath, F., Ehrenberg, L., and Tornqvist, M. (1992) Degree
of alkylation of macromolecules in vivo from variable exposure. Mutat.
Res. 284, 297–306.
(574) Tornqvist, M., Fred, C., Haglund, J., Helleberg, H., Paulsson,
B., and Rydberg, P. (2002) Protein adducts: quantitative and qualitative
aspects of their formation, analysis and applications. J. Chromatogr., B
778, 279–308.
(575) Miller, E. C., and Miller, J. A. (1947) The presence and
significance of bound aminoazo dyes in the livers of rats fed p-dimethyl-
aminoazobenzene. Cancer Res. 7, 468–480.
(576) Miller, E. C., Miller, J. A., Sapp, R. W., and Weber, G. M.
(1949) Studies on the protein-bound aminazo dyes formed in vtro from
4-dimethylaminoazobenze and its C-monomethyl derivatives. Cancer
Res. 9, 336–343.
(577) Ehrenberg, L., Hiesche, K. D., Osterman-Golkar, S., and
Wenneberg, I. (1974) Evaluation of genetic risks of alkylating agents:
tissue doses in the mouse from air contaminated with ethylene oxide.
Mutat. Res. 24,83–103.
(578) Osterman-Golkar, S., Ehrenberg, L., Segerb€ack, D., and Hallstrom,
I. (1976) Evaluation of genetic risks of alkylating agent s. II. Haemoglobin as a
dose monitor. Mutat. Res. 34,1–10.
(579) Sabbioni, G., Skipper, P. L., Buchi, G., and Tannenbaum, S. R.
(1987) Isolation and characterization of the major serum albumin
adduct formed by aflatoxin B1 in vivo in rats. Carcinogenesis 8, 819–824.
(580) Peters, T., Jr., and Peters, J. C. (1972) The biosynthesis of rat
serum albumin. VI. Intracellular transport of albumin and rates of
albumin and liver protein synthesis in vivo under various physiological
conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 247, 3858–3863.
(581) Bryant, M. S., Vineis, P., Skipper, P. L., and Tannenbaum, S. R.
(1988) Hemoglobin adducts of aromatic amines: associations with smoking
status and type of tobacco. Proc.Natl. Acad.Sci.U.S.A.85, 9788–9791.
(582) Beyerbach, A., Rothman, N., Bhatnagar, V. K., Kashyap, R.,
and Sabbioni, G. (2006) Hemoglobin adducts in workers exposed to
benzidine and azo dyes. Carcinogenesis 27, 1600–1606.
(583) Bartsch, H., Caporaso, N., Coda, M., Kadlubar, F., Malaveille,
C., Skipper, P., Talaska, G., Tannenbaum, S. R., and Vineis, P. (1990)
Carcinogen hemoglobin adducts, urinary mutagenicity, and metabolic
phenotype in active and passive cigarette smokers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.
82, 1826–1831.
(584) Yu, M. C., Skipper, P. L., Taghizadeh, K., Tannenbaum, S. R.,
Chan, K. K., Henderson, B. E., and Ross, R. K. (1994) Acetylator
phenotype, aminobiphenyl-hemoglobin adduct levels, and bladder
cancer risk in white, black, and Asian men in Los Angeles, California.
J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 86, 712–716.
(585) Gan, J., Skipper, P. L., Gago-Dominguez, M., Arakawa, K.,
Ross, R. K., Yu, M. C., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (2004) Alkylaniline-
hemoglobin adducts and risk of non-smoking-related bladder cancer.
J Natl. Cancer Inst. 96, 1425–
1431.
(586) Turesky, R. J., Skipper, P. L., and Tannenbaum, S. R. (1987)
Binding of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline to hemoglobin
and albumin in vivo in the rat. Identification of an adduct suitable for
dosimetry. Carcinogenesis 8, 1537–1542.
(587) Lynch, A. M., Murray, S., Zhao, K., Gooderham, N. J., Boobis,
A. R., and Davies, D. S. (1993) Molecular dosimetry of the food-borne
carcinogen MeIQx using adducts of serum albumin. Carcinogenesis
14, 191–194.
(588) Dingley, K. H., Freeman, S. P., Nelson, D. O., Garner, R. C.,
and Turteltaub, K. W. (1998) Covalent binding of 2-amino-3,8-
dimethylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoxaline to albumin and hemoglobin at en-
vironmentally relevant doses. Comparison of human subjects and F344
rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 26, 825–828.
(589) Umemoto, A., Monden, Y., Tsuda, M., Grivas, S., and Sugimura,
T. (1988) Oxidation of the 2-hydroxyamino derivative of 2-amino-6-
methyl-dipyrido[1,2-a: 3
0
,2
0
-d] imidazole(Glu-P-1) to its 2-nitroso form,
an ultimate form reacting with hemoglobin thiol groups. Biochem. Biophys.
Res. Commun. 151, 1326–1331.
(590) Peters, T., Jr. (1996) All about Albumin. Biochemistry, Genetics,
and Medical applications, Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
(591) Magagnotti, C., Orsi, F., Bagnati, R., Celli, N., Rotilio, D.,
Fanelli, R., and Airoldi, L. (2000) Effe ct of diet on serum albumin and
hemoglobin adducts of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-
(PhIP) in humans. Int. J. Cancer 88,1–6.
(592) Chepanoske, C. L., Brown, K., Turteltaub, K. W., and Dingley,
K. H. (2004) Characterization of a peptide adduct formed by N-acetoxy-
2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP), a reactive
1212 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
intermediate of the food carcinogen PhIP. Food Chem. Toxicol.
42, 1367–1372.
(593) Funk, W. E., Li, H., Iavarone, A. T., Williams, E. R., Riby, J., and
Rappaport, S. M. (2010) Enrichment of cysteinyl adducts of human
serum albumin. Anal. Biochem. 400,61–68.
(594) Carballal, S., Radi, R., Kirk, M. C., Barnes, S., Freeman, B. A.,
and Alvarez, B. (2003) Sulfenic acid formation in human serum albumin
by hydrogen peroxide and peroxynitrite. Biochemistry 42, 9906–9914.
(595) Beck, J. L., Ambahera, S., Yong, S. R., Sheil, M. M., de, J. J., and
Ralph, S. F. (2004) Direct observation of covalent adducts with Cys
34
of
human serum albumin using mass spectrometry. Anal.Biochem.325,
326–336.
(596) Rappaport S. M., Li H, Grigoryan H, Funk W. E., Williams
E. R. Adductomics: Characterizing exposures to reactive electrophiles.
Toxicol. Lett. In press.
(597) Reistad, R., Frandsen, H., Grivas, S., and Alexander, J. (1994) In
vitro formation and degradation of 2-amino-1-methyl-6- phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) protein adducts. Carcinogenesis 15, 2547–2552.
(598) Noort, D., Fidder, A., and Hulst, A. G. (2003) Modification of
human serum albumin by acrylamide at cysteine-34: a basis for a rapid
biomonitoring procedure. Arch. Toxicol. 77 , 543–545.
(599) Noort, D., Hulst, A. G., de Jong, L. P., and Benschop, H. P.
(1999) Alkylation of human serum albumin by sulfur mustard in vitro
and in vivo: mass spectrometric analysis of a cysteine adduct as a
sensitive biomarker of exposure. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 12, 715–721.
(600) Bechtold, W. E., Willis, J. K., Sun, J. D., Griffith, W. C., and
Reddy, T. V. (1992) Biological markers of exposure to benzene:
S-phenylcysteine in albumin. Carcinogenesis 13, 1217–1220.
(601) Hoffmann, K. J., Streeter, A. J., Axworthy, D. B., and Baillie,
T. A. (1985) Structural characterization of the major covalent adduct
formed in vitro between acetaminophen and bovine serum albumin.
Chem.-Biol. Interact. 53, 155–172.
(602) Kim, D., Kadlubar, F. F., Teitel, C. H., and Guengerich, F. P.
(2004) Formation and reduction of aryl and heterocyclic nitroso
compounds and significance in the flux of hydroxylamines. Chem. Res.
Toxicol. 17, 529–536.
(603) DuPont, R. L., and Baumgartner, W. A. (1995) Drug testing
by urine and hair analysis: complementary features and scientific issues.
Forensic Sci. Int. 70,63–76.
(604) Hegstad, S., Lundanes, E., Reistad, R., Haug, L. S., Becher, G.,
and Alexander, J. (2000) Determination of the food carcinogen 2-amino-
1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) in human hair by so-
lid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chro-
matographia 52, 499–504.
(605) Hashimoto, H., Hanaoka, T., Kobayashi, M., and Tsugane, S.
(2004) Analytical method of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-
b]pyridine in human hair by column-switching liquid chromatography-
mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr., B 803, 209–213.
(606) Kobayashi, M., Hanaoka, T., Hashimoto, H., and Tsugane, S.
(2005) 2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) level
in human hair as biomarkers for dietary grilled/stir-fried meat and fish
intake. Mutat. Res. 588, 136–142.
(607) Bessette, E. E., Yasa, I., Dunbar, D., Wilkens, L. R., Marchand,
L. L., and Turesky, R. J. (2009) Biomonitoring of carcinogenic hetero-
cyclic aromatic amines in hair: A validation study. Chem. Res. Toxicol.
22, 1454–1463.
(608) Reistad, R., Nyholm, S. H., Huag, L. S., Becher, G., and
Alexander, J. (1999) 2-Amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-
(PhIP) in human hair as biomarker for dietary exposure. Biomarkers
4, 263–271.
(609) Kobayashi, M., Hanaoka, T., and Tsugane, S. (2007) Validity
of a self-administered food frequency questionnaire in the assessment of
heterocyclic amine intake using 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo-
[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) levels in hair. Mutat. Res. 630,14–19.
(610) Hegstad, S., Reistad, R., Haug, L. S., and Alexander, J. (2002)
Eumelanin is a major determinant for 2-amino-1-methyl-6-pheny-
limidazo[4,5-b]pyridine(PhIP) incorporation into hair of mice. Pharmacol.
Toxicol. 90,333–337.
(611) Ozeki, H., Ito, S., Wakamatsu, K., and Thody, A. J. (1996)
Spectrophotometric characterization of eumelanin and pheomelanin in
hair. Pigment Cell Res. 9, 265–270.
(612) Reisch, M. S. (2003) Flush with color: Continuing progress in
hair dye chemistry satisfies diverse desires of young and old. Chem. Eng.
News 81,25–27.
(613) Corbett, J. F., and Menkart, J. (1973) Hair Coloring. Cutis
12, 190–197.
(614) Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: a
Global Perspective, (2007) AICR, Washington, DC.
(615) Sinha, R., Kulldorff, M., Chow, W. H., Denobile, J., and
Rothman, N. (2001) Dietary intake of heterocyclic amines, meat-derived
mutagenic activity, and risk of colorectal adenomas. Cancer Epidemiol.
Biomarkers Prev. 10, 559–562.
(616) Cross, A. J., and Sinha, R. (2004) Meat-related mutagens/
carcinogens in the etiology of colorectal cancer. Environ. Mol. Mutagen.
44,44–55.
(617) Ferguson, L. R. (2010) Meat and cancer. Meat Sci. 84,
308–313.
(618) Zheng, W., and Lee, S. A. (2009) Well-done meat intake,
heterocyclic amine exposure, and cancer risk. Nutr. Cancer 61, 437–446.
(619) Nowell, S., Coles, B., Sinha, R., MacLeod, S., Luke, R. D.,
Stotts, C., Kadlubar, F. F., Ambrosone, C. B., and Lang, N. P. (2002)
Analysis of total meat intake and exposure to individual heterocyclic
amines in a case-control study of colorectal cancer: contribution of
metabolic variation to risk. Mutat. Res. 506-507, 175–
185.
(620) Butler, L. M., Sinha, R., Millikan, R. C., Martin, C. F., Newman,
B., Gammon, M. D., Ammerman, A. S., and Sandler, R. S. (2003)
Heterocyclic amines, meat intake, and association with colon cancer in a
population-based study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 157, 434–445.
(621) Wu, K., Giovannucci, E., Byrne, C., Platz, E. A., Fuchs, C.,
Willett, W. C., and Sinha, R. (2006) Meat mutagens and risk of distal
colon adenoma in a cohort of U.S. men. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers
Prev. 15, 1120–1125.
(622) Augustsson, K., Skog, K., Jagerstad, M., Dickman, P. W., and
Steineck, G. (1999) Dietary heterocyclic amines and cancer of the colon,
rectum, bladder, and kidney: a population-based study. Lancet 353,
703–707.
(623) Brockton, N., Little, J., Sharp, L., and Cotton, S. C. (2000) N-
acetyltransferase polymorphisms and colorectal cancer: a HuGE review.
Am. J Epidemiol. 151, 846–861.
(624) Agundez, J. A. (2008) Polymorphisms of human N-acetyl-
transferases and cancer risk. Curr. Drug. Metab. 9, 520–531.
(625) Dong, L. M., Potter, J. D., White, E., Ulrich, C. M., Cardon,
L. R., and Peters, U. (2008) Genetic susceptibility to cancer: the role of
polymorphisms in candidate genes. JAMA 299, 2423–2436.
(626) Welfare, M. R., Cooper, J., Bassendine, M. F., and Daly, A. K.
(1997) Relationship between acetylator status, smoking, and diet and
colorectal cancer risk in the north-east of England. Carcinogenesis
18, 1351–1354.
(627) Tiemersma, E. W., Bunschoten, A., Kok, F. J., Glatt, H., de
Boer, S. Y., and Kampman, E. (2004) Effect of SULT1A1 and NAT2
genetic polymorphism on the association between cigarette smoking
and colorectal adenomas. Int. J. Cancer 108,97–103.
(628) Chan, A. T., Tranah, G. J., Giovannucci, E. L., Willett, W. C.,
Hunter, D. J., and Fuchs, C. S. (2005) Prospective study of N-acetyl-
transferase-2 genotypes, meat intake, smoking and risk of colorectal
cancer. Int. J. Cancer 115, 648–652.
(629) Lilla, C., Verla-Tebit, E., Risch, A., Jager, B., Hoffmeister, M.,
Brenner, H., and Chang-Claude, J. (2006) Effect of NAT1 and NAT2
genetic polymorphisms on colorectal cancer risk associated with ex-
posure to tobacco smoke and meat consumption. Cancer Epidemiol.
Biomarkers Prev. 15,99–107.
(630) Nothlings, U., Yamamoto, J. F., Wilkens, L. R., Murphy, S. P.,
Park, S. Y., Henderson, B. E., Kolonel, L. N., and Le, M. L. (2009) Meat
and heterocyclic amine intake, smoking, NAT1 and NAT2 polymorph-
isms, and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort study. Cancer
Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 18, 2098–2106.
1213 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214

Chemical Research in Toxicology
REVIEW
(631) Ishibe, N., Sinha, R., Hein, D. W., Kulldorff, M., Strickland, P.,
Fretland, A. J., Chow, W. H., Kadlubar, F. F., Lang, N. P., and Rothman,
N. (2002) Genetic polymorphisms in heterocyclic amine metabolism
and risk of colorectal adenomas. Pharmacogenetics 12, 145–150.
(632) Wang, H., Yamamoto, J. F., Caberto, C., Saltzman, B., Decker,
R., Vogt, T. M., Yokochi, L., Chanock, S., Wilkens, L. R., and Le, M. L.
(2011) Genetic variation in the bioactivation pathway for polycyclic
hydrocarbons and heterocyclic amines in relation to risk of colorectal
neoplasia. Carcinogenesis 32, 203–209.
(633) Cotterchio, M., Boucher, B. A., Manno, M., Gallinger, S.,
Okey, A. B., and Harper, P. A. (2008) Red meat intake, doneness,
polymorphisms in genes that encode carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes,
and colorectal cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 17,
3098–3107.
(634) Kury, S., Buecher, B., Robiou-du-Pont, S., Scoul, C., Sebille, V.,
Colman, H., Le, H. C., Le, N. T., Bourdon, J., Faroux, R., Ollivry, J.,
Lafraise, B., Chupin, L. D., and Bezieau, S. (2007) Combinations of
cytochrome P450 gene polymorphisms enhancing the risk for sporadic
colorectal cancer related to red meat consumption. Cancer Epidemiol.
Biomarkers Prev. 16, 1460–1467.
(635) Barrett, J. H., Smith, G., Waxman, R., Gooderham, N., Lightfoot,
T., Garner, R. C., Augustsson, K., Wolf, C. R., Bishop, D. T., and Forman,
D. (2003) Investigation of interaction between N-acetyltransferase 2
and heterocyclic amines as potential risk factors for colorectal cancer.
Carcinogenesis 24, 275–282.
(636) Murtaugh, M. A., Ma, K. N., Sweeney, C., Caan, B. J., and
Slattery, M. L. (2004) Meat consumption patterns and preparation,
genetic variants of metabolic enzymes, and their association with rectal
cancer in men and women. J. Nutr. 134, 776–784.
(637) Kampman, E., Slattery, M. L., Bigler, J., Leppert, M., Samowitz,
W., Caan, B. J., and Potter, J. D. (1999) Meat consumption, genetic
susceptibility, and colon cancer risk: a United States multicenter case-
control study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 8,15–24.
(638) Lumbreras, B., Garte, S., Overvad, K., Tjonneland, A., Clavel-
Chapelon, F., Linseisen, J. P., Boeing, H., Trichopoulou, A., Palli, D.,
Peluso, M., Krogh, V., Tumino, R., Panico, S., Bueno-De-Mesquita,
H. B., Peeters, P. H., Lund, E., Martinez, C., Dorronsoro, M., Barricarte,
A., Chirlaque, M. D., Quiros, J. R., Berglund, G., Hallmans, G., Day,
N. E., Key, T. J., Saracci, R., Kaaks, R., Malaveille, C., Ferrari, P., Boffetta,
P., Norat, T., Riboli, E., Gonzalez, C. A., and Vineis, P. (2008) Meat
intake and bladder cancer in a prospective study: a role for heterocyclic
aromatic amines? Cancer Causes Control 19, 649–656.
(639) Le Marchand, L., Hankin, J. H., Wilkens, L. R., Pierce, L. M.,
Franke, A., Kolonel, L. N., Seifried, A.,Custer, L. J.,Chang,W., Lum-Jones,
A., and Donlon, T. (2001) Combined effects of well-done red meat,
smoking, and rapid N-acetyltransferase 2 and CYP1A2 phenotypes in
increasing colorectal cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 10,
1259–1266.
(640) Kristal, A. R., Peters, U., and Potter, J. D. (2005) Is it time to
abandon the food frequency questionnaire? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers
Prev. 14, 2826–2828.
(641) Knize, M. G., Kulp, K. S., Salmon, C. P., Keating, G. A., and
Felton, J. S. (2002) Factors affecting human heterocyclic amine intake
and the metabolism of PhIP. Mutat. Res. 506-507, 153–162.
(642) Loeb, L. A., and Harris, C. C. (2008) Advances in chemical
carcinogenesis: a historical review and prospective. Cancer Res.
68, 6863–6872.
(643) Wogan, G. N., Hecht, S. S., Felton, J. S., Conney, A. H., and
Loeb, L. A. (2004) Environmental and chemical carcinogenesis. Semin.
Cancer Biol. 14, 473–486.
(644) Ross, R. K., Yuan, J. M., Yu, M. C., Wogan, G. N., Qian, G. S.,
Tu, J. T., Groopman, J. D., Gao, Y. T., and Henderson, B. E. (1992)
Urinary aflatoxin biomarkers and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma [see
comments]. Lancet 339, 943–946.
(645) Greenblatt, M. S., Bennett, W. P., Hollstein, M., and
Harris, C. C. (1994) Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene:
clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 54,
4855–4878.
(646) Schmeiser, H. H., Stiborova, M., and Arlt, V. M. (2009)
Chemical and molecular basis of the carcinogenicity of Aristolochia
plants. Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Dev. 12, 141–148.
(647) Lai, M. N., Wang, S. M., Chen, P. C., Chen, Y. Y., and Wang,
J. D. (2010) Population-based case-control study of Chinese herbal
products containing aristolochic acid and urinary tract cancer risk. J Natl.
Cancer Inst. 102, 179–186.
’ NOTE ADDED AFTER ASAP PUBLICATION
This paper was published on the Web on June 20, 2011, with
an error in Figure 10. The corrected version was reposted on July
27, 2011.
1214 dx.doi.org/10.1021/tx200135s |Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1169–1214
