
ESRD Surveyor Training
Interpretive Guidance
Final Version 1.1
October 3, 2008
If found, return this manual to:
Name:
Address:
City: State: Zip:
Phone: ( ) Fax: ( ) Email:
Helpful Contact Name
Phone Number(s)
Fax Number(s)
Email Address(es)
Regional Office:
ESRD Network:
State Headquarters:

Revision History
Revision Effective Date Author Description of Change
1.1 05/07/2014 Helen Blakey This document had internal changes previously recorded by the ESRD team which
are identified with this version number. This table is for the purpose of recording
future changes.
This version is being released for the class offering beginning June 23, 2014.
iii
iv
PART 494 CONDITIONS FOR COVERAGE FOR END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE FACILITIES
Interpretive Guidance
Subpart A—General Provisions ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 1
§ 494.1 Basis and scope. ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 1
§ 494.10 Definitions. .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 2
§ 494.20 Condition: Compliance with Federal, State, and local laws and regulations. ............................................................................................. 3
Subpart B—Patient Safety .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 4
§ 494.30 Condition: Infection control. ....................................................................................................................................................................... 4
§ 494.40 Condition: Water and dialysate quality. .................................................................................................................................................... 33
§ 494.50 Condition: Reuse of hemodialyzers and bloodlines. ............................................................................................................................... 116
§ 494.60 Condition: Physical environment. ........................................................................................................................................................... 162
Subpart C—Patient Care ............................................................................................................................................................................................ 175
§ 494.70 Condition: Patients’ rights. ...................................................................................................................................................................... 175
§ 494.80 Condition: Patient assessment. ................................................................................................................................................................ 186
§ 494.90 Condition: Patient plan of care. ............................................................................................................................................................... 202
§ 494.100 Condition: Care at home. ....................................................................................................................................................................... 223
§ 494.110 Condition: Quality assessment and performance improvement. ........................................................................................................... 246
§ 494.120 Condition: Special purpose renal dialysis facilities. .............................................................................................................................. 260
§ 494.130 Condition: Laboratory services. ............................................................................................................................................................ 265
Subpart D – Administration ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 266
§ 494.140 Condition: Personnel qualifications. ..................................................................................................................................................... 266
§ 494.150 Condition: Responsibilities of the medical director. ............................................................................................................................. 276
§ 494.160 [Reserved]
§ 494.170 Condition: Medical records. .................................................................................................................................................................. 281
§ 494.180 Condition: Governance. ......................................................................................................................................................................... 286

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Subpart A—General Provisions
§ 494.1 Basis and scope.
(a) Statutory basis. This part is based on the following
provisions:
(1) Section 299I of the Social Security Amendments of
1972 (Pub. L. 92-603), which extended Medicare
coverage to insured individuals, their spouses, and their
dependent children with ESRD who require dialysis or
transplantation.
(2) Section 1861(e)(9) of the Act, which requires
hospitals to meet such other requirements as the
Secretary finds necessary in the interest of health and
safety of individuals who are furnished services in the
institution.
(3) Section 1861(s)(2)(F) of the Act, which describes
“medical and other health services” covered under
Medicare to include home dialysis supplies and
equipment, self-care home dialysis support services, and
institutional dialysis services and supplies.
(4) Section 1862(a) of the Act, which specifies
exclusions from coverage.
(5) Section 1881 of the Act, which authorizes Medicare
coverage and payment for the treatment of ESRD in
approved facilities, including institutional dialysis
services, transplantation services, self-care home dialysis
services, and the administration of erythropoiesis-
stimulating agent(s).
(6) Section 12(d) of the National Technology Transfer
and Advancement Act of 1995 (Pub. L. 104-113), which
requires Federal agencies to use technical standards that
are developed or adopted by voluntary consensus
standards bodies, unless their use would be inconsistent
with applicable law or otherwise impractical.
Final Version 1.1 Page 1 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(b) Scope. The provisions of this part establish the
conditions for coverage of services under Medicare and
are the basis for survey activities for the purpose of
determining whether an ESRD facility’s services may be
covered.
§ 494.10 Definitions
.
As used in this part–
Dialysis facility means an entity that provides outpatient
maintenance dialysis services, or home dialysis training
and support services, or both. A dialysis facility may be
an independent or hospital-based unit (as described in
413.174(b) and (c) of this chapter) that includes a self-
care dialysis unit that furnishes only self-dialysis
services.
Discharge means the termination of patient care services
by a dialysis facility or the patient voluntarily
terminating dialysis when he or she no longer wants to
be dialyzed by that facility.
Furnishes directly means the ESRD facility provides the
service through its own staff and employees or through
individuals who are under direct contract to furnish these
services personally for the facility.
Home dialysis means dialysis performed at home by an
ESRD patient or caregiver who has completed an
appropriate course of training as described in §
494.100(a) of this part.
Final Version 1.1 Page 2 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Self-dialysis means dialysis performed with little or no
professional assistance by an ESRD patient or caregiver
who has completed an appropriate course of training as
specified in § 494.100(a) of this part.
Transfer means a temporary or permanent move of a
patient from one dialysis facility to another that requires
a transmission of the patient’s medical record to the
facility receiving the patient.
V100
§ 494.20 Condition: Compliance with Federal, State,
and local laws and regulations.
This Condition emphasizes Centers for Medicare & Medicaid
Services’ (CMS) role as a partner with State and local governments
and with other Federal agencies. The purpose of this Condition is to
affirm the principle that Medicare reimbursement should be
distributed to ESRD facilities that comply with local, State and
Federal laws and rules. This Condition is not intended to adjudicate
laws and rules from state and local governmental agencies. This
Condition should only be cited when a specific “deficient” practice
has been completely settled with the appropriate entity, and a final
decision of non-compliance with the other entity’s requirement has
been reached. Facilities are expected to comply fully with
investigations conducted by public health, regulatory, or law
enforcement authorities.
V101
The facility and its staff must operate and furnish
services in compliance with applicable Federal, State,
and local laws and regulations pertaining to licensure and
any other relevant health and safety requirements.
Applicable laws and regulations of other Federal agencies which
could be cited here include the Department of Health & Human
Services’ Office of Civil Rights (DHHS OCR) for the privacy
provisions of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
(HIPAA), the Department of Justice Civil Rights Division for Title III
related to public accommodations under the Americans with
Disabilities Act (ADA); the Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (OSHA) for regulations related to employee safety;
and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for regulations related
to the safety of drugs and medical devices. If a drug or device may
have caused or contributed to a serious injury or illness, the facility
Final Version 1.1 Page 3 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
must notify the manufacturer and the FDA using FDA’s User Facility
reporting requirements. Clusters of adverse events (infectious or non-
infectious) should also be reported to the appropriate State or local
public health department, as required by those authorities. Because
these other Federal laws are complex, surveyors are not expected to be
their enforcement mechanism. If noncompliance with the laws or rules
of another Federal agency is suspected or noted, contact your CMS
Regional Office (RO) for guidance.
Compliance with reporting communicable diseases is addressed in the
Condition for Infection control at V145. Compliance with
requirements for FDA reporting related to dialyzer/bloodline reuse is
addressed in the Condition for Reuse at V383. Compliance with
licensure and certification of facility staff is addressed in the
Condition for Personnel qualifications at V681.
Subpart B—Patient Safety
V110
§ 494.30 Condition: Infection control.
This Condition incorporates as regulation two documents from the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and also includes
CMS-developed regulations. These infection control requirements
apply to both the chronic dialysis in-center facility and any home
dialysis program(s).
Survey of this Condition requires observations of care delivery,
interviews with staff and patients, and review of medical records,
facility logs, policies and procedures and quality assessment and
performance improvement (QAPI) documentation. Direct care staff
are observed and interviewed relative to infection control practices.
Administrative and supervisory staff, as well as the medical director,
may be interviewed to clarify issues. Medical and administrative
records must demonstrate recognition of any potential infection and
actions taken to decrease the transmission of infection within the
dialysis facility.
Final Version 1.1 Page 4 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
If deficient practices noted in infection control techniques are
multiple, pervasive, or of an extent to present a risk to patient health
and safety, Condition level non-compliance should be considered.
V111
The dialysis facility must provide and monitor a sanitary
environment to minimize the transmission of infectious
agents within and between the unit and any adjacent
hospital or other public areas.
The CDC defines a “sanitary environment” as an environment that
meets the “Standard Precautions” for an inpatient hospital setting plus
the more stringent precautions which are recommended for
hemodialysis units because of the increased potential for
contamination with blood and pathogenic microorganisms.
“Standard Precautions” apply to the care of all patients in any
healthcare setting and include the use of gloves, gown, or mask
whenever needed to prevent contact of the health-care worker with
blood, secretions, excretions, or contaminated items.
Standard Precautions are the CDC’s system of infection control
precautions for all health care settings. Standard Precautions emerged
from Universal Precautions and (UP) and Body Substance Isolation
(BSI) and are based on the principle that all blood, body fluids,
secretions, and excretions (except sweat), non-intact skin, and mucous
membranes may contain transmissible infectious agents.
Dialysis facilities should adhere to Standard Precautions for all health
care settings and the additional precautions recommended for
hemodialysis facilities for infection control. Infection control
requirements apply to both the chronic dialysis in-center facility and
any home dialysis program(s).
V112
(a) Standard: Procedures for infection control. The
facility must demonstrate that it follows standard
infection control precautions by implementing—
(1)(i) The recommendations (with the exception of
screening for hepatitis C), found in “Recommendations
for Preventing Transmission of Infections Among
Chronic Hemodialysis Patients,” developed by the
The CDC “Recommendations for Preventing Transmission of
Infections Among Chronic Hemodialysis Patients” (MMWR, Vol.
50/No. RR-5), pages 18 to 28, including the “Recommended Infection
Control Practices for Hemodialysis Units at a Glance,” is incorporated
by reference and has the authority of regulation. For purposes of these
Conditions for Coverage, the portions of the CDC infection control
recommendations which are incorporated by reference are mandatory
Final Version 1.1 Page 5 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Morbidity
and Mortality Weekly Report, volume 50, number RR05,
April 27, 2001, pages 18 to 28. The Director of the
Federal Register approves this incorporation by reference
in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR Part 51.
This publication is available for inspection at the CMS
Information Resource Center, 7500 Security Boulevard,
Central Building, Baltimore, MD or at the National
Archives and Records Administration (NARA). Copies
may be obtained at the CMS Information Resource
Center. For information on the availability of this
material at NARA, call 202–741–6030, or go to:
http://www.archives.gov/federal_register/code_of_regula
tions/ibr_locations.html. The recommendation found
under section header “HBV-Infected Patients”, found on
pages 27 and 28 of RR05 (“Recommendations for
Preventing Transmission of Infections Among Chronic
Hemodialysis Patients”), concerning isolation rooms,
must be complied with by February 9, 2009.
and must be adhered to and demonstrated within the dialysis facility.
When serving as Regulation text, the words of the CDC document are
excerpted exactly as written. When serving as a part of the
Interpretive Guidance, the language incorporated from these
documents has been edited for clarity, brevity, and to eliminate
redundant requirements. The entire CDC document includes
background information and rationale for the CDC recommended
practices and can be used as an informational resource.
According to the CDC, “preventing transmission among chronic
hemodialysis patients of bloodborne viruses and pathogenic bacteria
from both recognized and unrecognized sources of infection requires
implementation of a comprehensive infection control program. The
components of such a program include infection control practices
specifically designed for the hemodialysis setting, including routine
serologic testing and immunization, surveillance, training and
education.”
CDC’s components of a comprehensive infection control program to
prevent transmission of infections among chronic hemodialysis
patients include:
• Infection control practices for hemodialysis units
- Infection control precautions specifically designed to prevent
transmission of bloodborne viruses and pathogenic bacteria
among patients.
- Routine serologic testing for hepatitis B virus infections.
- Vaccination of susceptible patients against hepatitis B.
- Isolation of patients who test positive for hepatitis B surface
antigen.
• Surveillance for infections and other adverse events.
• Infection control training and education.
The infection control practices recommended by CDC for
Final Version 1.1 Page 6 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
hemodialysis units will reduce opportunities for patient-to-patient
transmission of infectious agents, directly or indirectly through
contaminated devices, equipment and supplies, environmental
surfaces, or hands of personnel. These practices should be carried out
routinely for all patients in the chronic hemodialysis setting because
of the increased potential for blood contamination during
hemodialysis and because many patients are colonized or infected
with pathogenic bacteria. Those infection control practices include
additional measures to prevent Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) transmission
because of the high titer of HBV in each milliliter of infected blood
and its ability to survive on environmental surfaces.
According to the CDC, for patients at increased risk for transmission
of pathogenic bacteria, including antimicrobial-resistant strains,
additional precautions might also be necessary. Patients with either an
infected skin wound with drainage uncontrolled by dressings or
uncontrolled fecal incontinence or diarrhea should be dialyzed at a
station with as few adjacent stations as possible. Staff members
treating the patient should wear a separate gown for the care of the
patient, and supplies and equipment (such as blood pressure cuffs)
should not be shared between patients who have uncontrolled draining
wounds.
Surveillance for infections and other adverse events is required to
monitor the effectiveness of infection control practices, as well as
training and education of both staff members and patients to ensure
that appropriate infection control behaviors and techniques are carried
out.
V113
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
Wear disposable gloves when caring for the patient or
touching the patient’s equipment at the dialysis station.
Staff must remove gloves and wash hands between each
According to the CDC, handwashing is the most important measure to
prevent contaminant transmission.
Because exposure to blood and potentially contaminated items can be
routinely anticipated during hemodialysis, gloves are required
Final Version 1.1 Page 7 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
patient or station.
whenever caring for a patient or touching the patient’s equipment. To
facilitate glove use, a supply of clean nonsterile gloves and waste
receptacles should be readily accessible to each dialysis station and
work area. Gloves should be changed frequently during patient care.
Examples of when gloves should be worn:
• Staff members should wear gloves while performing procedures
which have the potential for exposure to blood, dialysate and other
potentially infectious substances. This includes procedures such as
caring for patients' vascular accesses or catheters, setting up
reprocessed dialyzers pre dialysis treatment, inserting or removing
the vascular access needles, connecting the dialysis blood lines to
the vascular access needle lines or catheter lines, touching the
dialysis blood lines, dialyzer, or machine during or after a dialysis
treatment, administering intravenous medications, handling blood
lines, dialyzers, dialysate tubing and machines post dialysis
treatment, and cleaning and disinfecting the dialysis machine and
chair post dialysis treatment.
• Gloves must be provided to patients and visitors if these
individuals assist with procedures which risk exposure to blood or
body fluids, such as when self-cannulating or holding access sites
post treatment to achieve hemostasis.
• Chair-side computer keyboards/screens can easily become
contaminated because of their proximity to the patient station.
Hand hygiene is imperative after contact with the chair-side
computer and before contact with the patient, regardless of
whether contact with the computer occurred through gloved or
ungloved hands.
Examples of when gloves should be changed:
• When soiled (e.g., with blood, dialysate or other body fluids);
• When going from a “dirty” area or task to a “clean” area or task.
Final Version 1.1 Page 8 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The CDC defines a “dirty” area as an area where there is a
potential for contamination with blood or body fluids and areas
where contaminated or “used” supplies, equipment, blood supplies
or biohazard containers are stored or handled. A “clean” area is an
area designated only for clean and unused equipment and supplies
and medications;
• When moving from a contaminated body site to a clean body site
of the same patient; and
• After touching one patient or their machine and before arriving to
care for another patient or touch another patient’s machine.
In addition, a new pair of clean gloves must be used each time for
access site care, vascular access cannulation, administration of
parenteral medications or to perform invasive procedures. The
intention is to ensure that clean gloves which have not previously
touched potentially contaminated surfaces are in use whenever there is
a risk for cross contamination to a patient’s blood stream to occur.
“Hand hygiene” includes either washing hands with soap and water,
or using a waterless alcohol-based antiseptic hand rub with 60-90%
alcohol content. Hands should be washed with soap and water if
visibly soiled. If not visibly soiled, hand hygiene with alcohol-based
hand rub may be used. The CDC recommends that hand washing
incorporate rubbing hands together “vigorously” for 15 seconds, and
that the use of alcohol-based rubs incorporate covering all surfaces of
hands and fingers, until hands are dry. According to the CDC, even
with glove use, hand hygiene is necessary after glove removal because
hands can become contaminated through small defects in gloves and
from the outer surface of gloves during glove removal.
Examples of when hand hygiene should be performed:
• After touching blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, and
potentially contaminated items;
Final Version 1.1 Page 9 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
• Before and after direct contact with patients;
• Before performing any invasive procedure such as vascular access
cannulation or administration of parenteral medications;
• Immediately after gloves are removed;
• After contact with inanimate objects, including medical equipment
or environmental surfaces at the patient station;
• Before entering and on exiting the patient treatment areas; and
• When moving from a contaminated body site to a clean body site
of the same patient.
The CDC document, “Prevention of Intravascular Catheter-Related
Infections,” (“RR-10” which is adopted as regulation in this section),
states that staff should wear clean or sterile gloves when changing the
dressing on intravascular catheters. Staff must observe hand hygiene
before and after palpating catheter insertion sites, as well as before
and after accessing or dressing an intravascular catheter.
Hand hygiene is required after every direct contact with a patient and
between patient contacts, even if the contact is casual. Gloves are not
necessary for casual social contact with a patient, for example, staff
members may touch the patient’s shoulder, take his/her arm, or shake
hands without wearing gloves. However, gloves should always be
worn anytime contact with blood or body fluids is anticipated.
Physicians and non-physician practitioners functioning in lieu of
physicians (i.e., advanced practice registered nurses and physician
assistants), social workers and dietitians must follow these same
requirements for glove use and hand hygiene.
V114
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
A sufficient number of sinks with warm water and soap
A “sufficient number” means that sinks are easily accessible and
readily available in the patient treatment area and in other appropriate
areas such as the reuse room, medication area, home training room,
and isolation area/room to meet the needs of the staff and patients.
Final Version 1.1 Page 10 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
should be available to facilitate hand washing.
Sinks must be plumbed with both hot and cold water; if the flow of
water is started through motion detection, adjustments to the system
must assure that warm water is available to encourage staff to wash
their hands according to CDC recommendations (see V113).
Handwashing sinks should be dedicated only for handwashing
purposes and should remain clean. Avoid placing, cleaning, or
draining used items in handwashing sinks. Used or contaminated
items should be handled in designated utility sinks. The facility should
have a sink available for patients to wash their access sites prior to
treatment and their hands after treatment. This sink may also be used
by staff for handwashing. Soap and a supply of paper towels protected
from contamination must be available at each sink.
V115
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
Staff members should wear gowns, face shields, eye
wear, or masks to protect themselves and prevent soiling
of clothing when performing procedures during which
spurting or spattering of blood might occur (e.g., during
initiation and termination of dialysis, cleaning of
dialyzers, and centrifugation of blood). Staff members
should not eat, drink, or smoke in the dialysis treatment
area or in the laboratory.
Staff should wear personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriate to
the anticipated potential exposure. Staff should wear PPE during the
initiation and termination of dialysis treatment, manipulation of access
needles or catheters, administration of medications through the
extracorporeal circuit or by subcutaneous injection, the reprocessing
of dialyzers, and cleaning and disinfecting of patient care supplies and
equipment. Protective clothing or gear must be changed if it becomes
soiled with blood, body fluids (including dialysate), secretions, or
excretions.
Street clothes, scrub suits, or uniforms are sufficient attire within the
dialysis unit, except for times when the spurting or spattering of
blood, body fluids, potentially-contaminated substances, or chemicals
might occur. At those times a cover garment which provides an
impervious barrier to fluids must be worn. This could be a lab coat, a
gown, or an apron which incorporates sleeves. The garment may open
to the back or front, but must be closed in front during use for patient
care. The protective garment should fully cover the arms and torso
from the neck area to the thigh/knee area. Aprons without sleeves are
not sufficient PPE for procedures which may result in spurting or
Final Version 1.1 Page 11 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
spattering of blood.
Physicians, advanced practice registered nurses, physician assistants,
social workers and dietitians must wear a cover garment which
provides an impervious barrier to fluids if they are providing service
to any patient in the treatment area during a time of high risk for
spurting or spattering of blood, as, for example, during initiation or
termination of dialysis. The garment should be changed if it becomes
soiled. Visitors must be provided impervious cover garments if they
are in the treatment area during initiation or termination of dialysis.
Home patients do not have to wear gowns when they are caring for
themselves. The partner or caregiver of a home patient should wear
appropriate PPE, including gloves, and practice appropriate hand
hygiene.
Separate PPE (gown, face shield, etc.) should be used in the isolation
area/room and removed before leaving the isolation area/room. If a
patient’s family member or other visitors are allowed in the isolation
area, staff should provide these individuals barrier PPE, to be worn
during the visit and removed when leaving.
The “treatment area” includes the reuse room and home training area.
Staff must avoid any other activity which would allow self-
contamination, such as applying lip balm or handling/inserting contact
lenses in the treatment area. Patients may eat and drink at their
dialysis stations, depending on facility policies. If non-disposable
dishes are provided by the facility, they should be cleaned in the usual
manner; no special care of these items is needed.
V116
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
Items taken into the dialysis station should either be
According to the CDC, any item taken to a patient’s dialysis station
could become contaminated with blood and other body fluids and
serve as a vehicle of transmission to other patients either directly or by
contamination from the hands of personnel. Items taken to a patient’s
Final Version 1.1 Page 12 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
disposed of, dedicated for use only on a single patient, or
cleaned and disinfected before being taken to a common
clean area or used on another patient.
-- Nondisposable items that cannot be cleaned and
disinfected (e.g., adhesive tape, cloth covered blood
pressure cuffs) should be dedicated for use only on a
single patient.
-- Unused medications (including multiple dose vials
containing diluents) or supplies (syringes, alcohol swabs,
etc.) taken to the patient’s station should be used only for
that patient and should not be returned to a common
clean area or used on other patients.
dialysis station include those items placed on the top or sides (in
baskets) of dialysis machines and on dialysis chairs.
After use, all equipment and supplies must be considered as
potentially blood contaminated, and should be separated, handled with
caution, and either disinfected or discarded. If provided, linens should
be removed after use, separated from clean items and laundered. If
blood pressure cuffs are used for multiple patients, the coverings must
be disposable or able to be adequately disinfected.
If the facility provides linens or blankets for patient use, these items
should be considered as potentially contaminated with blood. If
patients bring their own blankets, pillows, etc. patients should be
instructed about washing the linen they bring to treatment and using
bleach to remove blood stains.
If the facility provides portable or cellular phones, remote controls, or
individual televisions for patient use during treatment, these need to
be cleaned if shared among patients.
V117
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
Clean areas should be clearly designated for the
preparation, handling and storage of medications and
unused supplies and equipment. Clean areas should be
clearly separated from contaminated areas where used
supplies and equipment are handled. Do not handle and
store medications or clean supplies in the same or an
adjacent area to that where used equipment or blood
samples are handled.
When multiple dose medication vials are used (including
vials containing diluents), prepare individual patient
According to the CDC, measures to prevent contamination of clean or
sterile items include a) preparing medications in a clean room or area
separated or away from the patient treatment area and designated only
for medications; b) not handling, cleaning, or storing potentially
contaminated (i.e., used) supplies, equipment, blood samples, or
biohazard containers in areas where medications and clean (i.e.,
unused) equipment and supplies are handled; and c) delivering
medications separately to each patient: common medication carts must
not be used to deliver medications.
It is acceptable for the medication prep area to be within the treatment
area, but the space should be away from individual patient stations
and a clean area must be provided. Medications used in the home
training area may be prepared in the same room where home training
Final Version 1.1 Page 13 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
doses in a clean (centralized) area away from dialysis
stations and deliver separately to each patient. Do not
carry multiple dose medication vials from station to
station.
Do not use common medication carts to deliver
medications to patients. If trays are used to deliver
medications to individual patients, they must be cleaned
between patients.
is conducted; a clean area should be provided for this activity.
The patient treatment area should have designated "clean" and "dirty"
areas. The CDC defines a “dirty” area as an area where there is a
potential for contamination with blood or body fluids and areas where
contaminated or “used” supplies, equipment, blood supplies or
biohazard containers are stored or handled. A “clean” area is an area
designated only for clean and unused equipment and supplies and
medications. Staff must remain aware of the separation of clean and
dirty areas to prevent cross-contamination.
Recognize that smaller, older facilities may face challenges in
achieving separate areas for clean and dirty equipment or tasks; the
key is protection of clean areas and items from cross contamination.
V118
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
Intravenous medication vials labeled for single use,
including erythropoietin, should not be punctured more
than once.
According to the CDC, once a needle has entered a vial labeled for
single use, the sterility of the product can no longer be guaranteed.
Residual medication from two or more vials should not be pooled into
a single vial.
Single use vials/ampules must be used for only one patient, should not
be entered more than once, and if entered, may not be stored for future
use.
Staff should only enter vials with a new sterile syringe and needle. If
both vials are single use and are discarded after the single entry into
each, the same syringe may be used. If either vial is multi-use, a
different syringe must be used for entry into each vial.
V119
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
If a common supply cart is used to store clean supplies in
the patient treatment area, this cart should remain in a
designated area at a sufficient distance from patient
According to the CDC, if a common supply cart is used, it must be
kept in a designated area away from any areas where the spurting or
spattering of blood or fluid may occur, and the cart should not travel
between stations.
Medication vials, patient care items including gloves, or other dialysis
Final Version 1.1 Page 14 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
stations to avoid contamination with blood. Such carts
should not be moved between stations to distribute
supplies.
Do not carry medication vials, syringes, alcohol swabs or
supplies in pockets.
supplies should not be in pockets, inside fanny packs, etc.
Supplies of gloves should be strategically placed so that staff has
adequate access for both routine and emergency use.
V120
CDC RR-5 as Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.30
(a)(1)(i)
Use external venous and arterial pressure transducer
filters/protectors for each patient treatment to prevent
blood contamination of the dialysis machines’ pressure
monitors.
If the external transducer protector becomes wet, replace
immediately and inspect the protector. If fluid is visible
on the side of the transducer protector that faces the
machine, have qualified personnel open the machine
after the treatment is completed and check for
contamination. This includes inspection for possible
blood contamination of the internal pressure tubing set
and pressure sensing port. If contamination has occurred,
the machine must be taken out of service and disinfected
using either 1:100 dilution of bleach (300–600 mg/L free
chlorine) or a commercially available, EPA-registered
tuberculocidal germicide before reuse.
Change filters/protectors between each patient treatment,
and do not reuse them. Internal transducer filters do not
need to be changed routinely between patients.
Recognize that some bloodlines do not have external transducer
protectors; this requirement would not apply in those cases, except for
changing the bloodlines between patients.
According to the CDC, external transducer protectors, [which provide
a protective barrier between dialysis bloodlines and the dialysis
machine], should not be reused. “Wet” (“wet with blood or other
fluid”) external transducer protectors must be changed immediately
and the side of the external transducer protector that faces the machine
should be inspected for visible fluid. If the external transducers are
wetted with blood, the staff should inspect the wetted transducer to
see if fluid has passed through. If fluid or blood is visible on the side
of the transducer protector that faces the machine, the machine must
be opened by qualified personnel after the dialysis treatment to allow
the internal transducer to be inspected for contamination, including
inspection for possible blood contamination of the internal pressure
tubing set and pressure sensing port. Frequent blood line pressure
alarms or frequent requirements for adjustment of the blood level in
the drip chamber can be indicators of contamination of the internal
transducer filter.
V121
(4) And maintaining procedures, in accordance with
applicable State and local laws and accepted public
health procedures, for the—
Potentially-infectious waste and soiled laundry should be removed
from the patient treatment area throughout the day as the containers
are filled in order to maintain an environment that enhances safe
Final Version 1.1 Page 15 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(i) Handling, storage and disposal of potentially
infectious waste; and
patient care. All disposable items should be placed in bags thick
enough to prevent leakage.
Any wastes contaminated with blood should be considered
“infectious” and handled according to local, State, and Federal
regulations governing medical waste disposal.
Biohazardous waste containers should be clearly labeled and sealed
prior to being full. Biohazardous waste should be stored in an area
that is protected from casual access and from the ability to
contaminate the water supply.
V122
(ii) Cleaning and disinfection of contaminated surfaces,
medical devices, and equipment.
A facility should establish written protocols for cleaning and
disinfecting surfaces and equipment, including careful mechanical
cleaning before any disinfection process. Refer to CDC RR 5 Table 2
included below for guidance.
Any manufacturer’s guidance for sterilization or disinfection of an
item should be followed, as well as guidance from the chemical
sterilant or disinfectant manufacturer, including appropriate dilution
and contact time.
Failures in environmental cleaning and disinfection have led to
transmission of bloodborne pathogens (e.g., hepatitis B virus) and
other infections from one patient to another in hemodialysis units.
Correct cleaning and disinfection of environmental surfaces
(including patient chair or bed surfaces, dialysis equipment surfaces,
adjacent tables and work surfaces) must be performed between patient
uses to prevent transmission of dangerous pathogens.
In hemodialysis units, cleaning and disinfection procedures during
patient changeover are particularly prone to error and contribute to
risk of cross-contamination if correct procedures are not observed. At
the end of each dialysis treatment, all surfaces without visible blood
Final Version 1.1 Page 16 of 299
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
should be cleaned following the low level disinfection protocol using
soap, detergent or detergent germicide. For visible blood, the
intermediate-level disinfection protocol must be followed, which
requires the area be immediately cleaned with a cloth soaked with
tuberculocidal disinfectant or 1:100 dilution of bleach (300-600 mg/L
free chlorine), following the manufacturer’s direction for contact time.
Gloves must be worn, and the used cloth placed into a leak proof
container. After cleaning up all visible blood, a disinfectant must be
applied a second time using a new cloth or towel. No patient should
be at the station during this time.
For each “station” (i.e., the machine, the purified water connection,
dialysate concentrate container(s) or connection(s), and the treatment
chair), the completion of one patient's treatment and post-dialysis care
must be separated by enough time from the initiation of the next
patient’s care to allow correct disinfection. If the previous patient
remains in the treatment chair while the machine is prepared for the
next patient, extreme caution must be employed to prevent cross-
contamination.
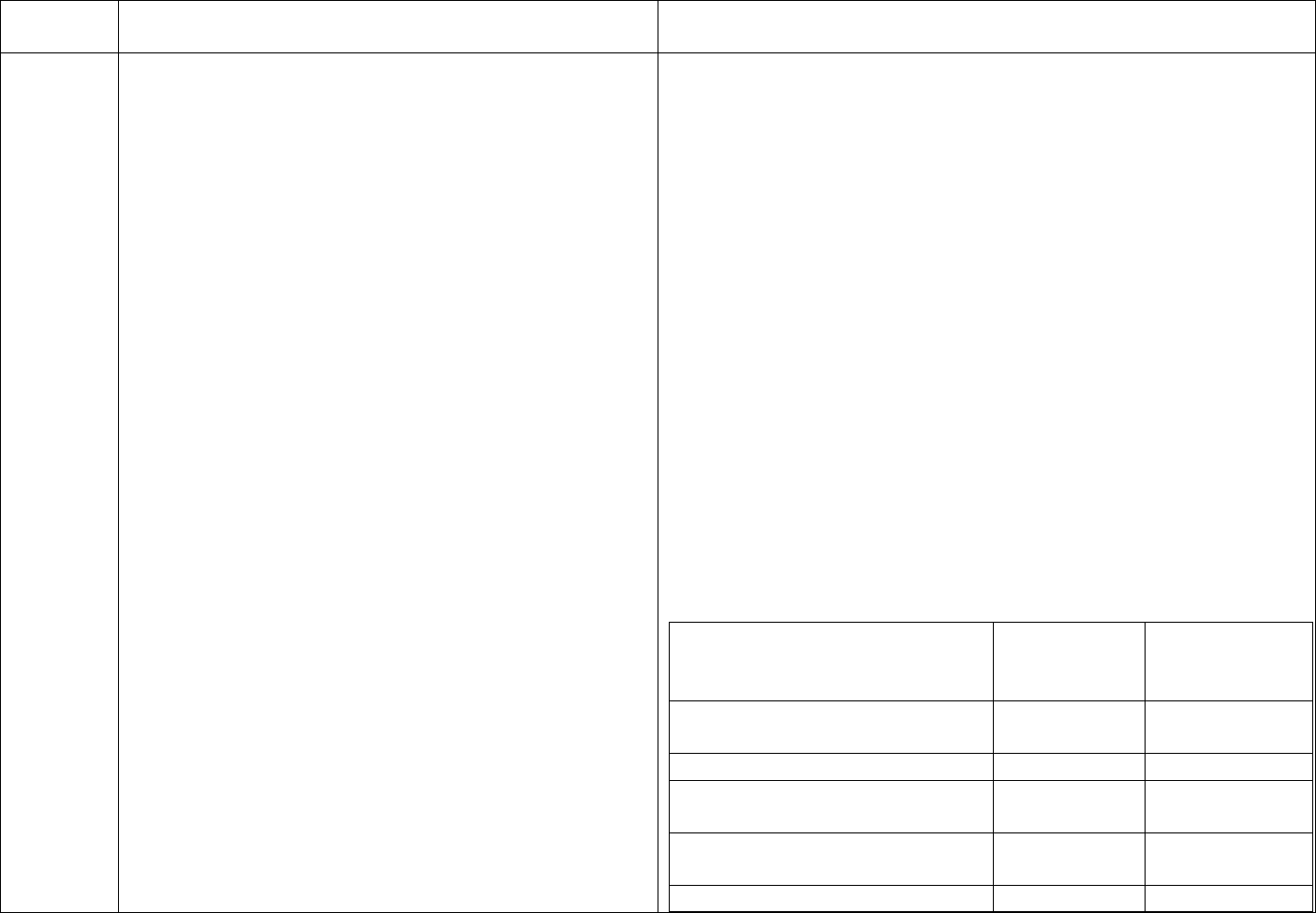
CDC Table 2. Disinfection procedures recommended for
commonly used items or surfaces in hemodialysis units
Intermediate-
Low-Level Level
Item or Surface
Disinfection*
Disinfection*
Gross blood spills or items
contaminated with visible blood
X
Hemodialyzer port caps
X
Interior pathways of dialysis
machine
X
Water treatment and distribution
X
†
system
X
X
§
Scissors, hemostats, clamps,
X
Final Version 1.1 Page 17 of 299
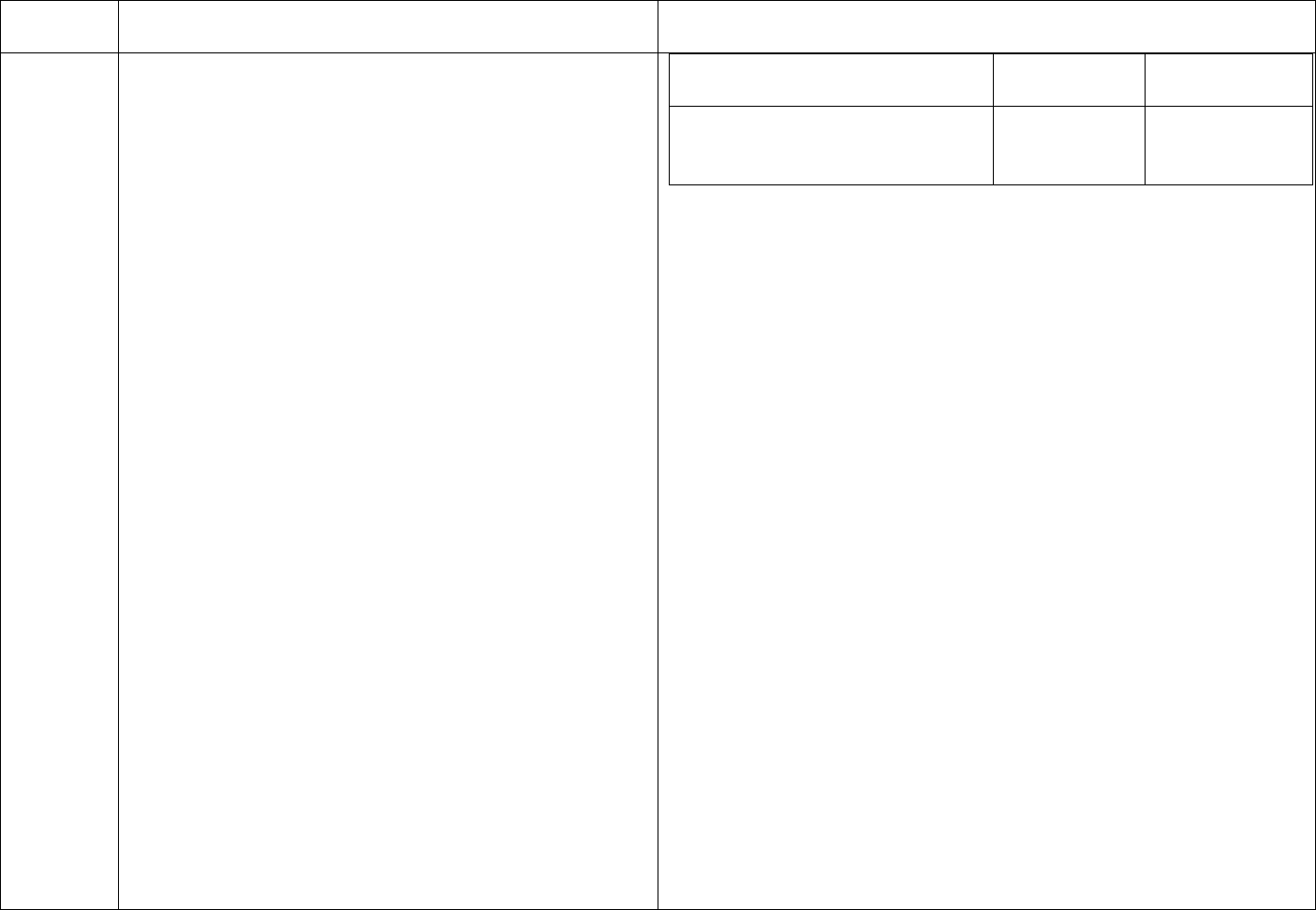
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
blood pressure cuffs,
stethoscopes
Environmental surfaces,
including exterior surfaces of
hemodialysis machines
X
*Careful mechanical cleaning to remove debris should always be done
before disinfection
†Water treatment and distribution systems of dialysis fluid
concentrates require more extensive disinfection if significant biofilm
is present within the system
§ If item is visibly contaminated with blood, use a tuberculocidal
disinfectant
Blood spills in the treatment area and other areas, such as the waiting
room and patient bathroom, need to be cleaned effectively and
immediately, or as soon as possible given the patient care situation. If
a blood spill occurs, staff must clean it up immediately [or as soon as
possible] with a cloth soaked with a tuberculocidal disinfectant or a
1:100 or stronger dilution of bleach (300-600 mg/L free chlorine) (i.e.,
intermediate-level disinfection). After all visible blood is cleaned,
staff should use a new cloth or towel to apply disinfectant a second
time.
“Intermediate-level disinfection” means disinfection that kills bacteria
and most viruses and is accomplished by using a tuberculocidal
“hospital disinfectant” or a 1:100 dilution of bleach (300-600 mg/L
free chlorine). “Low-level disinfection” means disinfection that kills
most bacteria and is accomplished by using general purpose
disinfectants.
At the end of each patient treatment, the staff should clean and
disinfect the dialysis station. Special attention should be given to
cleaning control panels on the dialysis machines, the treatment chairs
Final Version 1.1 Page 18 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
and other surfaces that are frequently touched and potentially
contaminated with patients' blood. The staff should discard all fluids
and clean and disinfect all surfaces of the containers associated with
the prime waste (including containers attached to the machines) after
each treatment.
After each treatment, the staff needs to clean and disinfect medical
devices and equipment. Items such as scissors, hemostats, clamps,
stethoscopes, and blood pressure cuffs need to be cleaned and
disinfected between patient uses. If the item is visibly contaminated
with blood, an intermediate-level disinfectant must be used.
Staff must appropriately clean and disinfect the internal circuits of the
dialysis machines. Single-pass machines may be rinsed and
disinfected at the beginning or end of each day, while batch
recirculating machines must be drained, rinsed and disinfected after
each use. If a blood leak occurs, the manufacturer’s recommendations
for additional disinfection should be followed.
A facility should document procedures for the dialysis machine
disinfection, including testing for residual disinfectant.
No tag
(3) Patient isolation procedures to minimize the spread of
infectious agents and communicable diseases;
This is an information tag. At the time of publication of these
regulations, isolation procedures required by the CDC were related to
the care and treatment of HBV+ patients. For guidance and references
to isolation, refer to the individual tags related to isolation which are
provided below in this section.
V124
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Routine Testing for Hepatitis B
The HBV serological status (i.e. HBsAg, total anti-HBc
and anti-HBs) of all patients should be known before
Clarification of terminology: “HBsAg positive” is used synonymously
with “HBV+” meaning that the person has tested positive for the
presence of Hepatitis B surface antigen. “HBsAg negative” is used
synonymously with “HBV-” meaning that the person does not have
the Hepatitis B surface antigen. “HBV susceptible” means that the
person does not have sufficient Hepatitis B surface antibody levels to
achieve immunity to the virus. “HBV immune” means the person has
Final Version 1.1 Page 19 of 299

TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
admission to the hemodialysis unit.
sufficient Hepatitis B surface antibodies to achieve immunity to the
virus.
Routinely test all patients [as required by the referenced
schedule for routine testing for Hepatitis B Virus]. According to CDC, although the incidence of HBV infection is low
Promptly review results, and ensure that patients are among chronic hemodialysis patients, preventing transmission
managed appropriately based on their testing results. depends on timely detection of patients converting from HBsAg
negative to HBsAg positive and rapid implementation of isolation
procedures before cross-contamination can occur.
In order to prevent the transmission of Hepatitis B among ESRD
patients, all new patients should be tested and their HBV serologic
status (i.e., HBsAg, total anti-HBc, and anti-HBs results) should be
known prior to admission for treatment. If the results of this testing
are not known at admission because of an emergency situation, the
patient should be tested immediately upon intake and results known
within 7 days of admission.
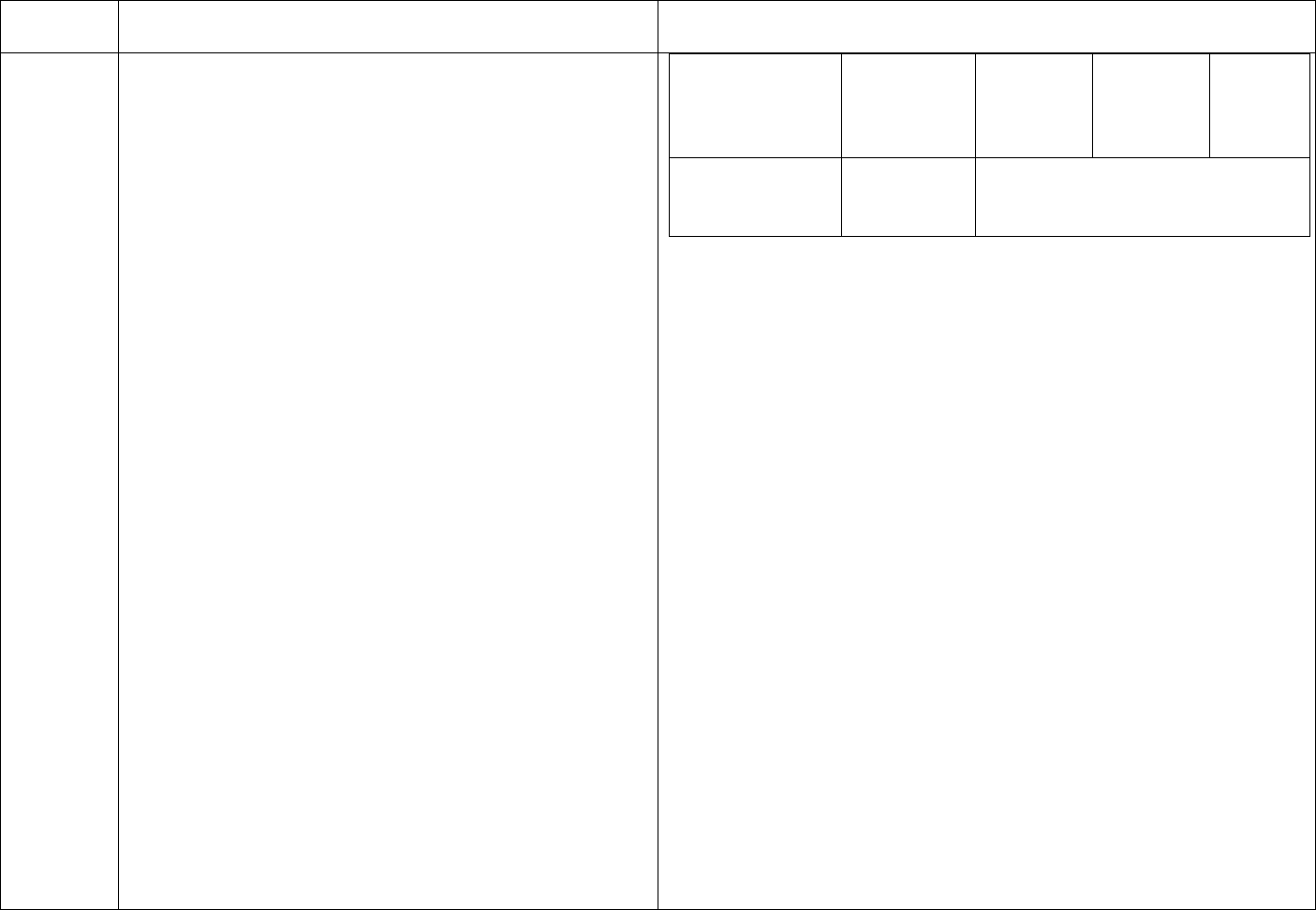
CDC’s schedule for Hepatitis B testing is below:
Schedule for Routine Testing for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
Infections
On
Semi-
Patient Status
Admission
Monthly
annual
Annual
HBsAg,*
Anti-HBc*
(total),
All patients
Anti-HBs,*
HBV-
susceptible,
including
nonresponders
to vaccine
HBsAg
Anti-HBs
Anti-
Final Version 1.1 Page 20 of 299
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
positive
HBs
(≥10 mIU/mL),
anti-HBc
negative
Anti-HBs and
anti-HBc
positive
No additional HBV testing needed
* Results of HBV testing should be known before the patient begins
dialysis.
† HBsAg = hepatitis B surface antigen; Anti-HBc = antibody to
hepatitis B core antigen; Anti-HBs = antibody to hepatitis B surface
antigen.
HBV-Susceptible Patients. Susceptible patients should begin receipt
of hepatitis B vaccine immediately upon admission. Test susceptible
patients monthly for HBsAg, including those who a) have not yet
received hepatitis B vaccine, b) are in the process of being vaccinated,
or c) have not adequately responded to vaccination. Note that, while
the patient’s anti-HBs is <10 mIU/mL, he/she is considered
susceptible to hepatitis B, and should be tested for HBsAg monthly.
Follow-Up of Vaccine Responders. Retest patients who respond to
the vaccine annually for anti-HBs.
HBV-Infected Patient. Chronically infected patients do not require
any routine follow-up testing for purposes of infection control. Annual
testing for HBsAg is reasonable to detect the small percentage of
HBV-infected patients who might lose their HBsAg.
HBV-Immune Patients. Annual anti-HBs testing of patients who are
positive for anti-HBs (>10 mIU/mL) and negative for anti-HBc
determines the need for booster doses of vaccine to ensure that
protective levels of antibody are maintained. Follow-up testing after
Final Version 1.1 Page 21 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
booster doses of vaccine are given is not recommended, nor is routine
follow-up testing necessary for patients who are positive for both anti-
HBs and anti-HBc.
A facility should have systems in place for communicating these test
results to other units or hospitals when patients are transferred for
care.
V125
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Routine Testing for Hepatitis B: seroconversion
When a seroconversion occurs, review all patients’
routine laboratory test results to identify additional cases.
Investigate potential sources for infection to determine if
transmission might have occurred within the dialysis
unit, including review of newly infected patients’ recent
medical history (e.g., blood transfusion, hospitalization),
history of high-risk behavior (e.g., injecting-drug use,
sexual activity), and unit practices and procedures.
According to the CDC, in patients newly infected with HBV, HBsAg
often is the only serologic marker initially detected. HBsAg-positive
seroconversions must be reported to the State or local health
department as required by law or regulation. Patients with a positive
HBsAg must be isolated. Patients newly identified with a positive
HBsAg should be evaluated for the need for counseling, medical
evaluation, and vaccination of contacts. Repeat HBsAg testing should
be conducted and patient should be tested for anti-HBc (including
IgM anti-HBc) 1–2 months later. Six months later, the facility should
repeat HBsAg testing and test for anti-HBs to determine clinical
outcome and need for counseling, medical evaluation, and referral of
contacts for vaccination. Patients who become HBsAg negative are no
longer infectious and can be removed from isolation.
If there have been any seroconversions since last survey, there should
be documentation of actions taken in response. Recognize that
seroconversions should be relatively rare, and each seroconversion
should be carefully analyzed for any potential that transmission
occurred within the dialysis unit.
V126
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Hepatitis B Vaccination
Vaccinate all susceptible patients and staff members
against hepatitis B.
According to the CDC, hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all
susceptible chronic hemodialysis patients and staff members, whether
or not the facility accepts HBV+ patients. OSHA mandates that each
facility provide HBV vaccine to all susceptible staff members.
Hepatitis B vaccination is also recommended for Stage 1-5 chronic
kidney disease patients not yet on dialysis and peritoneal dialysis (PD)
and home hemodialysis (home HD) patients because they might
Final Version 1.1 Page 22 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
require in-center hemodialysis. While not a requirement, best practice
would suggest that the home training nurse advise anyone who assists
in the home hemodialysis treatment of an HBV+ patient to ask their
physician to vaccinate them against hepatitis B.
The patient’s physician should refer to the CDC recommendations or
the vaccine literature for guidance in dosing. Higher doses of the
vaccine are recommended for hemodialysis patients due to their
immuno-compromised state.
Since patients and staff have the right to refuse a vaccination, this rule
is interpreted to mean that all susceptible patients and staff are
“offered” an appropriate Hepatitis B vaccination schedule in an
appropriate timeframe. “Appropriate timeframe” means that
vaccinations should be offered and initiated at hire for employees and
upon admission or earlier for patients, and the course completed
according to the timeline suggested by the manufacturer of the
vaccine.
Personnel files should demonstrate compliance with this regulation:
OSHA requires facilities to maintain a record of their employee’s
Hepatitis B immunization history and to contact past employers to
obtain records of vaccination, if applicable. OSHA requires these
records be maintained for 30 years after the person leaves
employment. If the employee states he/she has been vaccinated, but
the records are not obtainable, the personnel record should include a
statement attesting to the employee having received the vaccine with
dates (or approximate dates) signed by the employee.
Patient medical and personnel records respectively must show
whether susceptible patients and staff are offered hepatitis B
vaccination. There must be a system in place to track vaccination
administration to assure completion of the ordered course.
Final Version 1.1 Page 23 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V127
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Hepatitis B Screening: Patients and Staff
Test all vaccines [patients and staff] for anti-HBs 1-2
months after last primary vaccine dose.
-- If anti-HBs is <10 mIU/mL, consider patient or staff
member susceptible, revaccinate with an additional three
doses, and retest for anti-HBs.
-- If anti-HBs are ≥10 mIU/mL, consider immune, and
retest patients annually.
-- Give booster dose of vaccine to patients if anti-HBs
declines to <10 mIU/mL and continue to retest patients
annually.
According to the CDC, all vaccinees (patients and staff) must be
tested for anti-HBs 1–2 months after the last primary vaccine dose to
determine their response to the vaccine. Patients and staff members
who do not respond to the primary vaccine series should be
revaccinated with a full course of vaccine and retested for response.
No additional doses of vaccine are warranted for those who do not
respond to the second series. Patients who require a booster dose of
the HBV vaccine should not be assigned to a staff member
concurrently caring for HBV+ positive patients.
The CDC defines an adequate response to vaccination as a laboratory
result of ≥10 mIU/mL anti-HBs. The laboratory performing the testing
for anti-HBs must be able to define a 10 mIU/mL concentration.
Results should be reported as a numeric value; a result of “positive” or
“negative” is not sufficient. Some manufacturers of anti-HBs assays
consider a level of anti-HBs that is slightly higher than 10mIU/mL to
be protective. For these assays, the higher level of titer considered to
be protective by the manufacturer of the kit should be used to
determine whether or not the patient or staff member is immune.
Primary nonresponders to vaccination who are HBsAg negative
should be considered susceptible to HBV infection.
Patients who respond to the vaccine should be retested annually for
anti-HBs. If anti-HBs declines to <10 mIU/mL, these patients should
receive a booster dose of hepatitis B vaccine and continue to be
retested for anti-HBs annually. Retesting immediately after the
booster dose is not necessary.
For staff members who initially respond to the vaccine, neither
booster doses of vaccine nor periodic serologic testing to monitor
antibody concentrations are necessary.
Final Version 1.1 Page 24 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The facility and the responsible physicians should consult the CDC
recommendations on dosing and revaccination.
V128
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Isolation of HBV+ Patients
To isolate HBsAg positive patients, designate a separate
room for their treatment.
For existing units in which a separate room is not
possible, HBsAg positive patients should be separated
from HBsAg susceptible patients in an area removed
from the mainstream of activity.
Beginning February 9, 2009, all new facilities must have a separate
isolation room unless the facility has obtained a waiver from CMS for
this requirement. See V129 for the details of this requirement.
According to the CDC, HBV+ patients must dialyze in a separate
isolation room during dialysis to prevent contact and transmission by
contact with blood spills, splattering, or spurting of blood and other
body fluids.
A separate room with a door is required both to contain any spurting
of blood, body fluids, and other contaminates and to prevent cross-
transmission that can occur as a result of environmental
contamination. HBV is stable in the environment and can survive on
surfaces (and remain infectious) for at least 1 week. Since Hepatitis B
is not airborne, the walls of the room do not need to reach the ceiling,
but would need to go to the floor in order to contain blood spills and
the door must be closed during times when blood spurting or
spattering is possible, e.g., at initiation and termination of treatment.
The walls need to allow visual monitoring of the patients in the room
(unless a staff member is continually present in the room) and to
contain any potential blood or fluid spills or spurts.
A separate room is the safer and preferred method of isolation;
however, “existing” facilities, meaning those facilities that were
treating HBV+ patients as of the effective date of the regulations, i.e.
October 14, 2008, and that were using a separate area rather than a
separate room, may continue to use the separate “isolation” area,
unless they are expanding the physical location, in which case they
must add an isolation room or obtain a waiver of the requirement. If
an existing facility uses a designated isolation area rather than a room,
the area used for HBV+ patients must be separated from other stations
Final Version 1.1 Page 25 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
by a space at least equivalent to the width of one hemodialysis station.
The “isolation” station could be an “end of row” station to facilitate
the separation of the area from the mainstream of the dialysis
facility’s activities and to decrease the number of adjacent dialysis
stations.
If there are current HBV+ patients on census, the isolation area/room
and equipment cannot be used for HBV- patients on other shifts or
days due to the risk of cross-contamination. When any HBV+ patients
are no longer on census, the “isolation” area/room may be terminally
cleaned, disinfected and used for HBV- patients.
Existing units, currently without HBV+ patients, that accept HBV+
patients after the effective date of these regulations may establish a
separate area (as described above) for the care of these patients. Any
facility which expands its physical capacity after February 9, 2009
must include an isolation room or secure a waiver. See V129.
Every facility must have the capacity to separate potentially HBV+
patients during treatment. Existing units which do not currently accept
or treat HBV+ patients may have a transfer agreement with a local
chronic facility which has capacity for isolation stations. If there is no
local facility available to accept such transfers, the existing facility
must establish an isolation room or area for use with HBV+ patients.
If an HBV+ patient chooses home dialysis, precautions must be
exercised during the training of that patient to prevent potential cross-
contamination of the training environment and other home patients.
These could include conducting the training in the patient’s home,
rather than at the dialysis facility, or limiting the use of the training
space to the HBV+ patient until training is completed. Different
precautions would be necessary depending on the modality: home HD
vs. PD. Relatives or other individuals who assist with dialysis for an
Final Version 1.1 Page 26 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
HBV+ patient should be instructed to ask their physician regarding
vaccination against hepatitis B infection.
V129
(ii) When dialysis isolation rooms as required by (a)(1)(i)
are available locally that sufficiently serve the needs of
patients in the geographic area, a new dialysis facility
may request a waiver of such requirement. Isolation
room waivers may be granted at the discretion of, and
subject to, additional qualifications as may be deemed
necessary by the Secretary.
As of February 9, 2009, all new facilities must have an isolation room
or have been granted a waiver of this requirement from CMS by
showing there is sufficient capacity in their geographic area for
isolation rooms. New facilities that have not obtained approval for all
required building permits or have not completed the required plan
reviews in a jurisdiction that does not require building permits prior to
the effective date of these regulations (October 14, 2008), must either
provide a separate isolation room by February 9, 2009, or obtain a
waiver of the requirement for an isolation room. Waiver requests,
including information on geographical accessibility of isolation
rooms, should be referred to the applicable CMS Regional Office.
V130
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Isolation of HBV+ Patients
To isolate HBsAg positive patients,… dedicate
machines, equipment, instruments, supplies, and
medications that will not be used by HBV susceptible
patients.
Separate dedicated supplies and equipment, including blood glucose
monitors, must be used to provide care to the HBV+ patient. All
supplies used in the isolation room/area, such as clamps, blood-
pressure cuffs, testing reagents, etc., should be labeled "isolation" and
not routinely removed from the isolation room/area.
Refillable concentrate containers must be surface disinfected at the
completion of each treatment. Refillable concentrate containers may
be kept in the isolation area and refilled at the door or removed for
cleaning and disinfection. In the disinfection area, the “isolation”
container(s) and pick-up tube(s) must be segregated in a dedicated,
designated area away from all other containers and pick-up tubes. If
the container/pick-up tube is to be rotated out of the isolation area, it
must be bleached before subsequent use.
Separate gowns should be used in the isolation area and removed
before leaving the isolation area/room. Any one entering the isolation
area/room during the patient’s treatment must wear a protective gown.
HBV+ patients must undergo dialysis on dedicated machines. Because
Final Version 1.1 Page 27 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
of the risk of cross-contamination, facilities should avoid switching
equipment used for HBV+ patients for use with HBV- patients.
Equipment used for HBV+ patients should be reserved for the HBV+
patients unless repair or maintenance is needed, or until all HBV+
patients have been discharged.
Dialyzers for HBV+ patients must not be reused. Refer to V301 under
Reuse.
When the machine is no longer dedicated to an HBV+ patient, internal
pathways of the machine can be disinfected using conventional
protocols, external surfaces cleaned and disinfected and the machine
returned to general use.
V131
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Isolation of HBV+ Patients
Staff members caring for HBsAg positive patients should
not care for HBV susceptible patients at the same time,
including during the period when dialysis is terminated
on one patient and initiated on another.
One staff person may care for one or more HBV+ patients and one or
more immune patients at the same time, but may not simultaneously
care for Hepatitis B susceptible patients. Hepatitis B status should be
considered when patients are assigned to stations nearest the isolation
area. If a staff member assigned to care for an HVB+ patient must
concurrently care for someone other than another HBV+ patient, the
additional patient(s) must be HBV immune. Patients who require a
booster dose of the HBV vaccine should not be assigned to a staff
member concurrently caring for HBV+ positive patients. When
possible, only HBV immune staff should be assigned to care for
HBV+ patients.
V132
CDC RR-5 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(1)(i)
Infection Control Training and Education
Infection control practices for hemodialysis units:
intensive efforts must be made to educate new staff
members and reeducate existing staff members regarding
these practices.
Training and education in infection control rationales and practices
appropriate to the responsibilities and task assignments of the staff
member at risk for occupational exposure to blood must be provided
initially on employment and periodically, as determined by facility
policy, but at least annually. OSHA mandates dialysis staff receive
bloodborne pathogen training annually and CDC recommends
infection control training initially on employment and annually.
Topics must include (but are not limited to):
Final Version 1.1 Page 28 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
End CDC RR-5 Requirements
• Proper hand hygiene technique
• Proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
• Infection control practices recommended for hemodialysis units
and differences from Standard Precautions
• Special precautions for HBsAg-positive patients
• Proper infection control techniques for initiation, care, and
maintenance of access sites
• Modes of transmission for bloodborne viruses, pathogenic
bacteria, and other microorganisms as appropriate
• Proper handling, preparation, and administration of parenteral
medications maintaining aseptic technique; and
• Proper methods to clean and disinfect equipment and
environmental surfaces to minimize transmission of
microorganisms.
Staff must demonstrate knowledge of infection control
policies/procedures and practices. Personnel records must reflect staff
having received appropriate infection control training.
V142
(b) Standard: Oversight. The facility must—
(1) Monitor and implement biohazard and infection
control policies and activities within the dialysis unit;
The facility should have written policies and procedures covering the
infection control program and practices including, but not limited to,
isolation and any additional precautions for patients with
communicable diseases with different modes of transmission such as
tuberculosis (TB), influenza, and multidrug resistant organisms. The
facility must review practices and update policies and procedures as
needed to ensure infection control practices are rigorously followed.
V143
(2) Ensure that clinical staff demonstrate compliance
with current aseptic techniques when dispensing and
administering intravenous medications from vials and
ampules; and
The facility must have a mechanism in place to ensure expired
medications are not available for use. Opened multiple-dose vials
should be handled aseptically and used and discarded in accordance
with the manufacturer’s set time frames and/or other accepted
standards for use (e.g., US Pharmacopeia). Staff preparing
medications should clean the septum of any multi-use vial with
alcohol before inserting the needle and the injection port before using
Final Version 1.1 Page 29 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the port to administer a medication.
V144
(3) Require all clinical staff to report infection control
issues to the dialysis facility’s medical director (see §
494.150 of this part) and the quality improvement
committee.
There should be a documented reporting mechanism for infection
control issues. The nurse manager, administrator and medical director
should each be able to describe the infection control program and
reporting mechanisms.
Infection control and patient safety issues should be continuously
reported and discussed in QAPI meetings, and the response taken to
address these issues should be documented. Records of tracking
infections should be a part of the facility’s QAPI program. Refer to
V637.
V145
(c) Standard: Reporting. The facility must report
incidences of communicable diseases as required by
Federal, State, and local regulations.
The reporting of incidences of communicable diseases should be
documented and become a part of the QAPI record. Clusters of
adverse events should be promptly reported to the appropriate State or
local public health authority. The QAPI process does not preclude the
need to report serious adverse events to public health authorities in a
timely manner.
V146
(a)(2) The “Guidelines for the Prevention of
Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections” entitled
“Recommendations for Placement of Intravascular
Catheters in Adults and Children” parts I – IV; and
“Central Venous Catheters, Including PICCs,
Hemodialysis, and Pulmonary Artery Catheters in Adult
and Pediatric Patients,” Morbidity and Mortality Weekly
Report, volume 51 number RR-10, pages 16 through 18,
August 9, 2002. The Director of the Federal Register
approves this incorporation by reference in accordance
with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR Part 51. This
publication is available for inspection as the CMS
Information Resource Center, 7500 Security Boulevard,
Central Building, Baltimore, MD or at the National
Archives and Records Administration (NARA). Copies
may be obtained at the CMS Information Resource
It is the intention of the Conditions for Coverage to incorporate
relevant guidance from the CDC “Guidelines for the Prevention of
Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections,” MMWR August 9,
2002/Vol. 51/No. RR-10 into the requirements for facility infection
control practices. Much of the material in this referenced guideline is
general or relates to catheter selection, insertion, and use in acute or
relatively short-term situations. The elements of this guidance which
are most on point for hemodialysis facilities address the risks posed
by intravascular catheters and the need for appropriate staff education,
surveillance, vascular access care, and rigorous hand hygiene in order
to reduce these risks.
For purposes of these Conditions for Coverage the portions of this
document which are incorporated by reference are mandatory and
must be adhered to and demonstrated within the dialysis facility.
Language incorporated from these documents has been edited for
Final Version 1.1 Page 30 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Center. For information on the availability of this
material at NARA, call 202–741–6030, or go to:
http://www.archives.gov/federal_register/code_of_regula
tions/ibr_locations.html
clarity, brevity and to eliminate redundant requirements when utilized
in the “Interpretive Guidance.” However, the language incorporated
into the “Regulation” column represents excerpted exact language.
The entire CDC document “Guidelines for the Prevention of
Intravascular Catheter-Related Infections” includes background
information and rationale for the CDC recommended practices and
can be used as an informational resource.
V147
CDC RR-10 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(2)
Recommendations for Placement of Intravascular
Catheters in Adults and Children
I. Health care worker education and training
A. Educate health-care workers regarding the …
appropriate infection control measures to prevent
intravascular catheter-related infections.
B. Assess knowledge of and adherence to
guidelines periodically for all persons who
manage intravascular catheters.
II. Surveillance
A. Monitor the catheter sites visually of individual
patients. If patients have tenderness at the
insertion site, fever without obvious source, or
other manifestations suggesting local or BSI
[blood stream infection], the dressing should be
removed to allow thorough examination of the
site.
Central Venous Catheters, Including PICCs,
Hemodialysis, and Pulmonary Artery Catheters in
Adult and Pediatric Patients.
According to the CDC, intravascular catheters solve the problem of
attaining vascular access quickly when there is insufficient time for
development of a longer-term internal access: ideally a fistula, or
secondarily a graft. Catheters also provide a solution of last resort
when internal access site opportunities have been exhausted.
However, despite their expedience, these catheters pose a threat of
infection with the potential for immediate and long-term morbidity
and mortality consequences for the patient.
The use of catheters for hemodialysis is the most common factor
contributing to bacteremia in dialysis patients and the relative risk for
bacteremia in patients with dialysis catheters is seven times the risk
for patients with primary arteriovenous fistulas. Staff must maintain
aseptic technique for the care of all vascular accesses, including
intravascular catheters.
The CDC lists the two most common routes of catheter infection as
(1) migration of skin organisms through the insertion site and into the
cutaneous catheter tract resulting in colonization of the catheter tip;
and (2) contamination of the hub, resulting in intraluminal
colonization of the catheter. The initiation and termination of the
dialysis process and manipulation and tension on the catheter provide
frequent opportunity for such contamination. Minimizing the use of
intravascular catheters and protection of the insertion site and the
catheter hub from contamination through education and training about
rigorous care is important in reducing catheter-related infections.
Final Version 1.1 Page 31 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
VI. Catheter and catheter-site care
B. Antibiotic lock solutions: Do not routinely use
antibiotic lock solutions to prevent CRBSI [catheter
related blood stream infections].
Catheter insertion sites should be routinely assessed by staff at each
treatment. Most catheter sites are covered with either transparent
dressings or gauze. Patients with catheters should be instructed to
replace the dressing if a catheter site has sufficient bleeding or
drainage to dampen or soil the dressing between treatments.
The CDC advises that prophylactic antibiotic lock solutions be
reserved for use only in special circumstances, e.g. in units where the
rate of catheter-related bloodstream infection (CRBSI) has not
decreased despite optimal maximal adherence to aseptic technique.
Facility staff should follow guidance from the NKF KDOQI Vascular
Access Guideline (2006), which states “Airborne contaminants from
both patients and staff are prevented best by the use of surgical masks
when the catheter lumens or exit site are exposed. Wearing clean
gloves and avoiding touching exposed surfaces further decreases the
risk for infection. Aseptic technique includes minimizing the time that
the catheter lumens or exit site are exposed.”
Manufacturers' directions should be adhered to for the types of
antiseptics recommended for safe cleaning of the skin and catheter.
The facility should have an initial and ongoing training program for
infection control practices, which includes information on the
prevention of intravascular catheter-related infections.
Facility policies should address the training and qualifications of staff
who may access catheters, in accordance with any State licensure
requirements, as well as the frequency for periodic practice audits to
verify staff knowledge and adherence to infection control guidelines
for intravascular catheters.
V148
CDC RR-10 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
Non-compliance with this requirement should be considered if there is
Final Version 1.1 Page 32 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
42 CFR 494.30 (a)(2)
Central Venous Catheters, Including PICCs,
Hemodialysis, and Pulmonary Artery Catheters in
Adult and Pediatric Patients.
I. Surveillance
A. Conduct surveillance …to determine CRBSI rates,
monitor trends in those rates, and assist in identifying
lapses in infection-control practices.
C. Investigate events leading to unexpected life-
threatening or fatal outcomes. This includes any process
variation for which a recurrence would likely present an
adverse outcome.
End CDC Requirements
lack of evidence of surveillance for catheter-related infections. A log
or another tracking mechanism, such as the Dialysis Module of the
National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN), should be used. Both
the surveillance log/database and the patient's individual medical
records should contain detailed information on catheter infections and
other adverse events, such as, but not limited to prolonged bleeding,
stenosis/clotting, allergic reactions, pyrogenic reactions, cardiac
arrests, hospitalizations, and deaths.
Refer to V637 under the Condition: Quality assessment and
performance improvement (QAPI).
V175
§ 494.40 Condition: Water and dialysate quality.
This Condition incorporates by reference the Association for the
Advancement of Medical Instrumentation’s (AAMI’s) “American
National Standard for Dialysate for Hemodialysis,” 2004
(RD52:2004) and has the authority of regulation. This AAMI
document references portions of their “American National Standard
for Water Treatment Equipment for Hemodialysis Applications
(RD62:2001) as the specifications for various water treatment
components. The referenced portions of RD62:2001 are also
incorporated by reference, and have the authority of regulation. When
“should” or “recommend” are included in the AAMI language
adopted as regulation (i.e., the language in the “Regulation” column),
the referenced item or practice must be in use or in place.
Survey of this Condition requires inspection of the water treatment
and dialysate preparation equipment and their distribution systems;
interview of personnel responsible for day-to-day operation of those
Final Version 1.1 Page 33 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
systems; and review of the records of operation and testing for those
systems. Supervisory personnel may be interviewed to clarify issues
or questions. Critical to ensuring patient safety is the expectation that
every survey visit include direct observation of water testing for
chlorine/chloramine.
Noncompliance at the Condition level should be considered if
identified deficient practices are pervasive throughout the Standards
included in this Condition, serious in nature, or a potential risk to
patient health and safety. Examples of potential Condition level non-
compliance may include, but are not be limited, to:
• Demonstrated lack of knowledge or training of staff assigned
responsibility for the operation or monitoring of the water
treatment or dialysate preparation systems;
• Failure to perform and document the test(s) for chlorine and
chloramine accurately, including use of testing strips or reagents
that are expired or not sensitive to the required levels;
• Unsafe practices in the preparation, labeling or delivery of
dialysate;
• Failure to address out of range results for tests of water or
dialysate (bacteria, endotoxin or chemical analysis).
V176
The facility must be able to demonstrate the following:
(a) Standard: Water purity. Water and equipment used
for dialysis meets the water and dialysate quality
standards and equipment requirements found in the
Association for the Advancement of Medical
Instrumentation (AAMI) publication, “Dialysate for
hemodialysis,” ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004. The Director
of the Federal Register approves this incorporation by
reference in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552 (a) and 1 CFR
Part 51. This publication is available for inspection at the
CMS Information Resource Center, 75000 Security
The practice guideline of the Association for the Advancement of
Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) for “Dialysate for hemodialysis”
(ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004) is incorporated by reference at 42 CFR
494.40 and is reflected in the tags and the interpretative guidelines at
V176 to V278. AAMI is a professional organization in which
committees composed of representatives of the industry, providers,
and regulatory agencies develop voluntary guidelines for medical
products and procedures.
Some explanatory language from ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 and from
the Annex to that document has been included below as guidance to
surveyors. While the language in the “Regulation” column is taken
Final Version 1.1 Page 34 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Boulevard, Central Building, Baltimore, MD or at the
National Archives and Records Administration (NARA).
For information on the availability of this material at
NARA, call 202-741-6030, or go to:
http://www.archives.gov/federal_register/code_of_regula
tions/ibr_locations.html. Copies may be purchased from
the Association for the Advancement of Medical
Instrumentation, 1110 North Glebe Road, Suite 220,
Arlington, VA 22201-4795.
exactly from the document, the AAMI language in the Surveyor
Guidance area has been edited for clarity, brevity and to decrease
redundancy. The order of the AAMI document has in some cases been
altered, to organize requirements to more closely follow the survey
process.
AAMI standards, to be fully understood, should be read in their
entirety and anyone attempting to apply AAMI standards and
recommended practices is encouraged to obtain the complete
standard. The Association for the Advancement of Medical
Instrumentation (AAMI) disclaims responsibility for any
characterization or explanation of its standards and recommended
practices that was not developed and communicated in accordance
with AAMI procedures for the official interpretation of technical
documents. This CMS document does not meet the AAMI criteria for
official interpretations, therefore, all characterizations and
representations regarding the content of AAMI standards contained
within this document are solely the responsibility of CMS.
V177
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
4 Fluid quality
4.1 Water
4.1.1 Maximum level of chemical contaminants in
water: chem analysis
Product water used to prepare dialysate or concentrates
from powder at a dialysis facility, or to process dialyzers
for reuse, shall not contain chemical contaminants at
concentrations in excess of those listed in ANSI/AAMI
RD62, which is reproduced in Table 1 below:
Table 1—Maximum allowable chemical contaminant
levels in water used to prepare dialysate and concentrates
from powder at a dialysis facility and to reprocess
ANSI/AAMI RD52: 2004
4 Fluid quality
4.1 Water
The fluid quality requirements apply to the purified water as it enters
the equipment used to prepare dialysate or concentrates from powder
at a dialysis facility, and apply to the water treatment system as a
whole and collectively, and not to each of the devices that make up
the system.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.4 Fluid quality
A.4.1.1 Maximum level of chemical contaminants in water
ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001 sets forth maximum levels of chemical
contaminants in three categories: chemicals known to have particular
Final Version 1.1 Page 35 of 299
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
dialyzers for multiple uses (Reproduced from
toxicity for hemodialysis patients, chemicals included in the U.S.
ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001) Environmental Protection Agency’s Safe Drinking Water Act and
physiological substances that can adversely affect the patient if
Contaminant / Maximum
(mg/L)
present in the dialysate in excessive amounts.
concentration
Calcium
2 (0.1 mEq/L)
Several chemicals have been clearly shown to be toxic to dialysis
Magnesium
4 (0.3 mEq/L)
patients at concentrations that are not necessarily toxic to the general
Potassium
8 (0.2 mEq/L)
population. Those chemicals include aluminum, copper, chloramines,
fluoride, nitrate, sulfate, and zinc.
Sodium
70 (3.0 mEq/L)
Antimony
0.006
Uptake of aluminum from the dialysate is associated with bone
Arsenic
0.005
disease, anemia, and the dialysis encephalopathy syndrome, which is
Barium
0.10
usually fatal. The suggested maximum aluminum level has been
Beryllium
0.0004
specified to prevent accumulation of this toxic metal in the patient.
Cadmium
0.001
Aluminum is particularly likely to increase suddenly to high levels as
Chromium
0.014
a result of changing the method of water treatment to include
Lead
0.005
aluminum-containing compounds.
Mercury
0.0002
Selenium
0.09
Chloramines damage red blood cells by oxidizing hemoglobin to
Silver
0.005
methemoglobin and by inhibiting antioxidant pathways. Their toxicity
Aluminum
0.01
in hemodialysis patients is undisputed. Although the role of free
Chloramines
0.10
chlorine in oxidative blood damage is unclear, its high oxidation
Free Chlorine
0.50
potential and its ability to form chloramines suggest that the use of
Copper
0.10
highly chlorinated water in preparation of dialysate should be avoided.
Fluoride
0.20
Nitrate (as N)
2.0
High levels (>20 ppm) of fluoride in the water used to prepare
Sulfate
100
dialysate are clearly toxic to hemodialysis patients, and have resulted
Thallium
0.002
in patient deaths. Such high levels of fluoride have resulted from
Zinc
0.10
accidental over fluoridation of a municipal water supply, as well as
from deionizer exhaustion. Toxicity of fluoride in dialysis patients is
NOTE—American National Standards are revised every
questionable at the levels usually associated with fluoridated water (1
three to five years. Users should consult the most recent
ppm). However, in the absence of a consensus on its role in uremic
edition of ANSI/AAMI RD62 to ensure that the levels
bone disease, the AAMI Renal Disease and Detoxification (RDD)
Final Version 1.1 Page 36 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
listed in this table are still valid.
The manufacturer or supplier of a complete water
treatment system should recommend a system that is
capable of meeting the requirements of this clause at the
time of installation given the analysis of the feed water.
The system design should reflect possible seasonal
variations in feed water quality.
Following installation of a water treatment, storage, and
distribution system, the user is responsible for continued
monitoring of the levels of chemical contaminants in the
water and for complying with the requirements of this
standard.
Committee thought it prudent to restrict the fluoride level of dialysate.
Nitrates are a marker for bacterial contamination and fertilizer runoff
and have caused methemoglobinemia. Nitrates should be permitted
only at very low levels. Sulfate at levels above 200 mg/L has been
related to nausea, vomiting, and metabolic acidosis. The symptoms
disappear when the level remains below 100 mg/L. Both copper and
zinc toxicity have been demonstrated when those substances are
present in dialysate at levels below those permitted by the EPA
standard. Hence, a lower level has been chosen.
The second group of chemical contaminants included in ANSI/AAMI
RD62:2001 is based on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s
Safe Drinking Water Act (see 2.6). The standard specifies maximum
allowable limits for most contaminants in this group at 1/10 of the
EPA maximum allowable limit. The lower levels were chosen because
the volume of water used for dialysis far exceeds that used for
drinking water, because protein binding of these solutes may occur in
the blood, and because there is reduced renal excretion of these
substances. Selenium and chromium levels were set at the “no-
transfer” level. The no-transfer level was chosen even though it is
above the EPA limit for selenium and 28 % of the EPA limit for
chromium, because there is no need for a restriction below the level at
which there is no passage from the dialysate to the blood.
The third group of substances included in ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001
consists of physiological substances that can adversely affect the
patient if they are present in the dialysate in excessive amounts.
Calcium, potassium, and sodium are examples of those substances.
The chemical contaminants regulated by ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001
and reproduced in Table 1 should not be taken as a definitive list of
harmful substances; they are only a partial listing of the contaminants
Final Version 1.1 Page 37 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
that might reasonably be expected to be present and have clinical
implications. Iron is not included because it does not enter the
patient’s blood in sufficient quantities to cause toxicity. However, iron
may cause fouling of water purification devices or dialysate
proportioning systems. Furthermore, municipal water supplies are
dynamic systems, which may change with the seasons or in response
to new regulations from the EPA.
Additional Guidance:
Table 1 reflects the Standard adopted by CMS as regulation on April
15, 2008. Individual or groups of facilities may adopt newer
requirements by policy.
The medical director is ultimately responsible for the safety and
quality of the water used for patient treatments. Each product water
chemical analysis must be within the parameters listed in Table 1 at
V177. If any values are greater than those listed, facility staff must
notify the medical director of the results, repeat testing, and take
action to address any repeated high levels.
The medical director must be knowledgeable of the water treatment
system installed and assure that the system as installed will produce
AAMI quality water. Ways to assure this result would include use of
an analysis of the source water and consultation with experts in water
treatment, as well as confirmation that the planned installation would
be sufficient to produce AAMI quality water by the manufacturer or
vendor of the water treatment equipment. For initial surveys, the
facility should provide a copy of a chemical analysis with results
within AAMI standards accomplished prior to starting any patient
treatment in the new facility. For resurveys, there must be evidence of
on-going monitoring of the chemical quality of the water, and actions
taken when levels were outside the AAMI standards.
Final Version 1.1 Page 38 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The use of water outside of AAMI standards should be extremely rare,
considered only when no other option is available to provide
desperately needed dialysis, and limited to one treatment per patient.
An emergency “plan” that specifies the facility will use tap water or
dechlorinated tap water is not acceptable without evidence the source
water has been found safe for such use (i.e., has levels below AAMI
accepted limits of aluminum, copper, chloramines, fluoride, nitrate,
sulfate, zinc and other contaminates known to be toxic to dialysis
patients). The medical director is ultimately responsible for this
decision; short term exposure to contaminants is limited to one
treatment, rather than not receiving dialysis may be the optimal
choice. Refer to V182.
If the water supply utility has notified the city that the source water is
highly chlorinated due to a water main break, flooding, or bacterial
contamination of the municipal system, the dialysis facility will need
to do more frequent monitoring of chlorine/chloramines (i.e., every
30-60 minutes).
For frequency of monitoring water for chemical contaminants, refer to
V201 for Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems and to V206 for
Deionization (DI) systems.
V178
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
4.1.2 Bacteriology of water: max & action levels
Product water used to prepare dialysate or concentrates
from powder at a dialysis facility, or to process dialyzers
for reuse, shall contain a total viable microbial count
lower than 200 CFU/mL and an endotoxin concentration
lower than 2 EU/mL
The action level for the total viable microbial count in
the product water shall be 50 CFU/mL, and the action
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.4.1.2 Bacteriology of water
When ANSI/AAMI RD5:1981 was initially developed, it was
generally considered that the water used to prepare dialysate need not
be sterile. Studies have demonstrated that the incidence of pyrogenic
reactions is related directly to the number of bacteria in dialysate. It is
also known that a dialysate delivery system can amplify the level of
bacteria in the water used to supply the system. Those studies
provided the rationale for setting a recommended maximum
concentration of 200 bacteria per mL in the water used to prepare
Final Version 1.1 Page 39 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
level for the endotoxin concentration shall be 1 EU/mL.
If those action levels are observed in the product water,
corrective measures shall promptly be taken to reduce
the levels
dialysate.
Several groups of investigators have shown convincingly that
pyrogenic reactions are caused by lipopolysaccharides or endotoxins
associated with gram-negative bacteria. Gram-negative water bacteria
are able to multiply rapidly in the chemically pure water used to
supply hemodialysis systems. It has also been demonstrated clearly
that endotoxins and endotoxin fragments can cross both low-flux and
high-flux hemodialysis membranes.
Because 48 hours can elapse between sampling water to determine
microbial contamination and receiving results, and because bacterial
proliferation can be rapid, action levels for microbial counts and
endotoxin concentrations are included in these regulations. Those
action levels allow the user to initiate corrective action before levels
exceed the recommended maximum levels. Unlike cultures, endotoxin
testing does not require extended incubation times. Endotoxin testing,
if performed in the dialysis facility, can give results in about 1 hour,
eliminating the long delay between sampling and obtaining a result.
During the development of this recommended practice, the AAMI
RDD Committee was asked to recommend levels of bacteria and
endotoxin above which the water should not be used for dialysis
applications. In making the recommendations set forth in
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Section 4.1.2, the AAMI RDD Committee
understood that dialysis would be continued at contaminant levels
above the action level but below the recommended maximum level.
Establishing a recommended maximum level of contamination at
which dialysis should be stopped immediately is difficult, because the
risk of adverse events, such as pyrogenic reactions, must be balanced
against the risks of uremia if a patient is not dialyzed. The balance
between those two risks will depend on the level of contamination and
time of exposure on the one hand, and the medical condition of the
Final Version 1.1 Page 40 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
patient on the other hand. Because this balance will almost certainly
vary from circumstance to circumstance, the AAMI RDD Committee
felt that there was insufficient data on which to base levels of bacteria
and endotoxins above which dialysis should not be performed. The
final decision of whether to discontinue dialysis rests with the medical
director of a facility. Whatever decision is made, the AAMI RDD
Committee recommends that the water treatment and distribution
system be disinfected promptly any time the levels of bacteria or
endotoxins exceed the action levels recommended in AAMI 4.1.2. In
addition, it may be prudent to discontinue dialyzer reuse if the levels
of bacteria or endotoxins exceed the recommended maximum levels
set forth in AAMI 4.1.2, since the water is introduced directly into the
blood compartment of the dialyzer.
Additional Guidance:
If the facility reaches the “action” level, remedial action is required.
Action could be to repeat a culture, particularly if only one in a set of
cultures was above the action limit. Action could also be to disinfect
the system and repeat cultures at several sites.
Some states require this testing to be done in a laboratory approved
for analysis of potable water.
V179
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
4.1.2 Bacteriology of water: med dir resp
The facility medical director is responsible to ensure the
manufacturer or supplier of a complete water treatment
and distribution system demonstrates that the complete
water treatment, storage, and distribution system is
capable of meeting these requirements at the time of
installation
Following installation of a water treatment, storage, and
Additional Guidance:
Existing facilities must monitor the AAMI water chemical analysis
and microbial testing and take action if results are outside of the
AAMI standards. In the event of culture results above the action
levels, the facility may need to repeat cultures, or disinfect the system
and repeat cultures (depending on the number of positive cultures,
etc.) and continue treatment while awaiting results.
If the water supply for the facility is from a private well, annual
analysis of the quality of the product water may not be sufficient to
ensure the feed water requirements of the water treatment system in
Final Version 1.1 Page 41 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
distribution system, the user is responsible for continued
monitoring of the water bacteriology of the system and
for complying with the requirements of this standard,
including those requirements related to action levels.
use are continuously met. The quality of water from the well may
change over time, and private wells are not routinely monitored. More
frequent analysis may be needed if the well is subject to seasonal
changes or contamination from sources such as septic tanks,
underground fuel storage tanks, or agricultural waste and chemicals.
Such monitoring might not need to be the full AAMI analysis if only
certain contaminants are known to be of concern.
Frequency and methods for monitoring water bacteriology are
addressed at V252 & V255.
V180
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
4.3.2.1 Bacteriology of conventional dialysate: max &
action limits
Conventional dialysate should contain a total viable
microbial count lower than 200 CFU/mL and an
endotoxin concentration of lower than 2 EU/mL.
The action level for the total viable microbial count in
conventional dialysate should be 50 CFU/mL and the
action level for the endotoxin concentration should be 1
EU/mL. If levels exceeding the action levels are
observed in the dialysate, corrective measures, such as
disinfection and retesting, should promptly be taken to
reduce the levels.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems:
The concentrate shall be shown to routinely produce dialysate meeting
these regulations related to allowable bacterial and endotoxin levels.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.4.3.2.1 Bacteriology of conventional dialysate:
It is now clear that endotoxins, endotoxin fragments, or other bacterial
products cross at least some dialysis membranes under some operating
conditions.
In addition to the risk of acute pyrogenic reactions, indirect evidence
increasingly shows that chronic exposure to low amounts of endotoxin
may play a role in some of the long-term complications of
hemodialysis therapy. Patients treated with ultrafiltered dialysate have
demonstrated a decrease in serum β2-microglobulin concentrations, a
decrease in markers of inflammation, and an increased responsiveness
to erythropoietin. In longer-term studies, use of microbiologically
ultrapure dialysate has been associated with a decreased incidence of
β2-microglobulin-associated amyloidosis, better preservation of
residual renal function, and improved nutritional status. For those
reasons, the AAMI RDD Committee reduced the recommended
Final Version 1.1 Page 42 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
maximum microbial count in the dialysate to 200 CFU/mL and added
a recommendation that the endotoxin concentration not exceed 2
EU/mL. The values are the same as those for water used to prepare the
dialysate (ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001), implying that the dialysate
proportioning system should not add significantly to the
microbiological burden in the water. Although the AAMI RDD
Committee did not review supporting data, it considered
contemporary dialysate delivery systems to be fully capable of
performing at this level provided that the user followed the
manufacturer’s instructions on cleaning and disinfecting the system,
including disinfection of the line between the water distribution
system and the concentrate mixing chambers of the dialysate
proportioning system.
Additional Guidance:
“Conventional dialysate” is a term referring to the dialysate generally
used for hemodialysis in the U.S., as opposed to “ultrapure dialysate.”
Recognize that the purity of dialysate is important, in that “reverse”
ultrafiltration can occur, allowing dialysate to cross the dialyzer
membrane and enter the patient’s blood stream. This can occur with
most dialyzers, especially high flux dialyzers at the distal end of the
dialyzer and especially if the patient does not have much fluid weight
to remove (allowing less ultrafiltration pressure to be used). A
minimum ultrafiltration rate (UFR), as per the dialysis machine
manufacturer’s DFU should be maintained to prevent reverse
ultrafiltration.
It is not expected that concentrates would be cultured or tested for
endotoxin levels. Machine cultures (of dialysate) are the evidence
used to determine if this requirement is met.
“Promptly” would be met if action is taken within 48 hours of
receiving the results of testing. Action might be repeating cultures,
Final Version 1.1 Page 43 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
particularly in the case where one of several cultures are above the
action level; or disinfecting the system and repeating cultures. Action
would also include notifying the medical director of the results.
V181
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
4.3.2.2 Bacteriology of ultrapure dialysate: ultrapure
Ultrapure dialysate should contain a total viable
microbial count lower than 0.1 CFU/mL and an
endotoxin concentration lower than 0.03 EU/mL. If those
limits are exceeded in ultrapure dialysate, corrective
measures should be taken to reduce the levels into an
acceptable range. The user is responsible for monitoring
the dialysate bacteriology of the system following
installation. It is incumbent on the user to establish a
regular monitoring routine.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.4.3.2.2 Bacteriology of ultrapure dialysate
Ultrapure dialysate is defined as one having a bacterial content of less
than 0.1 CFU/mL and an endotoxin content of less than 0.03 EU/mL
using sensitive assays. This definition is now widely accepted,
particularly in Europe, and use of ultrapure dialysate is considered a
requirement for on-line convective therapies (see AAMI A.4.3.2.3).
Ultrapure dialysate is prepared by sequential ultrafiltration of
dialysate prepared from purified water meeting the requirements of
AAMI 4.1 and concentrates. Dry powder cartridges are frequently
used for on-line preparation of the bicarbonate concentrate to
minimize the potential for the bicarbonate concentrate to contribute
high levels of bacteria and endotoxin to the dialysate.
Additional Guidance:
At the time of publication of these regulations, most dialysis facilities
in the U.S. were using conventional dialysate, rather than ultrapure.
There is no requirement to use ultrapure dialysate.
V182
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5 Equipment
5.1 General: back up plan
A dialysis facility should develop contingency plans to
cover the failure of its water purification and distribution
system or a critical component of that system. Such
contingency plans should describe how to deal with
events that completely prevent dialysis from being
performed, such as failure of the facility’s municipal
water supply or electrical service following a natural
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5 Equipment
5.1 General
This section on equipment provides a brief description of the different
components that may be included in a water purification and
distribution system used for hemodialysis applications. Since feed
water quality and product water requirements may vary from facility
to facility, not all of the components described will be necessary in
every purification and distribution system.
Routine dialysis requires a well-functioning water purification and
Final Version 1.1 Page 44 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
disaster or water main break. Other plans should address
how to deal with sudden changes in municipal water
quality, as well as with failure of a critical component of
the water purification and distribution system.
distribution system, since dialysis cannot be performed without an
adequate supply of water. In addition, certain components of the water
purification and distribution system are critical to its operation. An
example of such a critical component is the circulating pump in an
indirect feed system.
Additional Guidance:
An emergency or contingency “plan” that specifies the facility will
use tap water or dechlorinated tap water is not acceptable without
evidence the water intended for use has been found safe for such use
(i.e., has levels below AAMI accepted limits of aluminum, copper,
chloramines, fluoride, nitrate, sulfate, zinc and other contaminates
known to be toxic to dialysis patients). Refer to also to the
requirements for emergency policies and procedures found under the
Condition for Physical Environment at V408.
No tag
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2 Water purification systems
5.2.1 General
Water purification systems consist of three basic
sections: a pretreatment section that conditions the water
supplied to the primary purification device, which may
be followed by other devices that polish final water
quality. The pre-treatment section commonly includes a
sediment filter, cartridge filters capable of retaining
particles of various sizes, a softener, and carbon
adsorption beds. The primary purification process most
commonly used is reverse osmosis, which may be
followed by deionization and ultrafiltration for polishing
the product water from the reverse osmosis system.
Whether a particular device is included in an individual
water purification system will be dictated by local
conditions.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5 Equipment
A.5.2 Water purification systems
Devices marketed to purify water for hemodialysis are also subject to
the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) 510(k) approval
process. The FDA has published guidelines for water purification
devices used in hemodialysis (Guidance for the Content of Premarket
Notifications for Water Purification Components and Systems for
Hemodialysis). Water purification devices marketed for use in
hemodialysis applications must be approved by the FDA, and users
should ensure that devices obtained from vendors have been approved
by the FDA.
Design and instrumentation of individual purification devices may
vary from these general descriptions. For example, softeners may be
configured as a single resin bed that is regenerated outside the normal
operating hours of the dialysis unit, or they may have a dual-bed
Final Version 1.1 Page 45 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
configuration that allows one bed to be regenerated while the other is
used to provide water for normal dialysis operations.
Depending on the feed water quality and product water requirements,
not every component may be required in a given facility. Likewise,
additional components may be required in certain circumstances. For
example, carbon adsorption may not provide adequate chloramine
removal if the water contains substances, such as polyphosphates, that
mask the reactive sites on the carbon particles. In those circumstances,
other processes, such as infusion of sodium metabisulfite, may be
required to achieve product water that meets these requirements.
Users are encouraged to obtain detailed descriptions of all purification
processes, together with operating manuals and maintenance
procedures, from the manufacturer or the vendor providing the water
purification and distribution system.
Additional Guidance:
This is an informational tag; specific requirements for various water
treatment components follow and deficient practices should be cited
under the applicable component tags.
Under FDA regulations at the time these regulations were published,
all water treatment devices and systems installed after May 30, 1997
must meet review requirements under section 510(k) of the Food,
Drug, and Cosmetic Act (21 USC sec. 360(k)) as described in
Guidance for the Content of Premarket Notifications for Water
Purification Components and Systems for Hemodialysis. Equipment
installed prior to that date is not required to have evidence of FDA
510(k) approval. Regardless of when a water purification system was
installed, the system must yield water and dialysate that meets these
AAMI standards and must be monitored and maintained in
accordance with the ANSI/AAMI RD52 guidelines, as incorporated
Final Version 1.1 Page 46 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
by reference in these regulations.
Each piece of water treatment equipment described below is not
required for every system. The water treatment system must be
designed to process the local source water into AAMI quality water.
All facilities must have primary and secondary carbon tanks to
remove chlorine/chloramines, and reverse osmosis (RO) or
deionization (DI) treatment systems. Any component in use must meet
the requirements specified in these rules for that component.
V184
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
8 Environment: secure & restricted
The water purification and storage system should be
located in a secure area that is readily accessible to
authorized users. The location should be chosen with a
view to minimizing the length and complexity of the
distribution system. Access to the purification system
should be restricted to those individuals responsible for
monitoring and maintenance of the system.
Additional Guidance:
Older systems (installed prior to the effective date of these
regulations) may have been installed in a small space, with
components added over the years to crowd the available space. To
ensure access is restricted, the delivery doors/loading dock must not
be left unlocked, open and unattended. Many water systems are in the
same room as stored treatment supplies; staff members who are not
responsible for the water system may come into that area to retrieve
supplies.
Hospital based chronic outpatient units may share the water room with
an acute unit; staff from each unit would be expected to have access to
the equipment.
V185
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
8 Environment: access to ports/meters
The layout of the water purification system should
provide easy access to all components of the system,
including all meters, gauges, and sampling ports used for
monitoring system performance.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
8 Environment
An area for processing samples and performing on-site tests is also
recommended.
Additional Guidance:
Older systems (installed prior to the effective date of these
regulations) may not be as easy to access: provision must be made to
allow staff to access all equipment, ports, etc. to operate and monitor
the system. In all cases, the operator should be able to describe and
identify the various components and the distribution system.
Final Version 1.1 Page 47 of 299
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
V186
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
Additional Guidance:
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
Responsible staff members must be able to test the alarms to validate
8 Environment: alarms in treatment area
they can be heard in the treatment area. If alarms normally sound
Critical alarms, such as those associated with deionizer during certain events during the treatment day, documenting that these
exhaustion or low water levels in a storage tank, should are heard in the treatment area will suffice for testing. The alarms in
be configured to sound in the patient treatment area, as the patient treatment area and water treatment rooms must be loud
well as in the water treatment room. enough to be heard while patients are on dialysis, and cannot be
muted for more than 3 minutes (reference AAMI RD62:2001).
V187
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a) 8 Environment
8 Environment: schematic diagrams/labels
The use of text labels, such as “RO Water,” and color-coded “arrow
Water systems should include schematic diagrams that tape” provide a convenient means of identifying pipe content and flow
identify components, valves, sample ports, and flow direction.
direction.
WATER SOFTENER: System protections RO membrane by removing calcium
and magnesium “hardness ions,” adding sodium ions in their place.
Additionally, piping should be labeled to indicate the
– Using sample port #4 [varies from system to system], test water hardness at
contents of the pipe and direction of flow.
end of each treatment day. Result must be 1 grain/gallon or less
– Check brine tank daily to be sure the tank is at least half filled with salt,
If water system manufacturers have not done so, users
adding salt pellets if necessary. Water may become “hard” if salt pellet level
should label major water system components in a manner
is low.
– Check timer daily to verify that it shows the correct time of day. Incorrect
that not only identifies a device but also describes its
timer settings may cause the softener to regenerate during dialysis and can
function, how performance is verified, and what actions
result in automatic shutdown of the RO.
to take in the event performance is not within an
– Notify charge nurse and facility technician if hardness test is greater than 1
acceptable range.
grain/gallon or if timer does not show correct time of day.
Figure 2 – An example of labeling for a regenerable softener.
Additional Guidance:
There must be a schematic diagram which allows the staff to follow
the flow of the water through the components and each component
and the piping must be labeled as described.
V188
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a) 5.2.2 Sediment filters
5.2.2 Sediment filters: config and monitoring
Permanent, backwashable sediment filters, also known as “bed
Final Version 1.1 Page 48 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
[Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.8 Sediment filters:]
Sediment filters shall have an opaque housing or other
means to inhibit proliferation of algae.
5.2.2 Sediment filters:
Bed filters should be fitted with gauges to measure the
hydrostatic pressure at the filters’ inlet and outlet.
6.2.2 Sediment filters:
Sediment filters should be monitored on a periodic basis
… [for a] pressure drop (∆P) across the filter [that] can
be used to determine when the filter is retaining
particulate matter to the point that the filter will no
longer allow the required water flow without an
excessive reduction in pressure at the outlet of the filter.
A backwash cycle is used to remove particulate matter
from the sediment filter. The frequency of backwashing
should follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Sediment filter monitoring should include daily
verification that the timer used to initiate backwashing
cycles is set to the correct time of day. A log sheet
should be developed to record the pressure drop
measurements and timer verifications.
filters,” are frequently located at or near the beginning of
hemodialysis water treatment systems and are intended to remove
relatively coarse particulate materials from incoming water. Although
a single filtration medium may be used, bed filters known as
multimedia filters are more commonly selected. These units contain
multiple layers, each layer retaining progressively smaller particles. In
this way, the bed is used to its fullest extent; the largest particles are
removed in the first layer contacted by the water and the smallest in
the final layer.
As the bed accumulates particulate material, open passages begin to
clog and resistance to the water flowing through the filter increases.
Ultimately, the increased resistance to flow will lead to a reduction in
water supply to downstream components. To prevent this situation
from occurring, bed filters are cleaned by periodic backwashing,
which is accomplished either manually or by using a timer-activated
control valve.
(Bed filter gauges) are used to determine the dynamic pressure drop
across the filter (delta pressure or ∆P), which serves as an index of
resistance to flow and provides a basis for setting the frequency of
backwashing of the filter.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For sediment filters: monitor for pressure drop across the
filter daily, looking for a pressure drop less than a number determined
by facility policy. For sediment filter backwashing cycle: monitor the
backwash cycle timer setting daily, at the beginning of the day,
looking for backwash clock set to time determined by facility policy.
Additional Guidance:
This is the first of many references to language from ANSI/AAMI
RD62, the AAMI “American National Standard for Water Treatment
Final Version 1.1 Page 49 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Equipment for Hemodialysis Applications” (RD62:2001) which is
referenced in RD52:2004 for the specifications for various water
treatment components. The referenced portions of RD62:2001
provided here are also incorporated by reference, and have the
authority of regulation.
Sediment filters are not required in every facility: the source water
should determine the water treatment components needed. If sediment
filters are in use, the facility must follow these requirements.
If a water treatment system includes multiple components that
backwash, the “time” set on each timer may need to be staggered to
allow sufficient water to be available for the backwashing. This may
result in some timers being set an hour or two different from the
correct time. If so, there should be a posted notice to that effect.
Pressure readings must be taken while the equipment is running. To
determine the pressure drop (or delta P), observe the pressure readings
on the gauges before and after the filter. If the gauge before the filter
reads 70 mmHg and the gauge after the filter reads 50 mmHg, the
pressure drop or “Delta P (∆P)” is 20. The ∆P must be within the
facility set limits; a result higher than the limits indicates that the filter
needs to be backwashed or replaced.
V189
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.3 Cartridge filters: config and monitoring
The cartridge is contained within an opaque filter
housing with seals to separate the feed and product water
streams.
When the maximum [pressure drop] ∆P recommended
by the filter manufacturer is reached, the cartridge should
be replaced according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.3 Cartridge filters
Cartridge filters consist of a cylindrical cartridge of the filter medium
with a central drainage core. Although cartridge filters may be
installed at the inlet to a water system, their usual application is as a
final filtration step prior to reverse osmosis.
As the cartridge accumulates particulate material, resistance to flow
through the filter increases, as indicated by an increase in ∆P.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4:
Final Version 1.1 Page 50 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
6.2.3 Cartridge filters
Cartridge filters should be monitored on a periodic….
basis for a [pressure drop] ∆P across the filter [that] can
be used to determine when the filter is retaining
particulate matter to the point that the filter will no
longer allow the required water flow without an
excessive reduction in pressure at the outlet of the filter.
A marked decrease in ∆P without a corresponding
decrease in flow rate may indicate a loss of filter
integrity. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations
concerning when to replace cartridge filters.
Replacement of the cartridge will usually be indicated by
an increase in ∆P to some specified value. A log sheet
should be developed to record the pressure drop
measurements.
include: For cartridge filters: monitor for pressure drop across the
filter daily, looking for a pressure drop less than a number determined
by facility policy.
Additional Guidance:
Cartridge filters are not required in every facility: the source water
should determine the water treatment components needed. If cartridge
filters are in use, the facility must follow these requirements.
A marked decrease in the ∆P could mean there is no filter in the
container.
V190
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.4 Softeners: auto regen/timers/salt/salt level
Prior to exhaustion, softeners should be restored; that is,
new exchangeable sodium ions are placed on the resin by
a process known as “regeneration,” which involves
exposure of the resin bed to a saturated sodium chloride
solution.
5.2.4 Softeners
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.10
Automatically regenerated water softeners:
Automatically regenerated water softeners shall be fitted
with a mechanism to prevent water containing the high
concentrations of sodium chloride used during
regeneration from entering the product water line during
regeneration.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.4 Softeners
Water that contains calcium or magnesium can form relatively hard
deposits and is called “hard water.” Water that has had these elements
replaced by sodium ion exchange is called “soft water,” hence, the
term “softener.” Softeners also remove other polyvalent cations, most
notably iron and manganese, although they are somewhat limited in
this regard. The primary use of softeners in hemodialysis water
systems is to prevent hard water deposits from damaging sensitive
reverse osmosis membranes.
A softener is a cylinder or vessel that contains insoluble spheres or
beads, called “resin,” to which sodium ions are attached. During
operation, exchangeable sodium ions in the resin are progressively
replaced by calcium and magnesium ions. When all the sodium ions
have been used, the resin bed has reached a condition referred to as
“exhaustion.”
Final Version 1.1 Page 51 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The face of the timers used to control the regeneration
cycle should be visible to the user.
6.2.4 Softeners
Timers should be checked at the beginning of each day
and should be interlocked with the RO system so that the
RO is stopped when a softener regeneration cycle is
initiated.
The softener brine tank should be monitored daily to
ensure that a saturated salt solution exists in the brine
tank. Salt pellets should fill at least half the tank. Salt
designated as rock salt should not be used for softener
regeneration since it is not refined and typically contains
sediments and other impurities that may damage O-rings
and pistons and clog orifices in the softener control head.
Softeners that automatically regenerate also include a brine tank, from
which saturated sodium chloride solution is drawn during
regeneration, and a control valve that regulates regeneration and
service cycles.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For water softener regeneration cycle: monitor the
regeneration cycle timer setting daily at the beginning of the day to
determine the softener timer is set to correct time or a time set by the
facility to allow multiple tanks to backwash in sequence, rather than at
once.
Additional Guidance:
Softeners are not required in every facility: the source water should
determine the water treatment components needed. If softeners are in
use, the facility must follow these requirements.
The requirement to prevent water with a high concentration of sodium
from entering the product water line is especially important when a
facility offers nocturnal dialysis, as regeneration cycles for most
components are set for nighttime.
The timer box cover must have a clear window allowing the timers to
be seen, or the cover must be removed when timers need to be
viewed. Facility policy should define the expected level of salt in the
brine tank, with a minimum requirement that salt pellets fill at least
half of the tank.
Rarely, dual bed softeners are used. These allow one bed to function
while the other bed regenerates. If used, expect installation to ensure
the effluent of the regenerating bed goes to drain, rather than
downstream to other water treatment components, or that the
regeneration occurs when the RO is not in use.
Final Version 1.1 Page 52 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V191
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.2.4 Softeners: Testing hardness/log
Users should ensure that test accuracy and sensitivity are
sufficient to satisfy the total hardness monitoring
requirements of the reverse osmosis machine
manufacturer. Total hardness of the water exiting the
water softener should be measured at the end of each
treatment day.
Water hardness test results should be recorded in a water
softener log.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
6.2.4 Softeners
Softener monitoring, which should be done each treatment day,
consists of testing effluent water for total hardness to ensure that
limits established by the reverse osmosis machine manufacturer are
not exceeded. In the case of automatically regenerating softeners,
monitoring also includes verification that the brine tank contains a
sufficient supply of undissolved sodium chloride and that the control
valve timer, when present, indicates the correct time of day.
Testing for hardness should be performed using an
ethylenediaminetetracetic acid (EDTA) titration test, with “dip and
read” test strips, or a similar method.
The hardness test at the end of the day will indicate the overall
effectiveness of the water softener under worst case conditions and
will ensure that the softener is sized properly—that is, that it has
sufficient capacity expressed in grains of calcium carbonate.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For softeners: monitor product water softness daily at the end
of the treatment day for hardness as calcium carbonate, <l grain/gal,
unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer of the reverse osmosis
equipment.
Additional Guidance:
The water softener log may be incorporated as a part of another log
kept for the water treatment system. For hardness tests requiring color
differentiation, the person performing the analysis should be able to
distinguish between the colors of blue, purple, and red. If the person
cannot differentiate these colors, an automated meter should be used.
V192
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption
Final Version 1.1 Page 53 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption: two tanks/sample ports
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.9 Carbon adsorption media:
Carbon adsorption systems shall be adapted specifically
to the maximum anticipated water flow rate of the
system. Two carbon adsorption beds shall be installed in
a series configuration.
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption
Two carbon beds shall be installed in series with a
sample port following the first bed. A sample port shall
also be installed following the second bed for use in the
event of free chlorine or chloramine breaking through the
first bed.
Carbon adsorption systems, often referred to as carbon filters, are the
principal means of removing both free chlorine and chloramine.
Removal of free chlorine to a maximum level of 0.5 mg/L and
chloramine to a maximum level of <0.1< mg/L is necessary to protect
hemodialysis patients from red cell hemolysis. In addition, free
chlorine may also degrade some reverse osmosis membranes,
depending on the membrane material.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5.2.5 Carbon adsorption
Although treatment of water by carbon adsorption is the method
usually used to meet these requirements for chloramines, the AAMI
RDD Committee recognized that in certain situations carbon
adsorption might not adequately remove chloramines. Inadequate
removal of chloramines may occur when the chloramines are in the
form of naturally occurring N-chloramines or when practices such as
the use of high pH or the inclusion of orthophosphate or
polyphosphates are used (by the supplier’s water treatment plant) to
comply with the EPA’s lead and copper rule. In such circumstances,
other strategies for chloramine removal may be needed to supplement
carbon adsorption. The AAMI RDD Committee is aware that adding
sodium metabisulfite prior to the reverse osmosis system has been
successful in eliminating chloramine in hemodialysis applications.
Other means of removing chloramines, such as redox alloy media and
ultraviolet irradiation at 185 nm, are used in the pharmaceutical and
electronics industries. These processes are currently being evaluated
for hemodialysis applications. The final choice of a system for
chloramine removal in hemodialysis settings will depend on local
conditions and may need to include more than one of the processes
outlined above.
Additional Guidance:
Final Version 1.1 Page 54 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
If a facility has employed supplemental strategies for chlorine
removal these must be in addition to the use of at least two carbon
tanks. The medical director and the chief technician should to be able
to discuss the rationale for use of supplemental strategies. Facility
records must document the systems in place protect patients from
exposure to chlorine and chloramine and are monitored according to
the manufacturer’s direction.
V193
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption: banks of tanks:
Carbon beds are sometimes arranged as series-connected
pairs of beds so that they need not be overly large. The
beds within each pair are of equal size and water flows
through them are parallel. In this situation, each pair of
beds should have a minimum empty bed contact time of
5 minutes at the maximum flow rate through the bed.
When series connected pairs of beds are used, the piping
should be designed to minimize differences in the
resistance to flow from inlet and outlet between each
parallel series of beds to ensure that an equal volume of
water flows through all beds
Additional Guidance:
Carbon beds may be plumbed in 2 ways: with the tanks/beds
connected consecutively, so that all of the water flows through both
tanks/beds; or in “parallel” so that approximately half of the water
flows through each set of tanks/beds. In the case of the latter, each
tank/bed can be of smaller size, as several smaller tanks would be in
use to provide the required empty bed contact time (EBCT). For
parallel-connected tanks/beds, there must be sample ports, as
addressed at V192, for each set of tanks/banks, as testing of one set of
tanks/beds is irrelevant to the function of the other set of tanks/beds.
V194
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption: Iodine #900/replacement
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.9 Carbon adsorption media:
Exhausted carbon adsorption media shall be discarded
and replaced with new media according to a replacement
schedule determined by regular monitoring.
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption
When granular activated carbon is used as the media, it
shall have a minimum iodine number of 900. Other
forms of carbon should not be used unless there is
ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001
4.3.9 Carbon adsorption media
For example, when testing between the beds shows that the first bed is
exhausted, the second bed should be moved into the first position, the
second bed replaced with a new bed, and the exhausted bed discarded.
When other forms of carbon are used, the manufacturer shall provide
performance data to demonstrate that each adsorption bed has the
capacity to reduce the chloramine concentration in the feed water to
less than <0.1 mg/L when operating at the maximum anticipated flow
rate for the maximum time interval between scheduled testing of the
product water for chloramines.
Final Version 1.1 Page 55 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
performance data to demonstrate that each adsorption
bed has the capacity to reduce the chloramine
concentration in the feed water to less than 0.1 mg/L
when operating at the maximum anticipated flow rate for
the maximum time interval between scheduled testing of
the product water for chloramines.
Regenerated carbon shall not be used for hemodialysis
applications.
ANSI/AAMI RD52
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption
Some granular activated carbon contains aluminum, which can elute
from the carbon and add to the burden of aluminum to be removed by
reverse osmosis or ion exchange. The use of acid-washed carbon
minimizes this source of aluminum in the water.
Additional Guidance:
Facilities using an exchange tank system should determine a schedule
of replacement of the exhausted carbon absorption media based on
their experience of use of these tanks to prevent interruption of patient
services. The date of exchange of tanks should be documented on the
tank and in the appropriate log. Facilities using back-washable carbon
systems should determine a schedule for the back-washing of the
tanks, and documentation of the function of that system. Back-
washing does NOT regenerate the carbon; it rearranges the carbon in
the tank, exposing sites that have not yet been used to adsorb chlorine
or chloramine. Back-washable systems do exhaust; the responsible
staff member should be able to describe how they will replace the
carbon when indicated. A “schedule” could refer to “every X months”
rather than a specific date or month, and should be based on past
experience at the facility. Carbon in the tanks can be removed and
replaced (“rebedding”) on site when the tanks are off line.
Granulated activated carbon (GAC) with a minimum iodine number
of 900 must be specified when replacement carbon is ordered. Acid-
washed carbon is recommended, as it will protect the RO from
exposure to excess aluminum, but is not required as the RO would
still protect the patient.
V195
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption: 10 min EBCT
Additional Guidance:
The empty bed contact time (EBCT) of the granulated activated
carbon (GAC) system should be periodically calculated for the
Final Version 1.1 Page 56 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.9 Carbon adsorption media:
When granulated activated carbon is used as the
adsorption medium… each adsorption bed shall have an
[empty bed contact time] EBCT of at least 5 minutes at
the maximum product water flow rate (a total EBCT of
at least 10 minutes).
maximum water flow through the carbon tanks. Water flows may
vary, altering the need for more or less GAC to achieve the 10
minutes total EBCT. If additional patient treatments or shifts are
added, the resultant greater water demand should cause the medical
director and technical staff to consider the need to add additional
carbon in order to maintain the minimum EBCT. “Each adsorption
bed” refers to the primary tank or tanks as one adsorption bed and the
secondary tank or tanks as another adsorption bed.
V196
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.2.5 Carbon adsorption: monitoring, testing freq
Testing for free chlorine, chloramine, or total chlorine
should be performed at the beginning of each treatment
day prior to patients initiating treatment and again prior
to the beginning of each patient shift. If there are no set
patient shifts, testing should be performed approximately
every 4 hours.
Results of monitoring of free chlorine, chloramine, or
total chlorine should be recorded in a log sheet.
Testing for free chlorine, chloramine, or total chlorine
can be accomplished using the N.N-diethyl-p-phenylene-
diamine (DPD) based test kits or dip-and-read test strips.
On-line monitors can be used to measure chloramine
concentrations. Whichever test system is used, it must
have sufficient sensitivity and specificity to resolve the
maximum levels described in [AAMI] 4.1.1 (Table 1)
[which is a maximum level of 0.1 mg/L].
Samples should be drawn when the system has been
operating for at least 15 minutes. The analysis should be
performed on-site, since chloramine levels will decrease
if the sample is not assayed promptly.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption
In addition to removing free chlorine and chloramine, carbon also
adsorbs a wide variety of other substances, including both naturally
occurring and synthetic organic compounds. The capacity of carbon to
remove free chlorine and chloramine may be reduced when other
substances “mask” reactive sites on the carbon media. In addition, the
efficiency of free chlorine and chloramine removal is reduced as pH
increases or as temperature decreases. The net effect of those variables
is that the finite capacity of carbon beds to remove free chlorine and
chloramine cannot be predicted with any certainty. Therefore, their
performance needs to be monitored frequently.
6.2.5 Carbon adsorption
Carbon adsorption performance is monitored by measuring free
chlorine and/or chloramine concentrations in the water exiting the first
carbon bed of a series-connected pair. It should be noted that sampling
for total chlorine (the sum of free chlorine and chloramine), allowing
a maximum level of <0.1 mg/L of total chlorine, is often simpler than
analyzing for free chlorine and chloramine separately.
More frequent monitoring may be appropriate during temporary
operation with a single carbon bed, which can occur following
breakthrough of the first bed. In such instances, testing is performed
on water exiting the second carbon bed in a series-connected pair. The
Final Version 1.1 Page 57 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
decision to increase the frequency of monitoring should be based on
the past performance of the system and on whether changes in feed
water quality have occurred.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.6 Monitoring
A.6.2.5 Carbon adsorption
Intensive monitoring of carbon adsorption beds is recommended
because of the long history of adverse events related to chloramine
contamination of dialysate. Chloramine concentrations in municipal
water may change from day to day and the capacity of carbon
adsorption beds to remove chloramine can vary with the pH and
temperature of the water, the nature of the chloramine compounds
present, and the presence of other substances in the water. The
dependence of chloramine removal on multiple factors makes the
performance of carbon adsorption beds unpredictable. Patient safety
can only be ensured by intensively monitoring the performance of the
carbon adsorption bed. Configuring carbon adsorption beds in series
and sampling from a port located between the two beds provides one
margin of protection against chloramine breakthrough. When
chloramine is first detected in the effluent from the first adsorption
bed, essentially the full capacity of the second bed remains available
for chloramine removal. This reserve capacity allows the user to
conveniently replace the exhausted bed without risk to patients. The
exhausted bed is discarded, the second bed is moved into the first
position, and a new bed is placed in the second position. A new bed of
virgin carbon shall be used for replacement. Carbon cannot be
regenerated in a dialysis facility, and the use of regenerated carbon is
prohibited by ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001 (see 2.3 in that AAMI
document). Backwashing of carbon beds does not regenerate the
carbon, although it may allow more efficient use of the bed’s capacity
by removing channels that can form in the bed during routine
Final Version 1.1 Page 58 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
operation.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.6.2.5 Carbon adsorption
The recommendation that the water purification system should operate
for at least 15 minutes before samples are drawn is to guard against
inadvertently sampling water that has been in the bed for an extended
period.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For carbon adsorption beds, monitor the product water levels
of free chlorine and/or total chlorine between the beds prior to
beginning each patient shift. Expected result is <0.1 mg/L of total
chlorine.
Additional Guidance:
For parallel connected tanks/beds, testing must be done for each set of
tanks/beds each time testing is performed.
Test strips with color comparison charts that indicate a low level
reading of zero and a first “number” of 0.5 are not sufficiently
sensitive to detect levels as low as 0.1 and must not be used for testing
of product water for safe levels of chlorine/chloramine. An indication
of “0” on the comparison charts does not suffice to demonstrate the
strips are sensitive to “0.” Consult the manufacturer’s guidance or
contact the manufacturer if there is any question regarding the
sensitivity of specific test strips. In choosing whether to use
“quantitative” or “qualitative test methodology, it is important to
recognize that the determination of low levels of chlorine (i.e., <0.1
ppm) requires the use of the quantitative method.
If an on-line chlorine/chloramines monitor is in use which
Final Version 1.1 Page 59 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
incorporates an automated alarm, particular testing times are not
required. Facility policy and practice must follow manufacturer’s
guidance regarding any required comparison testing and calibration of
the monitor.
The ability to discern colors is an essential job function for persons
responsible for reading colormetric tests. Depending on the test
method used, staff assigned this responsibility must be capable of
distinguishing between different shades of pink and other colors or a
digital meter must be used.
For deficient practices with exceeding the acceptable level of chlorine
or chloramine refer to V 270-273 of this section.
V197
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption: action if first test positive
When samples from the first sampling port are positive
for chlorine or chloramine, operation may be continued
for a short time (up to 72 hours) until a replacement bed
is installed, provided that samples from the second
sampling port remain negative. The replacement bed
should be placed in the second position, and the existing
second bed should be moved to the first position to
replace the exhausted bed. If it is not possible to rotate
the position of the beds, both beds should be replaced.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5.2.5 Carbon adsorption
The AAMI RDD Committee recognized that it might not be practical
to rotate the bed positions in installations that use large, backwashable
carbon beds. However, there was concern that the capacity of the
second bed might decrease unpredictably and no longer provide
adequate backup if there was breakthrough of the first bed. For this
reason, the AAMI RDD Committee recommended replacing both
beds if bed rotation was not possible.
Additional Guidance:
When facilities operate with one exhausted carbon bed for up to 72
hours, the log of testing should include the actual times testing was
done rather than indicating “1st, 2nd, or 3rd” shift.
V198
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.6 Chemical injection systems
Chemical injection systems consist of a reservoir that
contains the chemical to be injected, a metering pump,
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted by Reference
42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.5 Carbon adsorption:
In some circumstances, carbon adsorption may not adequately remove
chloramines from water. High pH of feed water, the occurrence of N-
Final Version 1.1 Page 60 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
and a mixing chamber located in the main water line.
Chemical injection systems also include some means of
regulating the metering pump to control the addition of a
chemical. This system should be designed to tightly
control the addition of the chemical. The control system
should ensure that a chemical is added only when water
is flowing through the pretreatment cascade and that it is
added in fixed proportion to the water flow or based on
some continuously monitored parameter, such as pH,
using an automated control system. If an automated
control system is used to inject the chemical, the
controlling parameter should be independently
monitored. There should also be a means of verifying
that the concentrations of any residuals arising from the
chemical added to the water are reduced to a safe level
before the water reaches its point of use.
When acid is added to adjust pH, a mineral acid should
be used.
6.2.6 Chemical injection systems
Systems for chemical injection should be monitored
according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If a facility
designs its own system, procedures should be developed
to ensure proper preparation of the chemical, adequate
mixing of the injected chemical with the water flowing
through the pretreatment cascade, and reduction to a safe
level of the concentration of any chemical residuals
before the point of water use. The facility should also
verify that the injected chemical does not degrade the
performance of downstream devices, including the
primary purification process. The adequacy of these
procedures must be verified using an independent
chloramines, and the use of orthophosphate or polyphosphate for
corrosion control have been associated with a decrease in the removal
of chloramines by carbon adsorption. In those situations, carbon
adsorption may need to be supplemented with other methods of
chloramine removal.
5.2.6 Chemical injection systems
Chemical injection systems may be used in the pretreatment section of
a water purification system to supplement the physical purification
processes described in the previous clauses. Applications of chemical
injection include the addition of sodium metabisulfite to remove
chloramines and the addition of acid to adjust pH.
Organic acids may act as a nutrient and allow bacteria to proliferate.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5.2.6 Chemical injection systems
The AAMI RDD Committee expressed reservations about the addition
of chemicals to the water. However, it recognized that the addition of
chemicals may be necessary in some circumstances if a facility is to
meet the maximum contaminant levels set forth in AAMI 4.1.1. For
example, if the municipal water contains high levels of N-chloramines
or chloramine in the presence of orthophosphate or polyphosphate,
injection of sodium metabisulfite may be one of the few options
available for chloramine removal.
If chemical injection is used in the pretreatment cascade, users should
ensure that the addition of the chemical does not interfere with the
operation of subsequent purification processes, including the primary
purification process. For example, the performance of thin-film
composite reverse osmosis membranes may be affected by the pH of
the feed water. At pH levels below 7, the rejection of fluoride may be
Final Version 1.1 Page 61 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
laboratory. Verification can be accomplished by testing
samples from the chemical reservoir and the water line
after the point of injection for at least three batches of
chemical.
When the chemical to be injected is prepared at a facility
from powder or by dilution of a liquid concentrate, the
chemical injection reservoir must be labeled with the
name of the chemical and its concentration, the date the
solution was prepared, and the name of the person who
mixed the solution.
Each batch of chemical should be tested for correct
formulation before use. A batch of chemical must not be
used or transferred to the injection system reservoir until
all tests are completed. The test results—and verification
that they meet all applicable criteria—should be recorded
and signed by the individual performing the tests.
Protective clothing and an appropriate environment,
including ventilation adequate to meet applicable OSHA
environmental exposure limits, should be provided when
chemicals for injection are prepared in a dialysis facility.
substantially reduced, compared to its rejection at a pH of 8.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For chemical injection systems, monitor the level of chemical
in the reservoir, injector function, and value of the controlling
parameter (pH) daily. Results should show that chemical level in the
reservoir greater than or equal to the facility set value, and the
controlling parameter in range of the facility set values.
Additional Guidance:
There are other chemicals that may be injected to address problems
with excessive chlorination or pH levels. If chemical injection is in
use, facility policy must address this, and reflect the manufacturer’s
direction in the use of any system. If the acid is being used to lower
pH, a monitor including an audible alarm in the treatment area is
needed. If a flocculant is being injected to address excessive organic
matter, an alarm will not be needed.
If the facility has designed its own system, the medical director should
be cognizant of the risks and benefits of the system and is expected to
have participated in the decision to install it. Verification of the
function and the safety of a self-designed chemical injection system
must be completed prior to placing the system online during an active
patient treatment time.
Labels must be updated at least every time solution for use in the
system is prepared.
The requirement for “testing of each batch” could be met by the use of
a test specified by the manufacturer of the chemical or the injection
device, such as pH or conductivity. “Verification that the test results
meet all applicable criteria” means the person doing the test compares
the test result with the expected result to ensure the test result is
Final Version 1.1 Page 62 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
within the expected range(s). If the test result does not match the
expected range, that batch of chemical must not be used. Policy
should direct the next steps: mixing another batch and retesting and
notifying supervisory staff for direction would be options.
Staff must follow manufacturer’s guidance (found in Material Safety
Data Sheets [MSDS]) for protective gear and ventilation necessary for
preparation of chemicals for injection.
Chemical injection systems are not required in every facility: the
source water should determine the water treatment components
needed. If chemical injection is in use, the facility must follow these
requirements.
V199
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.7 Reverse osmosis: meets
AAMI/monitored/recorded on log
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.7 Reverse osmosis: When used
to prepare water for hemodialysis applications, either
alone or as the last stage in a purification cascade,
reverse osmosis systems shall be shown to be capable, at
installation, of meeting the requirements of Table 1,
when tested with the typical feed water of the user, in
accordance with the methods of [AAMI] 5.2.2.
5.2.7 Reverse osmosis
Users should carefully follow the manufacturer’s
instructions for feed water treatment and monitoring to
ensure that the RO is operated within its design
parameters.
6.2.7 Reverse osmosis
All results of measurements of RO performance should
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.7 Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems have become widely used in
hemodialysis water purification systems, largely because these
devices remove dissolved inorganic solutes as well as bacteria and
bacterial endotoxins.
The RO membrane separation process components are a
semipermeable membrane, typically in a spiral-wound configuration,
a pump, and various flow and pressure controls to direct the flow of
water through the system. In operation, feed water is pressurized by
the RO pump and is then directed along the surface of the
semipermeable membrane. A portion of the water is forced through
the membrane, a process that removes inorganic salts, bacteria, and
bacterial endotoxins. The remainder of the water continues along the
membrane surface and is directed to drain. Water passing through the
membrane is referred to as “product water” or “permeate.” The water
that flows along the membrane surface and to the drain is known as
“reject water” or “concentrate.” This flow configuration, known as
“cross-flow filtration,” prevents a progressive build-up of materials on
Final Version 1.1 Page 63 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
be recorded daily in an operating log that permits
trending and historical review.
the membrane surface that would eventually lead to fouling and
membrane failure. In some reverse osmosis systems, a portion of the
reject water stream is recycled to the feed water stream. This recycling
allows higher velocities across the membrane surface, which may help
reduce membrane fouling, as well as allowing higher overall use of
water. RO systems usually operate in a single-stage configuration.
However, if a higher level of purification is required, a two-stage RO
can be used. In a two-stage RO, the product water from the first stage
acts as the feed water for the second stage.
Depending on membrane configuration and materials of construction,
RO systems are sensitive to various feed water conditions that may
lead to diminished performance or premature failure.
Additional Guidance:
DFU = directions for use.
The facility should have documentation of the RO manufacturer’s
DFU of feed water and monitoring, and facility procedures must
reflect them. The RO parameters must be recorded and monitored
each day the facility is operating. The medical director, nurse manager
and chief technician must be able to describe how trends in the RO
function are monitored to detect problems.
V200
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.7 Reverse osmosis: alarm/prevent use of unsafe
water
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.7 Reverse osmosis: Reverse
osmosis devices shall be equipped with on-line monitors
that allow determination of rejection rates and product
water conductivity. The product water conductivity
monitor should activate audible and visual alarms when
the product water conductivity exceeds the preset alarm
limit. The audible alarm must be audible in the patient
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.7 Reverse osmosis
RO systems should be fitted with a variety of sensors to monitor the
system’s performance. Conductivity or total dissolved solids (TDS)
sensors in the feed water and product water streams are used to
monitor the membrane’s ability to remove dissolved inorganic solutes.
Flow meters, usually in the product water and reject water streams,
are used to monitor the output of the RO system. RO systems are also
fitted with gauges to monitor the pressure at various points in the
system. Although not indicative of treated water quality, monitoring
flow rates and pressures can help ensure that the system is operating
Final Version 1.1 Page 64 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
care area when reverse osmosis is the last chemical
purification process in the water treatment system.
Monitors that measure resistivity or TDS may be used in
place of conductivity monitors.
6.2.7 Reverse osmosis:
Reverse osmosis systems should be monitored daily
using continuous-reading monitors that measure product
water conductivity (or total dissolved solids (TDS)).
5.2.7 Reverse osmosis:
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.7 Reverse osmosis: When a
reverse osmosis system is the last chemical purification
process in the water treatment system, it [should] include
a means to prevent patient exposure to unsafe product
water, such as diversion of the product water to drain, in
the event of a product water conductivity or rejection
alarm.
within the manufacturer’s specifications and thus will help ensure RO
reliability.
6.2.7 Reverse osmosis
Other parameters that must be measured daily include product and
reject stream flow rates and various internal pressures to the extent
permitted by RO instrumentation. Although these parameters are not
directly indicative of treated water quality, monitoring them can help
ensure that the system is operating within the manufacturer’s
specifications and thus will aid in maintaining the performance of the
RO membranes.
The measurements can be used to calculate rejection of solutes by the
RO membrane and provide a measure of equipment performance.
Percent rejection is calculated using the following formula:
Rejection (%) = Feed water conductivity-permeate conductivity x 100
Feed water conductivity
Newer RO systems may have a direct reading for percent rejection.
Flow rates can be used to calculate the percent recovery of the RO
using the following formula:
Recovery (%) = Permeate water flow rate x 100
Permeate water flow rate + Reject water flow rate
NOTE—The percent recovery is also known as the “water conversion
factor.” The terms are equivalent if none of the reject water stream is
recycled to the feed water stream (see AAMI 5.2.7). If some of the
reject water stream is recycled, the equation given above provides a
measure of overall water utilization by the reverse osmosis system,
rather than the recovery of water during a single pass through the
Final Version 1.1 Page 65 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
membrane module.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For reverse osmosis, 1) Monitor the product water
conductivity, total dissolved solids (TDS), or resistivity and calculated
rejection rate according to the manufacturer’s recommendations
(continuous monitors) with a result showing a rejection rate greater
than or equal to the facility set parameter percentage; 2) Monitor the
product and reject flow rates, and calculated recovery daily
(continuous monitors), with a result showing product water flow rate
greater than a facility set number of gpm; and recovery rate in the
facility set % range.
Additional Guidance:
All manufacturers do not incorporate a preset limit which would
activate an audible alarm when the quality of the product water
diminishes, but all do offer a process for the user to follow in
determining a limit to set. The medical director and the chief
technician should be able to discuss how the set point was determined.
The response should address the requirement that product water meet
these requirements for chemical contaminates. Different criteria
would apply if the RO is followed by DI polishing.
The conductivity or TDS of the product water is an important
monitoring parameter. There may be a lower percent rejection in areas
where the feed water is fairly pure (e.g., has a low TDS).
The determination of rejection rates may require staff to calculate this
from data displayed. If the RO does not display rejection rates, expect
any staff member assigned responsibility for monitoring the water
treatment system to be able to calculate the percent rejection. Normal
ranges should be known to the operator.
Final Version 1.1 Page 66 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
In the absence of an automatic divert to drain valve for the RO,
facility staff must demonstrate knowledge of the requirement to
manually stop water flow to the dialysis machines and other dialysis
related equipment (e.g., concentrate mixing stations, reprocessing
equipment) should the water quality alarm sound.
V201
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.2.7 Reverse osmosis: Chemical analysis: frequency
Chemical analysis for the contaminants listed in 4.1.1
(Table 1) should be done when the RO system is
installed, when membranes are replaced, and at not less
than annual intervals thereafter to ensure that the limits
specified in 4.1.1 are met (see Table 1). Chemical
analyses should be done when seasonal variations in
source water suggest worsening quality or when rejection
rates fall below 90 %.
Additional Guidance:
If your state has more stringent requirements, those must be followed
for this requirement to be met.
V202
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.8 Deionization: continuous monitor
resistivity/logged 2 X day
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.6 Deionization: Deionization
systems, when used to prepare water for hemodialysis
applications, shall be monitored continuously to produce
water of one megohm/cm or greater specific resistivity
(or conductivity of one microsiemen/cm or less) at 25°C.
6.2.8 Deionization
Deionizers shall be monitored continuously using
resistivity monitors that compensate for temperature and
are equipped with audible and visual alarms. Resistivity
monitors shall have a minimum sensitivity of 1.0
megohm-cm. Patients shall not be dialyzed on deionized
water with resistivity less than 1.0 megohm-cm
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.8 Deionization
Deionization (DI) is an ion exchange process that removes both
anions (negatively charged ions) and cations (positively charged ions)
from water. During the exchange process, hydroxyl ions replace other
feed water anions, and hydrogen ions replace other feed water cations;
the hydroxyl and hydrogen ions then combine to form pure water.
Water treated by DI may be very high quality with regard to the
absence of ionized contaminants, but the process does not remove
nonionized substances, including bacteria and bacterial endotoxins. DI
systems may contain anion and cation resin in separate vessels, known
as “dual-bed systems,” or may have both resin types mixed together in
a single vessel, known as “mixed-bed” or “unibed systems.”
Rationale for the Development and Provision of this
Recommended Practice
Final Version 1.1 Page 67 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
measured at the output of the deionizer
Resistivity monitor readings should be recorded on a log
sheet twice each treatment day.
A.5.2.8 Deionization
Deionizers are an effective means of removing ionic contaminants
from water. However, they do not remove nonionic species (such as
bacteria), and they may contribute bacterial contaminants to the water
rather than remove them. The inability of deionizers to remove
nonionic contaminants may limit aluminum removal by deionization.
Deionizers have a finite capacity for contaminant removal. Once the
deionizer is depleted of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, the next least
avidly bound ions will be displaced by more avidly bound ions. For
example, once the hydroxyl ions are depleted, anionic contaminants in
the water will displace fluoride ions from the anion exchange resin.
This phenomenon has led to high levels of fluoride in the product
water, with subsequent patient injury and death. For the above
reasons, use of deionization as the primary means of purification is
strongly discouraged. Deionization may be used to polish product
water from a reverse osmosis system or may be used as a standby if
the reverse osmosis system fails.
Deionizers offer a large surface area for bacterial proliferation and
deionizers generally contribute to the bioburden in the water. The
tendency for deionizers to contribute bacterial contaminants to the
water is greater when deionizers are kept as a backup for a reverse
osmosis system, particularly if there is no flow through the deionizers.
Some facilities counter this tendency by connecting the deionizers in
parallel to the main water line and by maintaining a low flow through
them. An alternative approach is to contract with a local vendor to
provide backup deionizers on demand.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For deionizers, product water resistivity must be continuously
monitored, with a result of resistivity >1 megohm-cm.
Additional Guidance:
Final Version 1.1 Page 68 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
If DI tanks are available for back-up use, the facility must take action
to counter the tendency of DI to contribute bacterial contaminants to
the water. This may be accomplished by either storing the tanks dry,
placing the tanks on line post-RO so that there is a low flow of water
through them, or flushing the DI tanks daily. DI tanks should not be
stored “wet,” i.e., filled with stagnant water.
Exhausted DI tanks (<1.0 megohm-cm) present a serious risk to
patients, and use of exhausted DI tanks have resulted in deaths. If the
water system uses DI as primary purification or as a polish, the system
must be closely monitored by knowledgeable staff. Pure water has a
resistivity of 18.3 megohms. Documentation of a reading greater than
18.3 megohms would indicate some error. Exhausted DI tanks must
be returned to the vendor for recharging. The date of exchange should
be posted on the tank(s) and recorded in a log.
Deionization is not required in every facility: the source water should
determine the water treatment components needed. If deionization is
in use, the facility must follow these requirements.
V203
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.8 Deionization: alarms/divert to drain
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.6 Deionization:
An audible and visual alarm shall be activated when the
product water resistivity falls below this level and the
product water stream shall be prevented from reaching
any point of use, for example by being diverted to drain.
The alarm must be audible in the patient care area.
The resistivity monitor following the final deionizer bed
shall be connected to an audible and visible alarm in the
dialysis treatment area, and the DI system shall divert
product water to drain or otherwise prevent product
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.8 Deionization
DI has a finite capacity that, when exceeded, will cause dangerously
high levels of contaminants in the product water. Fortunately, the
quality of product water from DI is easily monitored by resistivity
monitors that, when used as specified (e.g., minimum resistivity 1
megohm-cm or greater), can prevent inadvertent operation of an
exhausted deionization system.
Additional Guidance:
Except for home patients, there must be an automatic divert-to-drain
system for any DI system in use. While an RO system may use an
alarm to cause a staff member to stop flow before the RO product
water reaches patients, the increased risk to patient health and safety
Final Version 1.1 Page 69 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
water from entering the distribution system should an
alarm condition occur. Under no circumstances shall DI
be used when the product water of the final bed has a
resistivity below 1 megohm-cm.
of the use of water from an exhausted DI tank mandates the use of an
automated protection system, such as a divert-to-drain valve.
V204
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.8 Deionization: require carbon pre & UF post
Systems that include deionizers as a component shall
also contain carbon adsorption upstream of the deionizer
to avoid formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines.
In all instances, deionizers shall be followed by an
ultrafilter or other bacteria- and endotoxin-reducing
device to remove microbiological contaminants that may
originate in the deionizer resin bed.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.8 Deionization
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.6 Deionization: Feed water for deionization
systems shall be pretreated with activated carbon adsorption, or a
comparable alternative, to prevent nitrosamine formation.
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.6 Deionization: If a deionization system is
the last process in a water treatment system, it shall be followed by an
ultrafilter or other bacteria- and endotoxin-reducing device.
5.2.9 Ultrafiltration
Endotoxin-retentive ultrafilters should be placed in dialysis water
systems in locations downstream of deionization, if deionization is the
last process in a water treatment system.
Additional guidance: Endotoxin-reducing devices and endotoxin-
reducing ultrafilters may be used interchangeably in these
applications. The typical range of micron filter size is .001 to .05
microns.
V205
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.8 Deionization: polish or backup
The usual application for a deionizer is as a polisher
following reverse osmosis or as a standby process if the
reverse osmosis system fails. Use of deionization as the
primary means of purification in an outpatient facility is
not recommended because of the inability of deionization
and ultrafiltration to remove certain low-molecular-
weight toxic bacterial products, such as microcystins.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.8 Deionization
The most common configuration for DI is to have two mixed beds in
series, with resistivity monitors being placed downstream of each bed.
Upon exhaustion of the first bed, reliance for water of sufficiently
high resistivity shifts to the second bed, and dialysis operations may
be continued for a short time (up to 72 hours) until a replacement bed
is installed. Under no circumstances shall DI be used when the
product water of the final bed has a resistivity below 1 megohm-cm.
Final Version 1.1 Page 70 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Additional Guidance:
The routine use of DI as the primary means of water treatment in an
out-patient facility is rare.
V206
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.2.8 Deionization: chemical analysis: frequency
When deionization is employed as the primary method
for removing inorganic contaminants (reverse osmosis is
not employed), or when deionization is necessary to
polish RO-treated water, chemical analyses to ensure that
the requirements of AAMI 4.1.1 (Table 1) are met should
be performed when the system is installed and at annual
intervals thereafter.
Additional Guidance:
Samples for chemical analysis should be drawn after the last treatment
component; if the water treatment system includes DI as primary or
polish, the routine chemical analysis samples should be taken after the
DI. Taking the sample from the last patient treatment station would
also meet this requirement.
Note: requirements for preconfigured systems which may include DI
are given at V276.
V207
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.2.9 Ultrafiltration: effective/opaque
housing/monitoring
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.12 Ultrafilters: When used in a
water purification system for hemodialysis applications,
an ultrafilter shall be shown to reduce the concentrations
of bacteria and endotoxin in the feed water to the
ultrafilter by factors at least as great as those specified in
the manufacturer's labeling.
5.2.9 Ultrafiltration
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.12 Ultrafilters: Ultrafilters
[should] have an opaque housing or that other means be
used to inhibit proliferation of algae.
5.2.9 Ultrafiltration
Ultrafilters should be included in routine disinfection
procedures to prevent uncontrolled proliferation of
bacteria in the feed water compartment of the filter.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.2.9 Ultrafiltration
Ultrafilters are membrane-based separation devices that may be used
to remove particles as small as 1,000 daltons and are thus well suited
to remove both bacteria and endotoxins.
If bacterial proliferation is not controlled, bacteria may “grow
through” the membrane and contaminate the product water
compartment of the filter.
6.2.9 Ultrafiltration
Such monitoring will indicate when membrane fouling has progressed
to the point that membrane replacement or cleaning is needed.
Monitoring is also necessary to ensure that the device is being
operated in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: For ultrafilters, monitor pressure drops across the filter daily
for pressure drop less than a value set by the facility.
Final Version 1.1 Page 71 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
6.2.9 Ultrafiltration
The pressure drop across the ultrafilter (∆P) should be
measured using simple inlet and outlet pressure gauges.
Ultrafilters operated in the cross-flow mode should also
be monitored in terms of the flow rate of water being
directed to drain (concentrate).
Results of pressure measurements and bacteria and
endotoxin levels should be recorded in a log.
Additional Guidance:
Test results drawn pre and post ultrafilter should be used to determine
if the concentrations of bacteria and endotoxin are reduced as stated
by the manufacturer’s label. These samples can be drawn at usual
testing points: e.g., the post RO sample would function as the pre-UF
sample, and the sample from the first water distribution outlet would
serve as the post-UF sample. Such testing should be performed
whenever an UF is originally installed, and whenever the specific type
of UF is changed. Low levels of bacteria and endotoxin in the feed
water to the ultrafilter may prevent the user from being able to show
the manufacturer’s specified level of reduction; an acceptable test
result should be defined by facility policy, and in all cases must be
within the AAMI standards for microbial contamination.
Disposable ultrafilters do not require disinfection when used within
the manufacturer’s parameters and pressure monitored to detect
fouling.
Every filter has an initial pressure drop when installed new. Users
should monitor the change in pressure and validate the acceptable
pressure change each time the filter is replaced.
Ultrafilters are not required in every facility: the source water should
determine the water treatment components needed. As referenced in
V204, an ultrafilter is required if DI is the last water treatment
component in the system. If ultrafilters are in use, the facility must
follow these requirements. The typical range of micron filter size is
.001 to .05 microns.
V208
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.3 Water storage and distribution
5.3.1 General: Design
A water storage and distribution system should be
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.3 Water storage and distribution
5.3.1 General
The function of the water storage and distribution system is to
distribute product water from the purification cascade to its points of
Final Version 1.1 Page 72 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
designed specifically to facilitate bacterial control,
including measures to prevent bacterial colonization and
to allow for easy and frequent disinfection.
use, including individual hemodialysis machines, hemodialyzer
reprocessing equipment, and concentrate preparation systems. A water
storage and distribution system typically contains a large volume of
water exposed to a large surface area of piping and storage tank walls.
Because chlorine and chloramines are removed in the purification
process, the water does not contain a bacteriostatic agent. This
combination of circumstances predisposes wetted surfaces to bacterial
proliferation and biofilm formation.
5.3.3 Water distribution systems
Two types of water distribution systems are used: direct feed systems
and indirect feed systems. In a direct feed system, water flows directly
from the last stage of the purification cascade to the points of use. In
an indirect feed system, water flows from the end of the purification
cascade to a storage tank. From there, it is distributed to the points of
use. In general, direct feed systems offer the least favorable
environment for bacterial proliferation. However, with a direct feed
system the purification cascade must be sized to provide sufficient
water to meet the peak demand, and the system must have sufficient
pressure at the end of the purification cascade to distribute the water
to the points of use. Those two requirements often preclude the use of
a direct feed system.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5.3 Water storage and distribution
Direct feed water distribution systems typically return unused water to
the feed side of the reverse osmosis unit. If the pressure at the end of
the distribution loop decreases to a value below the water pressure at
the inlet to the reverse osmosis pressurizing pump, retrograde flow of
nonpurified water into the distribution loop can occur. To minimize
this risk, the AAMI RDD Committee recommends that dual check
valves be used to prevent retrograde flow and that the pressure at the
Final Version 1.1 Page 73 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
end of the distribution loop be monitored.
V209
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.3.2 Water storage tank: shape/vent/disinfected/filter
post
When used, storage tanks should have a conical or bowl-
shaped base and should drain from the lowest point of
the base. Storage tanks should have a tight-fitting lid and
be vented through a hydrophobic 0.2 µm air filter. The
filter should be changed on a regular schedule according
to the manufacturer’s instructions. A means shall be
provided to effectively disinfect any storage tank
installed in a water distribution system.
7.1 General strategies for bacterial control [in storage
tanks]:
An ultrafilter, distal to the storage tank, or some other
form of bacterial control device is recommended.
Storage tanks are therefore not recommended for use in
dialysis systems unless they are frequently drained and
adequately disinfected.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.3.2 Water storage
Internal spray mechanisms can facilitate effective disinfection and
rinsing of a storage tank.
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
A storage tank in the distribution system greatly increases the volume
of fluid and surface area available and can serve as a niche for water
bacteria. It may be necessary for the user to scrub the sides of the tank
to remove bacterial biofilm if the tank design and maintenance are not
adequate to prevent bacterial proliferation.
Additional Guidance:
If existing facilities with older storage tanks can demonstrate a history
of water and dialysate cultures being below action levels, replacement
of the existing tanks is not required.
Bacterial control device(s) in use following the storage tank may
include an ultrafilter or individual filters in the water supply line in
each patient’s dialysis machine.
The facility must follow the manufacturer’s guidance for the
disinfection of the water storage tank. Tanks which fill from the top
and drain from the bottom may, in fact, drain several times a day. The
goal is to not have stagnant water. A properly designed and functional
storage tank replaces its total volume throughout the day as part of the
normal operation and does not require manual or frequent draining of
the tank.
V210
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.3 Water storage and distribution
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: To monitor the water storage tank, measure bacterial growth
and pyrogens, weekly, until a pattern of consistent compliance can be
Final Version 1.1 Page 74 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
6.3.2 Water storage: monitoring
Routine monitoring of water storage tanks for bacteria
and endotoxin levels is generally accomplished indirectly
by monitoring the water at the first outlet to the
distribution loop (see 6.3.3). If direct monitoring of a
water storage tank is performed as part of a
troubleshooting process, bacteria and endotoxin levels
shall be measured as specified in ANSI/AAMI
RD62:2001 (see 2.3). All bacteria and endotoxin results
should be recorded on a log sheet.
demonstrated. Action levels for bacterial growth are 50 CFU/mL; for
endotoxin 1 EU/mL. While Table 4 includes a “<” sign before these
numbers, section 4.1.2 does not include that “<” designation, and the
designation is removed here. Expect action to be taken for levels
above 50 CFU/mL and above 1 EU/mL.
Additional Guidance:
A “pattern of consistent compliance” could be demonstrated by
showing results within these limits on weekly cultures for at least four
weeks in a row. Laboratory generated reports are an acceptable
alternative to recording results on a log if the laboratory provides an
aggregate report allowing multiple monthly reports to be easily
compared for trends.
V211
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.3.3 Water distribution systems: continuous flow
rates/no dead ends
Water distribution systems should be configured as a
continuous loop and designed to minimize bacterial
proliferation and biofilm formation. A centrifugal pump
made of inert materials is necessary to distribute the
purified water and aid in effective disinfection.
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
To minimize biofilm formation, there should always be
flow in a piping system. A minimum velocity of 3 ft/sec
in the distal portion of the loop of an indirect feed system
and a minimum velocity of 1.5 ft/s in the distal portion of
a direct feed system are recommended when the system
is operating under conditions of peak demand.
Dead-end pipes and unused branches and taps that can
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.3.3 Water distribution systems
A multistage centrifugal pump is preferred for this purpose.
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
Other measures can also help protect pipes from contamination.
Additional Guidance:
It is not the intent of this regulation to dictate the type of pump used
for this purpose, other than that the pump be made of inert material.
It is not intended that surveyors would measure flow rates; responsible
staff (i.e., the chief technician) should be able to describe how the
system is monitored to assure at least minimum flow during operation.
The facility must identify and remove any potential dead-end pipes.
For example, if the facility has discontinued reprocessing dialyzers,
any unused piping should be removed to prevent stagnant water or
trapping of disinfectant.
Final Version 1.1 Page 75 of 299
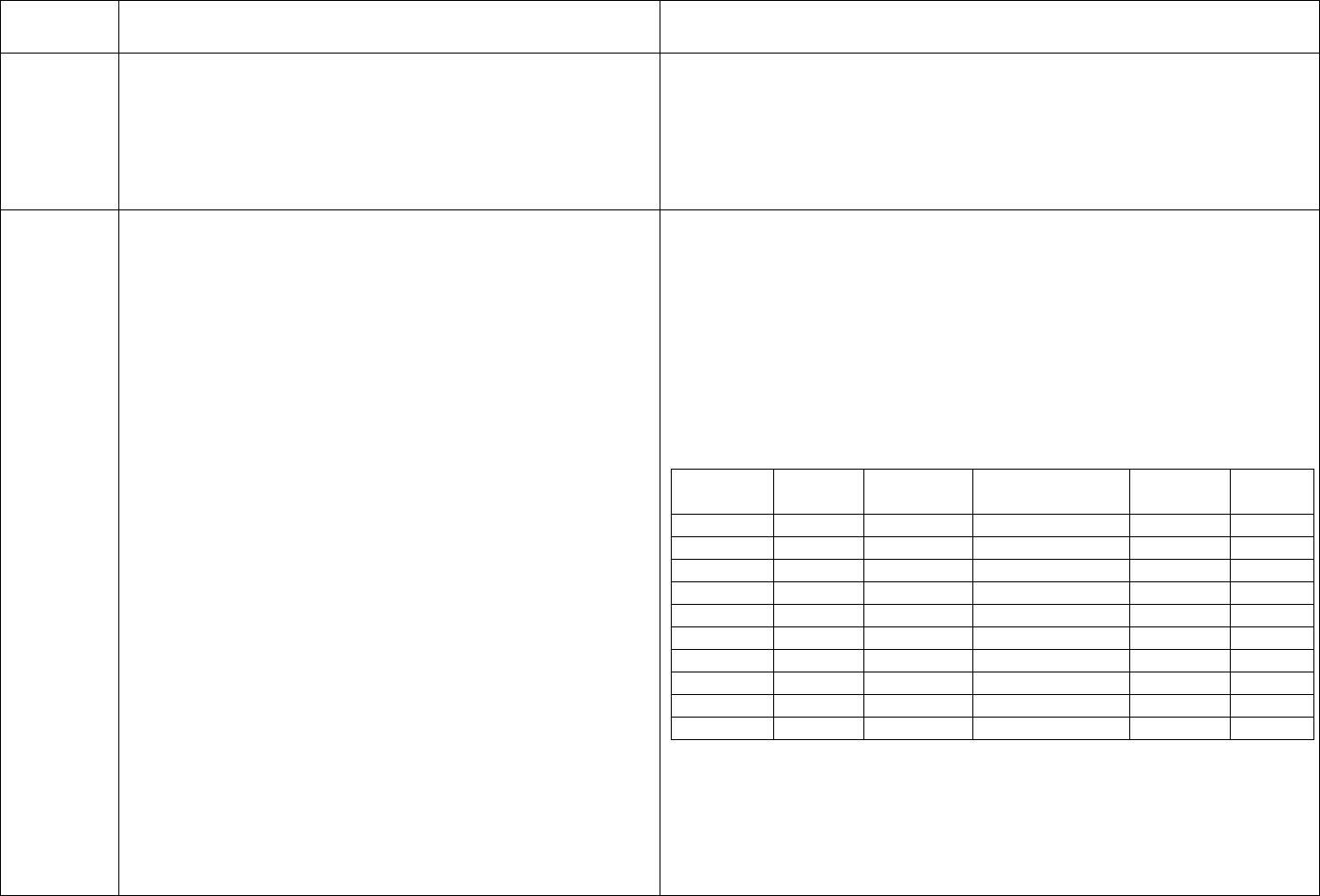
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
trap fluid must be eliminated because they act as
reservoirs of bacteria and are capable of continuously
inoculating the entire volume of the system. These
measures also minimize the possibility that pockets of
residual disinfectant could remain in the piping system
after disinfection
V212
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a) 5.3.3 Water distribution systems
5.3.3 Water distribution systems: no added burden
The choice of materials used for a water distribution system will also
Product water distribution systems shall be constructed depend on the proposed method of disinfection. Whatever material is
of materials that do not contribute chemicals, such as used, care should be taken to select a product with properties that
aluminum, copper, lead, and zinc, or bacterial provide the least favorable environment for bacterial proliferation,
contaminants to the purified water. such as smooth internal surface.
Table 2—Compatibility of common disinfectants with piping
materials used in water distribution systems
Material
Bleach
Peracetic
Formaldehyde
Hot
Ozone
Acid
water
PVC
X
X
X
CPVC
X
X
X
X
PVDF
X
X
X
X
X
PEX
X
X
X
X
SS
X
X
X
X
PP
X
X
X
X
PE
X
X
X
ABS
X`
PTFE
X
X
X
X
X
Glass
X
X
X
X
X
PVC = polyvinylchloride, CPVC = chlorinated polyvinylchloride,
PVDF = polyvinylidene fluoride, PEX = cross-linked polyethylene,
SS = stainless steel, PP = polypropylene, PE = polyethylene, ABS =
acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, PTFE = polytetrafluoroethylene.
NOTE—Table 2 is not intended as an exhaustive compilation of all
Final Version 1.1 Page 76 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
possible compatible combinations of piping material and disinfectant.
Users should verify compatibility between a given germicide and the
materials of a piping system with the supplier of that piping system
before using the germicide. Considerations of compatibility should
include any joint materials and pipe fittings, as well as the actual
piping material. The concentration of germicide and the duration and
frequency of exposure also should be taken into account.
Additional Guidance:
In the event a facility is using piping in the water distribution system
which is not indicated as compatible with the disinfectant in use per
Table 2, expect responsible staff (medical director, chief technician)
to provide evidence that the disinfectant in use has been verified by
the manufacturer of the disinfectant or the 510(k) licensed disinfection
device as compatible with their distribution piping.
V213
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.3.3 Water distribution systems: culture/LAL sample
sites/frequency (new)/log
Water distribution piping systems should be monitored
for bacteria and endotoxin levels. Bacteria and
endotoxins shall not exceed the levels specified in
[AAMI] 4.1.2. [(i.e., bacteria <200 CFU/mL and
endotoxin <2 EU/mL]
Bacteria and endotoxin testing should be conducted at
least monthly. For a newly-installed water distribution
piping system, or when a change has been made to an
existing system, it is recommended that weekly testing
be conducted for 1 month to verify that bacteria or
endotoxin levels are consistently within the allowed
limits.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7.2 Microbial monitoring methods
7.2.1 General
Additional testing, such as at the end of the water purification cascade
and at the outlet of the storage tank, if one is used, may be necessary
during initial qualification of a system or when troubleshooting the
cause of contamination within the distribution loop.
Suggested monitoring guidelines from ANSI/AAMI RD52, Table 4
include: To monitor the water distribution piping system, measure
bacterial growth and pyrogens, weekly, until a pattern of consistent
compliance can be demonstrated, then monthly. Action levels for
bacterial growth are >50 CFU/mL; for endotoxin >1 EU/mL.
Additional Guidance:
An example of a change to the existing system would be changes to
the RO membranes or installation of a new storage tank. Changes to
the pre-treatment components (e.g., sediment filters, cartridge filters,
Final Version 1.1 Page 77 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Monitoring should be accomplished by taking samples
from the first and last outlets of the water distribution
loop and the outlets supplying reuse equipment and
bicarbonate concentrate mixing tanks. If the results of
this testing are unsatisfactory, additional testing (e.g.,
ultrafilter inlet and outlet, RO product water, and storage
tank outlet) should be undertaken as a troubleshooting
strategy to identify the source of contamination, after
which appropriate corrective actions can be taken.
Bacteria and endotoxin levels shall be measured as
specified in ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001 (see 2.3).
All bacteria and endotoxin results should be recorded on
a log sheet to identify trends that may indicate the need
for corrective action.
softener, or carbon tanks) do not require a period of more frequent
testing.
The sites listed must be cultured routinely, with additional sites
considered if the results of routine test sites indicate a problem.
The log could be graphic reports or documents generated by the
laboratory, or created by staff from laboratory data, in order to include
results from multiple months to allow identification of trends.
V252 should be used when routine cultures/endotoxin testing is not
done at least monthly. Use this tag if more frequent testing is not done
when indicated (e.g., for new facilities, when a major change has been
made to an existing water system, or when monthly cultures taken
from several sites are repeatedly positive).
Note: refer to V276 for requirements for preconfigured systems.
V214
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.3.4 Bacterial control devices:
5.3.4.1 Ultraviolet irradiators: UV dose
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.13 Ultraviolet irradiators: When
used to control bacterial proliferation in water storage
and distribution systems, UV irradiation devices shall be
fitted with a low-pressure mercury lamp that emits light
at a wavelength of 254 nm and provides a dose of radiant
energy of 30 milliwatt-sec/cm
2
, [except in the case
described below]. The device shall be sized for the
maximum anticipated flow rate according to the
manufacturer's instructions.
5.3.4.1 Ultraviolet irradiators
If the irradiator includes a meter as described above, the
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.3.4 Bacterial control devices
5.3.4.1 Ultraviolet irradiators
The recommendations provided in this clause concern UV irradiators
used specifically for bacterial control.
Ultraviolet irradiators (also known as UV lights) may be used to
control bacterial proliferation in purified water storage and
distribution systems. UV irradiators contain a low-pressure mercury
lamp that emits ultraviolet light at a wavelength of 254 nm. The lamp
is housed in a transparent quartz sleeve that isolates it from direct
contact with the water. If the irradiator is not fitted with a calibrated
ultraviolet intensity meter that is filtered to restrict its sensitivity to the
disinfection spectrum and that is installed in the wall of the
disinfection chamber at the point of greatest water depth from the
lamp, the dose of radiant energy provided by the lamp shall be at least
Final Version 1.1 Page 78 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
minimum dose of radiant energy should be at least 16
milliwatt-sec/cm
2
.
To prevent the use of sublethal doses of radiation that
may lead to the development of resistant strains of
bacteria, UV irradiators shall be equipped with a
calibrated ultraviolet intensity meter …or with an on-line
monitor of radiant energy output that activates a visible
alarm, which indicates that the lamp should be replaced.
Alternatively, the lamp should be replaced on a
predetermined schedule according to the manufacturer’s
instructions to maintain the recommended radiant energy
output.
6.3.4 Bacterial control devices
6.3.4.1 Ultraviolet irradiators
Ultraviolet irradiators intended for use as a direct means
of bacterial control shall be monitored for radiant energy
output. UV irradiators should be monitored at the
frequency recommended by the manufacturer. A log
sheet should be used to indicate that monitoring has been
performed.
30 milliwatt-sec/cm2.
6.3.4 Bacterial control devices
6.3.4.1 Ultraviolet irradiators
UV irradiators are available equipped with radiant energy intensity
sensors. A visual alarm or an output meter is acceptable for
determining if the UV lamp is emitting sufficient radiant energy.
Because the radiant energy decreases with time, annual lamp
replacement is typically required. Periodic cleaning of the quartz
sleeve may also be required, depending on the water quality.
Additional Guidance:
Monitoring may be accomplished by either of the following options:
use of a meter to monitor intensity of the lamp, use of an on-line
monitor that activates an alarm; or replacement on a predetermined
schedule.
The use of a UV irradiator in a bicarbonate distribution system may
have a totally different role. If ozone is used to disinfect that system,
the UV irradiator may be used to break down the ozone. If the UV
irradiator is part of the bicarbonate distribution system, responsible
staff must be able to describe the intended purpose of the UV in that
application. Monitoring of the irradiator is still required, but there is
no need to follow an irradiator used in the bicarbonate distribution
system with an ultrafilter or other endotoxin-retentive device.
V215
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.3.4.1 Ultraviolet irradiators: filters post
UV irradiators [shall] be followed by a means of
reducing endotoxin concentrations, such as an ultrafilter
in the purified water distribution system or reverse
osmosis in the pretreatment cascade.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.3.4.1 Ultraviolet irradiators
Ultraviolet irradiation also can be used to control bacteria in the
pretreatment section of a water purification system, such as following
carbon adsorption beds to reduce the bacterial burden presented to a
reverse osmosis unit. Using UV irradiation to kill bacteria increases
the level of endotoxins in the water.
Final Version 1.1 Page 79 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Additional Guidance:
An ultrafilter or other endotoxin-retentive device may be used. If an
RO follows the UV, the RO functions as an ultrafilter. This
requirement is not intended to apply to UV irradiators placed in some
bicarbonate distribution systems.
V216
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.3.4.2 Ozone generators: system
requirements/monitoring
Ozone can be used for bacterial control only in systems
constructed from ozone-resistant materials (see AAMI
5.3.3 for suitable piping materials).
5.3.4.2 Ozone generators
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.15 Ozone disinfection systems:
When used to control bacterial proliferation in water
storage and distribution systems, an ozone generator
shall be capable of delivering ozone at the concentration
and for the exposure time specified by the manufacturer.
6.3.4 Bacterial control devices
6.3.4.2 Ozone generators
Ozone generators should be monitored for ozone output
at a level specified by the manufacturer. The output of
the ozone generator should be measured by the ozone
concentration in the water. A test based on indigo
trisulfonate chemistry, or the equivalent, should be used
to measure the ozone concentration…each time
disinfection is performed. An ozone-in-ambient-air test
should be conducted on a periodic basis, as
recommended by the manufacturer, to ensure compliance
with the OSHA permissible exposure limit of 0.1 ppm. A
log sheet should be used to indicate that monitoring has
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.3.4.2 Ozone generators
Ozone may be used to control bacterial proliferation in water storage
and distribution systems. Ozone may also degrade endotoxins. Ozone
generators convert oxygen in air to ozone using a corona discharge or
ultraviolet irradiation. The ozonated air is then injected into the water
stream. An ozone concentration of 0.2 mg/L to 0.5 mg/L, combined
with a contact time of 10 minutes, is capable of killing bacteria,
bacterial spores, and viruses in water. Destruction of established
biofilm may require longer exposure times and/or higher
concentrations of ozone.
Ozone may degrade many plastic materials, including PVC and
elastomeric O-rings and seals.
Additional Guidance:
Ozone is not recommended for disinfection of many of the water
distribution loop materials. Refer to Table 2 at V212.
Refer to the manufacturer’s guidance for required concentrations and
contact time.
Staff must monitor the system being disinfected with ozone for the
expected concentration of ozone during the disinfection and for the
absence of ozone when the disinfection is completed. Facility policy
must define the frequency for “periodic basis” for testing the ozone-
in-ambient-air levels; this policy should reflect the manufacturer’s
guidance and OSHA requirements for exposure limits.
Final Version 1.1 Page 80 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
been performed.
V217
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.3.4.3 Hot water disinfection systems:
temp/time/follow DFU/piping
Refer to RD62:2001, 4.3.14 Hot water disinfection
systems: When used to control bacterial proliferation in
water treatment, storage, and distribution systems, the
water heater of a hot water disinfection system shall be
capable of delivering hot water at the temperature and for
the exposure time specified by the manufacturer.
5.3.4.3 Hot water disinfection systems
Hot water disinfection systems can be used only in
systems constructed from heat-resistant materials, such
as crosslinked polyethylene, polypropylene, and stainless
steel (see [AAMI] 5.3.3).
The manufacturer’s instructions for using hot water
disinfection systems should be followed. If no
manufacturer’s instructions are available, the
effectiveness of the system can be demonstrated by
verifying that the system maintains a specified
temperature for a specified time and by performing
ongoing surveillance with bacterial cultures and
endotoxin testing.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.3.4.3 Hot water disinfection systems
Hot water (≥80 °C) may be used to control bacterial proliferation in
water storage and distribution systems. Bacterial kill studies are not
required
Additional Guidance:
See Table 2 at V212 for acceptable heat-resistant materials.
V218
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.3.4 Bacterial control devices
6.3.4.3 Hot water disinfection systems: monitoring
Hot water disinfection systems should be monitored for
temperature and time of exposure to hot water as
specified by the manufacturer. Also, hot water
Additional Guidance:
Records of use of hot water disinfection systems must include logs or
recorded evidence to verify that the specified water temperature was
maintained for the specified period of time in order to accomplish the
intended disinfection.
Final Version 1.1 Page 81 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
disinfection should be performed at least as often as
recommended by the manufacturer. The temperature of
the water should be recorded at a point farthest from the
water heater—that is, where the lowest water
temperature is likely to occur…and measured each time
a disinfection cycle is performed. A record that verifies
successful completion of the heat disinfection should be
maintained. Successful completion is defined as meeting
temperature and time requirements specified by the
equipment manufacturer.
V219
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General: disinfect monthly/disinfection dwell
Routine low-level disinfection of the pipes should be
performed to control bacterial contamination of the
distribution system. The frequency of disinfection will
vary with the design of the system and the extent to
which biofilm has already formed in existing systems,
but disinfection must be performed at least monthly.
A mechanism should be incorporated in the distribution
system to ensure that disinfectant does not drain from
pipes during the disinfection period.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
The strategy for controlling the proliferation of microorganisms in
hemodialysis systems primarily involves proper system design and
operation, and regular disinfection of water treatment system and
hemodialysis machines. A key concept in ensuring compliance with
water bacteriology standards is that disinfection schedules should be
designed to prevent bacterial proliferation, rather than being designed
to eliminate bacteria once they have proliferated to an unacceptable
level (i.e., above the action level). With this strategy, monitoring
levels of bacteria and endotoxin serves to demonstrate that the
disinfection program is effective, not to indicate when disinfection
should be performed. Gram-negative water bacteria, their associated
lipopolysaccharides (bacterial endotoxins), and nontuberculous
mycobacteria (NTM) most frequently come from the community
water supply, and levels of those bacteria can be amplified depending
on the water treatment system, dialysate distribution system, type of
dialysis machine, and method of disinfection.
Two components of hemodialysis water distribution systems—pipes
and storage tanks—can serve as reservoirs of microbial
contamination. Hemodialysis systems frequently use pipes that are of
Final Version 1.1 Page 82 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
larger diameter and longer than are needed to handle the required
flow. Oversized piping slows the fluid velocity and increases both the
total fluid volume and the wetted surface area of the system. Gram-
negative bacteria in fluids remaining in pipes overnight multiply
rapidly and colonize the wet surfaces, thus producing bacterial
populations and endotoxin quantities in proportion to the volume and
surface area. Such colonization results in the formation of protective
biofilm that is difficult to remove once formed and that provides a
barrier between the bacteria and germicide during disinfection.
Biofilms are communities of microorganisms attached to surfaces.
They form just about anywhere a nonsterile fluid flows over a surface.
Biofilm increases the ability of microorganisms to compete for
nutrients and other resources. The complexity of biofilm depends on
the degree of water or fluid movement and the availability of
nutrients. Thicker biofilm, and usually a greater diversity of
microorganisms, will form in slower moving waters; in faster moving
waters, it is harder for microorganisms to become (and remain)
attached to the surface, so biofilm formation takes longer. Organisms
living within biofilm are shielded by an extracellular polymer or
glycocalyx. This glycocalyx provides the bacteria with some
protection from the action of disinfectants. Biofilm may exist
throughout a hemodialysis distribution system. Once established in a
distribution system or dialysis machine, biofilm can be difficult to
eradicate. Bleach and ozone are generally the most effective agents for
biofilm removal, and their use may be more efficacious if the pipes
are treated first with a descaling agent. However, in some cases,
complete or partial replacement of the distribution system may be the
only way to eliminate biofilm.
Additional Guidance:
In order to prevent or limit the development of biofilm, every dialysis
facility must disinfect their water distribution system at least monthly.
Final Version 1.1 Page 83 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
All surfaces in the water distribution system must have sufficient
contact time with the disinfectant prior to its being rinsed from the
system.
V220
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General: machine supply line disinfected
Users should establish a procedure for regular
disinfection of [the line between the outlet from the
water distribution system and the back of the dialysis
machine].
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
For most dialysis machines, routine disinfection with hot water or
with a chemical germicide connected to a disinfection port on the
machine does not disinfect the line between the outlet from the water
distribution system and the back of the dialysis machine. One
approach is to rinse the dialysis machines with water containing
germicide or hot water when the water distribution loop is disinfected.
If this procedure is used with a chemical germicide, each dialysis
machine should be rinsed and tested for the absence of residual
germicide following disinfection.
Additional Guidance: The machine supply line is the hose that
connects the dialysis machine to the treated water outlet. This hose
should be disinfected at the same frequency as the water distribution
loop is disinfected, i.e., monthly.
No tag
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4 Concentrate preparation
5.4.1 General
Dialysate is customarily prepared from two concentrates:
the bicarbonate concentrate, which contains sodium
bicarbonate (and sometimes additional sodium chloride),
and the acid concentrate, which contains all remaining
ions, acetic acid, and sometimes glucose.
Acid concentrate can be supplied by the manufacturer in
bulk (usually 55 gallon containers) or in gallon
containers.
There are systems available that allow a user at a dialysis
Additional Guidance:
This is an informational tag outlining the methods used for
bicarbonate and acid concentrate delivery.
Final Version 1.1 Page 84 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
facility to prepare acid concentrate from packaged
powder and purified water using a mixer. Acid
concentrate prepared at the dialysis facility from powder
and water is the responsibility of the user.
Bicarbonate concentrate can be supplied by the
manufacturer in one of three ways: (1) in gallon
containers, (2) as packaged powder that is mixed with
purified water at the dialysis facility, and (3) in powder
cartridges that are used to prepare concentrate on-line at
the time of dialysis.
V222
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4 Concentrate preparation
5.4.3 Bulk storage tanks (acid concentrate): safety
controls
Procedures should be in place to control the transfer of
the acid concentrate from the delivery container to the
storage tank to prevent the inadvertent mixing of
different concentrate formulations. If possible, the tank
and associated plumbing should form an integral system
to prevent contamination of the acid concentrate. The
storage tanks and inlet and outlet connections, if remote
from the tank, should be secure and labeled clearly.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.4 Concentrate preparation
5.4.1 General
Acid concentrates supplied in 55 gallon drums or gallon containers by
the manufacturer are the responsibility of that manufacturer (see
AAMI 2.4). In some cases, the manufacturer will pump the acid
concentrate from the 55 gallon drums into a holding tank at the
dialysis facility. In those cases, the user is responsible for maintaining
the concentrate in its original state and to ensure that the correct
formula is used according to the patient’s prescription.
Additional Guidance:
Acid concentrates supplied in 55 gallon drums or gallon containers are
the responsibility of the manufacturer until delivered; proper handling
after delivery is the responsibility of the dialysis facility. If an inlet
opening to the acid concentrate storage system is located on the
outside of the building, there must be safety controls in place to
prevent inadvertent mix-ups, tampering, or contamination of acid
concentrates.
V223
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4 Concentrate preparation
Final Version 1.1 Page 85 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
5.4.2 Materials compatibility
All components used in concentrate preparation systems
(including mixing and storage tanks, pumps, valves, and
piping) shall be fabricated from materials (e.g., plastics
or appropriate stainless steel) that do not interact
chemically or physically with the concentrate so as to
affect its purity, or with the germicides or germicidal
procedure used to disinfect the equipment. The use of
materials that are known to cause toxicity in
hemodialysis, such as copper, brass, galvanized material,
and aluminum, are specifically prohibited.
V224
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.1 Mixing systems: water/drain/electric
Concentrate mixing systems require a purified water
source, a suitable drain, and a ground fault protected
electrical outlet.
V225
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.1 Mixing systems: safe environment/PPE
Protective measures should be used to ensure a safe work
environment.
Operators should at all times use appropriate personal
protective equipment, such as face shields, masks,
gloves, gowns, and shoe protectors, as recommended by
the manufacturer.
ANSI/AAMI RD52
5.4.4.1 Mixing systems
For example, ventilation and personal protective equipment should be
used to handle any residual dust that is introduced into the atmosphere
as powdered concentrates are added to the system and to handle any
additional heat produced by the device.
Additional Guidance:
Shoe protectors are rarely, if ever, required by the manufacturers.
Process controls, such as limiting the number of bags emptied at one
time, may decrease the requirements for PPE.
V226
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.1 Mixing systems: follow
DFU/monitor/PM/log/sanitization
If a concentrate mixing system is used, the preparer
Additional Guidance:
There must be a log or other method of recording the preparation of
concentrates, to include the number of bags or weight of the powder
and the amount of water used. See also the requirements for records of
mixing detailed at V229.
Final Version 1.1 Page 86 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
should follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing
the powder with the correct amount of water.
If a concentrate mixing system is used, the number of
bags or the weight of powder added should be
determined and recorded.
Manufacturer’s recommendations should be followed
regarding any preventive maintenance and sanitization
procedures. Records should be maintained indicating the
date, time, person performing the procedure, and results
(if applicable).
6.4.1 Mixing systems:
Systems for preparing either bicarbonate or acid
concentrate from powder should be monitored according
to the manufacturer’s instructions.
The facility must have records of the manufacturer’s instructions for
the sanitizing, maintenance and monitoring of the mixing system.
Individuals assigned responsibility for mixing concentrates or for
preventative maintenance of these systems must demonstrate
competency in following the manufacturer’s DFU.
V227
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.4.1 Mixing systems: self designed
If a facility designs its own system, procedures should be
developed and demonstrated to ensure proper mixing of
the concentrate, including establishment of acceptable
limits for tests of proper concentration. The adequacy of
those procedures must be verified using an independent
laboratory that is capable of meeting the requirements of
ANSI/AAMI RD61:2000 (see 2.4). Verification can be
accomplished by testing a sample from each batch
prepared over a 3-day period
Additional Guidance:
If a facility designs its own mixing systems, there must be
documentation of the verification testing available for review.
V228
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.1 Mixing systems: labeling
Labeling strategies should permit positive identification
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.4.4.1 Mixing systems
Requirements for such positive identification will vary among
facilities, depending on the differences between concentrate
Final Version 1.1 Page 87 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
by anyone using the contents of mixing tanks, bulk
storage/dispensing tanks, and small containers intended
for use with a single hemodialysis machine.
Mixing tanks: Prior to batch preparation, a label should
be affixed to the mixing tank that includes the date of
preparation and the chemical composition or formulation
of the concentrate being prepared. This labeling should
remain on the mixing tank until the tank has been
emptied.
Bulk storage/dispensing tanks: These tanks should be
permanently labeled to identify the chemical
composition or formulation of their contents.
Concentrate jugs: At a minimum, concentrate jugs
should be labeled with sufficient information to
differentiate the contents from other concentrate
formulations used at the facility.
formulations used and on whether single or multiple dialysate
proportioning ratios are used. The use of multiple dialysate
proportioning ratios (e.g., 35X and 45X) in a single facility is strongly
discouraged.
Using a photocopy of the concentrate manufacturer’s package label
provides a convenient and comprehensive means of identifying the
chemical composition or formulation of the concentrate; however, the
lot number and expiration date should be marked out because they
apply only to the dry powder.
As with mixing tanks, bulk storage/dispensing tank labeling can be
conveniently accomplished by affixing a copy of the concentrate
manufacturer’s package label.
Concentrate jugs are typically nondisposable vessels provided by
hemodialysis machine manufacturers and having a capacity sufficient
for one or two hemodialysis sessions. The extent of labeling for these
containers depends on the variety of concentrate formulations used
and on whether the facility uses dialysis machines with different
proportioning ratios (a practice that is strongly discouraged).
Additional Guidance:
If multiple dialysate proportioning ratios are in use, applicable staff
and the medical director must be able to describe safeguards in place
to prevent mismatching dialysate components/machines. There should
be no incidents of ratio mismatch, for example, 35X acid used with a
machine set for 45X. Labels made by the facility are acceptable as
long as the required information is included. Labels should be used to
alert staff when bleach or ozone is in a tank or concentrate jug during
disinfection. If a group of jugs are being disinfected at once, a process
control (such as a label or sign marking the area in use) could be used
rather than individual labels for each jug.
Final Version 1.1 Page 88 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V229
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.1 Mixing systems: perm record/verification
testing
In addition to container labeling, there should be
permanent records of batches produced. These records
should include the concentrate formula produced, the
volume of the batch, the lot numbers of powdered
concentrate packages, the manufacturer of the powdered
concentrate, the date and time of mixing, any test results,
the person performing the mixing, the person verifying
mixing and test results, and the expiration date (if
applicable).
6.4.1 Mixing systems
Acid and bicarbonate concentrates may be tested by
using conductivity or by using a hydrometer.
Concentrates should not be used or transferred to holding
tanks or distribution systems until all tests are completed.
The test results and verification that they meet all
applicable criteria should be recorded and signed by the
individuals performing the tests.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
6.4.1 Mixing systems
Although not required, some manufacturers may provide allowable
ranges for either the conductivity or the specific gravity of
concentrates prepared from their powder. The use of pH as an
indicator of proper dissolution is inappropriate for both acid and
bicarbonate concentrates, because large variations in concentration do
not produce significant changes in pH.
Additional Guidance:
The mixing logs must demonstrate complete documentation of this
required information. Test results may include conductivity or specific
gravity. Facility policy must stipulate the expected ranges for the
test(s) used to verify correct mixing. Standards used to calibrate the
instrument used to measure conductivity should encompass the
expected results; for example, it would be unacceptable to use a “14”
standard for an expected result of “70.” “Verifying mixing and test
results” means the staff member performing this task checks the
results against the expected ranges for the test and does not release
mixtures for use that test outside those ranges.
V230
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.4.1 Mixing systems: cleaning Concentrate mixing
equipment should be either: (1) completely emptied,
cleaned, and disinfected according to the manufacturer’s
instructions; or (2) cleaned and disinfected using a
procedure demonstrated by the facility to be effective in
routinely producing concentrate meeting [these
regulations related to allowable bacterial and endotoxin
levels].
Additional Guidance:
The log may be kept electronically or on paper and may be for only
this purpose or inclusive of other operations.
Final Version 1.1 Page 89 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The disinfection data should be recorded for each
…disinfection cycle using a dedicated log.
V231
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.2 Acid concentrate mixing systems: empty
completely/prevent corrosion
Acid concentrate mixing tanks should be designed to
allow the inside of the tank to be completely emptied and
rinsed according to the manufacturer’s instructions when
concentrate formulas are changed.
Acid concentrate mixing tanks should be emptied
completely before mixing another batch of concentrate.
Because concentrate solutions are highly corrosive,
mixing systems should be designed and maintained to
prevent corrosion.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.4.4.2 Acid concentrate mixing systems
Use of a tank with a sloping bottom that drains from the lowest point
is one means of facilitating this process.
Additional Guidance:
Facility policy and practice must ensure the tank is completely
emptied between mixing batches of concentrate.
Facilities generally have little control over the design of these
systems, but should maintain the system clean and free of spills of
concentrate to reduce the potential of corrosion.
V232
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems:
empty/ disinfect/prevent corrosion
Bicarbonate concentrate mixing tanks should be
designed to drain completely.
Mixing tanks should have a tight-fitting lid and should be
designed to allow all internal surfaces to be disinfected
and rinsed.
Because concentrate solutions are highly corrosive,
mixing systems should be designed and maintained to
prevent corrosion.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems
For example, they should have a sloping bottom and a drain at the
lowest point. High- and low-level alarms can prevent overfilling and
air damage to the pump.
A translucent tank allows users to see the liquid level; the use of sight
tubes is not recommended because of the potential for microbial
growth, such as bacteria, algae, and fungi.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems
Bicarbonate concentrates have been shown to support bacterial growth
and to provide another source of initial bioburden capable of rapidly
increasing after dilution. Therefore, additional precautions should be
Final Version 1.1 Page 90 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
taken when preparing and handling bicarbonate concentrate to avoid
excess growth of haloduric organisms. Also, prompt use of
bicarbonate concentrates prepared in dialysis facilities from powder
and purified water is strongly recommended.
Additional Guidance:
High and low level alarms are not required. Facilities generally have
little control over the design of these systems, but should maintain the
system clean and free of spills of concentrate to reduce the potential of
corrosion. Expect that systems will have little to no build-up of
precipitate.
V233
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems:
storage/use time limits/min combine
Once mixed, bicarbonate concentrate should be used
within the time specified by the manufacturer of the
concentrate.
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
Storage times for bicarbonate concentrate should be
minimized, as well as the mixing of fresh bicarbonate
concentrate with unused portions of concentrate from a
previous batch. The manufacturer’s instructions should
be followed if they are available.
Additional Guidance:
Bicarbonate concentrates must be used or discarded within the
manufacturer’s timelines, if these are available. If facility staff
members combine bicarbonate concentrate from partially used jugs,
there must be some system to ensure the concentrate is not kept past
the maximum storage time of the oldest portion. For example, if the
facility policy is to discard all unused concentrate at the end of each
treatment day, combining jugs during the day would not exceed the
limit if the allowable storage time was at least one day or 24 hours. If
the facility policy allows carryover of unused concentrate to the
following day, there could be potential for that time limit to be
exceeded should the contents of jugs (which may have been mixed at
various times) be combined.
Central delivery systems should be cleared of bicarbonate solution at
some point during the treatment day and rinsed clear. Generally this is
done at the end of the treatment day.
V234
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems: not
overmixed
Overagitating or overmixing of bicarbonate concentrate
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems
Systems designed for mixing dry acid concentrates may use methods
that are too vigorous for dissolving dry bicarbonate.
Final Version 1.1 Page 91 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
should be avoided, as this can cause CO
2
loss and can
increase pH.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5.4.4.3 Bicarbonate concentrate mixing systems
Overagitation or mixing of bicarbonate concentrate may result in loss
of CO
2
from the solution. Loss of CO
2
results in an increase in pH and
favors the formation of carbonate that can lead to precipitation of
calcium and magnesium carbonate in the fluid pathways of the
dialysis machine following dialysate proportioning.
Additional Guidance:
There must be a system to prevent overmixing of bicarbonate. This
could include a timer integrated into the mixing system for automatic
cut-off, or a policy to require staff to monitor the mixer and cut it off
immediately when the time period for mixing is completed. Use of
overmixed bicarbonate concentrate can result in a low calcium level in
the dialysate and a concomitant drop in patients’ serum calcium
levels.
V235
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.5 Additives: mixing spikes
Concentrate additives should be mixed with liquid acid
concentrates according to the manufacturer’s
instructions, taking care to ensure that the additive is
formulated for use in concentrates of the appropriate
dilution ratio. When liquid additives are used, the
volume contributed by the additive should be considered
when calculating the effect of dilution on the
concentration of the other components in the resulting
concentrate. When powder additives are used, care
should be taken to ensure that the additive is completely
dissolved and mixed before the concentrate is used.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.4.5 Additives
Manufacturers provide acid concentrates with a wide range of
electrolyte compositions for different proportioning ratios. Most
typical dialysate prescriptions can be obtained by using one or more
of these commercially available concentrates. If particular
formulations are not available, manufacturers provide additives that
can be used to adjust the level of potassium or calcium in the
dialysate. These additives are commonly referred to as “spikes.”
6.4.2 Additives:
When additives are used to increase concentrations of specific
electrolytes in the acid concentrate, mixing procedures shall be
followed as specified by the additive manufacturer.
Additional Guidance:
Final Version 1.1 Page 92 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The State nurse practice act must be considered in determining the
appropriateness of the staff allowed to use a “spike” to change the
concentration of electrolytes in the acid concentrate. Since the
concentrate is a prescription medication, many states require a
licensed nurse to perform this task. When facility policy allows use of
“spikes,” appropriate additives must be accurately mixed according to
manufacturer’s directions, labeled as required by these rules, and
documented in the patient record to accurately reflect the composition
of the dialysate used for treatment.
V236
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.4.5 Additives: labeling spiked jugs/labeling if for
specific pt
(5.4.4.1 Concentrate jugs): If a chemical spike is added
to an individual container to increase the concentration
of an electrolyte, the label should show the added
electrolyte, the date and time added, and the name of the
person making the addition.
Containers should be labeled to indicate the final
concentration of the added electrolyte…This information
should also be recorded in a permanent record. Labels
should be affixed to the containers when the mixing
process begins.
6.4.2 Additives
When additives are prescribed for a specific patient, the
container holding the prescribed acid concentrate should
be labeled with the name of the patient, the final
concentration of the added electrolyte, the date on which
the prescribed concentrate was made, and the name of
the person who mixed the additive
Additional Guidance:
Spiked jugs must be clearly labeled with this required information. If
the jug is prepared for a specific patient, the label must include the
name of the patient as well as the other required information.
V237
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
Final Version 1.1 Page 93 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5 Concentrate distribution:
5.5.1 Materials compatibility
All components used in concentrate distribution systems
(including concentrate jugs, storage tanks, and piping)
that contact the fluid shall be fabricated from nonreactive
materials (e.g., plastics or appropriate stainless steel) that
do not interact chemically or physically with the
concentrate so as to affect its purity. The use of materials
that are known to cause toxicity in hemodialysis, such as
copper, brass, galvanized material, and aluminum, are
specifically prohibited.
V238
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.2 System configurations: elevated tanks
Elevated tanks for bicarbonate concentrate distribution
should be equipped with conical or bowl-shaped
bottoms, tight-fitting lids, a spray mechanism, and high-
and low-level alarms. Any air vents should have 0.2 µm
hydrophobic vent filters.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.5.2 System configurations
Concentrate may be distributed from a central preparation point using
reusable concentrate jugs that contain sufficient concentrate for one to
two treatments, or it may be distributed through a piping system that
provides concentrate connections at each treatment station. A
combination of these two systems may also be used, with some
concentrates distributed by concentrate jug and others through a
piping system. Two common configurations used for distributing
concentrate through a piping system are gravity feed and pressurized.
Gravity feed systems require an elevated tank; pressurized systems
deliver the concentrate using a pump and motor and do not require an
elevated tank. The maximum allowable concentrate delivery pressure
is specified by the manufacturer of the dialysate delivery machine and
should not be exceeded.
Elevated tanks are usually smaller than those used for preparing
concentrates.
V239
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.4 Bicarbonate concentrate distribution systems:
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.5.4 Bicarbonate concentrate distribution systems
Bicarbonate concentrates provide excellent media for bacterial
Final Version 1.1 Page 94 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
weekly disinfection/dwell times/conc
Bicarbonate concentrate delivery systems should be
disinfected on a regular basis to ensure that the dialysate
routinely achieves the level of bacteriological purity
[required by these regulations].
For piped distribution systems, the entire system,
including patient station ports, should be purged of
bicarbonate concentrate before disinfection. Each patient
station port should be opened and flushed with
disinfectant and then rinsed; otherwise, it would be a
“dead leg” in the system.
Appropriate dwell times and concentrations should be
used as recommended by the manufacturer of the
concentrate system. If this information is not available,
bleach may be used at a dilution of 1:100 and proprietary
disinfectants at the concentration recommended by the
manufacturer for disinfecting piping systems.
6.5 Concentrate distribution:
The interval between disinfection should not exceed 1
week. If the manufacturer does not supply disinfection
procedures, the user must develop and validate a
disinfection protocol.
proliferation. The manufacturer’s instructions can provide an initial
disinfection schedule. This schedule may need to be adjusted on the
basis of the user’s bacteriological monitoring.
All chemical disinfectants (e.g., bleach and peracetic acid products)
that are compatible with dialysis machines can be used to disinfect
bicarbonate concentrate delivery systems. However, some
disinfectants attack biofilm better than others.
In the event that precipitation or salt build-up impedes flow through a
piping system, cleaning with a 1:34 solution of 5 % acetic acid (e.g.,
distilled white vinegar) is recommended. Some manufacturers supply
bicarbonate concentrate systems with UV irradiation or ozone systems
for bacterial control.
Additional Guidance:
Alternatively, a 5% citric acid solution may be used instead of acetic
acid if the manufacturer allows. It is not expected that concentrates
would be cultured or tested for endotoxin levels. Bicarbonate
concentrates are monitored via dialysate cultures.
V240
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.4 Bicarbonate concentrate distribution systems:
use of UV
UV irradiation devices that are used to control bacteria
proliferation in the pipes of bicarbonate concentrate
distribution systems should be fitted with a low-pressure
mercury lamp that emits light at a wavelength of 254 nm
Additional Guidance:
This requirement applies to UV irradiators used in the bicarbonate
delivery system, rather than to an UV irradiator used in the water
treatment/distribution system. A facility may have an UV irradiator in
one system, and not in the other. The UV irradiator in the bicarbonate
delivery system may also be used to help breakdown the ozone used
to disinfect the bicarbonate delivery system.
Final Version 1.1 Page 95 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
and provides a dose of radiant energy of 30 milliwatt-
sec/cm
2
. The device should be sized for the maximum
anticipated flow rate according to the manufacturer’s
instructions and be equipped with an on-line monitor of
radiant energy output that activates a visual alarm
indicating that the lamp should be replaced.
Alternatively, the lamp should be replaced on a
predetermined schedule according to the manufacturer’s
instructions to maintain the recommended radiant energy
output. Disinfection of the bicarbonate concentrate
distribution system should continue to be performed
routinely.
V241
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.4 Bicarbonate concentrate distribution systems:
ozone disinfection
When used to disinfect the pipes of a bicarbonate
concentrate delivery system, an ozone generator should
be capable of delivering ozone at the concentration and
for the exposure time specified by the manufacturer.
When ozone disinfection systems are used, ambient air
should be monitored for ozone as required by the U.S.
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
V242
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.5 Concentrate distribution: bicarb monitoring
initially
Once a bicarbonate distribution system has been
activated, dialysate should be monitored weekly until
sufficient data has been obtained to demonstrate
consistent compliance with acceptable levels of
contamination. The frequency of monitoring may then be
reduced, but monitoring should be performed at least
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
6.5 Concentrate distribution
Because acid concentrate distribution systems have been shown not to
be subject to bacterial proliferation, it is not necessary to perform
bacteria and endotoxin testing on those systems.
Additional Guidance:
Whenever use of a new bicarbonate distribution system is initiated,
weekly monitoring of dialysate should occur for at least four
consecutive weekly reports of acceptable levels. Evaluation of
Final Version 1.1 Page 96 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
monthly. If elevated bacteria or endotoxin levels are
found in the dialysate, all systems involved in dialysate
preparation, including the bicarbonate concentrate
distribution system should be evaluated and appropriate
action, such as disinfection, should be taken. The
frequency of monitoring should then be increased until it
can be demonstrated that the problem has been resolved.
positive culture or endotoxin reports should also consider the number
of positives in relationship to the number of samples taken. For
example, if one sample out of 10 has a count of 53, while the other 9
have no growth, doing a reculture of one or more sites may be the first
action taken. The medical director must be involved in these
decisions.
V243
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
6.5 Concentrate distribution: bicarb jugs rinsed
daily/stored dry
Bicarbonate concentrate jugs should be rinsed with
treated water and stored inverted at the end of each
treatment day. Pick-up tubes should also be rinsed with
treated water and allowed to air dry at the end of each
treatment day.
Additional Guidance:
Pick-up tubes are the tubes which go into the concentrate jugs to take
up the concentrate. These look like large straws, and are usually
attached to the lids of the jugs.
V244
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.4 Bicarbonate concentrate distribution systems:
jug disinfection
When reusable concentrate jugs are used to distribute
bicarbonate concentrate, they should be rinsed free of
residual concentrate before disinfection.
6.5 Concentrate distribution
When reusable concentrate jugs are used to distribute
bicarbonate concentrate, they should be disinfected at
least weekly.
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
Following disinfection, jugs should be drained, rinsed,
and inverted to dry.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7 Strategies for bacterial control
7.1 General
Facilities that reuse concentrate jugs for bicarbonate concentrate
should disinfect the jugs at least weekly. Bicarbonate concentrate can
support prolific growth of microorganisms. Jugs can be disinfected
with household bleach solutions (300 mg to 600 mg free chlorine, or
30 mL to 60 mL of 6.15 % household bleach per gallon of water) with
a contact time of about 30 minutes or another EPA-registered
disinfectant according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Additional Guidance:
A 1:100 solution of household bleach: treated water may be used,
which yields about 500-615 ppm available chloride. If the facility uses
less contact time than 30 minutes, there must be evidence of the use of
dialysate culture results to determine the needed disinfectant contact
time. In all cases, the bicarbonate container disinfection process must
Final Version 1.1 Page 97 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
result in compliance with the allowable dialysate microbiological
levels of <200 cfu and <2 EU.
V245
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.3 Acid concentrate distribution systems: labeled &
color-coded red
Acid concentrate delivery piping should be labeled and
color-coded red at the point of use (at the jug filling
station or the dialysis machine connection).
All joints should be sealed to prevent leakage of
concentrate. If the acid system remains intact, no rinsing
or disinfection is necessary.
More than one type of acid concentrate may be
delivered, and each line should clearly indicate the type
of acid concentrate it contains.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.5.3 Acid concentrate distribution systems
Acid concentrate is not susceptible to bacteria contamination, but
every effort should be made to keep the system closed to prevent
nonbacterial contamination and evaporation.
Additional Guidance:
If more than one acid is centrally delivered to treatment stations,
outlets must be clearly labeled with the acid type.
V246
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.4 Bicarbonate concentrate distribution systems:
color coded blue & sealed
Bicarbonate concentrate delivery piping should be color-
coded blue at the point of use (at the jug filling station or
dialysis machine connection). All joints should be sealed
to prevent leakage of concentrate.
V247
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.5.5 Concentrate outlets: separate/labeled/connection
safety
To prevent mix-ups with delivery of two or more types
of acid concentrate, each concentrate should have its own
outlet. Concentrate outlets should be compatible with the
dialysis machine and have a means of minimizing the
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.5.5 Concentrate outlets
For piped concentrate distribution systems, each treatment station is
equipped with a concentrate outlet for bicarbonate, one or more
outlets for acid concentrate, and a product water outlet for connection
to the inlet line of the dialysis machine.
Final Version 1.1 Page 98 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
risk that the wrong concentrate will be connected to an
outlet. The dispensing outlets should be labeled with the
appropriate symbol (see AAMI Table 3) indicating the
proportioning ratio for the dialysis machine and should
be color-coded blue for bicarbonate, red for acid.
6.5 Concentrate distribution
A daily check to ensure that the appropriate acid and
bicarbonate concentrate is connected to the
corresponding concentrate delivery line is recommended
if the storage tank is not permanently connected to its
distribution piping.
V248
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.6 Dialysate proportioning: match ratio all
conc/machine
The acid and bicarbonate concentrates [must] be matched
with respect to the proportioning ratio and with the
model and setup configuration of the dialysis machine.
Several types of three-stream concentrates are available,
with different ratios of acid concentrate to bicarbonate
concentrate to water (see Table 3). The different
proportioning types are not compatible with one another.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.6 Dialysate proportioning
Essentially, all dialysate is produced with three fluid streams: water,
acid concentrate, and bicarbonate concentrate. This three-stream
combination produces a highly buffered dialysate with a pH between
6.9 and 7.6. Dialysate can also be prepared from a single concentrate
that contains acetate to provide a dialysate in which buffer is provided
to the patient in the form of acetate, which is subsequently
metabolized to yield bicarbonate. However, acetate containing
dialysate is now rarely used in clinical practice.
Different manufacturers of dialysis machines use different methods of
controlling the proportions of the concentrates. These can be generally
grouped into two categories: “fixed proportioning” and “servo
control.” With both methods, the operator can select a desired sodium
and bicarbonate level, and the machine will make the necessary
adjustments to achieve the selected levels. Both types use a redundant
system of controls and monitoring. With fixed proportioning systems,
the pumps are set to established volumes, and the final conductivity is
verified. With servo control machines, the individual concentrates are
added until the conductivity achieves the expected value. A final
Final Version 1.1 Page 99 of 299
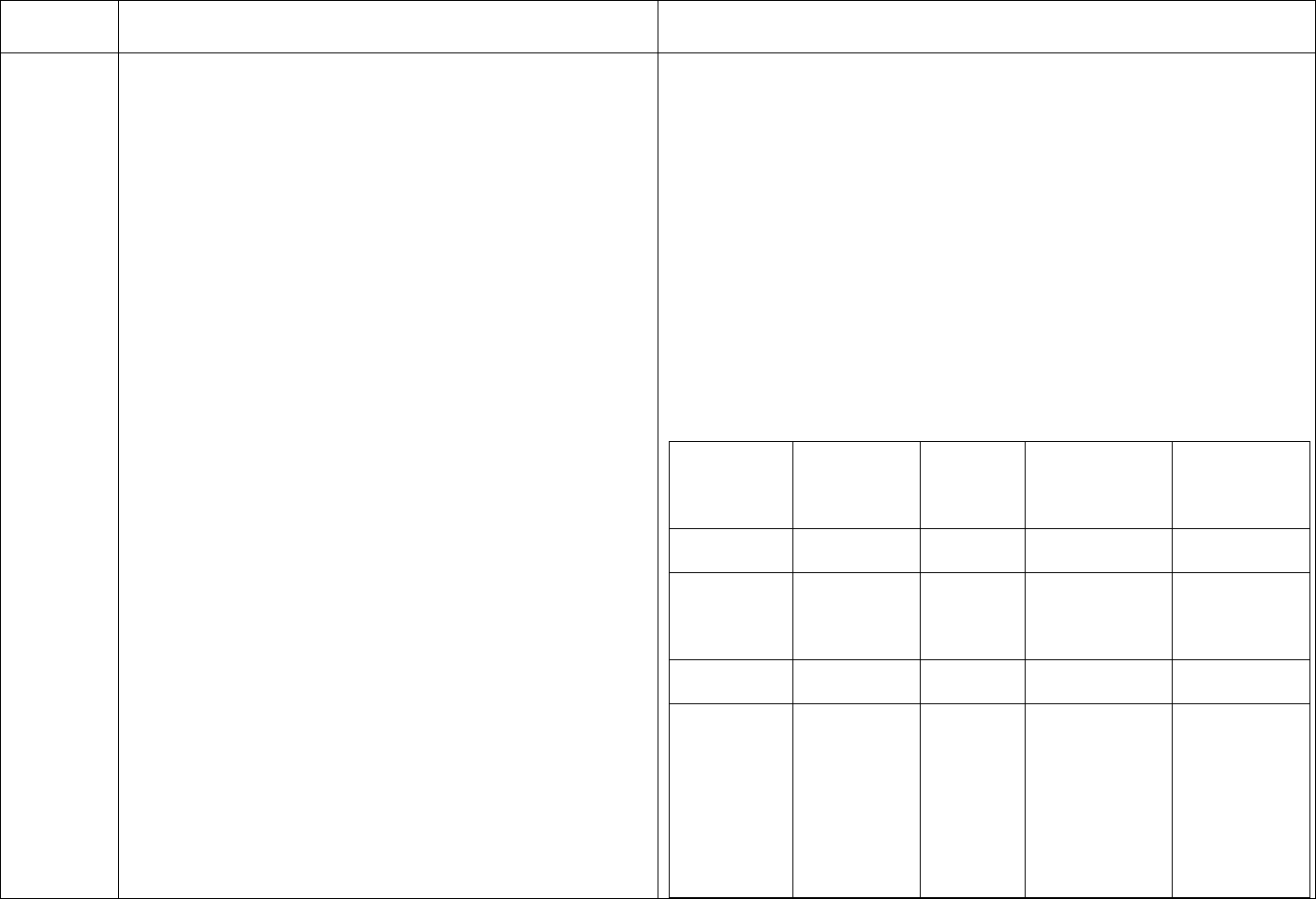
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
redundant conductivity monitor verifies the mixture. Some machines
may also monitor the pH of the dialysate as an additional safeguard
against gross errors in dialysate formulation.
Generally, bicarbonate is available in one or two forms for each
proportioning type (in liquid, cartridge, or dry powder, and in various
sizes). Each proportioning type has numerous acid concentrate
formulations (“codes”) with different amounts of potassium, calcium,
and magnesium ions, plus dextrose. To help differentiate between
concentrates of different proportioning types, AAMI recommends that
the manufacturer include a geometric symbol on the labels along with
acid/base color coding.
Table 3—Symbols and color coding for different concentrate
proportioning ratios
Acid
Bicarbonate
Concentrate proportionin concentrate
type g ratio (Red Geometric (Blue color
color coding)
symbol
coding)
Comments
35X
1:34
Square
Dry, liquid, or
cartridge
36.8X
1:35.83
Circle
Dry or liquid
Bicarbonate
concentrate
contains some
NaCl.
45X
1:44
Triangle
Dry, liquid, or
cartridge
36.1X
1:35.1
Hexagon
Cartridge
Powder
cartridges may
be used for
other
proportioning
ratios, except
for 36.83X, in
which the
bicarbonate
Final Version 1.1 Page 100 of 299

TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
concentrate
also contains
NaCl.
NOTE 1—The acid proportioning ratio refers to acid concentrate
water + bicarbonate concentrate.
NOTE 2—Acetate-containing concentrate is color-coded white.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.5.6 Dialysate proportioning
Dialysate is usually prepared by a proportioning system that
sequentially adds acid concentrate and bicarbonate concentrate to
purified water. These systems produce a buffered physiologic
dialysate with a pH between 6.9 and 7.6. More recently, systems have
been developed that use three concentrates (bicarbonate, sodium
chloride, and an acid concentrate containing the remaining
electrolytes) to allow more sophisticated variation of the dialysate
composition during dialysis.
V249
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a) 5.6 Dialysate proportioning
5.6 Dialysate proportioning: match machine config
Some models of dialysis machines can use concentrates of only one
w/ratio in use
type of proportioning ratio, but others may be set up or calibrated for
Changing from one proportioning ratio to another use with concentrates of more than one proportioning type.
requires recalibration for some models of dialysis
machines. For those machines, the type of concentrate
Additional Guidance:
should be labeled on the machine or clearly indicated by The medical director and responsible staff must be knowledgeable of
the machine display. It is strongly recommended that the mixing ratio the machines are set up to use and all dialysate
facilities configure every machine to use only one type of supplies in the facility must match that ratio.
concentrate.
Rarely, a facility may have machines set for different ratios; this is a
6.6 Dialysate proportioning
risky practice, and would require very close monitoring to prevent
Dialysate proportioning should be monitored following
mis-matching of supplies and machines. If machines are available for
Final Version 1.1 Page 101 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the procedures specified by the equipment manufacturer.
The user should maintain a record of critical parameters
such as conductivity and approximate pH. When the user
has specific requirements for monitoring dialysate
proportioning, such as when dialysis machine settings
are changed to allow the use of concentrates with a
different proportioning ratio, the user should develop
procedures for routine monitoring of dialysate electrolyte
values.
different ratios in the same facility, each machine must be clearly
labeled for the applicable ratio, and supplies for the different ratios
must be segregated and labeled clearly to avoid mis-match. The
medical director must be aware of this practice, and be involved in
quality control to avoid any patient consequence from potential mis-
match of supplies and machines.
If machines are changed from one ratio to another, responsible staff
members must be able to describe how they verified the machine
functioned correctly after the change was made and how they
monitored the dialysate electrolyte values.
V250
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
5.6 Dialysate proportioning: monitor pH/conductivity
It is necessary for the operator to follow the
manufacturer’s instructions regarding dialysate
conductivity and to measure approximate pH with an
independent method before starting the treatment of the
next patient.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
5.6 Dialysate proportioning
Injuries related to improper dialysate are rare, but they can and do
happen when all procedures are not followed. Frequently, when the
error occurs, several patients have been exposed before the facility
recognizes the mistake. For example, because one of the concentrates
is quite acidic and the other is basic, connecting the wrong
concentrates to the machine could result in dialysate that could harm
the patient.
Even though a single concentrate is used to prepare acetate dialysate,
conductivity and pH should be checked, because certain mix-ups
involving acid concentrate and other chemicals can result in an
acceptable conductivity and very low pH.
Additional Guidance:
Each machine must be tested for pH using a hand held meter or other
appropriate testing device (i.e., adequately-sensitive testing strips)
before every dialysis treatment and whenever a different composition
of acid concentrate is used. If the dialysis machine manufacturer
requires testing of conductivity, this must also be tested using an
independent testing device prior to each treatment and before using a
Final Version 1.1 Page 102 of 299

TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
different composition of acid concentrate during the same treatment.
The facility must have set limits for the allowable variability of the
hand held values from the machine readings. As new technology
evolves, the manufacturer’s guidance related to this requirement
should be followed.
No tag
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
Additional Guidance:
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
This is an informational tag. Expected monitoring is listed under each
6 Monitoring
water system and dialysate component; there may be some variation
6.1 General
from this Table based on specific equipment in use.
Quality control and quality assurance procedures should
be established to ensure ongoing conformance to policies
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
and procedures regarding dialysate quality. This clause
6 Monitoring
defines some of the monitoring activities to be conducted
6.1 General
at the dialysis facility as part of the quality assurance
process. The test methods described in [AAMI] 6.2 do Table 4—Monitoring guidelines for water purification equipment and
not represent the only acceptable methods available, but distribution systems and dialysate
are intended to provide examples of acceptable methods.
The frequency of monitoring is generally recommended NOTE—Refer to footnote for an explanation of the use of Xs in the
by the equipment manufacturer. Table 4 can be used as a Specification column.
guideline for setting up a quality assurance monitoring
Item to
What to
Special
Normal interval Specification
monitor
monitor
interval
program in the absence of a manufacturer’s
Sediment
Pressure drop
Pressure drop
NA Daily
recommendations or to supplement those
Filter
across the filter
less than XXXX
recommendations.
Sediment
filter Backwash cycle
Daily-beginning of Backwash clock
NA
backwashin timer setting
the day set to XX:XX
g cycle
Cartridge
Pressure drop
Pressure drop
NA Daily
filter
across the filter
less than XXXX
Hardness as
calcium
carbonate less
Water Product water Daily-end of the
than 1 grain/gal,
NA
softener softness day
unless otherwise
specified by the
manufacturer of
the reverse
Final Version 1.1 Page 103 of 299
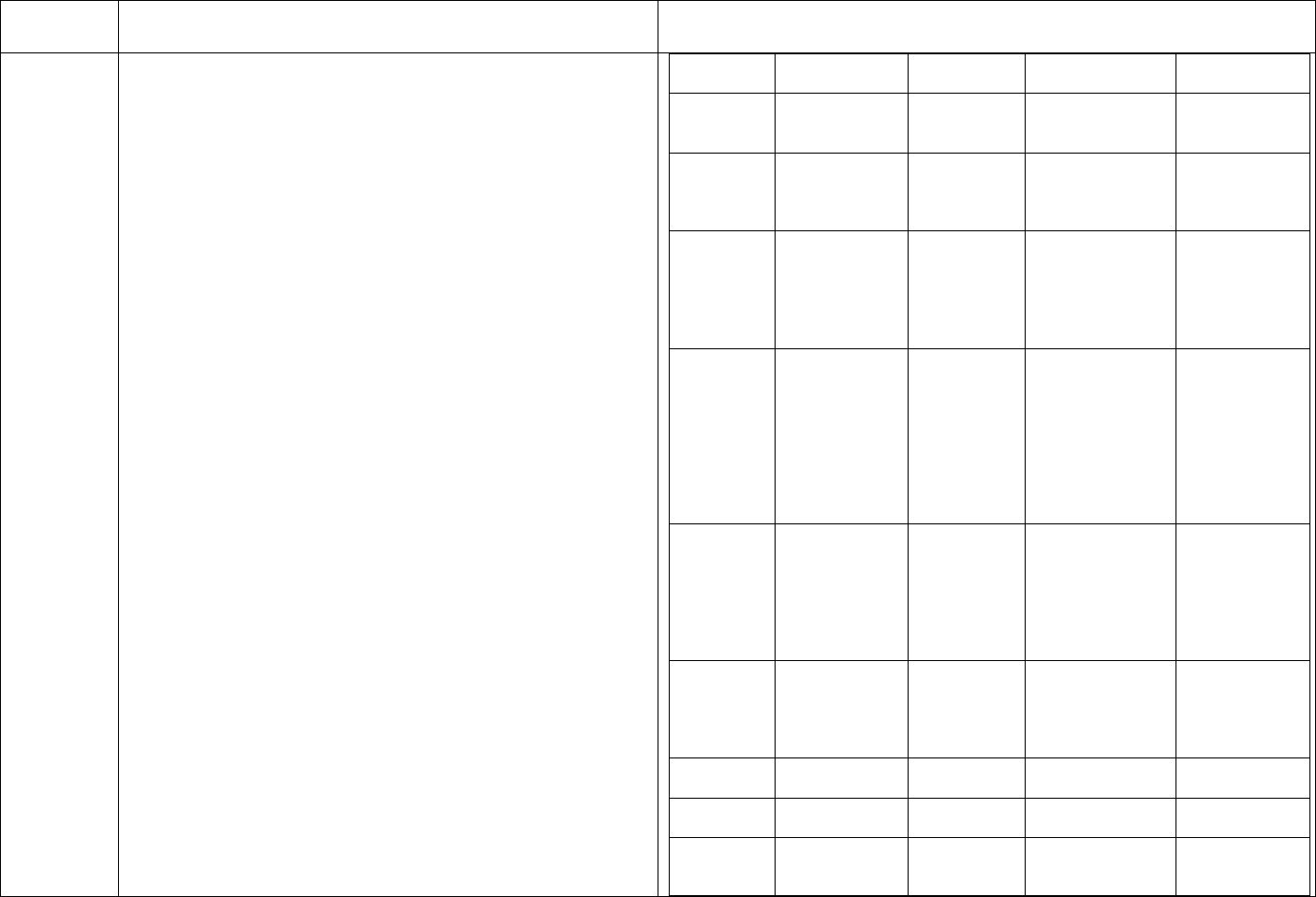
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
osmosis
equipment
Water
softener
brine tank
Level of
undissolved salt
in tank
NA
Daily-end of the
day
Salt level at
XXX
Water
softener
regeneration
cycle
Regeneration
cycle timer
setting
NA
Daily-beginning of
the day
Softener timer
set to XX:XX
Carbon
adsorption
beds
Product water
free chlorine
and/or total
chlorine
between the
beds
NA
Prior
each
to beginning
patient shift
<0.1 mg/L of
total chlorine
Chemical
injection
system
Level of
chemical in the
reservoir,
injector
function, value
of the
controlling
parameter (e.g.,
pH)
NA Daily
Chemical level
in reservoir
≥XXX;
controlling
parameter in
range XX–XX
Reverse
Osmosis
Product water
conductivity,
total dissolved
solids (TDS), or
resistivity and
calculated
rejection
NA
According to the
manufacturer’s
recommendations
(continuous
monitors)
Rejection
≥XX%
Reverse
Osmosis
Product and
reject flow rates,
and calculated
recovery
NA
Daily (continuous
monitors)
Product water
flow rate >X.X
gpm; recovery
in the range
XX–XX %
Deionizers
Product water
resistivity
NA Continuous
Resistivity >1
megohm-cm
Ultrafilters
Pressure drops
across the filter
NA Daily
Pressure drop
less than XXXX
Water
storage
tanks
Bacterial growth
and pyrogens
Weekly, until
pattern of
consistent
NA
Bacterial growth
≤50 CFU/mL;
endotoxin ≤1
Final Version 1.1 Page 104 of 299
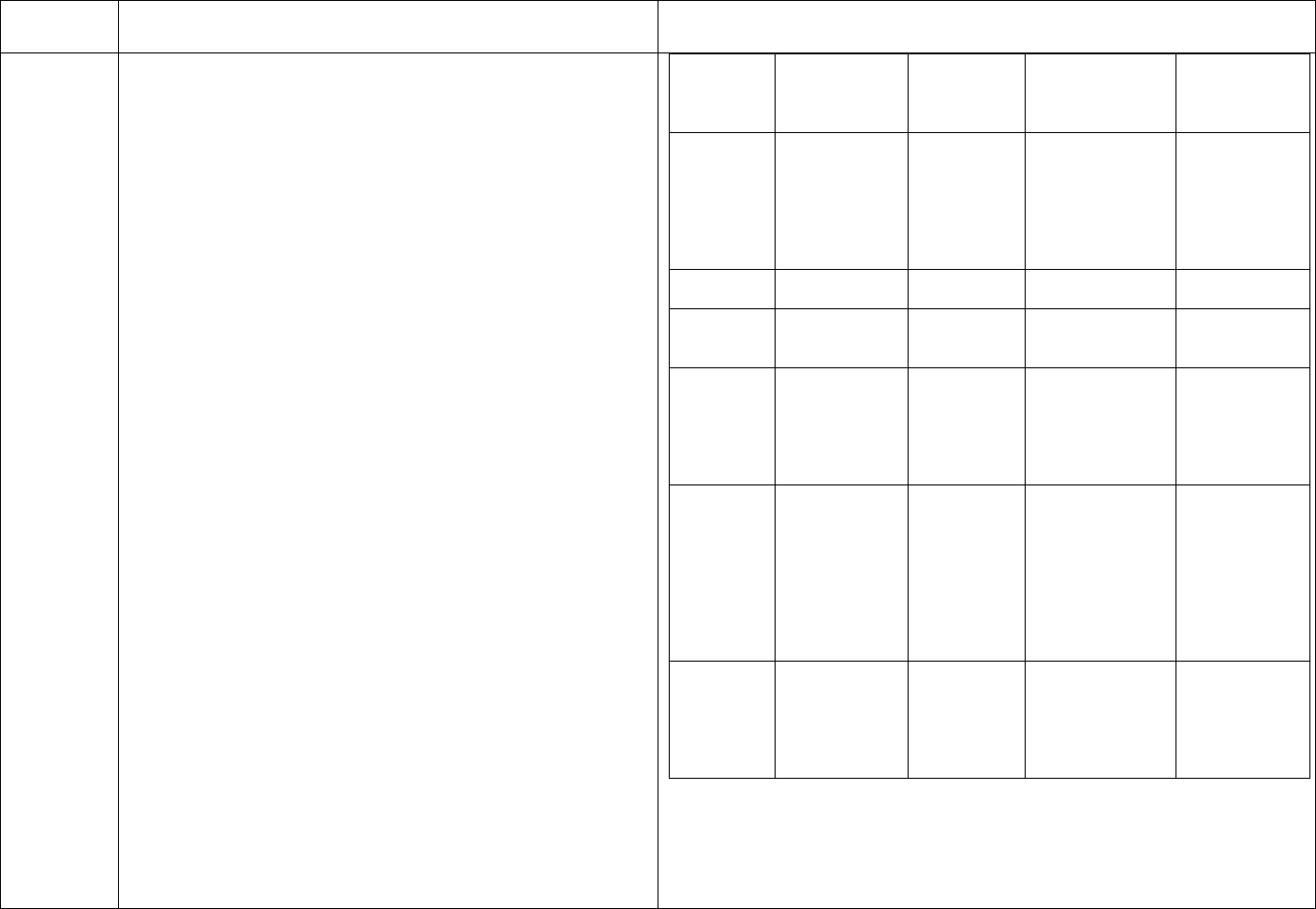
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
compliance
EU/mL
with limits
can be
demonstrated
Weekly, until
pattern of
Water Bacterial growth
consistent
distribution Bacterial growth ≤50 CFU/mL;
compliance
Monthly
piping and pyrogens endotoxin ≤1
with limits
system EU/mL
can be
demonstrated
UV Light
Light output
Energy output NA Monthly
source
>XXX
Ozone
Ozone Concentration in
During each
NA
concentration
generators the water
disinfection
>XXX
Temperature not
Temperature
less than XX C;
Hot water
and time of
During each
minimum
disinfection
exposure of the
NA
disinfection
exposure time at
systems
system to hot
temperature
water
≥XX minutes
Monthly rotated
among machines
so that at least two
Bacterial growth
Bacterial growth
machines are
≤50 CFU/mL;
Dialysate and endotoxin in NA
tested each month
endotoxin ≤1
the dialysate
and so that each
EU/mL
machine is tested
at least once per
year
Conductivity
within ± 5% of
Conductivity
the nominal
Dialysate NA Each treatment
and pH
machine value;
pH in the range
6.9–7.6
NOTE—It is not possible to specify universally acceptable operating
ranges for each device listed in the table, since some of these values
will be system-specific. In those cases (denoted by Xs in the
Specification column of the table), the facility should define an
acceptable operating range based on manufacturer’s instructions or
Final Version 1.1 Page 105 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
measurements of system performance.
V252
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7.2 Microbial monitoring methods: monthly water
samples/method
7.2.1 General
Culture water …weekly for new systems until a pattern
has been established. For established systems, culture
monthly unless a greater frequency is dictated by
historical data at a given institution.
Monitoring can be accomplished by direct plate counts,
in conjunction with the measurement of bacterial
endotoxin.
7.2.2 Sample collection
Water samples should be collected directly from outlet
taps situated in different parts of the water distribution
system. In general, the sample taps should be opened and
the water should be allowed to run for at least 60 seconds
before a sample is collected in a sterile, endotoxin-free
container. A minimum of 50 mL of water, or the volume
specified by the laboratory performing the test, should be
collected. Sample taps should not be disinfected.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7.2.2 Sample collection
All new sterile plastic ware is endotoxin-free because of the high
temperatures involved in the manufacturing process.
Additional Guidance:
Bacterial colony counts may be done by an outside lab (thus the
reference to direct plate counts) or by the use of dip samplers, as
described at V256. If a pattern of results greater than the accepted
limits is identified, the frequency of cultures (and subsequent
disinfection) should be increased to reach a frequency that ensures the
system is being maintained below the allowed contamination level
between scheduled sampling. Refer to V255.
V253
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7.2 Microbial monitoring methods:
7.2.1 General: Dialysate: monthly dialysate
sample/collection/freq
Culture …dialysate fluid weekly for new systems until a
pattern has been established. For established systems,
culture monthly unless a greater frequency is dictated by
historical data at a given institution.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7.2.2 Sample collection
In some newer dialysis machines, dialysate flow stops when the
effluent line is disconnected from the port. In these instances, the
machines are equipped with dialysate sampling ports that can be
accessed using a syringe. These sample ports may be disinfected with
alcohol and allowed to air dry. A 30 mL sterile syringe should then be
used to aspirate dialysate out of and into the port before filling the
syringe. The filled syringe should be discarded, and a fresh sample of
Final Version 1.1 Page 106 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Dialysate samples should be collected from at least two
machines monthly and from enough machines so that
each machine is tested at least once per year. If testing of
any dialysis machine reveals a level of contamination
above the action level, an investigation should be
conducted that includes retesting the offending machine,
reviewing compliance with disinfection and sampling
procedures, and evaluating microbiological data for the
previous 3 months to look for trends. The medical
director also should be notified. An example of a
decision tree for this process is given in Figure 1.
7.2.2 Sample collection
Dialysate samples should be collected from a dialysate
port of the dialyzer… [or] dialysate sampling ports that
can be accessed using a syringe. At least 25 mL of fluid,
or the volume specified by the laboratory performing the
test, should be collected in sterile endotoxin-free
specimen containers.
dialysate collected using a new sterile syringe.
Additional Guidance:
Facilities may take samples of dialysate using a “clean catch”
technique of the effluent from the Hansen connectors into sterile
endotoxin-free collection containers, use a needleless system to access
the port on the dialysate line, or use a syringe and needle to aspirate a
sample from the port on the dialysate line.
A flow chart which gives suggestions for actions can be found in the
original AAMI RD52:2004 document.
V254
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7.2 Microbial monitoring methods
7.2.1 General: samples before disinfect
Samples should always be collected before
sanitization/disinfection of the water treatment system
and dialysis machines.
Additional Guidance:
Samples must be collected in the “worst case” scenario: before
sanitation and disinfection, with consideration of logistics: i.e.,
samples sent to labs must arrive during the lab’s hours of operation. If
disinfection is scheduled for Sunday, for example, samples may need
to be collected on Wednesday or Thursday to allow transit time and
arrival before the lab closes on Friday.
V255
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7.2 Microbial monitoring methods
7.2.1 General: repeat cultures
Cultures should be repeated when bacterial counts
exceed the allowable levels. If culture growth exceeds
Additional Guidance:
Responsible staff members must be able to describe what is done
when counts exceed action levels.
Final Version 1.1 Page 107 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
permissible standards, the water system and dialysis
machines should be cultured weekly until acceptable
results are obtained. Additional samples should be
collected when there is a clinical indication of a
pyrogenic reaction or septicemia, and following a
specific request by the clinician or the infection control
practitioner.
If repeat cultures are performed after the system has been
disinfected (e.g., with formaldehyde, hydrogen peroxide,
chlorine, or peracetic acid), the system should be flushed
completely before collecting samples. Drain and flush
storage tanks and the distribution system until residual
disinfectant is no longer detected before collecting
samples.
V256
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7.2.3 Heterotrophic plate count: dip samplers require
QC
Dip samplers may be used for bacterial surveillance… in
conjunction with a quality assurance program designed
to ensure their appropriate use. Elements of the quality
assurance program should include staff training in areas
such as the correct methods of inoculation, incubation,
and interpretation, and verification involving duplicate
samples sent to a certified laboratory on at least an
annual basis. Plates shall be incubated at 35 °C for 48
hours.
Colonies should be counted using a magnifying device.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7.2.3 Heterotrophic plate count
This method is an indicator of water quality only and is not to be
confused with total heterotrophic plate counts, which require much
longer incubation times at 28° C.
If a more accurate count from plates containing fewer than 30 or more
than 300 colonies is desired, larger or smaller volumes may be
cultured. Smaller volumes can be obtained by making 1:10 serial
dilutions in sterile phosphate buffer. If larger volumes are required,
the membrane filtration method should generally be used.
Erratic colony counts may indicate the presence of biofilm since
sloughing of biofilm may occur with release of bacteria into the water.
When contamination persists in spite of frequent and aggressive
disinfection, if may be necessary to determine if biofilm is present in
the system.
Final Version 1.1 Page 108 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Additional Guidance:
Facilities that use dip samplers must send duplicate samples to a
laboratory at least annually to evaluate the accuracy of the testing
done with the dip samplers.
V257
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7.2.3 Heterotrophic plate count: refrig if delay >2
hours/no calib loop
Samples that cannot be cultured within 1 to 2 hours can
be refrigerated for up to 24 hours.
Use of a calibrated loop to apply the sample to the agar
plate is not permitted.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7.2.3 Heterotrophic plate count
The reference method for culturing is the membrane filtration
technique. With this method, a known volume of sample or diluted
sample is filtered through a 0.45 µm membrane filter and the
membrane filter is aseptically transferred to the surface of an agar
plate. Trypticase soy agar (TSA, a soybean casein digest agar) is the
medium of choice for culturing water and dialysate; other acceptable
media include standard methods agar and plate count agar (also
known as TGYE). Blood and chocolate agars are not appropriate for
this test. The spread plate technique may also be used. With this
method, an inoculum of at least 0.5 mL of sample is spread equally
over the surface of the agar plate.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provision of This
Recommended Practice
A.7 Strategies for bacterial control
A.7.2.3 Heterotrophic plate count
Sensitive culturing methods must be used to measure the low total
viable microbial counts permitted for water used for hemodialysis
applications under the provisions of ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001 and
recommended for dialysate in this recommended practice. The
membrane filter technique is particularly suited for this application
because it permits large volumes of water to be assayed. Because the
membrane filter technique may not be readily available in clinical
laboratories, the spread plate assay can be used as an alternative.
However, if the spread plate assay is used, a calibrated loop shall not
be used to apply sample to the plate. The sensitivity of an assay
performed with a calibrated loop is low. A standard calibrated loop
Final Version 1.1 Page 109 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
transfers 0.001 mL of sample to the culture medium, so that the
minimum sensitivity of the assay is 1,000 CFU/mL. This sensitivity is
unacceptable when the maximum allowable limit for microorganisms
is 200 CFU/mL. Therefore, when the spread plate method is used, a
pipette should be used to place 0.1 mL to 0.5 mL of water on the
culture medium.
Additional Guidance:
Responsible staff must be knowledgeable of the culture methods in
use and must inform any outside labs that the samples are water and
dialysate and that use of a calibrated loop to inoculate the culture plate
is not acceptable.
V258
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
7.2.4 Bacterial endotoxin test: LAL testing in house:
how to
At a minimum, two tubes should be run each time the
assay is performed. The first tube contains LAL reagent
and the sample to be tested. The second tube contains
LAL reagent, a known amount of endotoxin, and the
sample to be tested. The second tube acts as a positive
control to confirm the absence of any interference that
might lead to a false negative result.
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004
7.2.4 Bacterial endotoxin test
Bacterial endotoxin testing is done using the Limulus amoebocyte
lysate (LAL) assay. Two basic types of assay can be performed. The
first is a kinetic assay, which is available in a colorimetric or
turbidimetric format, and the second is a gel-clot assay.
The kinetic LAL assay uses control standard endotoxin to generate a
standard curve to which unknowns are compared and concentrations
are determined using linear regression. The kinetic assays employed
in laboratories generally use a computer-driven spectrophotometer
that automatically calculates the amount of endotoxin on the basis of
color development or onset times for gel formation.
The gel-clot LAL assay is not as sensitive as the kinetic assay and
provides only a positive or negative result; that is, it shows if
endotoxin is present—or not—at a particular concentration. Single
tube gel-clot tubes are available from several commercial sources, and
kits with the following sensitivities are available: 0.015 EU, 0.03 EU,
0.06 EU, 0.125 EU, 0.25 EU, and 0.5 EU.
Final Version 1.1 Page 110 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Positive control tubes are available from the suppliers of commercial
LAL assays. More sophisticated testing protocols involving reagent
controls may also be used (see 2.7), but their use is optional in this
application.
Additional Guidance:
Technology for endotoxin testing is evolving and these regulations are
not meant to prevent the use of a newer testing methodology, once
such methodology is approved by FDA.
V259
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
9 Personnel: P & P
Policies and procedures that are understandable and
accessible are mandatory.
V260
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.40 (a)
9 Personnel: training program/periodic audits
A training program that includes quality testing, the risks
and hazards of improperly prepared concentrate, and
bacterial issues is mandatory.
Operators should be trained in the use of the equipment
by the manufacturer or should be trained using materials
provided by the manufacturer.
The training should be specific to the functions
performed (i.e., mixing, disinfection, maintenance, and
repairs).
Periodic audits of the operators’ compliance with
procedures should be performed.
The user should establish an ongoing training program
The operators of the water/dialysate system equipment must be
trained by the manufacturer of the equipment, or the training must be
done from materials provided by the manufacturer. Water treatment
service vendors may do the training using materials from the
manufacturer.
The facility must define the frequency of audits to evaluate the
operators’ compliance: these should include actual observation of the
work: e.g., collecting samples, performing water testing. Audits
should be done at least annually and more frequently if problems are
identified.
This tag addresses the content of the training for personnel responsible
for the water and dialysate systems, and audits for compliance with
procedures. Whether the personnel responsible for the water treatment
system have been trained is addressed in the Condition for Personnel
qualifications, at V696.
Final Version 1.1 Page 111 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
designed to maintain the operator’s knowledge and
skills.
End of ANSI/AAMI RD52 requirements
No Tag
(b) Standard: chlorine/chloramines.
(1) The water treatment system must include a
component or carbon tank which removes
chlorine/chloramine along with a backup component or
second carbon tank in series for chlorine/chloramine
removal.
(2)(i) If the test results from the port of the initial
component or carbon tank referred to in section 6.2.5 of
AAMI RD52:2004 are greater than 0.5 mg/L for free
chlorine or 0.1 mg/L for chloramines, or equal to or
greater than 0.1 mg/L of total chlorine, then the second
component or carbon tank which removes
chlorine/chloramine must be tested;
These requirements are duplicative of requirements in AAMI
RD52:2004, adopted by reference.
For (b)(1): Refer to V192 for the failure to have primary and
secondary carbon tanks for removing chlorine/chloramines.
For (b)(2)(i): Refer to V197 for the failure to test after the secondary
method of removing chlorine/chloramines when the test results after
the primary method indicate breakthrough.
V270
Ch/chl breakthrough: corrective action
(ii) If the test results from the last component or carbon
tank are greater than the parameters for chlorine or
chloramine specified in paragraph (b)(2)(i) of this section
the facility must—
(A) Immediately take corrective action to bring chlorine
or chloramine levels into compliance with paragraph
(b)(2)(i) of this section and confirm through testing that
the corrective action has been effective, or terminate
dialysis treatment to protect patients from exposure to
chlorine/chloramine;
“Corrective action” here could include backwashing carbon tanks,
rebedding or replacement of the tanks or addition of an adjunct system
such as chemical injection to address an extremely high chlorine or
chloramine load from the municipal supplier. In any case, testing must
confirm acceptable levels of chlorine/chloramine before dialysis
treatments can resume. It could be necessary for the patient treatments
to be rescheduled, or patients to be transferred to another facility for
one or more treatments.
V271
Ch/chl breakthrough: holding tank use
(B) Only allow use of purified water in a holding tank, if
appropriate, and if testing shows water chlorine or
chloramine levels that are in compliance with paragraph
If the system includes a holding tank and the water in that tank tests
safe for chlorine and chloramine, that water may be used for patient
treatment. Responsible staff must know how to prevent the water
treatment system from continuing to make product water, thus adding
Final Version 1.1 Page 112 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(b)(2)(i) of this section; and
water containing unsafe levels of chlorine to the storage or holding
tank. Water produced by exhausted carbon tanks must not be used for
treatment.
V272
Ch/chl breakthrough: notify medical director
(C) Immediately notify the medical director; and
Policy and practice must demonstrate this requirement is met.
Responsible staff should list notifying the medical director as an
action they would take immediately in the event of a chlorine or
chloramine breakthrough.
V273
Ch/chl breakthrough: action = correction
(D) Take corrective action to ensure ongoing compliance
with acceptable chlorine and chloramine levels as
described in paragraph (b)(2)(i) of this section.
“Corrective action” in this context would include a root cause analysis
to determine the cause of the chlorine and chloramine breakthrough,
and development and implementation of a corrective action plan to
address the identified cause.
V274
Water test results: deviations require corrective action
plan
(c) Standard: Corrective action plan. Water testing
results including, but not limited to, chemical, microbial,
and endotoxin levels which meet AAMI action levels or
deviate from the AAMI standards must be addressed
with a corrective action plan that ensures patient safety.
Facility policy must include requirements to develop and implement a
corrective action plan that ensures patient safety if water testing
results are outside accepted limits or action levels.
A corrective action plan to ensure patient safety must be developed
and implemented if any of the results of water chemical analysis or
microbial and endotoxin testing for water and dialysate meet the
AAMI action levels or are outside the AAMI standards. Water and
dialysate monitoring must be reported in the QAPI materials and the
medical director must to be involved in analyzing and addressing test
results outside of expected parameters.
V275
(d) Standard: Adverse events. actions expected
A dialysis facility must maintain active surveillance of
patient reactions during and following dialysis. When
clinically indicated (for example, after adverse patient
reactions) the facility must—
(1) Obtain blood and dialysate cultures and endotoxin
levels;
(2) Evaluate the water purification system; and
(3) Take corrective action.
Responsible staff (nurses and patient care technicians) must be
familiar with symptoms which might indicate a patient could be
having a reaction related to water or dialysate and must be able to
describe appropriate actions to take in the event a patient or group of
patients experienced such symptoms.
Facility or patient medical records (as appropriate) must demonstrate
that any adverse incidents (fever, chills, or an infection) were
identified by staff and these required actions were taken.
The medical director must develop standard protocols which require
Final Version 1.1 Page 113 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
blood and dialysate cultures and endotoxin levels be collected in the
event of patient adverse reaction(s) during or following dialysis
treatment.
Responsible staff (i.e., the nurse manager, charge nurses, water
treatment technicians, chief technician and medical director) must
demonstrate recognition of the need to evaluate the water system in
the event of patient adverse reaction(s) during or following dialysis
treatment and to take indicated corrective action.
V276
(e) Standard: In-center use of preconfigured
hemodialysis system. follow FDA labeling
When using a preconfigured, FDA-approved
hemodialysis system designed, tested and validated to
yield AAMI quality (which includes standards for
chemical and chlorine/chloramine testing) water and
dialysate, the system’s FDA-approved labeling must be
adhered to for machine use and monitoring of the water
and dialysate quality.
At the time of publishing these regulations, several different
preconfigured hemodialysis systems were available. These included
conventional water treatment components and single-pass
(conventional) dialysis machines; integrated systems which
incorporated water treatment and dialysate preparation and delivery
into one system; and sorbent-based systems which utilized columns
(cartridges) of chemicals to regenerate the used dialysate for
recirculation through the dialyzer. Although primarily used for home
therapies, a preconfigured hemodialysis system may be used in-center.
Such use might be for training a home patient, for back-up treatment
of home patients, or for routine in-center treatment. In all cases, the
system’s FDA-approved labeling must be followed for machine use
and monitoring of the water and dialysate quality.
If the preconfigured hemodialysis system incorporates a water
treatment system, a chemical analysis of the product water must be
done at least annually near the end of the usability of any disposable
component, or when any modifications are made to the treatment
components (other than the replacement of disposable components).
When any repairs are made to water treatment equipment, the impact
on water quality should be evaluated and a chemical analysis
performed if indicated.
Chlorine/chloramine levels must be tested prior to the start of each
Final Version 1.1 Page 114 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
treatment (or before use of each new batch of dialysate) in accordance
with AAMI guidance and manufacturer’s
recommendations/instructions for that test method. An appropriate
volume of water for the testing method in use should be tested for the
presence of chlorine/chloramine. For batch systems (integrated
systems which prepare enough dialysate for multiple treatments), the
chlorine/chloramine testing must be performed at the worst case
scenario, i.e., after the preparation of each batch of dialysate, but
before use of that batch. If the test shows results above AAMI’s
maximum allowable level, then the user must discard that batch,
change any applicable components, prepare another batch of dialysate,
and test again.
Systems that use sorbent technology do not produce water; the
product of the sorbent cartridge is dialysate, thus the requirements for
the chemical, bacteriological and endotoxin testing of water do not
apply. With sorbent technology, due to the low volume of exposure of
patients to water (i.e., 6 liters per treatment) and the capacity of the
single use sorbent cartridge to remove chlorine and chloramine,
testing for chlorines and chloramine is not required. Sorbent system
users are expected to perform bacteriological and endotoxin testing on
dialysate.
Monitoring of the system must be in accordance with the FDA-
approved labeling, which includes the manufacturers' directions for
use (DFU). The facility should have the manufacturers' DFUs on file,
and facility procedures should reflect those.
V277
In-center preconfigured HD: meets AAMI RD52
The facility must meet all AAMI RD52:2004
requirements for water and dialysate.
If the facility is using a preconfigured FDA-approved hemodialysis
system for in-center treatments, the facility must meet the
requirements of ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 in the use of that system.
V278
In-center preconfigured HD: quarterly cultures/LALs
Moreover, the facility must perform bacteriological and
endotoxin testing on a quarterly, or more frequent basis,
Preconfigured systems used for in-center treatments must be tested at
least quarterly for bacteria and endotoxins.
Final Version 1.1 Page 115 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
as needed, to ensure that the water and dialysate are
within AAMI limits.
V300
§ 494.50 Condition: Reuse of hemodialyzers and
bloodlines.
This Condition applies only if the facility reuses hemodialyzers or
bloodlines. The AAMI “Reuse of Hemodialyzers,” third edition,
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 is incorporated by reference as
regulation as part of this Condition (V304-V368).
The observation of actual practice of reprocessing and reuse is critical
to the survey of this Condition, as are interviews with the staff
responsible for reprocessing and reuse. Additionally, records of the
reprocessing process and medical records of patients included in the
reuse program must be reviewed. Surveys of facilities that participate
in centralized reprocessing programs require onsite visits at the
reprocessing site, on a rotating basis, as part of the survey process.
Deficiencies identified at the centralized reprocessing site apply to all
user facilities.
Condition-level citation should be considered if there are major
deficient practices that have affected, or could potentially affect
patient health and safety. Examples would include, but are not limited
to:
• Staff members assigned responsibility do not demonstrate
competency;
• Less than sufficient concentration of germicide is in use;
• Direct care staff do not test for residual levels of germicide prior
to reusing a dialyzer or the testing methods in use are not
sufficiently sensitive;
• Reprocessing a dialyzer of a HBV+ patient.
V301
(a) Standard: General requirements for the reuse of
hemodialyzers and bloodlines: no reuse for HBV+ pts.
Certain hemodialyzers and bloodlines–
(1) May be reused for certain patients with the exception
of Hepatitis B positive patients;
Note that, in the Interpretive Guidance, the term “reprocessing” refers
to the processes of cleaning and the installation of germicide into a
dialyzer, and the term “reuse” refers to the clinical use of a
reprocessed dialyzer for hemodialysis.
Final Version 1.1 Page 116 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Hepatitis B positive (HBV+) patients must be excluded from any
reprocessing/reuse program. Facilities must provide single-use
dialyzers and bloodlines for patients who are HBV+.
If the facility reuses dialyzers and/or bloodlines for Hepatitis B
positive patients, this requirement is not met. This practice may
impact the health and safety of the other patients whose dialyzers are
reprocessed and should be considered as Condition level non-
compliance.
No tag
(2) Must be reused only for the same patient; and
This tag is informational. This requirement is addressed in the
ANSI/AAMI RD:47 guideline 10 at V327 and should be cited there.
V303
Dialyzer must be labeled for multiple use per FDA
(3) Must be labeled for multiple reuse in accordance with
the premarket notification provisions of section 510(k) of
the Food, Drug, and Cosmetics Act and 21 CFR
876.5860.
Any dialyzer included in the reprocessing/reuse program must be
labeled by the manufacturer for multiple use and must have a
manufacturer’s label indicating the dialyzer may be used multiple
times.
V304
(b) Standard: Reprocessing requirements for the reuse of
hemodialyzers and bloodlines: reprocessing
requirements: meets AAMI RD47 2002:A1:2003
A dialysis facility that reuses hemodialyzers and
bloodlines must adhere to the following reprocessing
guidelines:
(1) Meet the requirements of AAMI published in “Reuse
of Hemodialyzers,” third edition, ANSI/AAMI
RD47:2002 and RD47:2002/A1:2003. The Director of
the Federal Register approves this incorporation by
reference in accordance with 5 U.S.C. 552(a) and 1 CFR
Part 51. This publication is available for inspection at the
CMS Information Resource Center, 7500 Security
Boulevard, Central Building, Baltimore, MD or at the
National Archives and Records Administration (NARA).
For information on the availability of this material at
NARA, call 202-741-6030, or go to:
The AAMI “Reuse of Hemodialyzers,” third edition, ANSI/AAMI
RD47:2002/A1:2003 is incorporated by reference. The
recommendations are provided in the “Regulation” column and carry
the full weight of regulation. Language from the AAMI
recommendations that is explanatory and portions of the AAMI
rationale for the development and provisions of the recommended
practice are provided in the “Interpretive Guidance" column as an aid
to understanding the regulation. In some cases, the AAMI
identification numbers may appear out of order, as they have been
rearranged for better flow with the survey process. While exact
language from the AAMI document has been incorporated as
regulation, the language in the “Interpretive Guidance” column has
been edited for clarity, brevity and to minimize redundancy.
When “should” or “recommend” are included in the AAMI language
adopted as regulation (i.e., the language in the “Regulation” area), the
referenced item or practice must be in use or in place.
Final Version 1.1 Page 117 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
http://code_of_regulations/ibr_locations.html.Copies
may be purchased from the Association for the
Advancement of Medical Instrumentation, 3300
Washington Boulevard, Suite 400, Arlington, VA 22201-
4598.
AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
11 Reprocessing
The multiple use of a dialyzer begins with the labeling of the new
dialyzer (see AAMI section 10) and then continues with the
reprocessing procedures described in this section. Preparation of the
reprocessed dialyzer for the next dialysis is described in AAMI
section 12. The cycle is repeated after the next use of the dialyzer until
the dialyzer does not meet the criteria for continued use. The results of
the tests and the signature or other unique means of identifying the
person performing each step should be maintained in a permanent
record (see AAMI 4.2). Completion of all reprocessing steps, tests,
and inspections should be documented in the reprocessing record,
accompanied by the signature or other unique means of identification
of the person completing them. When appropriate for the reprocessing
procedure in use, all dialyzer manufacturer’s instructions regarding
reuse should be carefully followed.
V305
AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as Adopted
by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
4 Records: meet req for medical records
All records described in this recommended practice shall
meet the requirements for medical records, including
completeness, legibility, and security. A place should be
provided for the signature or other unique mark of
identification of the person completing each step of the
reprocessing procedure (i.e., the person performing
preventive maintenance procedures, the person[s]
investigating complaints, and the person[s] conducting
quality assurance [QA] and quality control [QC]
activities). Maintaining these records is the responsibility
of the medical director.
Additional Guidance:
Reprocessing records must be complete, legible and protected from
unauthorized access. The record of use of a dialyzer may be included
in the patient record, in computer listings, and in separate records of
reprocessing. The history of each dialyzer from first use to discard
must be able to be followed. Staff may use computer entries to “sign”
as completing various steps of the process.
V306
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
Final Version 1.1 Page 118 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
4.1 Dialyzer reprocessing manual: dialyzer
reprocessing manual
The dialyzer reprocessing manual should be a
compilation of all specifications, policies, training
materials, manuals, methodologies, and procedures that
may be integrated into the dialysis facility’s policy and
procedures manual. The dialyzer reprocessing manual
should also contain samples of forms and labels, if
appropriate. The operational logs, manuals, and files may
be kept separate from the dialyzer reprocessing manual.
The dialyzer manufacturer’s labeling should be consulted
to determine if a specific dialyzer requires special
considerations.
A.4 Records
Documentation is essential to a safe, effective hemodialyzer
reprocessing program. The overall dialyzer reuse procedure
documentation includes reference materials, procedures, and policies,
some of which may be distributed in the facility for operating
purposes. The other records serve to document aspects of the reuse
procedure for each dialyzer, along with QC and QA measures, so that
a complete history of the reprocessing of each dialyzer and QC/QA
procedures exists.
Allowance is made for keeping the reprocessing record data in the
reprocessing log, the patient’s chart, or a combination of the two,
because both of them are traceable, permanent records, and it may be
inconvenient to record all of the information in one location.
Additional Guidance:
The reprocessing manual must be complete for the reprocessing
method, germicide, and system in use. The manual must address test
procedures, maintenance and calibration of the reprocessing
equipment and training and competency testing of personnel. The
manual may be separate or combined with the general policy and
procedure manual. The manufacturer’s “labeling” of a dialyzer
includes the package insert, usually found in the shipping container
for multiple dialyzers of the same type, and contains the dialyzer
manufacturer’s directions for use. If a specific dialyzer in use requires
special consideration, the reprocessing manual should reflect the
manufacturer’s guidance.
V307
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
5 Personnel qualifications and training
5.1 Qualifications
Personnel shall possess adequate education, training, or
experience to understand and perform procedures
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
5 Personnel qualifications and training
New personnel range in knowledge from those with no medical
background who are fully trained by the facility, to licensed
practitioners with extensive medical background.
Final Version 1.1 Page 119 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
outlined by the individual dialysis facility relevant to the
facility’s multiple-use program. Education shall be
geared to meet the needs of this wide range of personnel.
Additional Guidance:
The reuse education provided must be sufficient to ensure patient
safety and an effective and safe reprocessing/reuse program.
V308
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
5.2 Training
5.2.1 Curriculum
The dialysis facility’s physician or director shall
establish a training course for the persons performing
hemodialyzer reprocessing. A written document should
give details about the curriculum and, in particular,
address the potential risks to patients and staff members
of not following correct procedures. The curriculum
should include at least the following information:
a) the facility’s specific reprocessing procedure,
including a rationale for each step;
b) basic documentation requirements of the program;
c) the operation and maintenance of the facility’s specific
equipment for reprocessing hemodialyzers and, if
appropriate, the dialysis systems and components;
d) microbiology with respect to aseptic technique, the
collection and handling of samples, and personnel safety
precautions for infectious hazards;
e) the risks and hazards of multiple use of
hemodialyzers;
f) the consequences of not performing tasks properly;
g) the risks and hazards associated with toxic substances
used in reprocessing hemodialyzers, proper handling of
these substances, and procedures for handling spills and
proper disposal of toxic substances;
h) the use and location of protective eyewear, respirators,
masks, and special clothing;
i) emergency procedures as required by the facility; and
Additional Guidance:
Available training materials must include all required topics and be
congruent with the processes observed.
Final Version 1.1 Page 120 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
j) the principles of dialysis, emphasizing the
characteristics of the hemodialyzer and the effect of
reuse on these characteristics.
V309
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
5.2.2 Documentation: includes med dir certification
Each person performing procedures for the multiple use
of dialyzers shall have successfully completed the
dialysis facility’s training course relevant to that person’s
task and demonstrated competence in the area covered
by his or her training. Successful completion of training
shall be certified by the medical director or his or her
designated representative and recorded in the trainee’s
personnel file along with verification of the trainee
having received the instruction. Retraining is necessary
when new procedures are undertaken. Annual review of
competence is required with appropriate retraining if
deficiencies are found.
Additional Guidance:
Facilities may cross-train staff from other positions, such as
hemodialysis technicians or clerical staff, to perform reprocessing.
Each person who is assigned dialyzer reprocessing must complete all
the components of the training and demonstrate competency.
Personnel files should include:
• Evidence the medical director/designee has certified each of the
reprocessing personnel who have successfully completed the
required training;
• Annual competence review and applicable retraining;
• Retraining for any major change in the reuse program (e.g., a
change in equipment or germicide).
V310
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
4 Records
4.4 Personnel health monitoring records
A file must be kept of the results of medical
examinations of personnel that are required by OSHA or
other regulatory agencies.
Additional Guidance:
Health screening of personnel is dependent on the germicide in use.
Specific requirements may be found on the OSHA material safety data
sheets (MSDS) on file in each facility for applicable germicides.
Personnel files of reprocessing personnel should reflect any required
testing. Specific requirements for testing may be obtained from
www.osha.gov and www.cdc.gov/niosh/.
V311
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
6 Patient considerations
6.1 Medical issues
An order to reprocess hemodialyzers shall be made by a
physician knowledgeable about reprocessing and its
medical and economic implications. Because the current
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B, or
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
6 Patient considerations
6.1 Medical issues
Dialyzers should not be reprocessed from patients who have tested
positive with hepatitis B surface antigens.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
Final Version 1.1 Page 121 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
hepatitis C status of a patient cannot be known with
certainty, all staff potentially exposed to the patient’s
blood shall observe Standard Precautions. Precautions
for all infectious hazards should be emphasized and
included in the reprocessing procedures. Written
procedures should stipulate whether and how
reprocessing will be done for patients who have shown
sensitivity to materials used in the reprocessing of
hemodialyzers.
A.6 Patient considerations
A.6.1 Medical issues
The AAMI Renal Disease and Detoxification (RDD) Committee’s
primary objective was not to recommend medical indications for
reprocessing or evaluate the medical or economic implications of
reprocessing but to provide recommendations for safe reuse practice.
At the time of this writing, the Centers for Disease Control and
Prevention (CDC) does not object to reprocessing and reusing
dialyzers from patients with hepatitis C or patients with known HIV
infection because of the low viral burden and transmission
efficiencies. The AAMI RDD Committee recommends, however, that
standard precautions be used in the reprocessing of all dialyzers.
These precautions include the use of gowns, masks, and gloves. Each
facility should be aware of the hazards of infection and set policies
accordingly.
Additional Guidance:
Dialyzers of patients who are positive for Hepatitis B must not be
reprocessed. Refer to V301.
Facilities may also opt to exclude patients with other conditions from
their reuse program. Facility reuse policies must specify which
patients would be excluded.
There should be evidence in policy or in the minutes of the governing
body that the medical director has made the decision to reprocess
dialyzers. Orders for treatment (which may be provided by the
physician, advanced practice registered nurse or physician assistant)
must include whether or not the patient will participate in the reuse
program. If a patient has shown sensitivity to the materials used in
reprocessing, this problem must be addressed in the patient
assessment and plan of care.
Final Version 1.1 Page 122 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Standard precautions must be followed in all reprocessing/reuse
activities; PPE appropriate to the task must be worn; all blood spills
must be immediately cleaned. While it is not expected that
reprocessing staff would change gloves between handling separate
dialyzers during routine tasks, gloves that are visibly soiled with
blood, as would occur during header cleaning, must be changed
between dialyzers, as well as when reprocessing staff goes from
“dirty” tasks to a “clean” task, with appropriate hand hygiene
performed prior to donning fresh gloves.
V312
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
6.2 Informed consent: regarding dialyzer reuse process
All patients in a dialysis facility will be fully informed
regarding reuse of dialyzers. Printed material such as
brochures describing the facility’s services should
contain a statement about dialyzer reprocessing if reuse
is performed.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.6.2 Informed consent
Establishing QA practices such as those recommended here and
sharing information with patients, may aid in solutions to these
problems.
The National Kidney Foundation and the American Association of
Kidney Patients recommend that patient consent for dialyzer reuse be
obtained.
Additional Guidance:
CMS does not require specific written patient consent, but does
require that patients be informed that the facility does reprocess
dialyzers and about that process. Refer to V460 under the Condition
for Patients’ rights.
V313
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
7 Equipment: design/construction/function
Each piece of equipment used for reprocessing shall be
appropriately designed, constructed, and tested to
perform its intended task. Satisfactory operation of
manual and automated systems shall be ensured by
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.7 Equipment
Types of reprocessing systems vary from sophisticated
microprocessor-controlled systems to hand-operated valving systems.
It is particularly important that all water that comes into contact with
Final Version 1.1 Page 123 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
appropriate functional tests. Strict QC and QA shall be
maintained for any type of dialyzer reprocessing
equipment. Additionally, complete documentation of
system function, operating procedures, potential system
failures, and dialyzer-reuse criteria shall be included in
the dialyzer reprocessing manual, known to the operator,
and available for review.
the fluid pathways for blood or dialysate be of AAMI quality because
the blood side of the dialyzer might take up endotoxin that could be
released into the circulation system during the subsequent dialysis.
V314
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
7.1 Water systems: meet AAMI bacti/chem quality
monitoring
The system providing water for reprocessing shall meet
all of the requirements for pressure and flow rate for
operating the reprocessing equipment under minimal and
peak load conditions. Product water used for rinsing,
cleaning, filling, and diluting the germicide shall be
shown to comply with the chemical and microbiological
quality requirements [specified in these regulations].
Water bacteriology monitoring shall be carried out where
the dialyzer is connected to the reuse system or as close
as possible to that point.
11.4 Germicide
11.4.1.5 Water quality monitoring
The water used to rinse and clean dialyzers and dilute the
germicide should be tested for bacterial contamination
and pyrogens according to the requirements [of these
regulations] before a reprocessing program is
undertaken. Once dialysis with the reprocessed
hemodialyzers has begun, testing for bacterial
contamination should be frequent (e.g., weekly). Less
frequent testing, but not less than monthly, may be
appropriate if there is a documented history of at least 3
Additional Guidance:
The product water chemical and microbiological requirements
outlined in this section are the same as those in ANSI/AAMI
RD52:2004 incorporated by reference in these regulations under the
Condition for Water and dialysate quality.
Water samples for microbial and endotoxin testing must be routinely
taken each month from the water supplying each reprocessing system,
as close as possible to the point where the dialyzer would be
connected to the system. If more than one automated reprocessing
system is in use, the water supply to each system must be monitored
monthly.
New facilities or facilities which add dialyzer reprocessing must
validate the safety of the water supply to the reprocessing system by
testing for bacteria (microbial content) and pyrogens (endotoxins)
weekly for at least 3 months, and at least monthly thereafter. The sites
to be tested include the water supply to the sinks used for rinsing
dialyzers, to outlets used for mixing germicide, and to each
reprocessing system.
Final Version 1.1 Page 124 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
months of results consistently below the required levels.
V315
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
7.2 Reprocessing systems
7.2.1 Utility requirements
The quality, pressure, flow rate, and temperature of the
water used for reprocessing should be specified in the
dialyzer reprocessing manual, established before the
initiation of a reprocessing program, and maintained
thereafter. The manufacturer or designer’s
recommendations for the water supply should be
followed. Provision should also be made for adequate
drains, ventilation, and electrical power.
Additional Guidance:
In the reprocessing area, there must be sufficient drains to
accommodate the reprocessing systems, air ventilation equipment to
minimize exposure to germicide vapors (as listed in AAMI 8.1
"Reprocessing area and ventilation"), and an adequate number of
electrical outlets for the equipment in use.
The pressure of the water used for reprocessing should be monitored.
There should be a pressure gauge in the water line of any sink used for
dialyzer rinsing, with defined parameters for the accepted pressures to
use during that procedure. Dialyzer manufacturers specify maximum
pressures for rinsing; exceeding those pressures can result in rupture
of the dialyzer membranes and a potential for blood leaks. Use this tag
if there is no pressure gauge in the water line at the rinse sink; use
V332 if the manufacturer’s specified pressures are exceeded.
V316
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
7.2.3 Maintenance: per DFU or
semiannual/maintenance record
Written maintenance procedures and a schedule of
preventive maintenance activities designed to minimize
equipment malfunctions should be established. In the
case of purchased reprocessing equipment or safety
equipment, the recommendations of the vendor should be
followed unless documented experience supports
alternative approaches. If the manufacturer’s
recommendations are not available, reuse equipment and
safety equipment should be inspected on a semiannual
basis.
4 Records
4.3 Equipment maintenance record
Additional Guidance:
There should be a written plan which incorporates the manufacturer’s
guidance detailing expected preventative maintenance of the
reprocessing systems in use. The records of maintenance should be
congruent with the plan. If manufacturer’s guidance is not available,
preventative maintenance of reprocessing systems must be done on a
semiannual basis, at a minimum.
Final Version 1.1 Page 125 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Records shall be maintained of the dates of preventive
maintenance procedures and the results of scheduled
testing in order to ensure the proper functioning of
reprocessing equipment, environmental-control
equipment, safety equipment, or other equipment.
4 Records
A place should be provided for the signature or other
unique mark of identification of the person…performing
preventative maintenance procedures.
V317
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
7.2.4 Repairs: by qualified personnel: fxn test before
return to use
If the reprocessing system fails to function as expected,
qualified personnel should investigate and repair the
problem. The reprocessing system function testing
should be repeated after repairs of automated equipment
and, if appropriate, after repairs of manual equipment
before either the dialyzer is reprocessed or the
reprocessed dialyzer is used for clinical dialysis.
Additional Guidance:
There should be documentation to verify that testing of repaired
equipment for expected functioning was completed successfully prior
to returning the equipment to service.
V318
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1
8 Physical plant and environmental safety
considerations
8.1 Reprocessing area and ventilation
The reprocessing area should be designed to suit the
operation carried out and maintain acceptable ambient
concentrations of harmful substances (see Table 1). The
area should be kept clean and sanitary. It may be part of
the dialysis treatment area, as long as equipment used is
properly designed and vented to meet the requirements
for environmental safety (see [AAMI] 8.5).
Additional Guidance:
Although the equipment for air testing may not be kept on-site, it
should be available for use if staff or patients complain about
germicide vapors.
There should be a schedule for routine air-level testing for germicides
vapors, along with references describing the safe exposure levels, and
if there are any circumstances which would require an unscheduled
test.
The reprocessing area must be kept clean and free of clutter. Blood
splashes should be immediately cleaned and the affected surfaces
Final Version 1.1 Page 126 of 299
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
disinfected.
Table 1—OSHA environmental exposure limits (29 CFR
1910, 1 July 1998), except as indicated
Substance/material
Limits (PEL)
a
Acetic acid
10 ppm TWA
b
Chlorine dioxide (syn:
0.1 ppm TWA
chlorine oxide)
Citric acid
None developed
Formaldehyde
0.75 ppm TWA
2 ppm STEL
c
(15 min)
0.5 ppm action level
Glutaraldehyde
0.2 ppm ceiling
NIOSH/OSHA
Hydrogen peroxide
1 ppm TWA
Peracetic acid
None developed
Phenol
5 ppm TWA
ppm = parts per million
a
) PEL (permissible exposure limit) represents the limit
of what employees can be exposed to; PELs can be
TWAs or STELs.
b
) TWA (time-weighted average) represents the limit of
what an employee can be exposed to in an eight-hour
period.
c
) STEL (short-term exposure limit) represents the limit
of what an employee can be exposed to in any 15-minute
time period.
V319
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Additional Guidance:
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
MSDS must be available in the facility for the germicide in use.
8.5 Environmental safety: regarding chemicals
Policy must address and personnel must be knowledgeable of
The dialysis facility shall have written procedures for procedures for minor and major germicide spills.
safe storage and handling of chemicals used in
reprocessing (see National Institute for Occupational
Final Version 1.1 Page 127 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Safety and Health [NIOSH]/OSHA, 1980; Sax, 1979;
material safety data sheets [MSDS]).
V320
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
8.4 Personnel protection: gear
Personnel shall wear durable gloves and protective
clothing when handling the dialyzer during initiation and
termination of dialysis and during the reprocessing
procedure. Standard Precautions shall be observed.
Personnel shall wear eye protection when performing
steps that may result in spills or splashes of substances of
known or suspected toxicity. These agents shall be
handled only in areas with adequate ventilation, washing
facilities, eyewash stations, appropriate respirators, and
spill control materials. When personnel are handling
concentrated toxic substances, they shall wear aprons
impervious to these substances.
Additional Guidance:
Reprocessing personnel and patient care staff must wear PPE
appropriate to the risk of potential exposure to germicide, blood and
other potentially infectious substances for the tasks performed.
Various germicides require different precautions as to PPE, eyewash,
respirators, and spill control materials. The germicide manufacturer’s
guidance or the MSDS provide this specific information.
The supplies for managing a minor germicide spill (containment
materials, additional protective equipment, etc.) must be easily
accessible from the reuse room.
V321
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
8.2 Storage area: segregation of dialyzers in process
Reprocessing materials, hemodialyzers awaiting
reprocessing, and reprocessed hemodialyzers should be
stored so as to minimize deterioration, contamination, or
breakage. New, used, and reprocessed dialyzers should
be segregated to make clear the status of each group of
dialyzers. Environmental contamination of the storage
area should be controlled and monitored, if the personnel
determine those actions to be necessary. Storage areas
for new dialyzers and reprocessing materials should be
designed to facilitate rotation of stock and cleaning.
Storage arrangements should also take into account fire
safety considerations, OSHA regulations, and other
appropriate regulations.
Additional Guidance:
“Clean” and “dirty” dialyzers must be stored separately; the status (in
the reprocessing cycle) of any dialyzer must be clearly apparent at all
times. Stock must be organized to allow rotation and prevent use of
out-of-date materials. Reprocessed dialyzers in storage should be
protected from unauthorized access to prevent tampering and to
protect the confidentiality of the patients involved in the reuse
program.
Final Version 1.1 Page 128 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V322
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
9 Reprocessing supplies
9.1 Specifications and testing
Each reprocessing material should meet a written
specification. The fulfillment of that requirement may be
determined by certification by the product’s supplier that
the product meets necessary specifications, labeling for
its intended purpose, or by testing procedures by trained
personnel, as appropriate. The requirement may also be
complied with by purchasing a specific grade as
specified by the process, such as USP citric acid. When
the user performs testing, he or she should maintain a log
of the date of test, the identifying number (lot number) of
the batch, the person performing any testing, and the test
results.
When bleach is purchased from a commercial outlet, the
labeled concentration should be between 5.25% and
6.15%, and the formula should not contain fragrances or
scents.
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
9 Reprocessing supplies
9.1 Specifications and testing
Over the past few years, bleach (sodium hypochlorite) manufacturers
have begun selling household bleach in many new formulas. The
concentration of sodium hypochlorite has gone from 5.25% to 6.15%
in many cases. The CDC has not changed its recommendations for
diluting the bleach to take into account these percentage changes.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.9 Reprocessing supplies
A.9.1 Specifications and testing
Testing of all incoming materials had been proposed. In recognition of
the fact that most medical supplies are certified by the vendor and not
tested by the user, the AAMI RDD Committee decided to recommend
that supplies need not be tested by the facility doing hemodialyzer
reprocessing if they are marketed for hemodialyzer reprocessing.
Additional Guidance:
Most materials used in reprocessing will not require testing by the
user. If the facility is using a material not commonly used in
reprocessing, there must be documentation of testing done to verify
that the product meets the necessary specifications.
V323
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
9.2 Inventory control
Reprocessing supplies should be used on a first-in, first-
out basis, and outdated supplies should be identified and
discarded.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.9.2 Inventory control
The AAMI RDD Committee suggested that supplies should be used
on a first-in, first-out basis to avoid deterioration over time in storage.
Additional Guidance:
Expired supplies must be discarded or quarantined for return to the
vendor. Note that testing strips (which may be found in multiple
Final Version 1.1 Page 129 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
locations in the reuse room and treatment floor) may require dating
when opening and discard based on the number of days since opening.
Note that some reprocessing supplies, such as blood port caps, do not
have expiration dates.
V324
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
7.2.2 Process control testing: methods established
7.2.2.1 Dialyzer test methods ([AAMI] 11.3) shall be
established before clinical use of the reprocessed
dialyzers.
Verification of tests should be repeated after each
significant change in the reprocessing system. For
automated systems, adherence to the manufacturer’s
instructions can verify the tests. For manual systems,
confirmation of the accuracy of total cell volume (TCV)
measurement and the membrane integrity test can verify
the tests.
Additional Guidance:
Process control allows the user to ensure the equipment is functioning
correctly. This can be done by testing for the expected parameters
(e.g., checking the accuracy of the measurement of the TCV) or by
adherence to the manufacturer’s guidance for automated equipment.
A “significant change” would include a change from a manual to an
automated system, a change from one automated system to another, a
change in the germicide, or a major repair of the reprocessing
equipment.
V325
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
7.2.2 Process control testing: concentration of
germicide
7.2.2.2 The test for the concentration of germicide or
chemical shall be established before clinical use of the
reprocessed dialyzers ([AAMI] 11.4.1.6 and 12.3.2). For
systems using heat disinfection, verifiable evidence shall
be available before the next use that dialyzers have been
exposed to the appropriate temperature for the time
required. If chemicals are used to enhance heat
disinfection, both a presence test and a verification of
time and temperature shall be performed.
Additional Guidance:
The reuse manual should document how the concentration of
germicide will be tested.
If heat disinfection is the reprocessing method, records of each batch
of dialyzers processed must include an indicator, such as an
automated time/temperature recording log, that the dialyzers were
exposed to the appropriate temperature for the time required. If a
chemical, such as citric acid, is used to enhance heat disinfection, a
presence test for citric acid is also required before clinical use of the
dialyzers.
If an incubator or oven is used to raise the dialyzer storage
temperatures, a recording thermometer should be in use to assure
sufficient temperature is consistently maintained. Records should
document that these devices functioned as expected.
Final Version 1.1 Page 130 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V326
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
4 Records
4.2 Reprocessing record: complete/available to patient
Records shall be kept that identify the new dialyzer, the
date of each reprocessing step, the person performing the
procedure, his or her signature or other identifying mark,
and the results of tests of device performance and safety.
This information should be recorded in a reprocessing
log or the patient’s chart, whichever is more convenient.
Patients must be permitted to read records pertaining to
the reprocessing and reuse of their own dialyzers.
Additional Guidance:
A permanent record (paper or electronic) must be maintained to
enable tracking each dialyzer's history and performance testing;
information recorded on the dialyzer label must also be recorded
either in a log or in the patient record, as the labels are discarded with
the dialyzers.
The record of reprocessing of the dialyzer is considered part of the
patient's medical record, and must be kept separate from the dialyzer
reprocessing records of other patients and not be combined into one
document.
The systems in place must allow patients access to the record of
use/reprocessing of their dialyzer while ensuring the privacy of the
other patients’ records.
V327
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
10 Hemodialyzer labeling: unique to patient
Each reprocessed hemodialyzer shall be used for only
one patient. The labeling shall uniquely identify the
patient who is using the dialyzer. The dialyzer should
also be labeled with other information essential to proper
reuse procedure.
Additional Guidance:
There must be precautions in place to assure each dialyzer is used
only for one patient. Each reprocessed dialyzer must have a
permanently affixed label uniquely identifying the patient using that
dialyzer. Each patient must always receive treatment on his/her own
dialyzer and dialyzers must not be mis-matched to patients.
V328
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
10.1 Time of labeling: before or at first use, updated p
each use
Each hemodialyzer shall be labeled before or at the first
use of the device, and the label shall be updated after
each use (see AAMI 10.3).
Additional Guidance:
When a patient is provided a new dialyzer that is intended to be
reprocessed, that dialyzer must be labeled with the patient’s name
before or at the first use. Dialyzers that are used without being labeled
with the applicable patient’s name must be discarded.
V329
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
10.2 Label composition and placement
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.10.2 Label composition
Final Version 1.1 Page 131 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Markings should be resistant to normal reprocessing and
dialysis procedures. The dialyzer labeling should not
obscure the manufacturer’s model number, lot number,
or indicators of the direction of blood or dialysate flow
or other pertinent information unless provision is made
for recording this information on the label. The label on
hemodialyzers with transparent casings should permit the
blood path to be readily inspected.
The AAMI RDD Committee initially recommended using indelible
ink to label the dialyzer, but changed the recommendation to any
method resistant to normal reprocessing and use procedures; other
satisfactory materials exist, and requiring indelible ink might preclude
some techniques, such as bar coding.
Additional Guidance:
Facility-applied labels must not obscure the pertinent information on
the manufacturer’s label and must leave at least a portion of the blood
path uncovered to allow visualization of a section of the fibers from
header to header.
V330
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
10.3 Information recorded on label/similar name
warning
The dialyzer shall be labeled with the patient’s name, the
number of previous uses, and the date of the last
reprocessing. Dialyzers of patients with similar last
names should have a warning to the user to take extra
care in ensuring that the name or other identifying
information on the label corresponds to that of the
patient. If there is sufficient room, the dialyzer may also
be labeled with the results of tests, the signature or other
unique means of identifying the person performing the
various steps in the reprocessing procedure, and the
reference values for performance parameters. If this
information appears on the label, a permanent record
should also be kept (see [AAMI] 4.2) Electronic records
are acceptable. If records are electronic, the test results
should be available to the user.
Home dialysis patients are exempted from the
recommendation that the patient’s name appear on the
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.10.3 Information recorded
A proposal that the label contain all of the recommended information
was rejected because space is limited on the label, and such extensive
labeling is unnecessary. Displaying the number of previous uses on
the label is recommended so that this information is readily available.
Displaying the date of the last reprocessing facilitates verification that
sufficient time has elapsed since the introduction of the germicide to
achieve sterilization or disinfection.
Additional Guidance:
At a minimum, each dialyzer must be labeled with the patient’s name,
the number of previous uses, and the date and time of the last
reprocessing.
For patients with similar names, a warning is necessary to alert staff
and prevent dialyzer mix ups. Direct care staff must be knowledgeable
of the method used to alert them about dialyzers of patients with
same/similar names. Dialyzers in use must demonstrate use of
warning labels if there are two or more patients with similar names on
census.
Final Version 1.1 Page 132 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
label, unless the dialyzers are taken to a dialysis facility
for reprocessing.
Since the labels are discarded with the dialyzer, the information on the
label must also be kept in a permanent record, which may be
electronic. The record of reprocessing of the dialyzer is considered
part of the patient’s medical record.
V331
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11 Reprocessing
11.1 Transportation and handling
Persons handling used dialyzers during transportation
shall do so in a clean and sanitary manner maintaining
Standard Precautions until the dialyzer is disinfected
both internally and externally. To inhibit bacterial
growth, dialyzers that cannot be reprocessed within 2
hours should be refrigerated and not allowed to freeze.
Other transportation and handling issues (such as
prolonged delays in reprocessing) not described in this
recommended practice shall be validated and
documented by the responsible party.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.1 Transportation and handling
During the 2002 revision of this recommended practice, the AAMI
RDD Committee recognized that the refrigeration temperature of the
dialyzers stored for extended periods of time was not specified. It was
decided to recommend that dialyzers not reprocessed within 2 hours
should be refrigerated and not allowed to freeze. The AAMI RDD
Committee believed that this was sufficient to retard bacterial growth.
Additional Guidance:
Personnel should wear appropriate PPE to handle used dialyzers until
reprocessing is complete. The infection control recommendations
from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for transporting
dialyzers include the following: "For dialyzers and blood tubing that
will be reprocessed, cap dialyzer ports and clamp tubing. Place all
used dialyzers and tubing in leakproof containers for transport from
station to reprocessing or disposal area." This requirement would be
considered met if the tubing is disposed of at the patient’s chairside
directly into a waste receptacle and all the ports on the dialyzer are
immediately capped.
All dialyzer ports should be capped when the dialyzer is not in use or
not being currently reprocessed, to prevent spills of blood or blood
products, leakage of germicide, and entrance of air into the dialyzer. If
used dialyzers are transported in a common carrier (e.g., a basket) the
potential for cross-contamination must be eliminated (i.e. exteriors
must be free of visible blood and all ports capped or each dialyzer
Final Version 1.1 Page 133 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
contained in a sealed bag).
If used dialyzers are refrigerated prior to reprocessing, facility policy
must define and personnel must be aware of maximum refrigeration
times, temperature ranges, and quality controls in place to assure the
practice is safe.
Practices such as allowing dialyzers to remain at room temperature for
prolonged periods during the reprocessing process (e.g., after rinsing
and prior to filling the dialyzer with germicide) must be validated to
ensure patient safety is not impacted.
If dialyzers are sent to an off-site location for reprocessing, the survey
process must include a visit to that site to determine compliance with
this and all other reprocessing requirements.
V332
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.2 Rinsing/cleaning: precleaning
equipment/pressures
11.2.1 When precleaning is done, it is part of the
reprocessing procedures. All applicable requirements for
design and maintenance of equipment included in this
document should be adhered to for precleaning of
equipment. The maximum pressures for the dialyzer, or
other limits set by the manufacturer, should be adhered
to.
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
11.2.1 Rinsing/cleaning
Many facilities preclean dialyzers. This process is typically
accomplished with an apparatus developed by users and is intended to
remove gross deposits of blood and products before rinsing and
cleaning with a reprocessing machine or device.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.2.1 Rinsing/cleaning
Aqueous liquids rather than gases such as air are the preferred fluid
for rinsing and cleaning.
Additional Guidance:
Maximum pressures allowed during reprocessing will be defined in
the dialyzer manufacturer’s directions for use (DFU). Use of higher
pressures may cause breaks in the dialyzer fibers and potential blood
leaks. A pressure gauge must be in place to monitor the pressure of
Final Version 1.1 Page 134 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the treated water source used for rinsing the used dialyzers, and the
maximum limits of the pressure to be used must be defined and
known to the operator.
Use V315 if there is no pressure gauge in the water line at the rinse
sink; use this tag if the manufacturer’s specified pressures are
exceeded.
V333
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.2 Rinsing/cleaning: use AAMI quality water
11.2.3 Precleaning the dialyzer (rinsing and cleaning)
shall be done with a fluid or fluids made with water that
meets the requirements of these regulations related to
allowable bacterial and endotoxin levels.
Additional Guidance:
All water that is used in rinsing and reprocessing the interior of the
dialyzer must meet the requirements of AAMI RD52:2004 related to
the allowable bacterial and endotoxin levels. Refer to V178. The
interior of the dialyzer should never be exposed to tap water. The
facility must monitor the water supply to the reprocessing station(s)
for bacteria and endotoxins.
V334
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.4.1.2 Dialyzer header cleaning and disinfection
The cleaning and disinfection of the header space should
be done only when necessary and only before the
dialyzer is reprocessed. The manufacturer’s instructions
should be followed. Header caps and O-rings shall be
kept with their respective dialyzers.
If the header cap is removed to clean the header space,
cleaning shall be done with water meeting the
requirements of these regulations related to allowable
bacterial and endotoxin levels.
Once the O-ring and the header cap are cleaned and
before they are reassembled at the end of the dialyzer,
they should be disinfected. The disinfectant shall not be
rinsed and shall be allowed to remain on the dialyzer
components as they are reassembled. If any cracking of
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002
11.4.1.2 Dialyzer header cleaning and disinfection
Over tightening the header caps may cause damage to the cap, and
under tightening the cap may cause blood leaks.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.4.1.2 Dialyzer header cleaning and disinfection
The practice of header removal to remove clotted material has
increased over the years. Removing the header allows the user to
remove the clotted material from the end of the fiber bundle and the
O-ring header assembly. The method of removal of the clotted
material has been of concern. Some facilities use running water
(AAMI quality) to remove the clotted material, whereas others use
4x4s or instruments to scrape away the clotted material. The main
concerns of using 4x4s or instruments to scrape away the clotted
material are (1) infection, (2) plugging of fibers, and (3) damage to the
end of the fiber bundle.
Final Version 1.1 Page 135 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the header occurs, the process should be evaluated.
If the header space is cleaned with the header cap in
place, it is necessary to ensure that the end of the fiber
bundle is not damaged. If water is used, it shall meet the
requirements of these regulations.
If automated equipment is used, the manufacturer’s
instruction for use shall be followed.
In the past, removing the headers was associated with reported
incidents of bacterial and pyrogenic reactions in patients. The patient
reactions no longer occurred when the headers were disinfected by
dipping the O-ring, header, and end of the dialyzer into the
appropriate disinfectant. The research on this problem pointed to a
double-fault failure system: 1) the bacteria seemed to be coming from
a contaminated water source, and 2) the bacteria were not killed by
the normal disinfection process. Dipping the dialyzer corrected that
situation.
Several concerns are raised when the headers are not removed and the
user attempts to clear the header space of clots. These concerns
include infection and damage to the end of the fiber bundle. A
multitude of items are used to clean the header space, including water
sprays, paper clips, tie wraps, and the like. With water sprays, the
possibility of contaminated water always exists. Other items that are
inserted can damage the end of the fiber bundle. If the item inserted
into the dialyzer is not disinfected between uses, it can cause bacterial
transmission; however, the dialyzer is usually disinfected after the
header space is cleaned. Automated header cleaning devices are
commercially available.
Additional Guidance:
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC),
if the ends of the dialyzer (header caps) are removed for cleaning,
only a stream of AAMI quality water may be used to clean blood
clots, etc. from the exposed ends and the header caps of dialyzers.
If the header caps are removed during reprocessing, facility staff must
ensure that the caps, O-rings, and the ends of the dialyzer are
immersed or saturated with germicide prior to reassembly, and that
the components are reassembled wet with germicide. Cleaning of
header caps and dialyzer ends must be closely audited for any breaks
Final Version 1.1 Page 136 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
in technique which could put the patient at risk.
V335
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.2 Rinsing/cleaning: chemicals used/rinse after each
11.2.4 Diluted solutions of hydrogen peroxide, sodium
hypochlorite, peracetic acid, or other chemicals may be
used as cleaning agents for the blood compartment,
provided that the cleaning agent has been shown to be
reduced to safe levels by subsequent flushing and has no
significant adverse effects on the structural integrity and
performance of the dialyzer.
Each chemical shall be rinsed from the dialyzer before
the next chemical is added, unless mixing is known to be
safe and effective for reprocessing.
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
11.2 Rinsing/cleaning
11.2.4 A cleaning agent, such as sodium hypochlorite, shall be rinsed
from the dialyzer before adding formaldehyde in order to avoid
noxious fumes and degradation of disinfectant. Combining sodium
hypochlorite and peracetic acid may produce hydrochloric acid
vapors, which are harmful if inhaled.
Additional Guidance:
While one chemical may be used as a cleaning agent and a second
chemical used as a germicide, the first chemical must be rinsed from
the dialyzer before the next chemical is added, unless it has been
demonstrated that mixing of the two chemicals is safe and effective.
Allowing chemicals to mix may risk unexpected reactions that could
lead to staff injury or damage to the structural integrity and
performance of the dialyzer. If bleach is used as a cleaning agent, a
procedure must be in effect to limit the time the dialyzer may be
exposed to bleach, as prolonged exposure may damage the dialyzer
membrane.
V336
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.3 Performance measurements
11.3.1 Performance test after each use: TCV measured
after q use/original volume known
Total cell volume (TCV) may be used for hollow-fiber
dialyzers. The acceptable TCV is at least 80% of the
original TCV. The dialyzer prescription should take into
account the 10% loss in clearance (20% loss in TCV)
that may occur with dialyzer reuse.
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
11.3 Performance measurements
The performance characteristics of dialyzers may change following
reprocessing. The ultrafiltration coefficient may increase or decrease.
Clearances of small or large molecular weight solutes may also
increase or decrease depending on the chemicals, methods, and
dialyzer membrane used. The dialyzer labeling and medical literature
should be consulted for information related to changes in in vitro and
in vivo performance.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.3 Performance measurements
Final Version 1.1 Page 137 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The essential function of the hemodialyzer is mass transfer adequate
to provide the prescribed care to the patient. Change in TCV has been
documented in the medical literature as an indirect measurement
having a close relationship to the retained mass transfer of small
molecules by the hemodialyzer, and may be used for the routine test
of residual dialyzer performance.
A.11.3.1 Performance test after each use
Clearance, a measure of the solute transport of the hemodialyzer,
should be maintained within acceptable limits to ensure that dialysis is
adequate to prevent uremic complications. Although direct clearance
measurements could be used to demonstrate compliance with the ±
10% change in urea clearance, determining the urea clearance for each
dialyzer reprocessed is impractical. There are also indirect tests that
reflect the mass transfer characteristics of a dialyzer, which may be
used in lieu of clearance measurements. A change in the residual TCV
of hollow-fiber hemodialyzers is the most widely used indirect test for
changes in small molecule clearance. This method has been shown to
be a good index to monitor the solute transport capacity of the
reprocessed hollow-fiber hemodialyzer. The volume of a hollow-fiber
hemodialyzer (TCV) is readily measured in the clinical setting. When
methods of reprocessing are used that do not cause a significant
change in the permeability or geometry of the membrane, a loss of
TCV of 20% corresponds to a loss of urea clearance of less than 10%.
Volume change is recommended as a QC test only for hollow-fiber
hemodialyzers because other hemodialyzer geometries do not have the
relatively noncompliant blood compartment necessary for the validity
of this measurement in predicting solute transport.
The AAMI RDD Committee recognized that other factors can
influence the effective clearance of toxins during the dialysis session
or can influence interpretation of the results. These factors include the
following:
Final Version 1.1 Page 138 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
a) Fistula recirculation;
b) Accurate blood and dialysate flow rates;
c) Accurate time of dialysis;
d) Compliance with dietary limitations;
e) Selection of appropriate hemodialyzer type and blood and
dialysate flow rates;
f) Membrane surface coating that may affect higher molecular
weight toxins;
g) Variations in the original clearance of the hemodialyzer;
h) Variations in the clearance of the hemodialyzer caused by reuse.
Users should be aware that the HEMO Study in 1999 identified
reductions as well as increases in the clearance of ß2 microglobulin
with the use of certain combinations of dialyzers, cleaning agents, and
reuse germicides.
Of particular concern to the AAMI RDD Committee were any
variations in hemodialyzer functions related to reuse procedures.
Although cases have been documented, they are rare, especially when
compared to the frequency of other factors listed above. For this
reason, the AAMI RDD Committee strongly felt that the monitoring
requirements of AAMI section 13 are of great importance to use in
conjunction with the individual hemodialyzer measurements
recommended in AAMI 11.3.
Additional Guidance:
Every dialyzer expected to be reprocessed must have its original total
cell volume (TCV) measured prior to the first use. “Dry pack”
dialyzers, i.e., dialyzers used without preprocessing, must be
discarded and not reprocessed. Refer to the Measures Assessment
Tool (MAT) for this current community-accepted standard.
All staff who reprocess or reuse dialyzers must demonstrate
Final Version 1.1 Page 139 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
understanding that a drop in TCV to less than 80% of the dialyzer’s
original volume requires discard of that dialyzer, to prevent that
patient from receiving a less than adequate treatment. Staff must also
be aware of other criteria dialyzers must meet for continued reuse
(e.g., limit on number of times a dialyzer may be reused, reasons for
discard).
If a manual reprocessing system is in use, the graduated cylinder used
for measuring TCV must be emptied completely between uses and
placed on a level surface to be read. The reading should be made at
eye level, and the operator should have charts available to use in
determining whether the remaining volume is sufficient (at least 80%
of original volume) to continue using that dialyzer.
For automated systems, a system must be in use to validate that the
volume measurements are accurate.
V337
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.3.3 Blood path integrity test after q use
A membrane integrity test such as an air pressure leak
test shall be done between uses.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.3.3 Blood path integrity test
The 1986 edition of the AAMI recommended practice did not include
a blood path integrity test. Because of recommendations by the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the AAMI RDD
Committee agreed to add such a test to the second edition of the
recommended practice. This test is based on the observation that only
a small amount of air leaks through wetted membranes, resulting in a
pressure drop of less than 10% of the test pressure. A maximum
allowable pressure drop is not given because of variations among test
systems and dialyzers.
Additional Guidance:
Recognize that manual reprocessing systems may require each
dialyzer be tested separately. Automated systems must include the
pressure leak test in the program selected.
Final Version 1.1 Page 140 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V338
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.4 Germicide: sufficient for point of use
The rinsed and cleaned dialyzer shall be treated by a
process that prevents adverse effects caused by microbial
contamination. The blood and dialysate compartments of
the dialyzer shall be sterilized or subjected to high-level
disinfection because an inadequate germicidal process
may result in infection in the patient. Low-level
disinfection is sufficient for the exterior of the device.
The user shall consult the dialyzer labeling for
contraindications or warnings regarding methods and
applicability of specific germicidal processes or
chemicals.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.4 Germicide
In the early 1990s, the FDA began actively regulating all liquid
chemical germicides with health care indications. To avoid the
potential problem of regulating the same product under multiple
classes, the FDA decided to regulate liquid chemical germicides as a
separate type of medical device; therefore, it determined that they
were unclassified devices. In an effort to ease the burden of this dual
regulation, a memorandum of understanding (MOU) was signed
between the FDA and the EPA that gave the FDA primary
responsibility for premarket efficacy data review of liquid chemical
sterilants and high-level disinfectants and gave the EPA primary
responsibility for premarket efficacy data review of general purpose
disinfectants.
Additionally, the FDA adapted the basic terminology and
classification scheme described by Spaulding (1971) to categorize
medical devices, and the four levels of processing as proposed by the
CDC: sterilization, high-level disinfection, intermediate-level
disinfection, and low-level disinfection. Also, the FDA regulatory
authority over a particular instrument or medical device dictates that
the manufacturer is obligated to provide the user with adequate
instructions for the “safe and effective’’ use of that instrument or
device. Those instructions must include methods to clean and disinfect
or sterilize the item if it is marketed as a reusable medical device.
Additional Guidance:
The germicide in use must be approved for the dialyzers used at the
facility, and the concentration of germicide in the reprocessed
dialyzers must be sufficient to achieve high-level disinfection.
V339
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
11.4.1 Interior (blood/dialysate compartment)
Final Version 1.1 Page 141 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
11.4.1 Interior (blood/dialysate compartment)
11.4.1.1 Germicidal process: high-level disinfection
achieved
Chemical germicides or other procedures used for
disinfecting of hemodialyzers shall have been shown to
accomplish at least high-level disinfection when tested in
dialyzers artificially contaminated with appropriate
microorganisms.
If the germicide has an expiration date from the
manufacturer, staff members should be sure that the
chemical is not outdated. Some germicides have
recommendations for maximum storage time after
dilution or activation and before usage. If this is the case,
the expiration date of the prepared germicide solution
should be marked on the outside of the germicide
solution container, and that date should be checked at the
beginning of each day, before reprocessing begins.
The disinfection process shall not adversely affect the
integrity of the dialyzer. Germicides shall be rinsed from
the dialyzer to below known toxic levels within a rinse-
out period established for the particular germicide (see
AAMI 12.4). To prevent injury, staff members shall take
care not to mix reactive materials such as sodium
hypochlorite and formaldehyde.
11.4.1.1 Germicidal process
If formaldehyde is used as the sole germicidal agent, the CDC
recommends that a concentration of 4% (W/V) be used in both the
blood and dialysate compartments with a minimum contact time of 24
hours at a temperature of at least 20° C; lower concentrations or
shorter contact times are appropriate if equivalent results can be
demonstrated under other conditions. Formaldehyde used for
reprocessing dialyzers shall not be cloudy. Concentrated
formaldehyde stored under adverse conditions can polymerize to form
paraformaldehyde, a white precipitate. Formaldehyde should be of
United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) standards or better quality. When
other germicides are used, the manufacturer’s instructions should be
followed. If maximum storage temperature limitations exist, records
should be maintained to document this criterion.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.4.1.1 Germicidal process
Unfortunately, no realistic procedure exists whereby a dialysis center
can monitor the effectiveness of the disinfection procedure. Such
sophisticated microbiologic tests cannot be performed in dialysis
centers, because the tests require the use of specialized equipment and
highly-trained microbiologists. Instead, a center should adhere rigidly
to established protocols for QC and QA. Tests for total bacteria and
endotoxin in the water used to make up the germicide should be
conducted at least monthly. If there are problems in maintaining water
quality at the level established by ANSI/AAMI RD62:2001, Water
treatment equipment for hemodialysis applications, (referenced in
RD52:2004) the testing may need to be performed more frequently.
Testing the germicide’s final-use concentration should be a part of the
center’s QC program as well as verifying that each dialyzer was filled
with germicide.
Final Version 1.1 Page 142 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Potency testing of each batch of germicide is specifically
recommended for batches of manually-prepared germicides regardless
of whether they are used with a manual or an automated system.
Germicide solutions that are diluted on-line by automated machines
are to be checked for concentration at least monthly. Other
requirements for verification of germicide presence are contained in
section 12.
CMS requires (at 42 CFR § 494.50) that dialyzers not be subjected to
multiple germicide solutions because of possible combined actions of
the germicides on the hemodialyzer membrane. This requirement does
not apply to the original sterilization process or chemical cleaning
agents that the hemodialyzer might be exposed to for short periods
during the cleaning process for reuse.
Additional Guidance:
The reuse staff must be knowledgeable about the germicide used and
the risks this germicide presents to him/her and to the patients.
Containers of germicide should be dated to indicate dilution and
discard dates.
V340
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.4.1.4 Chemical germicidal procedure: = 90%
conc/port caps disinfected
If applicable, the hemodialyzer shall be filled with the
germicide solution until the concentration in the
hemodialyzer is at least 90% of the prescribed
concentration.
The ports of chemically disinfected dialyzers shall be
disinfected and then capped with new or disinfected
caps. The caps may be disinfected with dilute bleach,
with the chemical used for disinfecting the hemodialyzer,
Additional Guidance:
If a manual reprocessing system is in use, the blood and dialysate
compartments must be filled with a volume of germicide equal to
three times the total volume of the blood and dialysate compartments
of the dialyzer (to equal three compartment volumes) in order to reach
at least 90% of the prescribed germicide concentration. Reuse logs
must include documentation of verification of the desired (prescribed)
concentration of germicide.
Used and new port caps must be disinfected prior to use. The reuse
technician should be knowledgeable about the minimum germicide
contact time required for port cap disinfection.
Final Version 1.1 Page 143 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
or with any other germicide approved by the FDA as a
disinfectant that does not adversely affect the materials
of the dialyzer.
V341
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.4.1.6 Chemical germicide concentration:
verification testing
Reprocessing systems in which each batch of germicide
is manually prepared, each batch of germicide shall be
tested before use to verify the proper concentration of the
germicide. This requirement does not apply in cases in
which each dialyzer is tested for concentration before
setup.
When the germicide is diluted on-line, its concentration
in the hemodialyzer immediately after reprocessing
should be checked at least monthly for each reprocessing
system.
When the germicide is partially or fully diluted by the
user,… the solution [should] be thoroughly mixed.
Additional Guidance:
The system in use must include verification of germicide
concentration in the dialyzers after reprocessing.
If the germicide is diluted by the user (batch), the germicide
manufacturer's instructions for dilution must be followed, and the
solution thoroughly mixed before use. If each dialyzer is tested for
germicide concentration prior to rinsing, it is not necessary to test the
germicide concentration before use of the batch.
If the germicide is diluted on-line, the concentration in a dialyzer from
each reprocessing system must be checked immediately after
reprocessing at least monthly.
V342
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.4.2 Exterior: low-level disinfection
The outside of the dialyzer should be soaked or wiped
clean of visible blood and other foreign material. For
chemically disinfected dialyzers, a low-level germicide
that is compatible with the dialyzer’s materials of
construction should be used for this purpose.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.4.2 Exterior
Sodium hypochlorite at a concentration of 0.05% is usually suitable
for external cleaning. Certain commercial low-level disinfectants may
cause some plastics used for dialyzers to crack after repeated or
prolonged exposure.
Low-level germicides satisfactorily clean the exterior of the device to
a degree comparable with what a new dialyzer receives. For example,
1:100 dilution of household bleach will achieve the concentration of
sodium hypochlorite specified here.
Final Version 1.1 Page 144 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Additional Guidance:
The exterior of each dialyzer must be cleaned after reprocessing steps
are complete. Spraying the dialyzer with germicide is generally
unsatisfactory, unless all the surfaces of the dialyzer are covered with
the spray. Dialyzers may be dipped or allowed to soak in a germicide
solution, or wiped with a disposable cloth saturated with a germicide
solution.
V343
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.5 Inspection: after reprocessing: all
aspects/aesthetics
The hemodialyzer shall be examined after reprocessing
to ensure that the external surface is clean, the dialyzer is
not damaged, and the rinsing of blood has been
satisfactorily completed. The dialyzer should also be
aesthetically acceptable in appearance to patients and
staff.
11.5.1
The dialyzer jacket should be free of visible blood or
other foreign material.
11.5.2
There shall be no leaks or cracks in the dialyzer jacket or
the blood or dialysate ports.
11.5.3
No more than a few dark, clotted fibers should be evident
on inspection of the exterior of the hollow fibers.
11.5.4
The headers of hollow-fiber dialyzers should be free of
all but small peripheral clots or other deposits.
11.5.5
Blood and dialysate ports shall be capped without
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.5 Inspection
The AAMI RDD Committee considered a recommendation not to
accept hemodialyzers with visible clots because venous filters are not
used for all hemodialyzer circuits, leading to the risk of embolization
to the patient if a clot were to break loose. The AAMI RDD
Committee decided to reject this proposal because the allowable clots
are required to be small and in stagnant areas that are present during
the first use of the hemodialyzer and because there is no evidence of
embolization from reprocessed hemodialyzers that meet this criterion.
A proposal that the number of dark, clotted fibers evident upon
external inspection be limited to five was not accepted because a
considerably larger number may be clotted without significant adverse
effect on performance and because some authorities do not agree that
this criterion is essential to an aesthetically pleasing appearance. A
recommendation that hemodialyzers with a pink or brownish tint not
be acceptable was also deleted because this condition is difficult to
define and because glutaraldehyde disinfection results in a slight tan
color of the membranes that has not been shown to impair the safety
or performance of the hemodialyzer.
Final Version 1.1 Page 145 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
evidence of leakage.
11.5.6
The label shall be properly filled out and legible.
V344
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.6 Disposition of rejected dialyzers
Reprocessed dialyzers that have been rejected for failure
to meet performance, inspection, or other release criteria
should either be immediately discarded or further
reprocessed and subjected to the performance
requirements of [AAMI] 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5. If the
dialyzer is to be further reprocessed, rather than
discarded, it shall be labeled as rejected and stored in a
quarantine area to preclude use until requirements are
met.
Additional Guidance:
The status of all dialyzers being reprocessed must be clear. If facility
policy allows dialyzers which initially fail criteria to be repeatedly
reprocessed, or if dialyzers which have failed are not immediately
discarded, the status of those “failed” dialyzers must be clearly
indicated.
V345
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11.7 Storage: reprocessed dialyzer
Reprocessed dialyzers that meet the performance and
inspection criteria for multiple use should be stored
according to the provisions of [AAMI] 8.2. Prolonged
storage (greater than 1 month) should be documented to
be safe and effective.
Dialyzers that have exceeded the facility’s maximum
storage time shall be reprocessed or discarded. The
dialyzer and disinfectant labeling should be consulted
regarding proper storage conditions.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.7 Storage
The AAMI RDD Committee acknowledged that the selection of 1
month as the maximum storage period permitted without validation
was arbitrary. They were, however, unaware of any adverse effects of
storage for up to 1 month and, therefore, felt that this period of time
was reasonable.
Additional Guidance:
There might be occasions when reprocessed dialyzers are stored for
extended periods of time, such as when patients are absent (e.g.
hospitalized, vacation). There must be a system for ensuring dialyzers
are not stored longer (without reprocessing) than the maximum time
limit specified by the germicide manufacturer and facility policy.
V346
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
Prep for dialysis: written P&P for germicide testing
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.12 Preparation for dialysis and testing for chemical germicides
Final Version 1.1 Page 146 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
12 Preparation for dialysis and testing for chemical
germicides and potentially toxic residues
A written procedure that has been shown to be effective
shall be followed.
12.5 Written procedure for tests for germicide or
other residues
There shall be a written procedure for all tests employed
in preparing the dialyzer for use, including mention of
each test’s sensitivity. The germicide manufacturer’s
instructions for use should be consulted in determining
the maximum residual level. The physician in charge of
the reuse program shall approve any alterations in the
procedures.
and potentially toxic residues
When the AAMI RDD Committee revised RD:47 in 2002, it decided
that there was sufficient information available to indicate that the
residual level of formaldehyde should be reduced to less than 3 ppm.
The testing technology for residual formaldehyde had also improved,
and it was feasible to easily test to less than 3 ppm.
The AAMI RDD Committee considered establishing maximum
residual levels for germicides other than formaldehyde. Because these
newer germicides are all cleared by the FDA and could have different
allowable levels of residuals even for the same generic type of
germicide, they determined that it is best to recommend that the
manufacturer’s instructions for use be followed. The AAMI RDD
Committee noted that toxicology studies are favorable for some of
these agents, and the FDA reviews labeling information for them,
which includes the maximum residual level.
When checking for the presence or concentration of the germicide in
the hemodialyzer, do not place anything into the blood or dialysate
ports of the device (e.g., test strip or syringe) to withdraw the sample.
Doing so may damage the fibers of the dialyzer and lead to blood
leaks during dialysis. If a germicide test strip or kit is being used, the
instructions provided by the manufacturer should be followed.
Additional Guidance:
The reagents used for the germicide tests must be sensitive to the
levels specified by the germicide manufacturer (i.e. high level for
presence test, low level for residual test).
V347
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
12.1 Visual inspection: prep for dialysis; all aspects
The dialyzer should be inspected before it is prepared for
use. Completion of this inspection should be recorded in
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.5 Inspection
The AAMI RDD Committee recognized that the patient should be
included in the aesthetic evaluation of the hemodialyzer.
Final Version 1.1 Page 147 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the reprocessing record (see [AAMI] 4.2), along with the
signature or other unique means of identifying the person
completing the inspection. The inspection should include
the following:
a) The reprocessed dialyzer shall be legibly labeled with
the information recommended in [AAMI] 10.3.
b) There should be no indication of structural damage or
tampering with the dialyzer.
c) The ports of the dialyzer should be properly capped.
d) The presence of germicide in the dialysate and blood
compartments, including headers, should be confirmed,
and there should be no evidence of leakage from the
ports or other portions of the dialyzer.
e) The duration and conditions of storage should be
appropriate for the agent or method used to sterilize or
disinfect the dialyzer; and
f) The cosmetic appearance of the dialyzer should be
aesthetically acceptable to the staff and the patient.
V348
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
12.2 Verification of patient identification: 2 people
Except in the case of home dialysis, two persons should
check that the first and last names on the dialyzer and
any other appropriate identifying information correspond
to the identifying information on the patient’s permanent
record. If possible, one of the persons checking
identification should be the patient. Completion of this
step shall be recorded, along with the signature or other
unique means of identifying the person verifying patient
identification.
NOTE—This step may be done later in the procedure but
shall precede initiation of dialysis.
Additional Guidance:
Standard of practice requires the final check be done when the patient
is present for that treatment. If possible, patients should be encouraged
to check their dialyzers for their names. Patients who sign the
treatment record for this item should understand what their signature
means. If patients are unable to identify their dialyzers, two staff
should do so and record the verification prior to initiating the dialysis.
Note that some facility policies require two staff to verify
patient/dialyzer identification for all reused dialyzers.
Final Version 1.1 Page 148 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V349
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
12.3 Verification of germicidal contact
The contact time of the germicide or disinfection
procedure shall comply with the facility’s protocol and
the manufacturer’s recommendations.
The presence of chemical germicide in each
hemodialyzer shall be ensured through either direct
testing or an on-line process and procedural control.
If other disinfection (e.g., heat) procedures are used,
there shall be methods to ensure that each hemodialyzer
has been properly subjected to the disinfection process.
A record shall be kept indicating that the dialyzer has
undergone the appropriate storage time, and the record
shall be appropriately verified.
Additional Guidance:
Staff must be able to determine the date and time of each dialyzer's
last reprocessing. Responsible staff (e.g., reuse technician, direct care
staff) must ensure the dialyzers have been exposed to the germicide
for the required contact time before set up and use.
For systems using heat disinfection, staff must verify the dialyzer was
exposed to the appropriate temperature for the required time period to
assure disinfection.
V350
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
12.3.1 Presence test of each hemodialyzer
Certain germicide manufacturers require testing for the
presence of germicide in each hemodialyzer before the
rinsing step. These instructions should be followed.
Additional Guidance:
Manufacturers of peracetic acid and glutaraldehyde require every
dialyzer be tested for presence of a sufficient concentration of
germicide after storage and before use.
The test for germicide presence (at the potency recommended by the
germicide manufacturer) should be done before rinsing and priming.
V351
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
12.3.2 Process control and sampling: germicide
presence
[If a germicide manufacturer does not require testing
each hemodialyzer for the presence of germicide], the
presence of germicide may be ensured by [either] a direct
presence test of each hemodialyzer or the use of process
control and sampling of the dialyzer for germicide.
12.3.2.1 Process control
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
12.3.2.1 Process control
Note that use of dye may be inappropriate with certain germicides
such as peracetic acid.
12.3.2.2 Sampling for process validation
NOTE—The requirements of this section are fulfilled if every
dialyzer is subjected to post-storage/pre-priming direct presence
testing.
Additional Guidance:
Final Version 1.1 Page 149 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
a) Use hemodialyzer germicide filling equipment with
on-line automatic monitors during the germicide dilution
and hemodialyzer filling process; or
b) Use an indicator substance (e.g., FD&C Blue #1),
which has been added to the germicide, and that reliably
indicates the presence of germicide. If blue dye is used, it
should be added to the germicide concentrate before
dilution, not to the fully diluted solution.
12.3.2.2 Sampling for process validation
a) Sample at least one hemodialyzer per patient shift per
reuse system with a direct presence test (do not use a
Schiff test for formaldehyde for this purpose because it
will detect the presence of inadequate concentrations of
formaldehyde). Samples should be taken immediately
after the dialyzers have been reprocessed.
b) For germicide prepared in batches, sample at least one
hemodialyzer from each batch with a direct presence test.
Samples should be taken immediately after the dialyzers
have been reprocessed.
c) Sampling and testing are to be accomplished before
patients use any hemodialyzers processed on this shift.
This tag refer to procedures which may be used to validate that
dialyzers, reprocessed with germicides that don't require presence
testing of each dialyzer, are adequately disinfected and safe for use. If
each dialyzer is not tested for germicide presence, procedures for both
process control and testing a sample of dialyzers for germicide
concentration are required.
For certain germicides, the facility may use a blue dye (as process
control) to indicate the presence of germicide in the dialyzers. The
absence of blue coloring must not be used as an indicator of the
absence of germicide. Any process control procedure must be used in
conjunction with a procedure for testing a sampling of dialyzers as
described at this tag.
V352
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
12.4 Priming the dialyzer and rinsing the germicide
If the manufacturer’s instructions so require, a germicide
presence test shall be performed before the germicide is
rinsed from the dialyzer.
The dialyzer shall be rinsed and primed according to a
written procedure that has been documented to produce a
reduction in the concentration of germicide to an
acceptable level and result in a physiological solution in
Additional Guidance:
The dialyzer rinsing/priming and preparation for use procedures
followed must be in accordance with the dialyzer manufacturer's
requirements for the germicide in use.
Final Version 1.1 Page 150 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the blood and dialysate compartments. The dialyzer
manufacturer’s instructions should be considered in
developing these procedures.
V353
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
12.4.1 Testing for residual germicide: max time rinsed
to use
Residual germicide shall be measured by a test of
appropriate sensitivity according to a written procedure
to ensure that the germicide level is below the maximum
recommended residual concentration. Completion of this
step shall be documented, along with the signature or
other unique means of identifying the person performing
the test.
A written policy should establish the maximum
allowable time between rinsing the germicide from the
dialyzer and beginning dialysis. The priming, removal,
and residual testing process should be reinstituted after a
delay sufficient to bring concentrations of germicide
above the recommended level (rebound). Additional
rinsing should be performed to yield a germicide level
below the maximum recommended concentration before
initiating of dialysis.
A rinse procedure should be defined and documented
step by step, and all personnel should be familiar with
and follow it.
If heat disinfection is used, the dialyzer should be cool to
the touch before it is primed with saline.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.12.4.1 Testing for residual germicide
Germicides have been demonstrated to disperse into the solid
components of the hemodialyzer.
A number of procedural steps have been identified that, if not
followed, may cause residual germicide to remain in the hemodialyzer
following rinsing. The following list of instructions, though not all
inclusive, have been developed by AAMI to help facilities develop
facility’s rinsing procedure.
a) Air bubbles in the fibers can cause individual fibers to become
blocked. Be sure that the arterial line is fully primed before it is
connected to the hemodialyzer. If using peracetic acid-type
germicide, the blood side should be flushed before beginning
dialysate flow.
b) Air trapped in the dialysate side of the hemodialyzer may cause
germicide to also remain trapped in portions of the hemodialyzer.
The dialyzer should be rotated during the rinsing process. This
action normally will release the trapped air and allow the
germicide to be fully rinsed.
c) Germicide may back up into the heparin or monitor lines. The
heparin line must be clamped so that fluid is not forced into the
monitor lines.
d) Germicide may back up into the saline bag during the rinsing
procedure. Procedures for initiation of treatment must account for
all situations that may force fluid from the dialysis circuit back
into the saline bag.
e) Sampling too quickly after a quantity of saline has been infused
may result in a false negative residual disinfection test.
Final Version 1.1 Page 151 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
f) The prime solution should be discarded when beginning blood
flow to the hemodialyzer.
Additional Guidance:
If the extracorporeal circuit is prepared ahead of time, staff must
repeat the residual germicide test just prior to treatment initiation to
allow detection of any “rebound” of germicide. This is particularly a
concern if fluid circulation through the circuit and dialyzer is stopped,
as may happen when a patient is late coming to treatment.
If facility practice is to discard the priming solution by “bleeding
patients on,” policy and practice must reflect a requirement that a staff
member constantly attend that patient while the venous line is open as
blood fills the extracorporeal circuit, to prevent accidental blood loss.
Generally, manufacturers of dialyzers labeled for reuse address the
need to discard the prime solution by advising users to replace the
saline bag used for priming and refresh all fluid in the extracorporeal
circuit with saline from the new bag prior to beginning patient
treatment.
V354
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
13 Monitoring
13.1 Dialysis: patient’s clinical course
The clinical course of the patient should be observed and
recorded during each dialysis to identify possible
complications caused by new or reprocessed dialyzers.
Dialyzer failures should be recorded and systematically
evaluated. Applicable home dialysis patients and their
assistants should be instructed in the appropriate
observation, recording requirements, and reporting
procedures.
Additional Guidance:
Adequacy, fluid removal, anemia management and patterns of
infection may be related to poor reprocessing practices. If reuse is
being done for home patients, which is rare, those patients or their
dialysis helpers must be instructed in and fully cognizant of their
responsibilities for reuse.
V355
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Final Version 1.1 Page 152 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
13.2 Symptoms
13.2.1 Fever and chills: other symptoms
Patients’ temperatures should be measured and recorded
at least before and after dialysis with new and
reprocessed dialyzers. A temperature of over 37.8° C or
100° F, taken orally, or chills should be reported to the
physician, [advanced practice registered nurse or
physician assistant]. Any patient with an unexplained
fever and/or chills should be evaluated for the possibility
of a pre-existing infection (e.g., [at an] access site). The
dialysis procedure should also be evaluated to rule out
the use of contaminated water, errors in treatment
delivery, or incorrect dialyzer reprocessing.
13.2.2 Other symptoms
Other unexplained symptoms such as pain in the blood-
access arm at the onset of dialysis should be evaluated by
the physician, [advanced practice registered nurse or
physician assistant] and consideration given to the
possibility that the symptom may be attributed to
residual disinfectant in the new or reprocessed dialyzer
or contamination of the water treatment equipment.
Suspected reactions to the residual germicide should
prompt reevaluation of the rinsing procedure and a test
for residual germicide (see [AAMI] 12.4.1).
Recommended Practice
A.13.2 Symptoms
Evaluation by a physician is required to determine whether symptoms
might constitute an adverse reaction to the reprocessed dialyzer
because symptoms during dialysis are commonly the result of other
factors, such as infections not attributable to dialysis, and to
hypovolemia. First-use syndrome is a symptom complex characterized
by nervousness, chest pain, back pain, palpitations, pruritus, and other
usually mild symptoms, occurring minutes following the initiation of
dialysis with a new dialyzer. The syndrome is defined by some
authorities to include the anaphylactoid reaction occurring usually
immediately after the initiation of dialysis in some patients using
dialyzers sterilized with ethylene oxide. In addition to first-use
syndrome, serious reactions have been reported in patients taking
ACE inhibitors and dialyzed on certain synthetic membranes. This
reaction is now known to involve increased bradykinin release
accompanied by suppression of bradykinin degradation.
Additional Guidance:
Physicians or non-physician practitioners (i.e., advanced practice
registered nurses or physician assistants) functioning in lieu of
physicians are responsible to evaluate the symptoms discussed in this
regulation. Patient temperatures must be checked pre and post
treatment, and signs of infection must be evaluated for any potential
relationship to reprocessing/reuse.
One of the symptoms of germicide infusion is severe pain and burning
in the patient's vascular access. Patients may interpret pain in the
vascular access at the onset of dialysis as pertaining to needle
insertion pain.
V356
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
13.2.3 Recording: adverse events dialyzer complaint
Additional Guidance:
In dialyzer reprocessing, the term “complaint” refers to deviations
from expected outcomes (e.g. dialyzer failures, patient reactions,
Final Version 1.1 Page 153 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
log
Any significant events such as the occurrence of
symptoms listed in [AAMI] 13.2.1 and 13.2.2 should be
recorded on an incident report form which would include
the results of any evaluations conducted by the physician
and others, and the event should be considered for
reporting to the manufacturer(s) in accordance with the
FDA’s Medical Device User Reporting procedures. The
resolution of actual or suspected problems caused by
reprocessed dialyzers should be indicated. This form
should be kept in the complaint investigation record file
(see [AAMI] 4.5).
4 Records
4.5 Complaint investigation record
Records shall be kept of all complaints by patients and
staff members about failures of preprocessed and
reprocessed dialyzers or possible adverse reactions to
any dialyzers; the results of a comprehensive
investigation of these alleged problems; and, if
appropriate, the corrective actions taken. The records
shall be reviewed periodically for trends of adverse
reactions. Compliance with the FDA’s Medical Device
User Reporting procedures shall be demonstrated.
blood leaks), as well as to patient complaints related to reused
dialyzers.
The facility must maintain a record of dialyzer complaints. Each
complaint should be investigated, and any reuse incidents reported in
the QAPI records with corrective actions as indicated.
Responsible staff (e.g., the chief technician, area technical manager,
nurse administrator, medical director) should consider if there have
been any trends in complaints, and take indicated action. This
information should be incorporated into the facility’s QAPI program.
Refer to V635.
Facility staff must comply with the FDA’s Medical Device User
Reporting requirements. Refer to V383.
V357
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
13.3 Dialyzer failures: blood leaks recorded
Dialyzer blood leaks should be recorded in a log kept in
the complaint investigation record file (see [AAMI] 4.5).
If there is excessive deviation from the expected
performance, testing should be repeated (see [AAMI]
11.3.1) and appropriate adjustments made in the
reprocessing procedure.
Additional Guidance:
The complaint investigation records should include reports of any
blood leaks.
Final Version 1.1 Page 154 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V358
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
13.4 Clinical results: monitoring Kt/V
Monitoring of relevant patient results is recommended to
ensure that all parameters relating to hemodialyzer
clearance are being met. Specifically, examination of
urea reduction ratio (URR) or Kt/V over time is
necessary. The failure of these results to meet the
expectations of the dialysis prescription should be
investigated. Deterioration of a patient’s clinical
condition or variability of routine dialysis procedures
(heparinization, ultrafiltration, erythropoietin
requirement) requires investigation of all practices,
including reuse. Reports of investigations should be filed
in the complaint log.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.13.4 Clinical results
Critical assessment of chemistries and the delivered dose of dialysis
(Kt/V or urea reduction ratio), as is done monthly, provides a clear
trend line to assess treatment. This scrutiny of the patient’s treatment
and course is the primary confirmation that hemodialyzer performance
anticipated from TCV or other indirect estimation is accurate and
adequate. The overall effectiveness of the entire treatment, not only
the clearance of the dialyzers, is measured. No other measure of the
effectiveness of new or reused dialyzers is as clear or relevant. Trend
lines developed from this data characterize the quality of therapy. If
the practitioner has concerns for “middle molecules” or other clinical
parameters, these factors should also be part of the assessment of the
delivered therapy.
There are many reasons for an apparent reduction in the mass transfer
of urea, other than decreased hemodialyzer clearance as a result of
inadequate reprocessing (such as recirculation, decreased dialysis time
or blood flow rate, or an inappropriate dialysis prescription). To
document adequate mass transfer parallel measurements of pre- and
post-creatinine levels are helpful. When problems develop with any
patient or group of patients, monitoring intensity should be increased,
and other methods should be used to analyze the problem and define
corrective action.
V359
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
11 Reprocessing
11.3.2 Ultrafiltration: monitoring patient’s weight
If the expected weight loss is not achieved with the
reprocessed dialyzer, the reprocessing method and all
other weight removal variables should be reevaluated.
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
11.3.2 Ultrafiltration
In vitro ultrafiltration coefficients should not be used to predict in
vivo results.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
A.11.3.2 Ultrafiltration
Final Version 1.1 Page 155 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Ultrafiltration rate (UFR) is the flow rate of fluid that passes through
the membrane under a given pressure gradient at a given temperature.
It is the product of the ultrafiltration coefficient of the hemodialyzer
(K
UF
) and the transmembrane pressure. The K
UF
, and thus the UFR at
a given transmembrane pressure, may be affected by changes in the
intrinsic permeability of the membrane, the surface area of the
membrane, and the presence of hydraulically resistive deposits on the
membrane. Cleaning agents, such as sodium hypochlorite, may affect
the intrinsic water permeability of many types of dialysis membranes.
In vitro K
UF
is not recommended to predict in vivo ultrafiltration
performance because the former overestimates the latter in hollow-
fiber hemodialyzers. This difference occurs in part because of the
additional hydraulic resistance of the formed elements and proteins in
blood.
Additional Guidance:
Assessment for compliance with this requirement should find patients
are weighed before and after each treatment. Missed weights should
be rare and include an explanation for the weight not being obtained.
Repeated entries of “unable to stand” should result in a change in the
plan of care to allow determination of pre- and post-treatment
weights.
V360
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14 Quality assurance: general/records/trend analysis
The criteria chosen as the internal standards of a facility
shall be documented in its policy and/or procedure
manual. Process review should be part of the activity of
the individual carrying out the process, and oversight of
that review by another qualified member of the staff or a
group of staff members should affirm, modify, or repeat
these observations to confirm or improve the process.
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
It is the responsibility of all staff members to critically scrutinize all
materials, practices, operations, and outcomes. Criteria that serve as
the scale for evaluation may be drawn from local experience and
practice relative to the specific activity under review, consensus
documents such as AAMI guidelines or standards, aggregated
regional or national data, or other accepted norms.
AAMI Rationale for the Development and Provisions of this
Recommended Practice
Final Version 1.1 Page 156 of 299
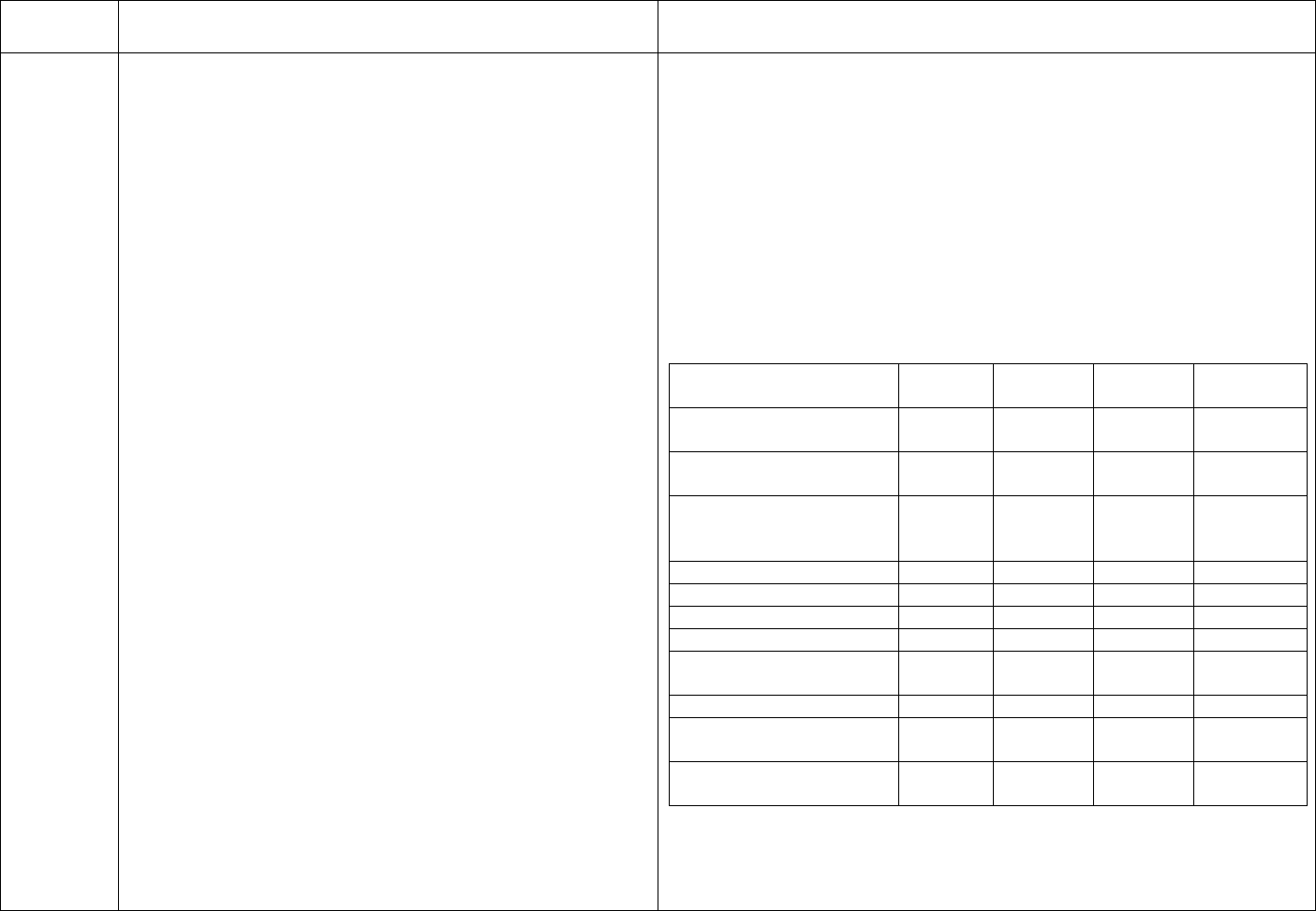
TAG
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
NUMBER
Clinical outcomes serve as the most important indicator
A.14 Quality assurance
of quality of all dialysis treatment practices including The FDA’s 1987 compliance policy guide (7124.16) advises reuse
reuse. Final oversight is the responsibility of the medical practitioners to establish the following: (a) adequate device cleaning
director. See Table 2 for a summary of the audit and sterilization; (b) the lack of adverse effects on device quality or
schedule. physical characteristics; and (c) certainty that the device remains safe,
reliable, and effective for its intended use. The AAMI RDD
14.1 Records
Committee believes that compliance with those recommendations
A record of review, comments, trend analysis, and necessitates use of regularly examined reprocessing procedures that
conclusions arising from QA practices serve as a are based on methods of demonstrated effectiveness and are carried
foundation for future review and as documentation to out under conditions safe to the patient and the personnel.
external evaluation.
Table 2—Quality assurance audit schedule
Monthly
Quarterly
Semi-
Annually
Annually
Patient information policy
x
(14.3)
Equipment manuals and
x
procedures (14.4)
Equipment maintenance
x
and repair policies
(14.4)
Environmental safety (8.1)
x
Environmental safety (8.2)
x
Environmental safety (8.4)
x
Reprocessing supplies (9)
x
Water treatment* (11.4.1.5)
x
Hemodialyzer labeling (10)
x
Reprocessing procedures**
x
x
(14.8)
Procedures for preparation
x
for dialysis (14.9)
* More frequent monitoring may be required initially as described in
11.4.1.5.
** These functions may allow for the less frequent review period
indicated according to the circumstances specified in their respective
Final Version 1.1 Page 157 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
sections.
Numbers in parenthesis refer to AAMI sections.
Additional Guidance:
Reuse audits must be performed on the required schedule and reported
in the QAPI activities. For many of the audits, there is a two tier
system of review required: the review of the process by the person
assigned (i.e. reprocessing by the reuse technician), and oversight of
that review by another person qualified to do so (i.e. the technical
supervisor observing the reuse technician performing reprocessing).
If the facility participates in a centralized reprocessing program, the
QA audits done in the reprocessing facility must be provided to the
patient treatment facility and reviewed as part of the QAPI of that
facility. Any complaints related to the reprocessing of dialyzers would
need to be reported to the patient treatment facility sending the
applicable dialyzers.
V361
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.2 Schedule of quality assurance activities: medical
director responsible
Problems in a particular aspect of operations should be
reviewed and tracked until a solution is in place and
demonstrated to be effective. The medical director is
responsible for scheduling review, endorsing findings,
and, when appropriate, implementing changes.
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003
14.2 Schedule of quality assurance activities
High-volume tasks that are recognized as hazardous should have
frequent (weekly or daily) oversight. Practices with little potential for
harm may need critical scrutiny on only a quarterly or annual basis.
Additional Guidance:
Reuse procedures/tasks/logs must be audited according to Table 2
(above at V360). The medical director is responsible to assure these
audits are done, and may not routinely authorize less frequent audits
than specified in this table.
V362
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.3 Patient considerations: audit annually
Personnel should audit at least annually compliance with
the facility’s policy to inform patients of the facility’s
Final Version 1.1 Page 158 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
reuse practices.
V363
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.4 Equipment Manuals and Procedures: audit
annually & prn
Designated staff members should audit written
procedures and manuals for relevance at least annually
and whenever adverse findings could be attributed to
equipment failure. Designated staff should also audit
maintenance and repair policies at least annually.
Additional Guidance:
Centralized reprocessing requires that relevant procedures and
manuals be audited at both the reprocessing site and the user facility.
V364
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.5 Physical plant and environmental safety
considerations: audit annually
Designated staff members should audit the provisions of
[AAMI] 8.1, [Reprocessing area and ventilation], at least
annually. The provisions of [AAMI] 8.2, [Storage area],
and [AAMI] 8.4, [Personnel protection] should be
audited quarterly.
Additional Guidance:
There must be documentation to support that designated staff
conducted an annual review of the implementation of germicide air
testing procedures, and the physical condition of the reprocessing
area.
Quarterly evaluations of the area where dialyzers and supplies are
stored are required, as well as evaluation of the implementation of
policies for use of PPE and Standard Precautions when direct care and
reprocessing staff are working with reprocessed dialyzers.
Centralized reprocessing requires that this audit be done at the
reprocessing site as well as at the user facility.
V365
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.6 Reprocessing supplies: audit semiannually
Designated staff members should audit the provisions of
[AAMI] section 9[: Reprocessing supplies:
Specifications and testing, and inventory control] at least
semiannually.
V366
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.7 Hemodialyzer labeling: audit quarterly
Additional Guidance:
AAMI Section 10 includes the following: Hemodialyzer labeling,
Time of labeling, Label composition, and Information recorded. These
Final Version 1.1 Page 159 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Designated staff members should audit the provisions of
[AAMI] section 10
audits should be recorded quarterly.
Centralized reprocessing requires that this audit be done at the
reprocessing site as well as at the user facility.
V367
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.8 Reprocessing: audit monthly; semiannually
Initially, designated staff members should audit the
written procedures for the various steps in this process
and verify implementation at least monthly.
Subsequently, semiannual audits may be sufficient if
there is a documented history of favorable results. Trend
analysis should be performed.
Additional Guidance:
For a new reuse program, monthly audits of reprocessing steps must
be done at a minimum. For an established program, audits of the
practice of reprocessing must be done semiannually, unless problems
are identified, which would require more frequent audits until a
pattern of compliance is established.
Centralized reprocessing requires that the reprocessing site perform
these audits and report the results to all user facilities.
V368
ANSI/AAMI RD47:2002/A1:2003 Requirements as
Adopted by Reference 42 CFR 494.50 (b)(1)
14.9 Preparation for dialysis: audit quarterly
At least quarterly, designated personnel should audit the
written procedures and verify their implementation. At
least quarterly, designated staff members should verify
the tests for the presence of germicide and the test for
residual germicide by using positive and negative control
solutions, on those products that are not specifically
intended for use in dialyzer reuse germicide indicator
tests and which have not been cleared by the FDA.
End AAMI RD:47 Requirements
Additional Guidance:
This regulation requires at least quarterly audits (observations) of the
set-up for dialysis, including testing for presence of germicide, testing
for residual germicide, and verification of the patient identity with the
reprocessed dialyzer.
Responsible staff (e.g., nurse manager, administrator, medical
director) must be able to describe these audits, provide documentation
the audits were accomplished, and provide evidence that any concerns
identified were addressed.
Facilities that participate in centralized reprocessing are responsible
for performing the audits of the steps in the reuse process which occur
during preparation for dialysis when reprocessed dialyzers are being
prepared for reuse.
V378
(2) Reprocess hemodialyzers and bloodlines–follow
DFU
(i) By following manufacturer’s recommendations; or
(ii) Using an alternate method and maintaining
documented evidence that the method is safe and
Each manufacturer of dialyzers for multiple use is required by FDA to
provide at least one acceptable reprocessing method with at least one
germicide. The facility may use that method/germicide or choose an
alternate method. If the facility has chosen an alternate method, there
must be documentation that the chosen method has been validated as
Final Version 1.1 Page 160 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
effective.
safe and effective.
V379
Dialyzers not exposed to more than one germicide
(3) Not expose hemodialyzers to more than one chemical
germicide, other than bleach (used as cleaner in this
application), during the life of the dialyzer. All
hemodialyzers must be discarded before a different
chemical germicide is used in the facility.
No tag
(c) Standard: Monitoring, evaluation, and reporting
requirements for the reuse of hemodialyzers and
bloodlines. In addition to the requirements for
hemodialyzer and bloodline reuse specified in
paragraphs (a) and (b) of this section, the dialysis facility
must adhere to the following:
(1) Monitor patient reactions during and following
dialysis.
This tag is informational, as this requirement is addressed in the
ANSI/AAMI RD:47, section 13, at tags V354 and V355.
V381
Blood/dialysate cultures for adverse patient reactions
(2) When clinically indicated (for example, after adverse
patient reactions), the facility must–
(i) Obtain blood and dialysate cultures and endotoxin
levels; and
The facility must have a standardized procedure to ensure blood and
dialysate cultures and dialysate endotoxin testing are obtained in the
event of a patient reaction possibly related to dialyzer reprocessing
and/or reuse.
V382
Cluster of adverse patient reactions = suspend reuse
(ii) Undertake evaluation of its dialyzer reprocessing and
water purification system. When this evaluation suggests
a cluster of adverse patient reactions is associated with
hemodialyzer reuse, the facility must suspend reuse of
hemodialyzers until it is satisfied the problem has been
corrected.
In this context, “cluster” refers to a group of hemodialysis patients
suspected of having adverse reactions that could be clinically related
to dialyzer reprocessing and/or reuse practices.
Responsible staff (e.g., chief technician, area technical manager,
medical director) must be able to describe actions to be taken if a
group of patients experience adverse reactions potentially related to
reprocessing/reuse. If a cluster of adverse patient reactions associated
with reprocessing/reuse was identified, dialyzer reprocessing/reuse
should have been suspended, pending investigation.
V383
FDA reporting of adverse outcomes
(iii) Report the adverse outcomes to the FDA and other
Federal, State or local government agencies as required
The dialyzer manufacturer is not responsible for adverse outcomes
related to reprocessing/reuse. The facility would be responsible for
reporting any adverse outcomes potentially related to
Final Version 1.1 Page 161 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
by law.
reprocessing/reuse, as required by law. Facility policy should address
adverse occurrence reporting.
V400
§ 494.60 Condition: Physical environment.
This Condition addresses the requirements related to the building and
equipment of the facility and incorporates by reference the ambulatory
health care occupancy provisions of the 2000 edition of the Life
Safety Code of the National Fire Protection Association. This
Condition also includes requirements for emergency preparedness for
medical and non-medical issues.
The primary survey task used in assessing compliance with this
Condition is observation: of the environment, equipment maintenance,
and readiness of emergency equipment. Survey of the requirements
found at V400-V416 of this Condition will be done by the health and
safety surveyors who conduct the usual ESRD surveys. Survey of the
requirements related to Life Safety Code (LSC), found at V417-V418,
will be done by specific surveyors trained as fire specialists and may
be conducted at a separate time.
Noncompliance at the Condition level should be considered if
identified deficient practices are pervasive, serious in nature, or a
potential risk to health and safety. Examples of potential Condition
level non-compliance would include, but not be limited, to:
• Serious deficient practices in the construction or maintenance of
the physical environment and/or equipment which have or are
likely to have an impact the health and safety of patients, staff or
the public;
• Serious deficient practices in the development and/or
implementation of an effective program for dealing with patient
medical emergencies and/or potential disaster situations.
V401
The dialysis facility must be designed, constructed,
equipped, and maintained to provide dialysis patients,
staff, and the public a safe, functional, and comfortable
treatment environment.
“Safe environment” means that there are no obstacles which would
present risks for trips and falls, such as loose floor tiles; no areas that
would pose infection control risks, such as broken work surfaces; and
no outside doors that remain propped open allowing entry of
Final Version 1.1 Page 162 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
unauthorized individuals, insects, or animals or creating a hazard in
the event of fire.
“Functional environment” means that all systems in the building, such
as lighting, heating and air conditioning, are operational.
“Comfortable environment” means providing sufficient space for
patient privacy and access for needed equipment; and maintaining a
reasonable noise level, e.g., requiring the use of earphones when
televisions or other entertainment devices are in use which may
disturb others. Monitoring a comfortable temperature is addressed at
V405.
V402
(a) Standard: Building. The building in which dialysis
services are furnished must be constructed and
maintained to ensure the safety of the patients, the staff
and the public.
The dialysis facility building must be constructed in accordance with
applicable State and local building codes. The plumbing, electrical
and heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems must be
appropriately constructed and effectively maintained.
All buildings and building systems must be maintained free from
defects and/or hazards to ensure safety and functionality. Integrity of
all surfaces, (e.g., countertops, floors, walls) must be intact, clean and
free from damage. Intact surface integrity allows for effective
cleaning and limits the potential for microbial growth on a porous
surface.
Systems to assure patient safety must be in place, such as a method for
patients to call for help from the restrooms and exam rooms. Access
to patient treatment areas, reprocessing areas, water treatment
systems, supply storage and dialysis equipment must be restricted to
authorized personnel only. Access limitation does not preclude visits
or tours by individual(s) authorized and supervised by facility
personnel.
V403
(b) Standard: Equipment maintenance. The dialysis
facility must implement and maintain a program to
All equipment used at the dialysis facility and dialysis equipment used
by home dialysis patients must be maintained in safe and functional
Final Version 1.1 Page 163 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
ensure that all equipment (including emergency
equipment, dialysis machines and equipment, and the
water treatment system) are maintained and operated in
accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
working condition. The facility’s program for preventive maintenance
and repair of all equipment must be in accordance with the equipment
manufacturer's instructions.
Staff must operate and maintain the equipment in accordance with
manufacturer’s instructions. Malfunctioning machines awaiting repair
must be removed from service and labeled or tagged to prevent use.
The facility should have a plan for the operation and routine
maintenance of at least the following equipment and equipment
systems:
Hemodialysis delivery system:
• High flux dialyzers may only be used with machines specified by
the manufacturer as capable of accurately monitoring and
controlling fluid removal
• If heparin pumps are incorporated into the delivery system, the
pumps must be maintained as clean and functional.
• As required by manufacturers, testing of safety features, e.g.,
alarms, pressure holding tests, and independent verification of
dialysate pH and conductivity should be conducted prior to each
dialysis treatment.
“Dummy” drip chambers:
• “Dummy” drip chambers are fluid-filled chambers that are used to
bypass the dialysis machine’s air detectors.
• The practice of using a “dummy” drip chamber to prepare a
dialysis machine for patient use is hazardous to patient safety and
risks the undetected infusion of air into a patient if the “dummy”
drip chamber is not removed at the initiation of dialysis.
• The presence and availability of “dummy” drip chambers in the
hemodialysis patient treatment area is considered an immediate
and serious threat to patient health and safety.
Final Version 1.1 Page 164 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
• The use of “dummy” drip chambers is acceptable only for
machine maintenance purposes and only for use outside of the
patient treatment area.
Water treatment system:
Requirements for monitoring and maintenance of the water treatment
system are incorporated into the Condition for Water and dialysate
quality at § 494.40 and should be cited there.
Dialyzer reprocessing system:
Requirements for monitoring and maintenance of dialyzer
reprocessing systems are incorporated into the Condition for Reuse of
hemodialyzers and bloodlines at § 494.50 and should be cited there.
Ancillary equipment:
• Ancillary equipment may include, but is not limited to: functional
and clean patient scales, centrifuge, refrigerators, incubators for
in-house performance of water/dialysate cultures, emergency
generators, blood pressure monitoring equipment, infusion pumps,
patient thermometers, eye wash stations, conductivity and pH
meters, Hoyer lifts, and equipment required to provide in-house
laboratory testing (e.g. blood glucose meters, heat blocks,
equipment for activated clotting times [ACT], supplies for testing
for occult blood and hematocrit levels).
• Maintenance of refrigerators should include the monitoring of
temperatures to assure these are appropriate for the items stored.
• If a generator is present, documentation should be available
regarding testing and maintenance per manufacturer’s instructions.
• Records should be available regarding the daily cleaning and
testing and periodic calibration of pH and conductivity meters as
recommended by the manufacturer.
• Documentation of periodic calibration of patient scales, blood
Final Version 1.1 Page 165 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
pressure devices, blood volume monitors, and laboratory
equipment, as applicable, should be available.
Emergency equipment:
• Emergency equipment as referenced at V413 of this section
should be clean, functional, and accessible. Use V413 for the lack
of required emergency equipment; use this tag for failure to
maintain the emergency equipment.
Furniture:
• Patient treatment chairs, facility wheelchairs, and waiting area
chairs must be maintained to allow effective cleaning/disinfection
• Torn upholstery must be repaired or replaced; broken mechanisms
(e.g. footrests, reclining levers) must be repaired or the equipment
removed from use.
The facility equipment maintenance program should include
documentation regarding all equipment or devices used for home
patients, whether maintained by the facility or by durable medical
equipment suppliers (DME). Refer to the Condition for Care at home
at V597 if problems with the maintenance and/or exchange of home
dialysis equipment are identified.
V404
(c) Standard: Patient care environment.
(1) The space for treating each patient must be sufficient
to provide needed care and services, prevent cross-
contamination, and to accommodate medical emergency
equipment and staff.
There are no specific square-footage requirements for dialysis
treatment areas unless specified by state or local regulations.
“Sufficient space” to provide needed care would allow space for:
• All dialysis equipment, supplies and items for each patient;
• Caregivers to provide emergency care including cardiopulmonary
resuscitation (CPR), the use of emergency equipment including
access to needed supplies, stretcher and emergency personnel; and
• The provision of personal privacy when needed, i.e., sufficient
space to allow for use of some type of privacy screens. Note that
Final Version 1.1 Page 166 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
privacy requirements are addressed in V406 of this section, and
under the Condition for Patients’ rights at V454.
“Sufficient space” to prevent cross-contamination would allow space
to:
• Prevent blood or body fluid spatters from one patient or station to
another;
• Prevent contact between machines, chairs and other equipment;
• Reasonably accommodate patient belongings;
• Provide privacy and aseptic care of catheters including dressing
changes;
• Safely dispose of bodily wastes/fluids and hazardous waste; and
• Readily access hazardous waste receptacles.
The space around the hemodialysis stations should be sufficient for all
of the above. The space allowance should take into consideration the
space taken up by patients’ dialysis chairs when reclined with foot
rests up.
V405
(2) The dialysis facility must:
(i) Maintain a comfortable temperature within the
facility; and
(ii) Make reasonable accommodations for the patients
who are not comfortable at this temperature.
The facility must make reasonable efforts to provide a comfortable
environment for patients and staff, in spite of conflicting perceptions
of “comfortable.” Staff's use of personal protective equipment paired
with the restricted activity levels of patients and the nature of dialysis
treatments affect the perceptions of what constitutes a “comfortable”
temperature. Generally, staff members are hot and patients are cold.
The facility must develop an acceptable plan to determine the
temperature in the patient treatment area. An “acceptable plan” could
be to set the thermostat for a reasonable temperature, inform patients
and staff of the set temperature, and suggest patients may want to
bring a light blanket. It is not acceptable to allow the temperature to
be randomly raised or lowered, dependent on one person’s comfort
level. If some areas of the treatment room are served by a different
thermostat, the facility may be able to set the thermostats at different
Final Version 1.1 Page 167 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
levels based on patients’ desires.
“Reasonable accommodations” would include moving patients who
are not comfortable with the set temperature to an area of the room
which is determined to be more comfortable in temperature due to the
location of vents, windows, etc. When cold, some patients find it
helpful to use a glove for the hand on their access arm, others find
wearing a cap helpful.
If patients choose to use a blanket or other covering, their vascular
access site, bloodline connections, and face must be visible
throughout the treatment. A head covering on a patient is acceptable,
as are gloves. If you note a problem in this area, refer to V407.
V406
(3) The dialysis facility must make accommodations to
provide for patient privacy when patients are examined
or treated and body exposure is required.
Privacy must be provided for the use of a bedpan or commode during
dialysis, initiating and discontinuing treatment when the vascular
access is placed in an intimate area, for physical exams, and for
sensitive communications.
There should be sufficient numbers of privacy screens or other
methods of visual separation available and used to afford patients full
visual privacy when indicated. Exam rooms should have a door or
other method to ensure privacy can be provided. Arrangements for
private conversations may need to be outside of the patient treatment
area in a private location.
V407
(4) Patients must be in view of staff during hemodialysis
treatment to ensure patient safety, (video surveillance
will not meet this requirement).
Each patient, including his/her face, vascular access site, and
bloodline connections, must be able to be seen by a staff member
throughout the dialysis treatment. Allowing patients to cover access
sites and line connections provides an opportunity for accidental
needle dislodgement or a line disconnection to go undetected. This
dislodgement or disconnection could result in exsanguination and
death in minutes.
V408
(d) Standard: Emergency preparedness. The dialysis
facility must implement processes and procedures to
Medical emergencies which may be anticipated in the dialysis setting
include, but are not limited to, cardiac arrest, air embolism, adverse
Final Version 1.1 Page 168 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
manage medical and non medical emergencies that are
likely to threaten the health or safety of the patients, the
staff, or the public. These emergencies include, but are
not limited to, fire, equipment or power failures, care-
related emergencies, water supply interruption, and
natural disasters likely to occur in the facility’s
geographic area.
drug reactions, suspected pyrogen reactions, profound hypotension or
hypertension and significant blood loss. Direct care staff should be
aware of how to recognize and respond to emergent patient medical
conditions.
Regularly-scheduled treatments are essential for dialysis patients. In
the event of a natural or man-made disaster, immediate action must be
taken to ensure prompt restoration of these treatments or to plan for
the safe transfer of patients to alternate location(s) for their treatments.
Each dialysis facility must have a facility-specific disaster/emergency
plan and be able to respond accordingly. Disaster/emergency plans
should address failure of basic systems such as power, source water,
air conditioning or heating systems as well as treatment specific
failures such as the facility water treatment system or supply delivery.
Dialysis facilities must consider the potential of and develop a plan
for natural disasters in their geographic locations (e.g., hurricanes in
FL and on the Gulf Coast, earthquakes in CA, ice storms in the
northern states, floods near rivers) and man-made disasters (e.g., fires,
power or water supply disruptions). Responsible staff and patients
should be knowledgeable regarding the emergency plan should the
facility be non-operational after a disaster.
Non-expired emergency/evacuation supplies, including site dressings,
saline, IV tubing, should be available to accommodate evacuated
hemodialysis patients.
V409
(1) Emergency preparedness of staff. The dialysis facility
must provide appropriate training and orientation in
emergency preparedness to the staff. Staff training must
be provided and evaluated at least annually and include
the following:
(i) Ensuring that staff can demonstrate a knowledge of
emergency procedures, including informing patients of—
Orientation for all staff must include emergency preparedness
training, and annual training thereafter. “Evaluated” would require
some feedback to ensure that the training was effective: either a
passing score on a written test or demonstrated competency in the
expected actions in an emergency situation.
Staff must have sufficient knowledge of emergency procedures to
Final Version 1.1 Page 169 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(A) What to do;
(B) Where to go, including instructions for occasions
when the geographic area of the dialysis facility must be
evacuated;
(C) Whom to contact if an emergency occurs while the
patient is not in the dialysis facility. This contact
information must include an alternate emergency phone
number for the facility for instances when the dialysis
facility is unable to receive phone calls due to an
emergency situation (unless the facility has the ability to
forward calls to a working phone number under such
emergency conditions); and
(D) How to disconnect themselves from the dialysis
machine if an emergency occurs.
educate patients/designees about how to handle emergencies, both in
and outside of the facility. At a minimum, all of the listed components
must be included in the staff and patient education programs.
If problems are identified regarding training patients in emergency
preparedness, refer to V412.
V410
(ii) Ensuring that, at a minimum, patient care staff
maintain current CPR certification; and
All direct patient care staff (i.e., nurses and patient care technicians)
must have current basic CPR certification.
V411
(iii) Ensuring that nursing staff are properly trained in the
use of emergency equipment and emergency drugs.
The minimum emergency equipment required is defined in V413. The
emergency drugs to be kept onsite may be determined by the medical
director and defined by facility policy.
If the facility has chosen to use a defibrillator (rather than an
Automated External Defibrillator [AED]), recognize that use of a
defibrillator requires recognition of arrhythmias and knowledge of
protocols to properly use the defibrillator. An AED can be used by
any person with appropriate instruction. If a traditional defibrillator is
present, written protocols approved by the medical director and a staff
member trained and competent to use that equipment should be
present whenever patients are dialyzing in the facility.
V412
(2) Emergency preparedness patient training. The
facility must provide appropriate orientation and training
to patients, including the areas specified in paragraphs
(d)(1)(i) of this section.
Patients must have sufficient knowledge of emergency procedures to
know how to handle emergencies, both in and out of the facility. Refer
to V409 for the required areas of patient emergency education.
Patients/designees should be instructed about the facility
Final Version 1.1 Page 170 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
disaster/emergency plan. Patients/designees should know how to
contact their facility during an emergency. Facilities should provide
patients/designees with an alternate emergency phone number in case
the facility phone is not answered and/or the facility is not functioning
during a disaster. The patients/designees should be able to describe
what they would do if they were not able to get to their regular
dialysis treatment, including dietary precautions. Patients/designees
should understand they must seek treatment promptly in the event that
a natural or man-made disaster results in the closure of their facility.
For emergencies occurring in the dialysis facility, patients should be
able to verbalize how they would disconnect themselves from the
machine and evacuate the facility, or if unable, how they will be
evacuated. The facility should have a system in place to identify
patients who will need assistance in disconnection and evacuation
during an emergency.
Medical records should include evidence of education in emergency
evacuation and emergency preparedness, to include some measure of
patient understanding, such as return teaching or demonstration.
V413
(3) Emergency equipment.
Emergency equipment, including, but not limited to,
oxygen, airways, suction, defibrillator or automated
external defibrillator, artificial resuscitator, and
emergency drugs, must be on the premises at all times
and immediately available.
The emergency equipment, as listed, must be clean, accessible, and
ready to use at all times.
“On the premises” and “immediately available” may include the use
of an emergency response team if the facility is located inside a
building which includes such a response team (e.g., a hospital-based
facility). The response time of personnel and equipment should be
demonstrated as being less than 4 minutes.
Refer to V403 for problems with maintenance of emergency
equipment.
V414
(4) Emergency plans. The facility must-
(i) Have a plan to obtain emergency medical system
All members of the facility staff must be able to demonstrate
knowledge of how to obtain emergency medical assistance, e.g., 911
Final Version 1.1 Page 171 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
assistance when needed;
system or equivalent for the locality.
V415
(ii) Evaluate at least annually the effectiveness of the
emergency and disaster plans and update them as
necessary; and
This annual evaluation process should include review of any medical
or non-medical emergencies that have occurred during the year to
determine opportunities for improvement, as well as re-evaluation of
the plans/procedures for current appropriateness and feasibility.
The facility must conduct drills or mock emergencies at least annually
in order to determine the staff's skill level/educational needs and
effectiveness of their plan.
V416
(iii) Contact its local disaster management agency at
least annually to ensure that such agency is aware of
dialysis facility needs in the event of an emergency.
The facility must contact and develop a communicative relationship
with the local disaster management agency. This relationship will help
expedite restoration of interrupted services due to an emergency or
disaster. There should be some documented evidence of this contact.
In order to ensure life saving dialysis services will be available in the
event of an emergency or disaster, facilities should collaborate with
their ESRD Network, suppliers, utility service providers, and their
State agencies for survey and for emergency preparedness as well as
with other dialysis facilities. Resources available from the Kidney
Community Emergency Response (KCER) Coalition can assist
facilities in meeting this requirement.
V417
(e) Standard: Fire safety.
(1) Except as provided in paragraph (e)(2) of this section,
by February 9, 2009. The dialysis facility must comply
with applicable provisions of the 2000 edition of the Life
Safety Code of the National Fire Protection Association
(which is incorporated by reference at § 403.744 (a)(1)(i)
of this chapter).
Effective February 9, 2009, dialysis facilities must comply with
Chapter 20 (for new dialysis facilities) or Chapter 21 (for existing
dialysis facilities) of the 2000 edition of the Life Safety Code (LSC)
for Ambulatory Health Care Occupancies of the National Fire
Protection Association (NFPA), 101.
An “existing” facility is defined as a facility that has received
approval of all of the required building permits (or completed all of
the plan reviews in jurisdictions that do not require building permits)
prior to February 9, 2009. A “new” facility is defined as a facility that
has received approval of all of its building permits (or completed all
of its plan reviews in jurisdictions that do not require building
Final Version 1.1 Page 172 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
permits) after February 9, 2009. A facility that is undergoing major
renovations or a facility that is relocating after February 9, 2009, is
also classified as a “new” facility.
These chapters of the LSC were written for ambulatory health care
occupancies. Because dialysis facilities do not use anesthesia and only
use life-support equipment intermittently for emergency purposes,
certain sections of these chapters do not apply. The non-applicable
portions are part of section 20.2.9.2 and the part of section 21.2.9.2
which require the facility to provide an “essential electrical system
(EES)” in accordance with NFPA 99 if “general anesthesia or life
support equipment” is used. “Life support equipment” is defined as
electrically-powered equipment whose continuous operation is
necessary to maintain a patient’s life.
Alternatively, Chapter 5 of the LSC allows a dialysis facility a
performance-based option for meeting the LSC occupant protection,
structural integrity, and systems effectiveness goals and objectives.
The Fire Safety Evaluation System (FSES), NFPA 101A, a fire safety
equivalency system, cannot be used in place of compliance with the
requirements of Chapters 20/21 New/Existing Ambulatory Health
Care Occupancies, 2000 edition, NFPA 101 since there is no FSES for
Ambulatory Health Care Occupancies.
A dialysis facility is classified as an “ambulatory health care
occupant.” However, a dialysis facility may be located in a mixed
occupancy building. If a dialysis facility is located in a building with
other tenants, it must be separated from the other tenants on the same
floor by a one-hour fire wall. For purposes of this regulation, when a
portion of the dialysis facility is used intermittently by another entity
(e.g., an exam room is used for the nephrologist’s office practice) it is
not intended that the portion used intermittently would be separated
Final Version 1.1 Page 173 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
from the dialysis facility by a one-hour fire wall.
If the dialysis facility is located within a hospital, but not separated
from the hospital by 2-hour fire wall construction, the dialysis facility
must meet the hospital LSC requirements. If a hospital-based chronic
outpatient facility provides acute services for hospitalized patients in
the same space and within the hospital walls, the outpatient dialysis
facility must meet the more-stringent hospital chapters of the LSC.
Survey instructions found in State Operations Manual (SOM),
Appendix I, are used as applicable, along with the Fire Safety Survey
Report Form, 2786U to survey for fire safety. The fire safety standard
will be surveyed by a fire specialist from the State Agency; generally,
the LSC inspections will be done separately from the rest of the ESRD
facility survey.
V418
(2) Notwithstanding paragraph (e)(1) of this section,
dialysis facilities participating in Medicare as of October
14, 2008 utilizing non-sprinklered buildings on such date
may continue to use such facilities if such buildings were
constructed before January 1, 2008 and State law so
permits.
The 2000 LSC only requires buildings with certain structural
configurations to have sprinkler systems. Specifically, the 2000 LSC
requires that only Type II (000) and ordinary constructed Type III
(200) buildings, and Type V (000) buildings of two or more stories
must be protected throughout by an approved, supervised automatic
sprinkler system (2000 LSC section 21.1.6.3).
These rules exempt existing dialysis facilities in operation on October
14, 2008, (i.e., that have a valid certificate of occupancy), from
needing to install sprinkler systems if the facility is located in a
building that was built before January 1, 2008, and if State law
permits.
Dialysis facilities that are new, relocated, undergoing major
renovation, or an existing facility participating in Medicare and
constructed after January 1, 2008, must comply with the LSC
provisions for sprinklered buildings. For the purposes of this part,
“constructed” before January 1, 2008 refers to facilities that had
Final Version 1.1 Page 174 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
obtained approval for all required building permits or had completed
all of the plan reviews in jurisdictions that do not require building
permits.
If the dialysis facility is in a mixed occupancy building, it must have a
one- or two-hour fire wall, depending upon the height and
combustibility of the construction materials or be in a completely-
sprinkled building. Multi-story buildings must meet the building
construction types with fire resistance hourly ratings of structural
elements such as walls and columns, as found at Section 20/21.1.6.3
of the LSC, NFPA, 101, 2000 edition.
419
(3) If CMS finds that a fire and safety code imposed by
the facility’s State law adequately protects a dialysis
facility’s patients, CMS may allow the State survey
agency to apply the State’s fire and safety code instead
of the Life Safety Code.
A State may apply to CMS for review to determine if a State’s fire
and LSC requirements adequately protect a dialysis facility’s patients
from fire hazards. The CMS review process will determine if a State
is allowed to substitute the state rules in this area for the requirements
of the LSC, NFPA 101. If CMS approves the State Code, the LSC,
NFPA 101 shall not apply.
420
(4) After consideration of State survey agency
recommendations, CMS may waive, for individual
dialysis facilities and for appropriate periods, specific
provisions of the Life Safety Code, if the following
requirements are met:
(i) The waiver would not adversely affect the health and
safety of the dialysis facility’s patients; and
(ii) Rigid application of specific provisions of the Life
Safety Code would result in an unreasonable hardship for
the dialysis facility.
CMS may waive specific provisions of the Life Safety Code (LSC).
This waiver may be granted if the facility is unable to comply with a
specific requirement of the LSC, and if complying with that
requirement would cause an unreasonable hardship for the dialysis
facility. The waiver will only be granted if it is determined that the
health and safety of the dialysis facility’s patients are not adversely
affected by the waiver. In some cases, the waiver may be limited to a
specific time period.
Guidance on the LSC waiver process is found in Appendix I of the
State Operations Manual (SOM).
Subpart C—Patient Care
V450
§ 494.70 Condition: Patients’ rights.
This Condition requires the facility to provide respect, privacy,
information, and appropriate services for their patients, as well as an
internal grievance mechanism and information about external
grievance mechanisms.
Final Version 1.1 Page 175 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The survey of this Condition is primarily accomplished by interviews
of patients and observations of care delivery and the interactions of
staff with patients. Review of medical records and applicable policies
for these requirements are indicated if any issues are identified by the
observations or interviews.
Condition level non-compliance should be considered if there are
serious and/or pervasive deficient practices identified that seriously
threaten one or more of these rights. Examples of Condition level non-
compliance include, but are not limited, to a pattern of:
• Failure to treat patients with respect and dignity, to provide an
opportunity for private communication, or to prevent exposure of
private body areas during dialysis causing patients emotional
discomfort;
• Cognizant patients/designees not being aware of their options for
treatment modalities or grievance mechanisms.
V451
The dialysis facility must inform patients (or their
representatives) of their rights (including their privacy
rights) and responsibilities when they begin their
treatment and must protect and provide for the exercise
of those rights.
“Inform” could include providing verbal explanations, audiovisual
presentations, and/or written materials. Documentation should
confirm that this information is provided.
“When they begin their treatment” means within the first six (6)
treatments after admission to the facility. While basic information
about all the “rights” listed in this Condition must be provided within
those first 6 treatments, it is expected that more in-depth discussions
regarding these “rights” may extend over a longer period of time.
A “patient representative” (also referred to as a “designee”) means a
legally-appointed representative or someone who the patient has
authorized to participate with or in the patient’s place. If patient-
appointed, the patient has the right to determine the extent to which
the designee serves as a health care decision-maker or proxy. The
parent of a child under age 18 is automatically determined to be a
Final Version 1.1 Page 176 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
“designee” for that child. However, older youths with decision-
making capacity may be included in decision-making with the
parent’s consent.
V452
(a) Standard: Patients’ rights.
The patient has the right to—
(1) Respect, dignity, and recognition of his or her
individuality and personal needs, and sensitivity to his or
her psychological needs and ability to cope with ESRD;
In all verbal and nonverbal communications, patients must be treated
with respect, dignity, and sensitivity. Interactions among patients,
staff, and others should demonstrate observance of patients’ rights and
consideration of a patient’s physical condition, emotional state, and
cultural background. Patients must be able to question procedures or
staff performance (e.g., whether or not a staff member washed their
hands prior to initiating the patient’s treatment) without fear of
reprisal.
Rude, abrupt or demeaning behavior, physical or mental harassment,
punishment, or the use of restraints or involuntary seclusion are not
acceptable and must not be imposed for purposes of discipline or staff
convenience. Rude or demeaning behavior would include name
calling. Harassment would include, but is not limited to, sexual
harassment.
Physical or chemical restraints may be imposed only upon the written,
specific order of a physician or other licensed practitioner permitted
by the State and facility to order restraints. In a dialysis unit, it may be
appropriate to use physical restraints to keep a patient from dislodging
or pulling out needles or to prevent a patient from falling out of a
dialysis chair. The need for restraints should be reassessed at each
treatment. If restraints are used, staff must document what, when,
how, and why restraints are needed. If restraints are used routinely on
a patient, staff should address this practice in the patient’s plan of
care. A restraint does not include a personal escort or orthopedic
device, surgical dressing or bandage, a protective helmet, or other
method to hold a patient while conducting routine aspects of the
dialysis treatment.
V453
(2) Receive all information in a way that he or she can
Patients and/or designees need to receive information in a way that
Final Version 1.1 Page 177 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
understand;
he/she can understand. Staff should consider patients’ literacy levels,
whether they have communication disorders (low vision/blindness,
hearing loss, or speech impairment), and whether a language other
than English is their primary language. Methods to validate that
provided information was understood should be employed; examples
would include “teach back,” asking the patient to reflect back to the
staff member what they understood, or return demonstration of a skill.
The interdisciplinary team comprehensive assessment and plan of care
must assess patient needs for information and barriers to receipt of
that information, and develop ways to address those barriers.
Communication options for those with vision loss include verbal
communications, large print, and Braille. Communication options for
those with hearing loss include lip reading, sign language, pictograms,
telecommunication devices for the deaf, and written communications.
Options to communicate with those who cannot speak include
providing written documents, audio formats, and using sign language.
There should be a reasonable facility plan for communicating
information in various languages if there is a need. Since there may be
a variety of languages spoken at any facility, it would be unreasonable
to expect that all written patient materials will be translated into every
language that is spoken at the facility. However, the facility must
comply with legal requirements for communicating with those with
limited English proficiency under Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of
1964 and Executive Order 13166 that require recipients of federal
funds to have policies and procedures for communicating with
patients who speak languages other than English, especially vital
documents such as consents for treatment, forms that require a legal
signature and patients' rights policies. Staff should document in the
patient’s medical record how forms requiring a signature were
explained to patients/designees who have vision, speech, or hearing
barriers and those who do not speak or read English. Facilities may
Final Version 1.1 Page 178 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
use web-based language translation services, such as Babel Fish to
translate words or phrases, or audio interpreter services, such as
Language Line, for communicating more than a short phrase.
V454
(3) Privacy and confidentiality in all aspects of
treatment;
Patients have the right to privacy and confidentiality in both the verbal
and physical aspects of their treatment.
Patients have the right to privately discuss their condition and
treatment. Staff should allow the patient to direct where discussions of
sensitive topics should occur, and ask the patient if he/she wants to
schedule a time to discuss a sensitive issue away from the treatment
area. Any staff-patient interactions that require privacy should be
conducted in private. To allow for private conversations between
patients and staff members, there should be ready access to a room in
the facility where patient and/or family meetings can be held in
private. Plan of care conferences may be conducted chairside rather
than in a private location if a patient grants permission.
Patients have the right to privacy during activities that expose private
body parts while in the dialysis facility. This includes activities related
to use of vascular access sites located in the groin or chest and
physical examinations. Options for ways to comply with this
requirement include the use of privacy screens, curtains, or blankets.
Staff must be able to observe the patient’s vascular access, bloodline
connections, and face at all times. Refer to V407 under the Condition
for Physical environment.
V455
(4) Privacy and confidentiality in personal medical
records;
Patients should be able to expect the facility to maintain
confidentiality of their medical record information. Patients’ health
records must be protected from casual access. Hard copy medical
records should be stored in a secure location when not in use.
Computer screens containing patient information should not be left
open and unattended with patient specific information on display and
computerized systems should require passwords and permissions to
access medical records.
Final Version 1.1 Page 179 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The facility must inform patients of their privacy rights under the
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
A signed release is not required by HIPAA to share protected health
information for continuity of care, such as but not limited to providing
emergency care or contacting other dialysis facilities as a part of the
protocol for involuntary discharge or termination of treatment or when
asking the police to help locate a patient so he/she can receive
dialysis.
Patients have the right to read their own medical record, have
corrections made to that record, and to have a copy of their record for
which a nominal fee may be charged. The facility must actively seek
to honor patients’ requests to have a copy of their medical record as
quickly as its recordkeeping system permits. Under HIPAA, reasons
why a patient or his/her designee would not have the right to review
his/her record include:
• The patient is an inmate of a correctional facility and access could
jeopardize the health, safety, security, custody or rehabilitation of
the patient, other inmates, or the safety of any officer, employee or
other correctional system employee, including the transporter;
• The patient is participating in a research project;
• Access to the medical record would reveal a confidential source;
• Access to the medical record could endanger the life or physical
safety of another;
• Access to the medical record by the patient’s authorized
representative is likely to cause substantial harm to patient or
another.
Confidential treatment and release of patient medical record
information is also addressed in the Condition for Medical records at
V727 and V728.
Final Version 1.1 Page 180 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V456
(5) Be informed about and participate, if desired, in all
aspects of his or her care, and be informed of the right to
refuse treatment, to discontinue treatment, and to refuse
to participate in experimental research;
Patients have the right to know about and participate in their care and
treatment to the extent they desire. Self-cannulation may be performed
by the patient in any facility upon receiving appropriate training and
demonstrating competence, should they so choose. The facility must
encourage patient participation in care planning. Examples of ways to
promote this participation include, but are not limited to, offering the
patient the option to participate in interdisciplinary team care planning
or to attend a planning meeting in-person or by teleconference from
home. “Chair-side” review of the plan of care is also acceptable, if
sufficient privacy can be provided. Patients also have the right to
accept or decline to participate in their care.
Patients must be notified of changes to their dialysis prescription and
the reason for those changes. Patients should be encouraged to
disclose any concerns they have with the proposed changes. Patients
have the right to refuse the change without fear of discharge.
Patients have the right to refuse any aspect of treatment, to refuse to
participate in experimental research, and to discontinue their dialysis
treatments completely.
V457
(6) Be informed about his or her right to execute advance
directives, and the facility’s policy regarding advance
directives;
This standard requires the facility to inform patients about advance
directives, including the right to formulate advance directives. The
standard does not require that all patients have an advance directive.
Advance directives establish in writing an individual’s preference
with respect to the degree of medical care and treatment desired or
who should make treatment decisions if the individual should become
incapacitated and lose the ability to make or communicate medical
decisions. Advance directives include written documents such as
living wills and durable powers of attorney for health care decisions
(also called a health care proxy or medical power of attorney) as
recognized by State law.
Final Version 1.1 Page 181 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Many states have enacted laws requiring patients’ advance directives
and “do not resuscitate” (DNR) preferences to be honored. Facilities
are required to know and comply with such state laws. If state law
does not address this facet of health care, and the facility’s policy does
not allow the honoring of a patient’s advance directive, there must be
a protocol in place for facilitating the patient’s transfer to a facility
that will honor the advance directive, if the patient so chooses.
The inclusion of patients’ advanced directives in their medical records
is addressed at V730.
V458
(7) Be informed about all treatment modalities and
settings, including but not limited to, transplantation,
home dialysis modalities (home hemodialysis,
intermittent peritoneal dialysis, continuous ambulatory
peritoneal dialysis, continuous cycling peritoneal
dialysis), and in-facility hemodialysis. The patient has
the right to receive resource information for dialysis
modalities not offered by the facility, including
information about alternative scheduling options for
working patients;
Documentation in patient records must demonstrate that facility staff
provide unbiased education to patients/designees about transplantation
and all dialysis treatment options (modalities and settings) offered for
kidney failure, whether or not those options are offered at the current
dialysis facility. This includes alternate scheduling options for in-
center hemodialysis patients who attend school or are working.
Patients who work or attend school should be encouraged to continue
doing so and facilities should recommend the most appropriate
modality and setting for their dialysis. Examples of how facilities may
meet this requirement include developing a resource information
packet for patients or providing patients an existing resource list of
facilities that offer alternate schedules or home dialysis treatment
options can be found at Medicare’s Dialysis Facility Compare, and
Home Dialysis Central.
The requirements for assessment of patients for home dialysis and
transplantation are addressed at V512 and V513 and at V553 and
V554 respectively under the Condition for Patient plan of care.
V459
(8) Be informed of facility policies regarding patient
care, including, but not limited to, isolation of patients;
Facility staff must inform patients regarding facility policies related to
patient care, including the isolation of patients with infectious
diseases. For example, patients should be informed if changes in their
treatment location and/or schedule can be expected if they are
diagnosed with an infectious disease requiring isolation (i.e., hepatitis
Final Version 1.1 Page 182 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
B). Refer to V128 under the Condition for Infection Control for
requirements regarding isolation of patients.
V460
(9) Be informed of facility policies regarding the reuse of
dialysis supplies, including hemodialyzers;
This requirement only applies to facilities that practice reprocessing
and reuse of dialyzers or dialysis supplies.
The patient must be informed if the facility practices reuse of
dialyzers and/or dialysis supplies and of options available if they opt
not to participate in the reuse program. Some State laws require
facilities to allow patients to opt not to reuse their dialyzers and/or
require the patient’s written consent for dialyzer reuse.
The requirements for informed consent for dialyzer reuse are
addressed at V312 under the Condition for Reuse.
V461
(10) Be informed by the physician, nurse practitioner,
clinical nurse specialist, or physician’s assistant treating
the patient for ESRD of his or her own medical status as
documented in the patient’s medical record, unless the
medical record contains a documented contraindication;
Medical records should show that a patient's medical status was
discussed with a patient/designee by a physician or a non-physician
practitioner (i.e., advanced practice registered nurse, or physician
assistant). There should be few, if any, cases when a patient/designee
cannot be informed about the patient’s medical status.
V462
(11) Be informed of services available in the facility and
charges for services not covered under Medicare;
Patients must be made aware of charges for any services that may not
be covered under Medicare. If a facility plans to bill a patient for
items and/or services which are usually covered by Medicare, but may
not be considered reasonable and necessary in a particular situation
(according to § 1862 of the Social Security Act), the patient must be
informed and be offered an Advanced Beneficiary Notice (ABN) to
sign pursuant to § 1879 of the Social Security Act.
V463
(12) Receive the necessary services outlined in the
patient plan of care described in § 494.90;
Patients have the right to receive individualized care as determined by
the facility interdisciplinary team and to be included on that team. The
care specified in the plan of care should be delivered to the patient or
the plan of care should be revisited.
V464
(13) Be informed of the rules and expectations of the
facility regarding patient conduct and responsibilities;
Facility staff should inform patients about what is expected of them
(the patient), while receiving services at the facility. Some examples
of facility expectations for patient conduct and responsibilities
include, but are not limited to, treating others (staff, patients, visitors)
Final Version 1.1 Page 183 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
with mutual respect; following the plan of care (e.g., taking ordered
medications, following fluid and diet restrictions); keeping
appointments and/or notifying the facility if he/she will be late or miss
a scheduled appointment: notifying the facility of changes in
residence and contact information; and providing information on
payers and changes in insurance.
V465
(14) Be informed of the facility’s internal grievance
process;
Each facility should develop and implement an internal grievance
process, as is stated in the Condition for Governance at V765.
Facility staff must inform patients about the internal grievance process
and the steps to follow for filing an internal grievance. Refer to V765
for the components of the internal grievance process. Use those tags
for failure to implement the process. Use this tag for failure to inform
patients about the process.
V466
(15) Be informed of external grievance mechanisms and
processes, including how to contact the ESRD Network
and the State survey agency;
The facility must establish a procedure for informing patients about
seeking external help to resolve grievances that cannot be resolved
internally or if patients are not comfortable using the internal process.
The facility staff must inform each patient/designee how to contact the
appropriate external entity to file a grievance, including the ESRD
Network and the State survey agency.
Refer to V470 for the requirement of posting contact information for
the Network and State survey agency.
V467
(16) Be informed of his or her right to file internal
grievances or external grievances or both without reprisal
or denial of services; and
(17) Be informed that he or she may file internal or
external grievances, personally, anonymously or through
a representative of the patient’s choosing.
Every patient must be free to file a complaint or grievance within the
facility or externally with the ESRD Network or State survey agency.
Facility staff should inform patients that they can file a grievance
anonymously or through a representative without being afraid that
they will be treated differently or denied services.
“Reprisal” would include retaliation or revenge and could include
perceived punishment, isolation, the intentional infliction of physical
pain or emotional distress or involuntary discharge from the facility.
V468
(b) Standard: Right to be informed regarding the
Patients must be given information about the facility policies for
Final Version 1.1 Page 184 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
facility’s discharge and transfer policies. The patient has
the right to –
(1) Be informed of the facility’s policies for transfer,
routine or involuntary discharge, and discontinuation of
services to patients; and
routine and involuntary discharges.
Refer to the Condition for Governance at V766-V767 for involuntary
discharge or transfer regulations and guidance, including acceptable
reasons for involuntary discharge. Use those tags for failure to follow
the involuntary discharge procedures. Use this tag for failure to
inform patients about the transfer and discharge policies.
V469
(2) Receive written notice 30 days in advance of an
involuntary discharge, after the facility follows the
involuntary discharge procedures described in §
494.180(f)(4). In the case of immediate threats to the
health and safety of others, an abbreviated discharge
procedure may be allowed.
The involuntary discharge procedures described at V767 identify the
steps that a facility must follow prior to the involuntary discharge of a
disruptive and abusive patient. After following the required
procedures, a facility must give at least 30-days prior notice to any
patient whom they opt to discharge involuntarily, except in the case of
a patient who makes severe and immediate threats to the health and
safety of others.
An "immediate threat to the health and safety of others" is considered
to be a threat of physical harm. For example, if a patient has a gun or a
knife or is making credible threats of physical harm, this can be
considered an “immediate threat.” Verbal abuse is not considered to
be an immediate threat. In instances of an immediate threat, facility
staff may utilize "abbreviated" involuntary discharge or transfer
procedures. These abbreviated procedures may include taking
immediate protective actions, such as calling “911” and asking for
police assistance. In this scenario, advance notice is not possible or
required and there may not be time or opportunity for reassessment,
intervention, or contact with another facility for possible transfer, as
outlined at V767.
V470
(c) Standard: Posting of rights. The dialysis facility must
prominently display a copy of the patient’s rights in the
facility, including the current State agency and ESRD
network mailing addresses and telephone complaint
numbers, where it can be easily seen and read by
patients.
The facility must post all of the rights listed in V452-V469 in a
common area of the facility which is routinely available to in-center
and home dialysis patients. This posting is meant to augment, not
substitute for communicating these rights to each individual patient in
a way the patient can understand.
Final Version 1.1 Page 185 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Information that must be posted includes the list of patient rights and
the mailing addresses and contact information for the applicable
ESRD Network and State survey agency, as well as the complaint
telephone numbers for each.
V500
§ 494.80 Condition: Patient assessment.
The requirements in this Condition address the requirements for an
interdisciplinary team assessment of patient needs; the requirements
related to meeting those needs are contained in the Condition for
Patient plan of care at 494.90.
Compliance with this Condition is determined by observation of
practices; interviews of patients, personnel and medical staff; and
review of medical records.
Condition level noncompliance should be considered if there are
serious and/or pervasive deficient practices identified in the provision
of individualized interdisciplinary comprehensive assessments of
patients and their care needs. Examples of Condition level
noncompliance include, but are not limited to:
• Assessments not being completed for multiple patients within the
timelines required;
• One or more professional members of the interdisciplinary team
(IDT) not participating in the patient assessment;
• A pattern of general standardized assessment “findings” without
evidence that individual patient needs are assessed.
V501
The facility’s interdisciplinary team, consists of, at a
minimum, the patient or the patient’s designee (if the
patient chooses), a registered nurse, a physician treating
the patient for ESRD, a social worker, and a dietitian.
The interdisciplinary team is responsible for providing
each patient with an individualized and comprehensive
assessment of his or her needs. The comprehensive
assessment must be used to develop the patient’s
treatment plan and expectations for care.
While multidisciplinary team members work sequentially and use the
medical record as the chief means of communication, interdisciplinary
teams work collaboratively with regular meetings to discuss patient
status and the evolving plan of care. Working as a team allows for
working toward common goals, pooling of expertise, and a forum for
problem solving.
The interdisciplinary team (IDT) is composed of the members
designated in the regulations, including the patient or a patient
Final Version 1.1 Page 186 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
designee if the patient so chooses. Patients must be given the option
and encouraged to participate in their assessment and care planning
process. The professional members of the IDT participating in the
patient comprehensive assessment must meet the qualifications
outlined in the Condition for Personnel qualifications at § 494.140.
“Individualized” means each assessment is unique to a particular
patient and addresses that patient’s needs. “Comprehensive” means
the assessment covers and addresses all issues that are actionable by
the dialysis facility; this could include referrals to specialists for
assessments that are beyond the capacity of a dialysis facility.
The comprehensive patient assessment must demonstrate a congruent
integration of the evaluations completed by each team member,
identifying the patient’s individual needs and allowing for planning
for necessary care and services. Team members may choose to
conduct one-on-one interviews with the patient or may opt to set up
team meetings which would include the patient in order to collect the
appropriate assessment information.
This assessment may be incorporated into one document or composed
of sections developed by each team member, but must address the
specific criteria as outlined in V502-V515. Electronic or paper
formats may be used.
Required frequencies of patient assessments are addressed at V516-
V520.
V502
(a) Standard: Assessment criteria. The patient’s
comprehensive assessment must include, but is not
limited to, the following:
(1) Evaluation of current health status and medical
condition, including co-morbid conditions.
ESRD patients may have many co-morbid conditions which impact
their individual care needs. The IDT evaluation of the patient’s
current medical and co-morbid conditions includes information from
medical history, physical exams, and nursing histories.
Non-physician practitioners, i.e., advanced practice registered nurses
Final Version 1.1 Page 187 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
or physician assistants, functioning in lieu of physicians may conduct
medical portions of this evaluation, in accordance with State law and
facility policy.
The nursing assessment must be conducted by a registered nurse and
include evidence of assessment of the clinical needs of the patient.
Documentation of the etiology of the patient's kidney disease and a
listing of any co-morbid conditions should be in the medical record.
While copies of histories and physicals (H&P) from hospital
admissions may be included, the assessment should address the
patient's current presentation and health status, including the patient’s
medical condition related to his/her kidney disease.
V503
(2) Evaluation of the appropriateness of the dialysis
prescription,
A hemodialysis (HD) prescription includes the number of treatments
per week, length of treatment time, the dialyzer, specific parameters
of the dialysis delivery system (e.g., electrolyte composition of the
dialysate, blood flow rate, dialysate flow rate), anticoagulation, and
the patient’s target weight. An appropriate HD prescription is
individualized to meet the dialysis needs of the patient. For example,
if the patient experiences intradialytic muscular cramping or a fall in
blood pressure, a reevaluation of the related components of the
dialysis prescription (e.g., target weight, ultrafiltration rate (UFR),
dialysate sodium level) would be indicated; if a patient’s laboratory
values show an elevated or low potassium, a change in the dialysate
potassium may be indicated.
A peritoneal dialysis (PD) prescription must take into consideration
the peritoneal transport rate (determined by peritoneal equilibration
testing [PET]), residual renal function, total body surface area, certain
medical conditions, and personal preference. The PD prescription
includes the number of exchanges or cycles to be done each day, the
volume of fluid to be used with each exchange, whether fluid is
always present in the peritoneal cavity (except for brief periods
Final Version 1.1 Page 188 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
between draining and reinfusion of dialysate), and the concentration
of glucose or other osmotic agent to be used for fluid removal (which
may vary according to a prescribed sliding scale). Use of an
automated, a manual, or a combination of automated/manual
techniques should also be addressed. An appropriate PD prescription
meets the dialysis needs of the patient. As examples: if the patient has
difficulty accomplishing 5 exchanges during the day, the IDT should
consider other options, such as overnight treatments using a cycler.
The patient record should show evidence that the patient's individual
dialysis needs have been assessed and the current dialysis prescription
evaluated as to whether it is meeting those needs. Refer to V715 for
the requirement for the initial dialysis prescription to be provided
prior to the patient’s first treatment in the facility.
V504
Blood pressure, and fluid management needs.
Because of the adverse effects of ESRD, many patients experience
lability of blood pressure and fluid management, the management of
which may require reassessment of medication needs, adjustments in
target weight, and changes to the POC.
The comprehensive assessment should include evaluation of the
patient’s pre/intra/post and interdialytic blood pressures, interdialytic
weight gains, target weight, and related intradialytic symptoms (e.g.,
hypertension, hypotension, muscular cramping) along with an analysis
for potential root causes.
For pediatric patients weighing less than 35 kg., blood volume
monitoring during hemodialysis should be available in order to
evaluate body weight changes for gains in muscle weight vs. fluid
overload.
V505
(3) Laboratory profile,
Laboratory work-up should include, but not be limited to,
comprehensive metabolic testing, dialysis adequacy, complete blood
count, iron studies and screening for HBV.
Final Version 1.1 Page 189 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The IDT evaluation should reflect recognition of values/results that
would need to be addressed in the patient plan of care.
As laboratory results may fluctuate, the IDT must evaluate the values
as they become available and take indicated actions
V506
Immunization history, and medication history.
“Immunization history” should include whether the patient has
received standard immunizations (pneumococcal, hepatitis, and
influenza), and has been screened for tuberculosis. The immunization
record is expected to include at least the patient’s immunization
history as of the effective date of this regulation.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends
that all dialysis patients:
• Be tested at least once for baseline tuberculin skin test results
(TST) and re-screened if TB exposure is detected. Chest x-rays
may be used for individuals for whom the TST is not an option.
• Be offered influenza and pneumococcal vaccine and have
immunization histories for these vaccines be tracked. Both are
universally recommended for this population and relate directly to
infection control issues.
• The CDC expectations for hepatitis vaccinations are detailed at
V126 and V127.
“Medication history” should include a review of the patient’s allergies
and of all medications including over-the-counter medications and
supplements that the patient is taking. The assessment should
demonstrate that all current medications were reviewed for possible
adverse effects/interactions and continued need.
V507
(4) Evaluation of factors associated with anemia, such as
hematocrit, hemoglobin, iron stores, and potential
treatment plans for anemia, including administration of
erythropoiesis-stimulating agent(s).
Each patient’s hematologic status must be evaluated for determination
of their individual anemia management needs.
Evaluation should address the patient’s anemia, including an
assessment of the need for erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA)
Final Version 1.1 Page 190 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
and/or iron therapy. Evaluation should also address the patient’s
volume status, potential for bleeding, infection and other causes of
hypo-response.
Requirements for the plan of care for anemia management are at
V547.
V508
(5) Evaluation of factors associated with renal bone
disease.
Disturbances in mineral and bone metabolism are common in patients
with ESRD, often resulting in hyperparathyroidism and Chronic
Kidney Disease (CKD) mineral and bone disorder if not managed
effectively.
Evaluation should include the patient's laboratory values for calcium,
phosphorous, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) along with a review of
the patient’s current CKD mineral and bone disorder medications (e.g.
phosphate binders, vitamin D analogs, calcimimetic agents), over-the-
counter medications, dietary factors, and medical conditions that
impact this issue.
Pediatric patients present significant special needs in the areas of
growth and development and CKD mineral and bone disorder. A
facility treating pediatric patients should follow current
professionally-accepted clinical practice standards for evaluating and
monitoring the pediatric patient population in this area.
Requirements for the plan of care for CKD mineral and bone disorder
management are at V546.
V509
(6) Evaluation of nutritional status by a dietitian.
The evaluation of each patient’s nutritional status must be conducted
by a qualified dietitian as defined in these regulations at V689 and
V690.
Examples of nutritional parameters to be addressed include, but are
not limited to:
•
Nutritional status;
Final Version 1.1 Page 191 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
• Hydration status;
• Metabolic parameters such as glycemic control (if diabetic) and
cardiovascular health;
• Anthropometric data such as height, weight, weight history,
weight changes, volume status, amputations;
• Appetite and intake;
• Ability to chew and swallow;
• Gastrointestinal issues;
• Use of prescribed and over-the-counter nutritional, dietary, or
herbal supplements;
• Previous diets and/or nutrition education;
• Route of nutrition;
• Self-management skills;
• Attitude to nutrition, health, and well-being; and
• Motivation to make changes to meet nutrition and other health
goals.
The assessment may include information from the person that cooks
and provides meals for the patient, whether this is the patient, family,
caregiver or nursing home. Before interviewing family members or
caregivers, the dietitian should seek the patient’s permission to
interview the relevant individual(s). If the patient is a resident of a
long-term care (LTC) facility, the dietitian should contact the staff of
the LTC facility as part of the assessment and to provide continuity of
care.
Other members of the IDT may contribute to portions of the
comprehensive assessment which correlate with the nutritional
evaluation (e.g., medical history/co-morbid conditions at V502, fluid
management at V504, laboratory profile at V505, medication history
at V506, CKD mineral and bone disorder at V508, psychosocial
factors at V510, and adequacy of the patient’s dialysis prescription at
Final Version 1.1 Page 192 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V518).
Recognize this area is critically important in pediatric patients. A
facility treating pediatric patients should follow current
professionally-accepted clinical practice standards for evaluating and
monitoring the pediatric patient population. The dietitian must
consider the special nutritional needs of these patients.
Requirements for the plan of care for nutritional status are at V545.
V510
(7) Evaluation of psychosocial needs by a social worker.
The evaluation of psychosocial needs must be conducted by a
qualified social worker as defined by these regulations at V691.
Examples of psychosocial parameters to be addressed by the qualified
social worker include, but are not limited to:
• Cognitive status and capacity to understand;
• Ability to meet basic needs;
• Ability to follow the treatment prescription;
• Mental health history, capacities, and needs for counseling;
• Substance abuse history, if any;
• Current ability to cope with and adjust to dialysis;
• Expectations for the future and living with kidney failure and
treatment;
• Educational and employment status, concerns, and goals;
• Home environment including current living situation;
• Legal issues ( e.g., court appointed guardian, advance directive
status, and health care proxy)
• Need for advocacy with traditional (nursing home) and non-
traditional housing (e.g., homeless shelters, group homes);
• Financial capabilities and resources;
• Access to available community resources; and
• Eligibility for Federal, State, or local resources.
Final Version 1.1 Page 193 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Other members of the IDT may contribute to portions of the
comprehensive assessment which correlate with the psychosocial
evaluation (e.g., patient preferences for modality and self-care at
V512, evaluation for transplant referral at V513, family/support
systems at V514, and evaluation for referral to rehabilitation services
at V515).
Requirements for the plan of care for psychosocial status are at V552.
V511
(8) Evaluation of dialysis access type and maintenance
(for example, arteriovenous fistulas, arteriovenous grafts
and peritoneal catheters).
The efficacy of the HD patient’s vascular access and the PD patient’s
peritoneal catheter correlates to the quality (adequacy) of their dialysis
treatments and is of vital importance to their overall health status.
Each HD patient should have an evaluation for the most appropriate
type and location of vascular access and of the capacity of the
vascular access to facilitate adequate dialysis treatments.
Completion of this evaluation may include referrals to other entities,
such as a radiologist or interventionist for vessel mapping or a
vascular surgeon for access placement. Such referrals might take place
as part of an assessment or as part of a plan of care, if the referral is to
address an inadequate vascular access.
Evaluation of a PD patient’s peritoneal catheter would include
assessment of the exit site and tunnel for condition and absence of
infection, and of the catheter for patency and function.
The requirements for vascular access plan of care are at V550 and
V551.
V512
(9) Evaluation of the patient’s abilities, interests,
preferences, and goals, including the desired level of
participation in the dialysis care process; the preferred
modality (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis), and
setting, (for example, home dialysis), and the patient’s
Evaluation of abilities, interests, preferences and goals would be
demonstrated by at least one member of the team documenting an
assessment of the patient’s current interests in life and ability to
pursue those interests, preferences for treatment, and goals, including
what he/she expects from dialysis treatment. Patients must be
Final Version 1.1 Page 194 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
expectations for care outcomes.
encouraged to participate in their care, within the limits of their
capacity and desire.
If patients express a desire for enhanced participation in their own
care (e.g., weighing themselves, monitoring blood pressure, holding
needle sites, self-cannulation), the facility staff should evaluate and
plan for applicable self-care training.
Refer to the Condition for Care at home at V585.
Evaluation of the preferred modality means that all options of
modalities (hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis) and settings (in-center,
home) were presented to each patient, and that their goals,
preferences, and expectations were given priority in decision-making.
If a patient is determined not suitable for or declines home dialysis
therapy, the reason must be documented in their plan of care, as
required at V553.
V513
(10) Evaluation of suitability for a transplantation
referral, based on criteria developed by the prospective
transplantation center and its surgeon(s). If the patient is
not suitable for transplantation referral, the basis for
nonreferral must be documented in the patient’s medical
record.
The IDT comprehensive assessment must demonstrate that each
patient is evaluated for suitability for transplantation referral, using
selection/exclusion criteria provided by the transplant center.
The regulations for transplant programs require written selection
criteria to be developed and provided upon request to patients and
dialysis facilities. Selection criteria vary among transplant centers; if
the dialysis facility refers patients to multiple transplant centers, the
dialysis facility should have the selection criteria for each center on
file and available to patients; patient are also free to select a transplant
center other than the ones normally utilized by the dialysis facility for
referrals.
If the assessment finds a patient is not suitable for transplantation, the
reason for the non-referral should be documented as part of the
Final Version 1.1 Page 195 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
comprehensive assessment.
The requirements for plan of care for transplant status are at V554.
V514
(11) Evaluation of family and other support systems.
This evaluation should start with an interview of the patient. If one or
more members of the IDT need to seek additional protected health
information about the patient from family or other supporting
individuals, they must obtain the patient’s permission to discuss these
topics with those individuals. It is not a breach of HIPAA privacy
requirements for staff to ask family or other caregivers for information
they may know about a patient to help the IDT provide care for the
patient. HIPAA does not prohibit a staff member from educating a
family member or other support person about how to help the patient
with diet, medications, and cope with kidney failure. Ideally, it is best
to seek approval from the patient. Educating the patient with family or
other caregiver(s) (when possible) assures that everyone receives the
same information.
Areas which would be included in this evaluation include family
composition and history, the patient’s willingness to ask for help;
spiritual or religious support systems; etc. Some or all portions of this
evaluation may overlap with the requirements for the psychosocial
assessment described at V510.
Pediatric patients present special situations. Facilities that treat
pediatric patients must have policies that address the need to evaluate
the family and other support systems of the pediatric patients.
V515
(12) Evaluation of current patient physical activity level.
(13) Evaluation for referral to vocational and physical
rehabilitation services.
These requirements are not intended to indicate that the facility is
responsible for fully assessing each patient’s activity level/physical
capabilities. It is expected that the IDT would be able to evaluate each
patient’s activity level to the extent necessary to determine whether
the patient is a candidate for referral to the appropriate professional(s)
for further evaluation and possible rehabilitation services.
Final Version 1.1 Page 196 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
A member of the IDT should interview the patient/designee about the
patient’s current level of “physical activity,” ability to perform
activities of daily living, and/or barriers to independence. The
assessment should include observation of the patient’s ability to
ambulate, transfer, and other physical activities pertinent to the
dialysis environment (e.g. holding needle sites, etc).
Pediatric patients may also warrant rehabilitation services. Pediatric
patients should be encouraged to attend school full-time if possible. If
school attendance is not possible, other options should be offered for
school-age children to obtain education.
Vocational rehabilitation referrals may be appropriate for older youth
and adult patients who desire to return to work and/or improve
independent living skills.
Patients who may warrant physical rehabilitation referrals include
those with physical limitations and/or difficulty in performing
activities of daily living independently.
The requirements for the plan of care for rehabilitation status
(including making referrals) are at V555.
V516
(b) Standard: Frequency of assessment for patients
admitted to the dialysis facility.
(1) An initial comprehensive assessment must be
conducted on all new patients (that is, all admissions to a
dialysis facility), within the latter of 30 calendar days or
13 hemodialysis sessions beginning with the first dialysis
session.
Each patient new to dialysis must have a comprehensive assessment
completed within 30 days or 13 treatments of admission. This
requirement applies to all new dialysis patients, without regard to the
modality of treatment. Patients returning to dialysis from a failed
transplant or changing modalities are also considered “new” patients.
If the comprehensive patient assessment and plan of care for an
experienced dialysis patient transferring from one dialysis facility to
another is received with the patient in transfer, the receiving facility’s
IDT must conduct a reassessment within three months of the patient’s
admission to the new facility. This same provision (i.e., completion of
Final Version 1.1 Page 197 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
a reassessment within 3 months of admission) would also apply to
transient patients received with an assessment and plan of care. Refer
to V408 for disaster situations and requirements.
Prior to the first dialysis treatment, an “initial assessment” must be
completed. This initial assessment is addressed in the Condition for
Medical director at V715 and is different from the “initial
comprehensive interdisciplinary” assessment.
Recognize that the transfer in of a large number of patients at once
(e.g., with the opening of a new facility, or in the event of an adverse
occurrence or disaster impacting the functionality of the transferring
facility) may affect the staff’s ability to complete this requirement
within the mandated timeline. If this is the case, the facility should
develop a plan to ensure completion of the assessments of the
transferred patients promptly and a method to triage patients’ needs
for assessment.
V517
(2) A follow up comprehensive reassessment must occur
within 3 months after the completion of the initial
assessment to provide information to adjust the patient’s
plan of care specified in § 494.90.
Patients new to dialysis and/or a new dialysis setting frequently need
time to adjust and adapt to the treatment. The 3 month comprehensive
reassessment enables the IDT to re-evaluate how well patients follow
their treatment plan, their educational, psychosocial, rehabilitation,
and nutritional needs, their current adjustment to the dialysis regimen
and coping, and the accuracy and appropriateness of patients’ plans of
care.
Determine what system is in place to ensure completion of the 3
month comprehensive patient reassessments.
V518
(c) Standard: Assessment of treatment prescription. The
adequacy of the patient’s dialysis prescription, as
described in § 494.90(a)(1), must be assessed on an
ongoing basis as follows:
(1) Hemodialysis patients. At least monthly by
calculating delivered Kt/V or an equivalent measure.
Monthly assessment of dialysis adequacy for all HD patients, and at
least every 4 months for PD patients must be demonstrated.
The facility must have a method or procedure in place for obtaining
the blood samples used for the Kt/V or an equivalent measure. The
facility must ensure the method/procedure used would result in an
Final Version 1.1 Page 198 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(2) Peritoneal dialysis patients. At least every 4 months
by calculating delivered weekly Kt/V or an equivalent
measure.
accurate result. At the time of the publication of these regulations, the
recommended method stipulated for drawing blood samples to
measure Kt/V included the following:
• Pre- and post- samples are drawn at the same treatment;
• Pre sample is drawn just prior to the start of treatment;
• Slow flow or stop pump technique is used for the post sample;
staff should slow the blood pump speed to 50-100 mL/min for 15
seconds before drawing blood; in the event the equipment in use
does not allow for “slow flow,” then “stop flow” may be
substituted;
• After 15 seconds, staff should draw the post dialysis BUN sample
from the arterial port closest to the patients.
All facility staff members must follow the same prescribed procedure
for obtaining blood samples used for assessing the adequacy of the
patient’s prescription.
Home hemodialysis patients should be instructed to draw their
samples in this same way.
Recognize that obtaining the sample to measure adequacy for PD
patients depends on their cooperation with bringing samples of
dialysate effluent and urine. If a scheduled sample is not obtained,
staff should document the missed test, reschedule the test (including
obtaining a blood sample on the same date as the fluid samples are
collected), and consider reminders and re-education of the patient.
V519
(d) Standard: Patient reassessment. In accordance with
the standards specified in paragraphs (a)(1) through
(a)(13) of this section, a comprehensive reassessment of
each patient and a revision of the plan of care must be
conducted—
(1) At least annually for stable patients; and
There must be a complete, comprehensive reassessment of all stable
patients annually. The first annual reassessment would be due 12
months after the 3 month reassessment, or 15 months after the
patient’s admission to the facility.
Annual reassessments for stable patients are the required minimum;
more frequent reassessments of stable patients may be done if
Final Version 1.1 Page 199 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
required by facility policy or by clinical concerns.
If patients who have been identified by staff as “stable” demonstrate
one of the issues listed as criteria for being considered “unstable,” this
finding would be cited at V520.
V520
(2) At least monthly for unstable patients including, but
not limited to, patients with the following:
(i) Extended or frequent hospitalizations;
(ii) Marked deterioration in health status;
(iii) Significant change in psychosocial needs; or
(iv) Concurrent poor nutritional status, unmanaged
anemia and inadequate dialysis.
The criteria listed here are the minimum criteria for classifying
patients as “unstable.” The IDT members have the flexibility to use
their professional judgment to develop more stringent policies
regarding the definition of "unstable,” based on their unique patient
population and patient characteristics and to add other assessment
criteria.
“Extended hospitalizations” would include hospitalizations longer
than 15 days, which was longer than the average length of stay
nationally at the time these regulations were published.
“Frequent hospitalizations” would include more than three
hospitalizations in a month, which was more than the average number
of hospitalizations annually at the time these regulations were
published. The reason for hospitalization may also result in a patient
being classified as “unstable,” for example, if the hospitalization
results in amputation of a limb.
“Marked deterioration in health status” would be specifically
identified and documented by the IDT. The following conditions have
been suggested by representatives of the renal community:
• Change in ambulation severe enough to interfere with the patient’s
ability to follow aspects of the treatment plan;
• Hypotension, restlessness, pruritus or other symptoms severe
enough to prevent completion of the majority of dialysis
treatments;
• Sudden onset of recurrent cardiac arrhythmias;
• Recurrent infections (not recurring hospitalization);
Final Version 1.1 Page 200 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
• Chronic congestive heart failure with chronic hypotension;
• Advanced or metastatic cancer or other organ system disease
which interferes with the patient’s ability to follow aspects of the
treatment plan;
• Chronic or recurrent peritonitis
“Significant change in psychosocial needs” would include any event
that interferes with the patient’s ability to follow aspects of the
treatment plan. Such events may include instability in one’s own or
immediate family member’s employment, physical or emotional
abuse, deterioration in mental or functional status, amputation,
housing instability, death or major illness in the family, consideration
of terminating treatment, and loss of emotional support. In addition,
any patient considered at risk for involuntary discharge or transfer
must be considered “unstable.” Note that V767 requires that patients
at risk for involuntary discharge be reassessed.
“Poor nutritional status” would include failure to thrive symptoms,
with loss of body weight and low serum albumin.
“Unmanaged anemia” would include continued lab findings of
hemoglobin/hematocrit values which are out of range as defined by
community-accepted standards or Centers for Medicare and Medicaid
Services (CMS) Clinical Performance Measures (CPMs). Refer to the
Measures Assessment Tool (MAT) which lists the current
professionally-accepted clinical standards and current CMS CPMs.
“Inadequate dialysis” would include a trend of results for Kt/V or
URR which do not meet minimum expectations as defined by
community-accepted standards or CMS CPMs for a three month
period of time. Refer to the MAT. Inadequate dialysis would also
include symptoms related to fluid management such as volume
overload or depletion; intradialytic symptoms such as syncope or
Final Version 1.1 Page 201 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
congestive heart failure; hypertension; or the need for extra
treatment(s) for fluid removal.
Facilities must have a method for classifying patients as “unstable.”
Documentation should be available of a monthly re-assessment and
plan of care revision that addresses the issues related to the
classification of the patient as “unstable” until the issues have been
resolved or the IDT (including the patient if possible) determine that
the condition is chronic and the active care plan adequately addresses
the issues.
Some “changes” leading to the patient classification of “unstable” are
clearly within the purview of a specific member of the IDT. For
example, while housing instability falls within the realm of the social
worker, expect to see documentation of communication regarding a
change in housing between the social worker and other members of
the IDT who can determine the specific impact of that change on their
specialty. The participation of some team members around some
changes that do not impact their specialty may be limited.
V540
§ 494.90 Condition: Patient plan of care.
The Condition is directly related to the Condition for Patient
assessment, as the plan of care is built upon the patient assessment.
The individual plan of care is revised after each patient assessment,
and portions of the plan of care must be updated if the target goals for
each area are not achieved or not sustained.
The Condition for Patient plan of care reviews individual patient
outcome data and addresses the goals and plans set for individual
patients, while the Condition for Quality assessment and performance
improvement (QAPI) reviews aggregate data for trends and
commonalities and addresses facility-wide goals and improvement
plans.
Survey tasks of observation, patient and staff interviews and medical
Final Version 1.1 Page 202 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
record review are used to evaluate compliance with this Condition.
Identification of issues such as lack of blood pressure monitoring at
the frequencies required by facility policy or as indicated by the
patient’s condition, or the failure to respond to hypertension or
hypotension may indicate a failure to develop or implement a portion
of the plan of care. Use the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT) during
review of records for a ready reference of the current professionally-
accepted clinical practice standards which facilities should be using to
establish targets for individual patient’s clinical outcomes. Recognize
that the standards included in the MAT are targets. Each patient
should be treated individually. When a specified target is not met, the
plan of care should either be adjusted to achieve the target or to
provide an explanation by the IDT in areas where the targets are not
able to be achieved.
Examples of Condition level non-compliance would include, but not
be limited to:
• Serious and/or pervasive deficient practices identified in the
development or implementation of individualized plans of care;
• A pattern of failure to revise the applicable portion of the plans of
care when the current plan did not result in achieving or sustaining
the intended outcome; or
• A pattern of failure in updating the plans of care when indicated
by the patient’s condition.
V541
The interdisciplinary team as defined at § 494.80 must
develop and implement a written, individualized
comprehensive plan of care that specifies the services
necessary to address the patient’s needs, as identified by
the comprehensive assessment and changes in the
patient’s condition, and must include measurable and
expected outcomes and estimated timetables to achieve
these outcomes. The outcomes specified in the patient
plan of care must be consistent with current evidence-
The interdisciplinary team (IDT) consists of, at a minimum, the
patient or the patient’s designee (if the patient chooses), a registered
nurse, a physician who is treating the patient for ESRD, a social
worker, and a dietitian. Each team member must meet the
qualifications outlined in the Condition for Personnel qualifications at
§ 494.140.
The facility must recognize the patient or his/her designee as a
member of the IDT and encourage the patient’s participation in
Final Version 1.1 Page 203 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
based professionally-accepted clinical practice standards.
developing and updating the plan of care. The patient’s needs, wishes,
and goals must be considered in making decisions about the plan of
care. If a patient chooses to use a designee, there must be written
authorization from the patient for sharing of protected health
information with the designee.
A registered nurse with knowledge of the patient must serve as a
member of the team. The registered nurse participating in the plan of
care for home dialysis patients should work in the home dialysis
program and have knowledge of the home dialysis patient.
The written patient plan of care must be individualized for the patient,
built on the comprehensive assessment as outlined at V502-515 under
the Condition for Patient assessment, and include at minimum:
problem(s) identified at assessment/reassessment, measurable
goals/outcomes, planned interventions for achieving the goals,
timetables and reassessment date(s). Review of the plan of care,
treatment records, progress notes, laboratory reports, etc. should
demonstrate implementation of the plan of care.
The patient plan of care includes all of the care, services, and
treatment interventions the IDT determines to implement to meet the
specific needs of the patient. The written patient plan of care may be
one document or composed of separate sections, but must be
congruent and reflect the integration of the comprehensive
assessments contributed by all the members of the IDT. Electronic or
paper formats may be used.
Timelines for meeting the specified targets should be based on setting
reasonable targets for the individual patient, and appropriate to the
severity of the problem and the extent of the planned interventions
(e.g., acute issues should have shorter timelines).
Final Version 1.1 Page 204 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Professionally-accepted clinical practice standards, guidelines and
CMS Clinical Performance Measures (CPM) must be used to derive
the measurable and expected outcomes. Where applicable, refer to the
"Measures Assessment Tool" (MAT) provided which lists the current
professionally-accepted clinical standards and current CMS CPMs.
Goals for some patients may need to be initially different from these
targets, then incrementally changed to the standard target value as the
patient outcome improves.
V542
(a) Standard: Development of patient plan of care. The
interdisciplinary team must develop a plan of care for
each patient.
There must be an interdisciplinary plan of care developed for each
patient. Facilities must have a system for developing patients’ plans of
care. The IDT members are expected to interact and share information
from the comprehensive assessment to facilitate the development of
the plan of care.
To ensure the development of a congruent, integrated patient plan of
care, the facility may conduct IDT conferences or use another
mechanism that ensures the development of an integrated plan. A
substitute mechanism for a team conference needs to facilitate
discussion among team members about the information gathered from
the comprehensive patient assessment and provide the opportunity for
team coordination and development of an effective, individualized
plan of care for the patient to ensure the desired outcomes are
achieved. To facilitate full team participation in conferences, any
member, including the patient, may participate through
telecommunication.
V543
The plan of care must address, but not be limited to, the
following:
(1) Dose of dialysis. The interdisciplinary team must
provide the necessary care and services to manage the
patient's volume status; and
Volume status is measured in terms of the dialysis patient’s “target
weight,” or estimated dry weight (EDW): what the patient would
weigh if he/she were “dry.” A patient at their EDW should be
asymptomatic and normotensive on minimum blood pressure
medications, while preserving organ perfusion and maintaining
existing residual renal function. A patient at their EDW attains
normotension for most of the interdialytic period, while avoiding
orthostatic hypotension or postural symptoms either during or after
Final Version 1.1 Page 205 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
dialysis. Excess fluid accumulation may have adverse effects (e.g.,
hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiovascular
complications, hospitalizations). Removal of too much fluid or
removing it too fast in one dialysis treatment or going below the
patient’s target weight may cause hypotension, muscle cramping, and
clotting of the vascular access. Each patient should be weighed before
and after each treatment. The ultrafiltration component of the
hemodialysis prescription should be optimized with a goal to render
the patient euvolemic and normotensive. With successful fluid
management, the number of medications a patient needs for blood
pressure control may be able to be reduced. There should be a target
weight identified for each patient, and evidence that failure to achieve
the target weight through the dialysis treatment is addressed.
Evidence of implementation of the plan of care for this aspect would
include treatment records reflecting attaining the target weight at the
end of each treatment or documentation acknowledging the target
weight was not attained with an assessment of the reason for not
attaining it, and a plan to correct this issue. The plan should include
frequent assessment of the target weight with changes as indicated;
scheduling an extra treatment; educating staff regarding machine
settings and monitoring; counseling the patient regarding fluid intake;
etc., as indicated for the specific patient and circumstance.
Patients’ blood pressures must be monitored pre, during, and post
treatment and abnormally high or low values must be addressed.
Excessively high or low blood pressure measurements during
treatment without evidence of assessment and action to address those
values would indicate the plan of care for this parameter was either
not developed or not implemented.
V544
Achieve and sustain the prescribed dose of dialysis to
meet a hemodialysis Kt/V of at least 1.2 and a peritoneal
dialysis weekly Kt/V of at least 1.7 or meet an alternative
The patient plan of care should use dialysis adequacy goals in
accordance with current professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards/CMS CPMs. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool
Final Version 1.1 Page 206 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
equivalent professionally-accepted clinical practice
standard for adequacy of dialysis.
(MAT) which lists those for dialysis adequacy.
The patients’ dialysis prescriptions (dialyzer, blood flow rate,
dialysate flow rate, length of treatment time) and the efficacy of the
vascular access affect the dose of dialysis delivered. If alarms stop the
dialysis ultrafiltration “clock”, the “remaining treatment time” or
planned treatment time may need to be extended to fulfill the patient’s
dialysis prescription.
In meeting this requirement, the IDT should review the Kt/V results to
determine if the patient’s adequacy values attain the goal; if not, the
IDT should compare treatment orders and dialysis treatment records
to determine if the prescribed dose of dialysis is being delivered. If the
patient is not receiving an adequate treatment, the IDT should develop
a plan to address the problem. For example, if a conventional 3 times
a week HD patient's Kt/V is below 1.2 for several testing consecutive
periods, a causal analysis should be done and the plan of care revised
to address the identified problems.
Patients should have an understanding of dialysis adequacy and the
consequences of skipping dialysis treatments or cutting treatments
short. If the patient shortens treatments, misses treatments, or gains
excessive fluid between treatments, the prescribed dose of dialysis
may not be able to be delivered. If a patient routinely shortens or skips
treatments, the plan of care for adequate treatment should investigate
the root cause(s) (e.g., fear of intradialytic morbidity, prolonged
recovery time, schedule conflicts with life responsibilities,
transportation issues) and work with the patient to reduce or correct
the cause(s). Ultimately, the patient can choose to continue behaviors
that result in lessened treatment results. With documentation of
educational efforts, the patient’s choice can be an explanation on a
plan of care for not achieving standard treatment results.
Final Version 1.1 Page 207 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The requirements for patient assessment of dose of dialysis are at
V518.
V545
(2) Nutritional status. The interdisciplinary team must
provide the necessary care and counseling services to
achieve and sustain an effective nutritional status. A
patient’s albumin level and body weight must be
measured at least monthly. Additional evidence-based
professionally-accepted clinical nutrition indicators may
be monitored, as appropriate.
The facility must have established target goals for patients' albumin
levels, and monitor each patient's body weight trends. Other
nutritional markers including, but not limited to, sodium, calcium,
phosphorus, and potassium, should also be routinely monitored.
Facilities may use additional nutritional markers and assessments as
determined by the IDT. The nutritional marker targets, including
albumin, should reflect professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT) which lists
the current professionally-accepted clinical standards for nutritional
status markers. At the time of publishing these regulations, there were
two methods of measuring albumin in use, with different ranges.
If the patient record shows a trend of problems in the patient’s
nutritional status, the IDT must develop an outcome-oriented plan of
care for nutritional status and implement the plan. For example, if the
patient's albumin levels were consistently below target levels, there
should be an individualized plan of care to address the possible causes
(e.g., inadequate dialysis, poor understanding of diet, limited
availability of nutritious food, fluid volume overload). To meet the
requirement to “achieve and sustain an effective nutritional status,”
the medical records of patients with outcomes lower than the expected
standard should demonstrate continuing efforts tailored, implemented,
assessed for success, and revised to address the individual patient
challenges in this area. In the event the patient has a wasting disease,
cachexia, or chronic inflammation contributing to a poor nutritional
state, the plan of care should acknowledge these as limiting factors in
achieving and sustaining the goal for nutritional status.
While it is not expected or required for facilities to provide nutritional
supplements, the dietitian is expected to assist patients in achieving
their nutritional goals by providing education, counseling and
Final Version 1.1 Page 208 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
encouragement.
The requirements for patient assessment of nutritional status are at
V509.
V546
(3) Mineral metabolism. Provide the necessary care to
manage mineral metabolism and prevent or treat renal
bone disease.
Disturbances in mineral and bone metabolism are common in patients
with ESRD, often resulting in hyperparathyroidism and Chronic
Kidney Disease (CKD) mineral and bone disorder, if not managed
effectively. The lab markers of calcium, phosphorous and parathyroid
hormone (PTH) are generally used to monitor mineral metabolism.
Expect the facility to have established target goals for patients'
calcium, phosphorus and PTH levels which reflect professionally-
accepted clinical practice standards and CMS CPMs. Refer to the
Measures Assessment Tool (MAT) which lists the targets for CKD
mineral and bone disorder.
Interventions for prevention and management of CKD mineral and
bone disorder may include nutritional counseling, and the
administration of medications (e.g., phosphate binders, vitamin D
analogs, calcimimetic agents). If the facility is using a medication
algorithm/protocol for managing CKD mineral and bone disorder, the
care for each patient must be individualized. The physician or non
physician practitioner (i.e., advanced practice registered nurse or
physician assistant) is responsible for ordering medications and
laboratory tests and may or may not prescribe standing orders or the
use of a standard algorithm.
Pediatric patients present special growth and development needs for
management in this area. Facilities treating pediatric patients should
have specialized methods for monitoring and management of CKD
mineral and bone disorder.
The methods used for management of CKD mineral and bone disorder
Final Version 1.1 Page 209 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
should be evident in review of records for laboratory reports, orders
for CKD mineral and bone disorder management medications (e.g.
vitamin D analogs) and medication administration records. Each
patient’s laboratory values must be monitored, values outside the
target levels addressed, doses adjusted, and medications administered
as ordered. If the patient’s mineral metabolism goals are not being
attained to “manage and prevent or treat” CKD mineral and bone
disorder, the team should identify potential causes and address the
barriers that may be preventing the patient from reaching the target
values (e.g., failure to take medications or follow prescribed diet, lack
of understanding or resources to obtain medications). Patients must be
educated to understand their role in managing the prescribed diet,
medications, and managing bone health. Enlistment of patients to be
involved in their care is critical to success and attainment of these
goals.
The requirements for patient assessment of CKD mineral and bone
disorder are at V508.
V547
(4) Anemia. The interdisciplinary team must provide the
necessary care and services to achieve and sustain the
clinically appropriate hemoglobin/hematocrit level.
The patient’s hemoglobin/hematocrit must be measured
at least monthly. The dialysis facility must conduct an
evaluation of the patient's anemia management needs.
The facility must establish targets in anemia management that reflect
professionally-accepted clinical practice standards/CMS CPMs. Refer
to the MAT which lists these for anemia management.
The IDT should have a plan for managing patients’ anemia. The
laboratory reports, orders for erythropoiesis-stimulating agents
(ESAs) and medication administration records should be considered
as a part of the anemia management program. Facilities that use
medication algorithms or protocols for managing anemia must ensure
that the care for each patient is individualized. The physician or a non-
physician practitioner (i.e., advanced practice registered nurse, or
physician assistant) is responsible for ordering medications and
laboratory tests and may or may not use standing orders or a standard
algorithm.
Final Version 1.1 Page 210 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Each patient’s laboratory values must be monitored, and values
outside the target levels must be addressed, doses adjusted, and ESAs
administered as ordered. Hemoglobin/hematocrit values must be
measured at least monthly; many facilities measure these more
frequently, especially if the values are outside the recommended target
range or the patient has co-morbid conditions (such as cardiovascular
disease) which may warrant more frequent monitoring. The IDT team
must assess each patient to identify his or her unique needs for anemia
management.
If there is a trend of problems in managing an individual patient’s
anemia, the IDT must develop an outcome-oriented plan based on
their assessment of the problem and identification of possible barriers
to attaining the goals. Due to various co-morbid conditions (e.g.,
sickle cell disease, persistent iron deficiency, frequent
hospitalizations, chronic blood loss, cancer, infection, fluid volume
overload), some patients may not respond to ESA therapy as expected.
In the event of hyporesponse, there must be evidence that the patient
was evaluated as to the possible underlying cause(s) for the resistance
to anemia management therapy and the plan of care revised
accordingly. ESA therapies have been found to be detrimental to some
patients when administered at high doses or when the hemoglobin
level is driven above 13. The IDT must take all information regarding
ESA therapies into account as they manage the anemia of individual
patients.
The requirements for patient assessment of anemia are at V507.
V548
For a home dialysis patient, the facility must evaluate
whether the patient can safely, aseptically, and
effectively administer erythropoiesis-stimulating agents
and store this medication under refrigeration if
necessary.
The home dialysis patient and/or caregiver must be trained and
determined competent by a home dialysis nurse in the safe
administration and storage of ESAs. Use this tag if issues specifically
related to safe use and storage of ESAs are identified. Refer to the
Condition for Care at home at V585.
V549
The patient's response to erythropoiesis-stimulating
The facility must monitor patients' blood pressures and act upon
Final Version 1.1 Page 211 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
agent(s), including blood pressure levels and utilization
of iron stores, must be monitored on a routine basis.
significant abnormalities for that patient. Hypertension may have
many causes; failure to develop and implement a plan to control high
blood pressure should be cited at V543.
Measurements of patients' iron stores include serum ferritin and
transferrin saturation. The facility must establish targets for iron
management that reflect professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards/CMS CPMs. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool
(MAT) which lists these for anemia/iron management.
If the IDT chooses to use medication algorithms or protocols for
anemia/iron management, the care for each patient must be
individualized. The physician or a non-physician practitioner (i.e.,
advanced practice registered nurse, or physician assistant) is
responsible for ordering medications and laboratory tests and may or
may not use standing orders or an algorithm.
The IDT must develop a program for anemia and iron management,
and monitor laboratory results, orders for intravenous iron
preparations and medication administration records to address values
outside the target levels. Laboratory values outside the target levels
must be addressed, doses adjusted, and medications administered as
ordered.
If there is a trend of problems in iron management for an individual
patient, the IDT must develop an outcome-oriented plan based on
their assessment of the problem and identification of possible barriers
to attaining the goals.
The requirements for patient assessment of anemia/iron are at V507
and for blood pressure/fluid management at V504.
V550
(5) Vascular access. The interdisciplinary team must
provide vascular access monitoring and appropriate,
Based on the comprehensive assessment, the facility IDT must
develop and implement a plan of care to facilitate each hemodialysis
Final Version 1.1 Page 212 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
timely referrals to achieve and sustain vascular access.
The hemodialysis patient must be evaluated for the
appropriate vascular access type, taking into
consideration co-morbid conditions, other risk factors,
and whether the patient is a potential candidate for
arteriovenous fistula placement.
patient receiving and maintaining the most appropriate and optimal
vascular access identified for that patient.
A well functioning vascular access enables the hemodialysis patient to
receive efficient/adequate dialysis treatments, enhancing their quality
of life. The determination of which type of vascular access is the most
appropriate for the individual patient requires the integration and
coordination between the facility IDT, including the patient/designee,
and may include referrals for vessel mapping, surgical consult,
Doppler studies, etc., enlisting the participation of other entities, such
as primary care physicians, surgeons, interventional radiology, and
surgical or vascular access centers for access placement and
maintenance.
To meet this requirement to “achieve and sustain” vascular access, the
patient's medical record must include evidence of the evaluation and
the basis for the decision for placement of the current vascular access.
If the records from the surgeon are not available, the patient’s
physician, advanced practice registered nurse or physician assistant is
expected to provide this information from communication with the
surgeon. If the patient's vascular access is not an arteriovenous fistula,
the record should indicate why the patient was determined to not be a
candidate for a fistula. If a patient has been dialyzed with a central
venous catheter in excess of 90 days, there should be an active plan in
process for the placement of a more permanent vascular access or
information in the record to demonstrate that a catheter is the most
appropriate vascular access for that patient. Some patients may not be
candidates for a fistula or graft; each patient has a right to make an
informed choice. Patients must be informed and educated about the
benefits, risks and hazards of each type of vascular access. Repeated
education may be needed. The IDT must involve the patient/designee
in the plan for vascular access. The facility social worker should be
involved and determine whether psychosocial considerations, such as
Final Version 1.1 Page 213 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
body image, needle fear or anxiety need to be addressed.
Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT) which lists the current
professionally-accepted clinical standards and CMS CPMs for
vascular access. The MAT incorporates measures/standards from the
Department of Health and Human Services’ Fistula First
Breakthrough Initiative. This initiative has joint goals of increasing
fistula use in dialysis patients, while also decreasing the inappropriate
use of catheters in these patients.
Vascular access monitoring is addressed in V551. Requirements for
vascular access assessment are at V511.
V551
The patient’s vascular access must be monitored to
prevent access failure, including monitoring of
arteriovenous grafts and fistulae for symptoms of
stenosis.
The facility must have an on-going program for vascular access
monitoring and surveillance for early detection of failure and to allow
timely referral of patients for intervention when indications of
significant stenosis are present. Patient education should address self-
monitoring of the vascular access.
“Monitoring” strategies may include physical examination of the
vascular access; observance of changes in adequacy or in pressures
measured during dialysis; difficulties in cannulation; or in achieving
hemostasis. Precipitating events should also be noted, such as
hypotension or hypovolemia. Surveillance strategies include device-
based methods such as access flow measurements, direct or derived
static venous pressure ratios, duplex ultrasound, etc.
For patients with grafts and fistulas, the medical record should show
evidence of periodic monitoring and surveillance of the vascular
access for stenosis and signs of impending failure. The documentation
of this may be on the dialysis treatment record, progress notes, or on a
separate log. A member of the facility staff must review the vascular
access monitoring/surveillance documentation to identify adverse
trends and take action if indicated.
Final Version 1.1 Page 214 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Refer to the Condition for Infection Control at V147 and V148 and
the Condition for QAPI at V633 which also cover monitoring and
surveillance of vascular accesses.
V552
(6) Psychosocial status. The interdisciplinary team must
provide the necessary monitoring and social work
interventions. These include counseling services and
referrals for other social services, to assist the patient in
achieving and sustaining an appropriate psychosocial
status as measured by a standardized mental and physical
assessment tool chosen by the social worker, at regular
intervals, or more frequently on an as-needed basis.
To address the patient’s psychosocial needs and “achieve and sustain”
an appropriate psychosocial status, each patient's plan of care must
reflect the information obtained from the applicable components of
the IDT comprehensive assessment under the Condition for Patient
assessment at V502-V515, including the psychosocial assessment at
V510. The plan of care must include interventions individualized to
meet that patient's psychosocial needs and aimed at optimizing the
patient’s adjustment to kidney failure and its treatment. The social
worker is expected to assist patients in achieving their psychosocial
goals. Counseling services to patients and their families should be
directed at helping the patient and family cope with kidney failure and
dialysis, follow the treatment plan, and achieve the patient’s goals for
rehabilitation.
While this regulation allows the social worker to choose a
“standardized mental and physical assessment tool,” the tool selected
by the National Quality Forum and the CMS CPMs for adult patients
is the KDQOL-36 assessment survey. In the future, the percentage of
patients taking this assessment survey annually will need to be
reported electronically to CMS. Facilities may choose to use the
KDQOL-36 from the implementation date of these regulations in
order to have more comparable data once the KDQOL-36 is
mandated. Pediatric patients should be assessed using an age
appropriate assessment tool.
“At regular intervals” means that the assessment survey is
administered by the time of the first reassessment (i.e., within 4
months of initiating treatment), and repeated at least annually.
Examples of an “as needed basis” would include repeat use of the
Final Version 1.1 Page 215 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
survey with the patient who has a significant life changing event (e.g.,
loss of spouse, loss of job, recent move to a nursing home) or a
change in health status.
The social worker must have a system for routine use of the
assessment survey, evaluation of the results, and incorporation of the
survey results into the development and updating of the psychosocial
portion of the plan of care.
Referrals for social services may include those to providers of
community mental health services, transportation providers, in-home
support services, food banks or other available community resources.
Patients will vary in their needs for interaction with the social worker
and referral for other social services. Enhanced and more frequent
social services interventions are expected for patients who present
with or develop greater psychological, social, and/or financial issues.
Refer to the MAT which lists the current professionally-accepted
clinical standards and current CMS CPMs for psychosocial status.
The requirements for assessment of patients' psychosocial needs are at
V510.
V553
(7) Modality.
(i) Home dialysis.
The interdisciplinary team must identify a plan for the
patient's home dialysis or explain why the patient is not a
candidate for home dialysis.
The patient plan of care must reflect the information from the IDT
evaluation of the patient’s suitability for and level of interest in home
dialysis modalities required under the Condition for Patient
assessment at V512.
Patient records must demonstrate that each patient was informed
about all available dialysis modalities and locations for home dialysis
training if that service is not available at this facility. If the patient
expressed interest in home dialysis and was determined to be a
suitable candidate, the plan of care should list use of this modality as a
goal and identify ways to achieve it (e.g., timeline for training in
Final Version 1.1 Page 216 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
home dialysis at current facility, referral to a facility certified for
home training and support). If the patient declined or was determined
not suitable for home dialysis, the IDT must document their rationale
for this decision.
V554
(ii) Transplantation status. When the patient is a
transplant referral candidate, the interdisciplinary team
must develop plans for pursuing transplantation. The
patient’s plan of care must include documentation of
the–
(A) Plan for transplantation, if the patient accepts the
transplantation referral;
(B) Patient’s decision, if the patient is a transplantation
referral candidate but declines the transplantation
referral; or
(C) Reason(s) for the patient’s nonreferral as a
transplantation candidate as documented in accordance
with § 494.80(a)(10).
The patient’s plan of care must reflect the information from the
interdisciplinary team’s evaluation of the patient's suitability for
transplantation referral, required under the Condition for Patient
assessment at V513.
The patient record must show evidence that the patient was informed
about transplantation as an option, living and deceased kidney
donation, area transplant center(s) and each transplant facility’s
selection criteria. Each patient's record must reflect the IDT's
determination about the patient's suitability and whether the patient
accepted or declined referral for transplantation and reason for
nonreferral.
If a patient was determined as suitable for transplantation referral, the
IDT must document making the referral and providing applicable
information to the transplant center as appropriate or when requested.
Documentation in patient records should agree with the patient’s
understanding of their status as a transplant candidate. Patients may
independently contact a transplant center for an appointment for more
information and evaluation. If this is the case, the IDT should be
aware of the self-referral. A patient’s insurance coverage and a
transplant center’s selection criteria may dictate which transplant
center(s) the patient can access.
V555
(8) Rehabilitation status. The interdisciplinary team must
assist the patient in achieving and sustaining an
appropriate level of productive activity, as desired by the
patient, including the educational needs of pediatric
patients (patients under the age of 18 years), and make
The patient plan of care must reflect the information from the
interdisciplinary patient evaluation/assessment for rehabilitation status
required at V515. The goals for the plan of care in this area must be
individualized for the patient (e.g., return to a former occupation,
attain an educational certificate or diploma, return to normal activities
Final Version 1.1 Page 217 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
rehabilitation and vocational rehabilitation referrals as
appropriate.
within a household, etc.) and reflect the patient's preferences.
Pediatric patient services should address normal growth and
development needs, education needs, and age-appropriate activities,
especially if dialysis treatments take place during hours when the
child would normally be in school.
The social worker should be aware of the availability of community
referral options for physical and vocational rehabilitation services for
all patients, and educational resources for pediatric patients, if
applicable for this facility. The IDT should have a plan and procedure
for making referrals for rehabilitation.
The IDT must provide and document assistance (e.g., education,
encouragement) and referrals, if indicated, which were aimed at
enabling patients to maintain or return to their desired level of
functioning at work, school, home and in their community.
V556
(b) Standard: Implementation of the patient plan of care.
(1) The patient’s plan of care must–
(i) Be completed by the interdisciplinary team, including
the patient if the patient desires; and
(ii) Be signed by the team members, including the patient
or the patient’s designee; or, if the patient chooses not to
sign the plan of care, this choice must be documented on
the plan of care, along with the reason the signature was
not provided.
The IDT consists of, at a minimum, the patient/designee, a registered
nurse, the qualified social worker, the qualified dietitian, and the
patient’s physician. Refer to the Condition for Patient assessment at
V501. The patient’s level of participation should be controlled by the
patient’s (not the staff’s) motivation; however, staff encouragement
can improve patient motivation. Each patient’s plan of care must show
evidence of the participation/contribution from all of the professional
members of the IDT.
Each team member is expected to sign the plan of care, including the
patient. The patient’s signature is to acknowledge the information in
the plan. If the patient chooses not to sign their plan of care, the
reason for refusal must be documented.
V557
(2) Implementation of the initial plan of care must begin
within the latter of 30 calendar days after admission to
the dialysis facility or 13 outpatient hemodialysis
The timeline for both the completion of the initial comprehensive
assessment and the beginning of implementation of the initial patient
plan of care is the latter of 30 days from the date of admission or 13
Final Version 1.1 Page 218 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
sessions beginning with the first outpatient dialysis
session.
hemodialysis treatments at the facility. Refer to V516. For patients
who have more than 3 treatments a week, e.g., those on peritoneal
dialysis or daily/nocturnal hemodialysis, the plan of care is expected
to be completed within 30 days from the date of admission, excluding
any days the patient is hospitalized during that period.
The plan of care should be dated to indicate when the plan was
initiated. Although the plan of care must be initiated within the
required timeline, the schedule for full implementation of the plan will
vary depending upon the complexity of the plan.
In order for dialysis treatment to be initiated, each patient must have
an initial dialysis prescription, orders for care, and baseline physical
and nursing assessments before treatment is begun at the facility. See
V715 under the Condition for Medical director for this requirement.
V558
Implementation of monthly or annual updates of the plan
of care must be performed within 15 days of the
completion of the additional patient assessments
specified in § 494.80(d).
As specified in the Condition for Patient assessment at V519 and
V520, when there is an interdisciplinary comprehensive reassessment
of the patient, the plan of care must be updated accordingly and
implementation initiated within this timeline.
Monthly updates of the plan of care are required for unstable patients,
while annual updates are acceptable for stable patients. Refer to V520
for the minimum criteria for stable vs. unstable status.
The implementation of updates to the patient plan of care must be
completed within 15 days of the reassessment.
V559
(3) If the expected outcome is not achieved, the
interdisciplinary team must adjust the patient’s plan of
care to achieve the specified goals. When a patient is
unable to achieve the desired outcomes, the team must—
(i) Adjust the plan of care to reflect the patient's current
condition;
(ii) Document in the record the reasons why the patient
If the current plan of care has not been successful in achieving the
goals identified by and for the patient within the identified timetables,
there must be evidence that barriers to achievement of the goals were
identified and that the plan was reviewed and revised, as indicated.
For example, if the patient's Kt/V is below the expected goal for more
than one month, the physician or the non-physician practitioner might
adjust the dialysis prescription by extending the treatment time or
Final Version 1.1 Page 219 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
was unable to achieve the goals; and
(iii) Implement plan of care changes to address the issues
identified in paragraph (b)(3)(ii) of this section.
changing the dialyzer. If the patient’s Kt/V remained below target the
following month, the team should collaboratively identify the
potential reasons the patient is not reaching the minimum goal for
hemodialysis adequacy and implement changes in the plan of care to
address and resolve the identified barriers. This example would not
require a reassessment and completely new plan of care; if this is the
only area where the goal was not met, the patient could be considered
“stable,” and only the plan of care for adequacy would require
adjustment.
This requirement is not met if the patient's plan of care is not adjusted
and there is no evidence the IDT is working to address ongoing
problems (e.g., uncontrolled hypertension, hyperkalemia, missed
treatments, inaccurate or unattainable target weight) which may result
in adverse outcomes for the patient. This requirement is not satisfied if
the only reason documented for failure to achieve goal(s) is “patient
non-compliance” or “non-adherence.” If the team believes the cause
of the failure to reach the goal is non-adherence, the IDT efforts
should focus on identifying potential causes of the non-adherence and
addressing those causes. The IDT must recognize each patient has the
right to choose less than optimal care when the patient determines
optimal care would negatively impact his/her quality of life.
These regulations require the IDT to demonstrate its members are
actively attempting to meet each patient’s plan of care goals. This
Condition does not “require” a patient to meet every goal. Any
member of the IDT, including the patient, may document why goals
are not met or cannot be met.
V560
(4) The dialysis facility must ensure that all dialysis
patients are seen by a physician, nurse practitioner,
clinical nurse specialist or physician's assistant providing
ESRD care at least monthly, as evidenced by a monthly
progress note placed in the medical record, and
This requirement is to ensure that patients see a medical practitioner
(i.e., physician, advanced practice registered nurse or physician
assistant) at least monthly. The patient may see the practitioner in the
dialysis facility (before, during or after treatment), or in the
physician’s office if the record of care for that visit is incorporated
Final Version 1.1 Page 220 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
periodically while the hemodialysis patient is receiving
in-facility dialysis.
into the dialysis facility medical record.
“Periodically while the hemodialysis patient is receiving in-facility
dialysis” is meant to refer to in-center patients and should generally
result in at least quarterly practitioner visits at the dialysis center
during dialysis treatment. By periodically visiting the patient in the
dialysis facility, the physician has an opportunity to assess the
patient’s response to treatment and to observe the team care.
At a minimum, monthly medical progress notes should document that
a physician or that a non-physician practitioner (i.e., advanced
practice registered nurse or physician assistant) who functions in lieu
of the physician, has seen each patient and addressed the status and
plan for that patient's renal and active comorbid problems.
This requirement applies equally to home patients, who are expected
to receive equivalent care to in-center patients. A monthly visit is
required for each home patient by either a physician, an advanced
practice registered nurse, or a physician assistant. This visit may be
conducted in the dialysis facility, at the physician’s office, or in the
patient’s home.
Any patient may choose not to be seen by a physician every month.
However, if there is a pattern of a patient consistently missing
physician visits, the IDT should determine whether or not the patient
is unstable according to these regulations, and should address the lack
of medical oversight with the patient in the plan of care.
V561
(c) Standard: Transplantation referral tracking. The
interdisciplinary team must—
(1) Track the results of each kidney transplant center
referral;
(2) Monitor the status of any facility patients who are on
the transplant wait list; and
Requiring the facility to track patients' transplant referrals and their
status on the transplant wait list is intended to enhance the
communication and coordination between the transplant center and
the dialysis facility so that patients do not get "lost" along the way in
the transplant referral, work up and waiting period.
Final Version 1.1 Page 221 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(3) Communicate with the transplant center regarding
patient transplant status at least annually, and when there
is a change in transplant candidate status.
Tracking completion of the tests and evaluations required for a
transplant work up and waiting list active status is primarily the
responsibility of the patient in partnership with the transplant center.
However, by communicating and coordinating activities with the
transplant center, the dialysis facility IDT may be able to adjust their
plan of care to facilitate the patient's transplantation goal. This
communication should be systematic and documented.
A “change in status” refers to a medical or psychosocial event that
could either temporarily or permanently change a transplant patient’s
status. The “change” could either enhance or limit a dialysis patient’s
opportunities to receive a transplant. Examples of “change” events are
cardiac events, weight loss, cessation of smoking, or identification of
a new potential living organ donor. The transplant center should be
notified at the time of any change in status.
The facility's patient transplant referral/waiting list status tracking
may be centralized, but must also be documented in each referred
patient's medical record.
V562
(d) Standard: Patient education and training. The patient
care plan must include, as applicable, education and
training for patients and family members or caregivers or
both, in aspects of the dialysis experience, dialysis
management, infection prevention and personal care,
home dialysis and self-care, quality of life, rehabilitation,
transplantation, and the benefits and risks of various
vascular access types.
The dialysis facility must provide patients and their family
members/caregivers with education and training in these listed areas,
at a minimum.
The IDT must have the skills and expertise needed to educate dialysis
patients in these subjects, and to provide this education in a manner
understood by the patient and family/caregiver.
Patients/designees must receive education regarding the types, risks,
benefits and care of their vascular access, personal hygiene related to
dialysis access, infection prevention, dietary and fluid management,
etc. The patient’s medical record must demonstrate the provision of
patient education and training in all of the listed subject areas. There
may be a single form or section of the medical record for information
Final Version 1.1 Page 222 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
on patient education or it may be located in various parts of the
record, such as the progress notes of the members of the IDT.
V580
§ 494.100 Condition: Care at home.
This Condition applies to those facilities that provide training and
support services for any type of home dialysis. This Condition focuses
on items that are unique to the home dialysis modality. All of the
ESRD Conditions must be met regardless of whether the setting is in-
center or at home.
Patient and staff interviews are critical to the survey of this Condition.
Other important aspects of the survey process for this Condition
include observation of training (if the opportunity is available) and
review of patient medical records and administrative records. Home
patients may be available for in-person interviews during training or a
clinic visit, or if there are no home dialysis patients on-site at the
facility during the survey, interviews with these patients or their
helpers may be conducted by phone.
Condition-level noncompliance should be considered in, but not
limited to, the following circumstances:
• Serious or pervasive problems with the oversight of care or
provision of services for home dialysis patients which has or could
impact the health and safety of those patients;
• Patients and/or helpers inadequately trained yet verified as
competent in performing home dialysis procedures, resulting in
poor clinical outcomes or adverse events;
• A pattern of failure to review clinical or technical lab reports and
records; and
• Insufficient monitoring of the water treatment system for home
hemodialysis.
V581
A dialysis facility that is certified to provide services to
home patients must ensure through its interdisciplinary
team, that home dialysis services are at least equivalent
to those provided to in-facility patients and meet all
Home dialysis patients are considered part of the census of the ESRD
facility and are entitled to the same rights, services, and efforts to
achieve expected patient outcomes as the in-center dialysis patients of
the facility. All of the requirements of these regulations including
Final Version 1.1 Page 223 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
applicable conditions of this part.
those listed at the Conditions for Patients' rights, Patient assessment,
Patient plan of care, and QAPI apply equally to home dialysis patients
as well as to in-center dialysis patients.
Home dialysis patients include those receiving peritoneal dialysis
(PD) and hemodialysis (HD) therapies in their homes. At the time of
publishing these regulations, there were:
• Two methods of PD routinely available to home patients:
continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and continuous
cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD) also known as automated PD
(APD); and
• Three methods of HD routinely available to home patients:
conventional home HD (treatments generally 3 to 4 hours, 3 days
a week); short daily home HD (2-3 hours, 5-6 days/week); and
nocturnal home HD (6-8 hours, 3 to 6 nights/week).
At the time of publishing these regulations, several different
technologies for home hemodialysis were available. These included
conventional water treatment components and single-pass
(conventional) dialysis machines; integrated systems which used
manufacturer packaged, bagged dialysate or which incorporated water
treatment and dialysate preparation and delivery into one system; and
sorbent-based systems which utilized columns (cartridges) of
chemicals to regenerate the used dialysate for recirculation through
the dialyzer. All of these, and any future home hemodialysis
technologies developed, present the home dialysis facility with both
common and unique challenges for monitoring to ensure the
continued efficacy and safety of the home hemodialysis patients'
treatments.
For all home dialysis patients of the certified ESRD facility whose
treatments incorporate the use of a dialysis machine, CMS
reimbursement rules require that there be one machine used
Final Version 1.1 Page 224 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
exclusively for each individual patient's home dialysis treatments. The
same dialysis machine must not be used for treatment of multiple
home patients.
The “interdisciplinary” team (IDT) consists of, at a minimum, the
patient or the patient’s designee (if the patient chooses), a registered
nurse, a physician treating the patient for ESRD, a social worker, and
a dietitian who meet the requirements as specified under the Condition
for Personnel qualifications. Most home dialysis patients are active
participants in their care and actively engaged with the
interdisciplinary team in their plan of care.
The medical records of home dialysis patients should contain
evidence of the care and management aspects of patient assessment,
plan of care development and implementation of that plan of care by
the facility interdisciplinary team as outlined in these regulations.
V582
(a) Standard: Training. The interdisciplinary team must
oversee training of the home dialysis patient, the
designated caregiver, or self-dialysis patient before the
initiation of home dialysis or self-dialysis (as defined in
§ 494.10) and when the home dialysis caregiver or home
dialysis modality changes.
As defined at § 494.10 Definitions, "Home dialysis” means dialysis
performed at home by an ESRD patient or “caregiver” (also called a
“helper”) who has completed an appropriate course of training as
described in § 494.100(a) of this part; “Self-dialysis” means dialysis
performed with little or no professional assistance by an ESRD patient
or helper who has completed an appropriate course of training as
specified in § 494.100(a) of this part.
A certified dialysis facility approved for outpatient maintenance
dialysis services needs no additional certification or approval to
provide in-center self-dialysis or to teach an in-center patient to
perform all or part of their dialysis treatment (e.g., self-cannulate,
monitor blood pressure). If a patient expresses the desire to perform
self-dialysis in-center, the facility interdisciplinary team's response
should incorporate assessment of that patient for self-care training and
planning for the goal of self-care as appropriate. Refer to V512 under
Patient assessment. Any patient who performs aspects of self-dialysis
Final Version 1.1 Page 225 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
care must be trained and verified as competent prior to independently
performing any part of his/her care.
Home dialysis training must be provided, and the patient and/or helper
verified as competent to perform home dialysis before they are
allowed to function independently. Although it is expected that most
training for home dialysis would take place at the facility, home
training may be provided in the patient’s home to meet the individual
needs of the patient and/or helper. Retraining must be provided
whenever there is a change in home dialysis helper, treatment
modality, or home dialysis equipment. Retraining may also be
indicated if there are problems such as repeated episodes of
peritonitis, vascular access infections, or a failure to achieve expected
outcomes, including goals for dialysis adequacy and anemia
management.
V583
The training must—
(1) Be provided by a dialysis facility that is approved to
provide home dialysis services;
For a dialysis facility to provide a home dialysis program, the facility
must be certified for home dialysis services including both training
and support. The facility may choose to apply for certification for
peritoneal dialysis (PD) only, home hemodialysis (HHD) only, or both
services. These services may be added to an existing facility. A new
facility may apply for home dialysis services in addition to in-center
services, or to provide only home dialysis services. The facility
application for home dialysis should be directed to the State survey
agency.
There are two “methods” of home dialysis delivery:
• Method I: the certified ESRD facility provides both training and
all support including equipment and supplies; and
• Method II: the ESRD facility provides training and most support,
but a Durable Medical Equipment (DME) supplier provides the
home dialysis equipment and supplies. DMEs are not certified for
and cannot provide home training.
Final Version 1.1 Page 226 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The CMS-3427 End Stage Renal Disease Application/Notification
and Survey and Certification Report should be completed to indicate
that the facility is approved for PD and/or HHD training and support.
V584
(2) Be conducted by a registered nurse who meets the
requirements of § 494.140(b)(2); and
The nurse responsible for home dialysis training must be a registered
nurse who meets the practice requirements of the State in which he or
she is employed; have at least 12 months experience in providing
nursing care; and an additional 3 months of experience working as a
nurse in the specific modality (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis) for
which the nurse will provide patient/helper training. Refer to V685.
While the qualified home training RN(s) is expected to be the primary
staff member providing training and support whether training occurs
in the dialysis facility or in the patient’s home, other members of the
clinical dialysis staff may assist in providing the home training, within
the scope of practice and expertise/competencies of those staff
members. For example, another nurse might reinforce earlier training
done by the qualified RN; the dietitian might educate the patient about
food and fluid limits based on the type of home dialysis treatment; the
social worker might offer suggestions for keeping one’s job or coping
with any stress potentially created by home treatment; and the biomed
staff might coach the patient/helper in troubleshooting equipment. The
qualified home training RN is responsible to ensure that the all of the
training is in accordance with the requirements listed in this
Condition.
Use V685 for the failure to have a qualified nurse; use this tag if the
qualified nurse is not primarily responsible for conducting training.
V585
(3) Be conducted for each home dialysis patient and
address the specific needs of the patient, in the following
areas:
(i) The nature and management of ESRD.
(ii) The full range of techniques associated with the
treatment modality selected, including effective use of
The training must be individualized to the needs of each home dialysis
patient. Patients/helpers may be trained in small groups or
individually, as long as the individual patient's needs are identified
and addressed. The information provided should be tailored to the
patient’s/helper's level of understanding. Each of the subject areas
listed here should be addressed in the record of the training. Examples
Final Version 1.1 Page 227 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
dialysis supplies and equipment in achieving and
delivering the physician’s prescription of Kt/V or URR,
and effective administration of erythropoiesis-
stimulating agent(s) (if prescribed) to achieve and
maintain a target level hemoglobin or hematocrit as
written in patient’s plan of care.
(iii) How to detect, report, and manage potential dialysis
complications, including water treatment problems.
(iv) Availability of support resources and how to access
and use resources.
(v) How to self-monitor health status and record and
report health status information.
(vi) How to handle medical and non-medical
emergencies.
(vii) Infection control precautions.
(viii) Proper waste storage and disposal procedures.
for clarification of the subject areas are as follows:
The "full range" of home dialysis techniques would include:
• Specific (step-by step) instructions on how to use the patient’s
prescribed dialysis equipment (e.g. hemodialysis machine and
water treatment components, peritoneal dialysis cycler);
• Specific (step-by step) instructions in home dialysis procedures
(e.g. self-cannulation, peritoneal dialysis exchange) to facilitate
adequate dialysis as prescribed by the physician; and
• Training in proper storage and administration of ESAs, if
applicable. Refer to V548 for anemia management requirements
for home patients.
Peritoneal dialysis patients must be taught to recognize, manage and
report dialysis complications, including catheter, tunnel or exit site
infection; peritonitis; catheter dislodgement; hypotension;
hypokalemia; failure of sufficient dialysate to drain from the
peritoneal space; protein malnutrition; etc. Home hemodialysis
patients must be taught to recognize, manage and report such potential
complications as vascular access problems (e.g., difficulty with
cannulation, a change in bruit or thrill, bleeding), infections,
hypertension or hypotension, hyperkalemia, etc.
Technical problems to be recognized, managed and reported would
include power outages, failure of the PD cycler or HD machine,
failure of water treatment components (e.g., chlorine/chloramine
breakthrough), clotting of the hemodialysis circuit, dialyzer blood
leaks, line disconnection, water supply problems or leaks, and
problems with supply delivery.
The facility training program should include instruction aimed at
enabling patients/helpers to detect, prioritize and report problems and
to ensure that they are prepared to recognize and promptly act upon
Final Version 1.1 Page 228 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
those situations which could present hazards to patient safety.
Training home dialysis patients/helpers to "handle" medical
emergencies that may be anticipated (e.g., syncope, significant blood
loss, cardiac events) would include immediate responses/actions and
methods for contacting emergency medical systems. Refer to V768.
Training for non-medical emergencies may include those related to
mechanical/technical equipment failures (as listed above), as well as
preparing for natural or man-made disasters that may result in the
inability to dialyze at home as scheduled and/or delays in supply
delivery. Refer to V412.
Patients need to understand how to contact and use their support
resources including their assigned facility staff coordinator, physician,
home training nurse, dietitian, social worker, dialysis equipment
suppliers, machine manufacturers, water treatment personnel. As with
in-center patients, facilities must provide home dialysis patients with
contact information for the applicable ESRD Network and State
survey agency.
Training for home patients to monitor their own health status should
include the use of equipment to monitor heart rate, blood pressure,
temperature, and weight; assessment of vascular or peritoneal dialysis
access; recognizing adverse signs and symptoms; and when, how, and
whom to contact if they experience problems with their health or
treatment. Recording treatment and health status information for home
dialysis patients includes documentation of the dialysis process, using
hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis specific treatment records.
The facility must provide home dialysis patients access to resources
and assistance 24 hours/day, 7 days/week. This may be through a call
system which can be reached by the patient/family/helper by phone,
beeper, answering service or similar arrangement. Also refer to V768
Final Version 1.1 Page 229 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
under the Condition for Governance.
Training for infection control precautions should include, at a
minimum, indications for the use of gloves, masks, and other personal
protective equipment, methods for hand hygiene, vascular access or
peritoneal catheter care and dressing changes, cleaning and
disinfecting dialysis equipment, cleaning and disinfection procedures
for spills and splashes of blood or effluent. Patients/helpers must
understand how to properly dispose of needles, effluents, disposable
items, blood tubing and dialyzers to minimize risks of infection or
injury to self and others and to prevent environmental contamination
(e.g. using impervious puncture resistant containers for disposal of
sharps, placing empty dialysate bags and dialysis tubing and other
contaminated items in intact plastic bags before discarding.). The
training staff must ensure that patients understand local waste
management rules.
According to AAMI, as part of their training for home hemodialysis,
the patient/helper should be instructed in any water/dialysate sample
collection or any water/dialysate quality tests that they will be
expected to perform in their homes. AAMI also states that the
patient/helper shall be trained how to perform the chlorine analysis
and shall be trained regarding what action to take if chlorine is
detected above the specified limit. Depending upon the chlorine test
used, the patient/helper should be capable of distinguishing between
different shades of pink or a digital meter should be used to indicate
the chlorine concentration.
Home dialysis training materials should address the training content
listed above, at a minimum.
V586
(b) Standard: Home dialysis monitoring. The dialysis
facility must –
(1) Document in the medical record that the patient, the
Medical records should include documentation of the training
provided, and evidence that the patient/helper demonstrated
competence in performing the home dialysis procedures.
Final Version 1.1 Page 230 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
caregiver, or both received and demonstrated adequate
comprehension of the training;
V587
(2) Retrieve and review complete self-monitoring data
and other information from self-care patients or their
designated caregiver(s) at least every 2 months; and
(3) Maintain this information in the patient’s medical
record.
The dialysis facility must obtain and maintain records on all home
patients including at a minimum, treatment records, flow sheets,
medications administered, equipment and water treatment system
checks, if applicable. The facility is responsible to assure that records
of dialysis treatments in the home setting are retrieved and reviewed
by the appropriate personnel at least every 2 months. Such review
assists staff in monitoring home patients’ status by determining if
patients are following their treatment plans and/or having problems
with their dialysis at home. When home hemodialysis or peritoneal
dialysis machines have the capacity for interactive electronic
documentation of the treatment data, the facility may obtain these data
electronically, if the security of the electronic submission is in
accordance with HIPAA privacy regulations, or from the patient,
through a disc/card brought to the facility.
Home dialysis patients' medical records must include dialysis
treatment records and evidence of their timely review by home
dialysis personnel. If the patient or helper has not provided the
appropriate records at least every 2 months, reasonable efforts by
facility staff to obtain these records must be made and documented.
The patient’s plan of care should address any problem with adherence
to this requirement. The applicable facility staff member (generally
either the nurse responsible for home training, the attending physician,
or a non-physician practitioner [i.e., advanced practice registered
nurse, or physician assistant]) is responsible for review upon receipt
of such time sensitive information as hospitalization data and
radiology, pathology, and laboratory results that cannot wait 2 months
for review.
V588
(c) Standard: Support services.
(1) A home dialysis training facility must furnish (either
directly, under agreement, or by arrangement with
Whether the home dialysis training facility provides the patients'
home dialysis equipment and supplies or the patient contracts with a
DME supplier to obtain the equipment and supplies, the dialysis
Final Version 1.1 Page 231 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
another ESRD facility) home dialysis support services
regardless of whether dialysis supplies are provided by
the dialysis facility or a durable medical equipment
company.
facility must provide all required support services, as listed in the
following tags, either directly or by arrangement, to all home dialysis
patients. A DME cannot provide home dialysis training or support
services; these services must be provided by an ESRD facility
certified for home training and support.
A facility that is certified to provide home dialysis services may also
apply to be certified to provide dialysis in long-term care facilities.
The special requirements for providing this service are detailed in a
Survey and Certification Letter.
V589
Services include, but are not limited to, the following:
(i) Periodic monitoring of the patient’s home adaptation,
including visits to the patient’s home by facility
personnel in accordance with the patient’s plan of care.
To assess a patient's home dialysis environment, a home visit should
be conducted at the initiation of home therapy and whenever a
problem is identified with either patient health or equipment that
could be related to treatment at home. Periodic routine replacement of
equipment would not necessarily require a home visit be scheduled.
The interdisciplinary team may designate the most appropriate staff
member(s) to make the home visit(s).
Documentation of home visits should be included in the medical
record. The number, timing, and frequency of home visits should be
based on individual patient need as indicated in the patient’s plan of
care. Distance from the facility or concerns about staff safety should
not preclude home visits. If a patient refuses a home visit, the
interdisciplinary team must evaluate his/her refusal and the potential
impact it may have on achieving the goals identified in the patient’s
plan of care as well as discuss alternative ways to assure the patient’s
health and safety at home.
V590
(ii) Coordination of the home patient’s care by a member
of the dialysis facility’s interdisciplinary team.
The home training and support facility must identify a specific
member of the interdisciplinary team to be responsible for the
coordination of each individual home patient’s care. ”Coordination of
care” does not mean that the staff member must deliver all of the care,
but that the coordinating staff member is the "contact person" on the
interdisciplinary team, is responsible for facilitating communication
Final Version 1.1 Page 232 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
between the interdisciplinary team and the patient/helper, and ensures
oversight/and monitoring of the patients' home dialysis in accordance
with the patient’s plan of care.
All patients should receive coordinated/integrated care no matter
which member of the interdisciplinary team coordinates that care.
V591
(iii) Development and periodic review of the patient’s
individualized comprehensive plan of care that specifies
the services necessary to address the patient’s needs and
meets the measurable and expected outcomes as
specified in § 494.90 of this part.
This tag should only be cited if there is no systematic care planning
for home dialysis patients. While the home patient is expected to play
a central role in the development and implementation of the plan of
care, the development and review of the home patients’ plans of care
must meet the same standards as for in-center patients, which are
addressed under the Condition for Patient plan of care. Problems with
individual plans of care for home patients should be cited at the
applicable tags under that Condition.
V592
(iv) Patient consultation with members of the
interdisciplinary team, as needed.
The home dialysis patients must have access to members of the
interdisciplinary team (i.e. registered nurse, dietitian, social worker,
physician treating the patient, as defined at V501), who must be
available to provide clinical services as needed by the patient. The
interdisciplinary team must include the staff member who is
responsible for the coordination of that patient’s care. Contact may be
in-person, by phone, by mail or by email with confirmation of patient
receipt. The required minimum frequency of contacts may be defined
by facility policy, but must meet the individual needs of each patient
in accordance with their plan of care.
Note the requirements at V510 for initial and periodic evaluation of
all patients by a qualified social worker and at V509 for evaluation by
a qualified dietitian.
Stable home dialysis patients are not seen frequently at the dialysis
facility. Medicare payment rules do not require a physician visit in
order for the physician to receive payment of the monthly capitated
payment (MCP) at the rate of two to three visits per month. The
Final Version 1.1 Page 233 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
requirement V560, which calls for at least monthly evaluation of all
patients by a physician, an advanced practice registered nurse or
physician assistant, applies to home dialysis patients, as well as in-
center patients. The facility must have a policy regarding how the
physician will consult with the home dialysis patient to meet this
requirement and to assure that the home patient’s medical supervision
is equivalent to in-center patients. Records of patient consultation by
the physician must be documented in the patient’s medical record at
the facility. Because they are not frequently on-site at the facility,
home dialysis patients may see their physicians in their offices instead
of seeing their physicians at the dialysis facility. If patients see their
physicians in the physician’s office, there must be a system in place to
transfer information related to the care of the home patient from the
physician’s office to the dialysis facility.
V593
(v) Monitoring of the quality of water and dialysate used
by home hemodialysis patients including conducting an
onsite evaluation and
At the time of publishing these regulations, several different
technologies for home hemodialysis were available. These included
conventional water treatment components and single-pass
(conventional) dialysis machines; integrated systems which used
manufacturer packaged, bagged dialysate or which incorporated water
treatment and dialysate preparation and delivery into one system; and
sorbent-based systems which utilized columns (cartridges) of
chemicals to regenerate the used dialysate for recirculation through
the dialyzer. All of these, and any future home hemodialysis
technologies developed, present the home dialysis facility with both
common and unique challenges for monitoring to ensure the
continued efficacy and safety of the home hemodialysis patients'
treatments. Because of their differences, the "Interpretive Guidance”
for the following tags (V593-V598), at times refers to one or more of
the above-mentioned home hemodialysis technologies as related to the
specific requirements and/or exclusions from certain requirements.
The facility home training staff must conduct on-site evaluations of
the home hemodialysis patient’s water supply prior to selecting a
Final Version 1.1 Page 234 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
water treatment system for home hemodialysis. There should be
evidence the source water to be used meets the minimum
requirements specified by the manufacturer of the water treatment
components or of the integrated system, if such is in use. If the source
water requirements are not met, there must be adequate pre-treatment
of the source water to meet those requirements. Each home water
treatment system must include either an RO or a DI treatment
component or alternate technology that achieves AAMI standards, and
a method to remove chlorine/chloramines.
According to AAMI RD52:2004/Annex C: Special considerations for
home hemodialysis at C.3.1 Water supply, if the home is served by a
small water system (serving less than 3000 persons), or one classified
as an economically or socially-disadvantaged system (serving less
than 500 persons), the water entering the residence is not regulated by
the EPA Safe Drinking Water Act. In addition, any municipal system
may have received a variance, which may be given for chemical
contaminants by State drinking water programs. If the water is
supplied from an individual well, the EPA standard may not be met.
Because of these variables with the regulation of the water supply to a
home for safe drinking water standards, annual analysis of the quality
of the product water may not be sufficient, since the quality of water
from the well may change over time, and since private wells are not
routinely monitored. More frequent analysis may be needed if the well
is subject to seasonal changes or contamination from sources such as
septic tanks, underground fuel storage tanks, or agricultural waste and
chemicals. The additional monitoring might not need to be the full
AAMI analysis if only certain contaminants are known to be of
concern.
The home patient’s record must include review and acknowledgement
of any problems with the source water, and a monitoring schedule for
Final Version 1.1 Page 235 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the source water. The patient’s physician should demonstrate
awareness of any issues with the source water, and the plan of care
should address any issues with source water for the home HD patient.
The home evaluation should address the storage of supplies, including
dialysate concentrate(s). The storage area should provide a year-round
environment that meets the manufacturer’s recommendations for the
storage of supplies.
For home water treatment systems, guidance is found throughout the
Condition for Water and dialysate quality at V595, which highlights
the recommendations in ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004: Annex C “Special
considerations for home hemodialysis."
V594
testing of the water and dialysate system in accordance
with—
(A) The recommendations specified in the
manufacturers’ instructions; and
(B) The system’s FDA-approved labeling for
preconfigured systems designed, tested, and validated to
meet AAMI quality (which includes standards for
chemical and chlorine/chloramine testing) water and
dialysate.
The home training and support facility is responsible for monitoring
the quality of the water/dialysate used by home hemodialysis patients
as required by the hemodialysis system manufacturer’s
recommendations and AAMI standards. Water treatment systems for
home hemodialysis patients must produce water that meets the AAMI
standards and the requirements specified in § 494.40(a) of these
regulations.
A chemical analysis of the product water must be done at the start of
home treatment and at least once a year near the end of the usability of
any disposable component, or when any modifications are made to the
treatment components (other than the replacement of disposable
components), to ensure that AAMI-defined maximum allowable
chemical contaminant levels are not exceeded. If chemical analysis is
not conducted as described here, refer to V201 for RO systems or to
V206 for DI systems. According to AAMI, more frequent than annual
analysis may be needed if there are seasonal variations in source water
quality or if the source water is supplied from a well, as detailed at
V593. When any repairs are made to water treatment equipment, the
impact on water quality should be evaluated and a chemical analysis
Final Version 1.1 Page 236 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
performed if indicated. Note: the requirements for in-center use of
preconfigured systems are detailed at V276.
V595
The facility must meet testing and other requirements of
ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004. In addition, bacteriological
and endotoxin testing must be performed on a quarterly,
or more frequent basis as needed, to ensure that the water
and dialysate are within the AAMI limits.
Chlorine/chloramine levels must be tested prior to the start of each
treatment (or before use of each new batch of dialysate) in accordance
with AAMI guidance and manufacturer’s recommendations or
instructions. An appropriate volume of water for the testing method in
use should be tested for the presence of chlorine/chloramines. For
batch systems (integrated systems which prepare enough dialysate for
multiple treatments), the chlorine/chloramines testing shall be
performed at the worst case scenario, i.e., after the preparation of each
batch of dialysate, but before use of that batch from a testing port that
meets specifications of the manufacturer to be in compliance with the
requirements of AAMI. If the test shows results above AAMI’s
maximum allowable level, then the user must discard that batch,
change any applicable components, prepare another batch of dialysate,
and test again.
Recognize that systems that use sorbent technology do not produce
water: the product of the sorbent cartridge is dialysate, thus the
requirements for the chemical, bacteriological and endotoxin testing
of water do not apply. With sorbent technology, due to the low
volume of exposure of patients to water (i.e. 6 liters per treatment) and
the capacity of the single-use sorbent cartridge to remove chlorine and
chloramines, testing for chlorines and chloramines is not required.
Sorbent system users are expected to perform bacteriological and
endotoxin testing on dialysate.
The medical director must review the results of all water and dialysate
cultures and endotoxin levels, and analysis of source and product
water for chemical contaminants of each home hemodialysis patient.
The facility must maintain documentation of the medical director’s
review, which should be incorporated as a part of the QAPI program
review.
Final Version 1.1 Page 237 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The results of water and dialysate testing for home hemodialysis
patients may be included in the patients' medical records or in separate
logs. According to AAMI, a log sheet should be provided by the
dialysis facility and used to record all measures of water treatment
system performance as required by the equipment manufacturer or the
dialysis facility.
The ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 "Dialysate for Hemodialysis" has been
incorporated by reference into these regulations, as stated in § 494.40
Condition for Water and dialysate quality. CMS interprets this
reference as inclusive of the "Amendment 1 to ANSI/AAMI
RD52:2004: Annex C Special Considerations for Home
Hemodialysis." This document addresses concerns particular to the
home hemodialysis setting. Be aware that many of the provisions of
RD52:2004, as outlined in the Condition for Water and dialysate
quality at § 494.40 pertain to the home hemodialysis setting when
conventional water treatment equipment is used for water purification.
The review of conventional water treatment equipment should
reference the requirements listed in that Condition for the specific
components in use in the home setting. Additional pertinent excerpts
from ANSI/AAMI RD52:2004 Annex C, which clarify specific home
hemodialysis issues, are as follows:
C.3 Utilities
It is recommended that the utility companies providing water and
power to the patient’s home be notified that home dialysis is being
performed at that location and that restoring service after any
interruption should be a priority.
C.3.2 Drain
If the home has a septic tank, the septic tank should be able to process
the volume of water from a drain [that is one inch or larger in
Final Version 1.1 Page 238 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
diameter]. It may not be possible to perform nocturnal hemodialysis in
a home with a septic tank since this tank may not be able to support
the volume of water delivered to it over an extended period (8 hours).
Another possible limitation is that the septic system will be exposed to
disinfectant chemicals (bleach, peracetic acid, hydrogen peroxide,
etc.) which may kill the bacteria needed for the septic tank to function.
C.5.2 Softener
Attention must be paid to setting the time for softener regeneration,
particularly when daily nocturnal hemodialysis is being performed.
C.5.3 Carbon adsorption media
At least one carbon adsorption bed or filter should be installed even if
the water supply is from a well and no chlorine is present. In addition
to chlorine, carbon can remove organic contaminants from ground
water, including solvents, pesticides, industrial wastes, and substances
leaking from underground storage tanks. When water is obtained from
a municipal water supply, two carbon adsorption devices connected in
series and providing the equivalent of an empty bed contact time of 10
minutes, or some other process incorporating safety redundancy for
chloramine removal, is recommended. A means should be provided to
sample the water between the two carbon adsorption devices. If
chlorine is not present in the water, the carbon should be changed on a
routine schedule.
C.5.4 Reverse osmosis
Since the product flow rate will decrease with decreasing water
temperature, a reverse osmosis system installed without a tempering
valve to ensure constant feed water temperature may need to be
oversized so that it will deliver the quantity of water required by the
dialysis machine with the coldest anticipated water temperature.
C.5.5 Deionization
Final Version 1.1 Page 239 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Deionization systems for home hemodialysis are not required to have
a mechanism to prevent product water from reaching the point of use
if the conductivity of the water is one microsiemen/cm or more
(specific resistivity of one megohm-cm or less). However, this feature
is strongly recommended, particularly in situations where the water
treatment system is not located in the room where dialysis treatments
are performed or when nocturnal hemodialysis is being performed. If
a diversion system is not installed, the patient must be trained to stop
dialysis immediately if the conductivity/resistivity monitoring system
alarms.
C.5.6 Treated water distribution
Because systems used for home hemodialysis operate intermittently,
the distribution system should be designed and maintained to
minimize bacterial proliferation. The reverse osmosis system should
be disinfected at least monthly according to the manufacturer’s
instructions. The dialysis machine should be disinfected following
each treatment according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
C.6.2 Acid concentrate
The patient/helpers should be trained to know that different
hemodialysis machines use different proportioning ratios for
concentrate and water and that they should ensure use of the correct
acid concentrate for their hemodialysis machine. The acid concentrate
used should be documented as part of the treatment record.
C.7 Monitoring
C.7.1 Water and dialysate quality
Sampling for microbiological testing should be performed before
disinfecting the water treatment system and dialysis machine. To
avoid disconnecting hoses, and opening the system to possible
contamination, the system should be designed with the necessary
sampling valves.
Final Version 1.1 Page 240 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
C.7.2 Equipment
C.7.2.1 General
A log sheet should be provided by the dialysis facility and used to
record all measures of water treatment system performance as
required by the equipment manufacturer or the dialysis facility.
Measurements should be made at least 15 minutes after the water
treatment system has been set in operation and before dialysis is
initiated. Any alarm associated with a component of the water
treatment system should be audible and visible in the patient treatment
area. If any measure of water treatment system performance is found
to be outside its acceptable range, the dialysis center should be
notified.
C.7.2.2 Softener
[When a softener is used] the water hardness should be monitored
prior to each treatment using a sample obtained through a labeled
sample port located between the softener and the reverse osmosis
membranes. For hardness tests requiring color differentiation, the
person performing the analysis should be able to distinguish between
the colors of blue, purple, and red. If the person cannot differentiate
these colors, an automated meter should be used.
C.7.2.3 Carbon adsorption media
The chloramine concentration shall be checked prior to each
treatment. It may be more convenient to monitor total chlorine instead
of chloramine. In that case, the acceptable level for total chlorine shall
be 0.1 mg/L, or less. The patient/helper shall be trained how to
perform the chlorine analysis, and shall be trained regarding what
action to take if chlorine is detected above the specified limit.
Depending on the chlorine test used, the patient/helper should be
capable of distinguishing between different shades of pink or a digital
meter should be used to indicate the chlorine concentration.
Final Version 1.1 Page 241 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
C.7.2.4 Reverse osmosis
Prior to each treatment, the performance of the reverse osmosis
system should be monitored by checking the product water
conductivity and percent rejection.
End AAMI requirements
The facility home hemodialysis staff should be familiar with the
recommendations in ANSI/AAMI RD52 Annex C, and the facility
policies, procedures and practice must reflect those applicable to the
home hemodialysis systems in use.
The microbiological quality of the dialysate should be analyzed
quarterly using cultures and endotoxin measurements, or more
frequently, if indicated.
If integrated systems are in use, the dialysate should be tested for
bacteria and endotoxins near the end of the usability of any disposable
water treatment or dialysate components. If the patient uses
manufacturer-provided bagged dialysate, cultures of those fluids are
not required.
Refer to the Condition for Water and dialysate quality at V178 and
V180 for action and maximum allowable culture and endotoxin levels
in water and dialysate. Results that are out of range require patient
evaluation, notification of the patient’s physician/medical director,
and action taken per facility policy. Documentation should include
culture/endotoxin results, physician and medical director notification
of any abnormal levels, and a corrective action plan if results are out
of range.
Records of results of chemical and microbial testing of home
Final Version 1.1 Page 242 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
hemodialysis water and dialysate should be available in the home
setting and at the dialysis facility providing support; the log of these
results may be included the patient's medical record or in a separate
record.
V596
(C) The dialysis facility must correct any water and
dialysate quality problem for the home hemodialysis
patient, and if necessary, arrange for backup dialysis
until the problem is corrected if—
(1) Analysis of the water and dialysate quality indicates
contamination; or
(2) The home hemodialysis patient demonstrates clinical
symptoms associated with water and dialysate
contamination.
If analysis of the water and/or dialysate quality indicates
contamination (i.e. microbial "action" levels or maximum level(s) of
chemical contaminants are exceeded), the facility should evaluate for
possible sample contamination and at minimum, when the threat is
low, re-test. If the threat is higher or the re-test remains positive, the
facility must correct the water treatment and/or dialysate delivery
(machine) system to ensure product water and dialysate meet AAMI
standards for chemical levels and microbial counts.
When unable to make such corrections in time to allow home
hemodialysis to resume within an acceptable time frame, the dialysis
facility must arrange for back-up dialysis until the home system is
corrected. If an integrated system is involved and all applicable
disposable components are replaced, treatment may continue, with
testing to continue per schedule.
If the patient exhibits clinical symptoms associated with water and
dialysate contamination that cannot be readily attributed to other
causes, the facility must arrange for back-up dialysis until the problem
is investigated and resolved. Clinical symptoms for water/dialysate
contamination may include, but are not limited to, chills, shaking,
fever, vomiting, headache, dizziness, muscle weakness, skin flushing,
itching, diarrhea, hyper/hypotension, hemolysis and anemia. If such
symptoms are present, the facility must notify the patient’s
physician/medical director to determine appropriate action (i.e.,
culture and treatment).
Facility policies must address, and responsible staff members (e.g.,
home training nurse, chief technician responsible for the home
Final Version 1.1 Page 243 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
program) must be aware of what responsive and corrective actions
they should take if microbial and/or chemical test results were
elevated, or should a patient exhibit such clinical symptoms (e.g.
referral for immediate patient evaluation and treatment by the
patient’s physician or a non-physician practitioner (i.e., advanced
practice registered nurse, or physician assistant) and possible
arrangement for back-up dialysis, if needed, until the cause of the
symptoms is identified and any problems with the home water
treatment and dialysate delivery system are resolved).
V597
(vi) Purchasing, leasing, renting, delivering, installing,
repairing and maintaining medically necessary home
dialysis supplies and equipment (including supportive
equipment) prescribed by the attending physician.
The dialysis facility is responsible for the oversight and overall
management of the home dialysis patient, including assuring that the
patient is provided with functional prescribed equipment and supplies.
The dialysis facility or a DME supplier may be responsible for
purchasing, leasing, renting, delivering, installing, and maintaining
home dialysis supplies and equipment. If the dialysis facility or
patient contracts with a DME supplier, there must be a written
agreement between the DME supplier and the dialysis facility,
specifying the responsibilities of each. The dialysis facility is always
responsible for oversight of the patient and the dialysis process.
Machines and equipment must be repaired and routine preventive
maintenance completed in accordance with the manufacturer’s
recommendations. The facility should maintain records of preventive
maintenance and repairs, even if performed by a DME supplier. If the
facility staff members are responsible for performing the maintenance
and repair on the home dialysis equipment, personnel file review
should show evidence of training and competency verification for all
of the different systems the facility maintains.
Some manufacturers use a system for exchange of malfunctioning
equipment in lieu of maintenance. If so, documentation should detail
what was done to refurbish the equipment used in exchange. This
Final Version 1.1 Page 244 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
documentation might be a form or letter for each piece of equipment,
or could be in the form of a policy or manual from the manufacturer
detailing the extent of refurbishing done at each exchange. The
facility should keep a log of the serial numbers of all equipment in use
at patients’ homes; these logs should be updated to reflect any
exchange of equipment.
The preventative maintenance and repair logs for the equipment in use
at patients' homes should verify the manufacturer's directions were
adhered to for periodic preventative maintenance.
V598
(vii) Identifying a plan and arranging for emergency
back-up dialysis services when needed.
The dialysis facility is responsible for identifying a plan and arranging
for timely emergency back-up dialysis whenever needed by the home
dialysis patient. Examples of when back-up dialysis may be necessary
include (but are not limited to) when the patient's home dialysis
equipment is non-functional, the water quality is not within AAMI
standards, the patient's medical conditions warrant a change in
modalities, a PD patient requires peritoneal catheter replacement and
temporary HD. Back-up dialysis should also be available in the event
of the need for respite of either the patient or the helper.
The facility should assist each home dialysis patient in developing a
personal disaster plan that identifies actions to take in the event of a
natural or other disaster affecting his/her home treatment.
The dialysis facility must inform each patient/helper of the availability
and location of back-up dialysis if equipment fails or if dialysis at
home is not possible. The “back-up dialysis” plan should provide
dialysis services that are equivalent to a certified facility.
V599
(2) The dialysis facility must maintain a recordkeeping
system that ensures continuity of care and patient
privacy. This includes items and services furnished by
durable medical equipment (DME) suppliers referred to
in § 414.330(a)(2) of this chapter.
The facility must maintain a centralized recordkeeping system for
home dialysis patients, which includes documentation of patient
assessments and plans of care, training and competency verification,
patient monitoring, and records of machine and water
treatment/dialysate delivery systems, the latter of which may be in a
Final Version 1.1 Page 245 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
separate log.
Both the dialysis facility and DME supplier must have recordkeeping
systems that are HIPAA-compliant and effective in assuring
continuity of care. The regulations for DME suppliers at §
414.330(a)(2) require the DME to report all data for each patient
regarding services and items furnished to the home patient to the
supporting ESRD facility every 45 days, thus there should be no issue
with the DME supplier providing records within the 2 months allowed
by these regulations.
Use this tag if deficient practices in the content or maintenance of
home dialysis patients' records are identified. For major issues related
to the home patient records, refer to V731.
V625
§ 494.110 Condition: Quality assessment and
performance improvement.
This Condition looks at facility aggregate data and requires facility-
based assessment and improvement of care, while the Plan of care
Condition expects patient-based improvement of care.
Compliance with this Condition is determined by review of clinical
outcomes data and the records of the quality assessment performance
improvement activities of the facility, and by interviews of
responsible staff including the medical director.
Non-compliance at the Condition level may be warranted if a pattern
of deficient practices which could impact patient health and safety is
identified. Examples include, but are not limited to:
• Absence of an effective QAPI program;
• Failure to recognize and prioritize major problems that threaten
the health and safety of patients; or
•
Failure to take action to address identified problems.
V626
The dialysis facility must develop, implement, maintain,
and evaluate an effective, data-driven, quality assessment
and performance improvement program with
The professional members of the facility’s “interdisciplinary
team”(IDT) which must participate in the QAPI activities, must,
minimally, consist of a physician, registered nurse, masters-prepared
Final Version 1.1 Page 246 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
participation by the professional members of the
interdisciplinary team. The program must reflect the
complexity of the dialysis facility’s organization and
services (including those services provided under
arrangement), and must focus on indicators related to
improved health outcomes and the prevention and
reduction of medical errors. The dialysis facility must
maintain and demonstrate evidence of its quality
improvement and performance improvement program for
review by CMS.
social worker, and registered dietitian. This facility-based team is led
by the medical director, who may also serve as the physician
representative of the IDT. Each team member must meet the
qualifications outlined in the Condition for Personnel qualifications
for their respective disciplines. The interdisciplinary team must have
effective communications and must produce effective quality
assessment and performance improvement activities which positively
influence their patient’s outcomes. There must be an operationalized,
written plan describing the QAPI program scope, objectives,
organization, responsibilities of all participants, and procedures for
overseeing the effectiveness of monitoring, assessing and problem-
solving activities.
The scope of the QAPI program must be facility wide: all services
provided must be included in the review (e.g. in-center, home
hemodialysis, home peritoneal dialysis, reuse, central reprocessing,
self-care). Data on current professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards must be used to track health outcomes, and the program
must allow for identification, prevention and reduction of medical
errors, mortality and morbidities. Refer to the Measures Assessment
Tool (MAT) which lists the expected outcomes based on these
standards and CMS Clinical Performance Measures (CPMs).
The MAT is a reference for community-accepted standards and values
for listed elements of QAPI. Within their individual QAPI program,
facilities are expected to use the community-accepted standards and
values associated with clinical outcomes as referenced on the MAT.
Facilities are expected to use CROWNWeb and Dialysis Facility
Reports to determine comparison or “average” values associated with
clinical outcomes.
If a facility has areas of QAPI that do not meet target levels (per
MAT) or areas where the facility performance is below average (per
Final Version 1.1 Page 247 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
data reports), the facility is expected to take action toward improving
those outcomes.
The important aspects of the QAPI program are appropriately
monitoring data/information; prioritizing areas for improvement;
determining potential root causes; developing, implementing,
evaluating, and revising plans that result in improvements in care.
Records of QAPI activities including minutes or another method of
demonstrating this analysis and action must be available for review.
V627
(a) Standard: Program scope.
(1) The program must include, but not be limited to, an
ongoing program that achieves measurable improvement
in health outcomes and reduction of medical errors by
using indicators or performance measures associated
with improved health outcomes and with the
identification and reduction of medical errors.
An “ongoing” program continuously looks at indicators as they are
available, trends outcomes and develops an improvement plan when
indicated. Generally this would require at least monthly review of
indicators, since prescribed patient indicators are typically evaluated
with laboratory results monthly and this serves as a functional time
frame for trending of data within the facility.
“Indicators” or “performance measures” include at least those
specified in this Condition, as well as measures of water and dialysate
quality and safety, and safe machine maintenance. Performance
expectations are based on current professionally-accepted clinical
practice standards. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT)
provided which lists these and the CMS Clinical Performance
Measures (CPMs).
V628
(2) The dialysis facility must measure, analyze, and track
quality indicators or other aspects of performance that
the facility adopts or develops that reflect processes of
care and facility operations. These performance
components must influence or relate to the desired
outcomes or be the outcomes themselves. The program
must include, but not be limited to, the following:
The facility’s QAPI program monitors the assessment and
improvement of care in the facility.
CMS-generated data reports, including the Dialysis Facility Reports
(DFR) and other Consolidated Renal Operations in a Web-enabled
Network Web (CROWNWeb) provided data reports, are and will be
distributed to facilities to help them focus their QAPI improvement
programs. Each facility should be comparing their performance with
community-based standards and with other facilities in their State,
Final Version 1.1 Page 248 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
their Network and the U.S. and working to improve their outcomes
where needed. This comparative data is readily available to all
facilities, whether they are corporate owned or independent.
QAPI requires the use of aggregate patient data to evaluate the facility
patient outcomes. Hemodialysis patients and peritoneal dialysis
patients should be reviewed separately since factors affecting their
clinical outcomes may be different; both groups of patients must be
reviewed on an ongoing basis.
Data related to patient outcomes, complaints, medical injuries and
medical errors (e.g., clinical variances, occurrences, and adverse
events) should be used to identify potential problems and to identify
opportunities for improving care.
Data should be analyzed by the interdisciplinary team (IDT) on an
ongoing basis. Based upon the data review, the IDT should discuss the
areas which need improvement and develop, implement, and evaluate
a plan for such improvement. The facility must use broadly accepted,
community-developed standards (e.g., CMS CPMs, NKF KDOQI,
AAMI) as performance measures. Those standards which are
expected to be measured and tracked are detailed on the Measures
Assessment Tool (MAT). Where minimum outcome values have been
determined, facilities are expected to provide care directed at
achievement of at least the minimum outcome value by all patients.
The IDT must work with individual patients who do not reach the
target; this work must be reflected in the patient’s plan of care for that
outcome. Refer to the applicable tag under the Condition for Plan of
care for individual patient issues.
V629
(i) Adequacy of dialysis.
The intent of QAPI in addressing adequacy of dialysis is to maximize
the number of patients who achieve the goals for adequate dialysis,
which include both successful fluid volume management and
clearance of toxins.
Final Version 1.1 Page 249 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
To identify opportunities for improvement and track progress in
adequacy of dialysis for its hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis
population the IDT must:
• Review aggregate patient data;
• Identify any commonalities among patients who do not reach the
minimum expected targets;
• Develop a plan to address those causes;
• Implement the plan;
• Monitor the effectiveness of the plan; and
• Adjust portions of the plan that are not successful.
The IDT must use current professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards as target values. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool
(MAT) provided which lists these standards.
If a data report shows that the facility’s ranking for hemodialysis
adequacy is below the expected average, the facility must demonstrate
QAPI review of global factors that might affect adequacy, e.g.
missed/shortened treatments, less-efficient dialyzers, and failure to
achieve the ordered blood flow rates.
V630
(ii) Nutritional status.
The intent of QAPI in addressing nutritional status is to maximize the
number of patients who achieve the goals for this area.
Serum albumin is a valid and useful measure of protein-energy
nutritional status in maintenance dialysis patients. Serum albumin
levels are commonly and extensively used to evaluate the nutritional
status of ESRD patients; low albumin levels are highly predictive of
mortality risk. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT)
provided, which lists current professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards in this and other areas.
Final Version 1.1 Page 250 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Serum albumin is affected by inflammation and other factors as well
as by diet. The IDT may not be able to have a majority of its patients
achieve the desired goal for this area, but should be actively
intervening on actionable factors.
V631
(iii) Mineral metabolism and renal bone disease.
The intent of QAPI in addressing management of CKD mineral and
bone disorder is to maximize the number of patients who achieve the
goals for this area. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT),
which lists the current professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards in this and other areas.
Since this area is heavily influenced by patient diet, it is critical that
patient education, encouragement, and support be included in
improvement plans for this indicator. The IDT should evaluate the
efficacy of any standardized CKD mineral and bone disorder
guideline or algorithm in use if facility QAPI goals in this area are not
achieved over consecutive evaluation periods and other factors (e.g.,
transfers, new admissions, hospitalizations, discharges, recent access
surgeries, or acutely ill patients) are not responsible.
V632
(iv) Anemia management.
The intent of QAPI in addressing management of anemia is to
maximize the number of patients who achieve the goals for this area.
Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT) which lists the current
professionally-accepted clinical practice standards and CMS CPMs in
this and other areas.
For anemia management, factors which should be tracked monthly for
the facility patient population as a whole include laboratory values for
hemoglobin and hematocrit. If facility QAPI goals for anemia
management are not achieved over consecutive evaluation periods, the
facility IDT should conduct a review of transferrin saturation (TSAT)
levels, ferritin levels, and other iron indices; erythropoietin
stimulating agent (ESA) doses and response to those doses; and any
evidence of blood loss, such as repeated episodes of insufficient
rinseback of red blood cells or prolonged bleeding post treatment.
Final Version 1.1 Page 251 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
If the facility uses a standardized anemia management guideline or
algorithm, the IDT should evaluate the efficacy of this tool if facility
QAPI goals for anemia management are not achieved over
consecutive evaluation periods.
Home and in-center patient outcomes may need to be reviewed
separately by the facility in this area as the factors to be addressed
may be different. For example, a home peritoneal patient may be
reluctant to inject himself/herself with an ESA, resulting in lower
values for this measure in the home population.
V633
(v) Vascular access.
The intent of QAPI in addressing vascular access is first, to improve
the rate of use and preservation of fistulas; second, to decrease the
inappropriate use of catheters; and finally, to improve the care
provided for all types of vascular access.
To identify opportunities for improvement and track progress in
management of vascular access for its hemodialysis population, the
IDT must use a standard that has achieved broadly accepted use in the
ESRD community. Refer to the Measures Assessment Tool (MAT),
which lists the current professionally-accepted clinical practice
standards and CMS CPMs for this and other areas.
Fistula survival may be affected by:
• Cannulation technique problems such as frequent infiltrations
related to training issues or individual personnel difficulties;
• Episodes of hypotension or hypovolemia; and
• Differences in surgical outcomes.
The QAPI program should include efforts to reduce the use of
catheters and to reduce the incidence of infection related to catheter
use. Requirements related to the care of catheters can be found under
the Condition for Infection control, at V146, V147 and V148.
Final Version 1.1 Page 252 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V634
(vi) Medical injuries and medical errors identification.
The intent of QAPI in addressing medical injuries and identification
of medical errors is to minimize the number of occurrences and limit
the number of patients and staff who are adversely affected by such
occurrences.
The facility must compile and the QAPI team must review reports and
complaints related to any patient or staff injuries, and treatment or
medication errors. Part of the QAPI activity is to trend any injuries or
errors to identify the prevalence of occurrences, commonalities, and
causes.
An example of medical injury is a patient fall, which may occur post-
dialysis treatment. Information to allow identification of any trends
and to detail facility response in terms of risk assessment and
precautions in place to prevent future falls should be in evidence.
Similarly, occurrences such as treatment prescription errors,
intradialytic morbidities, and staff needle sticks should be identified,
reviewed and trended. “Intradialytic morbidities” is any adverse
symptom that occurs during the dialysis treatment to include but not
be limited to seizures, chest pain, hypotension and cardiac arrest.
Other events which should be tracked include hospitalizations, deaths,
acute allergic-type reactions, blood loss >100 ml, and patient transfers
by ambulance from the dialysis facility to a hospital emergency room.
The facility should collect and aggregate data regarding adverse
occurrences, and there should be a mechanism to ensure all adverse
events are recorded as soon as possible after they occur. The QAPI
committee should analyze both isolated and repeated events in their
review. In September, 2008, the Renal Physicians’ Association
launched a new website “Keeping Kidney Patients Safe” to serve as a
repository for ESRD patient safety best practices. In collaboration
with the Forum of ESRD Networks, the following areas were
identified through patient and professional surveys as the top five
Final Version 1.1 Page 253 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
areas of focus for adverse patient safety events:
“1. Hand hygiene: Accumulation and transmission of germs on hands
are transmitted by touching one's self, patients and surfaces in the
patient environment. Infections are a serious problem in healthcare
facilities and many infections are transmitted on the hands of
healthcare personnel. Hand hygiene practices - the use of alcohol-
based hand rubs or use of soap and water before and after patient
contact, removal of gloves and contact with the immediate patient
care environment - protect both healthcare personnel and patients
from contact with infectious agents. Failure to practice hand hygiene
may be caused by lack of equipment; low staffing ratios; allergies to
hand washing products; insufficient knowledge about risks posed by
not practicing hand hygiene; time required; or casual attitude by staff
towards hand hygiene. Proper hand hygiene breaks the chain of
infection transmission and minimizes microorganisms acquired by
contact with infected surfaces.
2. Patient falls: Patient falls are defined as any untoward event in
which the patient comes to rest unintentionally on the floor. Falls are
largely preventable occurrences that injure patients, cause
hospitalizations, and significantly increase healthcare costs. Most
ESRD patients who fall indicate they fall following dialysis treatment,
and they fall because they feel dizzy or weak. Additional attention to
post-dialysis blood pressure levels, assistance as patients initially
stand up coupled with queries about their steadiness, and removal of
physical obstacles to patient navigation could all serve to reduce
patient falls.
3. Incorrect dialyzer or dialyzing solution: The wrong dialyzer or
dialyzing solution being set-up for a patient is a dangerous event that
can result in great harm to patients. Feasible remedies for ensuring
that initial set-up errors do not result in patient harm range from
Final Version 1.1 Page 254 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
patient and professional education to procedural safeguards such as
technician checklists and rules for set-up procedures. Increasing
patient involvement in their dialysis care and safety issues may
provide another approach to safeguarding against dialyzer solution
errors.
4. Medication omissions or errors: Medication errors include giving a
patient the wrong medication, giving medication at the wrong time,
being given the wrong dose of a medication, or a patient failing to
receive one of his/her medications. The consequence of each
occurrence of a medication error, particularly omitting a patient's
medication, can be quite significant and result in medical harm
particularly when one considers that dialysis patients take large
numbers of different medications each day; most take between 6 and
10 medications per day (based on the patient survey). Patients ascribe
medication problems to inadequate communication. Medication
omission and errors might be resolved through a combination of
professional and patient education and systems changes that build
safeguards into medication routines and procedures.
5. Non-adherence to procedures: Failure to adhere to procedures,
including the performance of routine completion of pre- and post-
dialysis tasks such as taking patients' weight and blood pressure, leads
to medical errors, increased risk of hospitalization and mortality. Non-
adherence may also include failing to follow procedures regarding
trouble with needle insertion and failure to complete event reports
when medical errors occur. Non-adherence may also include patients'
skipping or shortening dialysis treatments thereby increasing their
odds of mortality. Non-adherence problems may reflect issues with
procedural guidance, training, and/or enforcement."
Definitions:
“Error” is defined as the failure of a planned action to be completed as
Final Version 1.1 Page 255 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
intended (error of execution) or the use of a wrong plan to achieve an
aim (error of planning). An error may be an act of commission or an
act of omission (Institute of Medicine, 2004).
“Medication error” is defined as any error occurring in the
medication-use process (Bates et al., 1995). Examples include wrong
dosage prescribed, wrong dosage administered for a prescribed
medication, failure to give (by the provider) or take (by the patient) a
medication, or administration of a drug to which the patient is known
to be allergic.
“Adverse drug event” is defined as any injury due to medication
(Bates et al., 1995). Examples include a wrong dosage leading to
injury (e.g., rash, confusion, or loss of function) or an allergic reaction
occurring in a patient not known to be allergic to a given medication.
V635
(vii) Hemodialyzer reuse program, if the facility reuses
hemodialyzers.
If a facility has a dialyzer reuse program, it must be compliant with
the quality assurance requirements specific to reuse, located at V360-
368. These requirements outline periodic reuse process and practice
audits which must be conducted and documented to ensure the reuse
program remains safe and effective. Refer to the Measures
Assessment Tool (MAT) for quality indictors related to the reuse of
hemodialyzers.
The QAPI meeting minutes should demonstrate oversight of the
reprocessing/reuse program and include at least summaries of the
required reuse audits.
This tag is used to cite major problems related to quality assessment
and performance improvement for the Condition for Reuse. Use
individual tags in the Condition for Reuse of hemodialyzers for
citations of specific or isolated issues in the required audits for quality
assurance (V360-V368).
V636
(viii) Patient satisfaction and grievances.
The intent of QAPI in this area is to use patient satisfaction surveys
Final Version 1.1 Page 256 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
and patient grievance investigations as a means to identify
opportunities to improve care. The survey should be non-threatening
and be conducted in a manner to protect the patient’s identity. QAPI
discussion of patient satisfaction survey results and patient grievance
information should focus on the use of data to inform the care delivery
system. If needed changes are identified, there should be evidence of
action taken to implement those changes.
Facilities must monitor and track patient grievance reports and
outcomes as required at V765; use that tag for issues related to
responding to individual grievances.
An In-Center Hemodialysis Consumer Assessment of Healthcare
Providers and Systems (ICH-CAHPS) survey instrument, which is a
standardized experience of care assessment tool appropriate for in-
center hemodialysis patients, is available for use. Effective 4/1/2008,
CMS endorsed the use of this tool to measure in-center hemodialysis
patient satisfaction as a CPM. As other measures of patient
satisfaction are standardized, refer to the Measures Assessment Tool
(MAT) for the current standard of practice.
V637
(ix) Infection control; with respect to this component the
facility must—
(A) Analyze and document the incidence of infection to
identify trends and establish baseline information on
infection incidence;
(B) Develop recommendations and action plans to
minimize infection transmission, promote immunization;
and
(C) Take actions to reduce future incidents.
The intent of QAPI in addressing infection control is to minimize the
number of patients and staff who are exposed to or acquire infectious
diseases at the facility.
The facility must record and follow up on all patient infections and
serious adverse events. The occurrence of these events should be
recorded using a centralized log book or other tracking mechanism
and regularly reviewed, with documentation of actions taken.
Surveillance information available for review should include, but not
be limited to, patients’ vaccination status (hepatitis B, pneumococcal
pneumonia, and influenza vaccines); viral hepatitis serologies and
seroconversions for HBV(and HCV and ALT, if known); bacteremia
episodes; pyrogenic reactions; vascular access infections; and vascular
Final Version 1.1 Page 257 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
access loss due to infection.
Surveillance information must include at a minimum, the date of
infection onset, site of infection, full identification of infecting
organism(s), and antimicrobial susceptibility results.
Responsible staff must review the results of all routine and diagnostic
testing (including culture and serology) upon receipt and ensure that
the medical director periodically reviews recorded episodes of
bacteremia, vascular access infections, soft tissue infections, and other
communicable diseases to aid in tracking, trending, and prompt
identification of potential environmental/staff practices issues or
infection outbreaks among patients. It is important to identify the
method of transmission whenever possible as well as the immune
status of affected and at risk patients. Appropriate State or local public
health officials should be notified of viral hepatitis seroconversions
and other infectious diseases, and clusters of adverse events that occur
among patients in the facility.
The analysis of patient infection incidence during the periodic QAPI
meetings may not be sufficiently timely for identification of an
outbreak of infections. Tracking of infections and serious adverse
events must be done on an ongoing basis to ensure the safety of the
patients.
Actions taken by the facility must be appropriate to the degree of risk
to patients and staff. Actions could include in-service training in
infection control; implementation of different protocols for cleaning
equipment between uses; and audits of practice regarding infection
control precautions for dialysis settings.
Information in this area may be recorded separately or incorporated
into the QAPI documents; either method is acceptable, as long as
Final Version 1.1 Page 258 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
review and analysis of the information collected is apparent.
As infection control indicators are developed, refer to the Measures
Assessment Tool (MAT) for the current standard of practice.
V638
(b) Standard: Monitoring performance improvement.
The dialysis facility must continuously monitor its
performance, take actions that result in performance
improvements, and track performance to ensure that
improvements are sustained over time.
“Continuously monitor” requires that outcome data, achievement of
treatment goals, adverse events, infections, falls, errors, etc. be
monitored as this data is available or these events occur. Tracking and
trending, analysis of root causes, development of improvement plans,
implementation of those plans, evaluation of the success of the plan,
and revision of the plan must occur as indicated.
Once improvement is made, the facility must have a mechanism to
ensure that improvement is sustained. This could include practice
audits, review of records, or repeat patient satisfaction surveys, etc.
The medical director should continuously communicate with the
governing body about the status of QAPI activities, particularly when
resources are required to address program improvements. See V756.
If the medical director is a part of the governing body, there should be
some evidence he/she provides information to members who do not
participate in the QAPI meetings. The minutes of the governing body
or the minutes of the QAPI committee should demonstrate
communication between the governing body and the medical director.
Refer to V756 for the requirements related to the responsibilities of
the governing body for QAPI.
V639
(c) Standard: Prioritizing improvement activities.
The dialysis facility must set priorities for performance
improvement, considering prevalence and severity of
identified problems and giving priority to improvement
activities that affect clinical outcomes or patient safety.
The facility must incorporate CMS-generated data reports, along with
data reports that the facility produces to identify all areas needing
improvement and to prioritize these, ranking those which have
potential to affect patient health and safety as more urgent than those
that do not have such potential. In setting priorities, the prevalence
and severity of the identified problems must be considered.
V640
The facility must immediately correct any identified
Examples of conditions which could pose a threat to the health and
Final Version 1.1 Page 259 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
problems that threaten the health and safety of patients.
safety of dialysis patients and require immediate correction include
but are not limited to:
• Dangerous levels of contaminants in product water;
• Unsafe levels of electrolytes in dialysate;
• Failure to conduct an accurate pre-assessment
• Setting an inaccurate fluid removal rate
• Failure to provide adequate observation of patient, patient vascular
access, patient equipment;
• Defective clinical equipment;
• Failure to adequately disinfect reprocessed dialyzers;
• Failure to reduce residual germicides in reprocessed dialyzers to
safe levels;
• Lack of qualified staff to perform crucial tests or to meet critical
patient needs;
• Evidence that staff assigned to perform crucial tests or to meet
critical patient needs are not competent;
• Potential for cross-contamination between infected and non-
infected patients; and
• Failure to use machine-provided safety devices (muting machine
alarms, bypassing the air detector, etc.).
The facility must take immediate, appropriate actions to address any
serious threats and ensure patient safety.
V660
§ 494.120 Condition: Special purpose renal dialysis
facilities.
This Condition outlines the requirements for dialysis facilities that
provide care to patients who need dialysis on a short-term basis
because of emergency conditions or because they are staying at
remote vacation camps. These “special purpose renal dialysis
facilities” (SPDF) require a special certification. This certification
may not exceed 8 months in any 12-month period of time.
This Condition only applies to SPDF; it provides information about
the availability of this special certification and defines which of the
Final Version 1.1 Page 260 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
regulatory requirements included in the other Conditions for Coverage
are required to be met by each type of SPDF. Deficiencies would be
cited under each of the applicable Conditions and Standards that are
outlined for either the vacation camp or the emergency circumstance
facility. This Condition would be cited in the event a facility that
applied as an SPDF did not meet the requirements for that
designation. Other Conditions and Standards would also be cited in
that situation.
V661
A special purpose renal dialysis facility is approved to
furnish dialysis on a short-term basis at special locations.
Special purpose dialysis facilities are divided into two
categories: vacation camps (locations that serve ESRD
patients while the patients are in a temporary residence)
and facilities established to serve ESRD patients under
emergency circumstances.
“Vacation camp” SPDFs are temporary vacation locations that
provide (and bill for) outpatient hemodialysis treatments at the camp
site. Camps that transport hemodialysis patients to local certified out-
patient facilities for dialysis are not considered SPDF and do not need
to be certified separately to accept the campers as transient patients.
Camps that provide only peritoneal dialysis on-site are not required to
be certified as the treatment provided would be considered a “home”
treatment.
“Emergency circumstances” for SPDF applies to a natural or man-
made disaster that prevents the use of established dialysis facilities,
and applies to a patient or group of patients who can not otherwise be
served in an area. The most common use of certification as an
emergency SPDF is when the usual treatment facility(ies) are
incapacitated by weather-related emergencies causing disruption to
electrical service, water supplies, or vehicular access. However, a
hospital, long-term care facility, or other provider could request SPDF
certification to provide dialysis to one or more patients that are denied
outpatient dialysis by all dialysis facilities within reasonable driving
distance because of medical complications (morbidly obese,
bedbound, respirator-dependent, tracheotomy requiring frequent
suctioning, etc.) or a history of disruptive or threatening behaviors.
In the event a new ESRD facility which has not yet been certified is
granted an emergency SPDF status, that facility would need to
Final Version 1.1 Page 261 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
undergo an initial survey for full certification within the 8 month
SPDF certification period in order to continue service and to expand
its census beyond those patients who could not otherwise be served in
that geographic locality.
V662
(a) Standard: Approval period.
The period of approval for a special purpose renal
dialysis facility may not exceed 8 months in any 12-
month period.
The maximum period of certification is 8 months in any 12-month
period. A vacation camp SPDF may be operational for as little as one
to two weeks, and the same facility may reapply for certification in
the following (or any subsequent) year.
Facilities applying for an SPDF “emergency ” designation in order to
accommodate longer term dialysis for patients who are unable to be
placed in an outpatient facility must recognize the time-limited nature
of this certification and the fact that admissions are limited to those
patients who were unable to obtain outpatient dialysis elsewhere in the
area. This type SPDF may also reapply for certification in the
following (or any subsequent) year.
V663
(b) Standard: Service limitation.
Special purpose renal dialysis facilities are limited to
areas in which there are limited dialysis resources or
access-to-care problems due to an emergency
circumstance. A special purpose renal dialysis facility
may provide services only to those patients who would
otherwise be unable to obtain treatments in the
geographic locality served by the facility.
An SPDF is to provide care that would not otherwise be available in
that geographic area. In the case of vacation camps, the “geographic
locality” factor is related to minimizing the time that the patient would
be away from camp activities. There may be a dialysis facility within
driving distance, but dialysis treatment would take the camper away
from the camp activities.
In the case of emergency circumstance facilities, the intent is to
temporarily provide service until permanent arrangements are
possible.
An SPDF established to provide care to patients with medical or
psychosocial needs which cannot be met in a standard outpatient
dialysis setting should define the population it intends to serve in its
admission criteria and include in those criteria the lack of outpatient
dialysis service for these patients within the geographic area.
No tag
(c) Standard: Scope of requirements.
This is an informational tag. The sections of the regulations listed here
Final Version 1.1 Page 262 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(1) Scope of requirements for a vacation camp. A
vacation camp that provides dialysis services must be
operated under the direction of a certified renal dialysis
facility that assumes full responsibility for the care
provided to patients. A special purpose renal dialysis
facility established as a vacation camp must comply with
the following conditions for coverage–
(i) Infection control at § 494.30;
(ii) Water and dialysate quality at § 494.40 (except as
provided in paragraph (c)(1)(viii) of this section);
(iii) Reuse of hemodialyzers at § 494.50 (if reuse is
performed);
(iv) Patients’ rights and posting of patients’ rights §
494.70(a) and § 494.70 (c);
(v) Laboratory services at § 494.130;
(vi) Medical director responsibilities for staff education
and patient care policies and procedures at § 494.150(c)
and (d);
(vii) Medical records at § 494.170; and
(viii) When portable home water treatment systems are
used in place of a central water treatment system, the
facility may adhere to § 494.100 (c)(1)(v) (home
monitoring of water quality) in place of § 494.40 (water
quality).
outline the survey of a vacation camp SPDF. If deficient practices are
identified, appropriate tags under the referenced regulations should be
used to identify deficiencies.
A vacation camp SPDF must be affiliated with a certified outpatient
dialysis facility but will have its own unique CCN.
Because the SPDF for a vacation camp will provide service on a
temporary basis, it must meet only the specified portions of these
regulations.
No tag
(2) Scope of requirements for an emergency
circumstance facility.
A special purpose renal dialysis facility set up due to
emergency circumstances may provide services only to
those patients who would otherwise be unable to obtain
treatments in the geographic areas served by the facility.
These types of special purpose dialysis facilities must
comply with (c)(1) of this section and addition to
complying with the following conditions:
This is an informational tag. Sections of the regulations listed here are
to be used to survey an emergency circumstance SPDF. If deficient
practices are identified, the appropriate tags under the referenced
regulations should be used.
An SPDF set up for an emergency circumstance will be issued a
unique CCN. These facilities may only provide care to those patients
who would otherwise be unable to obtain treatment in that geographic
area, and are limited to an 8-month period of operation.
Final Version 1.1 Page 263 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(i) Section 494.20 (compliance with Federal, State, and
local laws and regulations).
(ii) Section 494.60 (physical environment).
(iii) Section 494.70(a) through section 494.70(c) (patient
rights).
(iv) Section 494.140 (personnel qualifications).
(v) Section 494.150 (medical director).
(vi) Section 494.180 (governance).
V666
(d) Standard: Physician contact.
The facility must contact the patient’s physician, if
possible, prior to initiating dialysis in the special purpose
renal dialysis facility, to discuss the patient’s current
condition to assure care provided in the special purpose
renal dialysis facility is consistent with the patient plan
of care (described in § 494.90).
The facility must contact the patient’s physician prior to initiating care
in the SPDF to update that physician on the status of the patient and to
coordinate the patient’s plan of treatment. In the event of a natural
disaster, the facility must make every effort to contact the patient’s
physician; however when it is impossible to contact or communicate
with that physician, emergency dialysis care must be provided. In this
case, the SPDF should have standard orders for dialysis, diet/fluids,
and medications that the medical director of the SPDF could prescribe
until he/she communicates with the patient’s attending physician.
V667
(e) Standard: Documentation.
All patient care provided in the special purpose facility is
documented and forwarded to the patient’s usual dialysis
facility, if possible, within 30 days of the last scheduled
treatment in the special purpose renal dialysis facility.
Care in any SPDF should be documented at the time it is delivered
and sent to the patient’s permanent facility within 30 days of the last
treatment provided by the SPDF. Additional time may be needed for
the transfer of documentation of care in the event of a natural disaster.
For example, if a patient’s original facility was destroyed and not
rebuilt, the documentation transfer may be delayed or even
impossible.
Hospitals or skilled nursing facilities that obtain an “emergency
circumstance” SPDF designation to care for patients with medical or
psychosocial needs that cannot be met in a standard outpatient dialysis
facility may choose to maintain the original record of care at the
SPDF and forward copies of requested portions of the record to
another treatment setting that will be receiving the patient for care. In
this case, the records would be expected to be transferred within one
working day. Refer to V733.
Final Version 1.1 Page 264 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V675
§ 494.130 Condition: Laboratory services.
This Condition describes the requirements for clinical laboratory
services required to meet the needs of ESRD patients.
Compliance with this Condition is determined by clinical record
review and if indicated, staff interviews and review of agreements.
Examples of Condition level non-compliance include, but are not
limited to:
• The laboratory being used is not CLIA approved; or
• Serious and pervasive problems persist in the methods for
collecting and handling the specimens drawn for laboratory
analysis.
V676
The dialysis facility must provide or make available,
laboratory services (other than tissue pathology and
histocompatibility) to meet the needs of the ESRD
patient. Any laboratory services, including tissue
pathology and histocompatibility must be furnished by or
obtained from, a facility that meets the requirements for
laboratory services specified in part 493 of this chapter.
Under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988
(CLIA), laboratory services can only be provided by an appropriately
certified laboratory. Arrangements with these providers must be in
writing and signed and should specify the types of laboratory tests to
be performed; methods for collection and handling the specimen(s);
and delivering results, including a timeline for reporting of “alert”
(sometimes called “panic”) values to a responsible person.
Many facilities have agreements with distant laboratories for routine
services; there should also be a provision for service from a local
laboratory for time-sensitive testing.
The dialysis facility may provide some testing directly. Generally this
is limited to CLIA-waivered tests, such as for blood glucose
determinations obtained by blood glucose monitoring devices cleared
by FDA specifically for home use; and for stool testing for occult
blood.
HLA Laboratories performing Panel Reactive Antibody (PRA) testing
for patients on the transplant waitlist must have a “regular” CLIA
certificate or certificate of accreditation which allows the laboratory to
Final Version 1.1 Page 265 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
perform high-complexity testing.
Laboratory reports should be included in facility records and should
include the patient’s name and identifier, the date and time the
specimen was taken, and the name and address of the laboratory
performing the test. Facility policies should address methods for
specimen collection, especially pertaining to post-dialysis samples for
dialysis adequacy testing to ensure accurate results.
Subpart D – Administration
V680
§ 494.140 Condition: Personnel qualifications.
This Condition defines the qualifications of dialysis facility staff and
lists the minimum required content for patient care technician training
programs.
Compliance with this Condition is determined primarily by review of
medical staff and personnel credential files, educational programs,
policies and procedures for determining “competency” of the various
staff members. Facilities must maintain current documentation to
demonstrate personnel meet the basic requirements of their assigned
roles, including any State specific requirements. When patient or staff
interviews or observations of practice raise concerns about
competency, the survey process may become more focused to ensure
staff members are competent to perform assigned duties and to fulfill
their roles in providing safe and effective patient care.
Examples of Condition level noncompliance would include, but not be
limited to:
• Required interdisciplinary team member(s) do not meet the
qualifications listed,
• Serious or pervasive problems with qualifications and/or
competency of the direct care staff, including the patient care
technicians.
V681
All dialysis facility staff must meet the applicable scope
of practice board and licensure requirements in effect in
All dialysis facility staff, including non-physician practitioners
(whether employee, contractor, or credentialed as a member of the
Final Version 1.1 Page 266 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the State in which they are employed. The dialysis
facility’s staff (employee or contractor) must meet the
personnel qualifications and demonstrated competencies
necessary to serve collectively the comprehensive needs
of the patients. The dialysis facility’s staff must have the
ability to demonstrate and sustain the skills needed to
perform the specific duties of their positions.
medical staff), must meet the applicable qualifications; scope of
practice; and board and licensure requirements in effect in the State in
which they are employed. All staff members are expected to practice
within the licensure and/or certification requirements for their degree,
practice setting, and scope of practice as defined by their individual
State.
All facility staff must be able to demonstrate competency required to
serve the complex needs of dialysis patients and must have the ability
to sustain and demonstrate the skills needed to perform the specific
duties of their positions. Each facility is expected to determine how
each staff member will “demonstrate” competency. Specific
competencies expected to be able to be demonstrated by staff assigned
to these tasks include, but are not limited to, skills at testing for
chlorine/chloramine levels; operating reuse equipment; following
infection control practices designated for dialysis facilities by CDC;
identifying and treating intradialytic morbidities, and monitoring
patients and equipment alarms during treatment.
V682
(a) Standard: Medical director.
(1) The medical director must be a board-certified
physician in internal medicine or pediatrics by a
professional board who has completed a board-approved
training program in nephrology and has at least 12-
months of experience providing care to patients receiving
dialysis.
The facility is expected to maintain verification of the medical
director’s board certification and documentation that he/she has
completed a board-approved training program in nephrology or
pediatric nephrology and has the required experience.
According to the websites of the American Board of Internal
Medicine (ABIM) and the American Board of Pediatrics (ABP), a
physician does not need to maintain certification in internal medicine
or general pediatrics to recertify in nephrology or pediatric
nephrology. Therefore, a medical director may maintain current
certification in nephrology or pediatric nephrology or current
certification in internal medicine or general pediatrics. CMS accepts
the position of the ABIM and ABP and accepts current board
certification in internal medicine, pediatrics, nephrology, or pediatric
nephrology as meeting this requirement.
Final Version 1.1 Page 267 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Completion of a “board-approved training program” means the
physician has completed a two-year nephrology fellowship, which
would serve as evidence of the required 12-months of nephrology
experience.
V683
(2) If a physician, as specified in paragraph (a)(1) of this
section, is not available to direct a certified dialysis
facility another physician may direct the facility, subject
to the approval of the Secretary.
If the facility is using a physician as medical director who does not
meet the requirement at § 494.140(a)(1), there must be documentation
available that the Secretary of DHHS approved the facility’s use of
the physician as medical director.
V684
(b) Standard: Nursing services.
(1) Nurse manager. The facility must have a nurse
manager responsible for nursing services in the facility
who must—
(i) Be a full time employee of the facility;
(ii) Be a registered nurse; and
(iii) Have at least 12 months of experience in clinical
nursing, and an additional 6 months of experience in
providing nursing care to patients on maintenance
dialysis.
“Responsible for nursing services” means the nurse manager provides
oversight and direction to all direct care staff that provide dialysis and
nursing care in the facility, including input into hiring, evaluating, and
terminating these staff. Two or more qualified nurses may share this
responsibility, but the facility must designate one of these nurses as
primarily responsible.
The nurse manager is the only staff person who must be a direct
employee of the facility rather than a contracted employee.
“Full-time” means the nurse manager is available to work in the
dialysis facility the number of hours that the facility is open or as
facility policy requires for full-time employment. For example, a
dialysis facility that is only open for 24 hours a week, would need to
employ the nurse manager for 24 hours a week to satisfy this
requirement. If the facility is open 6 days a week or provides
nocturnal dialysis, the nurse manager would need to be available to
work at least 40 hours a week, and provide on-call coverage, in
rotation with other qualified staff, all hours that the facility is open,
including night and weekend hours.
“Employee” means a person for whom the facility files a W-2 Tax
Form. A “contract” staff person is not considered an “employee.”
Final Version 1.1 Page 268 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The nurse manager must be registered and licensed to practice in the
applicable State. He/she must have at least 12 months experience as a
registered nurse, plus 6 months experience as a registered nurse
providing clinical nursing care to dialysis patients, in either a chronic
or acute setting.
The same registered nurse(s) who meets these requirements may
fulfill multiple nursing roles in the dialysis facility as long as the
facility has an adequate number of qualified nurses present while
patients are dialyzing to meet patients’ clinical needs for the level of
dialysis care provided. Refer to V758.
V685
(2) Self-care and home dialysis training nurse. The nurse
responsible for self-care and/or home care training
must—
(i) Be a registered nurse; and
(ii) Have at least 12 months experience in providing
nursing care and an additional 3 months of experience in
the specific modality for which the nurse will provide
self-care training.
“Responsible for …training” means that the registered nurse must be
in charge of and provide self-care and home dialysis training for
dialysis patients and/or their caregivers. Although some portions of
the training may be delegated to other trainers with required specialty
knowledge, the “nurse responsible” must provide major portions of
the training and coordinate and oversee the program.
The registered nurse responsible for self-care and the home dialysis
training must have at least 12 months experience as a registered nurse,
plus 3 months experience as a registered nurse in the specific modality
of hemodialysis (HD) and/or peritoneal dialysis (PD). If one
registered nurse is responsible for both the HD and PD programs, that
nurse must have 12 months experience as a nurse plus at least three
months experience in each respective modality. The self-care and
home dialysis training nurse position may be filled by an employee or
a contracted nurse who meets these qualifications. This position is not
required to be full-time. However, if the position is part-time, the
facility must have personnel experienced in all home modalities
provided to respond to patients’ concerns and to troubleshoot
problems when the home training nurse is unavailable.
V686
(3) Charge nurse. The charge nurse responsible for each
shift must—
There must be one or more “charge nurses” designated as responsible
each shift. If the charge nurse is a registered nurse, he/she must be
Final Version 1.1 Page 269 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(i) Be a registered nurse, a licensed practical nurse, or
vocational nurse who meets the practice requirements in
the State in which he or she is employed;
(ii) Have at least 12 months experience in providing
nursing care, including 3 months of experience in
providing nursing care to patients on maintenance
dialysis; and
registered and licensed to practice in the applicable State. If the person
functioning in the charge role is a licensed practical nurse or licensed
vocational nurse, he/she must be legally authorized to practice as a
licensed practical or vocational nurse (LPN. or LVN) in that State.
A charge nurse must have a minimum of 9 months of nursing
experience, and an additional 3 months of specialized experience (to
total 12 months) providing clinical nursing care to dialysis patients, in
either a chronic or acute setting. The charge nurse position may be
filled by a full-time or part-time employee or a contracted nurse who
meets these qualifications.
V687
(iii) If such nurse is a licensed practical nurse or licensed
vocational nurse, work under the supervision of a
registered nurse in accordance with state nursing practice
act provisions.
Recognize that a licensed practical/vocational nurse cannot be in
charge of a dialysis facility without specific authority from the
applicable State board of nursing. CMS did not intend for, and State
boards of nursing may prohibit, a licensed practical/vocational nurse
supervising a registered nurse.
An LPN/LVN cannot be the only licensed person in a dialysis facility
while patients are on dialysis. Refer to V759 which requires a
registered nurse to be present whenever in-center patients are being
treated.
V688
(4) Staff nurse. Each nurse who provides care and
treatment to patients must be either a registered nurse or
a practical nurse who meets the practice requirements in
the State in which he or she is employed.
Each nurse must have the required State license (refer to V681), and
meet any practice requirements for the applicable State.
V689
(c) Standard: Dietitian. The facility must have a dietitian
who must—
(1) Be a registered dietitian with the Commission on
Dietetic Registration; and
The Commission on Dietetic Registration is the credentialing agency
for the American Dietetic Association. Dietitians working in dialysis
must have evidence of registration with that organization.
V690
(2) Have a minimum of 1 year professional work
experience in clinical nutrition as a registered dietitian;
The registered dietitian must have one year of professional work
experience in clinical nutrition after registration as a dietitian.
Experience in clinical nutrition as an intern (prior to registration)
would not count toward this requirement, nor would foodservice
Final Version 1.1 Page 270 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
experience after registration as a dietitian meet this requirement.
V691
(d) Standard: Social worker. The facility must have a
social worker who—
(1) Holds a master’s degree in social work with a
specialization in clinical practice from a school of social
work accredited by the Council on Social Work
Education; or
(2) Has served at least 2 years as a social worker, 1 year
of which was in a dialysis unit or transplantation
program prior to September 1, 1976, and has established
a consultative relationship with a social worker who
qualifies under § 494.140 (d)(1).
The social worker must have a master’s degree in social work from a
college or university that is accredited by the Council on Social Work
Education (CSWE). The CSWE website database lists accredited
masters level social work degree programs. The Association of State
Boards of Social Work website has links to State regulations and rules
for social work practice in each State.
The curriculum of masters-level programs in schools accredited by the
CSWE includes courses in human behavior, family dynamics,
diagnosis, mental health treatment, conflict management, and ethics.
Therefore, any one whose degree is from a school accredited by the
CSWE is presumed to have a “specialization in clinical practice.”
Licensure requirements for master-prepared social workers in clinical
practice vary from state to state. The masters prepared social worker
must meet the licensure requirements in the state of practice. Refer to
V681.
Staff without master’s degrees in social work, including bachelor’s
prepared social workers, may function as assistants under the
supervision of the qualified social worker and provide services such as
assisting with transportation arrangements; providing information and
helping patients apply for Medicare, Medicaid and other insurance
benefits to assure payment for care; and locating resources to assist in
payment for adequate nutrition, housing, and medications. Only
masters-prepared social workers may do assessments, develop
psychosocial plans of care, provide counseling to patients and
families, and participate as the social worker in the facility’s QAPI
program.
The grandfather clause at (2) applies to very few social workers, as it
only applies to those social workers who have worked in dialysis or
Final Version 1.1 Page 271 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
transplant facilities since September 1, 1975 and who had at least two
years of social work experience on September 1, 1976 when the
original ESRD Conditions for Coverage became effective. The social
worker who “qualifies” as a social worker through this grandfather
clause must have a “consultative relationship” with a qualified social
worker. A “consultative relationship” requires a written agreement
outlining the supervision that will be provided by the masters-
prepared social worker. Since the professional responsibility for
services lies with the masters-prepared social worker, this agreement
needs to be consented to and signed by both parties. Having the
masters-prepared social worker co-sign social service medical record
entries made by the other social worker is not sufficient to meet the
consultative relationship requirement.
V692
(e) Standard: Patient care dialysis technicians. Patient
care dialysis technicians must—
(1) Meet all applicable State requirements for education,
training, credentialing, competency, standards of
practice, certification, and licensure in the State in which
he or she is employed as a dialysis technician; and
(2) Have a high school diploma or equivalency;
A “patient care (dialysis) technician” (PCT) means any person who
provides direct care to patients and who is not classified as another
professional, e.g., nurse, dietitian, or social worker. A biomedical
technician or dialysis assistant would be classified as a PCT if he/she
has responsibility for direct patient care or to set up machines for
patient use. A technician who maintains or “takes down” machines
after use without direct patient contact is not considered a PCT under
these regulations.
Patient care (dialysis) technicians must meet requirements of the
applicable State for education and training to provide patient care in
dialysis facilities, including any State requirements related to practice
standards, certification or registration.
CMS recognizes there are some experienced PCTs working in dialysis
facilities as of the effective date of these rules who may not have
evidence of a high school diploma or equivalency. PCTs with greater
than 4 years work experience in dialysis as of 10/14/08 who lack
evidence of a high school diploma may use that work experience in
lieu of the requirement for high school diploma.
Final Version 1.1 Page 272 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V693
(3) Have completed a training program that is approved
by the medical director and governing body, under the
direction of a registered nurse, focused on the operation
of kidney dialysis equipment and machines, providing
direct patient care, and communication and interpersonal
skills, including patient sensitivity training and care of
difficult patients.
There must be a training program for patient care dialysis technicians,
approved by the medical director and governing body and directed by
a registered nurse. The training program may be conducted at the
facility or at another location. Community or corporate-based
programs are acceptable if the required components are included; the
program is under the direction of a registered nurse; and the program
has been approved by the medical director and governing body.
All patient care (dialysis) technicians (PCT) who are not yet certified
must have successfully completed the approved training program
before independently providing patient care. “Successfully
completed” means the PCT will have completed all didactic portions
of the course and demonstrated competency in the knowledge and
skills provided by the training.
For "experienced" PCTs, meaning those PCTS who have been
employed as a PCT for more than 2 years as of the effective date of
these regulations, who do not have documentation of having
completed a training program covering the listed content, competency
may be demonstrated by successful completion of a facility’s written
exam(s) over the required content and a skills checklist completed by
observation of the PCT's skills by a registered nurse. Successful
completion of these exam(s) and competency testing would not negate
the need for these experienced PCTs to achieve certification within
the specified time period.
Facility policies and procedures should define the curriculum; length
of training course; and the method for determining successful
completion of the course.
V694
The training program must include the following
subjects:
The training program must include the content referenced in the
regulation, at a minimum.
Final Version 1.1 Page 273 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(i) Principles of dialysis.
(ii) Care of patients with kidney failure, including
interpersonal skills.
(iii) Dialysis procedures and documentation, including
initiation, proper cannulation techniques, monitoring,
and termination of dialysis.
(iv) Possible complications of dialysis.
(v) Water treatment and dialysate preparation.
(vi) Infection control.
(vii) Safety.
(viii) Dialyzer reprocessing, if applicable.
V695
(4) Be certified under a State certification program or a
national commercially available certification program, as
follows—
(i) For newly employed patient care technicians, within
18 months of being hired as a dialysis patient care
technician; or
(ii) For patient care technicians employed on October 14,
2008, within 18 months after such date.
Certification can occur under the aegis of either a national
commercially-available program or a State program.
At the time of publication of these regulations, there were three
national commercially-available certification programs: the Certified
Clinical Hemodialysis Technician (CCHT) examination offered by the
Nephrology Nursing Certification Commission (NNCC), the Board of
Nephrology Examiners for Nursing and Technology (BONENT)
exam, and the National Nephrology Certification Organization
(NNCO) exam. CMS has approved these three national certification
programs for ESRD patient care technician certification. Additional
national programs that are interested in offering a certification
program may apply to CMS for approval.
These national commercially-available certification programs require
a patient care dialysis technician to successfully pass a standardized
certification examination in a proctored environment, and maintain
certification through current work experience and continuing
education.
State certification programs which have a formal certification and
competency program (including standardized tests, which reflect the
Final Version 1.1 Page 274 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
content listed in the regulation, administered in a proctored
environment by an independent examiner) that is specific to patient
care dialysis technicians, can satisfy this requirement. A “standardized
test” is one developed and tested to validly and reliably measure the
knowledge required to demonstrate competency in the area. If the
state requires certification by a national commercially-available
certification program, this regulation expects continued certification
under the requirements of the national commercially-available
program.
Patient care dialysis technicians working on October 14, 2008, who
are not yet certified under an approved program, must be certified
before April 15, 2010. Patient care technicians hired after October 14,
2008 must be certified within 18 months of their hire date as a patient
care technician. If a patient care technician who is not certified
changes jobs from one dialysis facility to another, the time he/she was
employed in the first facility will count toward the 18-month deadline
for certification unless he/she had a gap in employment as a patient
care technician of more than 18 months.
A reuse technician or a water treatment technician who does not
provide direct patient care does not require certification as a patient
care dialysis technician. The training curriculum for persons
performing hemodialyzer reprocessing is delineated under the
Condition for Reuse of hemodialyzers and bloodlines at V308. The
training for persons responsible for operating and testing the water
treatment and dialysate preparation systems is addressed under the
Condition for Water and dialysate quality at V260. If a reprocessing
technician or water treatment technician changes positions to become
a patient care technician, he/she must be certified in 18 months from
the date he/she begins the new PCT position.
V696
(f) Standard: Water treatment system technicians.
Technicians who perform monitoring and testing of the
Any staff member who operates the water treatment system must
complete a training program approved by the medical director and the
Final Version 1.1 Page 275 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
water treatment system must complete a training
program that has been approved by the medical director
and the governing body.
governing body prior to independently performing water treatment
system tasks.
Refer to V260 in the Condition for Water and dialysate quality for
additional requirements related to training for the persons operating
the water/dialysate systems.
V710
§ 494.150 Condition: Responsibilities of the medical
director.
This Condition defines the role the facility medical director is
expected to assume to ensure the delivery of quality patient care and
clinical outcomes. Most deficient practices identified in the delivery
of quality patient care and patient clinical outcomes are most
appropriately cited under the Conditions pertinent to the practice (e.g.,
infection control practices, lack of patient assessment or plan of care
implementation). Citation of these standards or this Condition should
be considered when deficient practices are pervasive, the results of the
deficient practices are egregious, or the deficient practice identified is
not covered under other Conditions.
Determine compliance with this Condition by patient and staff
interviews, review of clinical and QAPI records and review of survey
findings related to care delivery, patient assessments and plans of
care, water and dialysate quality, reuse, and QAPI.
Examples of Condition level non-compliance include, but are not
limited to:
• Serious and/or pervasive problems/trends identified in the quality
of care delivery, quality assurance and performance improvement
activities;
• Significant deficient practices in patient care policy and procedure
development or implementation in which a lack of involvement
and oversight by the medical director was a contributing factor.
V711
The dialysis facility must have a medical director who
meets the qualifications of § 494.140(a) to be responsible
for the delivery of patient care and outcomes in the
Each dialysis facility must have a single medical director who meets
the qualifications under the Condition for Personnel at V682
identified as responsible for carrying out the duties of this position.
Final Version 1.1 Page 276 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
facility. The medical director is accountable to the
governing body for the quality of medical care provided
to patients.
The position of medical director may not be shared by several
physicians. The governing body and medical director may designate
other physicians to direct different program components in that
facility (e.g., home hemodialysis program, home peritoneal program),
as long as all components ultimately report to the facility medical
director and are under the same QAPI and governing body oversight.
These regulations do not preclude the medical director from also
serving as the chief executive officer/administrator of the facility
(refer to V752), as long as the responsibilities of both positions are
fulfilled.
The medical director is expected to be actively involved in the
oversight of the facility patient care delivery and outcomes (e.g., to
attend and contribute during interdisciplinary meetings for his/her
patients, to participate in performance improvement plans, and to be
involved in the education of staff).
The medical director should devote sufficient time to fulfilling these
responsibilities. As a guideline, the financial cost report each facility
must file annually with CMS considers the medical director position
to reflect a 0.25 FTE.
Refer to the Conditions for Infection control (V144); Water and
dialysate quality (V177, V179); Reuse of hemodialyzers and
bloodlines (V305, V309, V311, V361); and Governance (V766,
V767) for medical director oversight responsibilities specific to those
areas. Generally, unless they are serious or pervasive, findings in
those areas should be cited at the more specific tags rather than at this
tag.
V712
Medical director responsibilities include, but are not
limited to, the following:
(a) Quality assessment and performance improvement
While these regulations charge the facility governing body with the
responsibility for allocating necessary staff and resources for the
QAPI program (refer to V756), the medical director is assigned
Final Version 1.1 Page 277 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
program.
operational responsibility for the QAPI program. Operational
responsibility includes review of quality indicators related to
improved patient health outcomes and monitoring this data on a
continual basis as is required by the Condition for QAPI; education of
facility and medical staff in the QAPI objectives; reviewing the
method of prioritizing the importance of improvement projects;
inclusion/encouragement of all staff in participating towards
achievement of QAPI goals; communication with the governing body
regarding the needs identified by QAPI; and participating in the
evaluation of the effectiveness of performance improvement
plans/activities.
Materials documenting the QAPI program should include evidence of
active participation and oversight by the medical director (e.g.,
discussion of issues, guidance and contribution to the development of
performance improvement plans, assessment of the effectiveness of
those plans).
V713
(b) Staff education, training, and performance.
The medical director is responsible for ensuring that facility staff
members receive the appropriate education and training to
competently perform their job responsibilities.
“Performance” refers to the responsibility of the medical director to
assure that staff members are competent to carry out their assigned
duties (e.g., to adequately monitor the patient and the dialysis process,
to provide needed social services), and follow facility policy regarding
expected performance.
Refer to other Conditions in these regulations for specific
requirements for staff education, training and/or competency:
• V132 in Infection control;
• V260 in Water and dialysate quality;
• V308, 309 in Reuse;
• V409, V410, V411 in Physical environment;
Final Version 1.1 Page 278 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
• V693, V694, V696 in Personnel qualifications; and
• V760 in Governance.
Generally, these more specific tags should be used rather than this tag
if the problem identified in staff education, training or in the
performance of assigned responsibilities is related to one of these
areas.
V714
(c) Policies and procedures.
The medical director must—
(1) Participate in the development, periodic review and
approval of a “patient care policies and procedures
manual” for the facility; and
Written patient care policies and procedures are an essential reference
for clinical staff and should reflect current practice at the facility. The
patient care policies and procedures should address all areas of patient
assessment and care delivery for the dialysis modalities provided, and
the policies and procedures should reflect these regulations as well as
current practice standards and adherence to equipment manufacturers’
instructions for use.
There must be evidence that the medical director reviewed and
approved the patient care policies and procedures and any revisions as
they are made. Corporate-owned or corporate-managed facilities may
use standard policies and procedures developed by the corporation.
There should be a mechanism for the facility medical director to have
input into the policies and procedures, and to have some authority to
individualize corporate policies to address unique facility situations.
Policies are expected to be adequate, accurate and up to date.
V715
(2) Ensure that—
(i) All policies and procedures relative to patient
admissions, patient care, infection control, and safety are
adhered to by all individuals who treat patients in the
facility, including attending physicians and nonphysician
providers; and
The medical director is responsible for the implementation of the
policies and procedures by all staff. This includes holding medical
staff accountable for complying with facility policies and procedures,
e.g., updating plans of care, signing verbal orders, being
knowledgeable of the QAPI targets and working to achieve those
targets in their patients. In reviewing the performance of the medical
staff, the medical director should consider using currently-available
methods, such as practitioner profiles, to review and evaluate
performance.
Final Version 1.1 Page 279 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
The medical director is responsible for ensuring that the facility has an
established policy regarding admissions to the facility
Policies relative to patient admission must address the expectation for
an initial assessment by a member of the medical staff (i.e., physician,
APRN or PA) before the initiation of the patient’s first dialysis
treatment in the facility, in order to develop the admission treatment
orders and to provide for prompt recognition and action to address
urgent patient medical needs (e.g., anemia with Hgb <10 gm/dL, fluid
overload, hyperkalemia) prior to completion of the comprehensive
patient assessment. This evaluation could be accomplished by review
of medical records and consultation with the referring physician, and
is not intended to require the medical staff member to “see” the
patient in the facility prior to this first treatment.
Orders for treatment must be in place prior to the initial treatment, as
well as a patient evaluation by a registered nurse for any immediate
needs. At the time of publishing these regulations, according to the
American Nephrology Nurses’ Association, the minimal nursing
evaluation prior to initiating treatment for a patient new to the facility
should include:
• Neurologic: level of alertness/mental status, orientation,
identification of sensory deficits
• Subjective Complaints
• Rest and comfort: pain status
• Activity: ambulation status, support needs, fall risk
• Access: assessment
• Respiratory: respirations description, lung sounds
• Cardiovascular: heart rate and rhythm; presence and location of
edema
• Fluid gains, blood pressure and temperature pre-treatment
• Integumentary: skin color, temperature and as needed,
type/location of wounds
Final Version 1.1 Page 280 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Note that other parts of these regulations address adherence to policies
and procedures as applicable to specific Conditions, e.g., Infection
control at V142, Water and dialysate quality at V259, Reuse at V306,
and Physical environment at V408. Generally, these more specific
tags should be used for deficient practices identified in those areas.
V716
(ii) The interdisciplinary team adheres to the discharge
and transfer policies and procedures specified in §
494.180(f).
The medical director must monitor and review each involuntary
patient discharge to ensure that the facility interdisciplinary team
follows the discharge and transfer policies and completes the steps
required under the Condition for Governance at V766 and V767.
The records of any patients who have been involuntarily discharged
must show evidence of compliance with each of the requirements
detailed at V767, including evidence that the medical director as well
as the patient’s attending physician, signed the order for involuntary
discharge.
V725
§ 494.170 Condition: Medical records.
This Condition requires the facility to maintain complete and accurate
records and to protect them against loss and unauthorized use. The
requirements apply to both hard copy and electronic health records.
Compliance with this Condition is determined by observation and
review of medical records.
Condition level non-compliance should be considered when there are
serious and/or pervasive problems identified with the accuracy,
completion, accessibility, and/or protection of patients’ medical
record information.
V726
The dialysis facility must maintain complete, accurate,
and accessible records on all patients, including home
patients who elect to receive dialysis supplies and
equipment from a supplier that is not a provider of ESRD
services and all other home dialysis patients whose care
is under the supervision of the facility.
In ESRD, the term “medical records” includes printed or electronic
information such as, but not limited to consents, histories and
physicals, medication reports, radiology reports, laboratory reports,
dialysis treatment orders, patient assessments, patient plans of care,
treatment records, and progress notes regarding the condition and care
of the patient. Each patient’s medical record, whether hard copy,
electronic, or a combination of both, should include complete and
Final Version 1.1 Page 281 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
pertinent information about the condition of the patient, assessments
by the interdisciplinary team, updated plans of care, all interventions
and treatments prescribed and delivered, and details of any events
occurring with the patient during the course of treatment. No matter
what format, the record of care must be readily accessible to every
authorized member of the healthcare team so that care can be
coordinated to best meet the needs of the patient.
The facility must create and maintain a complete and accurate record
of care for every patient that is unique for that patient. Each patient’s
medical record should clearly portray the patient, the care provided by
the facility personnel, and the outcomes of that care.
V731 in this Condition and V599 under the Condition for Care at
home also address the records of home patients.
V727
(a) Standard: Protection of the patient’s record.
The dialysis facility must—
(1)Safeguard patient records against loss, destruction, or
unauthorized use; and
(2) Keep confidential all information contained in the
patient’s record, except when release is authorized
pursuant to one of the following:
(i) The transfer of the patient to another facility.
(ii) Certain exceptions provided for in the law.
(iii) Provisions allowed under third party payment
contracts.
(iv) Approval by the patient.
(v) Inspection by authorized agents of the Secretary, as
required for the administration of the dialysis program.
The medical record system must protect the privacy and security of all
patients’ medical record information. The medical records system
must ensure that records are not lost, stolen, destroyed, altered, or
reproduced in an unauthorized manner. All locations where medical
records are stored or maintained must ensure the integrity, security,
controlled accessibility and protection of the records.
Electronic medical records systems must be designed to prevent
accidental loss or destruction of medical record information (e.g.,
have an automated backup system), and have safeguards to prevent
alteration of entries without notation of the alteration (e.g., a late entry
must be indicated as such). Facility personnel should have sufficient
knowledge of electronic system functions to assure their ability to
safeguard records on that system in the event of a problem, including
backup of electronic medical records and restoring data. Staff
members should be aware of the facility’s plan to ensure uninterrupted
maintenance of the patient’s medical record in the event of a computer
failure. Staff members should be able to provide a printed copy of
Final Version 1.1 Page 282 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
requested portions or the complete current medical record without
significant delay (e.g., less than one hour for a portion of the record,
less than four hours for the complete current record).
The accumulation of records for a patient treated several times a week
for years can become voluminous. The current working chart may
contain recent treatment records, and a year of patient assessments,
plans of care, progress notes, orders, lab reports, etc. Older records of
current patients may be stored in a convenient and secure location
where they can be readily accessed as needed. Electronic storage of
records is permissible if a secure means to protect the integrity of the
record and the privacy of the patient is provided.
The facility policy for stored medical records must ensure prompt
retrieval. Facility policy should address how staff members access
records that are stored offsite, and the expected time to retrieve them.
In the event of loss of medical records due to unavoidable
circumstances, (i.e., natural or man-made disaster) there should be
evidence in the QAPI documentation of the event, what records were
lost/destroyed, and what steps were taken to prevent similar losses in
the future. The facility must have a plan for protecting medical
records in an emergency (e.g. transport, secure in place, redundant
backup, continuous automatic off-site backup), and for minimizing
loss.
Facility policy and practices must reflect the requirements of the
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
requirements for paper and electronic medical records. HIPAA allows
release of protected health information (PHI) in certain emergency
circumstances, and for the continuity of health care. Also refer to the
Condition for Patients’ rights at V455.
Final Version 1.1 Page 283 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Facility policy should address the release of patient’s protected health
information to third parties.
V728
(3) Obtaining written authorization from the patient or
legal representative before releasing information that is
not authorized by law.
Medical records must contain written authorization for health
information release prior to release of any medical records that require
the patient’s/designee’s authorization to release.
42 CFR § 494.170(a)(2)(v) gives state surveyors and ESRD Networks
rights to access and review patient records, including taking copies of
medical records offsite for official purposes.
V729
(b) Standard: Completion of patient records and
centralization of clinical information.
(1) Current medical records and those of discharged
patients must be completed promptly.
“Completed promptly” for current (active) patient records means that
each clinical event is recorded as soon as possible after its occurrence,
care interventions are recorded when provided, and other pertinent
patient health information (e.g. assessments, plans of care, progress
notes, medication administration, labs, radiology reports, medical
orders) is recorded in a timeframe that provides other interdisciplinary
team members with an up-to-date picture of the status of the patient at
all times.
Facility policy must identify timeframes for the completion of medical
records (e.g. signing of verbal orders, completion of discharged
patients’ records). The medical record system must have a method for
identification of the author, date and time of each entry. The author’s
identification may be by written signature, initials, computer key, or
other code. If initials or computer codes are used as signatures, there
must be a means to identify the author of the entry. Rubber stamp
signatures are not permitted.
V730
(2) All clinical information pertaining to a patient must
be centralized in the patient’s record, including whether
the patient has executed an advance directive. These
records must be maintained in a manner such that each
member of the interdisciplinary team has access to
current information regarding the patient’s condition and
prescribed treatment.
“Centralized” means that the patient’s health information is
maintained in a common location, such as a “chart” or electronic
record system. At the time of publishing of these regulations, many
facilities had a combination of hard copy and electronic records. If
part or all of the record is maintained electronically, each member of
the interdisciplinary team must be familiar with and able to access
those areas of the patient record he/she would need to use to stay
Final Version 1.1 Page 284 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
current with the patient’s plan of care. The system in place must allow
the members of the interdisciplinary team to promptly access the most
current information about the patient and their treatment.
Dialysis treatment records (i.e., “flow sheets”) are the primary means
of documenting the daily care of hemodialysis patients. These records
should contain complete information about the treatment, such as pre
and post treatment assessments, vital signs, vascular access in use, pre
and post treatment weights, machine parameters and safety checks
(e.g. alarm tests, dialysate pH and conductivity, dialysis prescription
delivered (i.e. dialyzer, dialysate components, blood and dialysate
flow rates, length of treatment), medications given, any clinical events
that occurred during the treatment, actions taken and response.
V731
(3) The dialysis facility must complete, maintain, and
monitor home care patients’ records, including the
records of patients who receive supplies and equipment
from a durable medical equipment supplier.
The facility should have a system to maintain and regularly review
treatment records kept by all home patients (including those whose
equipment and supplies are furnished by a durable medical equipment
(DME) supplier) and to incorporate those records into the patient’s
medical record.
Refer to V599 if deficient practices in the content or maintenance of
individual home dialysis patients' records are identified. Use this tag if
there are facility-wide issues related to the records for multiple home
patients.
V732
(c) Standard: record retention and preservation.
In accordance with 45 CFR § 164.530(j)(2), all patient
records must be retained for 6 years from the date of the
patient’s discharge, transfer or death.
Note that some states have more stringent requirements for medical
record retention. Retention requirements begin after the patient is no
longer on census at the facility.
These retention requirements also apply to the records of machine
maintenance, dialyzer reprocessing/reuse, water treatment and
dialysate preparation as each of these records is part of the medical
record for the patients on service at the time those records were
completed. Documentation of these processes is retained in logs rather
than individual patient records. Since many patients are treated on the
Final Version 1.1 Page 285 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
equipment each day, determination of the retention period may be
difficult. Facility policy should address retention of these records.
V733
(d) Standard: Transfer of patient record information.
When a dialysis patient is transferred, the dialysis facility
releasing the patient must send all requested medical
record information to the receiving facility within 1
working day of the transfer.
The facility is responsible for transfer of requested medical record
information to the receiving facility within 1 working day. The intent
is to maintain continuity of care whenever patients leave the facility
temporarily (e.g., vacation, business, hospitalization), or transfer
permanently to a new facility.
V750
§ 494.180 Condition: Governance.
This Condition addresses the overall management of the facility. It
requires that an identifiable governing body demonstrate
responsibility for the operation of the facility, including fiscal
management, staff training and coverage, medical staff appointments
and coverage, and the QAPI program. This Condition also holds the
governing body accountable for establishing an internal grievance
process and decreasing the potential for involuntary discharge of
patients; for emergency coverage and backup; for electronic data
submission; and the relationship of the facility to the ESRD Network.
Compliance with this Condition is determined by patient and staff
interview, observations, and review of records. Because the governing
body is responsible for the total operation of the facility, the
responsibility of the governing body must be considered when serious
problems in other Conditions are identified.
Examples of Condition-level non-compliance include but are not
limited to:
• Major problems with care and safety of patients, patient rights, or
operations;
• Failure to follow the requirements for involuntary patient
discharge;
• Failure to respond to Network requests for corrective action plans
for problems identified by the Network;
• Failure to submit required data electronically; and
Final Version 1.1 Page 286 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
• Non compliance with another Condition for Coverage if the
governing body has some responsibility for the deficient practices.
V751
The ESRD facility is under the control of an identifiable
governing body, or designated person(s) with full legal
authority and responsibility for the governance and
operation of the facility. The governing body adopts and
enforces rules and regulations relative to its own
governance and to the health care and safety of patients,
to the protection of the patients’ personal and property
rights, and to the general operation of the facility.
“Identifiable” means that the individual or individuals that are
responsible for the conduct and oversight of the operations of the
facility are identified in writing. This may be demonstrated in
governing body bylaws or minutes, or in ownership documents.
Terminology related to ownership:
• “Hospital-based” means owned and operated by and located in a
hospital. A facility physically located inside a hospital but owned
by another entity, such as a dialysis corporation, would not be
considered “hospital-based.”
• “Satellite facility” means owned and operated by a hospital but
located away from the central hospital campus. A satellite facility
is surveyed separately and has its own CMS certification number
(CCN).
• “Corporate entity” means owned by a group, individual or
company; generally these facilities are part of a multi-facility
group numbering from several to hundreds of facilities.
• “Physician-owned” means owned by a physician through a sole
proprietorship, limited liability company, or corporation; may be
one or multiple facilities.
The governing body bylaws should clearly define the ownership of the
facility. In some cases, the owner has a contract with another entity
for management of the facility. If so, this relationship should be clear
in the governing body records of the facility.
Facilities that are part of a dialysis organization with multiple
widespread facilities must have a local governing body designated to
guide the day-to-day operation of the facility. The governing body
may consist of one person or a group of persons. It should be clear in
the governing body records who constitutes the governing body and
Final Version 1.1 Page 287 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
who has the legal authority and responsibility for the governance and
operation of the facility.
V752
(a) Standard: Designating a chief executive officer or
administrator. The governing body or designated person
responsible must appoint an individual who serves as the
dialysis facility’s chief executive officer or administrator
who exercises responsibility for the management of the
facility and the provision of all dialysis services,
including, but not limited to–
The qualifications for this position are not specified in these
regulations, but should be defined in facility policy, and include
sufficient educational and practical experience to fulfill the
responsibilities listed in this section. The governing body or its
designee must appoint the selected individual to this role. This
position may be held by a member of the staff who is holding a
different role, e.g., nurse manager, the medical director, as long as the
duties of each role are accomplished.
V753
(1) Staff appointments;
The governing body, through the CEO or administrator, is responsible
for the appointment of medical staff including physicians and non-
physician practitioners (i.e., advanced practice registered nurses and
physician assistants). These appointments must be documented either
in governing body minutes or in the applicable credential file.
V754
(2) Fiscal operations;
The governing body, through the CEO or administrator, is responsible
for maintaining sound fiscal operations. Issues which could indicate
problems with fiscal operations include (but are not limited to) missed
doses due to a lack of prescribed medications, broken equipment,
deterioration of the physical plant, or insufficient staff.
V755
(3) The relationship with the ESRD networks; and
The ESRD Networks are CMS contractors assigned responsibilities
via a Statement of Work to:
• Collect and analyze data on ESRD patients and their outcomes of
care, including the information that allows patients to be enrolled
into the ESRD Medicare benefit program
• Provide education and oversight to improve the quality of care
delivered to dialysis and kidney transplant patients
• Support facilities in developing and maintaining an effective
QAPI program
• Respond to complaints and grievances
At the time of publishing these regulations, there were 18 ESRD
Final Version 1.1 Page 288 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Networks, each covering a specified geographic area.
A signed agreement between the facility and the applicable Network
is required prior to the initial certification survey. The CEO or
administrator is responsible to receive and act on correspondence
from the ESRD Network and to promptly respond to any request from
the applicable Networks.
Additional requirements related to Networks are found at V772.
V756
(4) Allocation of necessary staff and other resources for
the facility’s quality assessment and performance
improvement program as described in § 494.110.
Under QAPI (at V626) requirements for the minimum professional
membership in the QAPI process are delineated. If those professional
members are not given enough time or support to participate in QAPI
activities, this tag should be considered. There must be
communication between the medical director and the governing body
regarding QAPI. The governing body must provide resources (time,
staff or funding) for QAPI audits, staff education, refurbishing, etc. as
needed to support correction of identified problems. The governing
body must review information related to significant problems
identified and their causes, and provide guidance and support for
proposed needed corrections.
V757
(b) Standard: Adequate number of qualified and trained
staff. The governing body or designated person
responsible must ensure that—
(1) An adequate number of qualified personnel are
present whenever patients are undergoing dialysis so that
the patient/staff ratio is appropriate to the level of
dialysis care given and meets the needs of patients; and
There must be sufficient numbers of qualified and trained staff on
duty while patients are on dialysis in-center to meet the individualized
needs of the patients. Consideration should be given to the acuity and
care needs of patients, staff experience and areas of expertise when
evaluating the adequacy of staffing. Sufficient numbers of staff must
be present in the treatment area to be able to see every patient during
treatment (including lunch breaks, shift change, etc.[refer to V407]);
to deliver routine care, patient assessment and monitoring per facility
policy; and to promptly respond to and address patient needs (such as
changes in physical or mental condition) and machine alarms. Staffing
assignments and schedules should demonstrate a pattern of sufficient
staff coverage to ensure safe patient care.
Final Version 1.1 Page 289 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
Facilities are expected to meet any applicable State regulations that
identify specific patient-to-staff ratio requirements. Failure to comply
with those State requirements may be cited at this tag.
V758
The registered nurse, social worker and dietitian
members of the interdisciplinary team are available to
meet patient clinical needs;
The governing body is expected to make diligent efforts to promptly
fill vacant positions. If the nurse manager, social worker, dietitian or
other required or necessary position is vacant for more than a month,
the governing body must make some provision for temporary
coverage. If the facility “shares” the social worker or dietitian with
multiple clinics or requires professional staff to perform non-clinical
tasks, it must not negatively impact the time available to provide the
clinical interventions required to achieve the goals identified in the
patient’s plan of care. The facility CEO or administrator is responsible
to assure the professional support staff members have sufficient time
available in the facility to meet the clinical needs of in-center and
home dialysis patients.
V759
(2) A registered nurse, who is responsible for the nursing
care provided, is present in the facility at all times that
in-center dialysis patients are being treated;
There must be a registered nurse (RN) on duty and available at all
times when in-center dialysis patients are being treated. This
requirement is based upon data in the nursing literature which
demonstrates a positive correlation between the availability of
professional nursing service and patient outcomes.
If only one RN is on duty, that RN is expected to spend the majority
of his/her time on the treatment floor. Short personal breaks away
from the treatment floor are acceptable. An RN must be on-duty
whenever patients are present, including the beginning and end of the
treatment day.
In some cases, the RN who is on duty may not be qualified under
these regulations as a “charge nurse” See V686-V687. In those
instances, if allowed under the applicable State nurse practice act, a
qualified licensed practical nurse or qualified licensed vocational
nurse may function in the charge role.
V760
(3) All staff, including the medical director, have
The CEO or administrator is responsible to ensure that each member
Final Version 1.1 Page 290 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
appropriate orientation to the facility and their work
responsibilities; and
of the staff receives an orientation to the facility, his/her job duties,
and how to do the work assigned. While the orientation of employees
should be documented in their personnel files, the orientation of
physicians and non-physician practitioners (i.e., advanced practice
registered nurses and physician assistants) should be documented in
their credential files and include evidence of understanding of and
agreement to medical staff bylaws, policies and procedures, and
responsibilities related to QAPI.
V761
(4) All employees have an opportunity for continuing
education and related development activities;
Continuing education programs should be offered to all staff to help
them maintain and improve their knowledge, skills, and licensure, if
applicable. “Continuing education” includes internal training
programs, as well as external professional educational programs.
These regulations also include specific requirements regarding the
provision of staff in-services and continuing education relating to
Infection control at V132; Water & dialysate quality at V260;
Physical environment at V409; and Personnel qualifications at V693,
V694, and V696. Those tags should be considered (rather than this
tag) if the deficient practice identified is related to one of those
specific areas.
V762
(c) Standard: Medical staff appointments. The governing
body—
(1) Is responsible for all medical staff appointments and
credentialing in accordance with State law, including
attending physicians, physician assistants, nurse
practitioners and clinical nurse specialists; and
Privileges for physicians and non-physician practitioners (i.e.,
advanced practice registered nurses and physician’s assistants) are
granted by the facility’s governing body based on the individual
practitioner’s qualifications and performance. The facility must define
the requirements for practice at the facility in accordance with any
applicable State laws. The medical staff credential files must include
evidence the individual meets those requirements, including current
licensure in the applicable State. Refer to V681 for issues related to
professional licensing.
If the State has more stringent licensure requirements for ESRD
facilities regarding medical staff appointments and those requirements
are not met, those findings may be cited at this tag.
Final Version 1.1 Page 291 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
V763
(2) Ensures that all medical staff who provide care in the
facility are informed of all facility policies and
procedures, including the facility’s quality assessment
and performance improvement program specified in §
494.110.
(3) Communicates expectations to the medical staff
regarding staff participation in improving the quality of
medical care provided to facility patients
The governing body must inform members of the medical staff of all
aspects of the facility’s QAPI program, including the requirement to
participate in efforts to improve the quality of medical care to their
patients. These efforts must be reflected both in documentation of the
QAPI program and in the medical records of individual patients. It is
not required that all members of the medical staff attend all the QAPI
meetings.
Examples of the lack of medical staff adherence to facility policies or
goals would include physician(s) not participating in the development
of the plan of care, or not addressing poor patient outcomes with a
change in the plan of care.
Medical staff “not informed” indicates this requirement is not met.
For medical staff “not compliant,” refer to V715 under the Condition
for Medical director.
V764
(d) Standard: Furnishing services. The governing body
is responsible for ensuring that the dialysis facility
furnishes services directly on its main premises or on
other premises that are contiguous with the main
premises and are under the direction of the same
professional staff and governing body as the main
premises (except for services provided under § 494.100).
Each separate physical location for dialysis services must be certified
separately, and all approved services for a particular facility must be
provided on the premises of that location. Hospital-based facilities
may be located on the same campus of the hospital, with various
services (e.g., home training vs. in-center dialysis) being provided in
different rooms or areas, but sharing the same address on that campus.
All services provided by the facility must be under the direction of the
same professional staff and governing body.
Training and support for home dialysis must be provided by a facility
certified for those services. On occasion, some home training may be
provided in the patient’s home to meet the needs of the patient and/or
helper. Training for care at home is discussed at V582 through V585.
Home patients may see their physicians or a non-physician
practitioner (i.e., advanced practice registered nurse or physician
assistant) in their offices instead of seeing these practitioners at their
Final Version 1.1 Page 292 of 299
TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
dialysis clinics. In-center patients may, on occasion, see their
practitioner in their offices, while periodically seeing their practitioner
during treatment at the dialysis facility. This requirement can be found
under the Condition for Patient plan of care at V560.
V765
(e) Standard: Internal grievance process. The facility’s
internal grievance process must be implemented so that
the patient may file an oral or written grievance with the
facility without reprisal or denial of services.
The grievance process must include—
(1) A clearly explained procedure for the submission of
grievances.
(2) Timeframes for reviewing the grievance.
(3) A description of how the patient or the patient’s
designated representative will be informed of steps taken
to resolve the grievance.
The facility’s policies and procedures must describe all available
grievance procedures to the patient. The facility must inform the
patient and/or the patient’s designated representative (also called
“designee”) of its internal grievance process. Refer to the requirement
at V465 under the Condition for Patients’ rights.
Each facility must implement a process to ensure that there will be no
reprisal or denial of services for any patient who files an internal
grievance and the grievance procedure will be clearly explained to
patients. The existence of grievances should not be viewed negatively,
as this would be an indication that patients understand the internal
grievance process and believe that filing a grievance will not result in
reprisal or denial of services. Lack of grievances does not indicate a
lack of an internal grievance process.
The facility’s grievance process should assure those grievances
involving situations or practices that place patients or staff members
in immediate danger (e.g. the patient's grievance brings attention to
hazardous environmental conditions) are resolved immediately.
The facility’s process must include clearly defined timeframes for a
grievance to be acknowledged, investigated, and addressed.
Timeframes should be sufficient to conduct an investigation yet
ensure that the grievance is addressed in a timely manner.
The patient/designee should be informed of the status of the
investigation periodically, and when resolution is attained or
considered attained by the facility. Each grievance should demonstrate
a completed cycle of reviewing the grievance and reporting back to
Final Version 1.1 Page 293 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
the patient.
V766
(f) Standard: Involuntary discharge and transfer policies
and procedures. The governing body must ensure that all
staff follow the facility’s patient discharge and transfer
policies and procedures.
The medical director ensures that no patient is
discharged or transferred from the facility unless –
(1) The patient or payer no longer reimburses the facility
for the ordered services;
(2) The facility ceases to operate;
(3) The transfer is necessary for the patient’s welfare
because the facility can no longer meet the patient’s
documented medical needs; or
Involuntary discharge or transfer should be rare and preceded by
demonstrated effort on the part of the interdisciplinary team to address
the problem in a mutually beneficial way. The facility must have and
follow written policies and procedures for involuntary discharge and
transfer.
If any patients have been involuntarily discharged or transferred since
the latter of either the effective date of these rules (October 14, 2008)
or the facility’s last survey, surveyors will review those patients’
medical records to ensure compliance with these regulations and
facility policy. See also requirements under Conditions for Patients’
rights at V468 and V469.
The medical director must be informed of and approve any
involuntary discharge or transfer of a patient. A facility may
involuntarily discharge or transfer a patient only for those reasons
listed here and at V767. The medical director must ensure that the
reasons for any involuntary discharge or transfer are consistent with
this requirement.
If a facility involuntarily discharges or transfers a patient for
nonpayment of fees, there must be evidence in the patient’s medical
record that the facility staff (e.g., billing personnel, financial
counselor, social worker) made good faith efforts to help the patient
resolve nonpayment issues.
In the event a facility ceases to operate, the governing body must
notify CMS, the State survey agency, and the applicable ESRD
Network. The facility’s interdisciplinary team must assist patients to
obtain dialysis in other facilities.
If the discharge or transfer is necessary for the patient’s welfare, the
Final Version 1.1 Page 294 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
patient’s medical record must include documentation of the medical
need and reasons why the facility can no longer meet that need.
V767
(4) The facility has reassessed the patient and determined
that the patient’s behavior is disruptive and abusive to
the extent that the delivery of care to the patient or the
ability of the facility to operate effectively is seriously
impaired, in which case the medical director ensures that
the patient’s interdisciplinary team—
(i) Documents the reassessments, ongoing problems(s),
and efforts made to resolve the problem(s), and enters
this documentation into the patient’s medical record;
(ii) Provides the patient and the local ESRD Network
with a 30-day notice of the planned discharge;
(iii) Obtains a written physician’s order that must be
signed by both the medical director and the patient’s
attending physician concurring with the patient’s
discharge or transfer from the facility; (iv) Contacts
another facility, attempts to place the patient there, and
documents that effort; and
(v) Notifies the State survey agency of the involuntary
transfer or discharge.
(5) In the case of immediate severe threats to the health
and safety of others, the facility may utilize an
abbreviated involuntary discharge procedure.
Patients should not be discharged for failure to comply with facility
policy unless the violation adversely affects clinic operations (e.g.,
violating facility rules for eating during dialysis should not warrant
involuntary discharge). Patients should not be discharged for
shortened or missed treatments unless this behavior has a significant
adverse affect on other patients’ treatment schedules. A facility may
evaluate the patient (who shortens or misses treatments) for any
psychosocial factors that may contribute to shortening or missing
treatments; for home dialysis; or, as a last resort to avoid
inconveniencing other patients, may alter the patient’s treatment
schedule or shorten treatment times for patients who persistently
arrive late.. Patients should not be discharged for failure to reach
facility-set goals for clinical outcomes. Facilities are not penalized if a
patient or patients do not reach the expected targets if the plan of care
developed by the IDT is individualized, addresses barriers to meeting
the targets, and has been implemented and revised as indicated.
In the event facility staff members believe the patient may have to be
involuntarily discharged, the interdisciplinary team must reassess the
patient with an intent to identify any potential action or plan that could
prevent the need to discharge or transfer the patient involuntarily. The
reassessment must focus on identifying the root causes of the
disruptive or abusive behavior and result in a plan of care aimed at
addressing those causes and resolving unacceptable behavior.
Evidence must be on file to substantiate that the patient received
notification at least 30 days prior to involuntary discharge or transfer
and that the ESRD Network was also notified at that time. While the
early notice to the State agency is not required, facilities may choose
to notify the patient, Network and the State agency at the same time.
A 30-day notice is not required in the case of imminent severe threat
Final Version 1.1 Page 295 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
to safety of other patients or staff. The State agency and Network
would need to be notified immediately if the use of the abbreviated
involuntary discharge procedure is necessary.
There must be a written order in the patient’s medical record, signed
by the attending physician and the medical director for the facility to
involuntarily discharge or transfer a patient. If the reason for
discharge is the physician’s determination to no longer care for a
particular patient and there is no other physician on staff available or
willing to accept the patient, generally the state practice boards for
physicians require the patient be given some notice to avoid a charge
of patient abandonment. The facility would need to follow this
regulation as to reassessment, 30 day notice, attempts for placement,
etc. during the physician’s period of notice to the patient.
Because the goal of contacting another dialysis facility is for
continuity of care, the HIPAA privacy rule does not require patient
consent to contact that other dialysis facility. However, it does limit
sharing of protected health information to medical records requested
by the other provider and prohibits sharing information obtained
through hearsay. Good faith efforts should be made to find the closest
facility to the patient’s residence that will accept the patient in
transfer. The applicable patient’s medical record must include
evidence of those placement efforts.
An "immediate severe threat" is considered to be a threat of physical
harm. For example, if a patient has a gun or a knife or is making
credible threats of physical harm, this would be considered an
"immediate severe threat." An angry verbal outburst or verbal abuse is
not considered to be an immediate severe threat. In instances of an
immediate severe threat, facility staff may utilize "abbreviated"
involuntary discharge or transfer procedures. These abbreviated
procedures may include taking immediate protective actions, such as
Final Version 1.1 Page 296 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
calling "911" and asking for police assistance. In this scenario, there
may not be time or opportunity for reassessment, intervention, or
contact with another facility for possible transfer. After the emergency
is addressed and staff and other patients are safe, staff must notify the
patient's physician and the medical director of these events, notify the
State agency and ESRD Network of the involuntary discharge, and
document this contact and the exact nature of the “immediate severe
threat” in the applicable patient’s medical record.
At the time of publication of these rules, each facility had received a
copy of an interactive program developed by the ESRD Networks on
Decreasing Dialysis Patient Provider Conflict (DPC) that addresses
proactive techniques to resolve such issues before progression to
involuntary discharge.
V768
(g) Standard: Emergency coverage.
(1) The governing body is responsible for ensuring that
the dialysis facility provides patients and staff with
written instructions for obtaining emergency medical
care.
The facility must provide information to all patients, including home
patients, regarding who to call and how to obtain emergency medical
care when away from the dialysis facility. The patients should be able
to contact a call service for a responsible staff member, physician, or
on call staff for dialysis-related emergencies 24 hours a day, 7 days a
week. In cases of need for emergent medical care (e.g., severe chest
pain, loss of consciousness, or uncontrollable bleeding), patients
should be instructed to call “911” for immediate medical care.
V769
(2) The dialysis facility must have available at the
nursing/monitoring station, a roster with the names of
physicians to be called for emergencies, when they can
be called, and how they can be reached.
There must be a listing available of physicians' names and contact
numbers and a call schedule if physicians rotate this responsibility.
Every facility must have a written plan for physician coverage during
illness, vacations, and holidays.
V770
(3) The dialysis facility must have an agreement with a
hospital that can provide inpatient care, routine and
emergency dialysis and other hospital services, and
emergency medical care which is available 24 hours a
day, 7 days a week. The agreement must:
(i) Ensure that hospital services are available promptly to
the dialysis facility’s patients when needed.
There must be an agreement with a hospital to provide inpatient
dialysis care. This could be in the form of a letter from the hospital
acknowledging their agreement to this requirement or a more formal
document signed by both the dialysis facility and hospital
representatives. This hospital does not have to be certified as an
ESRD provider, but must be able to provide hospital dialysis
treatment as well as emergency and inpatient treatment and other
Final Version 1.1 Page 297 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
(ii) Include reasonable assurances that patients from the
dialysis facility are accepted and treated in emergencies.
hospital services.
It is not required or expected that every patient admission would be to
the hospital with whom the agreement is signed.
V771
(8) Standard: Furnishing data and information for ESRD
program administration. Effective February 1, 2009,
the dialysis facility must furnish data and
information to CMS and at intervals as specified by
the Secretary. This information is used in a national
ESRD information system and in compilations
relevant to program administration, including claims
processing and reimbursement, quality improvement,
and performance assessment.
The data and information must—
(1) Be submitted at the intervals specified by the
Secretary;
(2) Be submitted electronically in the format specified by
the Secretary;
(3) Include, but not be limited to—
(i) Cost reports;
(ii) ESRD administrative forms;
(iii) Patient survival information; and
(iv) Existing ESRD clinical performance measures, and
any future clinical performance standards developed in
accordance with a voluntary consensus standards process
identified by the Secretary.
Beginning February 1, 2009, all dialysis facilities must electronically
submit data to allow patient enrollment in and disenrollment from the
ESRD benefit program, assessment of clinical outcomes, and claims
processing.
The facility must electronically submit required information at the
specified intervals, which vary depending on the data element. Data
required to be submitted electronically includes cost report data;
administrative data (such as changes in key staff and changes in
patient treatment modality); forms such as the CMS 2728 and 2746;
and clinical performance data on all patients regardless of payment
source, at the frequency determined by CMS. The clinical
performance measures required to be submitted are determined by the
Secretary of HHS, and any changes to these will be developed by a
standardized process.
V772
(i) Standard: Relationship with the ESRD network. The
governing body receives and acts upon recommendations
from the ESRD network. The dialysis facility must
cooperate with the ESRD network designated for its
geographic area, in fulfilling the terms of the Network’s
current statement of work. Each facility must participate
The ESRD facility must respond promptly within any specified
deadlines to requests for information, data, or corrective action plans
from its ESRD Network. The facility must participate in Network
projects and activities aimed at addressing identified needs and
improving quality of care in the individual facility or the Network-
wide area. Facilities may easily obtain copies of their Network’s goals
Final Version 1.1 Page 298 of 299

TAG
NUMBER
REGULATION
INTERPRETIVE GUIDANCE
in ESRD network activities and pursue network goals.
and objectives as each Network is required to post their annual report
on their website. These reports include the individual Network’s goals
and activities.
At the time of publication of these regulations, the goals of ESRD
Networks were to:
• Improve the quality and safety of dialysis-related services
provided for individuals with ESRD.
• Improve independence, quality of life, and rehabilitation (to the
extent possible) of individuals with ESRD through encouragement
of transplantation, use of self-care modalities (e.g., home
peritoneal dialysis, home hemodialysis, and in-center self care), as
medically appropriate, through the end of life.
• Encourage and support collaborative activities to ensure
achievement of these goals through the most efficient and
effective means possible, with recognition of the differences
among providers (e.g., independent, hospital-based, member of a
group, affiliate of an organization) and the associated
possibilities/capabilities.
• Improve the collection, reliability, timeliness, and use of data to:
measure processes of care and outcomes; maintain the patient
registry; and support the ESRD Network program.
V773
(j) Standard: Disclosure of ownership. In accordance
with § 420.200 through § 420.206 of this chapter, the
governing body must report ownership interests of 5
percent or more to its State survey agency.
The governing body of the ESRD facility must report to the State
survey agency a full and complete listing of any individuals with
ownership of 5% or more of the facility.
Any change in ownership must be reported in a timely manner to the
State survey agency.
Final Version 1.1 Page 299 of 299
