
www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b429
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SBI MUTUAL
FUND AND HDFC MUTUAL FUND
Bhakhar Deep
*1
, Bhagat Utsav
*2
Parul University, Parul Institute of Management & Research
ABSTRACT
This study looks at the evolution of two of India's leading mutual fund companies, SBI Mutual Fund and
HDFC Mutual Fund. The analysis uses secondary data to estimate risk and return indicators using various
metrics: standard deviation, alpha, beta, Sharpe ratio, and Treynor ratio. The objective of the study is to
identify which fund house offers better risk-adjusted returns based on historical data. The main objective of
this study is to identify which fund house offers better risk-adjusted returns based on historical data and
selected measurements By analyzing these metrics, the study aims to provide insight into the risk-return
characteristics of each fund house and their investment strategies..
INTRODUCTION
Mutual Fund of the State Bank of India (SBI):
SBI Mutual Fund is one of the largest and most well-known mutual fund companies in India. It is managed
by SBI Funds Management Private Limited, a joint venture between the State Bank of India, the biggest bank
in India, and Amundi, a well-known global asset management company with its headquarters situated in
France. SBI Mutual Fund offers a wide range of investment products, including debt funds, hybrid funds,
equity funds, and other expert funds, to meet the diverse financial needs of its clients. The fund company is
well-versed in research techniques, has a strong nationwide distribution network, and prioritizes its clients.
• HDFC Mutual Fund
Managed by HDFC Asset Management Limited, HDFC Mutual Fund is another prominent mutual fund
provider in India. It is a branch of the Housing Development Finance Corporation (HDFC), one of the
leading financial institutions in India. HDFC Mutual Fund offers a wide range of mutual funds, including
debt, hybrid, equity, and solution-oriented funds. This fund provider has a stellar reputation for its innovative
fund offerings, attentive customer care, and methodical approach to investing. HDFC Mutual Fund has a
significant market share and is renowned for its fund expertis

www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b430
LITERATURE REVIEW
1. 1. In her paper "Comparative Analysis on Performance of SBI and HDFC Equity, Balanced, and Gilt
Mutual Funds," Ms. Dhanalakshmi K. (2013) compared and examined the performance of SBI and HDFC
mutual funds, with an emphasis on equities, gilt, and balanced mutual funds.
2. Money in the connection between Treynor, Jensen, and Sharpe. Just three years of operating
finance—from January 2010 to December 2012—are covered by the study. He concluded that the funds'
returns changed according to the state of the market; that is, in 2010 and 2011, the return was impacted by
market volatility, but in 2012, scheme performance improved. Research has demonstrated that, in the long
run, investing in HDFC (Equity, Balanced, Gilt) mutual funds performs better than SBI funds.
3. In a 2013 study titled "A. A Comparative Study of Mutual Fund Performance SBI Mutual Funds V/S
Others," Dr. Rajesh Manikraoji Naik and MR Senapathy compared the 2011–2012 performance of the
SBI Magnum Equity mutual fund and the top 100 mutual funds from HDFC using standard deviation, beta,
and Sharpe ratio. Ultimately, the authors concluded that there is little difference between SBI and HDFC
mutual funds and that both are excellent mutual funds.
4. In a 2014 study titled "A Comparative Study of Diversified Mutual Fund Schemes of Selected Public
and Private Equity Funds in India," Dr. Vinay Kandpal and Prof. P. C. Kavi Dayal included HDFC
Premier Multi-Cap, HDFC Growth, and HDFC Core and Satellite funds. Examine the results for the private
sector mutual fund category during five years (2008–2013). chosen mutual funds for the public sector based
on the Jensen, Sharpe, standard deviation, and beta
5. In a study titled "Analysis and Comparative Study of SBI and HDFC Mutual Fund," Babasaheb Patil
(2012) evaluated the risk and return of the growth of the SBI Magnum Equity Fund and the HDFC Growth of
the share fund over one year (2.4.2007 - 31.3. 2008) using a variety of statistical techniques, including
variance, standard deviation, covariance, and correlation. He concluded that the SBI Magnum Equity fund
offered greater risk and returns than HDFC Equity, although both funds performed poorly when the author
took investor expectations into account.

www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b431
6. In a study titled "Comparison of Endowment Funds especially for SBI Mutual Funds," Mrinal
Manish (2010) examined the risk and returns of a few carefully chosen private sector mutual funds by
contrasting their five-year performance with that of SBI Magnum Equity and SBI Magnum Against. Upon
analysis of all statistical characteristics, Magnum Contra was confirmed to be the best foundation within its
class.
7. Investment policy, portfolio turnover rate, mutual fund performance, and stock market effects were
all examined by Irwin, Brown, and FE (1965). Research revealed that mutual funds significantly
influenced the movement of stock market prices. The study concludes that there was no consistent
correlation between portfolio turnover and fund performance and that on average, funds did not outperform
the composite markets.
8. Treynor (1965) employed the 'characteristic line' to establish a relationship between the predicted
rate of return of a fund and the rate of return of a representative market average. He developed a fund
performance metric that considered investment risk. The most prominent study is by sharp ratio.
Research Methodology
Research design: quantitative research and type is a comparative study
Sources of data: Financial news websites, company websites, research reports
Data collection: both funds 10 years of NAV data collected through websites. For yearly NAV I have
taken the difference between
31 December to 31 December each year.
Data collection instruments: Historical Performance Data: Get historical performance data directly from
official sources such as mutual fund company websites, financial news websites, or financial databases.
Focus on metrics or annual returns over some time.
METHOD OF CALCULATION
(1)
STANDARD DEVIATION = it is calculated after calculating the return of mutual funds.
RETURNS = NAV CURRENT CLOSE – NAV PREVIOUS CLOSE
(2)
return of portfolio; N = number of years
(3)
CORRELATION COEFFICIENT
It shows the linear dependency between fund returns and returns of the benchmark index. The
correlation coefficient is calculated here using MS Excel.
If 0.5 < r < 1, then there is a high positive correlation between the fund returns and the benchmark
returns.
If 0<r<0.5, then there is a low positive correlation between the fund returns and the benchmark
returns.

www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b432
(5)
BETA
Beta, also known as the "beta coefficient," is a measure of the value, or systematic risk, of a security
or fund compared to the market as a whole.
Beta here is calculated as (p,b). S.D.p/S.Db
r(p,b) = correlation coefficient between the returns of the concerned portfolio and the returns of the
benchmark index. (BSE 100)
S.D.p =Standard Deviation of the concerned portfolio , S.D.b = Standard Deviation of the
benchmark index (BSE 100)
ALPHA
Alpha measures the difference between a fund's actual returns and its expected performance, given
its level of risk. A fund's alpha is often considered to represent the value that a portfolio manager adds to or
subtracts from a fund's return above and beyond a relevant index's risk/reward profile.
Alpha (α) is calculated here as =X - β(Y) where,
X = average return to NAV returns; Y = average return to market
index,β=Be
SHARPE RATIO
The Sharpe ratio formula is:
Where,
Ra= Concerned portfolio return , Rf = Risk Free Rate , σ = Standard Deviation
Sharpe ratio can be used to rank the desirability of a fund or portfolio.
TREYNOR RATIO
The Treynor ratio is a measurement of the returns earned more than that which could have been
earned on an investment that has no diversifiable risk, per each unit of market risk assumed.
The higher the Treynor ratio, the better the performance of the portfolio under analysis.
Formula: T = Ri-Rf/Bi Where,
T= Treynor ratio , Ri= Portfolio I’s return , Rf = Risk Free Rate , β= Portfolio I’s Beta
Problem statement
The need to thoroughly examine and compare the investment strategies, performance indicators, and
operational frameworks of SBI Mutual Fund and HDFC Mutual Fund is the central challenge of this
comparative study. The study specifically aims to answer the following important question.
www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b433
What are the differences in the investment philosophies, asset allocation plans, and portfolio development
techniques of SBI Mutual Fund and HDFC Mutual Fund?
What past performance patterns have SBI Mutual Fund and HDFC Mutual Fund shown throughout many
mutual fund schemes and market cycles?
How are investment risks, including market, credit, and liquidity concerns, managed by SBI and HDFC
mutual funds within their separate portfolios?
objective
2.
Analysis of risk and return through using statistical methods with special reference to small-cap and
mid- and large-cap funds.
3.
To compare schemes' return and risk with benchmark i.e. S&P BSE 250
Hypothesis
The null hypothesis (H₀) states that the overall returns of Mutual Funds A and B do not differ significantly
from one another.
The alternative hypothesis, H₁, states that mutual funds A and B have significantly different total returns.
Data collection & analysis
BSE 250 TRI
year
S&P BSE TRI
2014
8324
2015
7786
2016
8082.4
2017
10333.25
2018
10888.35
2020
13529.1
2021
17511.3
2022
18609.35
This is the market return index BSE 250 TRI for comparison of mutual fund return with the market.
Standard deviation is calculated using this data for the beta calculation of selected mutual funds.
www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b434
SBI AND HDFC SMALL-CAP FUND
TABLE: 1 CALCULATION
S.D
Beta
Alpha
Sharp ratio
Treynor ratio
Correlation
coefficient
SBI small
cap fund
13.26
0.000092
0.1167
1.5180
21880.43
0.00961686
HDFC
small cap
fund
11.69
0.000072
0.0920
1.2275
19930.55
0.008542636
S&P BSE
250 (market
return )
1368.43
SBI SMALL CAP FUND
HDFC SMALL CAP FUND
Year( 1 Jan to 30
dec)
NAV
year
NAV
2014
29.37
2014
26.13
2015
35.72
2015
28.02
2016
36.33
2016
29.56
2017
66.2
2017
48.63
2018
53.83
2018
45.07
2019
57.8
2019
41.30
2020
78.16
2020
50.43
2021
115.11
2021
83.13
2022
126.24
2022
88.03
www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b435
mid &large cap fund of SBI And HDFC
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
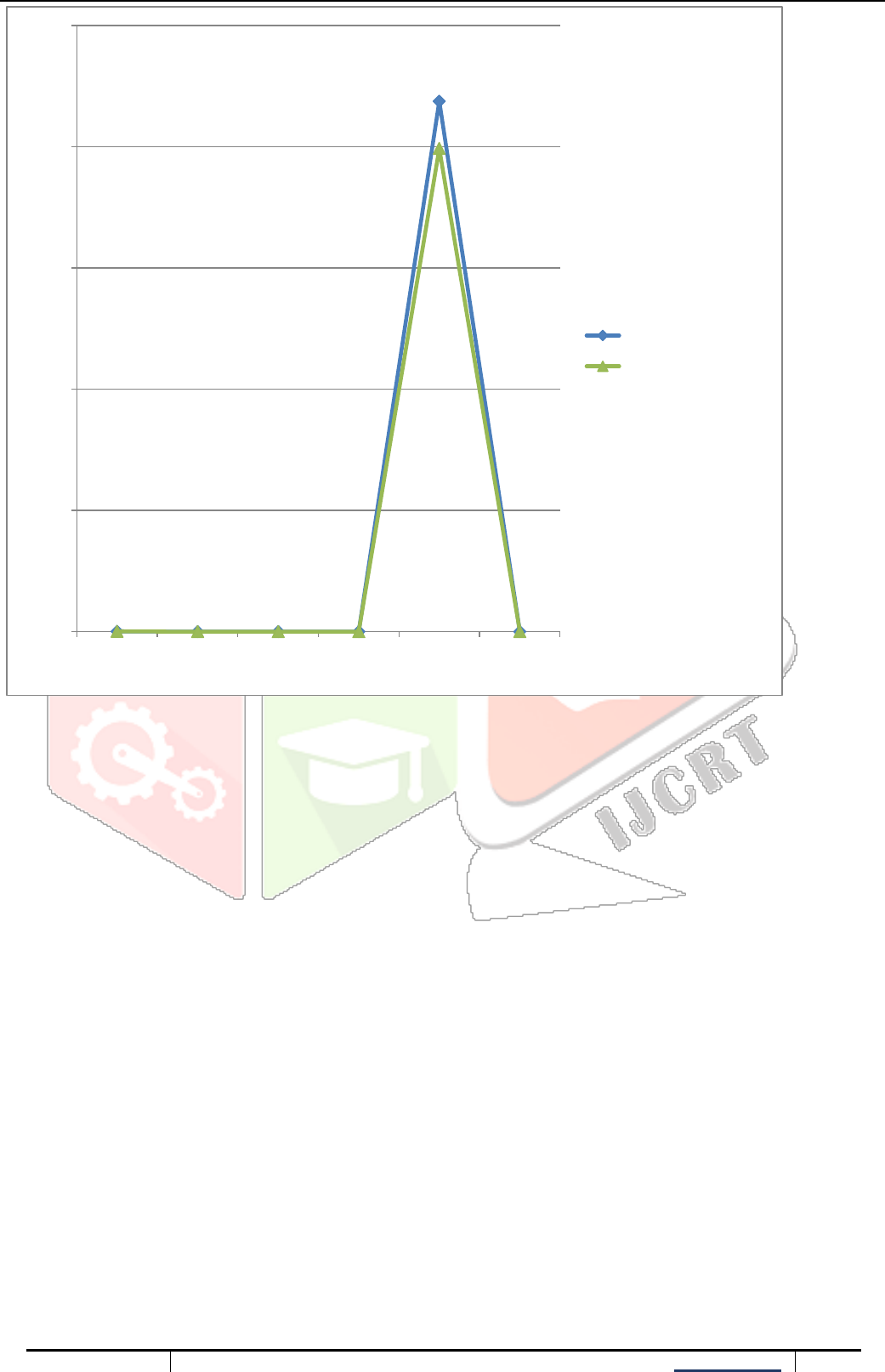
S.D Beta Alpha Sharp ratio Treynor
ratio
Co-relation
coefficient
SBI small cap fund
HDFC small cap fund
www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b436
MID &LARGE CAP FUND OF SBI
MID &LARGE CAP FUND OF HDFC
year
NAV
year
NAV
2013
96.78
2013
69.64
2014
142.06
2014
88.73
2015
161.18
2015
84.56
2016
160.30
2016
87.39
2017
229.36
2017
114.26
2018
217.36
2018
110.02
2019
234.76
2019
117.69
2020
271.70
2020
131.07
2021
382.73
2021
187.01
2022
418.04
2022
206.14
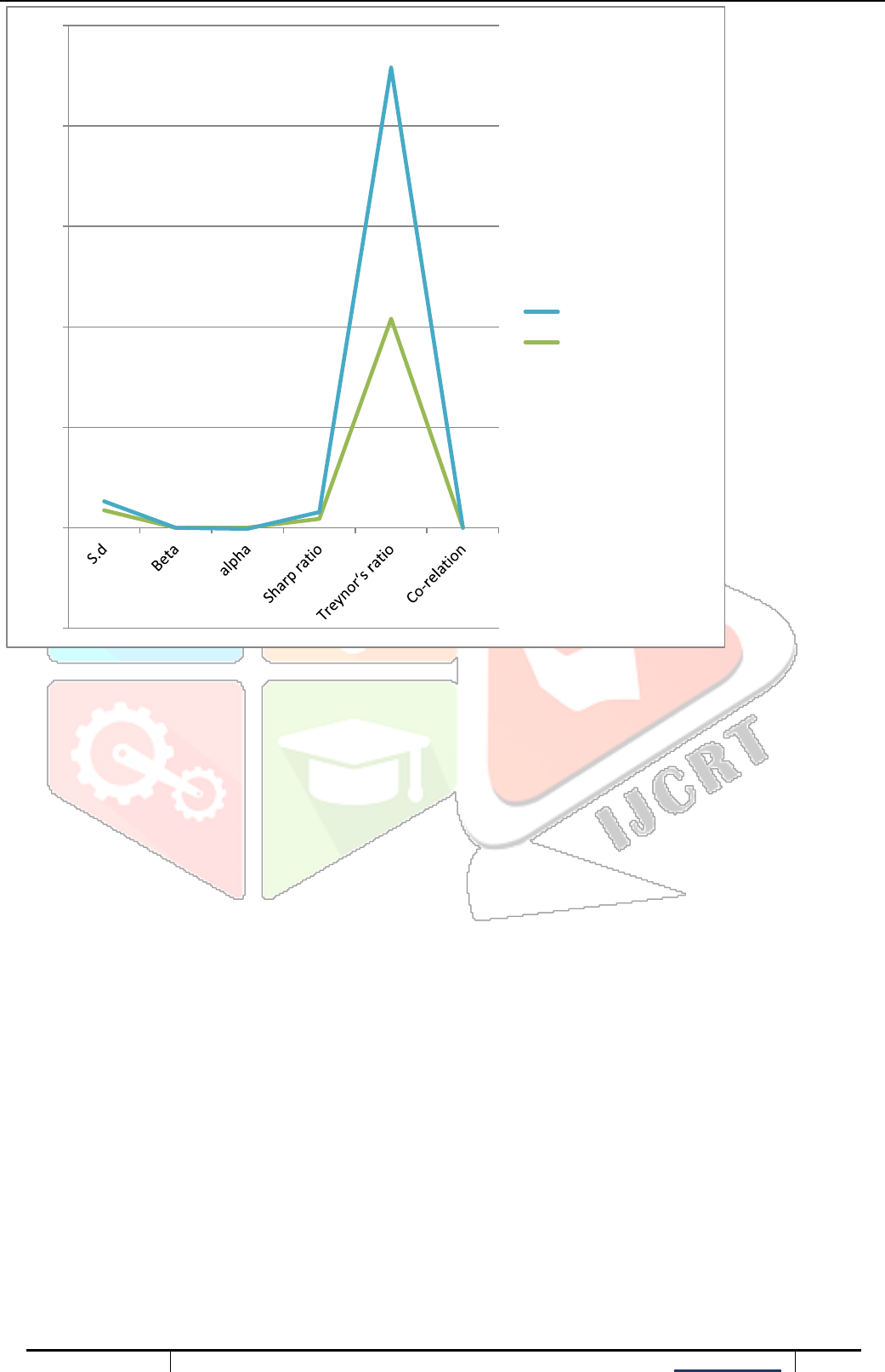
Table 2 CALCULATION
Funds
S.d
Beta
Alpha
Sharp ratio
Treynor ratio
Co-relation
Co-efficient
SBI mid
&large cap
35.125
0.000658851
0.570555556
17.84989324
416.0806442
0.02566810
1
HDFC mid
&large cap
17.61
0.000165605
-2.443333333
13.40091993
500.4360865
0.01286876
2
www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b437
FINDINGS&RESULT
FOR SMALL-CAP FUND
1. Since HDFC's S.D. is lower than SBI's, the HDFC small-cap fund's return is more consistent than that of
the SBI small-cap fund.
2. Both funds have very low market movement sensitivity because their betas are close to zero. The overall
market fluctuation has little effect on the performance of any fund.
3. Based on beta and the market as a whole, alpha calculates an investment's excess return about its
projected return. The positive alpha values in both funds show that they have both fared better than
predicted.
4. In this comparison, the HDFC Mid-Cap Fund has a Sharpe Ratio of 1.2275, whereas the SBI Mid-Cap
Fund's is 1.5180.
In comparison to HDFC Mid-Cap Fund, SBI Mid-Cap Fund has a higher Sharpe ratio, which suggests that
it has delivered superior risk-adjusted returns. SBI Mid- and Large-cap funds are worth considering by
investors because they have demonstrated superior risk-weighted returns in this situation.
The risk-adjusted return on systematic risk is measured by the Treynor ratio. When comparing the Treynor
ratios of the two funds, the HDFC small cap fund has a greater risk-adjusted return (1993.55) than the SBI
(2188.43).
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
HDFC mid &large cap
SBI mid &large cap

www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-
2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b438
In summary, the HDFC Small Cap Fund exhibits superior stability in returns and a higher risk-adjusted
return in comparison to systematic risk, as demonstrated by its larger Treynor ratio and smaller standard
deviation. However, the SBI Small Cap Fund offers a higher risk-adjusted return based on the Sharpe ratio,
indicating a better balance between risk and return, despite likewise having consistent returns and little
market sensitivity. HDFC Small Cap Fund may be the choice of investors wanting stability, while SBI
Small Cap Fund may appeal to those seeking a balance between risk and return.

www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b439
FOR MID&LARGE CAP FUND
1. Since HDFC's S.D. is lower than SBI's, the HDFC small-cap fund's return is more consistent than SBI's
small-cap fund's.
2. The beta coefficient calculates how sensitive a stock's price movement is to the market's general
movement. A beta of less than one suggests that the stock is less volatile than the market, whereas a beta of
more than one denotes higher volatility. With a beta of 0.000658851, the SBI MID & LARGE CAP is less
volatile in this instance than the HDFC MID & LARGE CAP fund, which has a beta of 0.000165605. Given
that both funds' betas are much below 1, they are both comparatively steady and have less volatility when
compared to the overall market.
3. After considering risk, alpha evaluates a fund manager's capacity to beat the benchmark index. In this
instance, HDFC Mid-Cap's negative alpha (-2.443333333) means that it underperformed its benchmark,
while SBI Mid-Cap's positive alpha (0.57055556) indicates that it has exceeded it. Consequently, in terms of
alpha, the SBI Mid-Cap Fund performed better than the HDFC Mid-Cap Fund.
4. The risk-adjusted return on an investment is measured by the Sharpe ratio. A greater Sharpe ratio
indicates a greater risk-adjusted return.
In this comparison, the Sharpe ratio of the SBI Mid-Cap Fund is 17.84989324 while the Sharpe ratio
of the HDFC Mid-Cap Fund is 13.40091993.
In comparison to HDFC Mid-Cap Fund, SBI Mid-Cap Fund has a higher Sharpe ratio, indicating
that it has delivered superior risk-adjusted returns.
Based on systematic risk (beta), the Treynor ratio calculates the risk-adjusted return on an investment. For
the amount of risk taken, a greater Treynor ratio indicates a better risk-adjusted return.
5. In this comparison, the HDFC Mid-Cap Fund has a Treynor ratio of 500.436, whilst the SBI Mid-Cap
Fund has a Treynor ratio of 416.080.
6. The Treynor ratio shows that the HDFC Mid-Cap Fund has outperformed the SBI Mid-Cap Fund in terms
of risk-adjusted return, suggesting that it has provided superior returns when taking systemic risk into
account.

www.ijcrt.org © 2024 IJCRT | Volume 12, Issue 4 April 2024 | ISSN: 2320-2882
IJCRT2404161
International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT)
www.ijcrt.org
b440
LIMITATION OF THE STUDY
1. This study has only looked at small, medium, and large mutual fund schemes. If additional scheme
types were included, including debt funds and sector-specific funds, a comparable analysis might be
performed.
2. A few statistical techniques have been used to analyze the performance of mutual funds. It could be
raised to get an exact outcome.
The performance and returns of the mutual fund schemes have only been contrasted with those of the S&P
BSE 100. The rate on Indian government 10-year bonds serves as a representative of risk-free returns, but
the same can be done with a range of alternative benchmarks
CONCLUSION
SBI mid-cap and large-cap funds have outperformed the other in terms of alpha and Sharpe ratio, indicating
superior risk-adjusted returns, even though both funds have low volatility and stable returns. However,
despite a greater Treynor ratio and a smaller standard deviation, HDFC Mid-Cap Fund exceeded Alpha and
Sharpe. Investors considering SBI's mid- and large-cap stocks may find stability and somewhat greater risk-
adjusted returns. Before making a decision, investors must take into account their own risk tolerance and
investing objectives.
REFERENCES
"A Comparative Analysis On Performance Of SBI And HDFC Equity, Balanced And Gilt Mutual Fund,"
Ms. Dhanalakshmi K - Vidyaniketan Journal of Management and Research, July–December 2013, Volume
1, Issue 2.
[2]. "A Project Report On The Analysis and Comparative Study Of SBI and HDFC Mutual Fund," written
by Babasaheb Patil
[3]. "Comparative Analysis of Mutual Funds with Special Reference to SBI Mutual Funds," by Mrinal
Manish
[4]. "A Comparative Study of Selected Public & Private Sector Equity Diversified Mutual Fund Schemes in
India," by Dr. Vinay Kandpal and Prof. P. C. Kavidayal - IOSR Journal of Business and Management,
February 2014, Volume 16, Issue 1, Ver. V, pp. 92–101
[5]. "A Comparative Study On The Performance Of Mutual Funds Sbi Mutual Funds V/S Others," by Dr.
Rajesh Manikraoji Naik and M R Senapathy -Global
