
Washington Apple Health (Medicaid)
Physician-Related
Services/Health Care
Professional Services
Billing Guide
September 1, 2020
Every effort has been made to ensure this guide’s accuracy. If an actual or apparent conflict between this
document and an HCA rule arises, HCA rules apply.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
2
About this guide
*
This publication takes effect September 1, 2020, and supersedes earlier guides to this program.
The Health Care Authority (HCA) is committed to providing equal access to our services. If you
need an accommodation or require documents in another format, please call 1-800-562-3022.
People who have hearing or speech disabilities, please call 711 for relay services.
Washington Apple Health means the public health insurance programs for eligible
Washington residents. Washington Apple Health is the name used in Washington
State for Medicaid, the children's health insurance program (CHIP), and state-
only funded health care programs. Washington Apple Health is administered by
the Washington State Health Care Authority.
What has changed?
Subject
Change
Reason for Change
Entire document
Housekeeping changes
Changed all reference to “BAHA”
or “bone-anchored hearing aid” to
“bone conduction hearing device”
To improve usability
To align with HCA’s
Hearing Hardware
Billing Guide
Medical policy updates
For policy updates effective
9/1/2020, added that HCA does
not consider bronchial
thermoplasty for asthma to be
medically necessary
For policy updates effective
9/1/2020, added that HCA does
not consider autologous
blood/platelet-rich plasma
injections to be medically
necessary
HTCC decision. See
findings and decision.
HTCC decision. See
findings and decision.
Varicose vein treatment
Revised language concerning
medical necessity of varicose vein
treatment and added reference to
HTCC decision
No policy was changed.
Revised to improve
clarity regarding medical
necessity
*
This publication is a billing instruction.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
3
Subject
Change
Reason for Change
Functional neuroimaging for
primary degenerative
dementia or mild cognitive
impairment
Revised language concerning
medical necessity of catheter
ablation and added reference to
HTCC decision
No policy was changed.
Revised to improve
clarity regarding medical
necessity
Bronchial thermoplasty for
asthma
Added that HCA does not
consider bronchial thermoplasty
for asthma to be medically
necessary
HTCC decision. See
findings and decision.
Catheter ablation for
supraventricular
tachyarrhythmias
Revised language concerning
medical necessity of catheter
ablation and added reference to
the HTCC decision
No policy was changed.
Revised to improve
clarity regarding medical
necessity
Withdrawal management
services
Added information on medical
necessity and instructions for
billing HCA for withdrawal
management services
To provide clarifying
information
Autologous blood/platelet-
rich plasma injections
Added that HCA does not
consider autologous
blood/platelet-rich plasma
injections to be medically
necessary
HTCC decision. See
findings and decision.
Organ procedure fees and
donor searches
Added bullet stating “include
donor operative notes with claim”
Providers must now
provide this information
with the claim when
billing for services

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
4
How can I get HCA provider documents?
To access provider alerts, go to HCA’s Provider alerts webpage.
To access provider documents, go to HCA’s Provider billing guides and fee schedules webpage.
Where can I download HCA forms?
To download an HCA form, see HCA’s Forms & Publications webpage. Type only the form
number into the Search box (Example: 13-835).
Copyright disclosure
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) copyright 2019 American Medical Association (AMA).
All rights reserved. CPT is a registered trademark of the AMA.
Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not
assigned by the AMA, are not part of CPT, and the AMA is not recommending their use. The
AMA does not directly or indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The AMA
assumes no liability for data contained or not contained herein.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
5
Table of Contents
Definitions .....................................................................................................................................19
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................22
Acquisition cost .......................................................................................................................22
Add-on codes ...........................................................................................................................22
By report ..................................................................................................................................22
Codes for unlisted procedures ..................................................................................................23
Conversion factors ...................................................................................................................23
Diagnosis codes .......................................................................................................................23
Discontinued codes ..................................................................................................................23
National correct coding initiative.............................................................................................24
Procedure codes .......................................................................................................................24
Provider Eligibility.......................................................................................................................25
Who may provide and bill for physician-related services? ......................................................25
Can naturopathic physicians provide and bill for physician-related services? ........................26
Can substitute physicians (locum tenens) provide and bill for physician-related
services? .............................................................................................................................27
Resident Physicians ...........................................................................................................28
Which health care professionals does HCA not enroll? ..........................................................28
Does HCA pay for out-of-state hospital admissions? ..............................................................29
Client Eligibility ...........................................................................................................................30
How do I verify a client’s eligibility? ......................................................................................30
Are clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization (MCO)
eligible? ..............................................................................................................................31
Managed care enrollment ...................................................................................................32
Apple Health – Changes for January 1, 2020 ..........................................................................33
Clients who are not enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care plan ...........................33
Integrated managed care (IMC) .........................................................................................34
Integrated managed care regions .......................................................................................34
Integrated Apple Health Foster Care (AHFC) ...................................................................35
Fee-for-service Apple Health Foster Care .........................................................................35
What if a client has third-party liability (TPL)? ......................................................................36
Coverage - General ......................................................................................................................37
What is covered? ......................................................................................................................37
Does HCA cover nonemergency services provided out-of-state? ...........................................39
What services are noncovered? ................................................................................................39
General information ...........................................................................................................39
Noncovered physician-related and health care professional services ................................40

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
6
Medical Policy Updates ...............................................................................................................43
Policy updates effective 9/1/2020 ............................................................................................43
Policy updates effective 7/1/2020 ............................................................................................43
Policy updates effective 1/1/2020 ............................................................................................43
Policy updates effective 10/1/2019 ..........................................................................................44
Billable Services Provided By Resident Physicians ..................................................................45
Billable services provided by resident physicians ...................................................................45
Billing requirements for teaching physicians ....................................................................45
General documentation guidelines .....................................................................................46
Billing codes ......................................................................................................................46
Medical students ................................................................................................................47
Evaluation and Management ......................................................................................................48
Evaluation and management documentation and billing .........................................................48
Advance directives/physician orders for life-sustaining treatment ..........................................49
Telephone services ...................................................................................................................50
Partnership Access Line ...........................................................................................................51
Office and other outpatient services ........................................................................................51
Office or other outpatient visit limits .................................................................................51
New patient visits ...............................................................................................................51
Established patient visits ....................................................................................................52
Nursing facility services ....................................................................................................52
Pre-operative visit before a client receives a dental service under anesthesia ...................52
Physical examination - clients of the DSHS’ Developmental Disabilities
Administration .............................................................................................................52
Office visit related to acamprosate, naltrexone, buprenorphine/naloxone ........................53
Aged, Blind, or Disabled (ABD) Evaluation Services ............................................................53
Behavior change intervention - tobacco/nicotine cessation .....................................................54
Services available...............................................................................................................54
Washington State Tobacco Quitline ..................................................................................54
Client eligibility .................................................................................................................55
Payment for a tobacco/nicotine cessation referral .............................................................55
Tobacco/nicotine cessation referral for an evaluation for a tobacco/nicotine
cessation prescription ...................................................................................................55
Tobacco/nicotine cessation for pregnant clients ................................................................56
Face-to-face visit requirements for pregnant women ........................................................56
Provider types for providing face-to-face tobacco/nicotine cessation counseling
for pregnant women .....................................................................................................56
Benefit limitations for providing face-to-face tobacco/nicotine cessation
counseling for pregnant women ...................................................................................56
Documentation requirements .............................................................................................57
Billing codes ......................................................................................................................57
Substance use disorder treatment .............................................................................................57
How to bill for combination therapy ..................................................................................58
How to bill for monotherapy ..............................................................................................58

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
7
Collaborative care model guidelines ........................................................................................59
Collaborative care ..............................................................................................................59
Psychiatric collaborative care model .................................................................................59
Core principles ...................................................................................................................60
Additional billing information ...........................................................................................67
Health and behavior codes .......................................................................................................67
Children's primary health care .................................................................................................68
Pediatric primary care rate increase ...................................................................................68
Consultations............................................................................................................................69
TB treatment services ........................................................................................................69
Critical care ..............................................................................................................................69
Billing for critical care .......................................................................................................70
Where is critical care performed? ......................................................................................70
What is covered? ................................................................................................................70
Domiciliary, rest home, or custodial care services ..................................................................71
Emergency department services ..............................................................................................71
Emergency physician-related services ...............................................................................71
Habilitative services .................................................................................................................72
Billing for habilitative services ..........................................................................................72
Home services ..........................................................................................................................73
Home evaluation and management ....................................................................................73
TB treatment services – performed by professional providers – in client’s home ............73
Hospital inpatient and observation care services .....................................................................73
Admission status ................................................................................................................73
Change in admission status ................................................................................................74
Payment..............................................................................................................................76
Other guidelines .................................................................................................................77
Inpatient neonatal and pediatric critical care ...........................................................................78
Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)/Pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) .......................78
Intensive (noncritical) low birth weight services ...............................................................79
Perinatal conditions ............................................................................................................80
Mental health .....................................................................................................................80
Services provided to an MCO client during BHO-approved admissions ..........................81
Newborn care ...........................................................................................................................81
Physician/Professional services ...............................................................................................82
Does HCA pay for newborn screening tests? ....................................................................82
Physicals for clients of DSHS’ Developmental Disabilities Administration...........................83
Physician care plan oversight...................................................................................................83
Physician supervision of a patient requiring complex and multidisciplinary care
modalities .....................................................................................................................84
Preventative medicine services ................................................................................................85
HIV/AIDS counseling/testing ............................................................................................85
Prolonged services ...................................................................................................................85
Prolonged services with direct patient contact...................................................................85
Physician standby services .................................................................................................86
Telemedicine ............................................................................................................................86

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
8
What is telemedicine? ........................................................................................................86
Who is eligible for telemedicine? ......................................................................................87
When does HCA cover telemedicine? ...............................................................................87
Telemedicine and COVID-19 ............................................................................................87
What are the documentation requirements? .......................................................................88
Originating site (location of client) ....................................................................................88
Distant site (location of consultant) ...................................................................................89
Store and Forward ..............................................................................................................90
Anesthesia .....................................................................................................................................92
General anesthesia ...................................................................................................................92
Regional anesthesia ..................................................................................................................94
Moderate sedation ....................................................................................................................94
Other ........................................................................................................................................95
Teaching anesthesiologists.......................................................................................................95
Physician fee schedule payment for services of teaching physicians ................................96
Anesthesia for dental................................................................................................................96
Anesthesia for maternity ..........................................................................................................97
Anesthesia for radiological procedures ....................................................................................98
Anesthesia payment calculation for services paid with base and time units ...........................98
Surgery ..........................................................................................................................................99
Tobacco/nicotine cessation ......................................................................................................99
Pain management services .......................................................................................................99
Pain management procedure codes ..................................................................................100
Interoperative or postoperative pain management ...........................................................101
Registered Nurse First Assistants ....................................................................................101
Billing/Payment .....................................................................................................................102
Bilateral procedures .........................................................................................................102
Bundled services ..............................................................................................................102
Global surgery payment ...................................................................................................104
Global surgery payment period ........................................................................................105
Multiple surgeries ............................................................................................................105
Other surgical policies .....................................................................................................106
Breast removal and breast reconstruction ........................................................................107
Panniculectomy ................................................................................................................108
Pre-/intra-/postoperative payment splits ..........................................................................108
Auditory system .....................................................................................................................109
Tympanostomies ..............................................................................................................109
Cochlear implant services (clients age 20 and younger) .................................................109
Bone conduction hearing devices for clients age 20 and younger ...................................109
Bariatric surgeries ..................................................................................................................110
Cardiovascular system ...........................................................................................................112
Carotid artery stenting......................................................................................................112
Implantable ventricular assist devices .............................................................................113
Varicose vein treatment ...................................................................................................114

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
9
Digestive system ....................................................................................................................115
Diagnostic upper endoscopy for GERD ..........................................................................115
Closure of enterostomy ....................................................................................................116
Fecal microbiota transplantation ......................................................................................116
Drug eluting or bare metal cardiac stents ..............................................................................117
Cardiovascular .......................................................................................................................117
Angioscopy ......................................................................................................................117
Apheresis..........................................................................................................................117
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy (ECMO) ...............................................118
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) .............................................................118
Percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation (PPVI) .......................................................119
Female genital system ............................................................................................................120
Hysterectomies .................................................................................................................120
Sterilizations ....................................................................................................................121
Integumentary system ............................................................................................................121
Clarification of coverage policy for miscellaneous procedures .......................................121
Male genital system ...............................................................................................................121
Circumcisions ..................................................................................................................121
Musculoskeletal system .........................................................................................................122
Artificial disc replacement ...............................................................................................122
Bone growth stimulators ..................................................................................................122
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 for lumbar fusion ............................................................122
Bone morphogenetic protein 7 for lumbar fusion ............................................................123
Cervical spinal fusion arthrodesis ....................................................................................123
Cervical surgery for radiculopathy and myelopathy ........................................................123
Endoscopy procedures .....................................................................................................124
Epiphyseal ........................................................................................................................124
Hip resurfacing.................................................................................................................124
Hip surgery for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome .............................................124
Knee arthroscopy for osteoarthritis ..................................................................................124
Microprocessor-controlled lower limb prostheses ...........................................................125
Osteochondral allograft and autograft transplantation .....................................................125
Osteotomy reconstruction ................................................................................................125
Percutaneous kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty and sacroplasty .............................................125
Sacroiliac joint fusion ......................................................................................................126
Robotic assisted surgery ..................................................................................................126
Nervous system ......................................................................................................................126
Discography .....................................................................................................................126
Facet neurotomy, cervical and lumbar .............................................................................127
Lumbar radiculopathy ......................................................................................................127
Implantable infusion pumps or implantable drug delivery systems ................................128
Spinal cord stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain ......................................................128
Spinal injections for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes (outpatient) ..............................128
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) device ...........................................130
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) .......................................................................................130
Skin substitutes ......................................................................................................................131

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
10
Limitations .......................................................................................................................131
Sleep apnea ............................................................................................................................132
Surgical treatment for sleep apnea ...................................................................................132
Urinary systems .....................................................................................................................132
Collagen implants ............................................................................................................132
Indwelling catheter...........................................................................................................132
Urinary tract implants ......................................................................................................133
Urological procedures with sterilizations in the description ............................................133
Radiology Services .....................................................................................................................134
Radiology services – general limits .......................................................................................134
Radiology modifiers for bilateral procedures ........................................................................134
Breast, mammography ...........................................................................................................135
Mammograms ..................................................................................................................135
Diagnostic radiology (diagnostic imaging) ............................................................................135
Multiple procedure payment reduction (MPPR) ..............................................................135
Which procedures require a medical necessity review by Comagine Health? ................136
Imaging for rhinosinusitis ................................................................................................138
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) ....................................................................139
Contrast material ..............................................................................................................139
Consultation on X-ray examination .................................................................................140
Coronary artery calcium scoring ......................................................................................140
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ................................................................................140
Portable X-rays ................................................................................................................141
Ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm .....................................................141
Virtual colonoscopy or computed tomographic colonography ........................................142
Screening and monitoring tests for osteopenia/osteoporosis ...........................................142
Functional neuroimaging for primary degenerative dementia or mild cognitive
impairment .................................................................................................................142
Diagnostic Ultrasound ...........................................................................................................143
Obstetrical ultrasounds.....................................................................................................143
Nuclear medicine ...................................................................................................................143
Which procedures require a medical necessity review from HCA? ................................143
Which procedures require a medical necessity review by Comagine Health? ................144
Radiopharmaceutical diagnostic imaging agents .............................................................145
Positron emission tomography (PET) scans for lymphoma ............................................145
Nuclear medicine - billing ...............................................................................................146
Radiation oncology ................................................................................................................146
Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) ................................................................146
Proton beam therapy ........................................................................................................147
Stereotactic radiation surgery ................................................................................................147
Stereotactic body radiation therapy .......................................................................................147
Tumor treating fields..............................................................................................................148
Pathology and Laboratory ........................................................................................................149
Certifications ..........................................................................................................................149

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
11
Independent laboratories - certification ...........................................................................149
Reference labs and facilities - CLIA certification ...........................................................149
Anatomic pathology ...............................................................................................................149
Pap smears .......................................................................................................................149
Screening exams ....................................................................................................................150
Cancer screens .................................................................................................................150
Disease organ panels--automated multi-channel tests .....................................................151
Fetal fibronectin ...............................................................................................................152
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy using cell-free fetal nucleic
acids in maternal blood (NIPT)..................................................................................153
Vitamin D screening and testing ......................................................................................153
Lead toxicity screening ....................................................................................................155
Drug Testing for Substance Use Disorder .............................................................................155
Drug screening for medication for opioid use disorder ...................................................155
Buprenorphine when used for pain control ......................................................................158
Enhanced reimbursement rate for medication for opioid use disorder ............................159
Immunology ...........................................................................................................................159
HIV testing .......................................................................................................................159
Targeted TB testing with interferon-gamma release assays ............................................160
Molecular Pathology Tests ....................................................................................................160
Genomic microarray ........................................................................................................161
Companion diagnostic tests .............................................................................................161
Organ and disease-oriented panels.........................................................................................162
Automated multi-channel tests - payment .......................................................................162
Disease organ panel - nonautomated multi-channel ........................................................163
Gene expression ...............................................................................................................163
Breast and ovarian genetic testing ...................................................................................163
Billing ....................................................................................................................................164
Billing for laboratory services that exceed the lines allowed ..........................................164
Clinical laboratory codes .................................................................................................164
Coding and payment policies ...........................................................................................164
Laboratory physician interpretation procedure codes ......................................................166
Laboratory codes requiring modifier and PA clarification ..............................................166
Laboratory modifiers .......................................................................................................166
Laboratory services referred by CMHC or DBHR-contracted providers ........................167
STAT laboratory charges .................................................................................................168
Medicine ......................................................................................................................................171
Allergen and clinical immunology.........................................................................................171
Allergen immunotherapy .................................................................................................171
Audiology ..............................................................................................................................172
Who is eligible to provide audiology services? ...............................................................172
What type of equipment must be used? ...........................................................................173
Audiology coverage .........................................................................................................173
Audiology billing .............................................................................................................173
Bronchial thermoplasty for asthma ..................................................................................173

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
12
Cardiovascular .......................................................................................................................174
Catheter ablation for supraventricular tachyarrhythmias .................................................174
Heart catheterizations.......................................................................................................174
Outpatient cardiac rehabilitation ......................................................................................174
Central nervous system assessments/tests .............................................................................176
Coverage for developmental screening for delays and surveillance and screening
for autism ...................................................................................................................176
Chemotherapy ........................................................................................................................177
Chemotherapy services ....................................................................................................177
Irrigation of venous access pump ....................................................................................178
Dialysis - end-stage renal disease (ESRD) ............................................................................178
Inpatient visits for hemodialysis or outpatient non-ESRD dialysis services ...................178
Inpatient visits for dialysis procedures other than hemodialysis .....................................179
Endocrinology ........................................................................................................................179
Professional or diagnostic continuous glucose monitoring .............................................179
Genetic testing .......................................................................................................................180
Whole exome sequencing ................................................................................................180
Hydration, therapeutic, prophylactic, diagnostic injections, infusions ..................................181
Hydration therapy with chemotherapy.............................................................................181
Therapeutic or diagnostic injections/infusions ................................................................182
Concurrent infusion .........................................................................................................182
Immune globulins, serum, or recombinant products .............................................................182
Hepatitis B (CPT code 90371) .........................................................................................182
Immune globulins ............................................................................................................183
Rabies immune globulin (RIg).........................................................................................183
Medical genetics and genetic counseling services .................................................................183
Genetic counseling and genetic testing ............................................................................183
Prenatal genetic counseling..............................................................................................184
Applying to HCA to become a genetic counseling provider ...........................................186
Miscellaneous ........................................................................................................................187
After-hours .......................................................................................................................187
Neurology and neuromuscular procedures ............................................................................188
Needle electromyography (EMGs) ..................................................................................188
Nerve conduction study (NCS) ........................................................................................188
Sleep medicine testing (sleep apnea) ...............................................................................189
Ophthalmology – vision care services ...................................................................................189
Eye examinations and refraction services ........................................................................189
Coverage for additional examinations and refraction services ........................................189
Visual field exams............................................................................................................190
Vision therapy ..................................................................................................................190
Corneal topography ..........................................................................................................191
Ocular prosthetics ............................................................................................................191
Eye surgery ......................................................................................................................191
Vision coverage table .......................................................................................................193
Manipulative therapy .............................................................................................................199
Other services and procedures ...............................................................................................200

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
13
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy ..............................................................................................200
Testosterone testing .........................................................................................................202
Transient elastography .....................................................................................................202
Neuropsychological testing ..............................................................................................202
Psychiatry ...............................................................................................................................202
Clozaril - case management .............................................................................................202
Pulmonary ..............................................................................................................................203
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy (ECMO) ...............................................203
Ventilator management ....................................................................................................203
Special dermatological services .............................................................................................203
Ultraviolet phototherapy ..................................................................................................203
Special services ......................................................................................................................204
Group clinical visits for clients with diabetes or asthma .................................................204
Therapies (physical, occupational, and speech therapy) ........................................................205
Modifier required when billing ........................................................................................206
Treatment of chronic migraines and chronic tension-type headaches ...................................206
Vaccines/toxoids (immunizations) .........................................................................................207
Clients from birth through age 18 ....................................................................................207
Clients age 19 and older ...................................................................................................207
How to bill HCA for adult immunizations ......................................................................208
Maternity Care and Delivery ....................................................................................................209
Confirmation of pregnancy ....................................................................................................210
Problem visits during pregnancy ...........................................................................................210
HIV/AIDS counseling/testing ................................................................................................211
Tobacco/nicotine cessation for pregnant clients ....................................................................211
Early pregnancy loss and abortion services ...........................................................................211
Global (total) obstetrical (OB) care .......................................................................................214
Unbundling obstetrical care ...................................................................................................214
Antepartum care .....................................................................................................................216
Coding for antepartum care only ...........................................................................................216
Coding for deliveries without antepartum care ......................................................................217
Coding for postpartum care only ...........................................................................................217
Additional monitoring for high-risk conditions .....................................................................218
Consultations..........................................................................................................................219
Elective deliveries ..................................................................................................................220
Labor management.................................................................................................................220
High-risk deliveries ................................................................................................................221
Additional delivery payment policies and limitations ...........................................................222
Global (total) obstetrical (OB) care .......................................................................................222
Antepartum care only .............................................................................................................223
Deliveries ...............................................................................................................................223
Postpartum care only..............................................................................................................223
Additional monitoring for high-risk conditions .....................................................................224
Labor management.................................................................................................................224
High-risk deliveries ................................................................................................................224

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
14
Billing with modifiers for maternity care ..............................................................................225
Medical Supplies and Equipment .............................................................................................226
Physician signature requirement ............................................................................................226
General payment policies .......................................................................................................227
Supplies included in an office call (bundled supplies) ..........................................................227
Alcohol and Substance Misuse Counseling..............................................................................231
What is included in SBIRT? ..................................................................................................231
What is covered? ....................................................................................................................232
Who is eligible to become a certified SBIRT provider? ........................................................233
What are the requirements to be a certified SBIRT provider? ...............................................234
Required training .............................................................................................................234
Who can bill for SBIRT services? .........................................................................................235
Alcohol and Substance Abuse Treatment Services .................................................................236
Medical services for clients in residential chemical dependency treatment ..........................236
Withdrawal management services .........................................................................................237
Blood, blood products, and related services ............................................................................238
Payment for blood and blood products ..................................................................................238
Autologous blood/platelet-rich plasma injections ...........................................................238
Fee schedule ...........................................................................................................................238
Centers of Excellence .................................................................................................................239
List of approved Centers of Excellence (COEs) ....................................................................239
Services which must be performed in a COE ........................................................................239
Hemophilia treatment COEs ............................................................................................239
Sleep studies.....................................................................................................................242
Transplants .......................................................................................................................243
Drugs Professionally Administered ..........................................................................................245
Invoice requirements ..............................................................................................................245
Drug pricing ...........................................................................................................................246
National drug code format .....................................................................................................246
Physicians billing for compound drugs..................................................................................247
Drugs requiring prior authorization .......................................................................................247
Contraceptives........................................................................................................................247
Injectable drugs - limitations .................................................................................................248
Billing for injectable drugs and biologicals ...........................................................................249
Chemotherapy drugs ..............................................................................................................249
Billing for single-dose vials ...................................................................................................250
Billing for multiple dose vials................................................................................................250
Billing for oral anti-emetic drugs when part of a chemotherapy regimen .............................251
Rounding of units ...................................................................................................................251

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
15
Unlisted drugs ........................................................................................................................252
Botulinum toxin injections (Botox) .......................................................................................253
Collagenase injections ...........................................................................................................253
Hyaluronic acid/viscosupplementation ..................................................................................253
Alpha Hydroxyprogesterone (17P) ........................................................................................255
How to bill for Alpha Hydroxyprogesterone (17P) .........................................................256
Makena® ................................................................................................................................256
Prolia/Xgeva ..........................................................................................................................256
Spinraza™ ..............................................................................................................................256
Synagis® ................................................................................................................................257
What are the requirements for administration and authorization of Synagis®? ..............257
Are there other considerations when administering Synagis®? ......................................257
What are the authorization and billing procedures for Synagis®? ..................................258
What is the criteria for coverage or authorization of Synagis®? .....................................258
What are the authorization procedures for Synagis? ....................................................259
Verteporfin injection ..............................................................................................................260
Vivitrol ...................................................................................................................................260
How do providers who participate in the 340B drug pricing program bill for drugs
and dispensing fees? ........................................................................................................261
Drugs administered to managed care clients but reimbursed through fee-for-service ..........261
Foot Care Services .....................................................................................................................263
Are foot care services covered? .............................................................................................263
What foot care services are not covered? ..............................................................................263
What foot care services does HCA pay for? ..........................................................................264
What foot care services does HCA not pay for? ....................................................................266
May I bill the client for foot care services which HCA does not pay for? ............................266
How do I bill for foot care services? ......................................................................................267
Home Health and Hospice .........................................................................................................268
Physician signature requirement for home health services ....................................................268
Physicians providing service to hospice clients .....................................................................268
Concurrent care for children who are on hospice ..................................................................268
Major Trauma Services .............................................................................................................269
Increased payments for major trauma care ............................................................................269
Client eligibility groups included in TCF payments to physicians ........................................269
Client eligibility groups excluded from TCF payments to physicians ..................................270
Services excluded from TCF payments to physicians ...........................................................270
TCF payments to physicians ..................................................................................................270
Enhanced rates for trauma care ........................................................................................270
Criteria for TCF payments to physicians .........................................................................271
TCF payments to providers in transferred trauma cases ........................................................272
Billing for trauma care services .............................................................................................273
Adjusting trauma claims ........................................................................................................273
Injury severity score (ISS) .....................................................................................................274

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
16
Physician/clinical provider list ...............................................................................................275
Oral Health .................................................................................................................................276
Access to Baby and Child Dentistry (ABCD) Program.........................................................276
What is the purpose of the ABCD program? ...................................................................276
Who may provide ABCD dentistry? ................................................................................276
What ABCD dental services are billable by certified primary care medical
providers? ...................................................................................................................277
Topical fluoride treatment................................................................................................278
Dental services coverage table for nondental providers ..................................................278
Oral surgery ...........................................................................................................................279
Services performed by a physician or dentist specializing in oral maxillofacial
surgery........................................................................................................................279
Provider requirements ......................................................................................................279
Oral surgery coverage table ...................................................................................................280
Prosthetic/Orthotics ...................................................................................................................288
Prosthetic and orthotics for podiatry and orthopedic surgeons ........................................288
Supplies paid separately when dispensed from provider’s office/clinic ...............................289
Casting materials ..............................................................................................................289
Inhalation solutions ..........................................................................................................289
Metered dose inhalers and accessories ............................................................................289
Miscellaneous prosthetics and orthotics ..........................................................................289
Miscellaneous supplies ....................................................................................................290
Radiopharmaceutical diagnostic imaging agents .............................................................290
Urinary tract implants ......................................................................................................290
Transgender Health Services ....................................................................................................291
What transgender health services are covered? .....................................................................291
Fee-for-service clients ......................................................................................................291
Managed care clients........................................................................................................292
What are the components of transgender health services? ....................................................292
Who can provide gender dysphoria-related treatment? .........................................................297
Medical Necessity Review by Comagine Health .....................................................................298
What is a medical necessity review by Comagine Health? ...................................................298
Who can request a review? ....................................................................................................298
How do I register with Comagine Health? ............................................................................299
Is authorization required for all Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) clients? ...................299
How do I submit a request to Comagine Health? ..................................................................300
What is the Comagine Health reference number for? ............................................................301
When does HCA consider retroactive authorizations? ..........................................................301
What are the authorization requirements for advanced imaging? .........................................302
How does HCA’s hierarchy of evidence protocol apply? .....................................................302

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
17
What are the authorization requirements for surgical procedures? .......................................303
Surgical modifiers ..................................................................................................................303
How does HCA’s hierarchy of evidence protocol apply? .....................................................304
What criteria will Comagine Health use to establish medical necessity? ..............................304
Is there a provider appeals process for Comagine Health? ....................................................304
Authorization..............................................................................................................................306
Prior authorization (PA) .........................................................................................................306
What is prior authorization (PA)? ....................................................................................306
How does HCA determine PA? .......................................................................................306
Services requiring PA ......................................................................................................307
Documentation requirements for PA or LE .....................................................................310
Requesting prior authorization (PA) ......................................................................................312
Online direct data entry into ProviderOne .......................................................................312
Written or Fax ..................................................................................................................312
Limitation extension (LE) ......................................................................................................313
What is a limitation extension (LE)? ...............................................................................313
How do I request an LE authorization? ...........................................................................313
Expedited prior authorization (EPA) .....................................................................................314
What is expedited prior authorization (EPA)? .................................................................314
EPA guidelines.................................................................................................................315
EPA criteria list ......................................................................................................................316
Modifiers .....................................................................................................................................338
CPT/HCPCS ..........................................................................................................................338
Anesthesia ..............................................................................................................................344
Site-of-Service .............................................................................................................................345
Payment Differential ..................................................................................................................345
How are fees established for professional services performed in facility and
nonfacility settings? .........................................................................................................345
How does the SOS payment policy affect provider payments? .............................................345
Does HCA pay providers differently for services performed in facility and nonfacility
settings?............................................................................................................................346
When are professional services paid at the facility setting maximum allowable fee?...........346
When are professional services paid at the nonfacility setting maximum allowable
fee? ...................................................................................................................................347
Which professional services have a SOS payment differential? ...........................................348
Fee Schedule Information .........................................................................................................349
Billing ..........................................................................................................................................350
What are the general billing requirements? ...........................................................................350
Billing for multiple services.............................................................................................350
Billing for outpatient hospital services in hospital-based clinics.....................................351

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
18
How do I resolve issues with gender indicator when billing for transgender clients? ..........352
How do I bill claims electronically? ......................................................................................353
Submitting professional services for Medicare crossovers ..............................................354
Utilization review...................................................................................................................355
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
19
Definitions
This section defines terms and abbreviations, including acronyms, used in this billing guide.
Refer to Chapter 182-500 WAC for a complete list of definitions for Washington Apple Health.
Acquisition cost (AC) – The cost of an item
excluding shipping, handling, and any
applicable taxes.
Acute care – Care provided for clients who
are not medically stable or have not attained
a satisfactory level of rehabilitation. These
clients require frequent monitoring by a
health care professional in order to maintain
their health status.
Add-on procedure(s) – Secondary
procedure(s) performed in addition to
another procedure.
Admitting diagnosis – The medical
condition responsible for a hospital
admission. [WAC 182-531-0050]
Assignment – A process in which a doctor
or supplier agrees to accept the Medicare
program’s payment as payment in full,
except for specific deductible and
coinsurance amounts required of the patient.
Base anesthesia units (BAU) – A number
of anesthesia units assigned to an anesthesia
procedure that includes the usual
preoperative, intra-operative, and
postoperative visits. This includes the
administration of fluids and/or blood
incident to the anesthesia care, and
interpretation of noninvasive monitoring by
the anesthesiologist.
Bone conduction hearing device – A type of
hearing aid that transmits sound vibrations
through bones in the head. The inner ear
translates the vibrations the same way a
normal ear translates sound waves. These
devices can be surgically implanted or worn
on headbands. (WAC 182-547-0200)
Bundled services – Services integral to the
major procedures that are included in the fee
for the major procedure. Bundled services
are not reimbursed separately.
Calendar year – January through
December.
Code of federal regulations (CFR) – A
codification of the general and permanent
rules published in the federal register by the
executive departments and agencies of the
federal government.
Global developmental delay (GDD) - A
significant delay in two or more
developmental domains, including gross or
fine motor, speech/language, cognitive,
social/personal, and activities of daily living
and is thought to predict a future diagnosis
of ID. Such delays require accurate
documentation by using norm-referenced
and age-appropriate standardized measures
of development administered by experienced
developmental specialists, or documentation
of profound delays based on age-appropriate
developmental milestones are present. GDD
is used to categorize children who are
younger than 5.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
20
HCPCS- See Healthcare Common
Procedure Coding System.
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding
System (HCPCS) - Standardized coding
system that is used primarily to identify
products, supplies, and services not included
in the CPT® codes, such as ambulance
services and durable medical equipment,
prosthetics, orthotics, and supplies
(DMEPOS) when used outside a physician's
office.
Informed consent – Where an individual
consents to a procedure after the provider
who obtained a properly completed consent
form has done all of the following:
(1) Disclosed and discussed the client’s
diagnosis
(2) Offered the client an opportunity to ask
questions about the procedure and to
request information in writing
(3) Given the client a copy of the consent
form
(4) Communicated effectively using any
language interpretation or special
communication device necessary per 42
C.F.R. Chapter IV 441.257
(5) Given the client oral information about
all of the following:
(a) The client’s right to not obtain the
procedure, including potential
risks, benefits, and the
consequences of not obtaining the
procedure
(b) Alternatives to the procedure
including potential risks, benefits,
and consequences
(c) The procedure itself, including
potential risks, benefits, and
consequences
Inpatient hospital admission – An
admission to a hospital that is limited to
medically necessary care based on an
evaluation of the client using objective
clinical indicators, assessment, monitoring,
and therapeutic service required to best
manage the client’s illness or injury, and that
is documented in the client’s medical record.
Intellectual disability (ID) - A life-long
disability diagnosed at or after age 5 when
intelligence quotient (IQ) testing is
considered valid and reliable. The
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
Disorders of the American Psychiatric
Association (DSM-V), defines patients with
ID as having an IQ less than 70, onset
during childhood, and dysfunction or
impairment in more than two areas of
adaptive behavior or systems of support.
Medical consultant – Physicians employed
by HCA who are authorities on the medical
aspects of the Medical Assistance program.
As part of their responsibilities, HCA
medical consultants:
• Serve as advisors in communicating to
the medical community the scope, limit,
and purpose of the program.
• Assist in the development of HCA
medical policy, procedures, guidelines,
and protocols.
• Evaluate the appropriateness and
medical necessity of proposed or
requested medical treatments in
accordance with federal and state law,
applicable regulations, HCA policy, and
community standards of medical care.
• Serve as advisors to HCA staff, helping
them to relate medical practice realities
to activities such as claims processing,
legislative requests, cost containment,
and utilization management.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
21
• Serve as liaisons between HCA and
various professional provider groups,
health care systems (such as HMOs),
and other state agencies.
• Serve as expert medical and program
policy witnesses for HCA at fair
hearings.
Newborn or neonate or neonatal - A
person younger than 29 days old.
Noncovered service or charge – A service
or charge not reimbursed by HCA.
Professional component – The part of a
procedure or service that relies on the
provider’s professional skill or training, or
the part of that reimbursement that
recognizes the provider’s cognitive skill.
Relative value unit (RVU) – A unit that is
based on the resources required to perform
an individual service. RBRVS RVUs are
comprised of three components – physician
work, practice expense, and malpractice
expense.
Resource based relative value scale
(RBRVS) – A scale that measures the
relative value of a medical service or
intervention, based on the amount of
physician resources involved.
RBRVS maximum allowable amount –
The Medicare Fee Schedule relative value
unit, multiplied by the statewide geographic
practice cost index, times the applicable
conversion factor.
Revised code of Washington (RCW) –
Washington State laws.
Significant delay - Performance two
standard deviations or more below the mean
on age-appropriate, standardized, normal-
referenced testing.
Technical component – The part of a
procedure or service that relates to the
equipment set-up and technician’s time, or
the part of the procedure and service
reimbursement that recognizes the
equipment cost and technician time.
Year – The time period starting 365 days
before the date of service.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
22
Introduction
Acquisition cost
Drugs with an acquisition cost (AC) indicator in the fee schedule with billed charges of
$1,100.00 or greater, or supplies with billed charges of $50.00 or greater, require a
manufacturer’s invoice in order to be paid. Attach the invoice to the claim, and if necessary, note
the quantity given to the client in the Claim Note section of the claim. DO NOT attach an
invoice to the claim for procedure codes with an AC indicator in the fee schedule for drugs with
billed charges under $1,100.00, or supplies with billed charges under $50.00, unless requested by
HCA.
Note: Bill HCA for one unit of service only when billing for drugs with an AC
indicator.
Add-on codes
HCA will not pay for procedure codes defined in the current CPT® manual as “add-on codes”
when these codes are billed alone or with an invalid primary procedure code.
Note: HCA has instituted claims edits requiring that “add-on” procedure codes
be billed with a correct primary procedure.
By report
Services with a by report (BR) indicator in the fee schedule with billed charges of $1,100.00 or
greater require a detailed report in order to be paid. Attach the report to the claim. For billed charges
under $1,100.00, DO NOT attach a report to the claim for services with a BR indicator in the fee
schedule, unless requested by HCA. HCA pays for medically necessary services on the basis of
usual and customary charges or the maximum allowable fee established by HCA, whichever is lower
according to WAC 182-502-0100.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
23
Codes for unlisted procedures
(CPT code XXX99)
Providers must bill using the appropriate procedure code. HCA does not pay for procedures
when they are judged to be less-than-effective (i.e., an experimental procedure), as reported in
peer-reviewed literature (see WAC 182-501-0165). If providers bill for a procedure using a code
for an unlisted procedure, it is the provider’s responsibility to know whether the procedure is
effective, safe, and evidence-based. HCA requires this for all its programs, as outlined in WAC
182-501-0050. If a provider does not verify HCA’s coverage policy before performing a
procedure, HCA may not pay for the procedure.
Conversion factors
Conversion factors are multiplied by the relative value units (RVUs) to establish the rates in
HCA’s Physician-related services/health care professionals fee schedule.
Diagnosis codes
HCA requires valid and complete ICD diagnosis codes. When billing HCA, use the highest level
of specificity (6
th
or 7
th
digits when applicable) or the services will be denied.
HCA does not cover the following diagnosis codes when billed as the primary diagnosis:
• V00-Y99 codes (Supplementary Classification)
• Most codes in Z00-Z99 (factors influencing health status and contact with health
services)
HCA reimburses providers for only those covered procedure
codes and diagnosis codes that are within their scope of
practice.
Discontinued codes
HCA follows Medicare and does not allow providers a 90-day grace period to use discontinued
CPT and HCPCS codes. Use of discontinued codes to bill services provided after the date that
the codes are discontinued will cause claims to be denied.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
24
National correct coding initiative
HCA continues to follow the National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) policy. The Centers for
Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) created this policy to promote national correct coding
methods. NCCI assists HCA to control improper coding that may lead to inappropriate payment.
HCA bases coding policies on the following:
• The American Medical Association’s (AMA) Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
manual
• National and local policies and edits
• Coding guidelines developed by national professional societies
• The analysis and review of standard medical and surgical practices
• Review of current coding practices
Procedure code selection must be consistent with the current CPT guidelines, introduction, and
instructions on how to use the CPT coding book. Providers must comply with the coding
guidelines that are within each section (e.g., E/M services, radiology, etc.) of the current CPT
book.
Medically Unlikely Edits (MUEs) - MUEs are part of the NCCI policy. MUEs are the
maximum unit of service per HCPC or CPT code that can be reported by a provider under most
circumstances for the same patient on the same date of service. Items billed above the established
number of units are automatically denied as a “Medically Unlikely Edit.” Not all HCPCS or CPT
codes are assigned an MUE. HCA follows the CMS MUEs for all codes.
HCA may have units of service edits that are more restrictive than MUEs.
HCA may perform a post-pay review on any claim to ensure compliance with NCCI. NCCI rules
are enforced by the ProviderOne payment system.
Procedure codes
HCA uses the following types of procedure codes within this billing guide:
• Current Procedure Terminology (CPT)
• Level II Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
• Current Dental Terminology (CDT)
Procedures performed must match the description and guidelines from the most current CPT or
HCPCS manual for all HCA-covered services. Due to copyright restrictions, HCA publishes
only the official short CPT descriptions. To view the full CPT description, refer to a
current CPT manual.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
25
Provider Eligibility
Who may provide and bill for physician-related
services?
(WAC 182-531-0250 (1))
The following health care professionals may request enrollment with HCA to provide and bill for
physician-related and health care professional services provided to eligible clients:
• Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioners (ARNPs)
• Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs)
• Genetic Counselors
• Health Departments
• Hospitals currently licensed by the Department of Health (DOH)
• Independent (outside) laboratories CLIA-certified to perform tests. See WAC 182-531-0800
• Licensed marriage and family therapists, only as provided in WAC 182-531-1400
• Licensed mental health counselors, only as provided in WAC 182-531-1400
• Licensed radiology facilities
• Licensed social workers, only as provided in WAC 182-531-1400 and 182-531-1600
• Medicare-certified Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs)
• Medicare-certified Rural Health Clinics (RHCs)
• Naturopathic physicians (see naturopathic physicians)
• Providers who have a signed agreement with HCA to provide screening services to eligible
persons in the Early and Periodic, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment (EPSDT) program
• Registered Nurse First Assistants (RNFAs)

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
26
• Persons currently licensed by the State of Washington DOH to practice any of the following:
Dentistry
Medicine and osteopathy
Nursing
Optometry
Podiatry
Psychiatry
Psychology
Can naturopathic physicians provide and bill for
physician-related services?
Yes. Effective for dates of service on and after January 1, 2014, HCA added naturopathic
physicians (taxonomy 175F00000X) to the list of professionals who can provide and bill for
physician-related services. HCA recognizes a naturopathic physician’s scope of practice in
accordance with RCW 18.36A.040.
Licensure
Naturopathic physicians with an active Washington State license may request enrollment with
HCA. If a naturopathic physician is practicing naturopathic childbirth, HCA requires the
naturopathic physician to have a separate active Washington State midwifery license.
Limitations
• HCA does not pay for:
Nonsurgical cosmetic procedures.
Prescription or nonprescription botanical, herbal, or homeopathic medicine.
• Manual manipulation - HCA applies the limitations for manual manipulation
(mechanotherapy). See manipulative therapy (CPT® codes 98925-98929).
• Malignancies – Treatment of a client with a malignancy must not be done independently
by a naturopathic physician.
• Controlled substance prescriptions – As authorized under WAC 246-836-211, these
are limited to testosterone and codeine-containing substances in Schedules III-V.
• Billing a client - A Medicaid client must not be charged for a covered over-the-counter
(nonprescription) drug which is dispensed in the office. Covered over-the-counter drugs
must be prescribed and the prescription filled by a pharmacy. Refer to HCA’s
Prescription Drug Program Billing Guide for complete instructions.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
27
• Injectable drugs – Physician-administered injectable drugs are subject to prior
authorization requirements as described in HCA’s Professional administered drugs fee
schedule.
Can substitute physicians (locum tenens) provide
and bill for physician-related services?
Yes. Physicians may bill under certain circumstances for services provided on a temporary basis
(i.e., locum tenens) to their patients by another physician [42 U.S.C. Chapter 7, Subchapter XIX,
Sec 1396a (32)(C)].
The physician’s claim must identify the substituting physician providing the temporary services.
Complete the claim as follows:
• Enter the provider NPI and taxonomy of the locum tenens physician who performed the
substitute services in the Rendering (Performing) Provider section of the electronic
claim.
• Any provider that will perform as a locum tenens provider that will treat a Medicaid
client must be enrolled as a Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) provider in order for
claims to be paid. For enrollment information, go to the Enroll as a provider webpage.
• Enter the billing provider information in the usual manner.
• Use modifier Q6 when billing.
Documentation in the patient’s record must show that in the case of:
• An informal reciprocal arrangement, billing for temporary services was limited to a
period of 14 continuous days, with at least one day elapsing between 14-day periods.
• A locum tenens arrangement involving per diem or other fee-for-time compensation,
billing for temporary services was limited to a period of 90 continuous days, with at least
30 days elapsing between 90-day periods.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
28
Resident Physicians
A resident cannot bill HCA for services they provide to a client. If a resident physician
prescribes, orders, or refers, the resident physician must be enrolled with HCA as a nonbilling
provider according to WAC 182-502-0006.
If a resident is involved in any part of the patient care or treatment, the billing provider must use
a GC modifier with the appropriate HCPCS or CPT code when billing. The modifier is for
tracking purposes only and does not affect payment.
Which health care professionals does HCA not
enroll?
(WAC 182-531-0250 (2))
HCA does not enroll licensed or unlicensed health care practitioners not specifically listed in WAC
182-502-0002, including but not limited to:
• Acupuncturists
• Christian Science practitioners or theological healers
• Counselors (i.e., M.A. and M.S.N.), except as provided in WAC 182-531-1400
• Herbalists
• Homeopathists
• Massage therapists as licensed by the Washington State Department of Health (DOH)
• Sanipractors
• Social workers, except those who have a master's degree in social work (MSW) and:
Are employed by an FQHC.
Who have received prior authorization from HCA to evaluate a client for bariatric
surgery.
As provided in WAC 182-531-1400.
• Any other licensed or unlicensed practitioners not otherwise specifically provided for in
WAC 182-502-0010
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
29
• Any other licensed practitioners providing services that the practitioner is not licensed or
trained to provide
HCA pays practitioners listed above for physician-related and health care professional services only
if those services are mandated by, and provided to, clients who are eligible for one of the following:
• The EPSDT program
• A Medicaid program for qualified Medicare beneficiaries (QMB)
• A waiver program (WAC 182-531-0250 (3))
Does HCA pay for out-of-state hospital
admissions?
(Does not include border hospitals)
HCA pays for emergency care at an out-of-state hospital, not including hospitals in bordering
cities, only for Medicaid and CHIP clients on an eligible program. See WAC 182-501-0175 for
recognized bordering cities.
HCA requires prior authorization (PA) for elective, nonemergency care and approves these
services only when both of the following apply:
• The client is on an eligible program (e.g., the Categorically Needy Program).
• The service is medically necessary and is unavailable in the State of Washington.
Providers requesting elective, out-of-state care must send a completed Out-of-State Medical
Services Request form, 13-787, with additional required documentation attached, to HCA
Medical Request Coordinator. (See HCA’s Billers, providers, and partners webpage. See also
Where can I download HCA forms?)
Providers must obtain prior authorization from the appropriate Behavioral Health and Service
Integration Administration (BHSIA) designee for out-of-state psychiatric hospital admissions
for all Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) clients. Neither HCA nor the BHSIA designee pays
for inpatient services for non-Medicaid clients if those services are provided outside of the state
of Washington. An exception is clients who are qualified for the medical care services (MCS)
program. For these clients, HCA and the BHSIA designee pays for inpatient psychiatric services
provided in bordering cities and critical border hospitals. All claims for admissions to out-of-
state hospitals are paid as voluntary legal status as the Involuntary Treatment Act applies only
within the borders of Washington State.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
30
Client Eligibility
Most Apple Health clients are enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization
(MCO). This means that Apple Health pays a monthly premium to an MCO for providing
preventative, primary, specialty, and other health services to Apple Health clients. Clients in
managed care must see only providers who are in their MCO’s provider network, unless prior
authorized or to treat urgent or emergent care. See HCA’s Apple Health managed care webpage
for further details.
It is important to always check a client’s eligibility prior to
providing any services because it affects who will pay for the services.
How do I verify a client’s eligibility?
Check the client’s Services Card or follow the two-step process below to verify that a client has
Apple Health coverage for the date of service and that the client’s benefit package covers the
applicable service. This helps prevent delivering a service HCA will not pay for.
Verifying eligibility is a two-step process:
Step 1. Verify the patient’s eligibility for Apple Health. For detailed instructions on
verifying a patient’s eligibility for Apple Health, see the Client Eligibility, Benefit
Packages, and Coverage Limits section in HCA’s ProviderOne Billing and Resource
Guide.
If the patient is eligible for Apple Health, proceed to Step 2. If the patient is not
eligible, see the note box below.
Step 2. Verify service coverage under the Apple Health client’s benefit package. To
determine if the requested service is a covered benefit under the Apple Health client’s
benefit package, see HCA’s Program benefit packages and scope of services webpage.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
31
Note: Patients who are not Apple Health clients may submit an application for
health care coverage in one of the following ways:
1. By visiting the Washington Healthplanfinder’s website at:
www.wahealthplanfinder.org
2. By calling the Customer Support Center toll-free at: 855-WAFINDER
(855-923-4633) or 855-627-9604 (TTY)
3. By mailing the application to:
Washington Healthplanfinder
PO Box 946
Olympia, WA 98507
In-person application assistance is also available. To get information about in-
person application assistance available in their area, people may visit
www.wahealthplanfinder.org or call the Customer Support Center.
Are clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted
managed care organization (MCO) eligible?
Yes. Most Medicaid-eligible clients are enrolled in one of HCA’s contracted managed care
organizations (MCOs). For these clients, managed care enrollment will be displayed on the client
benefit inquiry screen in ProviderOne.
All medical services covered under an HCA-contracted MCO must be obtained by the client
through designated facilities or providers. The MCO is responsible for:
• Payment of covered services
• Payment of services referred by a provider participating with the plan to an outside
provider
Note: A client’s enrollment can change monthly. Providers who are not
contracted with the MCO must receive approval from both the MCO and the
client’s primary care provider (PCP) prior to serving a managed care client.
Send claims to the client’s MCO for payment. Call the client’s MCO to discuss payment prior
to providing the service. Providers may bill clients only in very limited situations as described in
WAC 182-502-0160.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
32
Note: HCA continues to pay for the following through fee-for-service:
• Professional fees for dental procedures using CDT® codes
• Professional fees using CPT® codes only when the provider’s taxonomy
starts with 12
See the Dental-Related Services Billing Guide or the Physician-Related
Services/Health Care Professional Services Billing Guide, or both, for how to bill
professional fees.
Note: To prevent billing denials, check the client’s eligibility prior to scheduling
services and at the time of the service, and make sure proper authorization or
referral is obtained from HCA-contracted MCO, if appropriate. See HCA’s
ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide for instructions on how to verify a
client’s eligibility.
Managed care enrollment
Apple Health (Medicaid) places clients into an HCA-contracted MCO the same month they are
determined eligible for managed care as a new or renewing client. This eliminates a person being
placed temporarily in FFS while they are waiting to be enrolled in an MCO or reconnected with
a prior MCO. This enrollment policy also applies to clients in FFS who have a change in the
program they are eligible for.
New clients are those initially applying for benefits or those with changes in their existing
eligibility program that consequently make them eligible for Apple Health managed care.
Renewing clients are those who have been enrolled with an MCO but have had a break in
enrollment and have subsequently renewed their eligibility.
Checking eligibility
• Providers must check eligibility and know when a client is enrolled and with which
MCO. For help with enrolling, clients can refer to the Washington Healthplanfinder’s Get
Help Enrolling page.
• MCOs have retroactive authorization and notification policies in place. The provider
must know the MCO’s requirements and be compliant with the MCO’s policies.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
33
Apple Health – Changes for January 1, 2020
Effective January 1, 2020, the Health Care Authority (HCA) completed the move to whole-
person care to allow better coordination of care for both body (physical health) and mind (mental
health and substance use disorder treatment, together known as “behavioral health”). This
delivery model is called Integrated Managed Care (formerly Fully Integrated Managed Care, or
FIMC, which still displays in ProviderOne and Siebel).
IMC is implemented in the last three regions of the state:
• Great Rivers (Cowlitz, Grays Harbor, Lewis, Pacific, and Wahkiakum counties)
• Salish (Clallam, Jefferson, and Kitsap counties)
• Thurston-Mason (Mason and Thurston counties)
These last three regions have plan changes, with only Amerigroup, Molina, and United
Healthcare remaining. If a client is currently enrolled in a health plan that will be available in their
county in 2020, their health plan will not change.
Clients have a variety of options to change their plan:
• Available to clients with a Washington Healthplanfinder account:
Go to Washington HealthPlanFinder website.
• Available to all Apple Health clients:
Visit the ProviderOne Client Portal website:
Call Apple Health Customer Service at 1-800-562-3022. The automated system is
available 24/7.
Request a change online at ProviderOne Contact Us (this will generate an email to
Apple Health Customer Service). Select the topic “Enroll/Change Health Plans.”
For online information, direct clients to HCA’s Apple Health Managed Care webpage.
Clients who are not enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed
care plan
Each Integrated Managed Care (IMC) plan will have Behavioral Health Services Only (BHSO)
plans available for Apple Health clients who are not in managed care. Clients who are not
enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care plan are automatically enrolled in a BHSO. The
only difference is the BHSO covers only behavioral health treatment for those clients. The client’s
physical health care will be covered the same way it usually is. Some examples of populations
that may be exempt from enrolling into a managed care plan are Medicare dual-eligible,
American Indian/Alaska Native, Adoption support and Foster Care alumni.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
34
Integrated managed care (IMC)
Clients living in integrated managed care (IMC) regions will receive all physical health services,
mental health services, and substance use disorder treatment through their HCA-contracted
managed care organization (MCO).
American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) clients have two options for Apple
Health coverage:
• Apple Health Managed Care; or
• Apple Health coverage without a managed care plan (also referred to as
fee-for-service [FSS]).
If a client does not choose an MCO, they will be automatically enrolled into
Apple Health FFS for all their health care services, including comprehensive
behavioral health services. See HCA’s American Indian/Alaska Native webpage.
For more information about the services available under the FFS program, see
HCA’s Mental Health Services Billing Guide and the Substance Use Disorder
Billing Guide.
For full details on integrated managed care, see HCA’s Apple Health managed care webpage and
scroll down to “Changes to Apple Health managed care.”
Integrated managed care regions
Clients residing in integrated managed care regions and who are eligible for managed care
enrollment must choose an available MCO in their region. Details, including information about
mental health crisis services, are located on HCA’s Apple Health managed care webpage.
Region
Counties
Effective Date
Great Rivers
Cowlitz, Grays Harbor,
Lewis, Pacific, and
Wahkiakum
January 1, 2020
Salish
Clallam, Jefferson, Kitsap
January 1, 2020
Thurston-Mason
Thurston, Mason
January 1, 2020
North Sound
Island, San Juan, Skagit,
Snohomish, and Whatcom
July 1, 2019
Greater Columbia
Asotin, Benton, Columbia,
Franklin, Garfield, Kittitas,
Walla Walla, Yakima, and
Whitman
January 1, 2019
King
King
January 1, 2019
Pierce
Pierce
January 1, 2019
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
35
Region
Counties
Effective Date
Spokane
Adams, Ferry, Lincoln, Pend
Oreille, Spokane, and Stevens
counties
January 1, 2019
North Central
Grant, Chelan, Douglas, and
Okanogan
January 1, 2018
January 1, 2019 (Okanogan)
Southwest
Clark, Skamania, and
Klickitat
April 2016
January 1, 2019 (Klickitat)
Integrated Apple Health Foster Care (AHFC)
Children and young adults in the Foster Care, Adoption Support and Alumni programs who are
enrolled in Coordinated Care of Washington’s (CCW) Apple Health Foster Care program receive
both medical and behavioral health services from CCW.
Clients under this program are:
• Under the age of 21 who are in foster care (out of home placement)
• Under the age of 21 who are receiving adoption support
• Age 18-21 years old in extended foster care
• Age 18 to 26 years old who aged out of foster care on or after their 18
th
birthday (alumni)
These clients are identified in ProviderOne as
“Coordinated Care Healthy Options Foster Care.”
The Apple Health Customer Services staff can answer general questions about this program. For
specific questions about Adoption Support, Foster Care or Alumni clients, contact HCA’s Foster
Care Medical Team at 1-800-562-3022, Ext. 15480.
Fee-for-service Apple Health Foster Care
Children and young adults in the fee-for-service Apple Health Foster Care, Adoption Support and
Alumni programs receive behavioral health services through the regional Behavioral Health
Administrative Services Organization (BH-ASO). For details, see HCA’s Mental Health Services
Billing Guide, under How do providers identify the correct payer?

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
36
What if a client has third-party liability (TPL)?
If the client has third-party liability (TPL) coverage (excluding Medicare), prior authorization
must be obtained before providing any service requiring prior authorization. For more
information on TPL, refer to HCA’s ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
37
Coverage - General
What is covered?
(WAC 182-531-0100)
HCA covers health care services, equipment, and supplies listed in this guide, according to HCA
rules and subject to the limitations and requirements in this guide, when they are:
• Within the scope of an eligible client's medical assistance program.
Refer to WAC 182-501-0060 and 182-501-0065.
• Medically necessary as defined in WAC 182-500-0070.
HCA evaluates a request for a service that is in a covered category under the provisions of WAC
182-501-0165.
HCA evaluates requests for covered services that are subject to limitations or other restrictions
and approves such services beyond those limitations or restrictions as described in WAC 182-
501-0169.
HCA covers the following physician-related services and health care professional services,
subject to the conditions listed in this billing guide:
• Allergen immunotherapy services
• Anesthesia services
• Cosmetic, reconstructive, or plastic surgery, and related services and supplies to correct
physiological defects from birth, illness, or physical trauma, or for mastectomy
reconstruction for post cancer treatment
• Dialysis and end stage renal disease services (see HCA’s Kidney Center Services Billing
Guide)
• Early and periodic screening, diagnosis, and treatment (EPSDT) services (see HCA’s
Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment (EPSDT) Billing Guide)
• Emergency physician services
• ENT (ear, nose, and throat) related services
• Foot care and podiatry services

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
38
• Habilitative services (see Habilitative services)
• Hospital inpatient services (see HCA’s Inpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide)
• Maternity care, delivery, and newborn care services (see Maternity Care and Delivery)
• Office visits
• Osteopathic treatment services
• Pathology and laboratory services
• Physiatry and other rehabilitation services
• Primary care services
• Psychiatric services, provided by a psychiatrist (see HCA’s Mental Health Services
Billing Guide)
• Psychotherapy services (see HCA’s Mental Health Services Billing Guide)
• Pulmonary and respiratory services
• Radiology services
• Reproductive health services (see HCA’s Family Planning Billing Guide)
• Surgical services
• Vision-related services (see also HCA’s Vision Hardware for Clients 20 Years of Age
and Younger Billing Guide)
• Other outpatient physician services

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
39
HCA covers physical examinations for medical assistance clients only when the physical
examination is one or more of the following:
• A screening exam covered by the EPSDT program
• An annual exam for clients of the Developmental Disabilities Administration
• A screening pap smear performed according to nationally recognized clinical guidelines
• Mammogram performed according to nationally recognized clinical guidelines
• Prostate exam performed according to nationally recognized clinical guidelines
By providing covered services to a client eligible for a medical assistance program, a provider
who has signed an agreement with HCA accepts HCA's rules and fees as outlined in the
agreement, which includes federal and state law and regulations, billing guides, and HCA
issuances.
Does HCA cover nonemergency services
provided out-of-state?
(WAC 182-501-0182)
HCA covers nonemergency services provided out-of-state with prior authorization as described
in WAC 182-501-0182. A designated bordering city is considered the same as an in-state city for
the purposes of health care coverage (see WAC 182-501-0175).
What services are noncovered?
(WAC 182-501-0070)
General information
Procedures that are noncovered are noted with (NC) in the Nonfacility Setting (NFS) and Facility
Setting (FS) columns in the fee schedule.
HCA reviews requests for noncovered health care services according to WAC 182-501-0160 as
an exception to rule (ETR). To request a noncovered service using the ETR process, send a
completed typed General Authorization form (HCA13-835) and a Fax/Written Request Basic
Information form, 13-756, to HCA. (See HCA’s Billers, providers, and partners webpage. See
also Where can I download HCA forms?)
Refer to HCA’s ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide for information regarding noncovered
services and billing an HCA client who is on a fee-for-service program.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
40
The following are examples of administrative costs and/or services not
covered separately by HCA:
• Missed or canceled appointments
• Mileage
• Take-home drugs
• Educational supplies or services
• Copying expenses, reports, client charts, insurance forms
• Service charges/delinquent payment fees
• Telephoning for prescription refills
• Other areas as specified in this fee schedule
• After-hours charges for services during regularly scheduled work hours
Noncovered physician-related and health care professional
services
(WAC 182-531-0150)
HCA does not cover the following:
• Acupuncture, massage, or massage therapy
• Any service specifically excluded by statute
• Care, testing, or treatment of infertility, frigidity, or impotency. This includes procedures
for donor ovum, sperm, womb, and reversal of vasectomy or tubal ligation
• Cosmetic treatment or surgery, except for medically necessary reconstructive surgery to
correct defects attributable to trauma, birth defect, or illness
• Experimental or investigational services, procedures, treatments, devices, drugs, or
application of associated services, except when the individual factors of an individual
client's condition justify a determination of medical necessity under WAC 182-501-0165
• Hair transplantation
• Marital counseling or sex therapy
• More costly services when HCA determines that less costly, equally effective services are
available

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
41
• Vision-related services as follows:
Services for cosmetic purposes only
Group vision screening for eyeglasses
Refractive surgery of any type that changes the eye's refractive error (refractive
surgery is intended to reduce or eliminate the need for eyeglass or contact lens
correction, and does not include intraocular lens implantation following cataract
surgery)
• Payment for body parts, including organs, tissues, bones and blood, except as allowed in
this guide
• Physician-supplied medication, except those drugs administered by the physician in the
physician's office
• Physical examinations, routine checkups, and other preventive services, except as
provided in this guide
• Foot care to treat chronic acquired conditions of the foot such as, but not limited to:
Treatment of mycotic disease tinea pedis
Removal of warts, corns, or calluses
Trimming of nails and other regular hygiene care
Treatment of flat feet
Treatment of high arches (cavus foot)
Onychomycosis
Bunions and tailor’s bunion (hallux valgus)
Hallux malleus
Equinus deformity of foot, acquired
Cavovarus deformity, acquired
Adult acquired flatfoot (metatarsus adductus or pes planus
Hallux limitus
• Except as provided in this guide, weight reduction and control services, procedures,
treatments, devices, drugs, products, gym memberships, equipment for the purpose of
weight reduction, or the application of associated services
• Nonmedical equipment

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
42
• Nonemergency admissions and associated services to out-of-state hospitals or
noncontracted hospitals in contract areas
• Vaccines recommended or required for the sole purpose of international travel. This does
not include routine vaccines administered according to current Centers for Disease
Control (CDC) advisory committee on immunization practices (ACIP) immunization
schedule for adults and children in the United States.
Note: HCA covers excluded services listed in this section if those services are
mandated under and provided to a client who is eligible for one of the following:
• The EPSDT program
• A Medicaid program for qualified Medicare beneficiaries (QMBs)
• A waiver program

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
43
Medical Policy Updates
Policy updates effective 9/1/2020
• Based upon review of evidence provided by the Health Technology Clinical Committee
(HTCC), HCA does not consider bronchial thermoplasty for asthma to be medically
necessary. See Bronchial thermoplasty for asthma.
• Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA does not consider
autologous blood/platelet-rich plasma injections to be medically necessary. See
Autologous blood/platelet-rich plasma injections.
Policy updates effective 7/1/2020
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA considers whole exome sequencing
(WES) to be medically necessary for the evaluation of unexplained congenital or
neurodevelopmental disorders in a phenotypically affected individual when certain criteria are
met. For details, see Whole exome sequencing.
Policy updates effective 1/1/2020
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA considers proton beam therapy to
be medically necessary with limitations. For details, see Proton beam therapy.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
44
Policy updates effective 10/1/2019
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA does not consider minimally
invasive and open sacroiliac joint fusion procedures to be medically necessary for clients age 21
and older with chronic sacroiliac joint pain related to degenerative sacroiliitis or sacroiliac joint
disruption, or both. This decision does not apply to any the following:
• Low back pain of other etiology
• Sacroiliac joint pain related to recent major trauma or fracture
• Infection
• Cancer
• Sacroiliitis associated with inflammatory arthropathies
For these issues, see the fee schedule for coverage.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
45
Billable Services Provided By
Resident Physicians
Billable services provided by resident physicians
HCA follows Medicare’s rules for teaching physicians and residents. HCA also allows a teaching
physician to work with a resident physician providing services outside of the sponsoring teaching
facility (such as private practice).
The teaching physician-to-resident ratio is 1:1.
The resident must have completed a minimum of six months in a Graduate Medical Education
(GME) approved residency program and be assigned to a physician outside the sponsoring
teaching facility. The teaching physician can schedule a regular client load and allow the
resident-in-training to examine patients independently under the teaching physician’s
supervision.
The teaching physician is personally responsible for the care of each client and must be on-site at
all times. The teaching physician can bill for routine or low level services provided by the
resident physician after the teaching physician reviews and countersigns the resident physician’s
note, assuring that the resident has written a note appropriate to the service provided.
Billing requirements for teaching physicians
The primary physician must be identified on all claims as the teaching physician.
• Use the GC modifier when billing for a service performed in part by a resident physician
under the direction of a teaching physician.
• Use the GE modifier if the teaching physician is not physically present.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
46
General documentation guidelines
The teaching physician and the resident physician must document physician services in the
patient’s medical record. The documentation must be dated and contain a legible signature or
identity completed using one of these methods:
• Dictated and transcribed
• Typed
• Hand-written
• Computer-generated
Billing codes
The following codes are considered routine or low level under the primary care exception:
• 99381
• 99382
• 99383
• 99384
• 99385 (for ages 18-20 only)
• 99391
• 99392
• 99393
• 99394
• 99395 (for ages 18-20 only)
• 99201
• 99202
• 99203
• 99211
• 99212
• 99213
Claims must comply with requirements in the General documentation guidelines and
“Documentation guidelines for evaluation and management services” found on the Medicare
learning network® webpage.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
47
Medical students
A medical student is a person who is not an intern or resident and who is not in an approved
Graduate Medical Education (GME) program. The medical student must be in one of the
following programs: Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LCME), AOA Commission on
Osteopathic College Accreditation (COCA), or Association of Accredited Naturopathic Medical
Colleges (AANMC).
HCA allows medical students to review systems and past person, family, and social information
when done as a part of an Evaluation and Management (E/M) service. The teaching physician or
resident must be physically present during all portions of the E/M service.
The teaching physician must personally perform the physical exam and medical decision-making
activities of the billed E/M service. Medical students can document their own findings and
findings of the teaching physician. The teaching physician can review and verify a student’s
review without redoing or re-documenting it.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
48
Evaluation and Management
Evaluation and management documentation and
billing
The evaluation and management (E/M) service is based on key components listed in the CPT®
manual. Providers must use either the 1995 or 1997 “Documentation guidelines for evaluation
and management services” to determine the appropriate level of service. See the Medicare
learning network® webpage.
Once the licensed practitioner chooses either the 1995 or 1997 guidelines, the licensed
practitioner must use the same guidelines for the entire visit. Chart notes must contain
documentation that justifies the level of service billed.
Documentation must:
• Be legible to be considered valid.
• Support the level of service billed.
• Support medical necessity for the diagnosis and service billed.
• Be authenticated by provider performing service with date and time.
Keys to documenting medical necessity to support E/M service:
• Document all diagnoses managed during the visit.
• For each established diagnosis, specify if the patient’s condition is stable, improved,
worsening, etc.
• Document rationale for ordering diagnostic tests and procedures.
• Clearly describe management of the patient (e.g., prescription drugs, over the counter
medication, surgery).
A provider must follow the CPT coding guidelines and their documentation must support the
E/M level billed. While some of the text of CPT has been repeated in this billing guide, providers
should refer to the CPT book for the complete descriptors for E/M services and instructions for
selecting a level of service.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
49
Advance directives/physician orders for life-
sustaining treatment
HCA covers for counseling and care planning services for end of life treatment when conducted
by a licensed health care provider.
End of life service should be evidence-based and use tested guidelines and protocols. This
service may include assisting the client or the client’s authorized representative to understand
and complete advance directives and/or a physician orders for life-sustaining treatment (POLST)
form.
HCA pays separately for this counseling and planning in addition to the appropriate E/M code.
Bill for this service using one of the following procedure codes, as appropriate:
Procedure Codes
Short Descriptions
S0257
End of life counseling
99497
Advncd care plan 30 min
99498
Advncd care plan addl 30 min
This service may include:
• Assessing client readiness.
• Educating the client on their health status.
• Helping the client choose a suitable surrogate and involving the designated surrogate in
the conversation if appropriate.
• Discussing and clarifying values (e.g., “If you were in X situation, what would be most
important to you?”).
• Documenting the advance care plan with an advance directive and POLST if appropriate.
The Washington State Medical Association (WSMA) coordinates the Washington POLST Task
Force with the Washington State Department of Health. The WSMA offers up-to-date POLST
forms, frequently asked questions, and provides resources to providers and patients about the
legality of and operational uses of POLST.
For further information, see www.polst.org and www.wsma.org/polst.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
50
Telephone services
HCA pays for telephone services when used by a physician to report and bill for episodes of care
initiated by an established patient (i.e., someone who has received a face-to-face service from
you or another physician of the same specialty in your group in the past three years) or by the
patient's guardian. Report and bill for telephone services using the following CPT codes:
• CPT code 99441 - Telephone evaluation and management (E/M) service provided by a
physician to an established patient, parent or guardian not originating from a related E/M
service provided within the previous seven days nor leading to an E/M service or
procedure within the next 24 hours or soonest available appointment; 5–10 minutes of
medical discussion.
• CPT code 99442 - Same as CPT code 99441 except call includes 11–20 minutes of
medical discussion
• CPT code 99443 - Same as CPT code 99441 except call includes 21–30 minutes of
medical discussion.
Additional information when billing with these codes for telephone services:
1. Telephone services that are billed with CPT codes 99441, 99442 or 99443 must be
personally performed by the physician.
2. If the telephone service relates to and takes place within the postoperative period of a
procedure provided by the physician, the service is considered part of the procedure and
should not be billed separately.
3. Telephone services should not be billed when the same services are billed as care plan
oversight or anticoagulation management (CPT codes 99339-99340, 99374-99380 or
99363-99364).
4. When a telephone service refers to an E/M service performed and billed by the physician
within the previous seven days, it is not separately billable, regardless of whether it is the
result of patient-initiated or physician-requested follow-up.
5. This service should not be billed if the service results in the patient being seen within 24
hours or the next available appointment.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
51
Partnership Access Line
The Partnership Access Line (PAL) is a telephone-based child mental health consultation system
for Washington State. PAL employs child psychiatrists, child psychologists, and social workers
affiliated with Seattle Children’s Hospital to deliver its consultation services.
The PAL team is available to any primary care provider throughout Washington State.
Washington’s primary care providers are encouraged to call the PAL toll free number 866-599-
7257 as often as they would like. PAL provides rapid consultation responses during business
hours (Monday-Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m.) for any type of child mental health issue that
arises with any child.
Office and other outpatient services
(WAC 182-531-0950)
Office or other outpatient visit limits
HCA allows one office or other outpatient visit per noninstitutionalized client, per day for an
individual provider (except for call-backs to the emergency room). Refer to WAC 182-531-0500.
Certain procedures are included in the office call and cannot be billed separately.
Example: HCA does not pay separately for ventilation management (CPT codes
94002-94004, 94660, and 94662) when billed in addition to an Evaluation and
Management (E/M) service, even if the E/M service is billed with modifier 25.
New patient visits
HCA pays one new patient visit, per client, per provider or group practice in a three-year period.
Note: A new patient is one who has not received any professional services from
the physician (or qualified health care professional) or another physician (or
qualified health care professional) of the exact same subspecialty who belongs to
the same group practice, within the past three years.
An established patient has received professional services from the physician (or
qualified health care professional) or another physician (or qualified health care
professional) in the same group and the same specialty within the prior three
years.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
52
Established patient visits
(CPT code 99211)
When billing HCA for CPT code 99211, at a minimum, the client’s record must be noted with
the reason for the visit and the outcome of the visit. The note must be signed and dated (with
title) by the qualified health care professional who provided the service.
Nursing facility services
HCA allows two physician visits per month for a client residing in a nursing facility or an
intermediate care facility. Nursing facility discharges (CPT codes 99315 and 99316) are not
included in the two-visit limitation. HCA pays for one nursing facility discharge per client, per
stay.
Note: The two physician visits per month limit does not apply to pulmonologists
or their designee that are seeing clients who are ventilator and/or tracheostomy
dependent and residing in the respiratory care unit of a designated ventilator
weaning nursing facility. For these clients, the physician visit limit is five per
month.
Pre-operative visit before a client receives a dental service
under anesthesia
HCA allows one pre-operative evaluation and management (E/M) visit by the primary care
physician, per client, to provide medical clearance before the client receives the dental service
under anesthesia. Bill using the appropriate dental diagnosis codes as the primary diagnosis
along with the appropriate pre-op diagnosis codes as the secondary diagnosis.
Submit claims to the appropriate medical insurer (fee-for-service or the managed care
organization).
Physical examination - clients of the DSHS’ Developmental
Disabilities Administration
HCA allows one physical examination per client, per 12 months for clients of DSHS’
Developmental Disabilities Administration (DDA) as identified in ProviderOne. Use HCPCS
code T1023 with modifier HI and ICD diagnosis code Z13.40, Z13.41, Z13.42, Z13.49, or
Z13.89 to bill for an examination.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
53
Office visit related to acamprosate, naltrexone,
buprenorphine/naloxone
HCA will cover medication for opioid use disorder products for the treatment of substance use
disorders as an office-based therapy. The pharmacy will continue to require prior authorization
for some medications. For coverage details, see the Apple Health (Medicaid) drug coverage
criteria webpage.
HCA pays for office visits related to acamprosate (Campral®), naltrexone (ReVia®), naltrexone
(Vivitrol®) or buprenorphine.
Buprenorphine/naloxone (Suboxone®): HCA pays for office visits related to
buprenorphine/naloxone (Suboxone®). Clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care
organization (MCO) must contact their MCO for information regarding their coverage.
Acamprosate and oral naltrexone when prescribed for medication for opioid use disorder are
covered without prior authorization.
Coverage for naltrexone injections
HCA will cover naltrexone (Vivitrol®) injections for clients who have a diagnosis of moderate
to severe opioid or alcohol use disorder. See the Apple Health (Medicaid) drug coverage criteria
webpage.
Aged, Blind, or Disabled (ABD) Evaluation
Services
Effective for claims with dates of service on and after November 1, 2015, providers must be
enrolled with ProviderOne to claim and receive payment for ABD Evaluation Services. See the
Department of Social and Health Services’ (DSHS) Medical evaluation and diagnostic
procedures webpage.
Medical evidence reimbursements are solely for the cost of obtaining medical evidence of an
impairment that limits work activity, and for the purposes of an ABD disability determination.
See the DSHS Medical evidence requirements and reimbursements webpage.
For information regarding reimbursement for psychological evaluations and testing, see the
DSHS Community Services Division (CSD) Mental incapacity evaluation services webpage.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
54
Behavior change intervention - tobacco/nicotine
cessation
Tobacco/nicotine cessation, which can include free counseling, nicotine replacement therapy
(NRT), and prescription drugs, represents a major advancement in public health for Washington
State. Below is a brief overview of the way the benefit works and the services available for
clients in HCA fee-for-service program. Clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care
organization (MCO) must contact their MCO for information regarding the tobacco/nicotine
cessation benefit.
Services available
The following services are available:
1. Referral to the toll-free Washington State Tobacco Quitline for telephone counseling and
follow-up support calls for clients age 13 and older. When a client is receiving counseling
from the Quitline, the Quitline may recommend a tobacco/nicotine cessation prescription
for the client.
2. Nicotine replacement products and prescription drugs to promote tobacco/nicotine
cessation with a prescription, prescribed by a provider with prescriptive authority, when
submitted to a pharmacy
Washington State Tobacco Quitline
800-QUIT-NOW (1-800-784-8669) English
855-DEJELO-YA (1-855-335-3569) Spanish
1-877-777-6534 TTY Line & Video Relay

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
55
Client eligibility
• All Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) clients are eligible for tobacco/nicotine
cessation services through the Quitline.
• Clients eligible for the Alien Emergency Medical (AEM) program or enrolled in the
Family Planning Only – Pregnancy Related program or Family Planning Only program
(formerly referred to as TAKE CHARGE) are eligible for some of the above mentioned
services; however, these clients are not eligible for prescription drugs and
tobacco/nicotine cessation services provided by their primary care provider. These clients
qualify for tobacco/nicotine cessation services provided by the Department of Health
Tobacco Quitline.
Payment for a tobacco/nicotine cessation referral
HCA will pay a provider for a tobacco/nicotine cessation referral (T1016) when all of the
following are met:
• The client is eligible.
• The referral is billed with an appropriate ICD diagnosis.
This service may be provided in combination with another service or evaluation management
office visit within the provider’s scope of practice.
Tobacco/nicotine cessation referral for an evaluation for a
tobacco/nicotine cessation prescription
HCA pays the prescriber for a tobacco/nicotine cessation referral (T1016) for an evaluation for a
tobacco/nicotine cessation prescription when all of the following are met:
• The client is eligible.
• The referral is billed with the appropriate ICD diagnosis codes.
• An evaluation is done for a tobacco/nicotine cessation prescription, with or without the
client present.
• The referral is not billed in combination with an evaluation and management office visit.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
56
Additional information:
• Call HCA toll-free at 800-562-3022.
• Visit Washington State Department of Health’s Tobacco Quitline.
• Visit Secondhand Smoke.
Tobacco/nicotine cessation for pregnant clients
HCA pays for face-to-face counseling for tobacco/nicotine cessation for pregnant clients.
Tobacco/nicotine cessation counseling complements the use of prescription and nonprescription
tobacco/nicotine cessation products. These products are also covered by Medicaid.
Pregnant clients can receive provider-prescribed nicotine replacement therapy directly from a
pharmacy and can obtain prescription medications for tobacco/nicotine cessation without going
through the Quitline.
Face-to-face visit requirements for pregnant women
Providers must document the client’s pregnancy status and estimated date of confinement in the
medical record. Additionally, the provider must establish and document the client’s motivation to
quit tobacco/nicotine use and provide an appropriate intervention based on client’s readiness to
change.
Provider types for providing face-to-face tobacco/nicotine
cessation counseling for pregnant women
Office-based practitioners (physicians, advanced registered nurse practitioners (ARNPs),
physician-assistants-certified (PA-Cs), and naturopathic physicians), psychologists, pharmacists,
certified nurse-midwives (CNM), and licensed midwives (LM).
Benefit limitations for providing face-to-face
tobacco/nicotine cessation counseling for pregnant women
A cessation counseling attempt occurs when a qualified physician or other Medicaid-recognized
practitioner determines that a beneficiary meets the eligibility requirements and initiates
treatment with a cessation counseling attempt.
Face-to-face cessation counseling attempts are defined and limited as follows:
• HCA allows two tobacco/nicotine cessation counseling attempts every 12 months.
• An attempt is defined as up to four tobacco/nicotine cessation counseling sessions.
• HCA covers one face-to-face tobacco/nicotine cessation counseling session per client, per
day.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
57
This limit applies to the client regardless of the number of providers a client may see for tobacco
cessation. Providers can request a limitation extension by submitting a request to HCA.
Documentation requirements
Keep patient record information on file for each Medicaid patient for whom a tobacco/nicotine
cessation counseling claim is made. Medical record documentation must include standard
information along with sufficient patient history to adequately demonstrate that Medicaid
coverage conditions were met. The provider must keep written documentation in the client’s file
for each face-to-face tobacco/nicotine cessation counseling session for pregnant women.
Documentation must include the client’s EDC.
Diagnosis codes should reflect that the client is pregnant and has a tobacco/nicotine use disorder.
Billing codes
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Comments
99407
Behav chng smoking > 10 min
(for pregnant clients only)
See Benefit limitations for
providing face-to-face
tobacco/nicotine cessation
counseling for pregnant
women.
Substance use disorder treatment
HCA reimburses for buprenorphine/naloxone when administered or dispensed in an opioid
treatment program (OTP). The OTP must be Department of Health (DOH)-certified and have a
current certification on file with HCA. Before billing for this service, the OTP must submit a
copy of their DOH certification and their NPI number to HCA. Mail or fax certification to:
Provider Enrollment
PO Box 45562
Olympia, WA 98504-5562
Fax: 360-725-2144
Clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization (MCO) must contact their
MCO for information regarding their coverage.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
58
How to bill for combination therapy
Providers must bill according to the actual tablet strength dispensed and not the dose given. For
example, if dispensing a 10mg dose as a 1-2mg tablet and 1-8mg tablet, bill one unit of J0572
and 1 unit of J0574. You would not use J0575. For a 16mg dose, you would bill 2 units of J0574.
The J0575 should only be used when dispensing a tablet strength greater than 10mg.
HCA reimburses the following codes. For rates, see the Physician-related/professional services
or Professional administered drugs fee schedules.
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Limitation
Restricted to ICD Dx and/or Dosing
J0572
Buprenorphine/naloxone,
Oral, less than or equal to 3 mg
buprenorphine
J0573
Buprenorphine/naloxone,
Oral, greater than 3 mg, but less than or
equal to 3.1 to 6 mg
J0574
Buprenorphine/naloxone
Oral, greater than 6 mg, but less than or
equal to 10 mg buprenorphine
J0575
Buprenorphine/naloxone
Oral, greater than 10 mg buprenorphine
Note: HCA considers film to be included as orally administered buprenorphine/naloxone.
How to bill for monotherapy
All monotherapy must be given only as a witnessed dose. HCA does not reimburse for carry
medication for monotherapy. Use the following code:
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Limitation
Restricted to ICD Dx and/or Dosing
J0571
Buprenorphine
Oral, 1 mg, or J0592 Injection,
buprenorphine hydrochloride, 0.1 mg
Note: HCA considers film to be included as orally administered buprenorphine.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
59
Collaborative care model guidelines
(WAC 182-531-0425)
Collaborative care
The following are Washington State Health Care Authority guidelines for practicing a
Collaborative Care Model (CoCM).
Collaborative care is a specific type of integrated care developed at the University of
Washington where medical providers and behavioral health providers work together to address
behavioral health conditions, including mental health conditions and substance use disorders.
When behavioral health problems are not effectively treated, this can impair self-care and
adherence to treatments, and as a result are associated with poor health outcomes and increased
mortality.
Psychiatric collaborative care model
The Collaborative Care Model (CoCM) is a model of behavioral health integration that enhances
“usual” primary care by adding two key services: care management support for clients receiving
behavioral health treatment, and regular psychiatric or board-certified addiction medicine
consultation with the primary care team, particularly regarding clients whose conditions are not
improving.
Collaborative care is provided monthly for an episode of care that ends when targeted treatment
goals are met or there is failure to attain targeted treatment goals, culminating in referral to
behavioral health specialty care, or there is a break in episode (no collaborative care services for
six consecutive months).
Eligible behavioral health conditions include, but are not limited to, substance use disorders,
including opioid use disorder, anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and
depression that are being treated by the billing provider and, in the clinical judgment of the
provider, warrant enrollment in CoCM services.
There are five core principles to CoCM developed in 2011 in consultation with a group of
national experts in integrated behavioral health care with support from The John A. Hartford
Foundation, The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, HCA for Healthcare Research and Quality,
and the California HealthCare Foundation.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
60
Core principles
Patient-centered team care
Primary care and behavioral health providers collaborate with shared care plans that incorporate
patient goals. The ability to get both physical and behavioral health care at a familiar location is
comfortable to patients and reduces duplicate assessments. Increased patient engagement
oftentimes results in a better health care experience and improved patient outcomes.
The treating medical provider leads the care. The treating medical provider prescribes all
medications, including those recommended by the psychiatric consultant. The team structure in
CoCM includes the following team members. These team members are required to be part of the
care in order to be reimbursed for CoCM.
• Treating (Billing) Medical Provider: A physician and/or non-physician practitioner
(MD, ARNP, ND, DO); typically primary care, but may be of another specialty (e.g.,
cardiology, oncology). This provider leads the care and prescribes all medications,
including those recommended by the psychiatric consultant.
• Behavioral Health Care Manager: A designated licensed professional with formal
education or specialized training in behavioral health (including social work, nursing, or
psychology), working under the oversight and direction of the treating medical provider.
• Psychiatric Consultant: A medical professional trained in psychiatry and qualified to
prescribe the full range of psychotropic medications. This may be a board-certified
addiction medicine provider or an addiction psychiatrist when the client has a substance
use disorder.
• Beneficiary: The beneficiary is the patient who is a member of the care team.
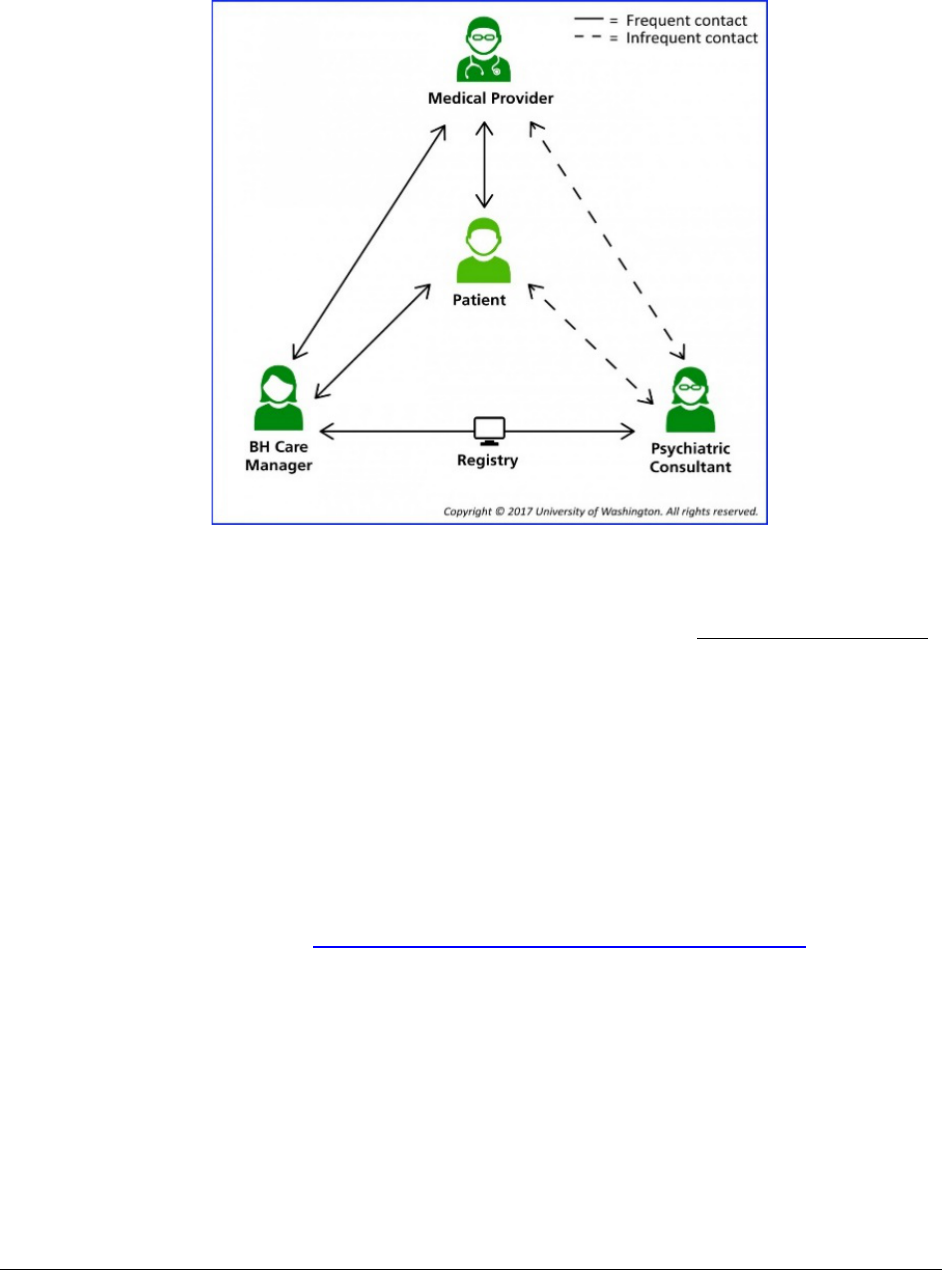
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
61
The following visual was developed by the University of Washington to demonstrate the team
structure and support that surrounds the client through CoCM:
Measurement-based treatment to target
A client’s treatment plan must clearly articulate personal goals and target clinical outcomes that
are routinely measured by using a validated clinical rating scale like the PHQ-9 depression scale.
Treatment adjustments are made for clients not improving as expected under their current
treatment plan. Treatment adjustments are made until clients achieve treatment goals or care is
discontinued due to referral or clients not participating.
Population-based care
The data-driven workflow to support CoCM requires the care team to use a registry to track
clients on a CoCM caseload and monitor individual client’s clinical outcomes over time. A
registry can be used in conjunction with the practice’s electronic health records (EHR) if not
built into it. The Advancing Integrated Mental Health Solutions (AIMS) Center offers registry
tools for use in conjunction with an EHR. Additional information is located in the AIMS
Center’s implementation guide: Identify a behavioral health patient tracking system.
Evidence-based treatment
Clients are offered evidence-based treatments to help meet treatment goals. These include
medications and brief psychotherapy interventions such as behavioral activation, problem
solving treatment, and motivational interviewing.
Accountable care
Providers are accountable for the treatment of all clients referred to the program, including
quality of care and clinical outcomes for the clients managed under CoCM.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
62
Additional Information
The University of Washington has additional information on the implementation of CoCM and
has a variety of tools to learn more about CoCM and assess a provider’s readiness to implement
CoCM.
What to do next
Review the guidelines and requirements for reimbursement for CoCM and assess practice
readiness through the AIMS tools. If a practice is able to meet the requirements, complete
HCA’s Attestation for Collaborative Care Model form (HCA 13-0017) and send completed form
to:
Provider Enrollment
PO Box 45562
Olympia, WA 98504-5562
Or fax to 360-725-2144, Attn: Provider Enrollment
Or email [email protected]
See Where can I download HCA forms? The treating (billing) medical provider submits the
attestation.
Once the attestation is received and reviewed, an indicator will be placed in the Medicaid billing
system, ProviderOne, allowing reimbursement for fee-for-service and notification will be
provided to all HCA-contracted managed care organizations. Provider Enrollment will contact
the provider if there are any issues with their attestation form.
If at any time a practice no longer meets the core principles and specific function requirements to
practice CoCM, notify HCA by calling Provider Enrollment at 360-725-2144. Providers are
subject to post pay review to ensure the CoCM model requirements are being met. If the CoCM
requirements were not met at the time of billing, recoupment of payment may occur.
Note: If a practice bills under one base location NPI and has several servicing
locations, each servicing location must submit an attestation to provide and be
reimbursed for CoCM service.
For general instructions on billing, please see the ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide. For
reimbursement rates see the Physician-related/professional health care services fee schedule.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
63
Psychiatric Collaborative Care Model (CoCM) Codes
Purpose:
This matrix is a tool to describe the requirements for selected codes. Licensed health care professionals
use these codes to bill only for those services that are within their scope of licensure as defined by the
Department of Health. Psychiatric CoCM typically is provided by a primary care team consisting of a
treating medical provider and a care manager who work in collaboration with a psychiatric consultant,
such as a psychiatrist or a psychiatric ARNP. See Collaborative care model guidelines. Care is directed by
the primary care team and includes structured care management with regular assessments of clinical status
using validated tools and modification of treatment as appropriate. Payments are based on services
provided by all team members. CoCM practices must meet model requirements as defined by CMS and
submit an attestation to HCA to be eligible for reimbursement. Additional information and introductory
resources around training for practice staff are available from the AIMS Center (Advancing Integrated
Mental Health Solutions.
99492– Initial psychiatric collaborative care
management, first 70 minutes in the first calendar
month of behavioral health care manager activities,
in consultation with a psychiatric consultant, and
directed by the treating physician or other qualified
health care professional.
With the following required elements:
• Outreach to and engagement in treatment of a
client directed by the treating physician or other
qualified health care professional
• Initial assessment of the client, including
administration of validated rating scales, with
the development of an individualized treatment
plan
• Review by the psychiatric consultant with
modifications of the plan if recommended
• Entering client in a registry and tracking client
follow-up and progress using the registry, with
appropriate documentation, and participation in
weekly caseload consultation with the
psychiatric consultant
• Provision of brief interventions using evidence-
based techniques such as behavioral activation,
motivational interviewing, and other focused
treatment strategies
Documentation:
The provider must:
• Use a registry to track the client’s clinical
outcomes.
• Use a validated clinical rating scale.
• Ensure the registry is used in conjunction with
the practice’s electronic health records (EHR).
• Include a plan of care.
• Identify outcome goals of the treatments.
Billing: First 70 minutes in the first calendar
month of behavioral health care manager activities
in consultation with a psychiatric consultant, and
directed by the treating physician or other
qualified health care professional.
Provider Type: Billable by medical provider with
collaborative care indicator (e.g. ARNP, DO, MD,
ND)
Place of Service: No limitations on the place of
service. Exception: Federally Qualified Health
Centers (FQHC’s) and Rural Health Clinics
(RHC’s) bill for CoCM using a specific code-see
code G0512 for details.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
64
Limitations:
• 99492 is used only for initial month of an
episode of care
• An episode of care starts the first calendar
month of behavioral health care manager
activities
• A new episode of care must be initiated after 6
month lapse in services
• If less than a 6 month lapse in service and new
episode of care is to be initiated, EPA (link to
end of this doc where it gives more EPA info) is
required
99493– Subsequent psychiatric collaborative care
management, first 60 minutes in the subsequent
month of behavioral health care manager activities,
in consultation with a psychiatric consultant, and
directed by the treating physician or other qualified
health care professional.
With the following required elements:
• Tracking client follow-up and progress using
the registry, with appropriate documentation
• Participation in weekly caseload consultation
with the psychiatric consultant
• Ongoing collaboration with and coordination
of the patient’s mental health care with the
treating physician or other qualified health
care professional and any other treating mental
health providers
• Additional review of progress and
recommendations for changes in treatment, as
indicated, including medications, based on
recommendations provided by the psychiatric
consultant
• Provision of brief interventions using
evidence-based techniques such as behavioral
activation, motivational interviewing, and
other focused treatment strategies
• Monitoring of client outcomes using validated
rating scales and relapse prevention planning
with clients as they achieve remission of
symptoms and/or other treatment goals and are
prepared for discharge from active treatment.
• Clients must have one face-to-face visit at
least every three months.
Documentation:
Documentation must include:
• Clients progress towards goals
• Updated results of the validated clinical
rating scales being utilized
• Modifications to treatment as appropriate
Billing: First 60 minutes in the subsequent
calendar months following the initial calendar
month of behavioral health care manager activities
in consultation with a psychiatric consultant, and
directed by the treating physician or other qualified
health care professional.
Provider Type: Billable by medical provider with
collaborative care indicator (e.g. ARNP, DO, MD,
ND)
Place of Service: No limitations on the place of
service. Exception: Federally Qualified Health
Centers (FQHC’s) and Rural Health Clinics
(RHC’s) bill for CoCM using a specific code-see
code G0512 for details.
Limitations:
• Bill once per month
• Billed for subsequent calendar months following
the initiation of an episode of CoCM services
• May bill 5 months of subsequent care for each
episode of care initiated without PA or EPA (see
Additional billing information)
• Requires EPA to continue the episode after 6
th
month (see Additional billing information)
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
65
• Clients must have a minimum of one face-to-
face visit every three months with the directing
treating physician or other qualified health care
professional
• Requires PA after 12 months (see Additional
billing information)
• A new episode of care must be initiated after 6
month lapse in services and include an initial
assessment and a treatment plan
• EPA is required if less than a 6 month lapse in
service and new episode of care is to be initiated
(see Additional billing information).
99494– Initial or subsequent psychiatric
collaborative care management, each additional 30
minutes in a calendar month of behavioral health
care manager activities, in consultation with a
psychiatric consultant, and directed by the treating
physician or other qualified health care professional.
Documentation:
Documentation must include:
• Client’s progress towards goals
• Updated results of the validated clinical rating
scales being used
• Modifications to treatment as appropriate
Billing: Additional 30 minute units of behavioral
health care manager activities in consultation with a
psychiatric consultant, and directed by the treating
physician or other qualified health care professional.
Provider Type: Billable by medical provider with
collaborative care indicator (e.g. ARNP, DO, MD,
ND)
Place of Service: No limitations on the place of
service. Exception: Federally Qualified Health
Centers (FQHC’s) and Rural Health Clinics
(RHC’s) bill for CoCM using a specific code-see
code G0512 for details.
Limitations:
• Use for additional 30 minutes of behavioral health
care manager activities
• 99494 to be used with 99492 or 99493
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
66
FQHC & RHC
G0512- Psychiatric Collaborative Care Model
services: Minimum of 60 minutes per calendar
month
Service elements provided by CoCM team for
CoCM services must include:
• Outreach and engagement of clients
• Initial assessment, including administration of
validated scales and resulting in a treatment plan
• A minimum of one face-to-face visit every three
months with the directing treating physician or
other qualified health care professional
• Entering clients into a registry for tracking client
follow-up and progress
• Participation in weekly caseload review with
psychiatric consultant and modifications to
treatment, if recommended
• Provision of brief interventions using evidence-
based treatments such as behavioral activation,
problem-solving treatment, and other focused
treatment activities
• Tracking client follow-up and progress using
validated rating scales
• Ongoing collaboration and coordination with
treating FQHC and RHC providers
• Relapse prevention planning and preparation for
discharge from active treatment
Documentation:
The provider must:
• Use a registry to track the clients clinical
outcomes
• Use a validated clinical rating scale
• Ensure the registry is used in conjunction
with the practice’s EHR
• Include a plan of care
• Identify outcome goals of the treatments
Billing: A minimum of 60 minutes in any month of
behavioral health care manager activities in
consultation with a psychiatric consultant, and
directed by the treating physician or other qualified
health care professional.
Provider Type: Billable by medical provider in a
FQHC or RHC with collaborative care indicator
(e.g. ARNP, DO/MD/ND)
Place of Service: Federally Qualified Health
Centers (FQHC’s) and Rural Health Clinics
(RHC’s)
Limitations:
• This code does not qualify for an encounter
• Once per month
• May bill 5 months of subsequent care for each
episode of care initiated without PA or EPA
• EPA is required to continue the episode after 6
th
month
• PA is required after 12 months following
initiation of episode
• A new episode of care must be initiated after 6
month lapse in services and include an initial
assessment and development of a treatment plan
• If less than a 6 month lapse in service and new
episode of care is to be initiated, EPA is
required

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
67
Additional billing information
Use expedited prior authorization (EPA) in the following circumstances:
• For additional services beyond the initial 6 months of CoCM services, an EPA is required.
See EPA #870001428.
• For starting a new episode of care 99492 or G0512 with less than a 6 month lapse in
services, an EPA is required. See EPA #870001427.
• If the client does not meet the EPA criteria, prior authorization (PA) is required.
Use prior authorization (PA) in the following circumstance:
• After 12 months of CoCM services, PA is required.
Note: A psychiatric consultant working in the CoCM model may also provide
traditional services directly to the client in the same month, but may not bill for the
same time using multiple codes. The time spent on these activities for services
reported separately may not be included in the services reported using time applied
to 99492, 99493, 99494 and G0512.
Health and behavior codes
HCA covers health and behavior codes when provided by a physician or licensed behavioral
health provider. Providers use health and behavior codes when the primary diagnosis is medical
and the provider is addressing the behavioral, emotional, cognitive, and social factors important
to the prevention, treatment or management of physical health problems. The focus of the
assessment is not mental health but on the biopsychosocial factors important to physical health
problems and treatments.
Use modifier HE to indicate the service is not part of a substance use disorder (SUD) or
maternity support service (MSS). If these health and behavior codes are billed with a mental
health diagnosis and the HE modifier, HCA will deny the claim.
CPT Code
Short description
96156
Hlth bhv assmt/reassessment
96158
Hlth bhv ivntj indiv 1st 30
96159
Hlth bhv ivntj indiv ea addl
96164
Hlth bhv ivntj grp 1st 30
96165
Hlth bhv ivntj grp ea addl
96167
Hlth bhv ivntj fam 1st 30
96168
Hlth bhv ivntj fam ea addl

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
68
CPT Code
Short description
96170
Hlth bhv ivntj fam wo pt 1st
96171
Hlth bhv ivntj fam w/o pt ea
For additional information on code descriptions and billing for health and behavior codes, visit
the Behavioral health and recovery webpage.
Children's primary health care
(CPT codes 99201-99215)
HCA pays a higher payment rate for primary health care performed in the office setting (CPT
codes 99201-99215) for children age 20 and younger. These are the only services that are paid at
the higher rate.
If a child is younger than 60 days of age and has not been issued an individual ProviderOne
Client ID, use the mother's ProviderOne Client ID, and put "SCI=B" in the claim notes field. Put
the child’s name, gender, and birth date in the client information fields. If the mother is enrolled
in an HCA-approved managed care organization (MCO), newborns will be enrolled in the same
MCO as their mother.
Pediatric primary care rate increase
A primary care provider rate increase is available for vaccine administration and certain pediatric
care services for clients age 18 and younger.
The rate increase is effective for dates of service beginning October 1, 2018 and ending no
sooner than June 30, 2020. Physician and non-physician practitioners are eligible for the
increase.
See the Pediatric primary care rate increase website for more information. To view the Enhanced
pediatric fee schedule, see HCA’s Provider billing guides and fees schedules webpage. Scroll
down to and select “Physician-related/professional services.”
Note: Providers serving clients covered by an HCA-contracted managed care
organization (MCO) should contact the individual MCO for rate information.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
69
Consultations
TB treatment services
Performed by professional providers – office visits only
The E/M codes 99201-99215 are for office visits only, and must be billed for professional
providers such as physicians (or nursing staff under a physician’s supervision), Advanced
Registered Nurse Practitioners (ARNPs), and Physician Assistants (PAs).
Performed by professional providers – in client’s home, see home services.
Performed by nonprofessional providers – office visits and in client’s home
Health departments billing for TB treatment services provided by nonprofessional providers in
either the client’s home or in the office must bill using HCPCS code T1020 (personal care
services). Do not bill the initial visit with a modifier. Follow-up visits must be billed using
T1020 with modifier TS (follow-up services modifier). Use the appropriate ICD diagnosis code.
Critical care
(CPT codes 99291-99292)
(WAC 182-531-0450)
Note: For neonatal or pediatric critical care services, see Neonatal intensive care
unit (NICU)/Pediatric intensive care unit (PICU).
Critical care is the direct delivery and constant attention by a provider(s) for a critically ill or
critically injured patient. A critical illness or injury acutely impairs one or more vital organ
systems such that there is a high probability of imminent or life threatening deterioration in the
patient’s condition.
Critical care involves high complexity decision making to assess, manipulate, and support vital
system function(s); to treat single or multiple vital organ system failure; and/or to prevent further
life threatening deterioration of the patient’s condition.
Providing medical care to a critically ill, injured, or postoperative patient qualifies as a critical
care service only if both the illness or injury and the treatment being provided meet the above
requirements. Critical care is usually, but not always, given in a critical care area, such as the
coronary care unit, intensive care unit, pediatric intensive care unit, respiratory care unit, or the
emergency care facility. Services for a patient who is not critically ill but happens to be in a
critical care unit are reported using other appropriate E/M codes.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
70
Billing for critical care
When billing for critical care, providers must bill using CPT codes 99291-99292:
• For the provider’s attendance during the transport of critically ill or critically injured
clients age 25 months or older to or from a facility or hospital.
• To report critical care services provided in an outpatient setting (e.g., emergency
department or office), for neonates and pediatric clients up through 24 months.
• To report the total duration of time spent by a physician providing critical care services to
a critically ill or critically injured client, even if the time spent by the physician on that
date is not continuous. For any given period of time spent providing critical care services,
physicians must devote their full attention to the client and cannot provide services to any
other patient during the same period of time.
Note: Surgery, stand-by, or lengthy consultation on a stable client does not
qualify as critical care.
Where is critical care performed?
Critical care is usually performed in a critical care area of a hospital, such as a(n):
• Coronary care unit.
• Intensive care unit.
• Respiratory care unit.
• Emergency care facility.
What is covered?
HCA covers:
• A maximum of three hours of critical care per client, per day.
• Critical care provided by the attending physician who assume(s) responsibility for the
care of a client during a life-threatening episode.
• Critical care services provided by more than one physician if the services involve
multiple organ systems (unrelated diagnosis). However, in the emergency room, payment
for critical care services is limited to one physician.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
71
The following services (with their corresponding CPT codes) are included in critical care.
Do not bill these separately:
• Vascular access procedures (CPT codes 36000, 36410, 36415, 36591, and 36600)
• Gastric intubation (CPT codes 43752 and 43753)
• Chest X-rays (CPT codes 71010, 71015, and 71020)
• Temporary transcutaneous pacing (CPT codes 92953)
• The interpretation of cardiac output measurements (CPT codes 93561-93562)
• Ventilator management (CPT codes 94002-94004, 94660, and 94662)
• Pulse oximetry (CPT codes 94760 and 94762)
• Blood gases, and information data stored in computers (e.g., ECGs, blood pressures,
hematologic data) (CPT code 99090)
Note: CPT code 43752 may be billed separately when it is the only procedure
code billed.
Domiciliary, rest home, or custodial care services
CPT codes 99304-99318 are not appropriate E/M codes for use in place of service 13 (Assisted
Living) or 14 (Group Home). Providers must use CPT codes 99324-99328 or 99334-99337 for E/M
services provided to clients in these settings.
Emergency department services
Emergency physician-related services
(CPT codes 99281-99285) (WAC 182-531-0500)
• For services performed by the physician assigned to, or on call to, the emergency
department, bill HCA using CPT codes 99281-99285.
Note: For multiple emergency room (ER) visits on the same day with related
diagnoses, the time(s) of the additional visit(s) must be noted in the Claim Note
section of the electronic claim.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
72
• HCA does not pay emergency room physicians for hospital admissions (e.g., CPT codes
99221-99223) or after-hours services (e.g., CPT codes 99050 and 99053).
• Physicians who perform emergency room services must not bill modifier 54 when billing
HCA for surgical procedures.
• Physicians who provide only the follow-up services for minor procedures performed in
emergency departments must bill the appropriate level of office visit code without
modifier 55.
• HCA follows Medicare’s policy to not pay emergency room providers for the following
procedure codes: CPT codes 96360-96361 or 96365-96368.
Habilitative services
Habilitative services are those medically necessary services provided to help a client partially or
fully attain or maintain developmental age-appropriate skills that were not fully acquired due to a
congenital, genetic, or early-acquired health condition. Such services are required to maximize
clients’ ability to function in their environment.
For those clients in the expanded population and covered by the Alternative Benefit Plan (ABP)
only, HCA covers prosthetic and orthotic (P&O) devices and supplies, medical equipment and
supplies, and outpatient therapy (physical, occupational, and speech) to treat one of the
qualifying conditions listed in HCA’s Habilitative Services Billing Guide, under Client
Eligibility.
Billing for habilitative services
Habilitative services must be billed using one of the qualifying diagnosis codes listed in HCA’s
Habilitative Services Billing Guide in the primary diagnosis field on the claim.
Neurodevelopmental Centers, Outpatient Hospital Services, Physician-Related Services/Health
Care Professional Services (includes Audiology), Home Health Services, and Outpatient
Rehabilitation providers who provide physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech language
pathology to treat a condition that qualifies for habilitative services, for a client enrolled in ABP,
must bill for these therapies according to HCA’s Habilitative Services Billing Guide.
Services and equipment related to any of the following programs must be billed using their
specific billing guide:
• Medical Equipment and Supplies
• Prosthetic/Orthotic Devices and Supplies
• Complex Rehabilitation Technology

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
73
All other program requirements are applicable to a habilitative service and should be followed
unless otherwise directed (e.g., prior authorization).
Home services
Home evaluation and management
HCA pays for home evaluation and management (CPT codes 99341-99350) only when services are
provided in place of service 12 (home).
TB treatment services – performed by professional
providers – in client’s home
When billing for TB treatment services provided by professional providers in the client’s home,
Health Departments may also bill CPT codes 99341 and 99347.
For TB treatment services performed by nonprofessional providers in client’s home, see TB
treatment services for nonprofessional providers – office or client’s home.
Hospital inpatient and observation care services
(CPT codes 99217-99239) (WAC 182-531-0750)
Inpatient admissions must meet intensity of service/severity of illness criteria for an acute
inpatient level of care. Admission status changes must be noted in the client’s chart.
Admission status
Admission status is a client’s level of care at the time of admission. Some examples of typical
types of admission status are: inpatient, outpatient observation, medical observation, outpatient
surgery or short-stay surgery, or outpatient (e.g., emergency room).
Admission status is determined by the admitting physician or practitioner. Continuous
monitoring, such as telemetry, can be provided in an observation or inpatient status; consider
overall severity of illness and intensity of service in determining admission status rather than any
single or specific intervention. Specialty inpatient areas (including intensive care unit or critical
care unit)) can be used to provide observation services. Level of care, not physical location of the
bed, dictates admission status.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
74
Change in admission status
A change in admission status is required when a client’s symptoms/condition and/or treatment
does not meet medical necessity criteria for the level of care the client is initially admitted to.
The documentation in the client’s medical record must support the admission status and the
services billed.
HCA does not pay for:
• Services that do not meet the medical necessity of the admission status ordered.
• Services that are not documented in the hospital medical record.
• Services greater than what is ordered by the physician or practitioner responsible for the
client’s hospital care.
Inpatient to outpatient observation
The attending physician or practitioner may make an admission status change from inpatient to
outpatient observation when:
• The attending physician/practitioner and/or the hospital’s utilization review staff
determine that an inpatient client’s symptoms/condition and treatment do not meet
medical necessity criteria for an acute inpatient level of care and do meet medical
necessity criteria for an observation level of care.
• The admission status change is made prior to, or on the next business day following,
discharge.
• The admission status change is documented in the client’s medical record by the
attending physician or practitioner. If the admission status change is made following
discharge, the document must:
Be dated with the date of the change.
Contain the reason the change was not made prior to discharge (e.g., due to the
discharge occurring on the weekend or a holiday).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
75
Outpatient observation to inpatient
The attending physician or practitioner may make an admission status change from outpatient
observation to inpatient when:
• The attending physician/practitioner and/or the hospital’s utilization review staff
determine that an outpatient observation client’s symptoms/condition and treatment meet
medical necessity criteria for an acute inpatient level of care.
• The admission status change is made prior to, or on the next business day following,
discharge.
• The admission status change is documented in the client’s medical record by the
attending physician or practitioner. If the admission status change is made following
discharge, the documentation must:
Be dated with the date of the change.
Contain the reason the change was not made prior to discharge (e.g., due to the
discharge occurring on the weekend or a holiday).
Inpatient or outpatient observation to outpatient
The attending physician or practitioner may make an admission status change from inpatient or
outpatient observation to outpatient when:
• The attending physician/practitioner and/or the hospital’s utilization review staff
determine that an outpatient observation or inpatient client’s symptoms/condition and
treatment do not meet medical necessity criteria for observation or acute inpatient level
of care.
• The admission status change is made prior to, or on the next business day following,
discharge.
• The admission status change is documented in the client’s medical record by the
attending physician or practitioner. If the admission status change is made following
discharge, the documentation must:
Be dated with the date of the change.
Contain the reason the change was not made prior to discharge (e.g., due to the
discharge occurring on the weekend or a holiday).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
76
Outpatient surgery/procedure to outpatient observation or inpatient
The attending physician or practitioner may make an admission status change from outpatient
surgery/procedure to outpatient observation or inpatient when:
• The attending physician/practitioner and/or the hospital’s utilization review staff
determine that the client’s symptoms/condition and/or treatment require an extended
recovery time beyond the normal recovery time for the surgery/procedure and medical
necessity for outpatient observation or inpatient level of care is met.
• The admission status change is made prior to, or on the next business day following,
discharge.
• The admission status change is documented in the client’s medical record by the
attending physician or practitioner. If the admission status change is made following
discharge, the documentation must:
Be dated with the date of the change.
Contain the reason the change was not made prior to discharge (e.g., due to the
discharge occurring on the weekend or a holiday).
Note: During post-payment retrospective utilization review, HCA may determine the
chronic care management is not supported by documentation in the medical record. HCA
may consider payment made in this circumstance an overpayment and payment may be
recouped or adjusted.
Payment
HCA pays for:
• One inpatient hospital call per client, per day for the same or related diagnoses. HCA
does not pay separately for the hospital call if it is included in the global surgery
payment. (See Other surgical policies for information on global surgery policy.)
• Professional inpatient services (CPT codes 99221-99223) during the global surgery
follow-up period only if they are performed on an emergency basis and are unrelated to
the original surgery. Use modifier 24 to indicate that the service is unrelated to the
original surgery.
Note: HCA pays providers for CPT codes 99221-99223 for scheduled hospital
admissions during the follow-up period only when billed with a modifier 24.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
77
HCA does not pay for:
• A hospital admission (CPT codes 99221-99223) and a planned surgery billed in
combination. The hospital admission is included in the global fee for the surgery.
• Inpatient or observation care services [including admission and discharge services (CPT
codes 99234-99236) for stays of less than 8 hours on the same calendar date.
Other guidelines
• When a hospital admission (CPT codes 99221-99223) and an emergency surgery is billed
in combination, HCA will pay when there is a decision to do surgery, the provider has not
seen the client for this condition, and modifier 57 is used. This only applies to surgical
procedures with a 90-day global period.
• When a client is admitted for observation care for less than 8 hours and is discharged on
the same calendar date, providers must bill using CPT codes 99218-99220. HCA does not
pay providers separately for discharge services.
• When a client is admitted for observation care and is discharged on a different calendar
date, providers must bill using CPT codes 99218-99220 and observation discharge CPT
code 99217.
• When a client qualifies for an inpatient hospital admission and is discharged on a
different calendar date, providers must bill using CPT codes 99221-99233 and hospital
discharge day management CPT code 99238 or 99239.
• When a client qualifies for an inpatient hospital admission and is discharged on the same
calendar date, providers must bill using CPT codes 99234-99236. HCA does not pay
providers separately for hospital discharge day management services.
• Providers must satisfy the documentation requirements for both admission to and
discharge from, inpatient or observation care in order to bill CPT codes 99234-99236.
The length of time for observation care or treatment status must also be documented.
• When clients are fee-for-service (FFS) when admitted to a hospital and then enroll in an
HCA managed care organization (MCO) during the hospital stay, the entire stay for
physician services is paid FFS until the client is discharged. Enter the initial
hospitalization date in the appropriate field for the claim billing format. For billing
details, see the ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
78
Inpatient neonatal and pediatric critical care
Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)/Pediatric intensive care
unit (PICU)
(CPT codes 99468-99480)
(WAC 182-531-0900)
NICU/PICU care includes management, monitoring, and treatment of the neonate/infant
including respiratory, pharmacological control of the circulatory system, enteral and parenteral
nutrition, metabolic and hematological maintenance, parent/family counseling, case management
services, and personal direct supervision of the health care team’s activities.
HCA covers:
• One NICU/PICU service per client, per day.
• Intensive observation, frequent interventions, and other intensive services for neonates.
Use CPT code 99477 for initial hospital care, per day, when a neonate requires intensive
observation, frequent interventions and other intensive services. Providers may report
CPT 99460 and 99477 when two distinct services are provided on the same day, but must
use modifier 25 with CPT code 99460. Bill CPT code 99460 with modifier 25 when a
normal newborn is seen after an uneventful delivery and then later the infant develops
complications and is transferred to an intensive setting for observation, frequent
interventions, and other intensive services.
• NICU/PICU services when directing the care of a neonate/infant in a NICU/PICU. These
codes represent care beginning with the date of admission to the NICU/PICU.
Note: Once the infant is no longer considered critically ill, hospital care CPT
codes 99231-99233 or 99478-99480 must be used.
• Newborn resuscitation (CPT code 99464, 99465) in addition to NICU/PICU services.
• The provider’s attendance during the transport of critically ill or critically injured
pediatric clients 24 months of age or younger to or from a facility or hospital (CPT code
99466 or 99467).
• CPT codes 99291-99292 for critical care services provided in an outpatient setting when
the client is 24 months of age or younger.
The following services and the subsequent intensive, noncritical services (with their
corresponding CPT codes) are included in neonatal or pediatric critical care. Do not bill these
separately. Providers must follow the national CCI edits as this list is not exhaustive:
• Bladder catheterization (CPT codes 51701- 51702)

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
79
• Central (CPT code 36555) or peripheral vessel catheterization (CPT code 36000)
• Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) (CPT code 94660)
• Endotracheal intubation (CPT code 31500)
• Initiation and management of mechanical ventilation (CPT codes 94002-94004)
• Invasive or noninvasive electronic monitoring of vital signs, bedside pulmonary function
testing (CPT code 94375), and/or monitoring or interpretation of blood gases or oxygen
saturation (CPT codes 94760-94762)
• Lumbar puncture (CPT code 62270)
• Oral or nasogastric tube placement (CPT code 43752)
• Other arterial catheters (CPT codes 36140 and 36620)
• Umbilical arterial catheterization (CPT code 36660)
• Umbilical venous catheterization (CPT code 36510)
• Suprapubic bladder aspiration (CPT code 51100)
• Surfactant administration, intravascular fluid administration (CPT codes 96360, 96361,
90780, and 90781)
• Transfusion of blood components (CPT codes 36430 and 36440)
• Vascular punctures (CPT codes 36420 and 36600)
• Vascular access procedures (CPT codes 36400, 36405, and 36406)
Note: Procedure code 43752 may be billed separately when it is the only procedure
code billed.
Intensive (noncritical) low birth weight services
(CPT codes 99478-99480)
• Bill the appropriate procedure codes only once per day, per client.
• These codes represent care that begins subsequent to the admission date.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
80
Perinatal conditions
HCA covers professional services related to conditions originating in the perinatal period if all of
the following are met:
• The services are considered to be medically necessary and would otherwise be covered
by HCA.
• Professional services are provided in an inpatient hospital (place of service 21).
• ICD diagnosis codes are listed as the primary diagnosis.
• An admission date is included on the claim.
• There are 28 or fewer days between the patient’s date of birth and the admission date
listed on the claim.
For clients who transfer between facilities for services not otherwise available, or to a higher
level of care, the original date of admission must be used on the claim to represent a continuous
episode of care. For clients greater than 28 days of age, the appropriate ICD diagnosis codes
may be listed as the secondary rather than the primary diagnosis.
Mental health
For coverage and billing information for mental health services for children and adults, including
evidence-based medicine, evidence-based practice, research-based practice, and evidence-based
health care (collectively “EBM”), see HCA’s Mental Health Services Billing Guide.
Note: The reimbursement rate may differ depending on the provider’s education
level. See the Mental health services and the Physician-related/professional
services fee schedules for details.
Depression Screening
Structured Depression screening
HCA covers one structured depression screening each year for clients age 12 and older. When
billing HCA, use CPT code 96127 or 96160. If more frequent screening is needed, providers can
submit a limitation extension (LE) request to HCA. See Limitation extension (LE).
Caregiver/Maternal depression screening
• Caregiver/Maternal depression screening is required at well-child checkups for
caregivers/mothers of infants up to age six months. Use procedure code 96161with EPA
number 870001424 for fee-for-service (FFS) with the infant’s ProviderOne ID number.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
81
• Caregiver/maternal depression screening completed by the caregiver’s provider during
the six months postpartum and billed under the caregiver’s Provider One ID number. Use
procedure code 96160 with EPA number 870001424.
For further information, see the Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment
(EPSDT) Billing Guide and the Mental Health Services Billing Guide.
Services provided to an MCO client during BHO-approved
admissions
How do I bill the professional mental health services for an inpatient MCO
client?
HCA pays for psychiatric services provided by a psychiatrist, psychologist, or psychiatric ARNP
to an MCO client during the BHO-authorized admission. Expedited prior authorization is
required. See EPA #870001369 for coverage criteria. If these services are provided by any other
provider during a BHO-authorized admission, the services must be billed to the MCO.
Newborn care
(CPT 99460, 99461)
To assist providers in billing CPT codes with "newborn" in the description, HCA defines a
newborn as 28 days old or younger.
Newborn diagnosis codes are to be used as the primary diagnosis during the newborn 28-day
period. After 28 days and throughout the life of the patient, a newborn code may be used as an
additional diagnosis if the condition is still present.
HCA covers:
• One newborn evaluation per newborn when they are not discharged on the same day
using either CPT code 99460 for hospital or birthing center or CPT code 99461 for home
births.
• Subsequent hospital care (other than initial evaluation or discharge) using CPT code
99462.
• One newborn evaluation and discharge per newborn performed in the hospital or birthing
center on the same day using CPT code 99463.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
82
Billing for infants not yet assigned a ProviderOne client ID
Use the mother’s ProviderOne Client ID for a newborn if the infant has not yet been issued a
ProviderOne Client ID. Enter indicator SCI=B in the Comments section of the claim to indicate
that the mom’s ProviderOne Client ID is being used for the infant. Put the child’s name, gender,
and birthdate in the client information fields. When using a mom’s ProviderOne Client ID for
twins, triplets, etc., use the following claim indicators to identify the infant being treated:
SCI=BA for twin A, SCI=BB for twin B, and SCI=BC for a third infant in the case of triplets,
using a separate claim for each. Note: For a mother enrolled in an HCA managed care
organization (MCO), the MCO is responsible for providing medical coverage for the
newborn(s).
For more information on billing for newborns and for newborns who will be placed in foster
care, see the Inpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide.
Physician/Professional services
Does HCA pay for newborn screening tests?
Yes. The initial screening is typically billed through the hospital.
For newborns born at a birthing center or at home, the midwife or physician collects the blood
for the newborn screening and sends it to the Washington State Department of Health (DOH).
The midwife or physician may bill for the blood collection using the appropriate CPT® code.
DOH bills HCA for the newborn screening tests using HCPCS code S3620. HCA reimburses
only DOH for this service.
For subsequent screenings done in an outpatient setting, the provider may bill for blood
collection using the appropriate CPT® code.
The newborn screening panel includes tests for treatable disorders as determined by DOH. For
the most current list of tests included in the screening panel, visit DOH’s webpage.
Note: Newborn screening includes two tests for two different dates of service,
allowed once per newborn.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
83
Physicals for clients of DSHS’ Developmental
Disabilities Administration
HCA covers one physical every 12 months for clients of the Developmental Disabilities
Administration (DDA) within the Department of Social and Health Services. Use HCPCS code
T1023 with modifier HI and the appropriate ICD diagnosis code Z13.4 or Z13.89 to bill for an
annual exam.
Physician care plan oversight
(CPT codes 99375, 99378, and 99380) (WAC 182-531-1150)
HCA covers:
• Physician care plan oversight services once per client, per month.
A plan of care must be established by the home health agency, hospice, or nursing
facility.
The provider must perform 30 or more minutes of oversight services for the client
each calendar month.
HCA does not cover:
• Physician care plan oversight services of less than 30 minutes per calendar month (CPT
codes 99374, 99377, and 99379).
• Physician care plan oversight services provided by more than one provider during the global
surgery payment period, unless the care plan oversight is unrelated to the surgery.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
84
Physician supervision of a patient requiring complex and
multidisciplinary care modalities
HCA covers CPT codes 99339 and 99340 with prior authorization. For supervision services that
are less than 30 minutes, use code 99339; and for services exceeding 30 minutes, use code
99340. There is a unit limit of one unit of CPT 99339 or one unit of CPT 99340 per calendar
month. Claims are subject to post-payment review.
Clear documentation of care plan oversight is required by HCA, including:
• Time allocation.
• Care plans.
• Review of diagnostic reports and laboratory studies.
• Treatment-related communications with other health care professionals and caregivers.
• Adjustment of medical therapy.
CPT
Code
Short Description
99339
Individual physician supervision of a patient (patient not present) in home,
domiciliary or rest home requiring complex and multidisciplinary care modalities
involving regular physician development and/or revision of care plans, review of
subsequent reports of patient status, review of related laboratory and other studies,
communication (including telephone calls) for purposes of assessment or care
decisions with health care professional(s), family member(s), surrogate decision
maker(s) and/or key caregiver(s) involved in patient’s care, integration of new
information into the medical treatment plan and/or adjustment of medical therapy,
within a calendar month; 15-29 minutes
99340
Within a calendar month; 30 minutes or more

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
85
Preventative medicine services
HIV/AIDS counseling/testing
(CPT code 99401) (WAC 182-531-0600)
HCA covers two sessions of risk factor reduction counseling (CPT code 99401) counseling per
client, each time tested (i.e., one pre- and one post-HIV/AIDS counseling/testing session). Use
ICD diagnosis code Z71.7 when billing CPT code 99401 for HIV/AIDS counseling.
HCA does not pay for HIV/AIDS counseling when billed with an E/M service unless the client is
being seen on the same day for a medical problem and the E/M service is billed with a separately
identifiable diagnosis code and with modifier 25.
See HCA’s HIV/AIDS Case Management Billing Guide for additional information on
HIV/AIDS case management billing.
Prolonged services
(CPT codes 99354-99357) (WAC 182-531-1350)
Prolonged services with direct patient contact
HCA covers prolonged services:
• Up to three hours per client, per diagnosis, per day.
Note: The time counted toward payment for prolonged E/M services includes
only direct face-to-face contact between the provider and the client, whether or
not the services were continuous.
• Only when the provider performs one of the services listed below for the client on the
same day:
Prolonged CPT Code
Outpatient
Other CPT Code(s)
99354
99201-99215, 99241-99245, 99324-99337, 99341-
99350, 90815
99355
99354 and one of the E/M codes required for 99354
Prolonged CPT Code
Inpatient
Other CPT Code(s)
99356
99218-99220, 99221-99233, 99251-99255, 99304-
99310
99357
99356 and one of the E/M codes required for 99356

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
86
Note: Both the prolonged services CPT code and any of the “Other CPT
Code(s)” listed above must be billed on the same claim.
Physician standby services
(CPT code 99360) (WAC 182-531-1250)
HCA covers physician standby services when those services are requested by another physician
and involve prolonged physician attendance without direct (face-to-face) client contact.
Note: The standby physician cannot provide care or services to other clients
during the standby period.
Limitations
• Standby services of less than 30 minutes are not covered.
• After the first 30 minutes, subsequent periods of standby services are covered only when
a full 30 minutes of standby is provided for each unit billed.
HCA does not cover physician standby services when:
• The provider performs a surgery that is subject to the global surgery policy.
• Billed in addition to any other procedure code, with the exception of CPT codes 99460
and 99465.
• When the service results in an admission to a neonatal intensive care unit (CPT code
99468) on the same day.
Telemedicine
(WAC 182-531-1730)
What is telemedicine?
Telemedicine is when health care practitioners use HIPAA-compliant, interactive, real-time audio
and video telecommunications (including web-based applications) or store and forward technology
to deliver covered services that are within their scope of practice to a client at a site other than the
site where the provider is located.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
87
If the service is provided through store and forward technology, there must be an associated office
visit between the client and the referring health care provider.
Using telemedicine when it is medically necessary enables the health care practitioner and the client
to interact in real-time communication as if they were having a face-to-face session. Telemedicine
allows HCA clients, particularly those in medically underserved areas of the state, improved access
to essential health care services that may not otherwise be available without traveling long
distances.
HCA does not cover the following services as telemedicine:
• Email, audio only telephone, and facsimile transmissions
• Installation or maintenance of any telecommunication devices or systems
• Purchase, rental, or repair of telemedicine equipment
Who is eligible for telemedicine?
Fee-for-service clients are eligible for medically necessary covered health care services delivered
via telemedicine. The referring provider is responsible for determining and documenting that
telemedicine is medically necessary. As a condition of payment, the client must be present and
participating in the telemedicine visit. Clients under the Family Planning Only – Pregnancy Related
program, Family Planning Only program (formerly referred to as TAKE CHARGE), First Steps,
and School-Based Health Care Services programs are eligible for telemedicine through fee-for-
service.
When does HCA cover telemedicine?
HCA covers telemedicine when it is used to substitute for an in-person face-to-face, hands-on
encounter for only those services specifically listed in this telemedicine section. MCO’s cover
the delivery of care via telemedicine. Follow the MCO’s policy and billing requirements.
Telemedicine and COVID-19
For updated information regarding COVID-19, see HCA’s Information about novel corona virus
(COVID-19) webpage.
Note: The telemedicine/telehealth guidance published on HCA’s Information about novel
corona virus (COVID-19) webpage found under Providers, billers, and partners and then
under Physical health providers supersedes the information on this billing guide.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
88
What are the documentation requirements?
The documentation requirements are the same as those listed in Evaluation and management
documentation and billing, in addition to the following:
• Verification that the service was provided via telemedicine
• The location of the client and a note of any medical personnel with the client
• The location of the provider
• The names and credentials (MD, ARNP, RN, PA, CNA, etc.) of all people involved in the
telemedicine visit, and their role in the encounter at both the originating and distant sites
Originating site (location of client)
What is an originating site?
An originating site is the physical location of the eligible HCA client at the time the professional
service is provided by a physician or practitioner through telemedicine. Approved originating
sites are:
• Clinics
• Community mental health/chemical dependency settings
• Dental offices
• Federally qualified health centers (FQHC)
• Homes or any location determined appropriate by the individual receiving service
• Hospitals (inpatient and outpatient)
• Neurodevelopmental centers
• Physician or other health professional’s offices
• Renal dialysis centers, except an independent renal dialysis center
• Rural health clinics (RHC)
• Schools
• Skilled nursing facilities
Is the originating site paid for telemedicine?
Yes. The originating site is paid an originating site facility fee per completed transmission for
telemedicine services. HCA does not pay the originating site facility fee to the client in any
setting.
How does the originating site bill HCA for the originating site facility fee?
• Hospital outpatient: When the originating site is a hospital outpatient agency, payment
for the originating site facility fee will be paid according to the maximum allowable fee
schedule. To receive payment for the originating site facility fee, outpatient hospital
providers must bill revenue code 0780 on the same line as HCPCS code Q3014.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
89
• Hospital inpatient, skilled nursing facility, home, or location determined
appropriate by the individual receiving service: There is no payment to the originating
site for the originating site facility fee in these settings.
• Critical access hospitals: When the originating site is a critical access hospital outpatient
agency, payment is separate from the cost-based payment methodology. To receive
payment for the originating site facility fee, critical access hospitals must bill revenue
code 0789 on the same line as HCPCS code Q3014.
• FQHCs and RHCs: When the originating site is an FQHC or RHC, bill for the
originating site facility fee using HCPCS code Q3014. This is not considered an FQHC
or RHC service and is not paid as an encounter.
• Physicians’ or other health professional offices: When the originating site is a
physician’s office, bill for the originating site facility fee using HCPCS code Q3014.
• Other settings: When the originating site is an approved telemedicine site, bill for the
originating site facility fee using HCPCS Q3014.
If a provider from the originating site performs a separately identifiable service for the client on
the same day as telemedicine, documentation for both services must be clearly and separately
identified in the client’s medical record.
Distant site (location of consultant)
What is a distant site?
A distant site is the physical location of the health care professional providing the health care
service to an eligible HCA client through telemedicine.
What services are covered using telemedicine?
HCA reimburses medically necessary covered services through telemedicine when the service is
provided by a Washington Apple Health provider and is within their scope of practice.
How does the distant site bill HCA for the services delivered through
telemedicine?
The payment amount for the professional service provided through telemedicine by the provider
at the distant site is equal to the current fee schedule amount for the service provided. Submit
claims for telemedicine services using the appropriate CPT or HCPCS code for the professional
service.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
90
Use place of service (POS) 02 to indicate that a billed service was furnished as a telemedicine
service from a distant site.
HCA discontinued the use of the GT modifier for claims submitted for professional services
(services billed on a CMS-1500 claim form, when submitting paper claims). Beginning January
1, 2018, distant site practitioners billing for telemedicine services under the Critical Access
Hospital (CAH) optional payment method must use the GT modifier. See HCA’s ProviderOne
Billing and Resource Guide for more information on submitting claims to HCA. See HCA’s
Inpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide for more information on billing for services under the
CAH optional payment method.
Follow CMS guidance for modifiers if Medicare is the primary insurance.
Add modifier 95 (via interactive audio and video telecommunications system) if the distant site
is designated as a nonfacility.
Nonfacility providers must add modifier 95 to the claim to receive the nonfacility payment.
Store and Forward
Store and Forward is the transmission of medical information to be reviewed at a later time by a
physician or practitioner at a distant site. A client’s medical information may include, but is not
limited to, video clips, still images, x-rays, laboratory results, audio clips, and text. The physician
or practitioner at the distant site reviews the case without the client present.
HCA pays for Store and Forward for teledermatology.
HCA pays for Store and Forward when all of the following conditions are met:
• It is associated with an office visit between the eligible client and the referring health care
provider. The associated visit can be done in person or via asynchronous telemedicine
and include one or more of the following types of information: video clips, still images,
x-rays, MRIs, electrocardiograms and electroencephalograms, laboratory results, audio
clips, and text. The visit results in a documented care plan that is communicated back to
the referring provider.
• The transmission of protected health information is HIPPA compliant.
• Written informed consent is obtained from the client that store and forward technology
will be used and who the consulting provider is.
If the consultation results in a face-to-face visit in person or via telemedicine with the specialist
within 60 days of the Store and Forward consult, HCA does not pay for the store and forward
consultation.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
91
Teledermatology does not include single-mode consultations by telephone calls, images
transmitted via facsimile machines, or electronic mail.
Teledermatology services provided via store and forward telecommunications system must be
billed with modifier GQ.
Only the portion(s) rendered from the distant site are billed with modifier GQ. The sending
provider bills as usual with the E/M and no modifier. The use of modifier GQ does not alter
reimbursement for the CPT or HCPCS code billed.
Note: The originating site for Store and Forward is not eligible to receive an
originating site fee.
The POS 02 must be used to indicate the location where health services are provided through
store and forward technology. The POS 02 code does not apply to the originating site.
Claims will be denied if a bill is submitted for Store and Forward services with POS code
02 but without the GQ modifier.
HCA may perform a post-pay review on any claim to ensure the above conditions were met.
The following codes are covered for teledermatology:
Procedure
Code
Short Description
E/M Services
99241-99243
Office consultation, new or established patient
99251-99253
Initial inpatient consultation
99211-99214
Office or other outpatient visit
99231-99233
Subsequent hospital care
Note: Teledermatology requires expedited prior authorization (EPA). See EPA
870001419.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
92
Anesthesia
(WAC 182-531-0300)
General anesthesia
• HCA requires providers to use anesthesia CPT® codes 00100-01999 to bill for anesthesia
services paid with base and time units. Do not use the surgical procedure code with an
anesthesia modifier to bill for the anesthesia procedure.
• HCA pays for CPT code 01922 for noninvasive imaging or radiation therapy when either
of the following applies:
The client is 17 years of age or younger.
There are client-specific reasons why the procedure cannot be performed without
anesthesia services. Documentation must be kept in the client's medical record.
• HCA pays providers for covered anesthesia services performed by one of the following:
Anesthesiologist
Certified registered nurse anesthetist (CRNA)
Other providers who have a contract with HCA to provide anesthesia services
(See also Oral surgery)
• For each client, the anesthesia provider must do all of the following:
Perform a pre-anesthetic examination and evaluation
Prescribe the anesthesia plan
Personally participate in the most demanding aspects of the anesthesia plan,
including, induction and emergence
Ensure that any procedures in the anesthesia plan that he or she does not perform are
done by a qualified individual as defined in program operating instructions
Monitor the course of anesthesia administration at frequent intervals
Remain physically present and available for immediate diagnosis and treatment of
emergencies
Provide indicated postanesthesia care
• The anesthesia provider may direct no more than four anesthesia services concurrently.
The anesthesia provider may not perform any other services while directing these
services, other than attending to medical emergencies and other limited services as
allowed by Medicare policy.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
93
• The anesthesia provider must document in the client's medical record that the medical
direction requirements were met. Providers do not need to submit documentation with
each claim to substantiate these requirements.
• Anesthesia time begins when the anesthesia provider starts to physically prepare the client
for the induction of anesthesia in the operating room area or its equivalent. When there is a
break in continuous anesthesia care, blocks of time may be summed as long as there is
continuous monitoring of the client within the blocks of time. An example of this includes,
but is not limited to, the time a client spends in an anesthesia induction room or under the
care of an operating room nurse during a surgical procedure. Anesthesia time ends when
the anesthesia provider or surgeon is no longer in constant attendance (i.e. when the client
can be safely placed under postoperative supervision).
• Do not bill CPT codes 01953 or 01996 with an anesthesia modifier or with the time in the
"units" field. HCA has assigned flat fees for these codes.
• HCA does not adopt any ASA RVG codes that are not included in the CPT book. Bill all
anesthesia codes according to the descriptions published in the current CPT book. When
there are differences in code descriptions between the CPT book and the ASA RVG, HCA
follows CPT code descriptions.
• HCA does not pay providers for anesthesia services when these services are billed using the
CPT surgery, radiology, and/or medicine codes with anesthesia modifiers. Continue to use
the appropriate anesthesia modifier with anesthesia CPT codes.
Exception: Anesthesia providers may bill CPT pain management/other services
procedure codes that are not paid with base and time units. These services are
paid as a procedure using RBRVS methodology. Do not bill time in the unit field
or use anesthesia modifiers.
• When billing for sterilization, details regarding anesthesia are located in the
Sterilization Supplemental Billing Guide.
• When multiple surgical procedures are performed during the same period of anesthesia,
bill the surgical procedure with the greatest base value, along with the total time in whole
minutes.
• When more than one anesthesia provider is present, HCA pays each provider 50% of the
allowed amount. HCA limits payment in this circumstance to 100% of the total allowed
payment for the service.
• Providers must report the number of actual anesthesia minutes (calculated to the next
whole minute) in the appropriate field on the claim. HCA calculates the base units.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
94
Note: When billing for Medicare crossovers, remember that Medicare pays per
the base units and HCA pays per minute of anesthesia. When billing a Medicare
crossover on a Direct Data Entry (DDE) claim, bill HCA using minutes in the unit
field. When billing a Medicare crossover on a HIPAA 837P transaction, bill units
the same as if billing Medicare.
Regional anesthesia
• Bill HCA the appropriate procedure code (e.g. epidural CPT code 62326) with no time
units and no anesthesia modifier. HCA determines payment by using the procedure’s
maximum allowable fee, not anesthesia base and time units.
• Local nerve block CPT code 64450 (other than digital and metacarpal) for subregional
anatomic areas (such as the hand, wrist, ankle, foot and vagina) is included in the global
surgical package and is not paid separately.
Moderate sedation
Moderate sedation is a drug induced depression of consciousness performed while the patient
responds purposefully to verbal commands, either alone or accompanied by light tactile
stimulation. Moderate sedation does not include minimal sedation, deep sedation, or monitored
anesthesia care.
Providers must report the appropriate CPT or HCPCS code that describes the moderate sedation
services provided. Moderate sedation services are provided in combination with and in support
of a procedural service, consistent with CPT guidance.
Moderate sedation is covered when medically necessary.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
95
Other
• Patient acuity does not affect payment levels. Qualifying circumstances (CPT codes
99100, 99116, 99135, and 99140) are considered bundled and are not paid separately.
• HCA follows Medicare’s policy of not paying surgeons for anesthesia services. Claims
for anesthesia services with modifier 47 will be denied. Under Medicare's payment
policy, separate payment for local, regional, or digital block or general anesthesia
administered by the surgeon is not allowed. These services are considered included in the
RBRVS payments for the procedure.
• When billing for anesthesia services using CPT unlisted anesthesia code 01999,
providers must attach documentation (operative report) to their claim indicating what
surgical procedure was performed that required the anesthesia, in order to receive
payment. HCA will determine payment amount after review of the documentation.
Teaching anesthesiologists
HCA pays teaching anesthesiologists for supervision of anesthesiology residents as follows:
• When supervising one resident only, the teaching anesthesiologist must bill HCA the
appropriate anesthesia procedure code with modifier AA. Payment to the teaching
anesthesiologist will be 100% of the allowed amount.
• When supervising two or more residents concurrently, the teaching anesthesiologist
must bill HCA the appropriate anesthesia procedure codes with modifier QK. Payment
to the teaching anesthesiologist will be 50% of the allowed amount for each case
supervised.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
96
Physician fee schedule payment for services of teaching
physicians
General rule: If a resident physician participates in providing a service in a teaching setting,
physician fee schedule payment is made only if a teaching physician is present during the key
portion of any service or procedure for which payment is sought.
• Surgical, high-risk, or other complex procedures: The teaching physician must be
present during all critical portions of the procedure and immediately available to furnish
services during the entire service or procedure.
Surgery: The teaching physician's presence is not required during opening and
closing of the surgical field.
Procedures performed through an endoscope: The teaching physician must be
present during the entire viewing.
• Evaluation and management services: The teaching physician must be present during
the portion of the service that determines the level of service billed. (However, in the case
of evaluation and management services furnished in hospital outpatient departments and
certain other ambulatory settings, the requirements of 42 C.F.R. §415.174 apply.)
Anesthesia for dental
General anesthesia is allowed when provided by an anesthesiology provider in a hospital for
dental admissions. To bill for dental anesthesia provided in a hospital, providers must use CPT
anesthesia code 00170 with the appropriate anesthesia modifier.
See HCA’s Dental-Related Services Billing Guide for information on billing for office-based
anesthesia for dental procedures.
Note: Bill HCA directly for dental anesthesia for all clients, including those
enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
97
Anesthesia for maternity
(WAC 182-531-0300(9))
• HCA pays a maximum of 6 hours (360 minutes) of anesthesia for labor and delivery time
(CPT codes 01960, 01961, 01967 and 01968) per delivery, including multiple births
and/or cesarean section delivery.
Exception: The following obstetrical anesthesia codes are not subject to the 6-
hour (360 minute) limitation: CPT codes 01962-01966 or 01969.
• When billing more than one time-limited anesthesia code, the total time may not exceed 6
hours (360 minutes).
• Bill the applicable CPT anesthesia code with applicable modifier and time. To determine
time for obstetric epidural anesthesia during normal labor and delivery and C-sections,
time begins with insertion and ends with removal for a maximum of 6 hours per delivery.
• CPT codes 01968 and 01969 are anesthesia add-on codes to be used for cesarean delivery
and cesarean hysterectomy following anesthesia given for a planned vaginal delivery. An
additional base of 3 is allowed for 01968 and an additional base of 5 is allowed for
01969, in conjunction with the base of 5 for 01967. The time involved with each portion
of the procedure should be reported with the appropriate CPT code.
For example: When a physician starts a planned vaginal delivery (CPT code
01967) and it results in a cesarean delivery (CPT code 01968), both of these
procedures may be billed. However, if both an anesthesiologist and a certified
registered nurse assistant (CRNA) are involved, each provider bills only for those
services he/she performed. The sum of the payments for each procedure will not
exceed HCA’s maximum allowable fee.
• Anesthesia time for sterilization is added to the time for the delivery when the two
procedures are performed during the same operative session. If the sterilization and
delivery are performed during different operative sessions, the time is calculated
separately.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
98
Anesthesia for radiological procedures
(WAC 182-531-0300 (2) and (7))
General anesthesia is allowed for radiological procedures for children and/or noncooperative
clients when the medically necessary procedure cannot be performed unless the client is
anesthetized.
Providers must use the anesthesia CPT code 01922 when providing general anesthesia for
noninvasive imaging or radiation therapy. Do not bill the radiological procedure code (e.g., CPT
code 71010) with an anesthesia modifier to bill for the anesthesia procedure. When using CPT
code 01922 for noninvasive imaging or radiation therapy, one of the following must be met:
• The client must be 17 years of age or younger.
• A statement of the client-specific reasons why the procedure cannot be performed
without anesthesia services must be kept in the client's medical record and made available
to HCA on request.
Anesthesia payment calculation for services paid
with base and time units
• HCA’s current anesthesia conversion factor is $21.20.
• Anesthesia time is paid using one minute per unit.
• Total anesthesia payment is calculated by adding the base value for the anesthesia
procedure with the actual time. Bill time in total minutes only, rounded to the next
whole minute. Do not bill the procedure’s base units.
The following table illustrates how to calculate the anesthesia payment:
Payment Calculation
A. Multiply base units by 15.
B. Add total minutes to value from step A.
C. Divide anesthesia conversion factor by 15, to obtain the rate per minute.
D. Multiply total from Step B by the rate per minute in Step C.
Anesthesia conversion factor is based on 15-minute time units.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
99
Surgery
(WAC 182-531-1700)
HCA requires prior authorization for selected surgical procedures. Providers must check the
Physician-related services fee schedule for those surgical services that require either prior
authorization (PA) or expedited prior authorization (EPA).
Tobacco/nicotine cessation
Nicotine use is a strong contraindication to spine surgeries. Patients undergoing cervical fusions
and repeat fusions for radiculopathy are required to abstain from nicotine for four weeks before
surgery. HCA covers tobacco/nicotine cessation which can include free counseling and
prescription drugs. See Behavior change intervention - tobacco/nicotine cessation.
Pain management services
• Pain management services and selected surgical services that are commonly performed
by anesthesiologists and CRNAs are not paid with anesthesia base and time units. These
services are paid using HCA’s assigned maximum allowable fee for the procedure code.
• When billing for pain management and other services that are payable using HCA’s
assigned maximum allowable fee, do not use anesthesia modifiers. HCA denies claims
for these services billed with an anesthesia modifier.
• Two postoperative procedures for pain management are allowed during the same
inpatient stay. Only one (1) unit may be billed per procedure. Do NOT bill time.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
100
Pain management procedure codes
The listings shown below are not guaranteed to be all-inclusive and are provided for convenience
purposes only.
The procedure codes listed in the following table with an asterisk (*) are limited to two (2)
during the postoperative period while the client is admitted to the hospital. Do not bill modifier
59, XE, XS, XP, or XU with any of these procedure codes.
Procedure
Code
11981*
11982*
11983*
20526*
20550
20551
20552
20553
20600
20605
20610
20612
27096
61790*
62264*
62270
62272
62273*
62280*
62281*
62282*
62284
62290
62291
62320*
62322*
62324*
62326*
62350*
62351*
62355*
Procedure
Code
62360*
62361*
62362*
62365*
63650*
63655*
63685*
63688*
64400*
64402*
64405*
64408*
64410*
64412*
64413*
64415*
64416*
64417*
64418*
64420*
64421*
64425*
64430*
64435*
64445*
64446*
64447*
64448*
64449*
64450*
64479*
Procedure
Code
64480*
64483*
64484*
64505*
64508*
64510*
64517*
64520*
64530*
64553*
64555*
64561*
64565*
64575*
64580*
64581*
64585*
64590*
64595*
64600*
64605*
64610*
64612*
64616*
64617*
64620*
64630*
64640*
64680*
64681*
64802*
Procedure
Code
64804*
64809*
64818*
Other Services
Procedure
Code
36400
36420
36425
36555
36566
36568
36580
36584
36589
36600
36620
36625
36660
62263
62287
63600
76000
76496
77001
77002
77003
93503
95970
95990
These codes are paid as a procedure using HCA’s maximum allowable fee, not with base units
and time.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
101
Interoperative or postoperative pain management
HCA covers interoperative and postoperative pain control using a spinal injection or infusion
(CPT® 62320 - 62327). Expedited prior authorization (EPA) is required. See EPA #870001351.
If the client does not meet the EPA criteria, prior authorization (PA) is required (see Prior
authorization). Authorization requests must be submitted to HCA, not Comagine Health.
Registered Nurse First Assistants
Registered Nurse First Assistants (RNFAs) are allowed to assistant at surgeries within their
scope of practice. Use modifier AS to bill HCA for these services.
New RNFA providers must meet all of the following criteria:
• Licensed in Washington State as a Registered Nurse in good standing
• Work under the direct supervision of the performing surgeon
• Hold current certification as a certified nurse operating room (CNOR)
Submit all of the following documentation to HCA along with the Core Provider Agreement:
• Proof of current certification as a CNOR from the Certification Board Perioperative
Nursing
• Proof of successful completion of an RNFA program that meets the Association of
Perioperative Registered Nurses (AORN) standards for RN first assistant education
programs. (See Perioperative Standards and Recommended Practices, Denver, CO:
AORN)
• Proof of allied health personnel privileges in the hospital where the surgeries are
performed
• Proof of liability insurance

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
102
Billing/Payment
Bilateral procedures
• If a procedure is done bilaterally and is identified by its terminology as bilateral (e.g.
CPT codes 27395 or 52290), do not bill the procedure with modifier 50.
• If a procedure is done bilaterally and is not identified by its terminology as a bilateral
procedure, bill the procedure using modifier 50 on one line only or include modifier LT
or RT on the separate lines when the surgical procedure is performed on both sides.
• Use modifiers LT and RT to indicate left and right for unilateral procedures.
Bundled services
The following procedure codes are bundled within the payment for the surgical procedure during
the global period. Do not bill these codes separately unless one of the conditions on the
following page exists:
Procedure Code
Short Description
E/M Services
99211-99223
Office visits, initial hospital observation care, and initial
hospital inpatient care
99231-99239
Subsequent hospital care, observation or inpatient care
services, and hospital discharge services
99241-99245
Office consultations
99291-99292
Critical care services.
99307-99310
Subsequent nursing facility care
99324-99337
Domiciliary, rest home, or custodial care services
99347-99350
Home services
Ophthalmological Services
92012-92014
General ophthalmological services

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
103
The E/M codes may be allowed if there is a separately identifiable reason for the additional E/M
service unrelated to the surgery. In these cases, the E/M code must be billed with one of the
following modifiers:
Modifier Description
• 24 Unrelated E/M service by the same physician during a postoperative period
(reason for the E/M service must be unrelated to the procedure)
• 25 Significant, separately identifiable E/M service by the same physician on the same
day of a procedure (reason for the E/M service must be unrelated to the
procedure)
• 57 Decision for surgery (only applies to surgeries with a 90-day global period)
• 79 Unrelated procedure or service by the same physician during the postoperative
period
• Professional inpatient services (CPT codes 99221-99223) are payable only during the
global follow-up period if they are performed on an emergency basis (i.e. they are not
payable for scheduled hospital admissions).
• Bundled procedure codes are not payable during the global surgery payment period.
A provider (other than the surgeon) who provides all postoperative care (including all inpatient
postoperative care) before discharge, must bill subsequent hospital care codes (CPT codes
99231-99233) for the inpatient hospital care, and the surgical code with modifier 55 for the post-
discharge care. The surgeon must bill the surgery code with modifier 54.
• Providers who perform only the follow-up services for minor procedures performed in
emergency agencies must bill the appropriate level E/M code. These services are not
included in the global surgical payment.
• The provider who performs the emergency room service must bill for the surgical
procedure without using modifier 54.
• Preoperative and postoperative critical care services provided during a global period for a
seriously ill or injured client are not considered related to a surgical procedure and are
paid separately when all of the following apply:
The client is critically ill or injured and requires the constant attendance of the
provider.
The critical care is unrelated to the specific anatomic injury or general surgical
procedure performed.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
104
The client is potentially unstable or has conditions that could pose a significant
threat to life or risk of prolonged impairment.
Bill the appropriate critical care codes with either modifier 24 or 25.
• HCA allows separate payment for:
The initial evaluation to determine need for surgery.
Preoperative visits that occur two or more days before the surgery. Use the
specific medical diagnosis for the client. Do not use Z01.89.
Postoperative visits for problems unrelated to the surgery.
Postoperative visits for services that are not included in the normal course of
treatment for the surgery.
Services of other providers, except when more than one provider furnishes
services that are included in a global package (see modifiers 54 and 55).
Global surgery payment
Global surgery payment includes all the following services:
• The surgical procedure
• For major surgeries (90-day global period), preoperative visits (all sites of service) that
occur the day before or the day of the surgery
• For minor surgeries (less than 90-day global period), preoperative visits (all sites of
service) that occur on the day of surgery
• Services by the primary surgeon (all sites of service) during the postoperative period
• Postoperative dressing changes, including all of the following:
Local incision care and removal of operative packs
Removal of cutaneous sutures, staples, lines, wires, tubes, drains and splints;
Insertion, irrigation and removal of urinary catheters, routine peripheral IV lines,
nasogastric and rectal tubes
Change and removal of tracheostomy tubes

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
105
• Additional medical or surgical services required because of complications that do not
require additional operating room procedures
Note: Casting materials are not part of the global surgery policy and are paid
separately.
Global surgery payment period
• The global surgery payment period applies to any provider who participates in the
surgical procedure. These providers include:
The surgeon.
The assistant surgeon (modifiers 80, 81, or 82).
Two surgeons (modifier 62).
Team surgeons (modifier 66).
Anesthesiologists and CRNAs.
Physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist for assistant at
surgery (modifier AS).
Multiple surgeries
When multiple surgeries are performed on the same client, during the same operative session,
HCA pays providers:
• 100% of HCA’s maximum allowable fee for the most expensive procedure; plus,
• 50% of HCA’s maximum allowable fee for each additional procedure.
To expedite payment of claims, bill all surgeries performed during the same operative
session on the same claim. This includes secondary claims with payment by a primary
commercial insurance and Medicare crossover claims.
If a partial payment is made on a claim with multiple surgeries, providers must adjust the paid
claim. Refer to the ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide, Key Step 6 under “Submit Fee for
Service Claims to Medical Assistance” which addresses adjusting paid claims. Providers must
adjust claims electronically.
Note: For second operative session performed on the same date of service (e.g.,
return to the operating room for a staged procedure), bill the second operative
session on a separate claim. Add in the claim comments, “Operative reports
attached” and submit claim to HCA with operative reports.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
106
Other surgical policies
• Use modifiers 80, 81, and 82 to bill for an assistant surgeon. An assistant at major
surgery is paid at 20% of the surgical procedure’s maximum allowable fee. The multiple
surgery rules apply for surgery assistants.
• Use modifier AS for an assistant at surgery for PA-Cs, ARNPs, or Clinical Nurse
Specialists – do not use modifier 80. An assistant at major surgery is paid at 20% of the
surgical procedure’s maximum allowable fee.
• To expedite payment of claims, bill for the assistant surgeon on a different claim.
• A properly completed consent form must be attached to all claims for sterilization and
hysterectomy procedures. For sterilizations, see the Sterilization Supplemental Billing
Guide. For hysterectomies, see Hysterectomies in this guide.)
• Microsurgery Add On CPT Code 69990
CPT indicates that CPT code 69990 is not appropriate when using magnifying loupes or
other corrected vision devices. Also, CPT code 69990 is not payable with procedures
where use of the operative microscope is an inclusive component of the procedure (i.e.
the procedure description specifies that microsurgical techniques are used).
HCA follows CCI guidelines regarding the use of the operating microscope. Do not bill
CPT code 69990 in addition to procedures where the use of the operating microscope is
an inclusive component.
• Salpingostomies (CPT codes 58673 and 58770) are payable only for a tubal pregnancy
(ICD diagnosis code O00.1).
• Modifier 53 must be used when billing for incomplete colonoscopies (CPT code 45378,
or HCPCS codes G0105 or G0121). Do not bill incomplete colonoscopies as
sigmoidoscopies. Modifier 53 indicates that the physician elected to terminate a surgical
procedure. Use of modifier 53 is allowed for all surgical procedures. Modifier 53 is a
payment modifier when used with CPT code 45378 or HCPCS codes G0105 or G0121. It
is informational only for all other surgical procedures.
• HCA requires EPA for reduction mammoplasties (CPT code 19318) and for mastectomy
for gynecomastia for men (CPT code 19300). See Expedited prior authorization (EPA)
for more information.
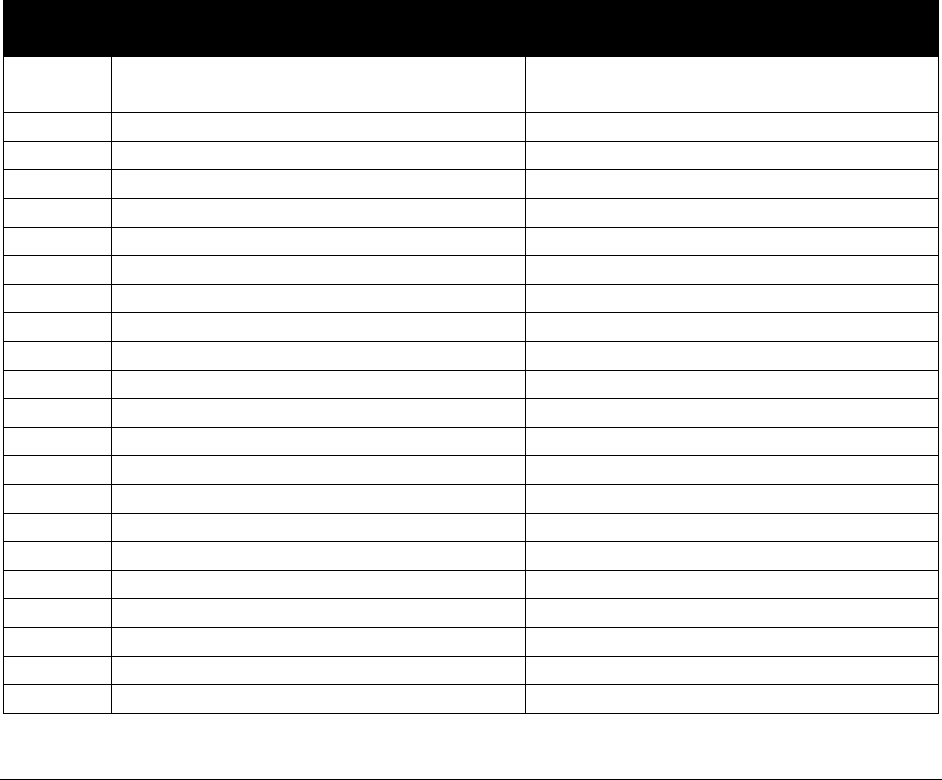
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
107
Breast removal and breast reconstruction
• HCA pays for the following procedure codes which include breast removal and breast
reconstruction for clients who have one of the conditions below. If a client does not have
one of the following conditions,
the service requires prior authorization (PA):
Breast cancer or a history of breast cancer
Tested positive for BRCA 1, BRCA 2, or other definitive genetic test for cancer
Burns, open wound injuries, or congenital anomalies of the breast.
• HCA allows ICD diagnosis Z42.1 and Z15.01 as primary diagnosis for surgical
consultation.
• HCA allows ICD diagnosis Z85.3 as a primary diagnosis for breast reconstruction.
• Removal of failed breast implants with the appropriate ICD diagnosis code T85.41XA or
T85.42XA requires PA. HCA will pay to remove implants (CPT codes 19328 and 19330)
but will not replace them if they were placed for cosmetic reasons.
CPT
Code(s)
Short Description
Limitations
11920
Correct skin color defects 6.0 cm (use
V10.3) (Tattoo)
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
11921
Correct skin color 6.1-20.0 cm
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
11960
Insertion tissue expander(s)
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
11970
Replace tissue expander
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
11971
Remove tissue expander(s)
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19301
Partial mastectomy
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19302
P-mastectomy w/ln removal
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19303
Mast simple complete
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19304
Mast subq
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19316
Suspension of breast
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19340
Immediate breast prosthesis
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19342
Delayed breast prosthesis
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19350
Breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19357
Breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19361
Breast reconstr w/lat flap
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19364
Breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19366
Breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19367
Breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19368
Breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19369
Breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19370
Surgery of breast capsule
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
19371
Removal of breast capsule
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
108
CPT
Code(s)
Short Description
Limitations
19380
Revise breast reconstruction
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
S2066
Breast GAP flap reconst
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
S2067
Breast "stacked" DIEP/GAP
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
S2068
Breast diep or siea flap
Limited to the appropriate ICD dx codes
Panniculectomy
Panniculectomy requires prior authorization (PA). Photographs and supporting clinical
documentation must be submitted with PA requests. See Prior authorization (PA).
All of the following must be present for panniculectomy:
• The pannus hangs at or below the level of the symphysis pubis
• The pannus causes a chronic and persistent skin condition (e.g., intertriginous dermatitis,
panniculitis, cellulitis, or skin ulcerations) that is refractory to at least three months of
medical treatment and associated with at least one episode of cellulitis requiring systemic
antibiotics. In addition to good hygiene practices, all of the following treatments (unless
contraindicated) have been tried and failed: topical antifungals, topical or systemic
corticosteroids, and local or systemic antibiotics
• The pannus causes a functional deficit because of a severe physical deformity or
disfigurement
• The surgery is expected to restore or improve the functional deficit
• The pannus is interfering with daily living
Pre-/intra-/postoperative payment splits
Pre-, intra-, and postoperative payment splits are made when modifiers 54, 55, 56, and 78 are
used.
HCA has adopted Medicare's payment splits. If Medicare has not assigned a payment split to a
procedure, HCA uses a payment split of 10%/80%/10% if modifiers 54, 55, 56, and 78 are used.
For current information and updates on Medicare payment splits, see the Medicare physician fee
schedule (MPFS).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
109
Auditory system
Tympanostomies
HCA covers tympanostomies for clients diagnosed with acute otitis media or otitis media with
effusion. Expedited prior authorization (EPA) is required. See EPA #870001382. If the client
does not meet the EPA criteria, prior authorization (PA) is required (see Prior authorization).
Cochlear implant services (clients age 20 and younger)
(WAC 182-531-0200(4) (c))
Unilateral (CPT code 69930) and bilateral (CPT code 69930 with modifier 50) cochlear
implantation require EPA (see EPA #870000423 for unilateral and EPA #870001365 for
bilateral). If a client does not meet the EPA criteria, PA is required.
HCA covers replacement parts for cochlear devices through HCA’s Hearing Hardware Program
only. HCA pays only those vendors with a current core provider agreement that supply
replacement parts for cochlear implants and bone conduction hearing devices.
Note: HCA does not pay for new cochlear implantation for clients age 21 and
older. HCA considers requests for removal or repair of previously implanted
cochlear implants for clients age 21 and older when medically necessary. Prior
authorization is required.
CPT Codes
Short Description
Comments
69930 Implant cochlear device
No corresponding removal
codes specific to cochlear
devices.
69715 Temple bne implnt w/stimulat
Bone conduction hearing devices for clients age 20 and
younger
Insertion or initial placement of bone conduction hearing devices (CPT codes 69714-69718;
HCPCS L8693) requires prior authorization (PA) (refer to Prior authorization). For billing the
initial placement of soft headband bone conduction hearing devices, use the appropriate E/M
procedure code and the appropriate hardware HCPCS code. See HCA’s Hearing hardware fee
schedule.
Note: This information relates only to those clients NOT enrolled in an HCA-
contracted managed care organization (MCO). For clients enrolled in an HCA-
contracted MCO, refer to the coverage guidelines in the enrollee’s plan.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
110
The procedure can be performed in an inpatient hospital setting or outpatient hospital setting.
HCA covers replacement parts or repair for bone conduction hearing devices through HCA’s
Hearing Hardware Program only. HCA pays only those vendors that supply replacement parts for
cochlear implants and bone conduction hearing devices who have a current Core Provider
Agreement.
Note: HCA does not pay for a new bone conduction hearing device for clients
age 21 and older. HCA considers requests for removal or repair of previously
implanted bone conduction hearing devices for clients age 21 and older when
medically necessary. PA is required.
CPT Code
Short Description
Notes
69710 Implant/replace hearing aid
Replacement procedure includes
removal of the old device
69711
Remove/repair hearing aid
69714
Implant temple bone w/stimul
69715
Temple bne implnt w/stimulat
69717
Temple bone implant revision
69718
Revise temple bone implant
Bariatric surgeries
(WAC 182-531-1600 and WAC 182-550-2301)
Bariatric surgery requires prior authorization (PA) and must be performed in a facility that is
accredited by the Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Accreditation and Quality Improvement
Program (MBSAQIP).
Clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization (MCO) may be
eligible for bariatric surgery. Clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted MCO must
contact their MCO for information regarding the bariatric surgery benefit.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
111
Clients age 21 through 59
HCA covers medically necessary bariatric surgery for clients 21 through 59 years of age in an
approved hospital with a bariatric surgery program in accordance with WAC 182-531-1600.
Prior authorization is required. To begin the authorization process, providers must fax HCA a
completed Bariatric Surgery Request form 13-785. (See HCA’s Billers, providers, and partners
webpage. See also Where can I download HCA forms?)
Clients age 18 through 20
HCA covers medically necessary bariatric surgery for clients age 18 through 20 years:
• For the laparoscopic gastric band procedure (CPT code 43770).
• When prior authorized.
• When performed in an approved hospital with a bariatric surgery program.
• In accordance with WAC 182-531-1600.
Bariatric case management fee
HCA may authorize up to 34 units of a bariatric case management fee as part of the Stage II
bariatric surgery approval. One unit of HCPCS code G9012 = 15 minutes of service. Prior
authorization is required.
This fee is given to the primary care provider or bariatric surgeon performing the services
required for Bariatric Surgery Stage II. This includes overseeing weight loss and coordinating
and tracking all the necessary referrals, which consist of a psychological evaluation, nutritional
counseling, and required medical consultations as requested by HCA.
Clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization (MCO) must contact their
MCO for information regarding coverage of bariatric case management.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
112
Cardiovascular system
Carotid artery stenting
HCA pays for extracranial carotid artery stenting:
• When performed in an HCA-accredited facility as determined by CMS. For a list of
accredited facilities, see CMS’s webpage for Carotid artery stenting facilities.
• For patients who are at high surgical risk for carotid endarterectomy (CEA) and who also
have one of the following:
Symptomatic carotid artery stenosis >50%
Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis ≥80%
Patients at high surgical risk for CEA are defined as having significant comorbidities and/or
anatomic risk factors (i.e., recurrent stenosis and/or previous radical neck dissection), and would
be poor candidates for CEA. Significant comorbid conditions include, but are not limited to the
following:
• Congestive heart failure (CHF) class III/IV
• Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 30 %
• Unstable angina
• Contralateral carotid occlusion
• Recent myocardial infarction (MI)
• Previous CEA with recurrent stenosis
• Prior radiation treatment to the neck
• Other conditions that were used to determine patients at high risk for CEA in the prior
carotid artery stenting trials and studies, such as ARCHER, CABERNET, SAPPHIRE,
BEACH, and MAVERIC II
HCA does not pay for carotid artery stenting of intracranial arteries.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
113
Implantable ventricular assist devices
Left ventricular assist devices (LVAD), right ventricular assist devices
(RVAD), Bi-ventricular assist devices (BiVAD)
HCA may consider implantable ventricular assist devices with FDA approval to be medically
necessary in the following situations:
• For use as a bridge to transplantation when both of the following requirements are met:
The client is currently listed as a heart transplantation candidate or under
evaluation to determine eligibility for heart transplantation.
The client is not expected to live until a donor heart is available.
• For use in the post-cardiotomy setting in clients who are unable to be weaned off
cardiopulmonary bypass.
• For use as a destination therapy when the following requirements are met:
The client is at end-stage heart failure.
There is documented ineligibility for human heart transplantation.
The client has either of the following:
New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III or IV* for at least 28 days
and received at least 14 days support with an intraaortic balloon pump or
is dependent on intravenous inotropic agents, with two failed weaning
attempt
NYHA class IV* heart failure for at least 60 days.
*NYHA Class III = marked limitation of physical activity; less than
ordinary activity leads to symptoms
NYHA Class IV= inability to carry on any activity without symptoms;
symptoms may be present at rest
Note: Destination therapy must be done at a CMS-approved VAD destination
therapy facility.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
114
Implantable ventricular assist devices battery replacement and accessories
• Battery replacement- 6 months
• Accessories- 1 year
Percutaneous ventricular assist devices (pVAD)
HCA considers a FDA-approved percutaneous left ventricular assist device (pVAD) medically
necessary for the following indications:
• Providing short-term circulatory support in cardiogenic shock
• As an adjunct to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in the following high-risk
patients:
Clients undergoing unprotected left main or last-remaining-conduit PCI with
ejection fraction less than 35 %
Clients with three vessel disease end diastolic ejection fraction less than 30 %
Pediatric VAD (age 0-18 years)
HCA considers FDA-approved pediatric VADs medically necessary when both of the following
criteria are met:
• The child has documented end-stage left ventricular failure.
• An age and size-appropriate VAD will be used until a donor heart can be obtained.
Varicose vein treatment
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA considers treatment for varicose
veins medically necessary when the following criteria are present:
• Demonstrated reflux in the affected vein
• Minimum of three months of symptoms of pain or swelling sufficient to interfere with
instrumental activities of daily living or presence of complications (e.g., ulceration,
bleeding, or recurrent thrombophlebitis)
• For tributary varicose veins, the previous two conditions must apply and must have a
diameter larger than 3 mm.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
115
Treatments included in this policy are:
• Endovenous Laser Ablation
• Radiofrequency Ablation
• Sclerotherapy
• Phlebectomy
Varicose vein treatment requires a medical necessity review by Comagine Health.
Contraindications for treatment for varicose vein include:
• Pregnancy
• Active infection
• Peripheral arterial disease
• Deep vein thrombosis
Digestive system
Diagnostic upper endoscopy for GERD
Diagnostic upper endoscopy for adults with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may be
considered medically necessary with one of the following conditions:
• Failure of an adequate trial of medical treatment to improve or resolve symptoms
• Presence of the following alarm symptoms:
Persistent dysphagia or odynophagia
Persistent vomiting of unknown etiology
Evaluation of epigastric mass
Confirmation and specific histological diagnosis of radiologically demonstrated
lesions
Evaluation for chronic blood loss and iron deficiency anemia when an upper
gastrointestinal source is suspected or when colonoscopy results are negative
Progressive unintentional weight loss
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
116
This policy does not apply to therapeutic endoscopy (e.g., removal of foreign body) or for clients
with known esophageal or gastric varices or neoplasms, inflammatory bowel disease, familial
adenomatous polyposis syndrome, biopsy confirmed Barrett’s esophagus, biopsy confirmed
esophageal or gastric ulcers, history of upper gastrointestinal stricture.
CPT Code
Short Description
43200
Esophagus endoscopy
43202
Esophagus endoscopy biopsy
43234
Upper gi endoscopy exam
43235
Uppr gi endoscopy diagnosis
43239
Upper gi endoscopy biopsy
Closure of enterostomy
Mobilization of splenic flexure (CPT code 44139) is not paid when billed with enterostomy
procedures (CPT codes 44625 and 44626). CPT code 44139 must be used only in conjunction
with partial colectomy (CPT codes 44140-44147).
Fecal microbiota transplantation
Based upon review of evidence provided by the Health Technology Clinical Committee (HTCC),
HCA considers fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) to be medically necessary for patients
with c. difficile infection who have undergone a failed course of appropriate antibiotic therapy.
HCA does not consider fecal microbiota transplantation medically necessary for treatment of
inflammatory bowel disease.
HCA may perform a post-pay review on any claim to ensure the treatment met coverage
conditions.
FDA position update:
The FDA announced that it would exercise enforcement discretion regarding FMT. As long as
the treating physician obtains adequate informed consent from the patient or the patient’s
legally authorized representative for the procedure, the FDA will not require submission of an
Investigational New Drug Application (IND). Informed consent should include, at a minimum,
a statement that the use of FMT products to treat c. difficile is investigational and include a
discussion of its potential risks. The FMT product is not obtained from a stool bank. The FDA
will exercise this discretion on an interim basis while HCA develops appropriate policies for
the study and use of FMT products under IND.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
117
Drug eluting or bare metal cardiac stents
HCA pays for drug eluting stents or bare metal cardiac stents when the technology criteria are
met. This procedure requires EPA. See expedited prior authorization (EPA) criteria for EPA
#870000422.
Cardiovascular
Angioscopy
HCA pays for one unit of angioscopy (CPT code 35400), per session.
Apheresis
Therapeutic apheresis (CPT codes 36511-36516) includes payment for all medical management
services provided to the client on the date of service. HCA pays for only one unit of either CPT
code per client, per day, per provider. Separate payment is not allowed for the following
procedures on the same date that therapeutic apheresis services are provided, unless a significant
and separately identifiable condition exists which is reflected by the diagnosis code and billed
with modifier 25:
CPT Code
Short Description
99211
Office/outpatient visit est
99212
Office/outpatient visit est
99213
Office/outpatient visit est
99214
Office/outpatient visit est
99215
Office/outpatient visit est
99231
Subsequent hospital care
99232
Subsequent hospital care
99233
Subsequent hospital care
Do not bill apheresis management when billing for critical care time (CPT codes 99291-99292).
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
118
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy (ECMO)
Based upon review of evidence provided by the Health Technology Clinical Committee (HTCC),
HCA considers extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy (ECMO) to be medically
necessary when used for clients:
• With severe life-threatening, but potentially reversible, acute respiratory or cardiac
dysfunction unresponsive to conventional management
• Who need a bridging therapy for pulmonary failure and who are on a pulmonary
transplant list
• Who need a bridging therapy for cardiac failure and who are eligible for a ventricular
assist device or cardiac transplantation
Note: All procedures must be provided at a facility participating in the
Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) case registry. To bill for
ECMO services, the facility must have, available on request, documentation
demonstrating current ELSO registration.
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
Transcatheter aortic valve (TAVR) is considered medically necessary only for the treatment of
severe symptomatic aortic valve stenosis when all of the following occur:
• Prior authorization (PA) must be obtained for the procedure.
• The NPI for each team surgeon must be provided for payment.
• The heart team and hospital must be participating in a prospective, national, audited
registry approved by CMS.
• Conditions of the CMS Medicare national coverage determinations must be met.
Note: HCA does not pay for TAVR for indications not approved by the FDA,
unless treatment is being provided in the context of a clinical trial and PA has
been obtained.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
119
Percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation (PPVI)
HCA will cover PPVI with prior authorization (PA) for adult patients and children. To obtain
PA, the client:
• Must have right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) dysfunction following prior RVOT
repair.
• Must have conduits equal to or larger than 16 millimeters (mm) and equal to or smaller
than 22 mm.
• Cannot undergo, or would like to delay, pulmonary valve replacement through open heart
surgery.
• Must have one of the following dx codes:
I37.x* – Nonrheumatic pulmonary valve disorders
I37.0 – Nonrheumatic pulmonary valve stenosis
I37.1 – Nonrheumatic pulmonary valve insufficiency
I37.2 – Nonrheumatic pulmonary valve stenosis with insufficiency
I37.8 – Other nonrheumatic pulmonary valve disorders
I37.9 – Nonrheumatic pulmonary valve disorder, unspecified
Q21.3 –Tetralogy of Fallot
Q22.x* – Congenital malformations of pulmonary and tricuspid valves
Q22.0 – Pulmonary valve atresia
Q22.1 – Congenital pulmonary valve stenosis
Q22.2 – Congenital pulmonary valve insufficiency
Q22.3 – Other congenital malformations of pulmonary valve
*The x represents a range of codes; it is dependent on the specific diagnosis.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
120
Female genital system
Hysterectomies
(WAC 182-531-0200(5))
Prior authorization for hysterectomies is required regardless of the client’s age. Some
hysterectomy procedures will require a medical necessity review by Comagine Health to
establish medical necessity. However, HCA will use expedited prior authorization (EPA) criteria,
instead of a medical necessity review, for one of the following clinical situations:
• Cancer
• Trauma
For more information, including the EPA numbers and specific criteria, refer to Expedited prior
authorization (EPA).
• Hysterectomies are paid only for medical reasons unrelated to sterilization. A
sterilization consent form is not required when a hysterectomy is performed.
• Federal regulations prohibit payment for hysterectomy procedures until a properly
completed Hysterectomy Consent and Patient Information Form, HCA 13-365, is
received. See Where can I download HCA forms? To comply with this requirement,
surgeons, anesthesiologists, and assistant surgeons must obtain a copy of a completed
HCA-approved consent form to attach to their claim. Note: A new version of this form is
available for use. For clients signing a hysterectomy consent form on or after January 1,
2020, use the November 2019 version of the form.
• ALL hysterectomy procedures require a properly completed HCA-approved
Hysterectomy Consent and Patient Information Form, 13-365, regardless of the client's
age or the ICD diagnosis. The form must be completed and signed by all parties prior to
the procedure. See Where can I download HCA forms?
• Submit the claim and completed HCA-approved consent form (see HCA’s Billers,
providers, and partners webpage).
Download the Hysterectomy Consent and Patient Information Form, 13-365. See Where can
I download HCA forms?

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
121
Sterilizations
(WAC 182-531-1550)
Information on sterilization, instructions on how to complete the sterilization consent form and
how to become an approved hysteroscopic sterilization provider are available in HCA’s
Sterilization Supplemental Billing Guide.
Integumentary system
Clarification of coverage policy for miscellaneous
procedures
Limitations on coverage for certain miscellaneous procedures are listed below:
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Prior
Authorization
Limitations
11980
Implant hormone pellet(s)
Y
N/A
S0189
Testosterone pellet 75 mg
Y
S0139
Minoxidil, 10 mg
N
I10 (essential hypertension)
Male genital system
Circumcisions
(CPT codes 54150, 54160, and 54161)
Circumcisions are covered when billed with one of the following diagnoses:
• Phimosis (ICD diagnosis code N47.3 - N47.8)
• Balanoposthitis (ICD diagnosis code N47.0 – N47.8, N48.1)
• Balanitis Xerotica (ICD diagnosis code N48.0)
Note: HCA covers circumcisions (CPT codes 54150, 54160, and 54161) only
with medical ICD diagnosis codes Phimosis, Balanoposthitis, or Balanitis
Xerotica.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
122
Musculoskeletal system
Artificial disc replacement
HCA pays for Cervical Disc Replacement when the technology criteria are met. These
procedures require a medical necessity review by Comagine Health.
HCA does not consider lumbar disc replacement to be medically necessary.
Bone growth stimulators
HCA pays for bone growth stimulators (CPT codes 20974, 20975, and 20979) when the
technology criteria are met. These procedures require prior authorization (PA) to establish
medical necessity.
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 for lumbar fusion
HCA requires that the following criteria be met for the use of bone morphogenetic protein -2
(rhBMP-2):
•
Clients are age 18 and older.
•
It is used only in the lumbar spine.
•
Either of the following:
It is used in primary anterior open or minimally invasive fusion at one level
between L4 and S1.
Revision of lumbar fusion when autologous bone or bone marrow harvest is not
technically feasible, or is not expected to result in fusion for clients who are
diabetic, smokers or have osteoporosis.
• Lumbar fusion is not covered for clients with a diagnosis of degenerative disc disease.
Note: The agency requires a medical necessity review by Comagine Health for
associated spinal fusion procedures. Include in the request for authorization:
• The anticipated use of BMP -2
• Either of the following:
The CPT code 20930.
Diagnosis code 3E0U0GB, insertion of recombinant bone
morphogenetic protein.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
123
Bone morphogenetic protein 7 for lumbar fusion
HCA will not pay for bone morphogenetic protein – 7 (rhBMP-7) as supporting clinical evidence
has not been established.
Cervical spinal fusion arthrodesis
HCA pays for cervical spinal fusion for degenerative disc disease with limitations.
For clients 20 age and younger, HCA does not require prior authorization for these services. For
clients age 21 and older, HCA requires a medical necessity review by Comagine Health.
Limitations of Coverage
Cervical spinal fusion is covered when all of the following conditions are met:
• Patients have signs and symptoms of radiculopathy
• There is advanced imaging evidence of corresponding nerve root compression
• Conservative (non-operative) care has failed
Cervical surgery for radiculopathy and myelopathy
HCA may cover cervical surgery for neck pain when there is subjective, objective and imaging
evidence of radiculopathy or myelopathy. For clients age 20 and younger, HCA does not require
prior authorization for the surgeries listed below. For clients age 21 and older the surgeries listed
below require a medical necessity review by Comagine Health.
• ACDF anterior cervical discectomy with fusion
• TDA total disc arthroplasty
• Laminotomy
• Laminectomy with or without a fusion
• Laminoplasty
• Foraminotomy
• Corpectomy
• Repeat surgeries
*For nicotine users: Abstinence from nicotine for at least four weeks before surgery as shown
by two negative urine cotinine tests is highly recommended for all fusions and repeat fusions
done for radiculopathy. This does not apply to progressive myelopathy or motor radiculopathy.
Tobacco/nicotine cessation services are a covered benefit. See Behavior change intervention –
Behavior change intervention - tobacco/nicotine cessation.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
124
Endoscopy procedures
Endoscopy procedures are paid as follows:
• When multiple endoscopies from the same endoscopy group are performed on the same
day, the procedure with the highest maximum allowable fee is paid the full amount. The
second, third, etc., are paid at the maximum allowable amount minus the base endoscopy
procedure's allowed amount.
• When multiple endoscopies from different endoscopy groups are billed, the multiple
surgery rules detailed above apply.
• When payment for other procedures within an endoscopy group is less than the
endoscopy base code, no payment is made.
• HCA does not pay for an E/M visit on the same day as the diagnostic or surgical
endoscopy procedure unless there is a separately identifiable service unrelated to the
endoscopy procedure. If it is appropriate to bill the E/M code, use modifier 25.
Epiphyseal
Epiphyseal surgical procedures (CPT codes 25450, 25455, 27185, 27475, 27477-27485, 27742,
and 27730-27740) are allowed only for clients age 17 and younger.
Hip resurfacing
HCA does not consider hip resurfacing to be medically necessary .
Hip surgery for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome
Based upon review of evidence provided by the Health Technology Clinical Committee (HTCC),
HCA does not consider hip surgery to be medically necessary for treatment of femoroacetabular
impingement syndrome.
Knee arthroscopy for osteoarthritis
HCA does not recognize lavage, debridement and/or shaving of the knee (CPT code 29877) as
medically necessary when these are the only procedure(s) performed during the arthroscopy.
HCA does not reimburse for CPT code 29877 under these circumstances. HCA will pay for
arthroscopies done for other diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. This requires a medical
necessity review by Comagine Health.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
125
Microprocessor-controlled lower limb prostheses
See HCA’s Prosthetic and Orthotic (P&O) Devices Billing Guide.
Osteochondral allograft and autograft transplantation
HCA does not recognize osteochondral allograft or autograft transplantation for joints other than
the knee as medically necessary. Osteochondral allograft or autograft transplantation in the knee
joint may be considered medically necessary.
Osteochondral allograft or autograft transplantation is considered medically necessary under all
of the following conditions:
• The client is younger than 50 years of age.
• There is no presence of malignancy, degenerative arthritis or inflammatory arthritis in the
joint.
• There is a single focal full-thickness articular cartilage defect that measures less than 3
cm in diameter and 1 cm in bone depth on the weight bearing portion of the medial or
lateral femoral condyle.
The following codes are covered and require a medical necessity review by Comagine Health for
clients age 21 and older:
CPT Code
Short Description
29866
Autgrft implnt knee w/scope
29867
Allgrft implnt knee w/scope
29868
Meniscal trnspl knee w/scpe
Osteotomy reconstruction
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Does not require PA when billed with
the appropriate ICD diagnoses
21198
Reconstr lwr jaw segment
Percutaneous kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty and sacroplasty
HCA does not recognize percutaneous kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty and sacroplasty as medically
necessary for relief of pain and improvement of function for spinal fractures.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
126
Sacroiliac joint fusion
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA does not consider minimally
invasive and open sacroiliac joint fusion procedures to be medically necessary for clients age 21
and older with chronic sacroiliac joint pain related to degenerative sacroiliitis or sacroiliac joint
disruption, or both. This decision does not apply to any the following:
• Low back pain of other etiology
• Sacroiliac joint pain related to recent major trauma or fracture
• Infection
• Cancer
• Sacroiliitis associated with inflammatory arthropathies
For these issues, see the fee schedule for coverage.
Robotic assisted surgery
Although robotic assisted surgery (RAS) may be considered medically necessary, HCA does not
pay separately for HCPCS code S2900 and reimburses only for the underlying procedure.
When billing for the underlying procedure, HCA requests billing providers to include RAS on
the claim in order to track utilization and outcome. HCA will monitor RAS through retrospective
auditing of billing and the review of operative reports.
Nervous system
Discography
The following procedures require prior authorization from HCA for clients age 21 and older.
Prior authorization is not required for clients age 20 and younger.
Discography for clients with chronic low back pain and uncomplicated lumbar degenerative disc
disease is considered not medically necessary. Conditions which may be considered for
authorization by HCA include:
• Radiculopathy.
• Functional neurologic deficits (motor weakness or EMG findings of radiculopathy).
• Spondylolisthesis (> Grade 1).
• Isthmic spondylolysis.
• Primary neurogenic claudication associated with stenosis.
• Fracture, tumor, infection, inflammatory disease.
• Degenerative disease associated with significant deformity.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
127
CPT Code
Short Description
62290
Inject for spine disk x-ray
62291
Inject for spine disk x-ray
72285
Discography cerv/thor spine
72295
X-ray of lower spine disk
Facet neurotomy, cervical and lumbar
Facet neurotomy requires a medical necessity review by Comagine Health. HCA has instructed
Comagine Health to use Washington State’s Labor & Industries (L&I) Medical Treatment
Guidelines (MTG) to establish medical necessity with the following exceptions:
A trial of conservative treatment modalities have been tried and failed for a minimum of three
months, instead of six months, including all of the following:
• Medications: NSAIDS, muscle relaxants, corticosteroids, antidepressants, anticonvulsants
or opiates
• Activity modification
• Physical therapy
Lumbar radiculopathy
HCA pays for surgery for lumbar radiculopathy or sciatica when criteria are met. For clients age
20 and younger, HCA does not require prior authorization for these services. For clients age 21
and older, HCA requires a medical necessity review by Comagine Health.
Limitations of coverage
HCA covers open discectomy or microdiscectomy with or without endoscopy (lumbar
laminectomy, laminotomy, discectomy, foraminotomy) with all the following conditions:
• For clients age 21 and older with lumbar radiculopathy with subjective and objective
neurologic findings that are corroborated with an advanced imaging test (i.e., Computed
Tomography (CT) scan, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), or myelogram)
• There is a failure to improve with a minimum of 6 weeks of nonsurgical care, unless
progressive motor weakness is present

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
128
HCA does not cover minimally invasive procedures that do not include laminectomy,
laminotomy, or foraminotomy, including but not limited to:
• Energy ablation techniques
• Automated Percutaneous Lumbar Discectomy (APLD)
• Percutaneous laser
• Nucleoplasty
HCA does not consider these minimally invasive procedures to be medically necessary.
Implantable infusion pumps or implantable drug delivery
systems
HCA pays for CPT codes 62350, 62351, 62360, and 62361 when medically necessary and only
for the indications below:
• Cancer pain
• Spasticity
Note: Implantable drug delivery systems (Infusion Pump or implantable drug
delivery system) are not considered medically necessary for treatment of
chronic pain not related to cancer.
Spinal cord stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain
HCA does not recognize spinal cord stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain as medically
necessary. HCA will consider requests for other diagnoses. CPT codes 64575, 64580, 64581,
64585 and 64595 require prior authorization (PA) through HCA.
Spinal injections for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes
(outpatient)
HCA requires medical necessity reviews for spinal injection procedures, including diagnostic
selective nerve root block through Comagine Health, which uses an established online
questionnaire. (See Comagine Health in this guide for additional information.)
Diagnostic selective nerve root block
HCA requires a medical necessity review for the diagnostic selective nerve root block through
Comagine Health.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
129
Sacroiliac joint injections
For this procedure, the following policy applies:
• The patient has chronic sacroiliac joint pain.
• There must be a failure of at least 6 weeks of conservative therapy.
• These injections must be done with fluoroscopic or CT guidance
Restrictions:
• There must be no more than 1 injection without medical record documentation of at
least 30% improvement in function and pain, when compared to the baseline documented
before the injections started.
• Requests for more than 2 injections require clinical review.
Therapeutic/diagnostic epidural injections in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar
spine
Therapeutic/diagnostic epidural injections in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine are
considered medically necessary for the treatment of chronic pain when the following criteria are
met:
• Radicular pain (such as, back pain radiating below the knee, with or without positive
straight leg raise) with at least 6 weeks of failed conservative therapy
• Radiculopathy (such as motor weakness, sensory low or reflex changes) with at least 2
weeks of failed conservative therapy
• The medical record with objective documentation of patient’s baseline level of function
and pain
• An injection that is given with anesthetic agent and/or steroid agent
• An injection that is transforaminal, translaminar or interlaminar
• Use of fluoroscopic, CT or ultrasound guidance

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
130
Restrictions:
• Prior authorization is required for the first injection, which will cover the second
injection, if indicated. Additional authorization is required for the third injection.
• No more than 2 injections (2 dates of service) may be given without medical record
documentation of a 30% improvement in function and pain when compared to the
baseline documented before the injections started. Function and pain must be measured
and documented on a validated instrument.
• There is a maximum of 3 injections within 6 months, and no more than 3 injections per a
12-month period.
• There should be no more than 2 vertebral levels and only one side injected (right or left)
per date of service.
• The MRI/CT scan is not a prerequisite for authorization of an epidural injection.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) device
HCA does not cover TENS devices, related supplies and services for independent home-use.
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)
(WAC 182-531-0200(4)(h))
HCA considers VNS for the treatment of epilepsy as medically necessary only for management
of epileptic seizures in clients age 12 and older who have a medically refractory seizure disorder.
VNS requires EPA. See EPA #870001554 for clinical criteria. If clients do not meet the EPA
criteria, PA is required.
VNS procedures can be performed in an inpatient hospital or outpatient hospital setting.
HCA does not pay for VNS and related procedures for a diagnosis of depression
(CPT 64553-64565, 64590-64595, 95970, 95974, and 95975).
VNS for the treatment of depression has no evidence to support coverage.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
131
Skin substitutes
HCA considers skin substitutes to be medically necessary for wound treatment under the
following conditions:
• For the treatment of partial and full-thickness diabetic foot ulcers of greater than 4
weeks duration that have not adequately responded to standard ulcer therapy (including
adequate off-loading and debridement) and that extend through the dermis but without
tendon, muscle, or bone exposure. Standard wound therapy is defined to include all the
following:
Assessment of vascular status with treatment as indicated
Nutritional optimization
Optimal blood glucose control
Adequate debridement
Moist dressing
Off-loading
Treatment of infection
Tobacco/nicotine cessation intervention when applicable.
• For the treatment of chronic, non-infected, partial and full-thickness venous stasis ulcers
that have failed standard ulcer therapy of greater than 4 weeks using regular dressing
changes and therapeutic compression
• For the treatment of burns, including partial-thickness and full-thickness burns
• For the treatment of wounds related to dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa when standard
wound therapy has failed
• For use in breast reconstruction surgery as a part of breast cancer treatment
Limitations
• HCA covers a maximum of 10 applications per year.
• HCA does not cover reapplication if the initial treatment episode is not successful.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
132
Sleep apnea
Surgical treatment for sleep apnea
HCA requires prior authorization for the following surgical treatment for obstructive sleep apnea
(OSA) or upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS) when billed with diagnosis code G47.33
(obstructive sleep apnea) or G47.30 (unspecified sleep apnea):
Procedure Codes
Short Descriptions
21199
Reconstr lwr jaw w/advance
21685
Hyoid myotomy & suspension
42120
Remove palate/lesion
42140
Excision of uvula
42145
Repair palate pharynx/uvula
42160
Treatment mouth roof lesion
42299
Palate/uvula surgery
See also Sleep medicine testing.
Urinary systems
Collagen implants
HCA pays for CPT code 51715 and HCPCS codes L8603, L8604 and/or L8606 only when the
appropriate diagnosis code N36.42 or N36.43 (Intrinsic sphincter deficiency) is used. See
Urinary tract implants for limitations.
Indwelling catheter
• Separate payment is allowed for insertion of a temporary, indwelling catheter when it is
used to treat a temporary obstruction and is performed in a physician's office.
• Bill for the insertion of the indwelling catheter using CPT code 51702 or 51703.
• HCA pays providers for insertion of an indwelling catheter only when performed in an
office setting.
• Insertion of an indwelling catheter is bundled when performed on the same day as a
major surgery.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
133
• Insertion of an indwelling catheter is bundled when performed during the postoperative
period of a major surgery.
Urinary tract implants
(CPT code 51715)
Prior to inserting a urinary tract implant, the provider must:
• Have urology training in the use of a cystoscope and must have completed a urinary tract
implant training program for the type of implant used.
• Document that the client has shown no incontinence improvement through other
therapies for at least 12 months prior to collagen therapy.
• Administer and evaluate a skin test for collagen sensitivity (CPT code 95028) over a
four-week period prior to collagen therapy. A negative sensitivity must be documented in
the client's record.
Refer to urinary tract implants covered by HCA. All services provided and implant codes must
be billed on the same claim.
Urological procedures with sterilizations in the description
These procedures may cause the claim to stop in HCA's payment system and trigger a manual
review as a result of HCA's effort to remain in compliance with federal sterilization consent form
requirements. If the surgery is not being done for the purpose of sterilization, or the sterilizing
portion of the procedure is not being performed, a sterilization consent form is not required.
However, one of the following must be noted in the Claim Note section of the claim:
• Not sterilized
• Not done primarily for the purpose of sterilization

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
134
Radiology Services
(WAC 182-531-1450)
Radiology services – general limits
• HCA does not pay radiologists for after-hours service codes.
• Claims must have the referring provider’s national provider identifier (NPI) in the
appropriate field on the claim.
• The following services are not usually considered medically necessary and may be
subject to post-pay review:
X-rays for soft tissue diagnosis
Bilateral X-rays for a unilateral condition
X-rays in excess of two views
Note: HCA does not pay for radiology services with diagnosis code Z01.89.
Providers must bill the appropriate medical ICD diagnosis code.
Radiology modifiers for bilateral procedures
• Bill the procedure on two separate lines using modifier 50 on one line only. In addition,
include modifier LT or RT on the separate lines when the radiological procedure is
performed on both sides.
• Do not use modifier 50, LT, or RT if the procedure is defined as bilateral.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
135
Breast, mammography
Mammograms
HCA has adopted the National Cancer Institute (NCI) recommendations regarding screening
mammograms. For clients age 40 and over, one annual screening mammogram is allowed per
calendar year. Screening mammograms, with or without tomosynthesis, for clients age 39 and
younger require prior authorization.
HCA covers digital breast tomosynthesis when performed with a screening mammography for
clients age 40 through 74 who are candidates for screening mammography. One annual screening
is allowed per calendar year. See HCA’s Physician-related/professional services fee schedule for
specific code details.
Diagnostic mammograms are a covered service when they are medically necessary. Digital
breast tomosynthesis is covered when medically necessary and performed with diagnostic
mammography.
Diagnostic radiology (diagnostic imaging)
Multiple procedure payment reduction (MPPR)
HCA applies the multiple payment model outlined by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid
Services (CMS) for multiple diagnostic radiology procedures. See MLN Matters® Number:
MM6993.
The MPPR applies to the technical component (TC) of certain diagnostic imaging procedures
when billed for the same client, on the same day and session, by the same billing provider.
The MPPR applies to:
• TC only services.
• TC portion of global services for the procedures with multiple surgery value of ‘4’ in the
Medicare Physicians Fee Schedule Database.
The MPPR does not apply to:
• The professional component (PC).
• The PC portion of global services.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
136
HCA’s payment is as follows:
• A full payment for the highest priced TC radiology code on the claim
• A 50% reduction applied to each subsequent TC radiology code on the same claim
Which procedures require a medical necessity review by
Comagine Health?
(WAC 182-531-1450)
HCA requires prior authorization for selected procedures
HCA and Comagine Health have contracted to provide web-based submittal for utilization
review services to establish the medical necessity of selected procedures. Comagine Health
conducts the review of the request to establish medical necessity, but does not issue
authorizations. Comagine Health forwards its recommendations to HCA for final authorization
determination. See Medical necessity review by Comagine Health for additional information.
Computed Tomography (CT)
Head
70450
70460
70470
Abdomen 74150 74160 74170
Pelvis
72192
72193
72194
Abdomen& Pelvis
74176
74177
74178
• Multiple CT Scans are allowed only if done at different times of the day or if modifiers
LT or RT are attached.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Head
70551
70552
70553
C – Spine
72141
72142
72156
L- Spine
72148
72149
72158
Upper Extremity
73221
73222
73223
Breast
77046
77047
77048
77049
C8903*
C8904*
C8905*
C8906*
C8907*
C8908*
Lower Extremity
73721
73722
73723
*Required for outpatient hospital claims
Reminder for outpatient hospitals: When requesting a medical necessity review by Comagine
Health for a breast MRI, use the 7xxxx CPT® code. However, when billing Medicaid, use the
“C” HCPCS code.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
137
Advanced imaging services do NOT require prior authorization when billed with either of the
following place of service (POS):
• (POS) 21 (Inpatient Hospital)
• (POS) 23 (Emergency Room)
When billing for a professional component performed in a POS other than POS 21 or 23 such as
a radiologist’s office, but the image was performed on a client who was in the ER or an inpatient
setting, use modifier 26 and enter “ER ordered service,” or “client inpatient,” or “client referred
from ER,” or “professional read only for image not done by our facility,” or “professional
services only for pre-authorized service” in the Claim Note section of the electronic claim.
A radiologist who performed a professional interpretation, referred to as a “read- only,” on an
outpatient advanced image must be added to HCA’s authorization record to receive payment.
• Contact HCA at 800-562-3022, ext. 52018, to add the reading radiologist’s NPI to the
record.
- OR –
• Submit a written request for an NPI add/update as follows:
Go to Document submission cover sheets.
Scroll down to PA (Prior Authorization) Pend Forms.
When the form appears on the screen, insert the Authorization Reference number
(ProviderOne authorization number) in the space provided and press enter to
generate the barcode on the form.
Note: Professionals who do “read-only” when another facility ordered and
performed the advanced imaging, but did not obtain prior authorization, must
add: “Professional read only for image not done by our facility” in the comments
field of the claim.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
138
Imaging for rhinosinusitis
HCA considers imaging of the sinus with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance
imaging (MRI) for rhinosinusitis to be medically necessary when one of the following is true:
• The client is experiencing the following “red flags:”
Swelling of orbit
Altered mental status
Neurological findings
Signs of meningeal irritation
Severe headache
Signs of intracranial complication, including, but not limited to:
Meningitis
Intracerebral abscess
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
Involvement of nearby structures, including, but not limited to periorbital
cellulitis
• Two of the following persistent symptom for more than 12 weeks AND medical therapy
has failed:
Facial pain-pressure-fullness
Mucopurulent drainage
Nasal obstruction (congestion)
Decreased sense of smell
• Needed for surgical planning.
HCA considers magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the sinus to be medically necessary when
the criteria in this section are met AND the client is younger than age 21 or is pregnant.
Note: Expedited prior authorization is required.
• Use EPA number 870001422 or 870001553 for MRI of the sinus.
• Use EPA number 870001423 for CT imaging of the sinus.
HCA considers repeat scanning (CT or MRI) to be medically necessary for “red flags” or
surgical planning only.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
139
Computed tomography angiography (CTA)
CPT code 75574 is restricted to place of service 19, 21, 22, 23.
HCA pays for CTA when:
• Using computed tomography machines with 64-slice or better capability
AND
• The following medical necessity criteria are met:
Patients have low to intermediate risk of coronary artery disease
Investigation of acute chest pain is conducted in an emergency department or
hospital setting
HCA will not pay for CTA when:
• Using a CT scanner that uses lower than 64-slice technology
OR
• The procedure is not medically necessary as follows:
Patients are asymptomatic or at high risk of coronary artery disease.
Investigation of coronary artery disease is conducted outside of the emergency
department or hospital setting.
Contrast material
(WAC 182-531-1450(2))
Contrast material is not paid separately, except in the case of low-osmolar contrast media
(LOCM) used in intrathecal, intravenous, and intra-arterial injections for clients with one or
more of the following conditions:
• A history of previous adverse reaction to contrast material, with the exception of a
sensation of heat, flushing, or a single episode of nausea or vomiting
• A history of asthma or allergy
• Significant cardiac dysfunction including recent or imminent cardiac decompensation, severe
arrhythmia, unstable angina pectoris, recent myocardial infarction, and pulmonary hypertension
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
140
• Generalized severe debilitation
• Sickle cell disease
To bill for LOCM, use the appropriate HCPCS procedure codes: Q9951, Q9965, Q9966 or
Q9967. The brand name of the LOCM and the dosage must be documented in the client's record.
Consultation on X-ray examination
When billing a consultation, the consulting physician must bill the specific X-ray code with
modifier 26 (professional component).
For example: The primary physician would bill with the global chest X-ray
(CPT code 71020), or the professional component (CPT code 71020-26), and the
consulting physician would bill only for the professional component of the chest
X-ray (e.g., CPT code 71020-26).
Coronary artery calcium scoring
HCA does not recognize computed tomography, heart, without contrast material, with
quantitative evaluation of coronary calcium as medically necessary.
Prior authorization from HCA is required for CPT code 75571.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
• Check the Physician’s related services fee schedule for authorization requirements for MRIs.
• HCA is implementing the Washington State Health Technology Clinical Committee
(HTCC's) decision that uMRI (upright MRI) is experimental and investigational; therefore,
according to WAC 182-501-0165, uMRI is a "D" level evidence that is not supported by any
evidence regarding its safety and efficacy. Medicaid will not reimburse unless one of the
following criteria is met:
The client must have a humanitarian device exemption.
There must be a local Institutional Review Board protocol in place.
• HCA covers fetal MRIs under CPT code 74712.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
141
Portable X-rays
• Portable X-ray services furnished in a client’s home or nursing facility and payable by
HCA are limited to the following:
Skeletal films involving extremities, pelvis, vertebral column, or skull
Chest or abdominal films that do not involve the use of contrast media
Diagnostic mammograms
• Bill for transportation of X-ray equipment as follows:
R0070 - If there is only one patient, bill one unit.
R0075 - If there are multiple patients, bill one unit per individual client’s claim
with one of the following modifiers, as appropriate. Bill using a separate claim
for each Medicaid client seen. HCA pays the fee for procedure code R0075
divided by the number of clients, as outlined by the modifiers in the following
table:
Procedure Code
Short Description
R0070
Transport portable x-ray
R0075-UN
Transport port x-ray multipl-2 clients seen
R0075-UP
Transport port x-ray multipl-3 clients seen
R0075-UQ
Transport port x-ray multipl-4 clients seen
R0075-UR
Transport port x-ray multipl-5 clients seen
R0075-US
Transport port x-ray multipl-6 or more clients seen
Note: The fee for HCPCS code R0075 is divided among the clients served, as
outlined by the modifiers indicated above. If no modifiers are used for HCPCS
code R0075, the code will be denied. Do not bill HCPCS code R0070 in
combination with HCPCS code R0075.
Ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm
(CPT 76706)
HCA covers ultrasound screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm only when both of the
following apply:
• Billed with diagnosis code Z13.6 (special screening for other and unspecified
cardiovascular conditions)
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
142
• A client meets at least one of the following conditions:
Has a family history of an abdominal aortic aneurysm
Is a male who is between 65 and 75 years old and has smoked at least 100
cigarettes in his lifetime
Virtual colonoscopy or computed tomographic colonography
HCA does not recognize computed tomographic colonography for routine colorectal cancer
screening as medically necessary.
CPT Code
Description
74261
Ct colonography dx
74262
Ct colonography dx w/dye
74263
Ct colonography screening
Screening and monitoring tests for osteopenia/osteoporosis
HCA covers bone mineral density testing and repeat testing with dual x-ray absorptiometry
(DXA) with limitations. These tests require expedited prior authorization. See EPA #870001363
and EPA #870001364 for criteria. If the EPA criteria are not met, prior authorization is required.
Note: Serial monitoring is not covered once treatment for osteoporosis has
begun.
Functional neuroimaging for primary degenerative
dementia or mild cognitive impairment
Based upon review of the evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA does not consider functional
neuroimaging for primary degenerative dementia or mild cognitive impairment to be medically
necessary. The following imaging technologies included in this policy are:
• Fludeoxyglucose (FDG) Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
• (11)C-dihydrotetrabenazine (C-DTBZ) PET
• Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
• Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
143
Diagnostic Ultrasound
Obstetrical ultrasounds
Routine ultrasounds for average risk pregnant women are considered medically necessary with
limitations. HCA considers two ultrasounds per average risk singleton pregnancy as medically
necessary. HCA pays for:
• One routine ultrasound in the first trimester (less than 13 weeks gestational age) for the
purpose of:
Identifying fetal aneuploidy
Anomaly
Dating confirmation
• One routine ultrasound for the purpose of anatomy screening between 16 and 22 weeks
gestation.
HCA does not pay for:
• Ultrasounds when provided solely for the determination of gender.
• Third trimester ultrasounds unless a specific indication has developed or the pregnancy is
considered high-risk.
The above conditions and limitations do not apply to multiple gestation pregnancies and/or fetus
with aneuploidy or known anomaly.
Note: Additional ultrasounds are subject to postpayment review.
Nuclear medicine
HCA requires prior authorization for selected procedures.
Which procedures require a medical necessity review from
HCA?
(CPT code 78459)
HCA requires prior authorization for myocardial PET imaging for metabolic evaluation.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
144
Which procedures require a medical necessity review by
Comagine Health?
(WAC 182-531-1450)
HCA and Comagine Health have contracted to provide web-based submittal for utilization
review services to establish the medical necessity of selected procedures. Comagine Health
conducts the review of the request to establish medical necessity, but does not issue
authorizations. Comagine Health forwards its recommendations to HCA for final authorization
determination. See Medical necessity review by Comagine Health for additional information.
Cardiac Imaging (SPECT)
Parathyrd planar w/wo subtrj
78071
Ht muscle image spect sing
78451
Ht muscle image spect mult
78452
Ht muscle image planar sing
78453
Ht musc image planar mult
78454
PET Scans
PET-CT Scans
Brain
78608
Limited Area (Chest, head, neck)
78814
Limited Area
78811
Skull base to mid thigh
78815
Skull base to mid thigh
78812
Whole body
78816
Full Body
78813
Advanced imaging services do NOT require PA when billed with either of the following place of
service (POS):
• (POS) 21 (Inpatient Hospital)
• (POS) 23 (Emergency Room)
When billing for a professional component performed in a POS other than POS 21 or 23 such as
a radiologist’s office, but the image was performed on a client who was in the ER or an inpatient
setting, enter “ER Ordered Service” or “client inpatient” in the Claim Note section of the
electronic claim.
A radiologist who performed a professional interpretation, referred to as a “read- only”, on an
outpatient advanced image must be added to HCA’s authorization record to receive payment.
Contact HCA at 800-562-3022, ext. 52018, to add the reading radiologist’s NPI to the record.
Note: Professionals who do read-only when another facility ordered and
performed the advanced imaging, but did not obtain prior authorization, must
add: “Professional read only for image not done by our facility” in the claim note
of the claim.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
145
Radiopharmaceutical diagnostic imaging agents
• When performing nuclear medicine procedures, HCA allows separate payment for
radiopharmaceutical diagnostic imaging agents. To see if a procedure code is covered,
see the Professional administered drugs fee schedule.
• HCA allows the following CPT codes for radiopharmaceutical therapy without PA: CPT
codes 79101, 79445, and 79005.
Positron emission tomography (PET) scans for lymphoma
• Based upon review of evidence provided by the Health Technology Clinical Committee
(HTCC), HCA in most cases considers positron emission tomography (PET) scans (i.e.,
PET with computed tomography or PET/computed tomography) for lymphoma to be
medically necessary under the following conditions:
Initial staging scan. Covered followed by up to three (3) scans per active
occurrence of lymphoma.
When used to assess a response to chemotherapy, scans should not be
done any sooner than 3 weeks after completion of any chemotherapy
cycle, except for advanced stage Hodgkin’s lymphoma, after four (4)
cycles of ABVD chemotherapy.
When used to assess response to radiation therapy, scans should not be
done any sooner than 8 weeks after completion of radiation or combined
chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Relapse. Covered when relapse is suspected in the presence of clinical symptoms
or other imaging finding suggestive of recurrence.
HCA does not consider PET scans to be medically necessary when done for surveillance.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
146
Nuclear medicine - billing
When billing HCA for nuclear medicine, the multiple surgery rules are applied when the coding
combinations listed below are billed:
• For the same client, on the same day, by the same physician or by more than one
physician of the same specialty in the same group practice
• With other codes that are subject to the multiple surgery rules, not just when billed in the
combinations specified below:
CPT code 78306 (bone imaging; whole body) and CPT code 78320 (bone
imaging; SPECT)
CPT code 78802 (radionuclide localization of tumor; whole body), CPT code
78803 (tumor localization; SPECT), and CPT code 78804 (radiopharmaceutic
localization of tumor requiring 2 or more days)
CPT code 78806 (radionuclide localization of abscess; whole body) and 78807
(radionuclide localization of abscess; SPECT)
Radiation oncology
Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)
IMRT is considered medically necessary:
• To spare adjacent critical structures to prevent toxicities within client’s expected life
span
See EPA #870001374.
To meet EPA criteria, any cancer that would require radiation to focus on the
head/neck/chest/abdomen meets the EPA criteria. Clinical documentation is
required that states which critical structure is spared. For example: “Critical
structure spared is bladder.” IMRT is considered medically necessary when there
is a concern about damage to surrounding critical structures with the use of
external beam or 3D conformal radiation therapy.
• For undergoing treatment in the context of evidence collection/submission of outcome
data - Prior authorization required

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
147
Proton beam therapy
Based upon review of evidence provided by the Health Technology Clinical Committee (HTCC),
HCA considers proton beam therapy to be medically necessary for:
• Clients age 20 and younger without conditions
• Clients age 21 and older for the treatment of the following primary cancers:
Esophageal
Head/neck
Skull-based
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Brain/spinal
Ocular
Other primary cancers where all other treatment options are contraindicated after
review by a multidisciplinary tumor board.
For clients age 21 and older, HCA does not consider proton beam therapy to be medically
necessary for all other conditions.
Stereotactic radiation surgery
Stereotactic Radiation Surgery (SRS) for Central Nervous System (CNS) primary and metastatic
tumors require prior authorization.
HCA pays for SRS for adults and children when both of the following criteria are met:
• Patient functional status score (i.e., Karnofsky score) is greater than or equal to 50
• Evaluation includes multidisciplinary team analysis (e.g., tumor board), including
surgical input
Stereotactic body radiation therapy
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) is covered for adults and children for the following
conditions only:
• For cancers of spine/paraspinal structures
• For inoperable non-small cell lung cancer, stage 1
Evaluation includes multidisciplinary team analysis (e.g., tumor board), including surgical input.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
148
Tumor treating fields
Based upon review of evidence provided by the Health Technology Clinical Committee (HTCC),
HCA in most cases does not consider tumor treating fields to be medically necessary for
treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme, recurrent glioblastoma multiforme, and
for treatment of other cancers.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
149
Pathology and Laboratory
(WAC 182-531-0800 and WAC 182-531-0850)
Certifications
Independent laboratories - certification
Independent laboratories must be certified according to Title XVII of the Social Security Act
(Medicare) to receive payment from Medicaid. HCA pays laboratories for Medicare-approved
tests only.
Reference labs and facilities - CLIA certification
All reference (outside) labs and facilities performing laboratory testing must have a Clinical
Laboratory Improvement Amendment (CLIA) certificate and identification number on file with
HCA in order to receive payment from HCA.
To obtain a CLIA certificate and number, or to resolve questions concerning a CLIA
certification, call (206) 361-2805 or write to:
DOH - Office of Laboratory Quality Assurance
1610 NE 150th Street
Shoreline, WA 98155
(206) 361-2805 (phone); (206) 361-2813 (fax)
Anatomic pathology
Pap smears
For professional services related to Pap smears, refer to Cancer screens.
• Use CPT® codes 88147-88154, 88164-88167, and HCPCS P3000-P3001 for conventional
Pap smears.
• HCA pays for thin layer preparation CPT codes 88142-88143 and 88174-88175. HCA
does not pay providers for HCPCS codes G0123-G0124 and G0141-G0148. HCA pays
for thin layer Pap smears at Medicare's payment levels. Thin layer preparation and
conventional preparation CPT codes cannot be billed in combination.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
150
• Use CPT code 88141 in conjunction with one of the following codes: 88142-88143,
88164-88167, or 88174-88175.
• Use the appropriate medical diagnosis if a condition is found.
• HCA pays providers for cervical cancer screening according to nationally recognized
clinical guidelines in conjunction with an office visit focused on family planning.
• For clients on the Family Planning Only – Pregnancy Related program or the Family
Planning Only program (formerly referred to as TAKE CHARGE), see the Family
Planning Billing Guide.
Screening exams
Cancer screens
(HCPCS codes G0101, G0103-G0105, G0121-G0122, G0297 and CPT codes 82270 and 81519)
HCA covers the following cancer screenings:
• Cervical or vaginal
• Colonoscopies
• Colorectal
• Lung (low dose CT)
• Oncology genomic testing (breast)
• Pelvic/breast exams
• Prostate
• PSA testing
• Screening sigmoidoscopies
HCPCS
Code
Short
Description
Limitations
G0101
CA screen; pelvic and
clinical breast
examination
Females only. As indicated by nationally recognized clinical
guidelines. This is an examination code. Do not use this code
for laboratory tests like Pap smears or HPV testing. Bill in
the same way as other exam codes. This may be billed in
conjunction with an E/M code.
G0103
PSA screening
Once every 12 months when ordered for clients age 50 and
older
G0104
CA screen; flexi
sigmoidscope
Clients age 50 and older who are not at high risk
Once every 48 months
G0105*
Colorectal scrn; hi risk
ind
Clients at high risk for colorectal cancer
One every 24 months
82270
Occult blood, feces
N/A
81519
Genomic testing (breast)
Requires EPA (see EPA #87001386 and EPA #870001420)
G0121*
Colon CA scrn; not high
risk ind
Clients age 50 and older
Once every 10 years
G0122
Colon CA scrn; barium
enema
Clients age 50 and older
Once every 5 years

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
151
HCPCS
Code
Short
Description
Limitations
G0297
Low-dose computed
tomography for lung
cancer screening
Requires EPA (see EPA #870001362). If the client does not
meet EPA criteria, PA is required (see Prior authorization).
HCA allows ICD diagnosis code Z87.891 as a primary
diagnosis.
*Note: Per Medicare guidelines, HCA’s payment is reduced when billed with
modifier 53 (discontinued procedure).
Disease organ panels--automated multi-channel tests
HCA pays for CPT lab panel codes 80047, 80048, 80050, 80051, 80053, 80061, 80069, and
80076. The individual automated multi-channel tests are:
Procedure Code
Short Description
82040
Albumin; serum
82247
Bilirubin; total
82248
Bilirubin; direct
82310
Calcium; total
82330
Calcium, ionized
82374
Carbon dioxide (bicarbonate)
82435
Chloride; blood
82465
Cholesterol, serum, total
82565
Creatine; blood
82947
Glucose; quantitative
82977
Glutamyltransferase, gamma (GGT)
83615
Lactate dehydrogenase (LD) (LDH)
84075
Phosphatase, alkaline
84100
Phosphorous inorganic (phosphate)
84132
Potassium; serum
84155
Protein; total, except refractometry
84295
Sodium; serum
84450
Transferase; apartate amino (AST)(SGOT)
84460
Transferase; alanine amino (AST)(SGPT)
84478
Tryglycerides
84520
Urea nitrogen; quantitative
84550
Uric acid; blood
85004
Automated diff wbc count
85007
B1 smear w/diff wbc count
85009
Manual diff wbc count b-coat
85027
Complete cbc, automated

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
152
• Providers may bill a combination of panels and individual tests not included in the panel.
Duplicate tests will be denied. Providers may not bill for the tests in the panel separately
per the National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI).
• Each test and/or panel must be billed on a separate line.
• All automated/nonautomated tests must be billed on the same claim when performed
for a client by the same provider on the same day.
Fetal fibronectin
The semiquantitative measurement of fetal fibronectin may be considered as medically necessary
with all of the following conditions:
• Singleton or multiple gestation pregnancies
• Intact amniotic membranes
• Cervical dilation <3 cm
• Signs or symptoms suggestive of preterm labor (such as, regular uterine contractions,
cramping, abdominal pain, change in vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding, pelvic
pressure, or malaise)
• Sampling that is performed between 24 weeks 0 days and 34 weeks 6 days of gestation
• Results available in less than 4 hours, for the test results to impact immediate care
decisions for the pregnant client
The use of fetal fibronectin assays is considered to be not medically necessary for the following
indications:
• No symptoms of preterm birth (there is no clinical evidence that treating women with no
labor symptoms or high risk for premature delivery benefits mother or baby)
• Routine screening or determination of risk of preterm delivery in asymptomatic women
• Outpatient tests and the woman awaits test results at home
• Monitoring of asymptomatic women at high-risk for preterm labor (PTL)
• Women not requiring induction due to likelihood of delivery within 24 to 48 hours
• Ruptured membranes or advanced cervical dilation (3 cm or more)
• Imminent birth

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
153
For all other indications, there is insufficient evidence to permit conclusions on efficacy and net
health outcomes.
CPT Code
Short Description
82731
Fetal fibronectin, cervicovaginal secretions, semi-quantitative
Examples of ICD diagnoses codes that support medical necessity are:
ICD Diagnoses Code
Short Description
N88.3
Incompetence of cervix
O34.32, O34.33
Cervical incompetence during pregnancy, childbirth and the
puerperium
O36.8190
Decreased fetal movement
O09.40, O09.529
Other indications for care or intervention related to labor and
delivery
R10.9
Abdominal pain
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy using
cell-free fetal nucleic acids in maternal blood (NIPT)
HCA pays for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy using cell-free fetal nucleic
acids in maternal blood (NIPT) (CPT code 81507 and 81420) when it is medically necessary.
Expedited prior authorization (EPA) is required. See EPA #870001344.
Vitamin D screening and testing
(CPT code 82306, 82652)
Routine Vitamin D screening for the general population (CPT codes 82306, 82652) is not
considered medically necessary.
Vitamin D testing (25-hydroxy vitamin D, calcidiol, CPT code 82306) may be considered
medically necessary for the following conditions:
• Chronic kidney disease stage 3 or greater
• End stage renal disease
• Evaluation of hypo- or hypercalcemia
• Hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia of newborn
• Hypophosphatemia

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
154
• Hypoparathyroidism
• Intestinal malabsorption including:
Blind loop syndrome
Celiac disease
Pancreatic Steatorrhea
• Secondary hyperparathyroidism
• Hypervitaminosis D
• Osteomalacia
• Osteopenia
• Rickets
• In the setting of other laboratory or imaging indicators of vitamin D deficiency for:
Calculus of kidney or ureter
Chronic liver disease in the absence of alcohol dependency
Protein-calorie malnutrition
Vitamin D testing (25-dihydroxy vitamin D, calcitriol, CPT 82652) may be considered medically
necessary as a second tier test for the following conditions:
• Disorders of calcium metabolism
• Familial hypophosphatemia
• Fanconi syndrome
• Hypoparathyroidism or hyperparathyroidism
• Vitamin D resistant rickets
• Tumor induced osteomalacia
• Sarcoidosis
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
155
Lead toxicity screening
Lead toxicity screening is mandatory at age 12 months and 24 months for all children, including
children enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization, regardless of lead exposure
risk.
Additionally, all children between age 36 months and 72 months must receive a lead toxicity
screening if they have not been tested previously.
Drug Testing for Substance Use Disorder
HCA pays for drug screens when both of the following apply:
• The screen is medically necessary and ordered by a physician as part of a medical
evaluation.
• The drug or alcohol screen is required to assess suitability for medical tests or treatment
being provided by the physician.
Note: HCA covers 12 breathalyzer tests (CPT 82075) per client, per year, without
authorization when medically necessary.
Drug screening for medication for opioid use disorder
Urine and blood drug assay tests are covered for Washington Apple Health clients receiving
medication for opioid use disorder for substance use disorders under the following conditions.
Other biological testing is noncovered.
For presumptive testing, use the following codes:
• CPT codes 80305, 80306, and 80307 (Only one of the three presumptive codes may be
billed per client per day.)
• Up to 24 presumptive tests will be reimbursed per client, per year
For definitive drug testing, use the following G codes:
• G0480, G0481, G0482 and G0483 (Only one of the four definitive G codes may be billed
per client per day.)
• Up to 16 definitive tests (follow-up tests to presumptive tests) will be reimbursed per
client, per year
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
156
If additional tests are needed, providers can submit a limitation extension request to HCA See
Limitation extension (LE).
For definitive testing, the unit used to determine the appropriate definitive G code to bill is “drug
class.” Each drug class may only be used once per day in determining the appropriate definitive
G code to bill. Drug classes are listed in the CPT Manual. The CPT Manual may be consulted
for examples of individual drugs within each class. Codes G0481, G0482 and G0483 are
reimbursed at the same rate.
The following testing codes are no longer covered:
• G0431, G0434
• HCPCS codes G6030 through G6058
• 80309 – 80377
For substance use disorder, HCA will not reimburse for serial quantitative testing to monitor
levels of drug metabolites.
(Monitoring for patients who are on chronic opioid therapy for the treatment of
chronic noncancer pain should follow the Agency Medical Director’s Group 2015
Interagency guideline on prescribing opioids for pain, Appendix D).
(These guidelines do not pertain to urine drug testing required for employment,
emergency department evaluation or those related to criminal justice requirements).
For monitoring patients receiving medication for opioid use disorder, drug assay tests are
considered medically necessary in the following instances:
Screening, presumptive, or in office testing with point of care immunoassays (IA) is considered
medically necessary to:
• Confirm the use of prescribed substances
• Identify the presence of illicit or non-prescribed substances
• Prior to starting a patient on medication for opioid use disorder for a substance use
disorder

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
157
Confirmatory or definitive testing with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GCMS) or
liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LCMS) is considered medically necessary to
interpret the findings on presumptive testing when there is a discrepancy between patient report,
the test and what is being prescribed:
For example:
• To confirm the presence of an unexpected or non-prescribed drug identified by an
IA
• To confirm that a prescribed drug or its metabolite not present on the IA are in
fact being taken
In addition, confirmatory testing should only be ordered and performed on a patient/drug specific
basis. Clinical documentation must support why a particular drug or class was tested for and
document a follow up plan based on the test results.
Note: HCA requires prior authorization for the use of presumptive or
confirmatory testing panels that test substances or drug groups not listed below.
Clinical documentation supporting the rationale for the particular tests being
ordered is required.
Serial quantitative monitoring of drugs or drug metabolite levels is not considered medically
necessary.
Periodic reviews of ordering patterns will be performed to look for and contact practices that
appear to be outliers compared to their peers.
Additional information when prescribing (Suboxone®)
The provider must have FDA approval to prescribe buprenorphine/naloxone (Suboxone®) for
opioid use disorders (OUD).
A provider must be categorized as a High Complexity MTS/CLIA by the Office of
Washington Laboratory Assurance, or be accredited as High Complexity MTS/CLIA by
COLA/College of American Pathologists Joint Commission if confirmatory testing is
performed at the site of practice.
Enter the following information on the claim forms: “Certified bupren provider” in the Claim
Note section of the electronic claim
More information regarding CLIA certification can be found on the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration website.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
158
For treatment of chronic noncancer pain, HCA has adopted the Agency Medical Directors’
Group (AMDG) drug screening guidelines outlined in the AMDGs’ interagency guidelines. For
more information, go online to Interagency guidelines on opioid dosing for chronic non-cancer
pain .
Risk Category
Recommended Urine Drug Testing
Frequency
Low Risk by Opiate Risk Tool (ORT) Periodic (e.g., up to one time per year)
Moderate Risk by ORT Regular (e.g., up to two times per year)
High Risk by ORT or opioid doses >120
MED/d
Frequent (e.g., up to three times per year)
Aberrant Behavior (lost prescriptions, multiple
requests for early refill, opioids from multiple
providers, unauthorized dose escalation,
apparent intoxication)
At the time of visit (address aberrant
behavior in person, not by telephone)
HCA does not pay for either of the following:
• Routine drug screening panels
• Monitoring for program compliance in either a residential or outpatient drug or alcohol
treatment program
Note: Labs must offer single drug testing. Drug screening must be medically
indicated and the reason for the specific drug screening must be documented in
the client record. Lab slips must be signed by the prescribing provider.
When monitoring a client for drug/alcohol use, refer the client to a Division of Behavioral Health
and Rehabilitation (DBHR)-approved program for evaluation and treatment. Clients served by
these programs may receive drug/alcohol screening according to an established treatment plan
determined by their treating provider.
For clients in the DBHR-contracted methadone treatment programs and pregnant women in
DBHR-contracted treatment programs, drug screens are paid through a contract issued to one
specific laboratory by DBHR, not through HCA.
Buprenorphine when used for pain control
HCA pays for drug screens when both of the following apply:
• They are medically necessary and ordered by a physician as part of a medical evaluation.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
159
• The drug and/or alcohol screens are required to assess suitability for medical tests or
treatment being provided by the physician.
See HCA’s Physician-related fee schedule for covered drug screening codes.
Enhanced reimbursement rate for medication for opioid use
disorder
HCA pays an enhanced reimbursement using the Medicare rate when medication for opioid use
disorder is part of the visit for selected evaluation and management (E/M) codes.
The purpose of this enhanced reimbursement is to encourage providers to obtain and use a Drug
Addiction Treatment Act of 2000 Waiver (DATA 2000 Waiver) to increase patient access to
evidence-based treatment using medications for opioid use disorder.
To receive this enhancement, providers must:
• Have a DATA 2000 Waiver.
• Currently use the waiver to prescribe medication for opioid use disorder to clients with
opioid use disorder.
• Bill for treating a client with a qualifying diagnosis for opioid use disorder.
• Provide opioid-related counseling during the visit.
• Bill with EPA #870001537.
HCA pays one enhanced reimbursement per client per day. HCA does not pay the enhanced
reimbursement if the client receives services for opioid use disorder through an opioid treatment
program facility licensed by the Department of Health.
Providers are subject to post-pay review to ensure the EPA criteria for the rate enhancement are
met. If the requirements are not met at the time of service, recoupment of payment may occur.
To view the medication for opioid use disorder fee schedule, see HCA’s Provider billing guides
and fee schedules webpage.
Immunology
HIV testing
HCA pays providers for HIV testing as recommended in the CDC guidelines.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
160
Targeted TB testing with interferon-gamma release assays
Targeted TB testing with interferon-gamma release assays may be considered medically
necessary for clients age 5 and older for one of the following conditions:
• History of positive tuberculin skin test or previous treatment for TB disease
• History of vaccination with BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guerin)
• Recent immigrants (within 5 years) from countries that have a high prevalence of
tuberculosis
• Residents and employees of high-risk congregate settings (homeless shelters, correctional
facilities, substance abuse treatment facilities)
• Clients with an abnormal chest X-ray (CXR) consistent with old or active TB
• Clients undergoing evaluation or receiving TNF alpha antagonist treatment for
rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease
• Exposure less than 2 years before the evaluation AND client agrees to remain compliant
with treatment for latent tuberculosis infection if found to have a positive test
The tuberculin skin test is the preferred method of testing for children under the age of 5.
CPT Code
Short Description
86480
Tb test cell immun measure
86481
Tb ag response t-cell susp
Providers must follow HCA’s expedited prior authorization (EPA) process to receive payment
for targeted TB testing. See EPA #870001325 in EPA Criteria Coding List.
Molecular Pathology Tests
Genetic testing may be considered as medically necessary to establish a molecular diagnosis of
an inheritable disease when all of the following are met:
• The client displays clinical features, or is at direct risk of inheriting the mutation in
question (pre-symptomatic) based on family history, an analysis of genetic relationships
and medical history in the family.
• Diagnostic results from physical examination, pedigree analysis, and conventional testing
are inconclusive.|

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
161
• The clinical utility of the test is documented in the authorization request, including how
the test results will guide decisions concerning disease treatment, management, or
prevention; AND these treatment decisions could not otherwise be made in the absence
of the genetic test results.
• Clients receive pre- and post-test genetic counseling from a qualified professional when
testing is performed to diagnose or predict susceptibility for inherited diseases.
Genetic testing is considered not medically necessary if any of the above criteria are not met.
Refer to the fee schedule for HCA coverage of Tier 1 and Tier 2 molecular pathology
procedures.
Genomic microarray
Genomic microarray is considered medically necessary under the conditions outlined
below.
HCA requires prior authorization (PA) when using CPT codes 81228 and 81229 for genomic
microarray to diagnose genetic abnormalities in children for any one of the following:
• Significant dysmorphic features or congenital anomalies
• Global developmental delay or clinical diagnosis of intellectual disability
• Clinical diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder
AND all of the following:
• Targeted genetic testing, if indicated, is negative
• Clinical presentation is not specific to a well-delineated genetic syndrome
• The results of testing could impact the clinical management
Note: HCA uses the following definitions:
• For clients younger than age 5, Global developmental delay (GDD). See
Definitions.
• For clients age 5 and older, Intellectual disability (ID). See Definitions.
Companion diagnostic tests
HCA considers companion diagnostic and certain pharmacogenetic tests to be medically
necessary and may require prior authorization.
HCA does not consider pharmacogenetic testing for patients treated with oral anticoagulants to
be medically necessary.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
162
HCA does not cover pharmaceutical tests (with CPT codes 81225, 81226, 81227, and 81291)
when the primary diagnosis is one of the following:
• Depression
• Mood disorders
• Psychosis
• Anxiety
• Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
• Substance use disorder
Organ and disease-oriented panels
Automated multi-channel tests - payment
For individual automated multi-channel tests, providers are paid on the basis of the total number
of individual automated multi-channel tests performed for the same client, on the same day, by
the same laboratory.
• When all the tests in a panel are not performed, each test must be billed as a separate line
item on the claim.
• When there are additional automated multi-channel tests not included in a panel, each
additional test must be billed as a separate line item on the claim.
• Bill any other individual tests as a separate line item on the claim.
Payment calculation for individual automated laboratory tests is based on the total number of
automated multichannel tests performed per day, per patient. Payment for each test is based on
Medicare’s fees multiplied by HCA’s fiscal year laboratory conversion factor.
For example:
If five individual automated tests are billed, the payment is equal to the internal code’s maximum
allowable fee.
If five individual automated tests and a panel are billed, HCA pays providers separately for the
panel at the panel’s maximum allowable. Payment for the individual automated tests, less any
duplicates, is equal to the internal code’s maximum allowable fee.
If one automated multi-channel test is billed, payment is at the individual procedure code or
internal code’s maximum allowable fee, whichever is lower. The same applies if the same
automated multi-channel test is performed with modifier 91.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
163
Disease organ panel - nonautomated multi-channel
Organ and disease panels (CPT codes 80055 and 80074) do not include automated multi-channel
tests. If all individual tests in the panel are not performed, payment is the individual procedure
code maximum allowable fee or billed charge, whichever is lower.
The nonautomated multi-channel tests are:
CPT Code
Short Description
83718
Assay of lipoprotein
84443
Assay thyroid stim hormone
85025
Automated hemogram
85651
Rbc sed rate, nonautomated
86255
Fluorescent antibody, screen
86430
Rheumatoid factor test
86592
Blood serology, qualitative
86644
CMV antibody
86694
Herpes simplex test
86705
Hep b core antibody, test
86709
Hep a antibody, igm
86762
Rubella antibody
86777
Toxoplasma antibody
86803
Hep c ab test, confirm
86850
RBC antibody screen
86900
Blood typing, ABO
86901
Blood typing, Rh(D)
87340
Hepatitis b surface ag, eia
Gene expression
HCA covers gene expression profile testing with conditions for breast or prostate cancer. See
EPA (#870001386, #870001420, #870001545, #870001546, #870001547, #870001548,
#870001549, #870001550, and #870001551) for details. HCA considers only the listed tests as
medically necessary.
HCA does not cover gene expression profile testing for multiple myeloma or colon cancer.
Breast and ovarian genetic testing
HCA requires prior authorization (PA) for all breast and ovarian cancer genetic testing. Effective
for dates of service on and after October 1, 2019, if the client meets expedited prior
authorization (EPA) criteria, providers may use EPA #870001603. If the client does not meet the
EPA criteria, providers must follow the full PA process (see Prior Authorization (PA)).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
164
Billing
Billing for laboratory services that exceed the lines allowed
• Electronic submitters are allowed 50 lines per claim. Use additional claim forms if the
services exceed the lines allowed. Enter the statement “Additional services” in the
Claim Note section when billing electronically. Total each claim separately.
• If HCA pays a claim with one or more automated/nonautomated lab tests, providers must
bill any additional automated/nonautomated lab tests for the same date of service as an
adjusted claim. Refer to Key Step 6 of the “Submit Fee for Service Claims to Medical
Assistance” in the ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide which addresses adjusting
paid claims. Currently, providers may adjust claims electronically in ProviderOne. Make
sure the claim is adjusted with the paid automated/nonautomated lab tests using the
comment "additional services."
Clinical laboratory codes
Some clinical laboratory codes have both a professional component and a technical component.
If performing only the technical component, bill with modifier TC. If performing only the
professional component bill with modifier 26. Laboratories performing both the professional and
the technical components must bill the code without a modifier. See Laboratory physician
interpretation procedure codes with both a technical and professional component.
Coding and payment policies
• Pathology and laboratory services must be provided either by a pathologist or by
technologists who are under the supervision of a physician.
•
HCA expects independent laboratories to bill hospitals for the technical component of
anatomic pathology services furnished to hospital inpatients and outpatients. To prevent
duplicate payment, HCA will not pay independent laboratories if they bill Medicaid for
these services.
•
An independent laboratory and/or hospital laboratory must bill using its NPI for any
services performed in its facility.
• Physicians must bill using their NPI for laboratory services provided by their technicians
under their supervision.
• HCA reimburses blood draw fees with the following limits:
For separate and distinct times
Up to two separate blood draw fees for CPT® codes 36415 or 36591 per day
Up to three separate blood draw fees for CPT® code 36416 per day

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
165
• HCA pays for one catheterization for collection of a urine specimen (HCPCS code
P9612) per day.
• Complete blood count (CPT code 85025) includes the following CPT codes: 85004,
85007, 85008, 85009, 85013, 85014, 85018, 85027, 85032, 85041, 85048, 85049, and
G0306. Complete blood count (CPT code 85027) includes the following CPT codes:
85004, 85008, 85013, 85014, 85018, 85032, 85041, 85048, 85049, and G0307.
• CPT codes 81001-81003 and 81015 are not allowed in combination with urinalysis
procedure 81000.
• CPT codes 86812-86822 are limited to a maximum of 15 tests total for human leukocyte
antigens (HLA) typing per client, per lifetime. Prior authorization is required for more
than 15 tests.
• Do not bill with modifier 26 if the description in CPT indicates professional services
only.
• Payment for lab tests includes handling, packaging and mailing fee. Separate payment is
not allowed.
• Laboratories must obtain PA from the ordering physician, or HCA-approved genetic
counselor to be paid for certain genetic testing requiring PA. All genetic testing must be
billed with the appropriate genetic testing modifier.
• CPT code 83037 [hemoglobin glycosylated (A1C)] does not require PA when performed
in a physician’s office; however, it can be billed only once every three months.
Note: Laboratory claims must include the provider’s national provider identifier
(NPI) and an appropriate medical diagnosis code and PA if applicable. The
ordering provider must give the appropriate medical diagnosis code, prior
authorization number, and modifier, if applicable, to the performing laboratory at
the time the tests are ordered. HCA does not pay a laboratory for procedures
billed using ICD diagnosis codes Z00.00, Z01.812, or Z01.89 as a primary
diagnosis. For lab services use the appropriate diagnosis for the service(s)
provided.
• CPT code 87999 can be used for billing the monogram Trofile test for AIDS patients
when physicians are prescribing the drug Selzentry®. HCA pays By Report for CPT code
87999.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
166
• For outpatient hospital laboratory services such as therapeutic blood levels and
electrocardiograms and related professional services that are denied by managed care
because the services were ordered or referred by a BHO, providers must do both of the
following:
Put “Referred by the BHO” in the Claim Note section of the claim.
Include the managed care denial with their claim when billing HCA.
Laboratory physician interpretation procedure codes
The following codes are clinical laboratory procedure codes for which separate payment for
interpretations by laboratory physicians may be made. The actual performance of the tests is paid
for under the Physician-related/professional services fee schedule. Modifier TC must not be
used with these procedure codes. The total RVUs for laboratory physician interpretation codes
include values for physician work, practice expense, and malpractice expense.
81200-81479
84181
86255
86327
87207
83020
84182
86256
86334
88371
84165
85390
86320
86335
88372
84166
85576
86325
87164
89060
Laboratory codes requiring modifier and PA clarification
Laboratory claims must include an appropriate medical diagnosis code, modifier, and PA, if
applicable. The ordering provider must give the appropriate medical diagnosis code, modifier,
and PA number, if applicable, to the performing laboratory at the time the tests are ordered. HCA
does not pay for laboratory procedures billed using the appropriate ICD diagnosis codes Z00.00,
Z01.812, or Z01.89. For lab services, use the appropriate diagnosis for the service(s) that was
provided.
Laboratory modifiers
Modifier QP
Modifier QP indicates documentation is on file showing that the laboratory test(s) was ordered
individually or ordered as a CPT-recognized panel. HCA recognizes this modifier as
informational only. This modifier is not appropriate to use for billing repeat tests or to
indicate the test was not done as a panel.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
167
Modifier 90
Reference (Outside) Laboratory: When a laboratory sends a specimen to a reference (outside)
laboratory, the referring laboratory may bill for the reference laboratory (pass-through billing) by
adding modifier 90 to the laboratory procedure code. The reference laboratory NPI must be
entered in the Referring Provider Information section on the claim.
Modifier 91
Repeat Clinical Laboratory Diagnostic Test
When it is necessary to repeat the same laboratory test on the same day for the same client to
obtain subsequent (multiple) test results, use modifier 91. Otherwise, the claim will be denied as
a duplicate.
Do not use this modifier when tests are rerun:
• To confirm initial results.
• Due to testing problems with specimens or equipment.
• For any reason when a normal, one-time, reportable result is all that is required.
• When there are standard procedure codes available that describe the series of results (e.g.,
glucose tolerance test, evocative/suppression testing, etc.).
Laboratory services referred by CMHC or DBHR-
contracted providers
When a community mental health center (CMHC) or DBHR-contracted providers refer clients
enrolled in an HCA managed care plan for laboratory services, the laboratory must bill HCA
directly. All of the following conditions apply:
• The laboratory service is medically necessary.
• The laboratory service is directly related to the client's mental health or alcohol and
substance abuse.
• The laboratory service is referred by a CMHC or DBHR-contracted provider who has a
core provider agreement with HCA.
• The laboratory must bill with a mental health, substance abuse, or alcohol abuse
diagnosis.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
168
To bill for laboratory services, laboratories must put the CMHC or DBHR-contracted referring
provider National Provider Identifier (NPI) number in the “Referring Provider Information”
section of the claim. CMHC and DBHR-contracted services are excluded from HCA’s managed
care contracts.
STAT laboratory charges
When the laboratory tests listed on the following page are performed on a STAT basis, the
provider may bill HCPCS code S3600 (STAT laboratory request).
• Payment is limited to one STAT charge per episode (not once per test).
• Tests must be ordered STAT and payment is limited to only those that are needed to
manage the client in a true emergency.
• The laboratory report must contain the name of the provider who requested the STAT.
• The medical record must reflect the medical necessity and urgency of the service.
Note: "STAT" must be clearly indicated by the provider and must be
documented in the laboratory report and the client’s record. Tests generated from
the emergency room do not automatically justify a STAT order. Use HCPCS
code S3600 with the procedure codes on the following page.
The STAT charge is paid only with the following tests:
Procedure Code
Short Description
G0306
CBC/diffwbc w/o platelet
G0307
CBC without platelet
80047
Metabolic panel ionized ca
80048
Metabolic panel total ca
80051
Electrolyte panel
80069
Renal function panel
80076
Hepatic function panel
80156
Assay, carbamazepine total
80162
Assay of digoxin
80170
Assay of gentamicin
80164
Assay dipropylacetic acid
80178
Assay of lithium
80184
Assay of phenobarbital
80185
Assay of phenytoin total
80188
Assay primidone
80192
Assay of procainamide
80194
Assay of quinidine
80197
Assay of tacrolimus
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
169
Procedure Code
Short Description
80198
Assay of theophylline
81000
Urinalysis nonauto w/scope
81001
Urinalysis auto w/scope
81002
Urinalysis nonauto w/o scope
81003
Urinalysis auto w/o scope
81005
Urnalysis
82009
Test for acetone/ketones
82040
Assay of serum albumin
82055
Assay of ethanol
82150
Assay of amylase
82247
Bilirubin total
82248
Bilirubin direct
82310
Assay of calcium
82330
Assay of calcium
82374
Assay blood carbon dioxide
82435
Assay of blood chloride
82550
Assay of ck (cpk)
82565
Assay of creatinine
82803
Blood gases any combination
82945
Glucose other fluid
82947
Assay glucose blood quant
83615
Lactate (LD) (LDH) enzyme
83633
Test urine for lactose
83664
Lamellar bdy fetal lung
83735
Assay of magnesium
83874
Assay of myoglobin
83880
Assay of natriuretic peptide
84100
Assay of phosphorus
84132
Assay of serum potassium
84155
Assay of protein serum
84157
Assay of protein other
84295
Assay of serum sodium
84302
Assay of sweat sodium
84450
Transferase (AST)(SGOT)
84484
Assay of troponin quant
84512
Assay of troponin qual
84520
Assay of urea nitrogen
84550
Assay of blood/uric acid
84702
Chorionic gonadotropin test
84704
Hcg free betachain test
85004
Automated diff wbc count
85007
Bl smear w/diff wbc count
85025
Complete cbc w/auto diff wbc
85027
Complete cbc automated
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
170
Procedure Code
Short Description
85032
Manual cell count each
85046
Reticyte/hgb concentrate
85049
Automated platelet count
85378
Fibrin degrade semiquant
85380
Fibrin degradj d-dimer
85384
Fibrinogen activity
85396
Clotting assay whole blood
85610
Prothrombin time
85730
Thromboplastin time partial
86308
Heterophile antibody screen
86367
Stem cells total count
86403
Particle agglut antbdy scrn
86880
Coombs test
86900
Blood typing ABO
86901
Blood typing rh (d)
86920
Compatibility test spin
86921
Compatibility test incubate
86922
Compatibility test antiglob
86923
Compatibility test electric
86971
Rbc pretx incubatj w/enzymes
87205
Smear gram stain
87210
Smear wet mount saline/ink
87281
Pneumocystis carinii ag if
87327
Cryptococcus neoform ag eia
87400
Influenza a/b ag eia
89051
Body fluid cell count
86367
Stem cells total count
86923
Compatibility test electric
88720
Bilirubin total transcut
88740
Transcutaneous carboxyhb
88741
Transcutaneous methb

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
171
Medicine
Allergen and clinical immunology
Allergen immunotherapy
(WAC 182-531-0950(10))
Subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy may be medically necessary for the following conditions
in children and adults:
• Allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, or allergic asthma
• History of systemic reaction to Hymenoptera
And the client:
• Has symptoms of allergic rhinitis and/or asthma after natural exposure to the allergen
OR
• Has life-threatening allergy to insect stings
AND
• Has a skin test and/or serologic evidence of IgE-medicated antibody to the allergen
AND
• Must have tried/failed attempt at allergen avoidance and pharmacologic therapy, or the
client has unacceptable side effects with pharmacologic therapy
And:
• The prescribing physician must be a board certified allergist
AND
• Immunotherapy injections must be administered in a setting that permits the prompt
recognition and management of adverse reactions, particularly anaphylaxis
AND
• If clinical improvement is not apparent after 12 months of maintenance therapy,
immunotherapy should be discontinued
HCA will pay for 50 units (CPT® 95165) per client, per year. HCA allows 30 unit to be billed
per date of service.
Prior authorization is required for amounts greater than 50 units per client, per year.
Payment for antigen/antigen preparation (CPT codes 95145-95149, 95165, and 95170) is per
dose.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
172
Service Provided
What should I bill?
Injection and antigen/antigen preparation for
allergen immunotherapy
One injection (CPT code 95115 or 95117);
and
One antigen/antigen preparation (CPT
codes 95145-95149, 95165 or 95170).
Antigen/antigen preparation for stinging/biting
insects
CPT codes 95145-95149 and 95170
All other antigen/antigen preparation services
(e.g., dust, pollens)
CPT code 95144 for single dose vials; or
CPT code 95165 for multiple dose vials.
Allergist prepared the extract to be injected by
another physician
CPT code 95144
Allergists who billed the complete services
(CPT codes 95120-95134) and used treatment
boards
One antigen/antigen preparation (CPT
codes 95145-95149, 95165, and 95170);
and
One injection (CPT code 95115 or 95117).
Physician injects one dose of a multiple dose
vial
Bill for the total number of doses in the
vial and an injection code
Physician or another physician injects the
remaining doses at subsequent times
Bill only the injection service
For an allergist billing both an injection and either CPT code 95144 or 95165, payment is the
injection fee plus the fee of CPT code 95165, regardless of whether CPT code 95144 or 95165 is
billed. The allergist may bill an Evaluation and Management (E/M) procedure code for
conditions not related to allergen immunotherapy.
Audiology
(WAC 182-531-0375)
HCA may pay for audiology program services for conditions that are the result of medically
recognized diseases and defects.
Who is eligible to provide audiology services?
(WAC 182-531-0375)
Audiologists who are appropriately licensed or registered to provide audiology services within
their state of residence to HCA clients.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
173
What type of equipment must be used?
Audiologists must use annually calibrated electronic equipment, according to RCW 18.35.020.
• For caloric vestibular testing (CPT code 92537), bill one unit per irrigation. If necessary,
providers may bill up to four units for each ear.
• For sinusoidal vertical axis rotational testing (CPT code 92546), bill 1 unit per
velocity/per direction. If necessary, providers may bill up to 3 units for each direction.
Unilateral (CPT code 69930) and bilateral (CPT code 69930 with modifier 50) cochlear
implantation require EPA. See Auditory system.
HCA considers requests for removal or repair of previously implanted bone conduction hearing
devices and cochlear devices for clients age 21 and older only when medically necessary. Prior
authorization from HCA is required.
Audiology coverage
Please see the Physician-Related Services Fee Schedule for covered services.
Audiology billing
The outpatient rehabilitation benefit limits do not apply to therapy services
provided and billed by audiologists. Audiologists (and physicians) must use AF
modifier when billing.
Bronchial thermoplasty for asthma
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA does not consider bronchial
thermoplasty for asthma to be medically necessary.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
174
Cardiovascular
Catheter ablation for supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
(CPT codes 93653, 93655, 93656, 93657)
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA considers ablation medically
necessary for adults with the following conditions:
• Reentrant tachycardias (e.g. Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, Atrioventricular
reentrant tachycardia, Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
• Symptomatic atrial flutter
• Symptomatic atrial fibrillation in patients for whom drug therapy is either not tolerated,
or ineffective.
HCA does not consider catheter ablation for adults medically necessary for other nonreentrant
supraventricular tachycardias.
Heart catheterizations
When a physician performs cardiac catheterization in a setting where the physician does not own
the equipment (e.g., a hospital or ASC), HCA pays providers for the appropriate procedure code
with modifier 26 (professional component) only.
Use cardiac catheterization and angiography to report services individually. It is not appropriate
to bill with modifier 51 (multiple procedures) with any of these codes. See HCA’s Physician-
related/professional fee schedule for covered codes and status indicators.
Outpatient cardiac rehabilitation
HCA covers outpatient cardiac rehabilitation in a hospital outpatient agency for eligible clients
who:
• Are referred by a physician.
• Have coronary artery disease (CAD).
• Do not have specific contraindications to exercise training.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
175
• Have:
A recent documented history of acute myocardial infarction (MI) within the
preceding 12 months.
Had coronary angioplasty (coronary artery bypass grafting [CABG].
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty [PTCA]).
Stable angina.
Bill physician services with CPT code 93797 or 93798 or HCPCS G0422 or G0423 (per session)
with one of the following diagnoses:
• Acute myocardial infarction
• Angina pectoris
• Aortocoronary bypass status
• Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty status
Note: Cardiac rehabilitation does not require PA, and it is only approved for the
above diagnoses.
The outpatient cardiac rehabilitation program hospital facility must have all of the following:
• A physician on the premises at all times, and each client is under a physician’s care
• Cardiopulmonary emergency equipment and therapeutic life-saving equipment available
for immediate use
• An area set aside for the program’s exclusive use while it is in session
• Personnel who are:
Trained to conduct the program safely and effectively.
Qualified in both basic and advanced life-support techniques and exercise therapy
for coronary disease.
Under the direct supervision of a physician
• Non physician personnel that are employees of the hospital

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
176
• Stress testing:
To evaluate a patient’s suitability to participate in the program
To evaluate chest pain
To develop exercise prescriptions
For pre- and postoperative evaluation of coronary artery bypass clients
• Psychological testing or counseling provided if either of the following are true. The
client:
Exhibits symptoms such as excessive fear or anxiety associated with cardiac
disease
Has a diagnosed mental, psychoneurotic, or personality disorder
HCA covers up to 24 sessions (usually 3 sessions a week for 4-6 weeks) of cardiac rehabilitation
sessions (phase II) per event. HCA covers continued participation in cardiac rehabilitation
programs beyond 24 sessions only on a case-by case basis with prior authorization. Phase II of
cardiac rehabilitation is the initial outpatient cardiac rehabilitation program. The goal of phase II
is to lower the risk of future heart problems.
Central nervous system assessments/tests
Coverage for developmental screening for delays and
surveillance and screening for autism
All children: As a part of routine well child exams for clients age 9 months, 18 months, and 30
months, HCA pays for one developmental screening for primary care providers when
performed by a physician, ARNP, or PA. For further information about well child exams, see
HCA’s Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment (EPSDT) Program Billing Guide.
To support timely access to a formal diagnostic evaluation and referral for applied behavioral
analysis (ABA) treatment or other medically necessary services, HCA pays for one autism
screening for all children at age 18 months, and a second screening before 36 months, when
performed by a physician, ARNP, or PA.
See HCA’s Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) Program Billing Guide for additional information.
*If additional units are necessary, providers must request prior authorization from HCA.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
177
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy services
(WAC 182-531-0950(11))
Bill the appropriate chemotherapy administration CPT code for each drug administered.
HCA’s chemotherapy administration policy is as follows:
• Providers may bill chemotherapy administration (CPT codes 96411 or 96417) and bill
one administration for each drug given. The administration and drug must be billed on
the same claim.
• HCA pays for only one initial drug administration code (CPT code 96409 or 96413) per
encounter unless one of the following applies:
Protocol requires the use of two separate IV sites.
The client comes back for a separately identifiable service on the same day (in
this case, bill the second initial service code with modifier -59).
• HCA does not pay for Evaluation and Management (E/M) CPT code 99211 on the same
date of service as the following drug administration codes: 96401-96549. If billed in
combination with one of these drug administration codes, HCA will deny the E/M code
99211. However, providers may bill other E/M codes on the same date of service using
modifier 25 to indicate that a significant and separately identifiable E/M service was
provided. If modifier 25 is not used, HCA will deny the E/M code.
• Items and services not separately payable with drug administration:
Some items and services are included in the payment for the drug administration service,
and HCA does not pay separately for them. These services include, but are not limited to
the following:
The use of local anesthesia
IV start
Access to indwelling IV (a subcutaneous catheter or port)
A flush at conclusion of an infusion
Standard tubing
Syringes and supplies
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
178
• Infusion vs. push:
An intravenous or intra-arterial push is defined as either of the following:
An injection in which the health care professional who administers the substance or
drug is continuously present to administer the injection and observe the patient.
An infusion of 15 minutes or less.
Note: Drug, infusion, and injection codes must be billed on the same claim.
Irrigation of venous access pump
CPT code 96523 may be billed as a stand-alone procedure. However, if billed by the same
provider/clinic on the same day as an office visit, modifier 25 must be used to report a separately
identifiable medical service. If modifier 25 is not used, HCA will deny the E/M code.
Dialysis - end-stage renal disease (ESRD)
Inpatient visits for hemodialysis or outpatient non-ESRD
dialysis services
(CPT codes 90935 and 90937)
Procedure Codes
Billed
Instructions
90935 and 90937
Bill these codes for the hemodialysis procedure with all E/M services
related to the client’s renal disease on the day of the hemodialysis
procedure. Bill these codes for the following clients:
• Clients in an inpatient setting with ESRD
• Clients receiving hemodialysis in an outpatient or inpatient
setting who do not have ESRD
Bill using ICD diagnosis code N18.6 or the appropriate diagnosis
code (N17.2–N19, E74.8) for clients requiring dialysis but who do
not have ESRD.
90935
Bill using procedure code 90935 if only one evaluation is required
related to the hemodialysis procedure.
90937
Bill using procedure code 90937 if a re-evaluation(s) is required during
a hemodialysis procedure on the same day.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
179
Inpatient visits for dialysis procedures other than
hemodialysis
(e.g., peritoneal dialysis, hemofiltration, or continuous renal replacement therapies)
(CPT codes 90945 and 90947)
Procedure Codes
Billed
Instructions
90945 and 90947
Bill these codes for E/M services related to the client’s renal disease on
the day of the procedure that includes peritoneal dialysis, hemofiltration,
or continuous renal replacement.
Bill using ICD diagnosis code N18.6 or the appropriate diagnosis
code (N17.2–N19, E74.8) for clients requiring dialysis but who do
not have ESRD.
90945
Bill using procedure code 90945 if only one evaluation is required
related to the procedure.
90947
Bill using procedure code 90947 if a re-evaluation(s) is required during
a procedure on the same day.
If a separately identifiable service is performed on the same day as a dialysis service, any of the
following E/M procedures codes may be billed with modifier 25:
• 99201-99205 Office or Other Outpatient Visit: New Patient
• 99211-99215 Office or Other Outpatient Visit: Established Patient
• 99221-99223 Initial Hospital Care: New or Established Patient
• 99238-99239 Hospital Discharge Day Management Services
• 99241-99245 Office or Other Outpatient Consultations: New or Established Patient
• 99291-99292 Critical Care Services
Endocrinology
Professional or diagnostic continuous glucose monitoring
HCA pays for the in-home use of professional or diagnostic continuous glucose monitoring
(CGM) for a 72-hour monitoring period with Expedited prior authorization (EPA). See EPA #
870001312 for coverage criteria.
Effective for dates of service on and after February 1, 2019, for CGM greater than 72 hours,
or CGM supplies, or both, see HCA’s Home Infusion Therapy/Parenteral Nutrition Program
Billing Guide for policy.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
180
Genetic testing
Whole exome sequencing
HCA considers whole exome sequencing (WES) to be medically necessary for the evaluation of
unexplained congenital or neurodevelopmental disorders in a phenotypically affected individual
when ALL of the following criteria are met:
• A board-certified or board-eligible medical geneticist, or an advanced practice nurse in
genetics (APGN) credentialed by either the Genetic Nursing Credentialing Commission
(GNCC) or the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), who is not employed by
a commercial genetic testing laboratory, has evaluated the patient and family history and
recommends or orders, or both, the test.
• A genetic etiology is considered the most likely explanation for the phenotype, based on
EITHER of the following:
Multiple abnormalities affecting unrelated organ systems (e.g., multiple
congenital anomalies)
TWO of the following criteria are met:
Significant abnormality affecting at a minimum a single organ system
Profound global developmental delay or intellectual disability (see
Definitions)
Family history strongly suggestive of a genetic etiology, including
consanguinity
Period of unexplained developmental regression (unrelated to autism or
epilepsy)
Biochemical findings suggestive of an inborn error of metabolism where
targeted testing is not available
• Other circumstances (e.g., environmental exposures, injury, infection, etc.) do not
reasonably explain the constellation of symptoms
• Clinical presentation does not fit a well-described syndrome for which single-gene or
targeted panel testing (e.g., comparative genomic hybridization [CGH]/chromosomal
microarray analysis [CMA]) is available

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
181
• The differential diagnosis list or phenotype warrant testing, or both, of multiple genes and
ONE of the following:
WES is more efficient and economical than the separate single-gene tests or
panels that would be recommended based on the differential diagnosis (e.g.,
genetic conditions that demonstrate a high degree of genetic heterogeneity)
WES results may preclude the need for multiple invasive procedures or screening
that would be recommended in the absence of testing (e.g., muscle biopsy)
• A standard clinical work-up has been conducted and did not lead to a diagnosis.
• Results will impact clinical decision-making for the individual being tested.
• Pre- and post-test counseling is performed by an American Board of Medical Genetics-
certified or American Board of Genetic Counseling-certified genetic counselor.
HCA does not consider WES to be medically necessary for any the following:
• Uncomplicated autism spectrum disorder, developmental delay, or mild to moderate
global developmental delay
• Other circumstances (e.g., environmental exposures, injury, infection, etc.) that
reasonably explain the constellation of symptoms
• Carrier testing for “at risk” relatives
• Prenatal or pre-implantation testing
Hydration, therapeutic, prophylactic, diagnostic
injections, infusions
Hydration therapy with chemotherapy
Intravenous (IV) infusion of saline (CPT codes 96360-96371) is not paid separately when
administered at the same time as chemotherapy infusion (CPT codes 96413- 96417). If hydration
is provided as a secondary or subsequent service after a different initial service (CPT codes
96360, 96365, 96374, 96409, 96413), and it is administered through the same IV access, report
with CPT code 96361 for the first hour and again for each additional hour.
Note: The CPT codes 96365-96368 are for administration of therapeutic,
prophylactic or diagnostic IV infusion or injection (other than hydration).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
182
Therapeutic or diagnostic injections/infusions
(CPT codes 96360-96379) (WAC 182-531-0950)
• If no other service is performed on the same day, a subcutaneous or intramuscular
injection code (CPT code 96372) may be billed in addition to an injectable drug code.
• HCA does not pay separately for intravenous infusion (CPT codes 96372-96379) if they
are provided in conjunction with IV infusion therapy services (CPT codes 96360-96361or
96365-96368).
• HCA pays for only one initial intravenous infusion code (CPT codes 96360, 96365, or
96374) per encounter unless either of the following are true:
Protocol requires the use of two separate IV sites.
The client comes back for a separately identifiable service on the same day. In this
case, bill the second initial service code with modifier 59, XE, XS, XP, or XU.
• HCA does not pay for CPT code 99211 on the same date of service as drug
administration. If billed in combination, HCA denies the E/M CPT code 99211.
Note: Other E/M codes may be billed on the same date of service using modifier
25 to indicate that a significant and separately identifiable service was provided.
If modifier 25 is not used, HCA will deny the E/M code.
Concurrent infusion
HCA pays for concurrent infusion (CPT code +96368) only once per day.
Immune globulins, serum, or recombinant
products
Hepatitis B (CPT code 90371)
Reimbursement is based on the number of 1.0 ml syringes used.
Bill each 1.0 ml syringe used as 1 unit.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
183
Immune globulins
Bill HCA for immune globulins using the HCPCS procedure codes listed below. HCA does not
reimburse for the CPT codes listed in the Noncovered CPT code column below.
Noncovered CPT Code
Covered HCPCS Code
90281
J1460-J1560
90283
J1566
90284
J1562
90291
J0850
90384
J2790
90385
J2790
90386
J2792
90389
J1670
J1568, J1569, J1572, J1561
Rabies immune globulin (RIg)
(CPT codes 90375-90376)
Medicaid pays for RIg when medically necessary as part of a post-exposure treatment protocol.
Use the appropriate administration code in addition to the product CPT code.
Note: Rabies post-exposure treatment may require RIg and rabies vaccine
(90675-90676).
Medical genetics and genetic counseling services
Genetic counseling and genetic testing
HCA covers genetic counseling for all fee-for-service adults and children when performed by a
physician.
• To bill for prenatal genetic counseling, use ICD diagnosis code Z31.5 and the appropriate
E/M code
• To bill for genetic counseling other than prenatal, use ICD diagnosis code Z71.83 and the
appropriate E/M code.
HCA covers genetic counseling (CPT 96040) when performed by a health care professional
appropriately credentialed by the Department of Health (DOH).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
184
Certain genetic testing procedure codes need PA. Providers must obtain PA if required for
certain genetic tests and must give both the PA number and the appropriate genetic testing
modifier to the laboratory or when the laboratory bills so they can bill correctly. Providers must
check the Physician-related services fee schedule for services that require either PA or EPA.
For procedure codes that require PA, use the General Information for Authorization form, 13-
835 and Fax/Written Request Basic Information form, 13-756. See Where can I download HCA
forms?
Prenatal genetic counseling
(Chapter 246-680 and 246-825 WAC)
Genetic counselors who meet the requirements in chapter 246-825 WAC are eligible to enroll
with HCA to provide and receive payment for providing prenatal genetic counseling services.
Genetic counselors must be approved by the Department of Health (DOH) Screening and
Genetics Unit and be supervised by a practicing licensed physician.
Coverage
HCA covers:
• Face-to-face encounters only, including telemedicine. Telephonic and email encounters are
not covered.
• One initial prenatal genetic counseling encounter. This encounter must be billed in 30-
minute increments and cannot exceed 90 minutes.
• Two follow-up prenatal genetic counseling encounters per pregnancy. The encounters must
occur no later than 11 months after conception. These encounters must be billed in 30-
minute increments and cannot exceed 90 minutes.
Prenatal procedures other than genetic counseling, such as laboratory or diagnostic testing, must
be requested directly through the client’s primary care provider (PCP) or PCCM.
Note: Clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization (MCO)
are covered under the fee-for-service benefit. Provider must bill HCA directly for
prenatal genetic counseling provided to MCO clients. Prior authorization is not
required.
Fee Schedule
See HCA’s Prenatal diagnosis counseling fee schedule.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
185
Billing for prenatal genetic counseling
Providers must follow the billing requirements listed in HCA’s ProviderOne Billing and
Resource Guide. The guide explains how to complete the claim. If you provide this service via
telemedicine, please see Telemedicine for information on billing telemedicine claims.
Note: Prenatal genetic clinics are asked to submit billings within 120 days of the date
of service to facilitate reconciliation of Department of Health’s accounts.
Enter the following information in the listed fields on the claim:
Name
Enter
Place of Service
The appropriate place-of-service code, which must be either:
11 (office),
21 (inpatient hospital), or
22 (outpatient hospital)
Rendering
(Performing) Provider
Taxonomy Code
The taxonomy for prenatal genetic counseling: 170300000X
Rendering
(Performing) Provider
NPI
The genetic counselor’s NPI number
Billing Provider NPI
The approved agency’s billing NPI
Billing Provider
Taxonomy Code
The approved agency’s billing taxonomy code, which cannot be
170300000X
Note: CPT code 96040 must be billed using taxonomy 170300000X for both the
initial visit and the two follow-up visits. To bill for genetic counseling, use an
ICD diagnosis code for genetic counseling and the appropriate E/M code. CPT
code 96040 is a time-based code and each visit is limited to no more than 3 x
96040 (i.e., no more than 90 minutes per session).
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
186
Applying to HCA to become a genetic counseling provider
• To apply to provide services, a genetic counselor must:
Complete a Core Provider Agreement (CPA) with HCA.
Send all the following to the DOH Screening and Genetics Unit at the address
listed below:
The completed CPA
A DOH ABMG/ABGC certification or a letter verifying the genetic
counselor's eligibility to sit for the upcoming examination
Each qualified genetic counselor’s National Provider Identification (NPI)
number
A photocopy of the supervising physician's license
Send to:
Debra Lochner Doyle, MS, LCGC
Department of Health, Screening and Genetics Unit
20425 72nd Ave. S. Suite 310, Kent, WA 98032
253-395-6742
Email: debra.lochnerdoyl[email protected]
DOH Website: Genetic Services
Regional: Washington’s Genetic Clinics
• The DOH Screening and Genetics Unit staff will send copies of the approved forms to
HCA. This will serve as a written request to HCA to authorize the facility and provider to
bill for genetic counseling.
After receiving the approved forms from DOH, HCA will enroll the provider as an approved
genetic counseling provider. After being enrolled as a genetic counseling provider, services
provided in accordance with HCA policies for clients under WAC 182-502-0150 may be billed
to HCA.
Note: DOH-approved genetic counselors provide counseling for pregnant
women (fee for service and healthy option clients) up to the end of the month
containing the 60
th
day after the pregnancy ends. This service does not require
authorization. To locate the nearest DOH-approved genetic counselor call DOH at
(253) 395-6742.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
187
Miscellaneous
After-hours
After-hours office codes are payable in addition to other services only when the provider’s office
is not regularly open during the time the service is provided. An after-hours procedure billed for
a client treated in a 24-hour facility (e.g., emergency room) is payable only in situations where a
provider who is not already on-call is called to the facility to treat a client. These codes are not
payable when billed by emergency room physicians, anesthesiologists/anesthetists, radiologists,
laboratory clinical staff, or other providers who are scheduled to be on call at the time of service.
The client’s file must document the medical necessity and urgency of the service. Only one code
for after-hours services will be paid per patient, per day, and a second day may not be billed for a
single episode of care that carries over from one calendar day.
For example: If a clinic closes at 5pm and takes a break for dinner, and then
opens back up from 6 pm-10 pm, these services are not eligible for after-hours
service codes.
Note: This policy does not include radiologists, pathologists, emergency room
physicians, or anesthesiologists. HCA does not pay these providers for after-hour
service codes.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
188
Neurology and neuromuscular procedures
Needle electromyography (EMGs)
HCA has adopted Medicare-established limits for billing needle EMGs (CPT codes 95860 –
95870) as follows:
CPT Code
Short Description
Limits
95860
Muscle test one limb
Extremity muscles innervated by three
nerves or four spinal levels must be
evaluated with a minimum of five
muscles studied.
95861
Muscle test 2 limbs
95863
Muscle test 3 limbs
95864
Muscle test 4 limbs
95865
Muscle test larynx
Limited to one unit per day
95866
Muscle test hemidiaphragm
Limited to one unit per day
95869 Muscle test thor paraspinal
Limited to one unit per day
For this to pay with extremity codes
95860-95864, test must be for T3-T11
areas only; T1 or T2 alone are not
separately payable.
95870 Muscle test nonparaspinal
Limited to one unit per extremity,
and one unit for cervical or lumbar
paraspinal muscle, regardless of
number of levels tested (maximum of
5 units).
Not payable with extremity codes
(CPT codes 95860-95864).
95885
Musc tst done w/nerv tst lim
3 units
95886
Musc test done w/n test comp
3 units
95887
Musc tst done w/n tst nonext
1 unit
Nerve conduction study (NCS)
CPT Code
Short Description
Limits
95907
Motor&/sens 1-2 nrv cndj tst
1-2 studies
95908
Motor&/sens 3-4 nrv cndj tst
3-4 studies
95909
Motor&/sens 5-6 nrv cndj tst
5-6 studies
95910
Motor&/sens 7-8 nrv cndj tst
7-8 studies
95911
Motor&sens 9-10 nrv cndj tst
9-10 studies
95912
Motor&/sens 11-12 nrv cndj tst
11-12 studies
95913
Motor&/sens 13 or more nrv cndj tst
13 or more

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
189
Sleep medicine testing (sleep apnea)
(WAC 182-531-1500)
See the Sleep Centers Billing Guide.
Ophthalmology – vision care services
(WAC 182-531-1000)
Eye examinations and refraction services
HCA covers, without prior authorization (PA), eye examinations and refraction and fitting
services with the following limitations:
• Once every 24 months for asymptomatic clients age 21 or older
• Once every 12 months for asymptomatic clients age 20 or younger
• Once every 12 months, regardless of age, for asymptomatic clients of the Developmental
Disabilities Administration (DDA)
Coverage for additional examinations and refraction
services
HCA covers additional examinations and refraction services outside the limitation described in
eye examinations and refraction services when:
• The provider is diagnosing or treating the client for a medical condition that has
symptoms of vision problems or disease. Supporting medical documentation must be
submitted with the claim.
• The client is on medication that affects vision. Supporting medical documentation must
be submitted with the claim.
OR
• The service is necessary due to lost or broken eyeglasses/contacts. In this case:
No type of authorization is required for clients age 20 or younger or for clients of the
Developmental Disabilities Administration (DDA), regardless of age. Authorization
is not required for two or less replacement glasses. More than two pairs of glasses in
a 12 month period requires Prior Authorization (PA).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
190
Providers must follow HCA’s expedited prior authorization (EPA) process to
receive payment for clients age 21 or older. See EPA #870000610 in Expedited
Criteria Coding List. Providers must also document the following in the client's
file:
The eyeglasses or contacts are lost or broken
The last examination was at least 18 months ago
Visual field exams
HCA covers visual field exams for the diagnosis and treatment of abnormal signs, symptoms, or
injuries. Providers must document all of the following in the client's record:
• The extent of the testing
• Why the testing was reasonable and necessary for the client
• The medical basis for the frequency of testing
Vision therapy
HCA covers orthoptics and vision therapy which involves a range of treatment modalities
including the following:
• Lenses
• Prisms
• Filters
• Occlusion or patching
• Orthoptic/pleoptic training which is used for eye movement and fixation training
Note: HCA requires PA for eye exercises/vision training/orthoptics/pleoptics.
HCA requires expedited prior authorization (EPA) for orthoptics/pleoptic training
(CPT code 97110, 97112, or 97530) when there is a secondary diagnosis of
traumatic brain injury (TBI). See EPA #870001371, #870001372, and
#870001373.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
191
Corneal topography
HCA considers corneal topography to be medically necessary for the following diagnoses:
• Central corneal ulcer
• Corneal dystrophy, bullous keratopathy, and complications of transplanted cornea
• Diagnosing and monitoring disease progression in keratoconus or Terrien's marginal
degeneration
• Difficult fitting of contact lens
• Post-traumatic corneal scarring
• Pre- and post-penetrating keratoplasty and post kerato-refractive surgery for irregular
astigmatism
• Pterygium or pseudo pterygium
HCA allows up to two tests per client, per calendar year. If the client meets the medical necessity
criteria, bill using EPA #870001609. Otherwise, PA is required. You must document clinical
rationale for each test in the medical record (e.g., change in condition). If needed more
frequently or for a different diagnosis than what is listed above, PA is required.
Ocular prosthetics
HCA covers ocular prosthetics when provided by any of the following:
• An ophthalmologist
• An ocularist
• An optometrist who specializes in prosthetics
See HCA’s Prosthetic and Orthotic Devices Billing Guide for more information on coverage for
ocular prosthetics.
Eye surgery
Cataract surgery
HCA covers cataract surgery, without PA, when either of the following clinical criteria are met:
• Correctable visual acuity in the affected eye is at 20/50 or worse, as measured on the
Snellen test chart
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
192
• One or more of the following conditions exist:
Dislocated or subluxated lens
Intraocular foreign body
Ocular trauma
Phacogenic glaucoma
Phacogenic uveitis
Phacoanaphylactic endopthalmitis
Increased ocular pressure in a person who is blind and is experiencing ocular pain
HCA does not cover the following procedure codes:
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Policy/
Comments
C1840
Telescopic intraocular lens
Not Covered
Strabismus surgery
HCA covers strabismus surgery as follows:
Clients Policy
Age 17 or
younger
The provider must clearly document the need in the client's record. HCA
does not require authorization.
Age 18 or older
Covered when the clinical criteria are met. To receive payment, providers
must follow the expedited prior authorization (EPA) process. The clinical
criteria are:
• The client has double vision.
• The surgery is not being performed for cosmetic reasons.
To receive payment for clients age 18 or older, providers must use
HCA’s EPA process. See Expedited prior authorization (EPA).
Blepharoplasty or blepharoptosis surgery
HCA covers blepharoplasty or blepharoptosis surgery when all of the clinical criteria are met. To
receive payment, providers must follow HCA’s EPA process. See Expedited prior authorization
(EPA). The following clinical criteria must be met:
• The client's excess upper eyelid skin is blocking the superior visual field.
• The blocked vision is within 10 degrees of central fixation using a central visual field test.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
193
Implantable miniature telescope
The implantable miniature telescope, CPT code 66999, is used in clients with untreated, end
stage, age related macular degeneration. It is a visual aid for clients with low vision, and like the
other adult low vision aids, is considered vision hardware. Like all vision hardware, this is not
included in the clients’ benefit package for clients age 21 and older.
Vision coverage table
Due to its licensing agreement with the American Medical Association, HCA publishes only the
official CPT procedure code short descriptions. To view the long description, refer to a current
CPT book.
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short Description
PA?
Policy/
Comments
Maximum
Allowable
Fee
Contact Lens Services
92071
Contact lens fitting
for tx
No
Ages 21-99
2 fittings every 24
months.
Ages 0-20
1 fittings every 12
months for
asymptomatic clients
Fee
Schedule
92072
Fit contact lens for
managmnt
No
Ages 21-99
2 fittings every 24
months
Ages 0-20
2 fittings every 12
months limited to the
appropriate diagnosis
code
Fee
Schedule
Spectacle Fitting fees, monofocal
92340
Fit spectacles
monofocal
No
Fee
Schedule
92352
Fit aphakia spectcl
monofocl
No
Fee
Schedule
Spectacle Fitting fees, bifocal
92341
Fit spectacles
bifocal
No
Fee
Schedule

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
194
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short
Description
PA?
Policy/
Comments
Maximum
Allowable
Fee
Spectacle Fitting fees, multifocal
92342
Fit spectacles
multifocal
No
Fee
Schedule
92353
Fit aphakia spectcl
multifoc
No
Fee
Schedule
Note: Fitting fees are not currently covered by Medicare and may be billed
directly to HCA without attaching a Medicare denial.
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short
Description
PA?
Policy/
Comments
Maximum
Allowable
Fee
Other
92354
Fit spectacles single
system
Yes
Fee
Schedule
92355
Fit spectacles
compound lens
Yes
Fee
Schedule
92370
Repair & adjust
spectacles
No
Applies only to clients
age 20 and younger.
Fee
Schedule
92371
Repair & adjust
spectacles
No
Applies only to clients
age 20 and younger.
Fee
Schedule
92499
Eye service or
procedure
Yes
Fee
Schedule
General Ophthalmological Services
92002
Eye exam new
patient
No
Fee
Schedule
92004
Eye exam new
patient
No
Fee
Schedule
92012
Eye exam establish
patient
No
Fee
Schedule
92014
Eye exam&tx estab
pt 1/>vst
No
Fee
Schedule
Special Ophthalmological Services
92015
Determine
refractive state
No
Fee
Schedule
92018
New eye exam &
treatment
No
Fee
Schedule
92019
Eye exam &
treatment
No
Fee
Schedule
92020
Special eye
evaluation
No
Fee
Schedule
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
195
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short
Description
PA?
Policy/
Comments
Maximum
Allowable
Fee
92025
Corneal topography
Yes
EPA required.
Limited to 2 per
calendar year.
EPA #870001609
Fee
Schedule
92025
TC
Corneal topography
Yes
EPA required.
Limited to 2 per
calendar year.
EPA #870001609
Fee
Schedule
92025
26
Corneal topography
Yes
EPA required.
Limited to 2 per
calendar year.
EPA #870001609
Fee
Schedule
92060
Special eye
evaluation
No
Fee
Schedule
92060
TC
Special eye
evaluation
No
Fee
Schedule
92060
26
Special eye
evaluation
No
Fee
Schedule
92065
Orthoptic/pleoptic
training
Yes
Fee
Schedule
92065
TC
Orthoptic/pleoptic
training
Yes
Fee
Schedule
92065
26
Orthoptic/pleoptic
training
Yes
Fee
Schedule
92081
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92081
TC
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92081
26
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92082
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92082
TC
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92082
26
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92083
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92083
TC
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
196
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short
Description
PA?
Policy/
Comments
Maximum
Allowable
Fee
92083
26
Visual field
examination(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92100
Serial tonometry
exam(s)
No
Fee
Schedule
92133
Cmptr ophth img
optic nerve
No
Limited to 1 per
calendar year
Fee
Schedule
92133 TC
Cmptr ophth img
optic nerve
No
Limited to 1 per
calendar year
Fee
Schedule
92133 26
Cmptr ophth img
optic nerve
No
Limited to 1 per
calendar year
Fee
Schedule
92134
Cptr ophth dx img
post segmt
No
Limited to 2 times per
calendar year.
Fee
Schedule
92134
Cptr ophth dx img
post segmt
Yes
EPA required.
Limited to 12 per
calendar year.
EPA #870000051
Fee
Schedule
92136
Ophthalmic
biometry
No
Fee
Schedule
92136
TC
Ophthalmic
biometry
No
Fee
Schedule
92136
26
Ophthalmic
biometry
No
Fee
Schedule
92140
Glaucoma
provocative tests
No
Fee
Schedule
Ophthalmoscopy
92230
Eye exam with
photos
No
Fee
Schedule
92235
Eye exam with
photos
No
Fee
Schedule
92235
TC
Eye exam with
photos
No
Fee
Schedule
92235
26
Eye exam with
photos
No
Fee
Schedule
92240
Icg angiography
No
Fee
Schedule
92240
TC
Icg angiography
No
Fee
Schedule
92240
26
Icg angiography
No
Fee
Schedule
92250
Eye exam with
photos
No
Fee
Schedule

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
197
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short
Description
PA?
Policy/
Comments
Maximum
Allowable
Fee
92250
TC
Eye exam with
photos
No
Fee
Schedule
92250
26
Eye exam with
photos
No
Fee
Schedule
92260
Ophthalmoscopy/
Dynamometry
No
Fee
Schedule
V2630
Anter chamber
intraocul lens
No
Fee
Schedule
V2631
Iris support
intraoclr lens
No
Fee
Schedule
V2632
Post chmbr
intraocular lens
No
Fee
Schedule
Other Specialized Services
92265
Eye muscle
evaluation
No
Fee
Schedule
92265
TC
Eye muscle
evaluation
No
Fee
Schedule
92265
26
Eye muscle
evaluation
No
Fee
Schedule
92270
Electro-
oculography
No
Fee
Schedule
92270
TC
Electro-
oculography
No
Fee
Schedule
92270
26
Electro-
oculography
No
Fee
Schedule
92275
Electroretinography
No
Fee
Schedule
92275
TC
Electroretinography
No
Fee
Schedule
92275
26
Electroretinography
No
Fee
Schedule
92283
Color vision
examination
No
Fee
Schedule
92283
TC
Color vision
examination
No
Fee
Schedule
92283
26
Color vision
examination
No
Fee
Schedule
92284
Dark adaptation eye
exam
No
Fee
Schedule

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
198
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short
Description
PA?
Policy/
Comments
Maximum
Allowable
Fee
92284
TC
Dark adaptation eye
exam
No
Fee
Schedule
92284
26
Dark adaptation eye
exam
No
Fee
Schedule
92285
Eye photography
No
Fee
Schedule
92285
TC
Eye photography
No
Fee
Schedule
92285
26
Eye photography
No
Fee
Schedule
92286
Internal eye
photography
No
Fee
Schedule
92286
TC
Internal eye
photography
No
Fee
Schedule
92286
26
Internal eye
photography
No
Fee
Schedule
92287
Internal eye
photography
No
Fee
Schedule
Contact Lens Services
92310
Contact lens fitting
No
Fee
Schedule
92311
Contact lens fitting
No
Fee
Schedule
92312
Contact lens fitting
No
Fee
Schedule
92313
Contact lens fitting
No
Fee
Schedule
Ocular Prosthesis
See the Outpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide and the Outpatient Prospective Payment
System (OPPS) fee schedule on HCA’s Hospital reimbursement webpage for more
information on coverage for ocular prosthetics.
Contact Lens Services
92314
Prescription of
contact lens
No
Fee
Schedule
92315
Prescription of
contact lens
No
Fee
Schedule
92316
Prescription of
contact lens
No
Fee
Schedule
92317
Prescription of
contact lens
No
Fee
Schedule

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
199
Manipulative therapy
(CPT codes 98925-98929) (WAC 182-531-1050)
HCA covers:
• Ten (10) manipulative therapy treatments per client, per calendar year.
• Manipulative therapy services only when provided by either an osteopathic physician
licensed under chapter 18.71 RCW or a naturopathic physician licensed under chapter
18.36A RCW.
• Manipulative therapy services by body regions. Body regions are defined as:
abdomen and viscera
pelvic
cervical
rib cage
head
sacral
lower extremities
thoracic
lumbar
upper extremities
• One manipulative therapy procedure code in the range 98925-98929 per client, per day.
Bill using the CPT code that describes the number of body regions involved. For
example, if three body regions are manipulated, bill one unit of CPT code 98926.
• An E/M service (billed with modifier 25) in addition to the manipulative therapy service,
under one of the following circumstances:
When a provider diagnoses the condition requiring manipulative therapy and
provides the therapy during the same visit
When the existing condition fails to respond to manipulative therapy or
significantly changes, requiring E/M services beyond those considered included in
the manipulation codes
When the provider treats the client for a condition unrelated to the manipulative
therapy during the same encounter
Justification for the E/M and manipulative therapy services must be documented and kept
in the client’s record for review.
Note: HCA does not cover physical therapy services performed by osteopathic
physicians or naturopathic physicians unless they are also physiatrists.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
200
Other services and procedures
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
(CPT code 99183 and HCPCS G0277)
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be considered medically necessary for treatment of the
following conditions in the inpatient or outpatient hospital setting:
• Decompression sickness
• Acute carbon monoxide poisoning
• Acute cyanide poisoning
• Acute gas or air embolism
• Gas gangrene (clostridial myositis and myonecrosis)
• Progressive necrotizing soft tissue infections
• Acute traumatic ischemia secondary to crush injuries
For prevention of loss of function or for limb salvage
Used in combination with standard medical and surgical management
• Late radiation tissue injury
• Prevention of osteoradionecrosis following tooth extraction in a previously radiated field
• Refractory osteomyelitis
Unresponsive to standard medical and surgical management
• Compromised flaps and skin grafts
For prevention of loss of function or for limb salvage
• Non-healing diabetic wounds of the lower extremities
Patient has type 1 or type 2 diabetes and has a lower extremity wound that is due
to diabetes
Patient has a wound classified as Wagner grade 3 or higher
Patient has failed an adequate course of standard wound therapy

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
201
The following are considered not medically necessary:
• Thermal burns
• Acute and chronic sensorineural hearing loss
• Cluster and migraine headaches
• Multiple sclerosis
• Cerebral palsy
• Traumatic and chronic brain injury
• Arterial, venous or pressure ulcers
Procedure Code
Short Description
99183
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
G0277
Hyperbaric oxygen
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy requires EPA. See Expedited Prior Authorization Criteria Coding
List, EPA #870000425. If the client does not meet the EPA criteria, prior authorization (PA) is
required (see Prior authorization (PA)). When requesting PA, provide the number of sessions
being requested and the amount of time requested per session. For example: If the client is
receiving a 90-minute session of hyperbaric oxygen therapy, the provider would request 1 unit of
99183 and 3 units of G0277.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
202
Testosterone testing
(CPT 84402, 84403, and 84410)
HCA covers medically necessary testosterone testing for any eligible client. See the following
table for cases in which prior authorization is required:
Client
Prior authorization required?
Female, any age
No
Male, age 18 and younger
No
Male, age 19 and older
Yes. When the client meets the
coverage criteria, you may use EPA
#870001368.
Male or female, any age, being treated for gender
dysphoria
Yes. When the client meets the
coverage criteria, you may use EPA
#870001368.
Transient elastography
HCA pays for a transient elastography such as a FibroScan® only for determining if qualifying
criteria measures are met for immune modulators and anti-viral medication treatment of chronic
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Transient elastography requires EPA. See Expedited Prior
Authorization Criteria Coding List, EPA #870001350.
Neuropsychological testing
For Neuropsychological testing, see HCA’s Mental Health Services Billing Guide.
Psychiatry
Clozaril - case management
• Physicians, psychiatrists, and ARNPs must bill for Clozaril case management using the
applicable E/M code for drug monitoring.
• For Pharmacist billing, see HCA’s Prescription Drug Program Billing Guide.
• Put “Clozaril Case Management” in the claim notes field on the claim.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
203
• HCA reimburses providers for one unit of Clozaril case management per week.
HCA reimburses providers for Clozaril case management when billed with the
appropriate ICD diagnosis codes.
Routine venipuncture (CPT code 36415) and a blood count (CBC) may be billed
in combination when providing Clozaril case management.
• HCA does not pay for Clozaril case management when billed on the same day as any
other psychiatric-related procedures.
For additional information, see HCA’s Mental Health Services Billing Guide.
Pulmonary
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy (ECMO)
See extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy (ECMO). ECMO is for both cardiovascular
and pulmonary services.
Ventilator management
Evaluation and Management (E/M) services are not allowed in combination with CPT codes
94002-94004, 94660, and 94662 for ventilator management on the same day, by the same
provider/clinic. However, E/M services may be billed for on the same date of service using
modifier 25 to indicate that a significant and separately identifiable service was provided. If
modifier 25 is not used, HCA will deny the E/M code.
Special dermatological services
Ultraviolet phototherapy
HCA does not cover ultraviolet phototherapy (CPT code 96910) when billed with ICD diagnosis
code L80 (vitiligo). HCA considers this a cosmetic procedure.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
204
Special services
Group clinical visits for clients with diabetes or asthma
Overview of the program
The intent of the Diabetes and Asthma Group Clinical Visits program is to provide clinical
services and educational counseling to HCA clients who have been diagnosed with diabetes or
asthma. These visits are limited to groups of two or more clients and are payable only to
physicians or advanced registered nurse practitioners (ARNPs). However, participation from
other professional staff, including physician assistants, physical therapists, nurses, and
nutritionists, is encouraged.
Program requirements
• Prior to a group clinical visit, the provider must perform an assessment of individual
client medical information and document the proposed treatment plan for each client.
• The group clinical visit must be led by a physician or ARNP, but may include other staff
as well.
• The group clinical visit must last at least one hour and include:
A group discussion on clinical issues to promote long-term disease control and
self-management. This discussion should include at least one of the following
topics:
Prevention of exacerbation or complications
Proper use of medications and other therapeutic techniques (spacers, peak
flow meter use; glucose measurement, foot care, eye exams, etc.)
Living with a chronic illness
A question and answer period
The collection of prevention-based care data needed to monitor chronic illness
(e.g., weight and blood pressure)
Short (approximately 5-10 minutes per client) one-on-one visits to gather needed
data and establish an individual management plan with the client
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
205
• The following must be documented in the medical record:
Individual management plan, including self-management capacity
Data collected, including physical exam and lab findings
Patient participation
Beginning and ending time of the visit
Billing and reimbursement
Providers must use the following CPT code when billing for diabetes or asthma group counseling
visits, subject to the limitations in the table below. Providers must bill visits in increments of
one-hour units (one hour = one unit). Multiple units may be billed on the same day.
CPT Code
Restricted to Diagnoses
Visit Limitations
99078
Diabetes and asthma.
Limited to four (4) one-hour units per
calendar year, per client, per condition
Note: HCA pays only for the time that a client spends in the group clinical visit.
Other limitations
HCA does not reimburse a diabetes or asthma group clinical visit in conjunction with an office
visit or other outpatient evaluation and management (E/M) codes for the same client, same
provider, and same condition on the same day.
A diabetes group clinical visit may be billed on the same day as a Department of Health (DOH) -
approved diabetes education core module as long as the times documented in the medical record
indicate two separate sessions.
Therapies (physical, occupational, and speech
therapy)
Physicians, Podiatrists, Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioners (ARNP), Physician
Assistants Certified (PA-C), and Wound Care Center Specialty Physicians - Billing
The outpatient rehabilitation benefit limits do not apply to therapy services provided and billed
by physicians, podiatrists, ARNPs, PA-Cs, and wound care center specialty physicians.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
206
Modifier required when billing
Physicians, podiatrists, ARNPs, and PA-Cs, and wound care center specialty physicians must use
the following modifier when billing for PT/OT/ST services:
Modality
Modifiers
PT/OT/ST
AF
Note: For additional information, see HCA’s Outpatient Rehabilitation Billing
Guide.
Treatment of chronic migraines and chronic
tension-type headaches
HCA requires prior authorization for OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) injections through a medical
necessity review by Comagine Health.
For treatment of chronic migraine (as defined by the International Headache Society), HCA
covers OnabotulinumtoxinA when the following criteria are met:
• The client has not responded to at least three prior pharmacological prophylaxis therapies
from two different classes of drugs.
• The condition is appropriately managed for medication overuse.
OnabotulinumtoxinA injections must be discontinued when the condition has shown inadequate
response to treatment (defined as less than a 50% reduction in headache days per month after two
treatment cycles.
A maximum of five treatment cycles is allowed in a 12 month period. HCA evaluates requests
for additional treatment cycles on a case-by-case basis.
Treatment of chronic migraine or chronic tension-type headache with acupuncture, massage,
trigger point injections, transcranial magnetic stimulation, or manipulation/manual therapy is not
a covered benefit.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
207
Vaccines/toxoids (immunizations)
HCA covers vaccines administered according to the current Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) immunization schedule for adults and
children in the United States, including make-up schedules. There is detailed guidance on
vaccines at the CDC website. Refer to the Professional administered drugs fee schedule for the
list of covered vaccines by CPT code.
HCA covers only those vaccines listed on the CDC immunization schedule for adults and
children in the United States. HCA does not cover vaccines recommended or required for the
sole purpose of international travel (such as yellow fever, typhoid, Japanese encephalitis, etc.).
Note: In the case of rabies vaccines, HCA does not cover pre-exposure
immunization for rabies. Medicaid pays for the rabies vaccine when medically
necessary as part of the post-exposure treatment protocol.
Clients from birth through age 18
DOH supplies free vaccines for children 0-18 years only. For clients 18 years of age and
younger, see HCA’s Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment (EPSDT) Program
Billing Guide.
Clients age 19 and older
HCA covers vaccines recommended by the CDC. HCA covers vaccines needed throughout the
client’s lifetime based on age, health conditions, or other factors.
Routine adult immunizations include an annual flu shot as well tetanus (Td or Tdap) shots at
intervals determined by healthcare professionals.
Health care providers should regularly review client immunization histories and offer any
vaccine indicated for their adult clients. HCA covers these vaccines as necessary.
Clients enrolled in the Family Planning Only – Pregnancy Related, Family Planning Only
(formerly referred to as TAKE CHARGE), and Alien Emergency Medicine programs are not
eligible for the vaccine program.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
208
How to bill HCA for adult immunizations
• The claim must include the CPT code for each vaccine product given.
• Include the appropriate vaccine administration CPT codes on the same claim form:
90471 if only one vaccine is injected
90472 for each additional vaccine injected at the visit
90473 if one vaccine is administered via the oral or intranasal route
90474 for each additional vaccine administered by the oral or intranasal route
• HCA reimburses providers for the vaccine product using HCA’s maximum allowable fee
schedule.
If an immunization is the only service provided, bill only for the vaccine and for the
administration of the vaccine.
Billing with an E/M code
Do not bill an E/M code unless a significant and separately identifiable condition exists and is
reflected by the diagnosis.
When a significant and separately identifiable condition exists, bill the appropriate E/M code
with modifier 25. If the E/M code is billed without modifier 25 on the same date of service as a
vaccine administration, HCA will deny the E/M code. Exception: The E/M code 99211 may not
be billed with a vaccine or the vaccine administration code.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
209
Maternity Care and Delivery
Policies and resources regarding maternity care
• For information regarding family planning services, including immediate postpartum long-
acting reversible contraceptive (LARC) insertion, see the Family Planning Billing Guide.
• For information regarding support services covered during and post pregnancy see the
Maternity Support Services/Infant Case Management Billing Guide. Maternity Support
Services/Infant Case Management (MSS/ICM) are services provided through the First
Steps program. Services are designed to help pregnant women and their newborns gain
access to medical, social, educational and other services. Services are provided in the home
or clinic throughout pregnancy and up to the infant’s first birthday.
• For information regarding childbirth education see the Childbirth Education Billing Guide.
• To bill for anesthesia during delivery, see Anesthesia for maternity.
• For deliveries in a birthing center, see HCA’s Planned Home Births and Births in
Birthing Centers Billing Guide.
• For deliveries in a home birth setting, see HCA’s Planned Home Births and Births in
Birthing Centers Billing Guide.
• For information on treating substance use in pregnancy:
See the Chemical-Using Pregnant (CUP) Women Program Billing Guide for
detoxification services.
See Drug screening for medication for opioid use disorder regarding drug
screening.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
210
Confirmation of pregnancy
If a client presents with signs or symptoms of pregnancy and the purpose of the client’s visit is to
confirm the pregnancy and:
• The obstetrical (OB) record is not initiated, bill this visit using the appropriate level E/M
code. Bill using the diagnosis code(s) for the signs and/or symptoms the client is having
[e.g. suppressed menstruation (ICD diagnosis code N92.5 or N93.8)]. Do not bill using the
pregnancy diagnosis codes (e.g. Z33.1, Z34.00, Z34.80, or Z34.90).
• The OB record is initiated at this visit the visit is considered part of the global OB package
and must not be billed separately. The pregnancy diagnosis codes (e.g. Z33.1, Z34.00,
Z34.80, or Z34.90) are used when billing the global OB package. (See below)
If some other source has confirmed the pregnancy and the provider wants to do his/her own
confirmation, bill this visit using the appropriate level E/M code if the OB record is not initiated. If
the OB record is initiated at this visit, the visit is considered part of the global OB package and
must not be billed separately.
Diagnostic testing to confirm pregnancy and gestational age:
• See the Physician-related/professional services fee schedule and clinical laboratory codes
for coverage of urine and blood testing for confirmation of pregnancy.
• See obstetrical ultrasounds in this guide.
Problem visits during pregnancy
If a client is seen for reasons other than routine antepartum or postpartum care, providers must
bill using the appropriate Evaluation and Management (E/M) procedure code with a medical
diagnosis code as the primary diagnosis. Claims with diagnosis codes Z33.1, Z34.00, Z34.80, or
Z34.90 will be denied if listed as the principal diagnosis.
For those clients who have non-maternity-related issues and diagnosis(es), the provider should
use the appropriate E/M code with the modifier GB.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
211
HIV/AIDS counseling/testing
(WAC 182-531-0600)
See HIV/AIDS counseling/testing for coverage policy.
Exceptions for pregnancy: HCA pays for counseling visits when billed with an
E/M service on the same day when either of the following is true:
• The client is being seen for a medical problem and modifier 25 is billed.
• The client is being seen for an antepartum visit and modifier TH is used.
HCA does not pay for a counseling visit if the client is being seen only to confirm pregnancy and
an office visit is billed, because the counseling is considered part of the office visit.
HCA covers HIV testing (86701-86703) for pregnant women when billed with the following
appropriate diagnosis codes: Z33.1, Z34.00, Z34.80, Z34.90 or Z36.
Tobacco/nicotine cessation for pregnant clients
See tobacco/nicotine cessation coverage and billing policies and resources.
Early pregnancy loss and abortion services
• Maternity services include the assessment, management, treatment of pregnancy loss, and
voluntary terminations. This includes spontaneous, incomplete, missed, induced, and
elective abortions.
• Providers must bill using the appropriate diagnosis codes for the type of abortion –
elective, induced, spontaneous, incomplete, or missed. An elective termination of
pregnancy requires the ICD diagnosis code Z33.2.
• Office visits, laboratory tests, and diagnostic tests performed for the purpose of
confirming pregnancy, gestational age, and successful treatment are covered.
• Rho(D) immune globulin must be billed using the appropriate HCPCS codes when it is
given. See Physician-related/professional services fee schedule and Professionally
administered drug fee schedule.
• Clients enrolled in an HCA managed care organization (MCO) may self-refer outside the
MCO for induced abortions.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
212
• Clients on the Family Planning Only – Pregnancy Related program or Family Planning
Only program (formerly referred to as TAKE CHARGE) are not covered for maternity
care including induced abortions. They must apply for pregnancy medical coverage.
• Medical abortions:
HCA pays a bundled rate (HCPCS S0199) for medical abortions administered in
an office or outpatient clinic setting.
HCPCS S0199 includes services rendered over an 18-day period,
including office visits, ultrasounds, laboratory studies, and
education/counseling.
Providers may bill HCPCS S0199 after the follow-up appointment or 18
days after the first visit, whichever comes first.
Reimbursement for HCPCS S0199 is limited to once every 5 weeks.
Bill HCPCS S0199 on professional (J) claims only.
Providers must bill for medical abortions using HCPCS S0199, unless
there is a complication.
Note: HCPCS S0199 does not include abortion medications, which must be billed
on different lines. Rho(D) immune globulin is not included in the bundled rate
and must be billed on a different line when administered.
Note: Do not use HCPCS S0199 when a medical abortion is incomplete. If
additional doses of medication are necessary or surgical evacuation is required,
bill separately for each individual service provided.
When a client does not present for a follow-up visit, use modifier TS when billing
HCPCS S0199. The provider payment for HCPCS S0199 is unchanged when
modifier TS is used.
HCA covers the following medications used according to nationally accepted
guidelines issued by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the American
College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG):
Methotrexate sodium, 50 mg (HCPCS J9260)
Mifepristone, oral, 200 mcg (HCPCS S0190)
Misoprostol, oral, 200 mcg (HCPCS S0191)

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
213
When telemedicine is used to provide HCPCS S0199 bundled services, HCA does
not pay any additional originating facility fees. See Telemedicine for more
information.
Note: Do not bill HCA for medical abortion services until all care is completed.
• Surgical abortions:
HCA pays for surgical abortions that occur in an ambulatory surgical center
(ASC), hospital, or HCA-approved and -contracted non-hospital based center
(abortion center).
ASCs and hospitals must bill for surgical services according to their billing
guides. See the Ambulatory Surgery Centers Billing Guide, the Inpatient Hospital
Services Billing Guide, and the Outpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide.
Abortion center:
Abortion centers must be approved by and contracted with HCA to bill for
facility fee payments for a surgical abortion. To become an approved
abortion center, mail a request to [email protected].
Abortion centers are reimbursed facility fees only for surgical abortions.
Abortion centers are not paid a facility fee for medical abortions not
requiring surgical intervention.
HCA-contracted abortion center facility fee payment includes all room
charges, equipment, supplies, drugs (including anti-anxiety, antibiotics,
pain medications, and miscellaneous drugs required for the procedure),
anesthesia, and injections and blood draws associated with the procedure.
HCA-contracted abortion center facility fee does not include professional
services, laboratory charges, ultrasound and other X-rays, and Rho(D)
immune globulin which may be billed separately.
Payment is limited to one HCA-contracted abortion center facility fee per
client, per abortion. The facility fee is not payable per visit, even though a
particular procedure or case may take several days or visits to complete.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
214
Global (total) obstetrical (OB) care
Global OB care (CPT codes 59400, 59510, 59610, or 59618) includes all the following:
• Routine antepartum care in any trimester
• Delivery
• Postpartum care
If the provider furnishes all of the client’s antepartum care, performs the delivery, and provides
the postpartum care, the provider must bill using one of the global OB procedure codes.
Use HCPCS code 0500F along with the appropriate billing code on the first prenatal visit. HCA
is tracking the date a client begins receiving obstetrical care (date the OB record is initiated).
Note this date by entering HCPCS code 0500F with the appropriate ICD diagnosis codes Z33.1,
Z34.00, Z34.80, or Z34.90 on the claim.
Note: When billing global Obstetrical Services, the place of service code must
correspond with the place where the child was born (for example: 25).
When more than one provider in the same clinic (same group NPI) sees the same client for
global maternity care, HCA pays only one provider for the global (total) obstetrical care.
Providers who are in the same clinic who do not have the same group NPI must not bill HCA
the global (total) obstetrical care procedure codes. In this case, the OB services must be
unbundled and the antepartum, delivery, or postpartum care must be billed separately.
Note: Do not bill HCA for maternity services until all care is completed.
Unbundling obstetrical care
In the situations described below, providers may not be able to bill HCA for global OB care as
HCA may have paid another provider for some of the client’s OB care, or a provider may have
been paid by another insurance carrier for some of the client’s OB care. In these cases, it may be
necessary to unbundle the OB services and bill the antepartum, delivery, and postpartum care
separately.
When a client transfers to a practice late in the pregnancy
• If the client has had antepartum care elsewhere, the subsequent provider must not bill the
global OB package. Bill the antepartum care, delivery, and postpartum care separately.
The provider that had been providing the antepartum care bills for the services that he/she
performed. Therefore, if the subsequent provider bills the global OB package, that
provider is billing for some antepartum care that another provider has claimed.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
215
- OR –
• If the client did not receive any antepartum care prior to coming to the provider’s office,
bill the global OB package.
In this case, the provider may actually perform all of the components of the global OB
package in a short time. HCA does not require this provider to perform a specific number
of antepartum visits in order to bill for the global OB package.
If a client transfers to another provider (not associated with the providers practice), moves
out of the area prior to delivery, or loses the pregnancy…
When provider A has seen the client for part of the antepartum care and has transferred the client
to provider B for care, and provider B is billing separately for the antepartum care being
delivered, provider B enters “transfer of care” in the Claim Note section of the electronic claim.
Provider B bills only those services actually provided to these clients.
If a client changes insurance during pregnancy…
Sometimes, a client is fee-for-service at the beginning of pregnancy and enrolled in an HCA
managed care organization (MCO for the remainder of the pregnancy. HCA is responsible for
paying only those services provided to the client while the client is on fee-for-service. The MCO
pays for services provided after the client is enrolled with the plan.
HCA encourages early prenatal care and is actively enrolling new clients into managed care. If a
client is on fee-for-service and is not yet enrolled in an MCO plan at the beginning of the client’s
pregnancy, consider billing the first visit as a secondary confirmation of pregnancy using ICD
diagnosis code N92.5 or N93.8 with the appropriate level of office visit as described under the
Confirmation of Pregnancy section.
When a client changes from one plan to another, bill those services that were provided while the
client was enrolled with the original plan to the original carrier, and those services that were
provided under the new coverage to the new plan. The provider must unbundle the services and
bill the antepartum, delivery, and postpartum care separately. For clients who move in and out of
managed care and fee for service, use TH and CG modifiers to unbundle the codes.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
216
Antepartum care
Per CPT guidelines, HCA considers routine antepartum care for a normal, uncomplicated
pregnancy to consist of:
• Monthly visits up to 28 weeks gestation.
• Biweekly visits to 36 weeks gestation.
• Weekly visits until delivery.
Antepartum care includes:
• Initial and subsequent history.
• Physical examination.
• Recording of weight and blood pressure.
• Recording of fetal heart tones.
• Routine chemical urinalysis.
• Maternity counseling, such as risk factor assessment and referrals.
Necessary prenatal monitoring, diagnostic, and laboratory tests may be billed in addition to
antepartum care, except for the following tests (CPT codes 81000, 81001, 81002, 81003, and
81007).
Coding for antepartum care only
If it is necessary to unbundle the OB package and bill separately for antepartum care, bill as
follows:
• If the client had a total of one to three antepartum visits, bill the appropriate level of E/M
service with modifier TH for each visit, with the date of service the visit occurred and
the appropriate diagnosis.
• If the client had a total of four to six antepartum visits, bill using CPT code 59425 with a
"1" in the units box. Bill HCA using the date of the last antepartum visit in the to and
from fields.
• If the client had a total of seven or more visits, bill using CPT code 59426 with a "1" in
the units box. Bill HCA using the date of the last antepartum visit in the to and from
fields.
Do not bill antepartum care only codes in addition to other procedure codes that include
antepartum care (i.e. global OB codes).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
217
Do not bill using CPT E/M codes for the first three visits, then CPT code 59425 for visits four
through six, and then CPT code 59426 for visits seven and on. These CPT codes are used to bill
only the total number of times the client was seen for all antepartum care during the client’s
pregnancy, and may not be billed in combination with each other during the entire pregnancy
period.
Note: Do not bill HCA until all antepartum services are complete. Hospital care
for pregnant women can be billed concurrently.
Coding for deliveries without antepartum care
If it is necessary to unbundle the OB package and bill for the delivery only, bill HCA using one
of the following CPT codes:
• 59409 (vaginal delivery only)
• 59514 (cesarean delivery only)
• 59612 [vaginal delivery only, after previous cesarean delivery (VBAC)]
• 59620 [cesarean delivery only, after attempted vaginal delivery after previous cesarean
delivery (attempted VBAC)]
If a provider does not furnish antepartum care, but performs the delivery and provides
postpartum care, bill HCA using one of the following CPT codes:
• 59410 (vaginal delivery, including postpartum care)
• 59515 (cesarean delivery, including postpartum care)
• 59614 (VBAC, including postpartum care)
• 59622 (attempted VBAC, including postpartum care)
Coding for postpartum care only
If it is necessary to unbundle the OB package and bill for postpartum care only, bill HCA using
CPT code 59430 (postpartum care only).
If a provider furnishes all of the antepartum and postpartum care, but does not perform the
delivery, bill HCA for the antepartum care using the antepartum care only codes, along with CPT
code 59430 (postpartum care only).
Do not bill CPT code 59430 (postpartum care only) in addition to any procedure codes that
include postpartum care. (i.e. global OB codes)
Postpartum care includes office visits for the six week period after the delivery and includes
family planning counseling and contraceptive management.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
218
Additional monitoring for high-risk conditions
When providing additional monitoring for high-risk conditions in excess of the CPT guidelines
for normal antepartum visits, bill using E/M codes 99211-99215 with modifier UA. The office
visits may be billed in addition to the global fee only after exceeding the CPT guidelines for
normal antepartum care. Providers must bill with a primary diagnosis that identifies that the high
risk condition is pregnancy related.
A condition that is classifiable as high-risk alone does not entitle the provider to additional
payment. Per CPT guidelines, it must be medically necessary to see the client more often than
what is considered routine antepartum care in order to qualify for additional payments. The
additional payments are intended to cover additional costs incurred by the provider as a
result of more frequent visits. For example:
Client A is scheduled to see a provider for the client’s antepartum visits on
January 4, February 5, March 3, and April 7. The client attends the January and
February visits, as scheduled. However, during the scheduled February visit, the
provider discovers the client’s blood pressure is slightly high and wants the
client to come in on February 12 to be checked again. At the February 12 visit,
the provider discovers the client’s blood pressure is still slightly high and asks
to see the client again on February 18. The February 12 and February 18 visits
are outside of the client’s regularly scheduled antepartum visits and outside of
the CPT guidelines for routine antepartum care since the client is being seen
more often than once per month. The February 12 and February 18 visits may
be billed separately from the global antepartum visits using the appropriate E/M
codes with modifier UA, and the diagnosis must represent the medical necessity
for billing additional visits. A normal pregnancy diagnosis (i.e. Z33.1,
Z34.00, Z34.80, or Z34.90) will be denied outside of the global antepartum
care. It is not necessary to wait until all services included in the routine
antepartum care are performed to bill the extra visits, as long as the extra
visits are outside of the regularly scheduled visits.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
219
Assessment and treatment of high risk conditions:
Preterm labor and birth:
• HCA does not pay separately for CerviLenz. It is considered bundled into the practice
expense.
• See fetal fibronectin in this guide.
• See Alpha hydroxyprogesterone (17P) and Makena in this guide.
Diagnostic and monitoring tests:
• See obstetrical ultrasounds in this guide.
Consultations
If another provider refers a client during her pregnancy for a consultation, bill HCA using
consultation CPT codes 99241-99245. If an inpatient consultation is necessary, bill using CPT
codes 99251 – 99255 or for a follow-up bill using CPT codes 99231-99233. The referring
physician’s name and NPI must be listed in the Referring Physician field on the claim.
If the consultation results in the decision to perform surgery (i.e. a cesarean section), HCA pays
the consulting physician for the consultation as follows:
• If the consulting physician does not perform the cesarean section, bill HCA the
appropriate consultation code.
• If the consulting physician performs the cesarean section and does the consultation two
or more days prior to the date of surgery, bill HCA the appropriate consultation code
with modifier 57 (e.g. 99241-57).
HCA does not pay the consulting physician if the following applies:
• If the consulting physician performs the cesarean section and does the consultation the
day before or the day of the cesarean section, the consultation is bundled within
payment for the surgery. Do not bill HCA for the consultation in this situation.
Bill HCA for consultations using an appropriate ICD diagnosis code. The medical necessity (i.e.
sign, symptom, or condition) must be demonstrated. HCA does not pay providers for a
consultation with a normal pregnancy diagnosis code (e.g. Z33.1, Z34.00, Z34.80, or Z34.90).
HCA pays consulting OB/GYN providers for an external cephalic version (CPT code 59412) and
a consultation when performed on the same day.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
220
Elective deliveries
HCA does not reimburse for early elective deliveries. An early elective delivery is defined in
WAC 182-500-0030 as any nonmedically necessary induction or cesarean section before 39
weeks gestation.
An early elective delivery is considered medically necessary if the mother or fetus has a
diagnosis listed in the Joint Commission’s current table of Conditions possibly justifying elective
delivery prior to 39 weeks gestation (WAC 182-533-0400). If the client meets the medical
necessity criteria, bill using EPA #870001375. This EPA also needs to be used for clients who
deliver naturally prior to 39 weeks.
If the early elective delivery does not meet medical necessity criteria, HCA will pay only for the
antepartum and postpartum professional services. When billing, these services must be
unbundled. HCA will not pay for the delivery services.
For all deliveries for a client equal to or over 39 weeks gestation, bill using EPA #870001378.
This applies to both elective and natural deliveries for clients equal to or over 39 weeks
gestation.
Labor management
Providers may bill for labor management only when a provider outside of the first provider’s
group practice performs the delivery. If a provider or clinic where a group NPI is used performed
all of the client’s antepartum care, admitted the client to the hospital during labor, delivered the
baby, and performed the postpartum care, do not bill HCA for the hospital admission or for labor
management. These services are included in the global OB package.
If, however, a provider performed all of the client’s antepartum care and admitted the client to
the hospital during labor, but another provider (outside of the first provider’s group practice)
takes over delivery, the global OB package must be unbundled and the providers must bill
separately for antepartum care, the hospital admission, and the time spent managing the client’s
labor. The client must be in active labor and admitted to a hospital when the referral to the
delivering provider is made.
To bill for labor management in the situation described above, bill HCA for one of the hospital
admission CPT codes 99221-99223 with modifier TH.
In addition to the hospital admission, HCA pays providers for up to three hours of labor
management using prolonged services CPT codes 99356-99357 with modifier TH.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
221
Payment for prolonged services is limited to three hours per client, per pregnancy,
regardless of the number of calendar days a client is in labor, or the number of providers
who provide labor management.
Labor management may not be billed by the delivering provider, or by any provider
within the delivering provider’s group practice even if the group practice does not
have a group NPI.
Note:
1. HCA pays for prolonged services CPT codes for labor management only
when the provider performs the hospital admission and labor management
services on the same day.
2. The hospital admission code and prolonged services code(s) must be
billed on the same claim with the same dates of services.
High-risk deliveries
Delivery includes management of uncomplicated labor and vaginal delivery (with or without
episiotomy, with or without forceps) or cesarean section. If a complication occurs during
delivery resulting in an unusually complicated, high-risk delivery, HCA pays providers an
additional add-on fee. Bill the high-risk add-on fee by adding modifier TG to the delivery code
(e.g. 59400 TG or 59409 TG).
The ICD diagnosis code must clearly demonstrate the medical necessity for the high-risk
delivery add-on (e.g. a diagnosis of fetal distress). A normal delivery diagnosis is not paid an
additional high-risk add-on fee, even if the mother had a high-risk condition during the
antepartum period. For example: For cesarean delivery, the primary diagnosis is the condition
that was responsible for the client’s admission. If a particular condition resulted in the admission
and the cesarean procedure, list that condition’s ICD diagnosis code first on the claim
2
.
Bill only ONE line of service (e.g. 59400 TG) to receive payment for BOTH the delivery and
the high-risk add-on. DO NOT bill the delivery code (e.g. 59400) on one line of the claim
and the high-risk add-on (e.g. 59400 TG) on a second line of the claim.
A physician who provides stand-by attendance for high-risk delivery can bill CPT code 99360
and resuscitation CPT code 99465, when appropriate.
Note: HCA does not pay an assistant surgeon, RNFA, or co-surgeon for a high-
risk delivery add-on. Payment is limited to one per client, per pregnancy (even in
the case of multiple births).
2
The agency follows the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines on diagnosis
when billing a high-risk delivery.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
222
Additional delivery payment policies and
limitations
• HCA pays a multiple vaginal delivery (for twins, triplets, etc.) at 100% for the first baby.
When billing for the second or third baby, bill using the delivery-only code (CPT code
59409 or 59612) for each additional baby. Payment for each additional baby will be 50%
of the delivery-only code's maximum allowance. Bill each baby's delivery on a separate
line.
• HCA pays for multiple births by cesarean delivery at 100% for the first baby. No
additional payment will be made for additional babies.
• Physician assistants-certified (PA-C) must bill for assisting during a C-section on their
own claim using modifier 80, 81, or 82 to the delivery-only code (e.g. 59514-80). The
claim must be billed using the PA-C’s NPI.
• Physician assistants (PA) must bill for an assist by adding modifier 80, 81, or 82 to the
delivery-only code (e.g. 59514-80).
• RNFAs assisting at C-sections may only bill using CPT code 59514 or 59620 with
modifier 80.
The following tables summarize billing HCA for maternity-related services.
Global (total) obstetrical (OB) care
Service
Procedure
Code/Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
Confirmation of
pregnancy
99201-99215
Office visits
Code the sign or symptom (e.g.
suppressed menstruation)
Global OB care
59400
Obstetrical care
Includes all antepartum,
delivery, and postpartum care;
bill after all services are
complete; limited to one per
client, per pregnancy; additional
vaginal deliveries for multiple
births must be billed with the
appropriate delivery-only code.
59510
Cesarean delivery
59610
Vbac delivery
59618
Attempted vbac delivery
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
223
Antepartum care only
Service
Procedure
Code/Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
Antepartum care
(bill only one of
these codes to
represent the total
number of times
the client was seen
for antepartum
care)
99201-99215
TH
Offices visits, antepartum
care 1-3 visits only, with OB
service modifier
Limited to 3 units when used for
routine antepartum care.
Modifier TH must be billed.
59425
Antepartum care only
Limited to one unit per client,
per pregnancy, per provider
59426
Antepartum care only
Limited to one unit per client,
per pregnancy, per provider.
Deliveries
Service
Procedure
Code/Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
Delivery only
59409
Obstetrical care
Must not be billed with any
other codes that include
deliveries; assist at c-section
must be billed with delivery-
only code with modifier 80.
59514
Cesarean delivery only
59612
Vbac delivery only
59620
Attempted VBAC delivery
only
Delivery with
postpartum care
59410
Obstetrical care
Must not be billed with any
other codes that include
deliveries; must not be billed
with postpartum only code;
limited to one per client, per
pregnancy; additional vaginal
deliveries for multiple births
must be billed using the
appropriate delivery-only code.
59515
Cesarean delivery
59614
Vbac care after delivery
59622
Attempted vbac after care
Postpartum care only
Service
Procedure
Code/Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
Postpartum care
only
59430
Care after delivery
Must not be billed with any
other codes that include
postpartum care; limited to one
per client, per pregnancy.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
224
Additional monitoring for high-risk conditions
Service
Procedure
Code/Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
Additional visits
for antepartum
care due to high-
risk conditions
99211-99215
UA
Office/outpatient visit est
Must not be billed with a normal
pregnancy diagnosis (Z33.1,
Z34.00, Z34.80, or Z34.90);
diagnosis must detail need for
additional visits; must be billed
with modifier UA.
Labor management
Service
Procedure
Code/Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
Labor
management
(may only be
billed when
another provider
takes over and
delivers the
infant)
99221-99223
TH
Initial hospital care
Prolonged services are limited
to 3 hours per client, per
pregnancy; must be billed with
modifier TH; must not be
billed by delivering provider.
Admit code with modifier TH
and the prolonged services
code(s) must be billed on the
same claim.
+99356
TH
Limited to 1
unit
Prolonged service inpatient
+99357
TH
Limited to 4
units
Prolonged service inpatient
High-risk deliveries
Service
Procedure
Code/Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
High-risk
delivery
[Not covered for
assistant
surgeons, co-
surgeons, or
RNFA]
Add modifier
TG to the
delivery code
(e.g. 59400 TG)
Complex/high level of care
Diagnosis must demonstrate
medical necessity; not paid with
normal delivery diagnosis;
limited to one per client, per
pregnancy.
Bill only ONE line of service
(e.g. 59400 TG) for BOTH the
delivery and high-risk add-on.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
225
Billing with modifiers for maternity care
Nonsupervision, not part of global, medical diagnosis is always primary.
Modifiers
GB
CG
TH
UA
All of these modifiers
must be used with E/M
only
Nonsupervision,
Not part of
global. Is a high
risk medical
condition or
condition
unrelated to the
pregnancy, which
is always primary
reason for the
visit.
Do not use a
supervision
diagnosis code.
Supervision
when client is in
and out of
managed care
Supervision
of the client
when the
provider
treats client
for less than
four visits and
unbundles
care
Supervision
with
additional
visits
beyond
global (for
high-risk
pregnancy)
Multiple providers for
OB care
X
Providers seeing client
for medical reasons
other than current
pregnancy
X
High risk pregnancy and
all prenatal OB care
X
Client moves to/from
managed care and FFS
X
Perinatologist visit for
pre-existing condition
and client is now
pregnant (visit is outside
of OB care/outside of
OB bundle)
X
Antepartum care and/or
postpartum care if only
1-3 visits
X

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
226
Medical Supplies and
Equipment
Physician signature requirement
(HCPCS code G0454)
To comply with federal regulations, medical supplies and equipment must be cosigned by a
physician, if ordered by a nonphysician provider. If the physician is cosigning the order (that was
written by a nonphysician practitioner) for medical equipment, the physician may bill using
HCPCS code G0454. For all other information regarding medical equipment, see HCA’s
Medical Equipment and Supplies Billing Guide.
The following drug-related and respiratory supplies do not require a physician signature/co-
signature when being ordered:
• Supplies and equipment necessary for or ancillary to the administration of
pharmaceuticals or monitoring their effectiveness including glucose monitors, glucose
test strips, lancets, insulin pens, needles, syringes, inhalation masks, nebulizers and
spacers may be ordered by non-physician practitioners (e.g., advanced registered nurse
practitioners, physician assistants, etc.) within their scope of practice without a physician
signature/co-signature.
This applies to orders and prescriptions signed before February 1, 2019, and to
future orders and prescriptions.
• All respiratory supplies and equipment necessary for or ancillary to the administration or
monitoring of medications, including oxygen, such as inhalation masks, spacers,
nebulizers, vents, positive airway pressure machines and associated supplies may be
ordered by non-physician practitioners (e.g., advanced registered nurse practitioners,
physician assistants, etc.) within their scope of practice without a physician signature/co-
signature.
This applies to orders and prescriptions signed before February 1, 2019, and to
future orders and prescriptions.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
227
General payment policies
• HCA pays providers for certain medical supplies and equipment (MSE) dispensed from
their offices when these items are considered prosthetics and are used for a client’s
permanent condition (see Supplies included in an office call (bundled supplies)).
• Most MSE used to treat a client’s temporary or acute condition are considered incidental
to a provider’s professional services and are bundled in the office visit payment (see
Supplies included in an office call (bundled supplies)). HCA pays providers separately
for only those MSE listed (see Supplies included in an office call (bundled supplies)).
• HCA does not pay providers separately for surgical trays, as these are bundled within the
appropriate surgical procedure. The fees for these procedures include the cost of the
surgical trays.
• Procedure codes for MSE that do not have a maximum allowable fee and cost less than
$50.00 are paid at acquisition cost. A manufacturer’s invoice must be maintained in the
client’s records for MSE under $50.00 and made available to HCA upon request. DO
NOT send in an invoice with a claim for MSE under $50.00 unless requested by HCA.
• Procedure codes for MSE that do not have a maximum allowable fee and cost $50.00 or
more are paid at acquisition cost. A copy of the manufacturer’s invoice must be
attached to the claim for MSE costing $50.00 or more.
Note: Refer to HCA’s Billers and providers webpage for information on prior
authorization.
Supplies included in an office call (bundled
supplies)
Items with an asterisk (*) in the following list are considered prosthetics when used for a
client’s permanent condition. HCA pays providers for these supplies when they are
provided in the office for permanent conditions only. They are not considered prosthetics
if the condition is acute or temporary. Providers must indicate “prosthetic for permanent
condition” in the Claim Note section of the electronic claim.
For example, if a patient has an indwelling Foley catheter for permanent incontinence and a
problem develops for which the physician is required to replace the catheter, it is considered a
prosthetic and is paid separately. The Foley catheter used to obtain a urine specimen, used after
surgery, or used to treat an acute obstruction is not paid separately because it is treating a
temporary problem.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
228
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
99070
Special supplies phys/qhp
A4206
1 CC sterile syringe&needle
A4207
2 CC sterile syringe&needle
A4208
3 CC sterile syringe&needle
A4209
5+ CC sterile syringe&needle
A4211
Supp for self-adm injections
A4212
Non coring needle or stylet
A4213
20+ CC syringe only
A4215
Sterile needle
A4220
Infusion pump refill kit
A4244
Alcohol or peroxide, per pint
A4245
Alcohol wipes per box
A4246
Betadine/phisohex solution
A4247
Betadine/iodine swabs/wipes
A4252
Blood ketone test or strip
A4253
Blood glucose/reagent strips
A4256
Calibrator solution/chips
A4258
Lancet device each
A4259
Lancets per box
A4262
Temporary tear duct plug
A4263
Permanent tear duct plug
A4265
Paraffin
A4270
Disposable endoscope sheath
A4300
Cath impl vasc access portal
A4301
Implantable access syst perc
A4305
Drug delivery system >=50 ML
A4306
Drug delivery system <=50 ml
A4310
Insert tray w/o bag/cath
A4311
Catheter w/o bag 2-way latex
A4312
Cath w/o bag 2-way silicone
A4313
Catheter w/bag 3-way
A4314
Cath w/drainage 2-way latex
A4315
Cath w/drainage 2-way silcne
A4316
Cath w/drainage 3-way
A4320
Irrigation tray
A4330
Stool collection pouch
A4335*
Incontinence supply
A4338*
Indwelling catheter latex
A4340*
Indwelling catheter special
A4344*
Cath indw foley 2 way silicn
A4346*
Cath indw foley 3 way
A4351
Straight tip urine catheter
A4352
Coude tip urinary catheter

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
229
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
A4353
Intermittent urinary cath
A4354
Cath insertion tray w/bag
A4355
Bladder irrigation tubing
A4356*
Ext ureth clmp or compr dvc
A4357*
Bedside drainage bag
A4358*
Urinary leg or abdomen bag
A4361*
Ostomy face plate
A4362*
Solid skin barrier
A4364*
Adhesive, liquid or equal
A4367*
Ostomy belt
A4368*
Ostomy filter
A4397
Irrigation supply sleeve
A4398*
Ostomy irrigation bag
A4399*
Ostomy irrig cone/cath w brs
A4400*
Ostomy irrigation set
A4402
Lubricant per ounce
A4404*
Ostomy ring each
A4421*
Ostomy supply misc
A4455
Adhesive remover per ounce
A4461
Surgicl dress hold non-reuse
A4463
Surgical dress holder reuse
A4465
Non-elastic extremity binder
A4470
Gravlee jet washer
A4480
Vabra aspirator
A4550
Surgical tray
A4556
Electrodes, pair
A4557
Lead wires, pair
A4558
Conductive paste or gel
A4649
Surgical supply
A5051*
Pouch clsd w barr attached
A5052*
Clsd ostomy pouch w/o barr
A5053*
Clsd ostomy pouch faceplate
A5054*
Clsd ostomy pouch w/flange
A5055*
Stoma cap
A5061*
Pouch drainable w barrier at
A5062*
Drnble ostomy pouch w/o barr
A5063*
Drain ostomy pouch w/flange
A5071*
Urinary pouch w/barrier
A5072*
Urinary pouch w/o barrier
A5073*
Urinary pouch on barr w/flng
A5081*
Continent stoma plug
A5082*
Continent stoma catheter
A5083*
Stoma absorptive cover
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
230
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
A5093*
Ostomy accessory convex inse
A5102*
Bedside drain btl w/wo tube
A5105*
Urinary suspensory
A5112*
Urinary leg bag
A5113*
Latex leg strap
A5114*
Foam/fabric leg strap
A5120
Skin barrier, wipe or swab
A5121*
Solid skin barrier 6x6
A5122*
Solid skin barrier 8x8
A5126*
Disk/foam pad +or- adhesive
A5131*
Appliance cleaner
A6021
Collagen dressing <=16 sq in
A6022
Collagen drsg>16<=48 sq in
A6023
Collagen dressing >48 sq in
A6024
Collagen dsg wound filler
A6025
Silicone gel sheet, each
A6154
Wound pouch, each
A6231
Hydrogel dsg <=16 sq in
A6232
Hydrogel dsg>16<=48 sq in
A6233
Hydrogel dressing >48 sq in
A6413
Adhesive bandage, first-aid

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
231
Alcohol and Substance Misuse
Counseling
HCA covers alcohol and substance misuse counseling through screening, brief interventions, and
referral to treatment (SBIRT) services when provided by, or under the supervision of, a certified
physician or other certified licensed health care professional within the scope of their practice.
SBIRT is a comprehensive, evidenced-based public health practice designed to identify people
who are at risk for or have some level of substance use disorder which can lead to illness, injury,
or other long-term morbidity or mortality. SBIRT services are provided in a wide variety of
medical and community health care settings such as primary care centers, hospital emergency
rooms, and trauma centers (see list of SBIRT places of service).
What is included in SBIRT?
Screening. With just a few questions on a questionnaire or in an interview, practitioners can
identify patients who have alcohol or other drug (substance) use problems and determine how
severe those problems already are. Three of the most widely used screening tools are the Alcohol
Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), the Alcohol, Smoking, and Substance Involvement
Screening Test (ASSIST) and the Drug Abuse Screening Test (DAST).
Brief intervention. If screening results indicate at risk behavior, individuals receive brief
interventions. The intervention educates them about their substance use, alerts them to possible
consequences and motivates them to change their behavior.
Referral to treatment. Individuals whose screening indicates a severe problem or dependence
should be referred to a licensed and certified behavioral health agency for assessment and
treatment of a substance use disorder (SUD).
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
232
What is covered?
SBIRT services are covered for determining risk factors that are related to alcohol and other drug
use disorders, providing interventions to enhance patient motivation to change, and making
appropriate referrals as needed.
SBIRT screening may occur during an E/M exam or the client may complete the questionnaire
and give it to the provider during the E/M exam. The screening form may be scored by a trained
staff member who is supervised by a certified SBIRT provider. If the screening is positive,
scoring time may be factored into the time requirement of the SBIRT CPT code. The provider is
then able to provide the brief intervention. An SBIRT CPT code may be billed in addition to the
E/M code.
Brief interventions are limited to four sessions per patient, per provider, per calendar year.
Providers may submit a limitation extension (LE) request to HCA for more sessions. Include
with the LE request any information that describes the medical necessity of the extra sessions.
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Comments
CPT 99408 Audit/dast 15-30 min
For structured screening and brief
intervention
CPT 99409 Audit/dast over 30 min
For structured screening and brief
intervention
SBIRT services will be covered by HCA when all of the following are met:
• The billing provider and servicing provider have submitted their SBIRT certification to
HCA.
• The billing provider has an appropriate taxonomy to bill for SBIRT.
• The diagnosis code is Z71.41 or Z71.51.
• The treatment or brief intervention does not exceed the limit of four (4) encounters per
client, per provider, per year.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
233
Who is eligible to become a certified SBIRT
provider?
The following categories of licensed or certified health care professionals are eligible to become
certified to provide or supervise staff that provides SBIRT services.
• Advanced registered nurse practitioners, in accordance with chapter 18.79 RCW and
chapter 246-840 WAC
• Chemical dependency professionals, in accordance with chapter 18.205 RCW and chapter
246-811 WAC
• Licensed practical nurse, in accordance with chapter 18.79 RCW and chapter 246-840
WAC
• Mental health counselor, in accordance with chapter 18.225 RCW and chapter 246-809
WAC
• Marriage and family therapist, in accordance with chapter 18.225 RCW and chapter 246-
809 WAC
• Independent and advanced social worker, in accordance with chapter 18.225 RCW and
chapter 246-809 WAC
• Physician, any specialty, in accordance with chapter 18.71 RCW and chapter 246-919
WAC
• Physician assistant, in accordance with chapter 18.71A RCW and chapter 246-918 WAC
• Psychologist, in accordance with chapter 18.83 RCW and chapter 246-924 WAC
• Registered nurse, in accordance with chapter 18.79 RCW and chapter 246-840 WAC
• Dentist, in accordance with chapter 18.260 and chapter 246-817 WAC
• Dental hygienists, in accordance with chapter 18.29 and chapter 246-815 WAC

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
234
What are the requirements to be a certified
SBIRT provider?
SBIRT services must be provided by or under the supervision of a certified physician or other
certified licensed health care professional. SBIRT services may be provided by a certified health
care professional under supervision of and as recommended by a certified physician or licensed
health care professional within the scope of their practice.
Required training
All licensed health care professionals must be trained in order to provide or supervise individuals
providing SBIRT services. Licensed health care professionals must complete SBIRT training
approved by HCA. This requirement is waived if a provider has an addiction specialist
certification. The provider must submit proof of this certification to HCA by mail or fax.
Training is available through a variety of entities. Distance learning is industry-recognized
education obtained through sources such as internet course work, satellite downlink resources, or
online courses. HCA-approved training is available through the following:
• Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
• An education program that includes SBIRT training that the practitioner has completed and
the provider has documentation showing the training was included
All health care professionals must document successful training of an approved course of
training in order to bill for services. This documentation will be used to identify the health care
professional through his/her National Provider Identifier (NPI) number for billing services.
Providers who are already enrolled and have completed the training must update their provider
profile in ProviderOne with the training certificate or other proof of completion.
Mail or fax certificate to:
Provider Enrollment
PO Box 45562, Olympia, WA 98504-5562
Fax: 360-725-2144
Health care professionals who are not enrolled with HCA, but who are licensed and have
completed the training, may enroll as a Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) provider to offer
this service.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
235
Who can bill for SBIRT services?
The following is a list of providers who can bill for SBIRT services when properly certified:
Advanced registered nurse practitioners
Mental health counselors
Marriage and family therapists
Independent and advanced social workers
Physicians (any specialty)
Psychologists
Dentists
Dental hygienists

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
236
Alcohol and Substance Abuse
Treatment Services
Medical services for clients in residential
chemical dependency treatment
HCA will pay medical professionals (within their scope of practice) for the following services
when the practitioner provides services at a Residential Chemical Dependency Treatment Center
(place of service 55).
Service
Procedure Code
Notes
E/M services
99201-99205; 99211-99215
Basic Laboratory Services
(e.g., dipsticks)
81000, 81002; 81025,
82948
Venipuncture 36415
Lab specimens processed
in the provider’s office
must be billed in POS 11;
Labs specimens processed
in a laboratory should be
billed in POS 81.
Clients requiring additional nonemergency medical services such as wound care must go to the
provider’s office or another medical setting.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
237
Withdrawal management services
HCA considers withdrawal management services to be medically necessary for clients receiving
alcohol or drug withdrawal services in an acute care hospital when the following conditions are
met:
• The stay meets the intensity of service and severity of illness standards necessary to
qualify for an inpatient hospital stay.
• The care is provided in a medical unit.
• The client is not participating in HCA’s Chemical-Using Pregnant (CUP) Women
program.
• Inpatient psychiatric care is not medically necessary.
• The person meets medical necessity criteria for hospital withdrawal management
services.
Note: The hospital’s NPI must be included in the Claim Note section when billing
electronically; otherwise, the claim will be denied.
When the medically necessary conditions are met, bill using the following information:
Procedure
Code
Modifier
Short Description
Limitations
H0009
3
Alcohol and/or drug services
Limited to one per
hospitalization. Restricted to the
appropriate ICD diagnosis codes.
H0009
4
TS
Alcohol and/or drug services
Limited to one per hospitalization.
Restricted to the appropriate ICD
diagnosis codes.
See HCA’s Inpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide and Substance Use Disorder Program Billing
Guide for more information.
3
Bill for the initial admission.
4
Bill for any follow-up days using follow-up service modifier.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
238
Blood, blood products, and
related services
Whole blood and components (red cells, plasma, platelets, cryoprecipitate) are used in the
treatment of a wide variety of conditions.
Blood products are therapeutic substances derived from human blood or plasma and produced by
a manufacturing process. Blood products are also used to treat a wide variety of conditions.
Examples of blood products are plasma derivatives such as:
• Albumin
• Coagulation factors
• Immunoglobulins
Payment for blood and blood products
• HCA does not pay for blood or blood products that are donated.
• HCA pays for the covered service charges necessary in handling and processing blood
and blood products.
• For managed care clients, hemophilia products are reimbursed through fee-for-service.
Contact HCA-contracted managed care organization for case management and service
coordination.
Autologous blood/platelet-rich plasma injections
Based upon review of evidence provided by the HTCC, HCA does not consider autologous
blood/platelet-rich plasma injections to be medically necessary.
Fee schedule
To view the fee schedules, see HCA’s:
• Physician-related/professional health care services fee schedule
• Professional administered drugs fee schedule
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
239
Centers of Excellence
(WAC 182-531-0650)
Note: When private insurance or Medicare has paid as primary insurance and the
provider is billing HCA as secondary insurance, HCA does not require PA or that
the transplant, or sleep study be done in a Center of Excellence or HCA-approved
hospital.
List of approved Centers of Excellence (COEs)
See HCA’s approved COEs for sleep centers, and transplants.
Services which must be performed in a COE
Hemophilia treatment COEs
(WAC 182-531-1625)
(For administration in the home only)
To be paid by HCA for hemophilia and von Willebrand-related products for administration to
Apple Health clients in the home, the products must be provided through an approved
hemophilia treatment Center of Excellence (COE). Center of Excellence is defined in WAC 182-
531-0050.
Note: HCA does not require the use of an approved hemophilia treatment COE to obtain
hemophilia and von Willebrand-related products when one of the following applies:
• HCA is not the primary payer
• The client receives the product in an outpatient hospital or clinic setting for
nonroutine or urgent care needs
• The product is provided by a hemophilia treatment center (HTC) for nonroutine
pediatric care and other urgent care needs

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
240
A hemophilia treatment COE uses a comprehensive care model to provide care for persons with
bleeding disorders. The comprehensive care model includes specialized prevention, diagnostic,
and treatment programs designed to provide family-centered education, state-of-the-art
treatment, research, and support services for individuals and families living with bleeding
disorders.
Qualified Centers of Excellence (COE)
For Hemophilia Treatment are:
Washington Center for Bleeding Disorders at Bloodworks NW
(formerly known as Puget Sound Blood Center) – Seattle
Hemophilia Center at Oregon Health Science University (OHSU) –
Portland
For managed care clients, hemophilia products are reimbursed through fee-for-service. Contact
HCA-contracted managed care organization for case management and service coordination.
What criteria must be met to qualify as a COE for hemophilia treatment?
To qualify as a COE, a hemophilia treatment center must meet all of the following:
• Have a Core Provider Agreement with HCA
• Be a federally-approved HTC as defined in WAC 182-531-0050
• Meet or exceed all Medical and Scientific Advisory Council (MASAC) standards of care
and delivery of services
• Participate in the public health service 340b provider drug discount program and be listed
in the Medicaid exclusion files maintained by the federal Health Resources and Services
Administration (HRSA) Office of Pharmacy Affairs (OPA)
• Submit a written request to HCA to be a qualified hemophilia treatment COE and include
proof of the following:
U.S. Center for Disease Control (CDC) and prevention surveillance site
identification number
Listing in the Hemophilia Treatment Center (HTC) directory
• Submit requests to:
Hemophilia Treatment COE
Health Care Authority–Health Care Services
PO Box 45506
Olympia WA 98504-5506
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
241
• Receive written approval including conditions of payment and billing procedures from
HCA
What documentation is required to continue as a qualified COE for
hemophilia treatment?
The HTC must annually submit to HCA:
• Copies of grant documents and reports submitted to the Maternal and Child Health
Bureau/Human Resources and Services Administration/Department of Health and Human
Services or to their designated subcontractors.
• Proof of continued federal funding by the National Hemophilia Program and listing with
the Regional Hemophilia Network and the CDC.
Are managed care clients required to receive their hemophilia or von
Willebrand-related products from a qualified COE?
Clients enrolled in a managed care plan must contact their plans for information.
Coverage table
Procedure Code
Short Description
J7175
Coagadex (Coagulation Factor X (Human) for Inj.
J7179
Vonvendi (Von Willebrand Factor (Recomb) for
Inj.)
J7180
Factor xiii anti-hem factor
J7181
Factor xiii recomb a-subunit
J7182
Factor viii recomb novoeight
J7183
Wilate injection
J7185
Xyntha inj
J7186
Antihemophilic viii/vwf comp
J7187
Humate-P, inj
J7188
Factor viii anti-hemophilic factor, recomb, (obizur)
J7189
Factor viia - Novoseven
J7190
Factor viii- Hemofil M
J7192
Factor viii recombinant NOS
J7193
Factor IX non-recombinant
J7194
Factor ix complex
J7195
Factor IX recombinant
J7198
Anti-inhibitor - FEIBA
J7199
Hemophilia clotting factor, not otherwise classified
J7200
Factor ix recombinan rixubis
J7201
Factor ix fc fusion recomb

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
242
Procedure Code
Short Description
J7202
Idelvioni (Coagulation Factor IX (RECOMB) (RIX-
FP) For Inj.
J7205
Factor viii fc fusion recomb - Eloctate
J7207
Adynovate (Antihemophilic Factor Recomb
Pegylated for Inj.)
J7209
Factor viii nuwiq recomb 1iu
J7210
Factor viii, anti-hemophilic, recombinant (afstyla)
Sleep studies
(WAC 182-531-1500)
Becoming an HCA-approved sleep center
To become an HCA-approved COE, a sleep center must send the following documentation to the
Health Care Authority, Provider Enrollment, PO Box 45510, Olympia, WA 98504-5510:
• A completed Core Provider Agreement
• Copies of the following:
The sleep center's current accreditation certificate by AASM
Either of the following certifications for at least one physician on staff:
Current certification in sleep medicine by the American Board of Sleep
Medicine (ABSM)
Current subspecialty certification in sleep medicine by a member of the
American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS)
The certification of an RPSGT who is employed by the sleep center
Note: Sleep centers must request reaccreditation from AASM in time to avoid
expiration of COE status with HCA.
At least one physician on staff at the sleep center must be board certified in sleep medicine. If the
only physician on staff who is board certified in sleep medicine resigns, the sleep center must
ensure another physician on staff at the sleep center obtains board certification or another board-
certified physician is hired. The sleep center must then send provider enrollment a copy of the
physician's board certification.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
243
If a certified medical director leaves a COE, the COE status does not transfer with the medical
director to another sleep center.
The COE must maintain a record of the physician's order for the sleep study.
For further information, see sleep medicine testing.
Transplants
(WAC 182-550-1900)
Who is eligible for transplants?
HCA pays for medically necessary transplant procedures only for eligible HCA clients who are
not otherwise subject to a managed care organization (MCO) plan.
Who is not eligible for transplants?
Clients eligible under the Alien Emergency Medical (AEM) program are not eligible for
transplant coverage.
Which transplant procedures are covered?
HCA covers the following transplant procedures when the transplant procedures are performed
in a hospital designated by HCA as a Center of Excellence for transplant procedures and meet
that hospital's criteria for establishing appropriateness and the medical necessity of the
procedures:
• Solid organs involving the heart, kidney, liver, lung, heart-lung, pancreas, kidney-
pancreas and small bowel
HCA pays for a solid organ transplant procedure only once per a client's lifetime, except
in cases of organ rejection by the client's immune system during the original hospital
stay.
• Nonsolid organs include bone marrow and peripheral stem cell transplants
Does HCA pay for skin grafts and corneal transplants?
HCA pays for skin grafts and corneal transplants to any qualified hospital when medically
necessary.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
244
Does HCA pay for organ procedure fees and donor searches?
HCA pays for organ procurement fees and donor searches. For donor searches, CPT codes
86812-86822 are limited to a maximum of 15 tests total for human leukocyte antigens (HLA)
typing per client, per lifetime. HCA requires PA for more than 15 tests.
To bill for donor services:
• Use the client’s ProviderOne Client ID.
• Use the appropriate Z52 series diagnosis code as the principal diagnosis code.
• Include donor operative notes with claim.
For example, if billing a radiological exam on a potential donor for a kidney transplant,
bill Z52.4 for the kidney donor and use Z00.5 or Z00.8 as a secondary diagnosis-
examination of a potential donor. Refer to WAC 182-531-1750, 182-550-1900, 182-550-
2100, and 182-550-2200.
Note: Use of Z00.5 or Z00.8 as a principal diagnosis will cause the line to be
denied.
Does HCA pay for experimental transplant procedures?
HCA does not pay for experimental transplant procedures. In addition, HCA considers as
experimental those services including, but not limited to, the following:
• Transplants of three or more different organs during the same hospital stay.
• Solid organ and bone marrow transplants from animals to humans.
• Transplant procedures used in treating certain medical conditions for which use of the
procedure has not been generally accepted by the medical community or for which its
efficacy has not been documented in peer-reviewed medical publications.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
245
Drugs Professionally
Administered
(WAC 182-530-2000(1))
HCA covers outpatient drugs, including over-the-counter drugs listed on HCA’s Covered over-
the-counter product list, as defined in WAC 182-530-1050, subject to the limitations and
requirements in this section, when:
• The drug is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
• The drug is for a medically accepted indication as defined in WAC 182-530-1050.
• The drug is not excluded from coverage (see WAC 182-530-2000 Covered – Outpatient
drugs, devices, and drug related supplies).
• The manufacturer has a signed drug rebate agreement with the federal Department of
Health and Human Services (DHHS). Exceptions to the drug rebate requirement are
described in WAC 182-530-7500 which describes the drug rebate program.
For more information, see HCA’s Prescription Drug Program Billing Guide.
Note: HCA requires prior authorization (PA) for all drugs new to market until reviewed and
evaluated by HCA’s clinical team according to WAC 182-530-3100. This applies to all products
billed under miscellaneous codes or product specific procedure codes. View the list of Drugs
billed under miscellaneous HCPCS codes for drugs that require authorization.
HCA’s fees for injectable drug codes are the maximum allowances used to pay covered drugs
and biologicals administered in a provider’s office only.
Invoice requirements
A copy of the manufacturer’s invoice showing the actual acquisition cost of the drug relevant to
the date of service must be attached to the claim for drug reimbursed by report (BR) or when
billing for compounded drugs. If needed, HCA will request any other necessary documentation
after receipt of the claim.
A copy of any manufacturer’s invoices for all drugs (regardless of billed charges) must be
maintained in the client’s record and made available to HCA upon request.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
246
Drug pricing
HCA follows Medicare’s drug pricing methodology of 106% of the Average Sales Price (ASP).
HCA updates the rates each time Medicare’s rate is updated, up to once per quarter. If a
Medicare fee is unavailable for a particular drug, HCA prices the drug at the Point-of-Sale (POS)
Actual Acquisition Cost (AAC). Unlike Medicare, HCA effective dates are based on dates of
service, not the date the claim is received.
National drug code format
All providers are required to use the 11-digit National Drug Code (NDC) when billing
HCA for drugs administered in the provider’s office.
• National Drug Code (NDC) – The 11-digit number the manufacturer or labeler assigns
to a pharmaceutical product and attaches to the product container at the time of
packaging. The 11-digit NDC is composed of a 5-4-2 grouping. The first 5 digits
comprise the labeler code assigned to the manufacturer by the Federal Drug
Administration (FDA). The second grouping of 4 digits is assigned by the manufacturer
to describe the ingredients, dose form, and strength. The last grouping of 2 digits
describes the package size. (WAC 182-530-1050)
• The NDC must contain 11-digits in order to be recognized as a valid NDC. It is not
uncommon for the label attached to a drug’s vial to be missing leading zeros.
For example: The label may list the NDC as 123456789 when, in fact, the correct NDC
is 01234056789. Make sure that the NDC is listed as an 11-digit number, inserting any
leading zeros missing from the 5-4-2 groupings, as necessary. HCA will deny claims for
drugs billed without a valid 11-digit NDC.
Electronic Claim Billing Requirements
Providers must continue to identify the drug given by reporting the drug’s CPT or
HCPCS code in the Procedure Code field and the corresponding 11-digit NDC in the
National Drug Code field. In addition, the units reported in the Units field must continue
to correspond to the description of the CPT or HCPCS code.
If the 11-digit NDC is missing, incomplete, or invalid, the claim line for the
drug or supply will be denied.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
247
Physicians billing for compound drugs
To bill for compounding of drugs, enter J3490 as the procedure code. Enter the NDC for the
main ingredient in the compound on the line level. Put compound in the notes field. Attach an
invoice showing all of the products with NDCs and quantities used in the compound. Claims are
manually priced per the invoice.
Drugs requiring prior authorization
Drugs requiring prior authorization are noted in the fee schedule with a PA next to them. For
information on how to request prior authorization, refer to Prior authorization.
HCA requires prior authorization for all new drugs to market until reviewed and evaluated by
HCA’s clinical team according to WAC 182-530-3100. This applies to all products billed under
miscellaneous codes or product specific procedure codes.
View the list of Drugs billed under miscellaneous HCPCS codes for drugs that require
authorization.
Contraceptives
See the Family Planning Billing Guide for information on coverage for contraceptives dispensed,
injected, or inserted in an office/clinic setting, and additional instructions on billing.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
248
Injectable drugs - limitations
Limitations on coverage for certain injectable drugs are listed below, all other diagnoses are
noncovered without prior authorization:
Procedure
Code
Short Description
Limitation
J0637
Caspofungin acetate
B37.81, B44.9, B48.4, B44.2, B44.7,
B44.1, B44.0, B44.89
J0725
Chorionic gonadotropin/1000u
Q53.01, Q53.02, Q53.10, Q53.11, Q53.12,
Q53.20, Q53.21, Q53.22, Q53.9, R01.0
J1212
Dimethyl sulfoxide 50% 50 ML
N30.10, N30.11, N30.20, N30.21
J1595
Injection glatiramer acetate
340 G35 (multiple sclerosis)
J1640
Hemin, 1 mg
Limited to office or outpatient hospital,
females only, 2 vials daily, 8 days per
month total. Prior authorization is required
for additional days/vials.
J1756
Iron sucrose injection
N18.1 – N18.9 (chronic kidney disease)
J2323
Natalizumab injection
Multiple sclerosis G35
Crohn’s disease Requires PA. Use
TYSABRI J2323 Request form 13-832.
See
Where can I download HCA forms?
J2325
Nesiritide
No diagnosis restriction
Restricted use only to cardiologists
J2501
Paricalcitol
N18.6 (End stage renal disease)
J2916
Na ferric gluconate complex
N18.6 (End stage renal disease)
J3398
(Luxturna)(Voretigeme
neparvovec-rzyl)
May only be provided by a Washington
Apple Health-enrolled provider who is
certified by the drug manufacturer to
administer the product
J3465
Injection, voriconazole
B44.9, B48.4, B44.2, B44.7, B44.1,
B44.0, B44.89
J9041
Bortezomib injection
C83.10 – C83.19, C90.00, C90.01
J3490
(Yescarta) Axicabtagene
ciloleucel suspension for IV
infusion
May only be provided by a Washington
Apple Health enrolled provider who is
certified by the drug manufacturer to
administer the product
Q2042
(Kymriah) Tisageneleucel
suspension for IV infusion
May only be provided by a Washington
Apple Health enrolled provider who is
certified by the drug manufacturer to
administer the product
Q3027
Inj beta interferon im 1 mcg
G35 (multiple sclerosis)
Q3028
Inj beta interferon sq 1 mcg
G35 (multiple sclerosis)

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
249
Billing for injectable drugs and biologicals
When billing for injectable drugs and biologicals, providers must use the description of the
procedure code to determine the units, and include the correct number of units on the claim to be
paid the appropriate amount. For drugs priced at acquisition cost, providers must do one of the
following:
• Include a copy of the manufacturer’s invoice for each line item in which billed charges
exceed $1,100.00
• Retain a copy of the manufacturer’s invoice in the client’s record for each line item in
which billed charges are equal to or less than $1,100.00
Do not bill using unclassified or unspecified drug codes unless there is no specific code for
the drug being administered. The National Drug Code (NDC) and dosage given to the client
must be included with the unclassified or unspecified drug code for coverage and payment
consideration.
HCPCS codes J8499 and J8999 for oral prescription drugs are not covered.
Injectable drugs can be injected subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously. Indicate that
the injectable drugs came from the provider's office supply. The name, strength, and dosage of
the drug must be documented and kept in the client’s record.
Chemotherapy drugs
(J9000-J9999)
The following payment guidelines apply to chemotherapy drugs (HCPCS codes J9000-J9999):
• HCA’s maximum allowable fee per unit is based on the HCPCS description of the
chemotherapy drug.
• HCA follows Medicare’s drug pricing methodology of 106% of the Average Sales Price
(ASP). If a Medicare fee is unavailable for a particular drug, HCA continues to price the
drug at 84% of the Average Wholesale Price (AWP).
• Preparation of the chemotherapy drug is included in the payment for the administration of
the drug.
• Bill number of units used based on the description of the drug code. For example, if 250
mg of Cisplatin (J9062) is given to the client, the correct number of units is five (5).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
250
Note: See Unlisted drugs for information on when it is necessary to bill HCA for
a chemotherapy drug using an unlisted drug code.
Billing for single-dose vials
For single-dose vials, bill for the total amount of the drug contained in the vial(s). Based on the
unit definition for the HCPCS code, HCA pays providers for the total number of units contained
in the vial. For example:
If a total of 150 mg of Etoposide is required for the therapy, and two 100 mg
single dose vials are used to obtain the total dosage, then the total of the two 100
mg vials is paid. In this case, the drug is billed using HCPCS code J9181
(Etoposide, 10 mg). If HCA’s maximum allowable fee is $4.38 per 10 mg unit,
the total allowable is $87.60 (200 mg divided by 10 = 20 units x $4.38).
HCA pays for justified waste when billed with the JW modifier, for Medicare
crossover bills only.
For HCA requirements for splitting single dose vials, see Billing for single dose vials (SDV) in
the Prescription Drug Program Billing Guide.
Billing for multiple dose vials
For multiple dose vials, bill only the amount of the drug administered to the client. Based on the
unit definition (rounded up to the nearest whole unit) of the HCPCS code, HCA pays providers
for only the amount of drug administered to the client. For example:
If a total of 750 mg of Cytarabine is required for the therapy, and is taken from a
2,000 mg multiple dose vial, then only the 750 mg administered to the client is
paid. In this case, the drug is billed using HCPCS code J9110 (Cytarabine, 500
mg). If HCA’s maximum allowable fee is $23.75 per 500 mg unit, the total
allowable is $47.50 [750 mg divided by 500 = 2 (1.5 rounded) units x $23.75].

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
251
Billing for oral anti-emetic drugs when part of a
chemotherapy regimen
In order to bill HCA for oral anti-emetic drugs (HCPCS codes Q0162-Q0181), the drug must be:
• Part of a chemotherapy regimen.
• Administered or prescribed for use immediately before, during, or within 48 hours after
administration of the chemotherapy drug.
• Billed using the appropriate ICD cancer diagnoses.
• Submitted on the same claim with one of the chemotherapy drug codes (HCPCS codes
J8530-J9999).
Rounding of units
The following guidelines should be used to round the dosage given to the client to the
appropriate number of units for billing purposes:
I. Single-Dose Vials:
For single-dose vials, bill for the total amount of the drug contained in the vial(s). Based on the
unit definition of the HCPCS code, HCA pays providers for the total number of units contained
in the vial. For example:
If a total of 150 mg of Etoposide is required for the therapy and two 100 mg single dose vials are
used to obtain the total dosage, the total of the two 100 mg vials is paid. In this case, the drug is
billed using HCPCS code J9181 (Etoposide, 10 mg). If HCA’s maximum allowable fee is $4.38
per 10 mg unit, the total allowable is $87.60 (200 mg divided by 10 = 20 units x $4.38).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
252
II. Billing for Multiple Dose Vials:
For multiple dose vials, bill only the amount of the drug administered to the client. Based on the
unit definition (rounded up to the nearest whole unit) of the HCPCS code, HCA pays providers
for only the amount of drug administered to the client. For example:
If a total of 750 mg of Cytarabine is required for the therapy and is taken from a 2,000 mg
multiple dose vial, only the 750 mg administered to the client is paid. In this case, the drug is
billed using HCPCS code J9110 (Cytarabine, 500 mg). If HCA’s maximum allowable fee is
$23.75 per 500 mg unit, the total allowable is $47.50 [750 mg divided by 500 = 2 (1.5 rounded)
units x $23.75].
Unlisted drugs
(HCPCS J3490, J3590, and J9999)
When it is necessary to bill HCA for a drug using an unlisted drug code, providers must
report the National Drug Code (NDC) of the drug administered to the client. HCA uses the
NDC when unlisted drug codes are billed to appropriately price the claim. To be reimbursed:
• Claims must include:
The dosage (amount) of the drug administered to the client.
The 11-digit NDC of the office-administered drug.
One unit of service.
• The drug must be approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
• The drug must be for a medically accepted indication as defined in WAC 182-530-1050
(see WAC 182-530-2000 Covered – Outpatient drugs, devices, and drug related
supplies).
• The drug must not be excluded from coverage.
• For claims billed using an electronic professional claim, list the required information in
the Claim Note section of the claim.
See Vaccines/toxoids (immunizations) for more detailed information on NDC billing.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
253
Note: If there is an assigned HCPCS code for the administered drug, providers
must bill HCA using the appropriate HCPCS code. Do not bill using an unlisted
drug code for a drug that has an assigned HCPCS code. HCA will recoup
payment for drugs paid using an unlisted drug code if an assigned HCPCS code
exists for the administered drug.
The list of all injectable drug codes and maximum allowable fees are listed in the
Professional administered drugs fee schedule.
Botulinum toxin injections (Botox)
HCA requires prior authorization for all Botox injections regardless of the diagnosis.
Prior authorization for Botox for treatment of chronic migraines and chronic tension-type
headaches must be submitted to Comagine Health for a medical necessity review. For more
information, see How do I submit a request to Comagine Health?
Prior authorization for other Botox treatments:
Must be submitted to HCA. Submission of an authorization request must be typed and submitted
on the General Information for Authorization (13-835) form along with a completed Botulinum
Toxin Provider Questionnaire (13-003) form. See Where can I download HCA forms?
Collagenase injections
(HCPCS code J0775, CPT codes 20527 and 26341)
HCA requires prior authorization for HCPCS code J0775, CPT codes 20527 and 26341.
Hyaluronic acid/viscosupplementation
HCA covers hyaluronic acid/viscosupplementation for the treatment of pain associated with
osteoarthritis of the knee (OA), as follows:
• Restricted to clients who have a documented medical contraindication to other forms of
non-surgical care including all of the following: NSAIDS, corticosteroid injections and
physical therapy/exercise
• Performed by an orthopedic surgeon, rheumatologist, or physiatrist only
• Limited to two courses per year with at least four months between courses
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
254
• Documented evidence of clinical benefit in terms of pain and function from the prior
course of treatment is required for subsequent treatment courses
Bill for the injectable drug after all injections are completed.
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
Limitations
J7320
GenVisc 850 inj
per dose
Five injections (1 week apart) covers a full course of
treatment per knee. Maximum of two courses of treatment
per year, per knee, at least four months apart
J7321
Hyalgan/supartz
inj per dose
Five injections (1 week apart) covers a full course of
treatment per knee. Maximum of two courses of treatment
per year, per knee, at least four months apart
J7322
Hymovis in per
dose
Two injections (1 week apart) covers a full course of
treatment per knee. Maximum of two courses of treatment
per year, per knee, at least four months apart
J7323
Euflexxa inj per
dose
Three to four injections (1 week apart) covers a full course
of treatment per knee. Maximum of two courses of
treatment per year, per knee, at least four months apart.
J7324
Orthovisc inj per
dose
Three to four injections (1 week apart) covers a full course
of treatment per knee. Maximum of two courses of
treatment per year, per knee, at least four months apart.
J7325
Synvisc inj per
dose
One unit equals one mg. Full course of treatment is 3
injections per knee, one week apart. Limited to 2 courses
of treatment per knee, per year, at least four months apart.
Maximum of 48 units per knee, per course of treatment.
J7326
Gel-One inj per
dose
Maximum of 2 injections per year, per knee at least 4
months apart
J7327
Monovisc inj per
dose
One injection is the full course of treatment. Maximum of
two courses of treatment per year, per knee, at least four
months apart.
J7328
GelSyn-3 inj per
dose
Three injections (1 week apart) covers a full course of
treatment per knee. Maximum of two courses of treatment
per year, per knee, at least four months apart.
Note: HCA requires PA for any off label use of these products. Failure to
obtain PA will result in denied payment or recoupment.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
255
• Hyaluronic acid/viscosupplementation injections are covered only with the following
ICD diagnosis codes:
Diagnosis Code
Description
M17.0, M17.9, M17.10, M17.11,
M17.12, M13.861, M13.862,
M13.869
Osteoarthritis, localized, primary lower leg.
M13.861, M13.862, M13.869
Osteoarthritis, localized, secondary, lower leg.
M17.9, M13.861, M13.862,
M13.869
Osteoarthritis, localized, not specified whether primary
or secondary, lower leg.
M13.861, M13.862, M13.869
Osteoarthritis, unspecified whether generalized or
localized, lower leg.
• The injectable drugs must be billed after all injections are completed.
• Bill CPT injection code 20610 or 20611 each time an injection is given, up to a
maximum of 5 per knee, per course of treatment.
• Bill both the injection CPT code and HCPCS drug code on the same claim.
Alpha Hydroxyprogesterone (17P)
HCA will cover the use of Alpha Hydroxyprogesterone (17P) as one strategy to reduce the
incidence of premature births. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
(ACOG) has indicated that 17P may be of benefit to pregnant women with:
• A singleton gestation.
• A history of prior spontaneous preterm delivery (between 20 weeks gestation and 36
weeks, 6 days gestation) which was either:
Due to preterm labor.
A spontaneous delivery due to unknown etiology.
HCA will reimburse administering providers (with the exception of hospitals) without prior
authorization for 17P and its administration as follows:
• 17P must be purchased by the provider from a sterile compounding pharmacy
• The compound is individually produced on a client-by-client basis
• One dose per week is covered during week 16 through week 36 of pregnancy

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
256
How to bill for Alpha Hydroxyprogesterone (17P)
When billing for 17P (HCPCS code J3490), enter the following information on the claim:
• The NDC for the main ingredient in the compound on the line level
• The word Compound in the Notes field
Attach to the claim the invoice from the pharmacy showing all of the products with NDCs and
quantities used in the compound.
Makena®
Makena® (HCPCS code J1726) is the commercially marketed form of 17P. Makena® is covered
for clients age 10 and older who have a history of pre-term labor and receive pregnancy
supervision. Makena® can be dispensed and billed by a retail pharmacy for administration by a
physician, or Makena® can be billed by the physician’s office.
Prolia/Xgeva
HCA covers denosumab injection (Prolia® and Xgeva®) as follows:
• Prior authorization is required
• Providers bill HCA using HCPCS code J0897
When submitting the General Information for Authorization (13-835) form to request PA, field
15 must contain the brand name (Prolia® or Xgeva®) of the requested product. See Where can I
download HCA forms? HCA will reject requests for J0897 without this information. Providers
must complete all other required fields.
Spinraza™
See Outpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide for information.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
257
Synagis®
What are the requirements for administration and
authorization of Synagis®?
(CPT code 90378)
HCA requires providers to follow the guidelines and standards as published in The Official
Journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics, Updated guidance for Palivizumab Prophylaxis
among infants and young children at increased risk of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial
virus infection for clients considered for Synagis® prophylaxis during the RSV season.
Note: This information relates only to those clients NOT enrolled in an HCA-
contracted managed care organization (MCO). For clients enrolled in an HCA-
contracted MCO, refer to the coverage guidelines in the enrollee’s plan.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) Season
HCA has established the RSV season as December through April. HCA monitors RSV incidence
as reported by laboratories throughout the state and may change the dates based on the data
collected. Unless otherwise notified by HCA, these dates are firm.
Criteria for the administration of Synagis® to HCA clients
HCA requires that the following guidelines and standards of care be applied to clients considered
for Synagis® prophylaxis during the RSV season. HCA established these guidelines and
standards as published in The Official Journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics, “Updated
guidance for Palivizumab Prophylaxis among infants and young children at increased risk of
hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection.”
Are there other considerations when administering
Synagis®?
Administer the first dose of Synagis® 48 to
72 hours before discharge or promptly after
discharge to infants who qualify for prophylaxis during the RSV season.
If an
infant or child who is receiving Synagis® immunoprophylaxis
experiences a breakthrough
RSV infection, continue administering monthly prophylaxis
for the maximum allowed doses as
above.
Note: HCA does not authorize Synagis® for children with cystic fibrosis.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
258
What are the authorization and billing procedures for
Synagis®?
Direct questions or concerns regarding billing and authorization of Synagis® to HCA at (800)
562-3022. Fax prior authorization requests on completed HCA prior authorization form(s) to
(866) 668-1214. See Where can I download HCA forms?
Bill HCA for Synagis® using the following guidelines:
• Synagis® may be dispensed and billed by a retail pharmacy for administration by a
physician, or may be billed by the physician’s office.
• Pharmacies bill through standard pharmacy Point-of-Sale electronic claim submission
using the appropriate National Drug Code for the product dispensed.
• Physician’s offices billing directly for Synagis® must bill on a professional claim using
CPT code 90378.
• To bill for the administration of Synagis® use CPT code 90471 or 90472 if:
Dispensed through the pharmacy POS.
Administered through the physician’s office.
What is the criteria for coverage or authorization of
Synagis®?
Note: Criteria for coverage or authorization vary depending on the patient’s age.
• Children younger than 1 year of age
HCA requires providers to use and accurately apply the criteria for the administration of
Synagis® to HCA clients. Billing for Synagis® outside of the guidelines mentioned in
the Official journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics will be considered an
overpayment and will be subject to recoupment.
HCA will continue to cover Synagis for clients younger than 1 year of age without
authorization, as long as utilization is appropriate. In this case, physicians and pharmacies
are not required to submit paperwork or obtain pre-approval for the administration of
Synagis.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
259
• Children age 1 and 2
Prior authorization is required to administer Synagis to HCA clients age 1 and 2.
Request authorization by faxing the Request for Synagis (13-771) form. See Where can
I download HCA forms?
• Children age 3 and older
HCA does not pay for administering Synagis® to clients age 3 and older.
What are the authorization procedures for Synagis?
• Pharmacy billers
Pharmacies must submit a request for authorization using HCA’s Pharmacy
Information Authorization (13-835A) form as the cover sheet. This form must be
typed. See Where can I download HCA forms?
Fax the form to HCA at: (866) 668-1214. If authorized, HCA may approve the
100mg strength, the 50mg strength, or both. However, pharmacies must use
National Drug Code (NDC) 60574-4113-01 in box #21 on Pharmacy
Information Authorization form (13-835A). After HCA reviews your request, you
will receive notification by fax of strengths, quantities, and NDC(s) approved. See
Where can I download HCA forms?
The Request for Synagis (13-771) form must accompany a typed Pharmacy
Information Authorization form (13-835A) as supporting documentation. See
Where can I download HCA forms?
Pharmacies billing for Synagis® through standard pharmacy Point-of-Sale
electronic claim submission must use the appropriate National Drug Code for the
product dispensed.
• Physician office billers
Physician offices must submit a request for authorization using HCA’s General
Information for Authorization form (13-835) as the cover sheet. This form must
be typed. See Where can I download HCA forms?
HCA’s Request for Synagis® form (13-771) must be submitted as supporting
documentation in addition to the General Information for Authorization form (13-
835). See Where can I download HCA forms?
Physician offices billing HCA directly for Synagis® must bill on a professional
claim using CPT code 90378. After HCA reviews your request, you will receive
notification by fax of the total milligrams and NDC(s) approved.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
260
• Requesting an increase in Synagis® dose
The quantity of Synagis® authorized for administration is dependent upon the weight of
the client at the time of administration. If you obtained authorization for a quantity of
Synagis® that no longer covers the client’s need due to weight gain:
Complete the appropriate ProviderOne Cover Sheet by entering the initial
authorization number.
Pharmacy billers use the Pharmacy PA Supporting Docs sheet.
Physician office billers use PA (Prior Authorization) Pend Forms sheet.
Complete the Request for Additional MG's of Synagis® Due to Client Weight
Increase (HCA 13-770) form and submit along with the ProviderOne Cover
Sheet. See Where can I download HCA forms?
HCA will update the authorization to reflect an appropriate quantity and return a fax to
the requestor confirming the increased dosage. See the Updated guidance for
Palivizumab Prophylaxis among infants and young children at increased risk of
hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection.
• Evaluation of authorization requests for Synagis®
HCA physicians will evaluate requests for authorization to determine whether the client
falls within 2014 AAP guidelines for the administration of Synagis®. HCA will fax an
approval or denial to the requestor.
Allow at least five business days for HCA to process the authorization request.
You may verify the status of a pending authorization by using the ProviderOne PA
Inquire feature.
Verteporfin injection
(HCPCS code J3396)
Verteporfin injections are limited to ICD diagnosis codes H35.30 and H35.32.
Vivitrol
(HCPCS J2315)
HCA does not require prior authorization for Vivitrol.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
261
How do providers who participate in the 340B
drug pricing program bill for drugs and
dispensing fees?
(WAC 182-530-7900)
• All provider NPI(s) used for billing 340B drugs to Washington Apple Health managed
care or fee for service programs must be accurately reported on the federal Office of
Pharmacy Affairs Medicaid Exclusion File (MEF).
• All drugs billed under the 340B participating NPI(s) must be purchased under the 340B
program.
• Only the qualified participating Public Health Services-covered entity (CE) may bill
340B drugs to Washington Apple Health managed care or fee for service programs.
• Providers must bill HCA the 340B actual acquisition cost (AAC) for all drugs purchased
under the 340B drug discount program—unless billing an outpatient prospective payment
system (OPPS) or ambulatory surgery center (ASC) claim paid under a grouper
methodology.
Drugs administered to managed care clients but
reimbursed through fee-for-service
For clients enrolled in an HCA-contracted managed care organization (MCO), HCA reimburses
providers through fee-for-service for the following professionally administered drugs:
Label name Generic name HCPCS code PA?
Adakveo Crizanlizumab-tmca J0791 Yes
Brineura Cerliponase alfa J0567 Yes
Crysvita Burosumab-twza J0584 Yes
Exondys 51 Eteplirsen J1428 Yes
Gamifant Emapalumab-lzsg J9210 Yes
Givlaari Givosiran J0223 Yes
Kymriah Tisagenlecleucel Q2042 Yes
Lutathera Lutetium Lu 177 dotatate A9513 Yes
Luxturna Voretigeme neparvovec-rzyl J3398 Yes
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
262
Label name Generic name HCPCS code PA?
Palynziq Pegyaliase-pgpz Bill under Misc. code Yes
Radicava Edaravone J1301 Yes
Reblozyl Luspatercept-aamt J0896 Yes
Revcovi Elapegademase-lvlr Bill under Misc. code Yes
Spinraza Nusinersen J2326 Yes
Vyondys 53 Golodirsen J1429 Yes
Yescarta Axicabtagene ciloleucel Q2041 Yes
Zolgensma Onasmnogene abeparvovec J3399 Yes
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
263
Foot Care Services
(WAC 182-531-1300)
This section addresses care of the lower extremities (foot and ankle) referred to as foot care and
applies to clients age 21 and older.
Note: Care of the lower extremity is defined as foot and ankle care.
Are foot care services covered?
HCA covers foot care services for clients age 21 and older as listed in this section when those
services are provided by any of the following health care providers and billed to HCA using
procedure codes and diagnosis codes that are within their scope of practice:
• Physicians and surgeons or physician's assistants-certified (PA-C)
• Osteopathic physicians and surgeons, or physician's assistant-certified (PA-C)
• Podiatric physicians and surgeons
• Advanced registered nurse practitioners (ARNP)
HCA covers evaluation and management visits to assess and diagnose conditions of the lower
extremities. Once diagnosis is made, HCA covers treatment if the criteria in WAC 182-531-1300
(4)(a) are met.
What foot care services are not covered?
(WAC 182-531-0150 (1)(n))
HCA does not cover:
• Treatment of or follow-up office visits for chronic acquired conditions of the lower
extremities. HCA pays for prescriptions using the criteria found in the Prescription Drug
Program Billing Guide.
• The following foot care services, unless the client meets criteria and conditions outlined
in WAC 182-531-1300:
Routine foot care, such as but not limited to:
Cutting or removing warts, corns and calluses
Treatment of tinea pedis
Trimming, cutting, clipping, or debriding of nails

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
264
Nonroutine foot care, such as, but not limited to treatment of:
Adult acquired flatfoot (metatarsus adductus or pes planus)
Bunions and tailor's bunion (hallux valgus)
Cavovarus deformity, acquired
Equinus deformity of foot, acquired
Flat feet
High arches (cavus foot)
Hallux malleus
Hallux limitus
Onychomycosis
• Any other service performed in the absence of localized illness, injury, or symptoms
involving the foot.
Note: Providers may request an exception to rule (ETR) for treatment of those
conditions not described in this section. See WAC 182-501-0160 Exception to
rule – Request for a noncovered health care service.
What foot care services does HCA pay for?
HCA considers treatment of the lower extremities to be medically necessary only when there is
an acute condition, an exacerbation of a chronic condition, or presence of a systemic condition
such as metabolic, neurologic, or peripheral vascular disease and evidence that the treatment will
prevent, cure or alleviate a condition in the client that causes pain resulting in inability to
perform activities of daily living, acute disability, or threatens to cause the loss of life or limb,
unless otherwise specified. (WAC 182-531-1300 (4)(a))
HCA pays for:
1) Treatment of the following conditions:
a) Acute inflammatory processes such as, but not limited to, tendonitis
b) Circulatory compromise such as, but not limited to:
i) Lymphedema
ii) Raynaud's disease
iii) Thromboangiitis obliterans
iv) Phlebitis
c) Injuries, fractures, sprains, and dislocations

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
265
d) Gout
e) Lacerations, ulcerations, wounds, blisters
f) Neuropathies (e.g., reflex sympathetic dystrophy secondary to diabetes and
charcot arthropathy
g) Osteomyelitis
h) Postoperative complications
i) Warts, corns, or calluses in the presence of an acute condition such as infection
and pain effecting the client’s ability to ambulate as a result of the warts, corns, or
calluses and meets the medical necessity criteria found under the heading What
foot care services does HCA pay for?
j) Tendonitis
k) Soft tissue conditions, such as, but not limited to:
i) Rashes.
ii) Infections (fungal, bacterial).
iii) Gangrene.
iv) Cellulitis of lower extremities.
v) Soft tissue tumors.
vi) Neuroma.
l) Nail bed infections (paronychia).
m) Treatment of tarsal tunnel syndrome.
2) Treatment of diabetic foot ulcers with skin substitutes. See HCA’s Outpatient prospective
payment system (OPPS) fee schedule for more information.
3) Trimming and/or debridement of nails to treat, as applicable, conditions found under #1
in this section.
Note: HCA pays for one treatment in a 60-day period. HCA covers additional treatments
in this period if documented in the client's medical record as being medically necessary.
4) A surgical procedure to treat one of the conditions found under #1 in this section
performed on the lower extremities, and performed by a qualified provider.
5) Impression casting to treat one of the conditions found under #1 in this section. HCA
includes 90-day follow-up care in the reimbursement.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
266
6) Custom fitted or custom molded, or both, orthotic devices to treat one of the conditions
found under #1 in this section.
Note: HCA's fee for the orthotic device includes reimbursement for a biomechanical
evaluation (an evaluation of the foot that includes various measurements and
manipulations necessary for the fitting of an orthotic device).
HCA includes an evaluation and management (E/M) fee reimbursement in addition to an
orthotic fee reimbursement if the E/M services are justified and well documented in the
client's medical record.
What foot care services does HCA not pay for?
(WAC 182-531-1300 (5))
HCA does not pay:
• For the following radiology services:
Bilateral X-rays for a unilateral condition
X-rays in excess of three views
X-rays that are ordered before the client is examined
• Podiatric physicians or surgeons for X-rays for any part of the body other than the foot or
ankle.
May I bill the client for foot care services which
HCA does not pay for?
A waiver is required when clients choose to pay for a foot care service for which HCA does not
pay. Requesting an ETR is optional for the client. See WAC 182-502-0160, Billing the Client for
details.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
267
How do I bill for foot care services?
HCA will pay for treatment of an acute condition only when the condition is the primary reason
for the service. This must be documented in the client’s record. When billing, the diagnosis code
for the acute condition must be on the service line for the foot care service being billed.
If the description of the orthotic code indicates the code is for a single orthotic or impression
casting of one foot, either modifier RT or LT must be included on the claim. Providers must use
an appropriate procedure code with the word "pair" in the description when billing for
fabrications, casting, or impressions of both feet.
HCA pays for an Evaluation and Management (E/M) code and an orthotic on the same day if the
E/M service performed has a separately identifiable diagnosis and the provider bills using
modifier 25 to indicate a significant and separately identifiable condition exists and is reflected
by the diagnosis.
If Medicare does not cover orthotics and casting, providers may bill HCA directly for those
services without submitting a Medicare denial, unless the client's eligibility check indicates
QMB - Medicare only, in which case the orthotics and casting is not covered by HCA. If
Medicare does cover the service, bill Medicare first.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
268
Home Health and Hospice
Physician signature requirement for home health
services
To comply with federal regulations, home health services must be cosigned by a physician, if
ordered by a nonphysician provider. If the physician is cosigning the order (that was written by a
nonphysician practitioner) for home health services, the physician may bill HCA using CPT®
code 99446. All other information regarding home health services may be found in HCA’s Home
Health Services (Acute Care Services) Billing Guide.
Physicians providing service to hospice clients
HCA pays providers who are attending physicians and not employed by the hospice agency:
• For direct physician care services provided to a hospice client
• When the provided services are not related to the terminal illness
• When the client’s provider, including the hospice provider, coordinates the health care
provided
Concurrent care for children who are on hospice
(WAC 182-551-1860)
In response to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, clients age 20 and younger who
are on hospice service are also allowed to have access to curative services.
Note: The legal authority for these clients’ hospice palliative services is Section 2302 of
the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 and Section 1814(a)(7) of the
Social Security Act; and for client’s curative services is Title XIX Medicaid and Title
XXI Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) for treatment of the terminal condition.
See the Hospice Services Billing Guide when billing for concurrent care treatment – life
prolonging/curative treatment.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
269
Major Trauma Services
Increased payments for major trauma care
The legislature established the Trauma Care Fund (TCF) in 1997 to help offset the cost of
operating and maintaining a statewide trauma care system. The Department of Health (DOH) and
the HCA receive funding from the TCF to help support provider groups involved in the state’s
trauma care system.
HCA uses its TCF funding to draw federal matching funds. HCA makes supplemental payments
to designated trauma centers and pays enhanced rates to physicians/clinical providers for trauma
cases that meet specified criteria.
The enhanced rates are available for trauma care services provided to a fee-for-service Medical
Assistance client with an Injury Severity Score (ISS) of:
(a) 13 or greater for adults.
(b) 9 or greater for pediatric patients (age 14 and younger).
(c) Less than (a) or (b) for a trauma patient received in transfer by a Level I, II, or III trauma
center.
Beginning with dates of service on and after July 1, 2012, physicians/clinical providers also
receive enhanced rates for qualified trauma care services provided to managed care enrollees
who meet trauma program eligibility criteria.
Client eligibility groups included in TCF
payments to physicians
Claims for trauma care services provided to the following client groups are eligible for enhanced
rates:
• Medicaid (Title XIX)
• CHIP (Title XXI)
• Medical Care Services (Aged, Blind, and Disabled (ABD)
• Apple Health for Kids (Children’s Health)

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
270
Client eligibility groups excluded from TCF
payments to physicians
Claims for trauma care services provided to the following client groups are not eligible for
enhanced rates:
• Refugee Assistance
• Alien Emergency Medical
• Family Planning Only – Pregnancy Related/Family Planning Only (formerly referred to
as TAKE CHARGE)
Services excluded from TCF payments to
physicians
Claims for the following services are not eligible for enhanced rates:
• Laboratory and pathology services
• Technical Component (TC)-only radiology services
• Services unrelated to a client’s traumatic injury (e.g., treatment for chronic diseases)
• Services provided after discharge from the initial hospital stay, except for inpatient
rehabilitation services and/or planned follow-up surgery related to the traumatic injury
and provided within six months of the date of the traumatic injury
TCF payments to physicians
Enhanced rates for trauma care
(WAC 182-531-2000)
To receive payments from the TCF, a physician or other clinician must:
• Be on the designated trauma services response team of any Department of Health (DOH)-
designated or DOH-recognized trauma service center.
• Submit all information to the TCF that HCA requires to monitor the trauma program.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
271
HCA makes a TCF payment to a physician or clinician:
• When the provider submits an eligible trauma claim with the appropriate trauma indicator
within the time frames specified by HCA.
• On a per-claim basis.
Each qualifying trauma service or procedure on the provider's claim is paid at HCA's current fee-
for-service rate, multiplied by the appropriate payment enhancement percentage at a rate of 2 ¾
times HCA's current fee-for-service rate for qualified trauma services, or other payment
enhancement percentage HCA deems appropriate. Laboratory and pathology services and
procedures are not eligible for payments from the TCF and are paid at HCA's current fee-for-
service rate.
For an eligible trauma service, payment is currently calculated as follows:
Trauma care payment = Base rate x 275%
Criteria for TCF payments to physicians
Physicians and clinical providers receive TCF payments from HCA:
1) For qualified trauma care services. Qualified trauma care services are those that meet the
ISS specified in subsection (3) below. Qualified trauma care services also include
inpatient rehabilitation and surgical services provided to Medical Assistance clients
within six months of the date of the qualifying injury when the following conditions are
met:
a) The follow-up surgical procedures are directly related to the qualifying traumatic
injury.
b) The follow-up surgical procedures were planned during the initial acute episode
of care (inpatient stay).
c) The plan for the follow-up surgical procedure(s) is clearly documented in the
medical record of the client’s initial hospitalization for the traumatic injury.
2) For hospital-based services only, except as specified in (4).
3) Only for trauma cases that meet the ISS of:
a) Thirteen or greater for an adult trauma patient (a client age 15 or older).
b) Nine or greater for a pediatric trauma patient (a client younger than age 15).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
272
c) Less than 13 for adults or 9 for pediatric patients for a trauma case received in
transfer by a Level I, II, or III trauma service center.
4) On a claim-specific basis. Services must have been provided in a designated trauma
service center, except that qualified follow-up surgical care within six months of the
initial traumatic injury, as described in subsection (1) above, may be provided in other
approved care settings, such as Medicare-certified ambulatory surgery centers.
5) At a rate determined by HCA. The enhanced rates are subject to the following
limitations:
a) Laboratory and pathology charges are not eligible for enhanced payments from
the TCF. Laboratory and pathology services are paid at the lesser of HCA’s
current FFS rate or the billed amount.
b) Technical component only (TC) charges for radiology services are not eligible for
enhanced rates when billed by physicians. (These are facility charges.)
c) The rate enhancement percentage is subject to periodic adjustments to ensure that
total payments from the TCF for the state fiscal year will not exceed the
legislative appropriation for that fiscal year. HCA has the authority to take
whatever actions are needed to ensure it stays within its TCF appropriation.
TCF payments to providers in transferred
trauma cases
When a trauma case is transferred from one hospital to another, HCA makes TCF payments to
providers as follows:
• If the transferred case meets or exceeds the appropriate ISS threshold (ISS of 13 or
greater for adults, and 9 or greater for pediatric clients), both transferring and receiving
hospitals and physicians/clinicians who furnished qualified trauma care services are
eligible for increased payments from the TCF. The transfer must be to a higher level
designated trauma service center, and the transferring hospital must be at least a level 3
hospital. Transfers from a higher level to a lower level designated trauma service center
are not eligible for the increased payments.
• If the transferred case is below the ISS threshold, only the receiving hospital and the
physicians/clinicians at the receiving facility who furnished qualified trauma care
services are eligible for increased payments from the TCF. The transferring hospital and
clinical team are paid the regular rates for the services they provided to the transferred
client with an ISS below the applicable threshold.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
273
Billing for trauma care services
To bill for qualified trauma care services, physicians and clinical providers must add the trauma
modifier ST to the appropriate procedure code line. Enter the required ST modifier into the
modifier field of the claim to receive the enhanced payment.
Note: The ProviderOne system can accommodate up to 4 modifiers on a line, if
multiple modifiers are necessary.
Claims for trauma care services provided to a managed care enrollee must be submitted to the
client’s managed care plan. Claims for trauma care services provided to a fee-for-service client
must be submitted to HCA. The payment for a trauma care service provided to a managed care
enrollee will be the same amount for the same service provided to a fee-for-service client.
Adjusting trauma claims
HCA considers a provider’s request to adjust a claim for the purpose of receiving TCF payment
(e.g., adding the ST modifier to a previously billed service, or adding a new procedure with the
ST modifier to the claim) only when the adjustment request is received within 1 year from the
date of service on the initial claim. See WAC 182-502-0150(11).
A claim which included a trauma service may be submitted for adjustment beyond 365 calendar
days when the reason for the adjustment request is other than TCF payment (e.g., adding lab
procedures, correcting units of service).
Note: HCA takes back the original payment when processing an adjustment
request. Electronic claims get a Julian date stamp on the date received, including
weekends and holidays. When a trauma care service that was billed timely and
received the enhanced rate and is included in a claim submitted for adjustment
after 365 days, HCA will pay the provider the regular rate for the service when
the adjustment is processed, and recoup the original enhanced payment.
All claims and claim adjustments are subject to federal and state audit and review requirements.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
274
Injury severity score (ISS)
Note: The current ISS qualifying score is 13 or greater for adults, and 9 or
greater for pediatric clients (through age 14 only).
The ISS is a summary severity score for anatomic injuries.
• It is based upon the Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) severity scores for six body regions:
Head and neck
Face
Chest
Abdominal and pelvic contents
Extremities and pelvic girdle
External
• The ISS values range from 1 to 75. Generally, a higher ISS indicates more serious
injuries.
Additional Information
For information on the statewide trauma system, designated trauma services, trauma service
designation, trauma registry, or trauma care fund (TCF), see the Department of Health’s Trauma
System webpage.
For information on a specific trauma claim, contact:
Health Care Authority
Customer Service Center
800-562-3022

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
275
Physician/clinical provider list
Below is a list of providers eligible to receive enhanced rates for providing major trauma care
services to Medical Assistance clients:
Advanced Registered Nurse Practitioner
Anesthesiologist
Cardiologist
Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist
Critical Care Physician
Emergency Physician
Family/General Practice Physician
Gastroenterologist
General Surgeon
Gynecologist
Hand Surgeon
Hematologist
Infectious Disease Specialist
Internal Medicine
Nephrologist
Neurologist
Neurosurgeon
Obstetrician
Ophthalmologist
Oral/Maxillofacial Surgeon
Orthopedic Surgeon
Pediatric Surgeon
Pediatrician
Physiatrist
Physician Assistant
Plastic Surgeon (not cosmetic surgery)
Pulmonologist
Radiologist
Thoracic Surgeon
Urologist
Vascular Surgeon
Note: Many procedures are not included in the enhanced payment program for
major trauma services.
The services of some specialists listed above are eligible for enhanced rates only
when provided in the context of major trauma care (e.g., stabilization services by
a General Practitioner prior to client’s transfer to a trauma care facility; C-Section
performed by obstetrician on pregnant accident victim when fetus is in danger).

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
276
Oral Health
Access to Baby and Child Dentistry (ABCD)
Program
(WAC 182-535-1245)
What is the purpose of the ABCD program?
The purpose of the ABCD program is to increase access to preventive dental services for infants,
toddlers, and preschoolers age five and younger who are eligible for Washington Apple Health
(Medicaid). To find out more about the ABCD program, visit Access to Baby & Child
Dentistry.
Who may provide ABCD dentistry?
Primary care medical providers (physicians, ARNPs, physician assistants) who are certified
through the Arcora (formerly known as The Washington Dental Service Foundation) are eligible
for select ABCD program enhanced reimbursement rates.
To become trained and certified to provide the services in the table above, primary care medical
providers must complete a class offered by Washington Dental Service Foundation (WDSF). The
1 ½ hour continuing medical education (CME) class is given in-office or in community settings
and teaches providers to deliver the following preventive services:
• Links between oral health and total health
• Oral health screening and risk assessment
• Providing oral health education and anticipatory guidance to clients and families
• Application of topical fluoride
• Billing
• Referrals for dental care
Contact Arcora at [email protected] or 206-473-9542 for questions about current
certification or for scheduling certification training.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
277
What ABCD dental services are billable by certified primary
care medical providers?
HCA pays enhanced fees to certified participating primary care medical providers for delivering
the following services:
• Periodic oral evaluations. One periodic evaluation allowed every 6 months, per client,
per provider.
• Topical application of fluoride (fluoride varnish). Three times within a 12-month period
with a minimum of 110 days between applications.
• Family oral health education. An oral health education visit must include all of the
following:
"Lift Lip" training: Show the "Lift Lip" flip chart or DVD provided at the
certification workshop. Have the parent(s)/guardian(s) practice examining the
child using the lap position. Ask if the parent(s)/guardian(s) feel comfortable
doing this once per month.
Oral hygiene training: Demonstrate how to position the child to clean the teeth.
Have the parent(s)/guardian(s) actually practice cleaning the teeth. Record the
parent/guardian’s response.
Risk assessment for early childhood caries: Assess the risk of dental disease for
the child. Obtain a history of previous dental disease activity for this child and
any siblings from the parent(s)/guardian(s). Also note the dental health of the
parent(s)/guardian(s).
Dietary counseling: Talk with the parent(s)/guardian(s) about the need to use a
cup, rather than a bottle, when giving the child anything sweet to drink. Note that
dietary counseling was delivered.
Discussion of fluoride supplements: Discuss fluoride supplements with the
parent(s)/guardian(s). Let the parent/guardian know fluoride supplements are
covered under HCA's Prescription Drug program. Fluoride prescriptions written
by the primary care medical provider may be filled at any Medicaid-participating
pharmacy. Ensure that the child is not already receiving fluoride supplements.
Documentation: Record the activities provided and the duration of the oral
education visit in the client’s or the client’s designated adult member’s (family
member or other responsible adult) file.
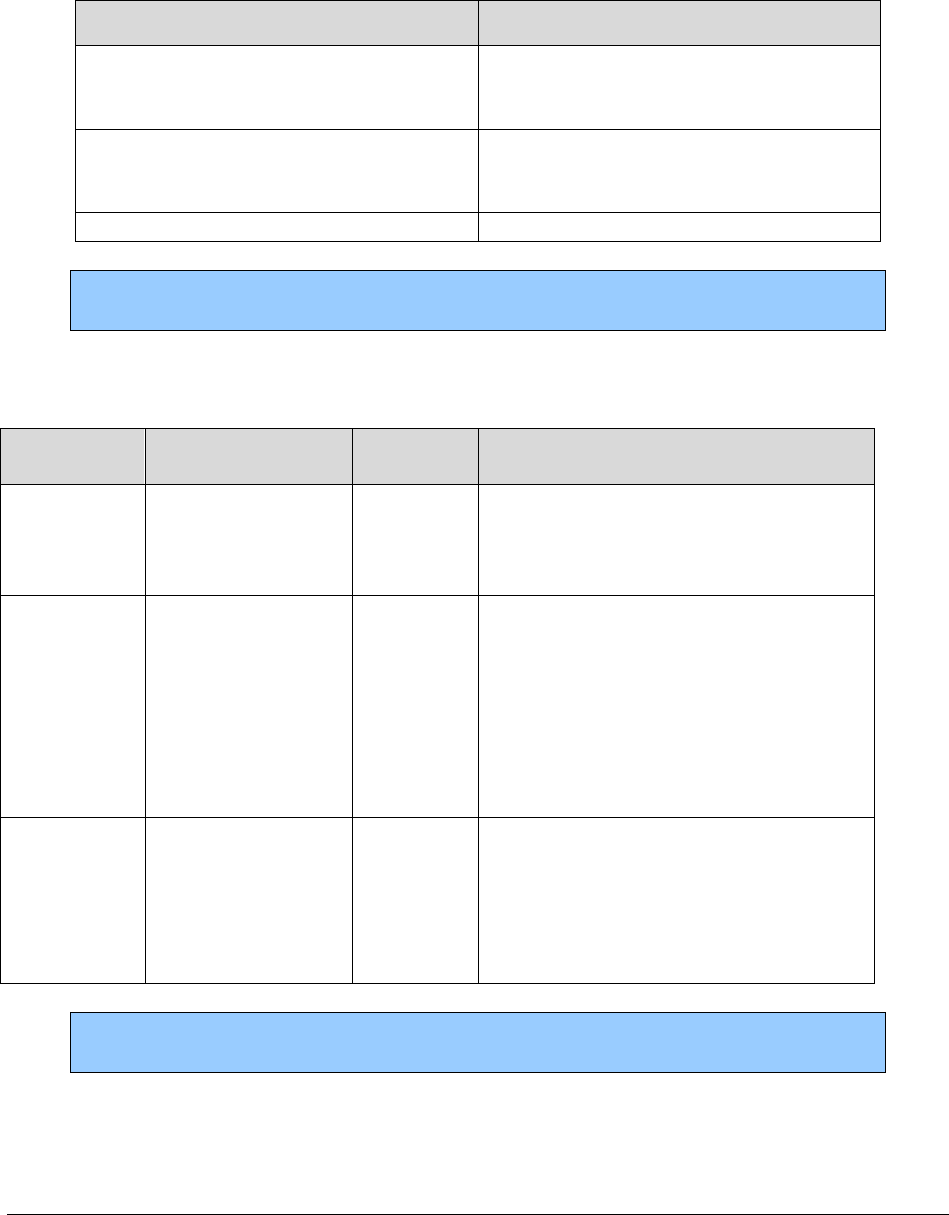
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
278
Topical fluoride treatment
HCA covers fluoride varnish per client, per provider or clinic as follows:
Clients who are…
Frequency
Age 6 and younger
Three times within a 12-month period
with a minimum of 110 days between
applications
Age 7 through 18 or
residing in ALFs or nursing facilities
Two times within a 12-month period
with a minimum of 170 days between
applications
Age 19 through 20
Once within a 12-month period
Note: Participating primary care medical providers do not need to be ABCD-
certified to be paid for administering fluoride varnish.
Dental services coverage table for nondental providers
Payment
CPT Code
Short Description
Modifier
needed
Comments
99188
App topical
fluoride varnish
DA
Limited to 3 times within a 12-month
period with a minimum of 110 days
between applications.
99429
Unlisted
preventive service
DA
Use for family oral health education.
Provider must be ABCD-certified.
Limited to 1 visit per day per family,
per provider and up to 2 visits in a 12-
month period through age 5 per
provider, per client.
99499
Unlisted E&M
service
DA
Use for a periodic oral evaluation.
Provider must be ABCD-certified.
Limited to 1 periodic evaluation
allowed every 6 months, per provider.
Note: Follow CPT® coding guidelines when billing two E/M services on the
same day by the same provider.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
279
Oral surgery
Services performed by a physician or dentist specializing in
oral maxillofacial surgery
(WAC 182-535-1094)
Provider requirements
• An appropriate consent form, if required, signed and dated by the client or the client’s
legal representative must be in the client’s record.
• An anesthesiologist providing oral health care under this section must have a current
provider’s permit on file with HCA.
• A health care provider providing oral or parenteral conscious sedation, or general
anesthesia, must meet all of the following:
The provider’s professional organization guidelines
The Department of Health (DOH) requirements in chapter 246-817 WAC
Any applicable DOH medical, dental, and nursing anesthesia regulations
• HCA-enrolled dental providers who are not specialized to perform oral and maxillofacial
surgery must use only the current dental terminology (CDT) codes to bill claims for
services that are listed in the Oral surgery coverage table. (See WAC 182-535-1070 (3)).
See HCA’s Dental-Related Services Billing Guide.
Note: If it is anticipated that the client will require orthognathic surgery as part of
orthodontic treatment, see HCA’s Orthodontic Services Billing Guide.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
280
Oral surgery coverage table
HCA covers the following services:
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
10060
N
Drainage of skin abscess
10120
N
Remove foreign body
10140
N
Drainage of hematoma/fluid
11000
N
Debride infected skin
11012
N
Deb skin bone at fx site
11042
N
Deb subq tissue 20 sq cm/<
11044
N
Deb bone 20 sq cm/<
11440
N
Exc face-mm b9+marg 0.5 < cm
11441
N
Exc face-mm b9+marg 0.6-1 cm
11442
N
Exc face-mm b9+marg 1.1-2 cm
11443
N
Exc face-mm b9+marg 2.1-3 cm
11444
N
Exc face-mm b9+marg 3.1-4 cm
11446
N
Exc face-mm b9+marg > 4 cm
11640
N
Exc face-mm malig+marg 0.5 <
11641
N
Exc face-mm malig+marg 0.6-1
11642
N
Exc face-mm malig+marg 1.1-2
11643
N
Exc face-mm malig+marg 2.1-3
11644
N
Exc face-mm malig+marg 3.1-4
11646
N
Exc face-mm mlg+marg > 4 cm
12001
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12002
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12004
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12005
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12011
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12013
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12014
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12015
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12016
N
Repair superficial wound(s)
12031
N
Intmd wnd repair s/tr/ext
12032
N
Intmd wnd repair s/tr/ext
12034
N
Intmd wnd repair s/tr/ext
12035
N
Intmd wnd repair s/tr/ext
12036
N
Intmd wnd repair s/tr/ext
12051
N
Intmd wnd repair face/mm
12052
N
Intmd wnd repair face/mm
12053
N
Intmd wnd repair face/mm
12054
N
Intmd wnd repair, face/mm
12055
N
Intmd wnd repair face/mm
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
281
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
12056
N
Intmd rpr face/mm 20.1-30.0
13121
N
Cmplx rpr s/a/l 2.6-7.5 cm
13122
N
Cmplx rpr s/a/l addl 5 cm/>
13131
N
Repair of wound or lesion
13132
N
Repair of wound or lesion
13133
N
Repair wound/lesion add-on
13151
N
Repair of wound or lesion
13152
N
Repair of wound or lesion
13153
N
Repair wound/lesion add-on
13160
N
Late closure of wound
14040
N
Skin tissue rearrangement
15120
N
Skn splt a-grft fac/nck/hf/g
15275
N
Skin sub graft face/nk/hf/g
15278
N
Skn sub grft f/n/hf/g ch add
15576
N
Form skin pedicle flap
15732
N
Muscle-skin graft head/neck
17110
N
Destruct b9 lesion 1-14
20220
N
Bone biopsy, trocar/needle
20520
N
Removal of foreign body
20552
N
Inj trigger point 1/2 muscl
20605
N
Drain/inject, joint/bursa
20615
N
Treatment of bone cyst
20670
N
Removal of support implant
20680
N
Removal of support implant
20690
N
Apply bone fixation device
20692
N
Apply bone fixation device
20902
N
Removal of bone for graft
20926
N
Removal of tissue for graft
20955
N
Fibula bone graft, microvasc
20969
N
Bone/skin graft, microvasc
20970
N
Bone/skin graft, iliac crest
21010
N
Incision of jaw joint
21013
N
Exc face tum deep < 2 cm
21015
N
Resect face tum < 2 cm
21016
N
Resect face tum 2 cm/>
21025
N
Excision of bone, lower jaw
21026
N
Excision of facial bone(s)
21029
N
Contour of face bone lesion
21030
N
Excise max/zygoma b9 tumor
21034
N
Excise max/zygoma mlg tumor
21040
N
Excise mandible lesion
21044
N
Removal of jaw bone lesion
21045
Y
Extensive jaw surgery
21046
N
Remove mandible cyst complex
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
282
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
21047
N
Excise lwr jaw cyst w/repair
21048
N
Remove maxilla cyst complex
21049
N
Excis uppr jaw cyst w/repair
21050
Y
Removal of jaw joint
21060
Y
Remove jaw joint cartilage
21070
Y
Remove coronoid process
21073
N
Mnpj of tmj w/anesth
21076
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21077
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21079
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21080
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21081
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21082
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21083
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21084
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21085
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21086
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21087
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21088
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21089
Y
Prepare face/oral prosthesis
21100
N
Maxillofacial fixation
21110
N
Interdental fixation
21116
N
Injection, jaw joint x-ray
21120
Y
Reconstruction of chin
21121
Y
Reconstruction of chin
21122
Y
Reconstruction of chin
21123
Y
Reconstruction of chin
21141
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21142
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21143
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21145
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21146
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21147
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21150
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21151
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21154
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21155
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21159
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21160
Y
Reconstruct midface, lefort
21193
Y
Reconst lwr jaw w/o graft
21194
Y
Reconst lwr jaw w/graft
21195
Y
Reconst lwr jaw w/o fixation
21196
Y
Reconst lwr jaw w/fixation
21198
Y
Reconstr lwr jaw segment
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
283
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
21206
Y
Reconstruct upper jaw bone
21208
Y
Augmentation of facial bones
21209
Y
Reduction of facial bones
21210
Y
Face bone graft
21215
Y
Lower jaw bone graft
21230
Y
Rib cartilage graft
21240
Y
Reconstruction of jaw joint
21242
Y
Reconstruction of jaw joint
21243
Y
Reconstruction of jaw joint
21244
Y
Reconstruction of lower jaw
21245
Y
Reconstruction of jaw
21246
Y
Reconstruction of jaw
21247
Y
Reconstruct lower jaw bone
21248
Y
Reconstruction of jaw
21249
Y
Reconstruction of jaw
21255
Y
Reconstruct lower jaw bone
21295
Y
Revision of jaw muscle/bone
21296
Y
Revision of jaw muscle/bone
21315
N
Closed tx nose fx w/o stablj
21320
N
Closed tx nose fx w/ stablj
21330
N
Open tx nose fx w/skele fixj
21337
N
Closed tx septal&nose fx
21338
N
Open nasoethmoid fx w/o fixj
21343
N
Open tx dprsd front sinus fx
21344
N
Open tx compl front sinus fx
21345
N
Treat nose/jaw fracture
21346
N
Treat nose/jaw fracture
21347
N
Treat nose/jaw fracture
21348
N
Treat nose/jaw fracture
21355
N
Treat cheek bone fracture
21356
N
Treat cheek bone fracture
21360
N
Treat cheek bone fracture
21365
N
Treat cheek bone fracture
21366
N
Treat cheek bone fracture
21386
N
Opn tx orbit fx periorbital
21387
N
Opn tx orbit fx combined
21390
N
Opn tx orbit periorbtl implt
21406
N
Opn tx orbit fx w/o implant
21407
N
Opn tx orbit fx w/implant
21421
N
Treat mouth roof fracture
21422
N
Treat mouth roof fracture
21423
N
Treat mouth roof fracture
21431
N
Treat craniofacial fracture
21432
N
Treat craniofacial fracture

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
284
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
21433
N
Treat craniofacial fracture
21435
N
Treat craniofacial fracture
21436
N
Treat craniofacial fracture
21440
N
Treat dental ridge fracture
21445
N
Treat dental ridge fracture
21450
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21451
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21452
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21453
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21454
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21461
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21462
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21465
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21470
N
Treat lower jaw fracture
21480
N
Reset dislocated jaw
21485
N
Reset dislocated jaw
21490
N
Repair dislocated jaw
21497
N
Interdental wiring
21550
N
Biopsy of neck/chest
21555
Y
Exc neck les sc < 3 cm
29800
Y
Jaw arthroscopy/surgery
29804
Y
Jaw arthroscopy/surgery
30580
N
Repair upper jaw fistula
30600
N
Repair mouth/nose fistula
31000
N
Irrigation, maxillary sinus
31030
N
Exploration, maxillary sinus
31032
N
Explore sinus remove polyps
31225
N
Removal of upper jaw
31502
N
Change of windpipe airway
31515
N
Laryngoscopy for aspiration
31525
N
Dx laryngoscopy excl nb
31530
N
Laryngoscopy w/fb removal
31584
N
Treat hyoid bone fracture
31600
N
Incision of windpipe
31603
N
Incision of windpipe
31830
Y
Revise windpipe scar
38510
N
Biopsy/removal lymph nodes
38700
N
Removal of lymph nodes neck
38724
N
Removal of lymph nodes neck
40490
N
Biopsy of lip
40510
N
Partial excision of lip
40700
N
Repair cleft lip/nasal
40701
N
Repair cleft lip/nasal
40702
N
Repair cleft lip/nasal
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
285
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
40720
Y
Repair cleft lip/nasal
40800
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
40801
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
40804
N
Removal, foreign body, mouth
40805
N
Removal, foreign body, mouth
40806
N
Incision of lip fold
40808
N
Biopsy of mouth lesion
40810
N
Excision of mouth lesion
40812
N
Excise/repair mouth lesion
40814
N
Excise/repair mouth lesion
40816
N
Excision of mouth lesion
40819
N
Excise lip or cheek fold
40830
N
Repair mouth laceration
40831
N
Repair mouth laceration
40840
N
Reconstruction of mouth
40842
N
Reconstruction of mouth
40845
Y
Reconstruction of mouth
41000
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41005
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41006
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41007
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41008
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41009
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41010
N
Incision of tongue fold
41015
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41016
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41017
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41018
N
Drainage of mouth lesion
41100
N
Biopsy of tongue
41105
N
Biopsy of tongue
41108
N
Biopsy of floor of mouth
41110
N
Excision of tongue lesion
41112
N
Excision of tongue lesion
41113
N
Excision of tongue lesion
41114
N
Excision of tongue lesion
41115
N
Excision tongue fold
41116
N
Excision of mouth lesion
41120
N
Partial removal of tongue
41130
Y
Partial removal of tongue
41135
N
Tongue and neck surgery
41520
N
Reconstruction tongue fold
41530
Y
Tongue base vol reduction
41599
N
Tongue and mouth surgery
41800
N
Drainage of gum lesion
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
286
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
41805
N
Removal foreign body, gum
41821
N
Excision of gum flap
41822
N
Excision of gum lesion
41823
N
Excision of gum lesion
41825
N
Excision of gum lesion
41826
N
Excision of gum lesion
41827
N
Excision of gum lesion
41828
N
Excision of gum lesion
41830
N
Removal of gum tissue
41850
N
Treatment of gum lesion
41899
Y
Dental surgery procedure
42100
N
Biopsy roof of mouth
42104
N
Excision lesion, mouth roof
42106
N
Excision lesion, mouth roof
42180
Y
Repair palate
42182
Y
Repair palate
42200
N
Reconstruct cleft palate
42205
N
Reconstruct cleft palate
42210
N
Reconstruct cleft palate
42215
N
Reconstruct cleft palate
42220
N
Reconstruct cleft palate
42225
N
Reconstruct cleft palate
42226
Y
Lengthening of palate
42227
Y
Lengthening of palate
42235
Y
Repair palate
42260
N
Repair nose to lip fistula
42280
N
Preparation, palate mold
42281
N
Insertion, palate prosthesis
42330
N
Removal of salivary stone
42335
N
Removal of salivary stone
42405
N
Biopsy of salivary gland
42408
N
Excision of salivary cyst
42409
N
Drainage of salivary cyst
42440
N
Excise submaxillary gland
42450
N
Excise sublingual gland
42500
N
Repair salivary duct
42505
N
Repair salivary duct
42600
N
Closure of salivary fistula
42700
N
Drainage of tonsil abscess
42720
N
Drainage of throat abscess
42725
N
Drainage of throat abscess
43200
N
Esophagus endoscopy
64400
N
N block inj trigeminal
64600
Y
Injection treatment of nerve
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
287
Procedure Code
PA?
Short Description
64774
N
Remove skin nerve lesion
64784
N
Remove nerve lesion
64788
N
Remove skin nerve lesion
64790
N
Removal of nerve lesion
64792
N
Removal of nerve lesion
64795
N
Biopsy of nerve
64864
N
Repair facial nerve
64910
N
Nerve repair w/allograft
70300
N
X-ray exam of teeth
70310
N
X-ray exam of teeth
99201
N
Office/outpatient visit, new*
99202
N
Office/outpatient visit, new*
99203
N
Office/outpatient visit new*
99204
N
Office/outpatient visit new*
99205
N
Office/outpatient visit new*
99211
N
Office/outpatient visit, est*
99212
N
Office/outpatient visit est*
99213
N
Office/outpatient visit est*
99214
N
Office/outpatient visit est*
99215
N
Office/outpatient visit est*
99231
N
Subsequent hospital care*
99232
N
Subsequent hospital care*
99233
N
Subsequent hospital care*
99241
N
Office consultation*
99242
N
Office consultation*
99243
N
Office consultation*
99244
N
Office consultation*
99245
N
Office consultation*
99251
N
Inpatient consultation*
99252
N
Inpatient consultation*
99253
N
Inpatient consultation*
99254
N
Inpatient consultation*
99255
N
Inpatient consultation*
*Billing evaluation and management (E/M) codes
Dentists specializing in oral surgery must use CPT codes and follow CPT rules when billing for
evaluation and management of clients. When billing for these services, the following must be
true:
• Services must be billed on an 837P HIPAA compliant claim.
• Services must be billed using one of the CPT codes above and modifiers must be used if
appropriate.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
288
Prosthetic/Orthotics
Prosthetic and orthotics for podiatry and orthopedic surgeons
The following codes are payable only to podiatrists and orthopedic surgeons:
HCPCS
Code
Short Description Policy Comments
A5500
Diab shoe for density insert
Limit 1 per client, per year
A5501
Diabetic custom molded shoe
Limit 1 per client, per year
A5503
Diabetic shoe w/roller/rocker
Limit 1 per client, per year
A5504
Diabetic shoe with wedge
Limit 1 per client, per year
A5505
Diab shoe w/metatarsal bar
Limit 1 per client, per year
A5506
Diabetic shoe w/offset heal
Limit 1 per client, per year
A5507
Modification diabetic shoe
Requires PA
A5512
Multi den insert direct form
Limit 1 per client, per year
A5513
Multi den insert custom mold
Limit 1 per client, per year
L1902
Afo ankle gauntlet
L1906
Afo multiligamentus ankle su
L3000
Ft insert ucb berkeley shell
EPA required
L3030
Foot arch support remov prem
EPA required
L3140
Abduction rotation bar shoe
L3150
Abduct rotation bar w/o shoe
L3170
Foot plastic heel stabilizer
PA required
L3215
Orthopedic ftwear ladies oxf
EPA required. Noncovered for clients age 21 and older
L3219
Orthopedic mens shoes oxford
EPA required. Noncovered for clients age 21 and older
L3310
Shoe lift elev heel/sole neo
Limit 1 per client, per year
L3320
Shoe lift elev heel/sole cor
Limit 1 per client, per year
L3334
Shoe lifts elevation heel /i
Limit 1 per client, per year
L3340
Shoe wedge sach
PA required
L3350
Shoe heel wedge
PA required
L3360
Shoe sole wedge outside sole
PA required
L3400
Shoe metatarsal bar wedge ro
PA required
L3410
Shoe metatarsal bar between
PA required
L3420
Full sole/heel wedge between
PA required
L3430
Shoe heel count plast reinfor
Limit 1 per client, per year
L4350
Ankle control orthosi prefab
Fractures only
L4360
Pneumatic walking boot prefab
Fractures only; PA required
L4386
Non-pneum walk boot prefab
PA required
(For authorization requirements, follow the Prosthetic and Orthotic Devices Billing Guide.)
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
289
Supplies paid separately when
dispensed from provider’s
office/clinic
Casting materials
Bill the appropriate HCPCS code (Q4001-Q4051) for fiberglass and plaster casting materials
limited to one unit per limb per day. Do not bill for the use of a cast room. Use of a cast room is
considered part of a provider's practice expense.
Inhalation solutions
Refer to the Professional administered drugs fee schedule for those specific codes for inhalation
solutions that are paid separately.
Metered dose inhalers and accessories
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
A4614
Hand-held PEFR meter
A4627
Spacer bag/reservoir
Miscellaneous prosthetics and orthotics
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
L0120
Cerv flexible non-adjustable
L0220
Thor rib belt custom fabrica
L1810
Ko elastic with joints
L1820
Ko elas w/ condyle pads & jo
L1830
Ko immobilizer canvas longit
L3650
Shlder fig 8 abduct restrain
L3807
WHFO,no joint, prefabricated
L3908
Wrist cock-up non-molded
L8000
Mastectomy bra
L8010
Mastectomy sleeve
L8600
Implant breast silicone/eq

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
290
For additional information and authorization requirements, see HCA’s Prosthetic and Orthotic
Devices Billing Guide.
Miscellaneous supplies
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
A4561
Pessary rubber, any type
A4562
Pessary, nonrubber, any type
A4565
Slings
A4570
Splint
L8695
External recharge sys extern. (Requires PA)
Radiopharmaceutical diagnostic imaging agents
Refer to the Professional administered drugs fee schedule for those specific codes for imaging
agents that are paid separately.
Urinary tract implants
See important policy limitations in Urinary systems.
Note: L8603, L8604 and/or L8606 must be billed on the facility claim only if the
implantation procedure is performed in place of service 21 and 22.
HCPCS
Code
Short Description
L8603
Collagen imp urinary 2.5 ml
L8604
Dextranomer/hyaluronic acid
L8606
Synthetic implnt urinary 1ml
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
291
Transgender Health Services
For resources that may be helpful for providing healthcare services to members of the
transgender community, go to the Transgender health services program webpage.
What transgender health services are covered?
(WAC 182-531-1675)
In addition to all the other services addressed in this billing guide, Medicaid covers the following
service related to transgender health and the treatment of gender dysphoria:
• Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
• Pre-puberty suppression therapy
• Mental health
• Surgical services
• Anesthesiology
• Labs
• Pathology
• Radiology
• Hospitalization
• Physician services
• Hospitalizations and physician services related to postoperative complications of
procedures performed for gender reassignment surgery
Fee-for-service clients
All the services listed in “What transgender health services are covered?” are covered for clients
who are enrolled under Medicaid’s fee-for-service program. Some services require prior
authorization (PA). See What is prior authorization (PA)?

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
292
Managed care clients
Services covered under a managed care organization (MCO): If the client is covered under
an HCA-contracted MCO, the MCO is responsible for all medical care including hormone and
mental health services to treat gender dysphoria. Contact the MCO for requirements for those
services. Some clients may meet the access to care standards, therefore these mental health care
services may be provided by a community mental health agency under the Behavioral Health
Organization (BHO).
Services covered under fee-for-service:
• If the client is covered under an MCO, fee-for-service is responsible for surgical
procedures, including electrolysis and post-operative complications if required, to treat
gender dysphoria. These services require PA by HCA. See What is prior authorization
(PA)?
• HCA pays for consultations related to gender reassignment surgery (GRS) and
electrolysis or laser hair removal. These consultations are paid for by HCA through fee-
for-service. To ensure payment, bill HCA directly for this consultative visit using an
expedited prior authorization (EPA) number. See EPA #870001400 for details.
• HCA pays for surgical procedures related to GRS and electrolysis and postoperative
complications through fee-for-service. The MCO is not responsible for surgical
procedures related to GRS, including electrolysis and postoperative complications. PA is
required from HCA for these procedures. When billing HCA for complications related to
GRS, providers must add “SCI=TC” in the Comments field on the claim.
What are the components of transgender health
services?
The gender dysphoria treatment program has four components. The MCO’s case managers and
the FFS staff coordinate care across the programs. The components described below are not
intended to be sequential and may run concurrently to meet the client’s medical needs.
Component 1 – Includes the following:
• Conducting an initial assessment and makes or confirms the diagnosis
• Developing an individualized treatment plan
• Managing referrals to other qualified providers as indicated and
• Assisting with navigation of other program requirements
Component one must be provided by a provider who is a board-certified physician, a
psychologist, a board-certified psychiatrist, or a licensed advanced registered nurse practitioner

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
293
(ARNP). Component one services provided should be consistent with World Professional
Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) Standards of Care and WAC 182-531-1675.
Component 2 – Includes mental health and medical services directly related to the pathway to
gender reassignment surgery.
• Medical treatment may include androgen suppression, puberty suppression, continuous
hormone therapy, and laboratory testing to monitor the safety of hormone therapy.
Providers must list a gender dysphoria (F64.0, F64.1, F64.2 and F64.9) diagnosis on
prescriptions for their clients receiving hormone replacement or puberty blocking agents.
• Mental health treatment, provided to the client, client’s spouse, parent, guardian, child, or
person with whom the client has a child in common, if the treatment is directly related to
the client’s care, is medically necessary and is in accordance with the provisions of WAC
182-531-1400.
These services must be provided by HCA-approved providers.
Component 3
– Includes pre-surgical requirements as follows:
• For top surgery: A referral to the surgeon from a PCP and a comprehensive evaluation
by an HCA-approved mental health professional.
• For bottom surgery: A referral to the surgeon from a PCP, a comprehensive evaluation
by two HCA approved mental health professionals and a pre-surgical consultation by an
HCA-approved surgeon.
Component 4 - Includes surgical interventions and requirements. Prior authorization is
required for this component only (surgical).
• Client requirements - The client must:
Be age 18 or older, unless allowed under the Early and Periodic Screening,
Diagnosis, and Treatment (EPSDT) program
Be competent to give consent for treatment and undergo a comprehensive
psychosocial evaluation
Have received continuous hormonal therapy as required by the treatment plan to
meet treatment objectives
Have lived in a gender role congruent with the client's gender identity
immediately preceding surgery as required by the treatment plan to meet
treatment objectives

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
294
Note for EPSDT: If gender dysphoria treatment is requested or prescribed for clients
age 20 and younger under the Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment
(EPSDT) program, HCA evaluates it as a covered service under the EPSDT program’s
requirement that the service is medically necessary, safe, effective, and not experimental.
• Prior authorization (PA) – PA is required for Component 4 only. Providers must fax a
completed General Authorization form, HCA 13-835 (See Where can I download HCA
forms?), along with any additional documentation required (see the following pages) to
HCA at 866-668-1214:
For top surgery
HCA requires referral letters from each of the following:
One mental health provider which addresses all of the following:
Confirm the diagnosis of gender dysphoria using current DSM 5
(Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) criteria
Assure the client is a good candidate
Assure the surgery is the next reasonable step in the care
Assure the client has no coexisting behavioral health conditions (substance
abuse problems, or mental health illnesses), which could hinder
participation in gender dysphoria treatment
Assure any coexisting behavioral health condition is adequately managed
The provider managing the hormonal therapy:
Outcome of clients current hormonal therapy
The surgeon performing surgery:
Written surgical consultation

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
295
For bottom surgery
HCA requires referral letters from each of the following:
Two mental health providers which addresses all of the following:
The psychosocial evaluation
Confirm the diagnosis of gender dysphoria using current DSM 5
(Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) criteria
Assure the client is a good candidate
Assure the surgery is the next reasonable step in the care
Assure the client has no coexisting behavioral health conditions (substance
abuse problems, or mental health illnesses), which could hinder
participation in gender dysphoria treatment
Assure any coexisting behavioral health condition is adequately manage
Description of the relationship between the mental health professional and
the client and treatment to date
The surgeon performing surgery:
Written surgical consultation
Clinical justification for surgery
Confirmation that the client is able to comply with the postoperative
requirements
Assurance that all surgical criteria has been met or medical necessity is
established
Copy of the signed Sterilization consent form (HHS-687) with the clients
understanding of the permanent impact on the reproductive system
consistent with the requirements of WAC 182-531-1550
The surgical plan description with listed all planned procedures and
timeline
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
296
Surgeons must indicate in Comments field 30 on HCA’s General Authorization
form (HCA 13-835) the suite of services being requested according to their Core
Provider Agreement contract addendum. See Where can I download HCA
forms?
The provider managing the hormonal therapy:
A statement regarding the client’s adherence to the medical and mental
treatment plan
Outcome of client’s current hormonal therapy
Assurance that all the members of the treatment team will be available to
coordinate or provide postoperative care as needed
Note: If the client fails to complete all of the requirements above, HCA will require
documentation of the clinical decision-making process in the prior authorization
submission in order to review for individual consideration.
• Covered services – HCA covers the following services in Component 4:
Blepharoplasty
Breast reconstruction (male to female)
Cliteroplasty
Colovaginoplasty
Colpectomy
Genital surgery
Genital electrolysis as required as part of the genital surgery
Hysterectomy
Labiaplasty
Laryngoplasty
Mammoplasty with or without chest reconstruction
Metoidioplasty
Orchiectomy
Panniculectomy
Penectomy
Phalloplasty
Placement of testicular prosthesis
Rhinoplasty
Salpingo-oophorectomy
Scrotoplasty
Urethroplasty
Vaginectomy
Vaginoplasty

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
297
• Noncovered services – For purposes of this section, HCA will review on a case-by-case
basis and may pay for the following noncovered services under exception to rule:
Cosmetic procedures and services:
Brow lift
Calf implants
Cheek/malar implants
Chin/nose implants
Collagen injections
Drugs for hair loss or growth
Facial or trunk electrolysis, except for the limited electrolysis
Facial feminization
Face lift
Forehead lift
Hair transplantation
Jaw shortening
Lip reduction
Liposuction
Mastopexy
Neck tightening
Pectoral implants
Reduction thyroid chondroplasty
Removal of redundant skin
Suction-assisted lipoplasty of the waist
Trachea shave
Voice modification surgery
Voice therapy
Note: Requests for any noncovered service listed above are reviewed as an exception to rule
under the provisions of WAC 182-501-0160. The justification included in the surgical plan for
any of the procedures listed may be recognized by HCA as meeting the documentation
requirements of WAC 182-501-0160.
Who can provide gender dysphoria-related
treatment?
Providers must meet the qualifications outlined in Chapter 182-502 WAC.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
298
Medical Necessity Review by
Comagine Health
What is a medical necessity review by Comagine
Health?
HCA contracts with Comagine Health to provide web-based access for reviewing medical
necessity for:
• Outpatient advanced imaging services
• Select surgical procedures
• Outpatient advanced imaging
• Spinal injections, including diagnostic selective nerve root blocks
• Botox injections (OnabotulinumtoxinA) for the treatment of chronic migraines and
chronic tension-type headaches
Comagine Health conducts the review of the request to establish medical necessity, but does not
issue authorizations. Comagine Health forwards its recommendations to HCA for final
authorization determination. The procedure codes that require review by Comagine Health can
be found in HCA’s Physician-related/professional health care services fee schedule.
Note: This process through Comagine Health is for Washington Apple Health
(Medicaid) clients enrolled in fee-for-service only. Authorization requests for
managed care clients will not be authorized.
Who can request a review?
Only the performing provider or facility (site of service) can request the medical necessity
review by Comagine Health. If initiating the request for authorization, the physician must
include the name and billing NPI of the facility where the procedure will be performed. If a
facility is requesting the authorization, the request must include the name and billing NPI of the
physician performing the procedure.
Note: Billing entities such as clearinghouses do not request authorization through
Comagine Health or HCA.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
299
How do I register with Comagine Health?
In order to submit requests to Comagine Health, providers must:
• Register as a provider through www.comagine.org.
• Register as a Washington State Medicaid provider.
• Be familiar with the criteria that will be applied to requests.
Comagine Health offers on-line training and a printable WA Medicaid Training Manuals.
Note: A username and password is needed for Washington State Medicaid even if a provider is
already a registered provider with Washington State Labor and Industries.
Is authorization required for all Washington
Apple Health (Medicaid) clients?
No. Authorization through Comagine Health is required only for Washington Apple Health
clients who are currently eligible and enrolled in fee-for-service as the primary insurance and
Emergency Related Services Only (ERSO) noncitizen program/Alien Medical Program (AMP)
clients.
DO NOT submit a request for a client who has:
• Medicaid Managed Care.
• Another insurance as primary (Third Party Liability or TPL).
• Medicare as the primary insurance.
• No current eligibility.
• Unmet spenddown.
• Detoxification only coverage.
If one of the above applies, HCA will reject the request for authorization
regardless of Comagine Health's medical necessity determination.
For ERSO/AMP clients in the cancer or end stage renal disease (ESRD) program
(WAC 182-507-0120), submit all imaging and surgical requests to Comagine
Health.
When Medicare is the primary payer and denies a service that is an HCA-covered
service with a prior authorization requirement, HCA waives the “prior”
requirement in this circumstance. Submit a request for authorization. Attach the
Explanation of Benefits (EOB) to the request for services denied by Medicare.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
300
Reminder: Check client eligibility before submitting a request! An
HCA Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) eligibility ID card does not guarantee
that a client is currently eligible. To save time, confirm eligibility through
ProviderOne before submitting an authorization request. To learn more about
confirming client eligibility in ProviderOne, go to the ProviderOne Billing and
Resource Guide.
How do I submit a request to Comagine Health?
Requests may be submitted electronically, by fax, or via telephone. Instructions for submitting a
medical necessity review request, including how to use OneHealthPort, are available at
Comagine Health.
Fax or Telephone Option through Comagine Health
Fax and telephone requests are available only to providers who do not have access to a
computer.
Requests initiated by telephone or fax will require supporting documentation to be faxed per the
instructions found at Comagine Health. Once supporting documentation is received, Comagine
Health will open a case in their system by:
• Entering the information.
• Responding to the provider with a Comagine Health reference number.
Once all necessary clinical information is received (either electronically or via fax), Comagine
Health staff will:
• Conduct the medical necessity review.
• Forward a recommendation to HCA.
Comagine Health will process telephone and fax requests during normal business hours. Faxed
requests can be sent at any time and Comagine Health will process them the following business
day.
Comagine Health provides the following toll-free numbers:
• Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) (phone) 888-213-7513
• Washington Apple Health (Medicaid) (fax) 888-213-7516

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
301
What is the Comagine Health reference number
for?
Upon successful submission of a request through iEXCHANGE® or when a request has been
faxed to Comagine Health, a provider will receive a 9-digit Comagine Health reference number
starting with the prefix 913 (e.g. 913-xxx-xxx). The Comagine Health reference number provides
verification that Comagine Health reviewed the request.
A Comagine Health reference number is NOT a billable authorization number.
Providers must not bill for or perform a procedure(s) until a written approval and an HCA-issued
ProviderOne authorization number is received. HCA approves or denies authorization requests
based on recommendations from Comagine Health.
For questions regarding the status of an authorization, need to update an authorization, or have
general questions regarding an authorization, contact HCA at 1-800-562-3022, ext. 52018.
Note: HCA has 15 calendar days from the time Comagine Health receives a
request for authorization to provide a written determination.
When does HCA consider retroactive
authorizations?
HCA considers retroactive authorization when one of the following applies:
• The client’s eligibility is verifiably approved after the date of service, but retroactive to a
date(s) that includes the date that the procedure was performed.
• The primary payer does not pay for the service and payment from Medicaid is being
identified as the primary payer.
Note: Retroactive authorizations must be submitted to Comagine Health within
5 business days for procedures or advanced imaging performed as urgent or
emergency procedures on the same day.
When requesting retroactive authorization for a required procedure, providers must check
authorization requirements for the date of service that the procedure was performed.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
302
What are the authorization requirements for
advanced imaging?
For advanced imaging, providers must complete the appropriate questionnaire form.
Questionnaires for radiology services are available online from Comagine Health and can be
printed out for provider convenience.
Some radiology codes continue to require prior authorization (PA) from HCA, but not from
Comagine Health. See the Physician-related/professional services fee schedule.
Note: The PA requirement is for diagnostics provided as urgent and scheduled.
HCA allows 5 business days to complete authorization for urgent or ordered-the-
same-day procedures when the authorization cannot be completed before the
procedure is performed. This authorization requirement does not apply to
diagnostics done in association with an emergency room visit, an inpatient
hospital setting, or when another payer, including Medicare, is the primary payer.
How does HCA’s hierarchy of evidence protocol
apply?
The criteria in the online Comagine Health questionnaires represent “B” level of evidence under
WAC 182-501-0165. In other words, this represents the clinical/treatment guideline* HCA has
adopted to establish medical necessity and make authorization decisions for these advanced
imaging procedures. “B” level evidence shows the requested service or equipment has some
proven benefit supported by:
• Multiple Type II or III evidence or combinations of Type II, III or IV evidence with
generally consistent findings of effectiveness and safety (A "B" rating cannot be based on
Type IV evidence alone).
• Singular Type II, III, or IV evidence in combination with HCA-recognized:
Clinical guidelines*.
Treatment pathways*.
Other guidelines that use the hierarchy of evidence in establishing the rationale
for existing standards.
If the criteria in the questionnaire are not met, the request will be denied.
*Note: In most circumstances, HCA’s program uses the same criteria and
questionnaires as Labor and Industries for MRIs and CT scans.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
303
What are the authorization requirements for
surgical procedures?
Requests initiated electronically will require supporting documentation to be included with the
electronic submission or faxed per the instructions found at Comagine Health.
Surgical services require HCA authorization regardless of place of service or when performed as:
• Urgent.
• An emergency.
• A scheduled surgery.
If the client is age 20 and younger, prior authorization for the surgical procedure may not be
required. See HCA’s Physician-related/professional services fee schedule to determine if a
procedure is exempt by client's age.
Surgical modifiers
Co-Surgeons, Assistants, Team Surgeries, and other surgical modifiers
When requesting an authorization for any surgical procedure requiring a medical necessity
review by Comagine Health, indicate if the authorization request also includes an assistant
surgeon, a co-surgeon, or a surgical team. For further information, see the Centers for Medicare
and Medicaid’s (CMS) Global surgery booklet or CMS’s Claims processing manual for
physicians/nonphysician practitioners.
When submitting an authorization request for a surgical service that requires additional surgeons,
include the following on the request:
• The appropriate modifier(s)
• If available, each surgeon’s billing NPI
• Clinical justification for an assistant surgeon, co-surgeon, or surgical team
Enter the information above in the Communication box when the case is either of the following:
• Loaded through Comagine Health iEXCHANGE®
• Submitted by fax, on the Request for Surgical Authorization form

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
304
How does HCA’s hierarchy of evidence protocol
apply?
Hierarchy of Evidence (See WAC 182-501-0165)
HCA recognizes the criteria described as “B” level of evidence.
If the request meets medical necessity criteria, the request will be approved.
What criteria will Comagine Health use to
establish medical necessity?
HCA has instructed Comagine Health to use the following surgical procedure criteria to establish
medical necessity:
• Health Technology Clinical Committee (HTCC) determinations reviewed and
implemented by Washington Apple Health
• Labor and Industries (LNI)
• InterQual criteria
If there is an applicable HTCC decision, HCA uses the decision during the medical necessity
review. If there are no HTCC criteria available, applicable criteria from Washington State’s
Labor & Industries (L&I) Medical treatment guidelines (MTG) will be applied. If L&I does not
have available criteria, InterQual criteria will be applied.
Is there a provider appeals process for Comagine
Health?
Yes. If HCA denies authorization as a result of a recommendation from Comagine Health,
Comagine Health offers providers an appeal process. Request an appeal as follows:
• Prepare a written request for appeal to Comagine Health indicating the Comagine Health
reference number (starting with 913…) for which the appeal is requested.
• Fax the request for appeal along with any appropriate clinical notes, laboratory, and
imaging reports to be considered with the appeal to Comagine Health at 888-213-7516.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
305
Note: If the clinical information that is submitted is NEW (information obtained
after the denial was issued), a new review will be initiated by Comagine Health
and a new reference number will be assigned. An appeal will be conducted if the
information submitted was available at the time of the initial review but not
submitted.
Upon receipt of a request for appeal, Comagine Health staff will review the documentation to
determine if the appeal meets the medical necessity criteria. If it is determined that the appeal
request does not meet the medical necessity criteria, the case will be referred to a physician to
make a final determination.
More information about Comagine Health's provider appeal process is available online at
Comagine Health (Washington State Medicaid).
If Comagine Health ultimately recommends the authorization be denied and Washington Apple
Health (Medicaid) agrees, the client has the right to appeal to the Administrative Hearings
Office.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
306
Authorization
(WAC 182-531-0200)
Authorization is HCA’s approval for covered services, equipment, or supplies before the services
are provided to clients, as a precondition for provider reimbursement. Prior authorization (PA),
expedited prior authorization (EPA), and limitation extensions (LE) are forms of
authorization.
Prior authorization (PA)
What is prior authorization (PA)?
Prior authorization (PA) is the process HCA uses to authorize a service before it is provided to a
client. The PA process applies to covered services and is subject to client eligibility and program
limitations. Bariatric surgery is an example of a covered service that requires PA. PA does not
guarantee payment.
For psychiatric inpatient authorizations, see HCA’s Inpatient Hospital Services Billing Guide or
Mental Health Services Billing Guide.
Note: In addition to receiving PA, the client must be on an eligible program. For
example, a client on the Family Planning Only program would not be eligible for
bariatric surgery.
For examples on how to complete a PA request, see HCA’s Billers, providers, and partners
webpage.
Note: HCA reviews requests for payment for noncovered health care services
according to WAC 182-501-0160 as an exception to rule (ETR).
How does HCA determine PA?
HCA reviews PA requests in accordance with WAC 182-501-0165. HCA uses evidence-based
medicine to evaluate each request. HCA considers and evaluates all available clinical
information and credible evidence relevant to the client’s condition. At the time of the request,
the provider responsible for the client’s diagnosis or treatment must submit credible evidence
specifically related to the client’s condition. Within 15 days of receiving the request from the
client’s provider, HCA reviews all evidence submitted and will either:
• Approve the request.
• Deny the request if the requested service is not medically necessary.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
307
• Request the provider to submit additional justifying information within 30 days. When
the additional information is received, HCA will approve or deny the request within 5
business days of the receipt of the additional information. If the additional information is
not received within 30 days, HCA will deny the requested service.
When HCA denies all or part of a request for a covered service or equipment, HCA sends the
client and the provider written notice within 10 business days of the date the information is
received that:
• Includes a statement of the action HCA intends to take.
• Includes the specific factual basis for the intended action.
• Includes references to the specific WAC provision upon which the denial is based.
• Is in sufficient detail to enable the recipient to learn why HCA’s action was taken.
• Is in sufficient detail to determine what additional or different information might be
provided to challenge HCA’s determination.
• Includes the client’s administrative hearing rights.
• Includes an explanation of the circumstances under which the denied service is continued
or reinstated if a hearing is requested.
• Includes example(s) of lesser cost alternatives that permit the affected party to prepare an
appropriate response.
Services requiring PA
(WAC 182-531-0200 (4)-(6))
HCA requires PA for the following:
• Abdominoplasty
• Bariatric surgery
• Eating disorders (diagnosis and treatment for clients age 21 and older)
• Elective surgical procedures (HCA may require a second opinion and/or consultation
before authorizing)
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
308
• Hysterectomies and other surgeries of the uterus – see fee schedule for codes requiring
PA (this policy applies to all ages)
When requesting surgery, also indicate if the request is for assistant or co-
surgeon. For further information, see the Centers for Medicare and
Medicaid’s (CMS) Global surgery booklet or CMS’s Claims processing
manual for physicians/nonphysician practitioners.
• Inpatient hospital stays for acute physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R).
• Mometasone sinus implant
• Oncotype DX
• Osseointegrated/bone conduction hearing devices (for clients age 20 and younger)
• Osteopathic manipulative therapy (in excess of HCA's published limits)
• Molecular pathology tests as specified on HCA’s Physician-related services/health care
professional services fee schedule
• Panniculectomy
• Removal or repair of previously implanted bone conduction hearing devices or cochlear
device for clients age 21 older when medically necessary
• Hematopoietic progenitor cell boost (CPT® code 38243)
• Vagus nerve stimulator insertion
For coverage, vagus nerve stimulator insertion must be performed in an
inpatient or outpatient hospital facility and for reimbursement, providers
must attach the invoice to the claim.
• Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
When requesting IMRT, providers must submit an initial request for treatment planning
(CPT code 77301) to HCA. Once a treatment plan is established, the number of treatment
units needed must be submitted to the existing prior authorization number using the
process below. HCA expedites requests for treatment planning.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
309
To submit additional information to the request for IMRT, use the following instructions:
Use HCA’s ProviderOne PA pend forms submission cover sheet.
Type the 9-digit Reference Number from your letter into the "Authorization
Reference #" field and hit Enter (this will expand the barcode shown).
Click on the "Print Cover Sheet" button; choose "Yes" if you're asked whether
you want to allow the document to print.
Fax the barcode sheet as the FIRST page, (no coversheet) then the supporting
documents to 1-866-668-1214 and the documents will be added to this
authorization.
Submit a new treatment request only when one of the following:
6 months has elapsed since the last request
The treatment plan has changed.
• The following surgical procedure codes require medical necessity review by Comagine
Health:
Procedure Code
Short Description
22899
Spine surgery procedure
23929
Shoulder surgery procedure
24999
Upper arm/elbow surgery
27299
Pelvis/hip joint surgery
27599
Leg surgery procedure
29999
Arthroscopy of joint
When requesting PA for surgical services where co-surgeons, a surgical team, or a surgical
assistant are needed, include all the following:
1. The General Information for Authorization form, 13-835. See Where can I download
HCA forms?
2. One PA request per client
3. One Basic Information form, 13-756 for each surgeon. See Where can I download HCA
forms?
4. All appropriate modifier(s)
5. Indicate in box 30 this is for co-surgeon, surgical team, or surgical assistant
6. Each surgeon’s billing NPI on the appropriate forms

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
310
Documentation requirements for PA or LE
PA Documentation
How do I obtain PA or an
LE?
For all requests for PA or LEs, the following documentation
is required:
• A completed, TYPED General Information for
Authorization form, 13-835. This request form MUST
be the initial page when of the request.
• A completed Fax/Written Request Basic Information
form, 13-756, if there is not a form specific to the
service being requested, and all the documentation is
listed on this form with any other medical justification.
Fax the request to: (866) 668-1214.
See HCA’s Billers, provider, and partners webpage.
See Where can I download HCA forms?
Forms Available to Submit PA Requests
• Botulinum Toxin Provider Questionnaire, 13-003
• Application for Chest Wall Oscillator, 13-841
• Bariatric Surgery Request form, 13-785
• Fax/Written Request Basic Information form, 13-756
• Insomnia Referral Worksheet, 13-850
• Nucala (mepolizumab SC injection), 13-0011
• Oral Enteral Nutrition Worksheet, 13-743
• Out of State Medical Services Request form, 13-787

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
311
Forms Available to Submit PA Requests for Medication
• Acetaminophen Injection, J0131, use Basic Information form, 13-756
• Alglucosidase alfa (lumizyme) 10 mg, J0221, use Basic Information form, 13-756
• Belimumab injection, J0490, use Basic Information form, 13-756
• Botulinum Toxin Provider Questionnaire, use form 13-003
• Cimzia (Certolizumab pegol Inj.), J0717, use CIMZIA J0717 Request form, 13-885
• Ceftaroline fosamil injection, J0712, use Fax/Written Request Basic Information form,
13-756
• Exondys 51 (eteplirsen), use form 13-0012
• Infliximab (Remicade) Injection, J1745, use form 13-897
• Ipilimumab injection, J9228, use Fax/Written Request Basic Information form, 13-756
• IV Iron, use form 13-0013
• Mannitol for inhaler, J7665, use Fax/Written Request Basic Information form, 13-756
• Nucala (mepolizumab SC injection), 13-0011
• Oncotype DX, 81519, use form 13-908
• Opdivo (nivolumab), J9299, use form 13-0010
• Pegloticase injection, J2507, use Fax/Written Request Basic Information form, 13-756
• Perjeta (pertuzumab), J9306, use form 13-916
• Photofrin (Porfimer Sodium Inj.) 75mg, J9600, use Fax/Written Request Basic
Information form, 13-756
• Prolia (Denosumab Inj.), J0897, use Fax/Written Request Basic Information form, 13-
756
• Stelara (Ustekinumab Inj.) J3357, use form 13-898
• Tysabri (Natalizumab Inj.) J2323, use TYSABRI J2323 Request form, 13-832
• Xolair (Omalizumab), J2357, use form 13-852a
See Where can I download HCA forms?
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
312
Requesting prior authorization (PA)
When a procedure’s EPA criteria has not been met or the covered procedure requires PA, providers
must request prior authorization from HCA. Procedures that require PA are listed in the fee
schedule. HCA does not retrospectively authorize any health care services that require PA after they
have been provided except when a client has delayed certification of eligibility.
Online direct data entry into ProviderOne
Providers may submit a prior authorization request by direct data entry into ProviderOne or by
submitting the request in writing (see HCA’s prior authorization webpage for details).
Written or Fax
If providers chose to submit a written or fax PA request, the following must be provided:
• The General Information for Authorization form, HCA 13-835. See Where can I
download HCA forms? This form must be page one of the mailed/faxed request and must
be typed.
• The program form. This form must be attached to the request.
• Charts and justification to support the request for authorization.
Submit written or fax PA requests (with forms and documentation) to:
• By Fax: (866) 668-1214
• By Mail:
Authorization Services Office
PO Box 45535
Olympia, WA 98504-5535
For a list of forms and where to send them, see Documentation requirements for PA or LE. Be
sure to complete all information requested. HCA returns incomplete requests to the provider.
Submission of photos and X-rays for medical and DME PA requests
For submitting photos and X-rays for medical and DME PA requests, use the FastLook™ and
FastAttach™ services provided by Vyne Medical.
Register with Vyne Medical through www.vynemedical.com/.
Contact Vyne Medical at 865-293-4111 with any questions.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
313
When this option is chosen, fax the request to HCA and indicate the MEA# in the NEA field
(box 18) on the PA Request form. There is an associated cost, which will be explained by the
MEA services.
Note: See HCA’s ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide for more information
on requesting authorization.
Limitation extension (LE)
What is a limitation extension (LE)?
A limitation extension (LE) is an authorization of services beyond the designated benefit limit
allowed in Washington Administration Code (WAC) and HCA billing guides.
Note: A request for an LE must be appropriate to the client’s eligibility and/or
program limitations. Not all eligibility groups cover all services.
How do I request an LE authorization?
Some LE authorizations are obtained by using the EPA process. Refer to the EPA criteria list for
criteria. If the EPA process is not applicable, an LE must be requested in writing and receive
HCA approval prior to providing the service.
The written request must state all of the following:
1. The name and ProviderOne Client ID of the client
2. The provider’s name, ProviderOne Client ID, and fax number
3. Additional service(s) requested
4. The primary diagnosis code and CPT code
5. Client-specific clinical justification for additional services

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
314
Expedited prior authorization (EPA)
What is expedited prior authorization (EPA)?
Expedited prior authorization (EPA) is designed to eliminate the need for written authorization.
HCA establishes authorization criteria and identifies the criteria with specific codes, enabling
providers to create an EPA number using those codes.
To bill HCA for diagnostic conditions, procedures and services that meet the EPA criteria on the
following pages, the provider must use the 9-digit EPA number. The first five or six digits of
the EPA number must be 87000 or 870000. The last 3 or 4 digits must be the EPA number
assigned to the diagnostic condition, procedure, or service that meets the EPA criteria (see EPA
criteria list for numbers). Enter the EPA number on the billing form in the authorization number
field, or in the Authorization or Comments section when billing electronically.
Example: The 9-digit authorization number for a client with the following criteria would be
870000421:
Client is age 11 through 55 and is in one of the at-risk groups because the client meets
one of the following:
1) Has terminal complement component deficiencies
2) Has anatomic or functional asplenia
3) Is a microbiologist who is routinely exposed to isolates of Neisseria meningitis
4) Is a freshman entering college who will live in a dormitory
HCA denies claims submitted without a required EPA number.
HCA denies claims submitted without the appropriate diagnosis, procedure code, or service as
indicated by the last three digits of the EPA number.
The billing provider must document in the client’s file how the EPA criteria were met and make
this information available to HCA on request. If HCA determines the documentation does not
support the criteria being met, the claim will be denied.
Note: HCA requires written/fax PA when there is no option to create an EPA
number.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
315
EPA guidelines
Documentation
The provider must verify medical necessity for the EPA number submitted. The client’s medical
record documentation must support the medical necessity and be available upon HCA’s request.
If HCA determines the documentation does not support the EPA criteria requirements, the claim
will be denied.
Note: For enteral nutrition EPA requirements, refer to the Prior Authorization
section in HCA’s Enteral Nutrition Billing Guide.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
316
EPA criteria list
A complete EPA number is 9 digits. The first five or six digits of the EPA number must be
87000 or 870000. The last 3 or 4 digits must be the EPA number assigned to the diagnostic
condition, procedure, or service that meets the EPA criteria. If the client does not meet the EPA
criteria, prior authorization (PA) is required (see Prior authorization).
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870000051
Scanning
computerized
ophthalmic
diagnostic
imaging, posterior
segment, with
interpretation and
report, unilateral
or bilateral,
retina.
CPT code:
92134
Limit to 12 per calendar year.
The client must meet both of the following
criteria:
• The client is undergoing active treatment
(intraocular injections, laser or incisional
surgery) for conditions such as cystoid
macular edema (CME); choroidal
neovascular membrane (CNVM) from
any source (active macular degeneration
(AMD) in particular); diabetic retinopathy
or macular edema; retinal vascular
occlusions; epiretinal membrane;
vitromacular traction; macular holes;
unstable glaucoma; multiple sclerosis
with visual symptoms; optic neuritis;
optic disc drusen; optic atrophy; eye
toxicity or side-effects related to
medication use; papilledema or
pseudopapilledema
• There is documentation in the client’s
record describing the medical
circumstance and explaining the need for
more frequent services.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
317
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870000241
Reduction
Mammoplasties/
Mastectomy for
Gynecomastia
CPT codes:
19318, 19300
Dx codes: N62,
N64.9, or L13.9
A female with a diagnosis for hypertrophy
of the breast with:
1) Photographs in client's chart
2) Documented medical necessity including:
a) Back, neck, and/or shoulder pain for a
minimum of 1 year, directly
attributable to macromastia
b) Conservative treatment not effective
3) Abnormally large breasts in relation to
body size with shoulder grooves
4) Within 20% of ideal body weight, and
5) Verification of minimum removal of 500
grams of tissue from each breast
870000242
Reduction
Mammoplasties/
Mastectomy for
Gynecomastia
CPT codes:
19318, 19300
Dx codes:
N62, N64.9, or
L13.9
A male with a diagnosis for gynecomastia
with:
1) Pictures in clients' chart
2) Persistent tenderness and pain
3) If history of drug or alcohol abuse, must
have abstained from drug or alcohol use
for no less than 1 year
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
318
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870000421
Meningococcal
Vaccine
CPT: 90734
(Conjugate
Vaccine –
Menactra®)
Client is age 19 through 55 and is in one of
the at-risk groups because the client meets
one of the following:
1. Not routinely recommended for ages 19-
21, but may be administered as catch-up
vaccination for those who have not
received a dose after their 16
th
birthday
2. Has persistent complement deficiencies
3. Has anatomic or functional asplenia
4. Are at risk during a community outbreak
attributable to a vaccine serogroup
5. Infected with human immunodeficiency
virus (HIV), if another indication for
vaccination exists
6. Is a microbiologist who is routinely
exposed to isolates of N. meningitidis
7. Is a freshman entering college who will
live in a dormitory
870000422
Placement of
Cardiac Drug
Eluting or Bare
Metal Stent and
Device
HCPCS codes:
C1874, C1875,
C9601, C9602,
C9603, C9604,
C9605, C9606,
C9607, and
C9608
(Institutional
only)
Bare Metal –
92928, 92929
Either drug eluting or bare metal cardiac
stents are covered when cardiac stents are
indicated for treatment when medically
necessary.
For patients being treated for stable angina,
cardiac stents are a covered benefit with the
following conditions:
1. Angina refractory to optimal medical
therapy
2. Objective evidence of myocardial
ischemia
870000423
Unilateral
cochlear implant
for clients age 20
and younger
CPT: 69930
HCA pays for cochlear implantation only
when the products come from a vendor
with a Core Provider Agreement with
HCA, there are no other contraindications
to surgery, and
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
319
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
Note: See EPA #870001365 for criteria
for bilateral cochlear implantation.
One of the following must be true:
1) Unilateral cochlear implantation for
clients age 18 through 20 with post-
lingual hearing loss and clients (12
months-17 years old) with prelingual
hearing loss when all of the following
are true:
a) The client has a diagnosis of
profound to severe bilateral,
sensorineural hearing loss
b) The client has stimulable auditory
nerves but has limited benefit from
appropriately fitted hearing aids
(e.g., fail to meet age-appropriate
auditory milestones in the best-
aided condition for young children,
or score of less than ten or equal to
40% correct in the best-aided
condition on recorded open-set
sentence recognition tests
c) The client has the cognitive ability
to use auditory clues
d) The client is willing to undergo an
extensive rehabilitation program
e) There is an accessible cochlear
lumen that is structurally suitable
for cochlear implantation
f) The client does not have lesions in
the auditory nerve and/or acoustic
areas of the central nervous system

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
320
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
Note: See HCA’s Hearing Hardware
Billing Guide for replacement parts for
cochlear implants.
870000425
Hyperbaric
Oxygen Therapy
CPT code:
99183
HCPCS code:
G0277
(Institutional
only)
All of the following must be true:
• Patient has type 1 or type 2 diabetes and
has a lower extremity wound that is due
to diabetes
• Patient has a wound classified as Wagner
grade 3 or higher
• Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is being done
in combination with conventional
diabetic wound care
870000610
Visual
Exam/Refraction
(Optometrists/
Ophthalmologists
only)
CPT codes:
92014-92015
Eye Exam/Refraction - Due to loss or
breakage: For adults within 2 years of last
exam when no medical indication exists and
both of the following are documented in the
client’s record:
1) Glasses are broken or lost or contacts that
are lost or damaged
2) Last exam was at least 18 months ago
Note: EPA # is not required when billing for
children or clients with developmental
disabilities.
870000630
Blepharoplasties
CPT codes:
15822, 15823,
and 67901,
67902, 67903,
67904,
67906, 67908
Blepharoplasty for noncosmetic reasons when
both of the following are true:
1) The excess upper eyelid skin impairs the
vision by blocking the superior visual
field
2) On a central visual field test, the vision is
blocked to within 10 degrees of central
fixation
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
321
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870000631
Strabismus
Surgery
CPT codes:
67311-67340
Dx Code:
H53.2
Strabismus surgery for clients 18 years of age
and older when both of the following are
true:
1) The client has a strabismus-related double
vision (diplopia) and
2) It is not done for cosmetic reasons
870001300
Injection,
Romiplostim, 10
Microgram
HCPCS code:
J2796
All of the following must apply:
1) Documented diagnosis of Idiopathic
Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
2) Patient must be at least 18 years of age
3) Inadequate response (reduction in
bleeding) to one of the following:
a. Immunoglobulin treatment
b. Corticosteroid treatment
c. Splenectomy
870001302
Hysterectomies
for Cancer
CPT codes:
58150, 58152,
58180, 58200,
58210, 58260,
58262, 58263,
58267, 58270,
58275, 58280,
58285, 58290,
58291, 58292,
58293, 58294,
58541, 58542,
58543, 58544,
58550, 58552,
58553, 58554,
58570, 58571,
58572, 58573
Client must have a diagnosis of cancer
requiring a hysterectomy as part of the
treatment plan.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
322
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001303
Hysterectomies -
Complications
and Trauma
CPT codes:
58150, 58152,
58180, 58200,
58260, 58262,
58263, 58267,
58270, 58275,
58280, 58285,
58290, 58291,
58292, 58293,
58294, 58541,
58542, 58543,
58544, 58545,
58546, 58550,
58552, 58553,
58554, 58570,
58571, 58572,
58573,
Client must have a complication related to a
procedure or trauma (e.g., postprocedure
complications; postpartum hemorrhaging
requiring a hysterectomy; trauma requiring a
hysterectomy)
870001312
Professional or
diagnostic
continuous
glucose
monitoring
(CGM)
CPT codes:
95250, 95251
Allowed for the in-home use of professional
or diagnostic CGM for a 72-hour period.
The client must:
• Have diabetes mellitus (DM).
• Be insulin dependent.
The CGM must be:
• Ordered by a provider.
• Provided by an FDA-approved CGM
device.
Limit: 2 monitoring periods of 72 hours each,
per client, every 12 months.
870001321
Orencia
(abatacept)
HCPCs code:
J0129
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis when
prescribed by a rheumatologist in patients who
have tried and failed one or more DMARDs.
Dose is subcutaneous injection once weekly.
IV dosing is up to 1000mg dose to start,
repeated at week 2 and 4, then maintenance up
to 1000mg every 4 weeks.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
323
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001325
Targeted TB
testing with
interferon-gamma
release assays
CPT codes:
86480, 86481
Targeted TB testing with interferon-gamma
release assays may be considered medically
necessary for clients 5 years of age and older
for any of the following conditions:
• History of positive tuberculin skin test or
previous treatment for TB disease
• History of vaccination with BCG (Bacille
Calmette-Guerin)
• Recent immigrants (within 5 years) from
countries that have a high prevalence of
tuberculosis
• Residents and employees of high-risk
congregate settings (homeless shelters,
correctional facilities, substance abuse
treatment facilities)
• Clients with an abnormal CXR consistent
with old or active TB
• Clients undergoing evaluation or receiving
TNF alpha antagonist treatment for
rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or
inflammatory bowel disease
• Exposure less than 2 years before the
evaluation
AND
• Client in agreement to remain in
compliance with treatment for latent
tuberculosis infection if found to have a
positive test.
The tuberculin skin test is the preferred
method of testing for children under the age of
5.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
324
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001342
Alloderm
CPT code:
Q4116
All of the following must be met:
• It is medically necessary.
• The client has a diagnosis of breast cancer.
• The servicing provider is either a general
surgeon or a plastic surgeon.
870001344
Noninvasive
prenatal diagnosis
of fetal
aneuploidy
(NIPT)
CPT code:
81507 and
81420
HCA considers NIPT for serum marker
screening for fetal aneuploidy to be medically
necessary in women with high-risk singleton
pregnancies, who have had genetic counseling,
when one or more of the following are met:
• Pregnant woman is age 35 years or older at
the time of delivery
• History of a prior pregnancy with a trisomy
or aneuploidy
• Family history of aneuploidy (first degree
relatives or multiple generations affected)
• Positive first or second trimester standard
biomarker screening test for aneuploidy,
including sequential, or integrated screen,
or a positive quadruple screen
• Parental balanced Robertsonian
translocation with increased risk for fetal
T13 or T21
• Findings indicating an increased risk of
aneuploidy
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
325
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001350
Transient
elastograph
CPT code:
91200
All of the following must be met:
• Baseline detectable HCV RNA viral load
• Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and
BMI < 30
• Both APRI (AST to platelet ratio index)
and FibroSURE™ tests have been
completed with one of the following
results:
FibroSURE™ < 0.49 and APRI > 1.5
FibroSURE™> 0.49 and APRI < 1.5
870001351
Interoperative or
postoperative
pain control using
a spinal injection
or infusion
CPT codes:
62320 and
62327
These CPT codes may be billed with this EPA
when they are done interoperatively or
postoperatively for pain control.
870001362
Low dose CT for
lung cancer
screen
HCPCS code:
G0297
The client must meet all of the following
criteria:
• Is age 55-80
• Has a history of smoking 30 packs a year
and either of the following:
Still smokes
Has quit smoking in the last 15 years
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
326
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001363
Bone mineral
density testing
with dual x-ray
absorptiometry
(DXA) - initial
screening
CPT codes:
77080 and
77081
Bone mineral density testing with dual x-ray
absorptiometry (DXA) is a covered benefit
with the following conditions:
Asymptomatic women
Either of the following:
• Women 65 years of age and older
• Women 64 years of age and younger with
equivalent 10-year fracture risk to women
age 65 as calculated by FRAX (Fracture
Risk Assessment) tool or other validated
scoring tool
Men or women
Either of the following:
• Long term glucocorticoids (i.e. current or
past exposure to glucocorticoids for more
than 3 months)
• Androgen deprivation or other conditions
known to be associated with low bone
mass

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
327
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001364
Bone mineral
density testing
with dual x-ray
absorptiometry
(DXA) - repeat
test
CPT codes:
77080 and
77081
Repeat bone mineral density testing with dual
x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is a covered
benefit when the client meets one of the
following:
• T-score** > -1.5, 15 years to next
screening test
• T-score -1.5 to -1.99, 5 years to next
screening test
• T-score ≤ -2.0, 1 year to next screening
test
• Use of medication associated with low
bone mass or presence of a condition
known to be associated with low bone
mass
870001365
Bilateral cochlear
implants
See EPA
#870000423 for
unilateral
cochlear implants
CPT: 69930
Modifier: 50
The client must:
• Be age 12 months through 20 years old
• Have bilateral severe to profound
sensorineural hearing loss.
• Be limited or no benefit from hearing aids
• Have cognitive ability and willingness to
participate in an extensive auditory
rehabilitation program
• Have freedom from middle ear infection,
an accessible cochlear lumen that is
structurally suited to implantation, and
freedom from lesions in the auditory nerve
and acoustic areas of the central nervous
system
• Have no other contraindications for surgery
• Use device in accordance with the FDA
approved labeling
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
328
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001368
Testosterone
testing
CPT: 84402,
84403, 84410
Covered:
• For males age 19 and older when at least
one of the following conditions are met:
Suspected or known primary
hypogonadism
Suspected or known secondary
hypogonadism with organ causes such
as:
Pituitary disorder
Suprasellar tumor
Medications suspected to cause
hypogonadism
HIV with weight loss
Osteoporosis
Monitoring of testosterone therapy
• As part of the treatment for gender
dysphoria when a client has a diagnosis of
gender dysphoria and is being treated with
one of the following:
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone suppression therapy
870001369
Professional
services provided
to an MCO client
during the BHO
authorized
admission
See HCA’s
Mental Health
Services
Billing Guide
All of the following conditions must be met:
• The client’s inpatient hospital (POS 21, 51)
admission was authorized by the BHO.
• The client’s primary diagnosis is in the
psychiatric range.
• The services are provided by a psychiatrist,
psychologist, or psychiatric ARNP.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
329
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001371
Orthoptic/pleoptic
training
CPT: 97110
Dx: H50.411
or H50.412
with
secondary dx
of TBI
Documented diagnosis of convergence
insufficiency, convergence excess, or
binocular dysfunction, with a secondary
diagnosis of traumatic brain injury (TBI)
870001372
Orthoptic/pleoptic
training
CPT: 97112
Dx: H51.12
with
secondary dx
of TBI
Documented diagnosis of convergence
insufficiency, convergence excess, or
binocular dysfunction, with a secondary
diagnosis of traumatic brain injury (TBI)
870001373
Orthoptic/pleoptic
training
CPT: 97530
Dx: H53.30
with
secondary dx
of TBI
Documented diagnosis of convergence
insufficiency, convergence excess, or
binocular dysfunction with a secondary
diagnosis of traumatic brain injury (TBI)
870001374
Intensity
modulated
radiation therapy
(IMRT)
CPT: 77301,
77338, 77370,
G6015, G6016
• Any cancer that would require radiation to
focus on the head/neck/chest/abdomen
• Document in the clinical notes which
critical structure is being spared
870001375
Early elective
delivery or
natural delivery
prior to 39 weeks
gestation
CPT: 59400,
59409,
59410,
59510,
59514,
59515,
59610,
59612,
59614,
59618,
59620, 59622
Client is under 39 weeks gestation and the
mother or fetus has a diagnosis listed in the
Joint Commission’s current table of
Conditions possibly justifying elective
delivery prior to 39 weeks gestation, or mother
delivers naturally
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
330
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001378
Elective delivery
or natural
delivery at or
over 39 weeks
gestation
CPT: 59400,
59409,
59410,
59510,
59514,
59515,
59610,
59612,
59614,
59618,
59620, 59622
Client is 39 weeks gestation or over 39 weeks
gestation
870001381
HPV genotyping
CPT: 87625
For females age 30 and older, when the
following conditions are met:
• Pap negative and HPV positive
• Pap no EC/TZ and HPV positive
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
331
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001382
Tympanostomy
tubes
69433 or
69436
The client is age 16 or younger and is
diagnosed with one of the following:
• Acute otitis media (AOM) and the client
has either of the following:
Complications, is
immunocompromised, or is at risk for
infection
Both of the following are true:
Has had 3 episodes of AOM in the
last 6 months with one occurring in
the last 6 months
Has the presence of effusion at the
time of assessment for surgical
candidacy
• Otitis media with effusion (OME) and
the client has one of the following:
An effusion for 3 months or greater and
there is documented hearing loss
A disproportionate risk from the effects
of hearing loss, such as those with
speech delay, underlying sensory-neuro
hearing loss or cognitive disorders
870001400
Surgical
consultation
related to
transgender
surgery
Dx:
F64.0, F64.1,
F64.2 and
F64.9
All of the following must be met:
• Client has gender dysphoria diagnosis
• Appointment is done as a consultation to
discuss possible transgender related surgery
including hair removal by electrolysis or
laser
870001386
Gene expression
profile (breast
cancer) Oncotype
Dx
81519
Breast cancer gene expression testing is
covered when all of the following conditions
are met:

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
332
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001420
Gene expression
profile (breast
cancer)
Endopredict
81599
• Stage 1 or 2 cancer
• Estrogen receptor positive and Human
Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2
(HER2-NEU) negative
• Lymph node negative or 1-3 lymph node(s)
positive
• The test result will help the patient and
provider make decisions about
chemotherapy or hormone therapy
870001545
Gene expression
profile (breast
cancer) Prosigna
81520
870001546
Gene expression
profile (breast
cancer)
MammaPrint
81521
870001547
Gene expression
profile (breast
cancer)
Mammostrat
81599
Breast cancer gene expression testing is
covered when all of the following conditions
are met:
• Stage 1 or 2 cancer
• The test result will help the patient make
decisions about hormone therapy
870001548
Gene expression
profile (breast
cancer) Breast
Cancer Index
81479
870001549
Gene expression
profile (prostate
cancer)
Oncotype Dx
prostate cancer
assay
0047U
Prostate cancer gene expression is covered
when the following conditions are met:
• Low and favorable intermediate risk
disease as defined by the National
Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN)
• Test result will help inform treatment
decision between definitive therapy
(surgery or radiation) and conservative
management
870001550
Gene expression
profile (prostate
cancer) Prolaris
81541
870001551
Gene expression
profile (prostate
cancer)
Decipher prostate
cancer classifier
assay
81479
Is covered if both of the following are true:
• The client is post radical prostatectomy.
• The test result will help the client decide
between active surveillance and adjuvant
radiotherapy.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
333
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001419
Teledermatology
CPT: 99241-
99243, 99251-
99253- 99211-
99214, 99231-
99233.
All of the following must be met:
• The teledermatology is associated with an
office visit between the eligible client and
the referring health care provider.
• The teledermatology is asynchronous
telemedicine and the service results in a
documented care plan, which is
communicated back to the referring
provider.
• The transmission of protected health
information is HIPPA compliant.
• Written informed consent is obtained from
the client that store and forward technology
will be used and who the consulting
provider is.
•
GQ modifier required.
870001422
Magnetic
Resonance
Imaging (MRI) of
the sinus for
rhinosinusitis
CPT: 70540,
70542, and
70543
Criteria for sinus MRI listed below AND
client is younger than age 21 OR pregnant:
•
Red Flags; OR
• Two of the listed persistent symptoms
longer than 12 weeks AND failure of
medical therapy; OR
• Surgical planning.
HCA does not consider repeat scanning to be
medically necessary except for Red Flags or
Surgical Planning.
870001553
Magnetic
Resonance
Imaging (MRI)
orbit
CPT: 70540,
70542, and
70543
Evaluation of one of the following:
• Suspected or known infection
• A mass or other structural abnormality
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
334
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001423
Sinus Computed
Tomography
(CT) for
rhinosinusitis
CPT: 70450,
70460, 70470,
70486, 70487,
and 70488
• Red Flags OR
• Two of the listed persistent symptoms
longer than 12 weeks AND failure of
medical therapy; OR
• Surgical planning.
Repeat scanning is not covered except for Red
Flags or surgical planning.
870001424
Caregiver/
Maternal
depression
screening
CPT: 96160,
96161
• Caregiver/maternal depression screening is
required at well-child checkups for
caregivers/mothers of infants up to age 6
months. Use procedure code 96161with
EPA.
• Caregiver/maternal depression screening
completed by the caregiver’s provider
during the 6 months postpartum and billed
under the caregiver’s ProviderOne ID
number. Use procedure code 96160 with
EPA.
870001427
Initial psychiatric
collaborative care
management
CPT: 99492,
G0512
To be used to initiate new episode of care when t
less than a 6 month lapse in services:
• Provider has identified a need for a new
episode of care for an eligible condition
• There has been less than 6 months since
the client has received any CoCM services
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
335
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001428
Subsequent
psychiatric
collaborative care
management
CPT: 99493,
G0512
To be used to continue the episode of care
after 6
th
month when:
• Identified need to continue CoCM episode
of care past initial 6 months
• Client continues to improve as evidenced
by improved score from a validated
clinical rating scale
• Targeted goals have not been met
• Patient continues to actively participate in
care
870001537
Enhanced
medication for
opioid use
disorder provider
rate
CPT: 99201,
99202, 99203,
99204, 99205,
99211, 99212,
99213, 99214,
99215, 99251,
99252, 99253,
99254, 99255
All of the following criteria must apply:
The client must have an opioid use disorder
diagnosis code listed on the claim.
The provider meets all of the following
criteria:
• Has a DATA 2000 Waiver.
• Currently uses the waiver to prescribe
medication for opioid use disorder to
clients with opioid use disorder.
• Bills for treating a client with a qualifying
diagnosis for opioid use disorder.
• Provides opioid-related counseling during
the visit.
*HCA reimburses the enhancement once per
client, per day.
870001554
Vagus nerve
stimulation
(VNS)
61880, 61885,
61886, 61888,
64568, 64569,
64570
For management of epileptic seizures for
clients that meet both of the following criteria:
• Age 12 and older
• With a medically refractory seizure
disorder
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
336
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001603
BRCA Genetic
Testing
81162, 81163,
81164, 81165,
81166, 81167,
81212, 81215,
81216, 81217
Client must be one of the following:
• Of any age with a known pathogenic gene
variant in a cancer susceptibility gene or
with a blood relative with a known gene
variant in a cancer susceptibility gene
• Diagnosed at any age with any of the
following:
Ovarian cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Metastatic prostate cancer
Breast cancer or a high grade (Gleason
score > 7) prostate cancer and of
Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry
• With a breast cancer diagnosis meeting any
of the following:
Breast cancer diagnosed < age 50
Triple negative breast cancer diagnosed
age < age 60
Two breast cancer primaries
Breast cancer at any age and both of
the following:
One or more close blood relatives*
with any of the following:
Breast cancer < age 50
Male breast cancer
Pancreatic cancer
High grade or metastatic
prostate cancer
Two or more close blood relatives*
with breast cancer at any age
*First, second, and third degree relatives
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
337
EPA
Number-
Service Name CPT/HCPCS/Dx Criteria
870001609
Corneal
topography
92025
Limited to two tests per calendar year.
Client has one of the following diagnoses:
• Central corneal ulcer
• Corneal dystrophy, bullous keratopathy,
and complications of transplanted cornea
• Diagnosing and monitoring disease
progression in keratoconus or Terrien's
marginal degeneration
• Difficult fitting of contact lens
• Post-traumatic corneal scarring
• Pre- and post-penetrating keratoplasty and
post kerato-refractive surgery for irregular
astigmatism
• Pterygium or pseudo pterygium

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
338
Modifiers
(WAC 182-531-1850(10) and (11))
CPT/HCPCS
Italics indicate additional HCA language not found in CPT.
22: Unusual Procedural Services: When the service(s) provided is greater than that usually
required for the listed procedure, it may be identified by adding modifier 22 to the usual
procedure code number. This modifier is not to be used to report procedure(s)
complicated by adhesion formation, scarring, and/or alteration of normal landmarks due
to late effects of prior surgery, irradiation, infection, very low weight or trauma.
For informational purposes only; no extra allowance is allowed.
23: Unusual Anesthesia: For informational purposes only; no extra allowance is allowed.
24: Unrelated Evaluation and Management (E/M) by the Same Physician During a
Postoperative Period: The physician may need to indicate that an evaluation and
management service was performed during a postoperative period for a reason(s)
unrelated to the original procedure. This circumstance may be reported by adding the
modifier 24 to the appropriate level of E/M service. Payment for the E/M service during
postoperative period is made when the reason for the E/M service is unrelated to original
procedure.
25: Significant, Separately Identifiable Evaluation and Management Service by the
Same Physician on the Day of a Procedure: The physician may need to indicate that on
the day a procedure or service identified by a CPT® code was performed, the client’s
condition required a significant, separately identifiable E/M service above and beyond the
usual preoperative and postoperative care associated with the procedure that was
performed. This circumstance may be reported by adding the modifier 25 to the
appropriate level of E/M service. Payment for the E/M service is the billed charge or
HCA’s maximum allowable, whichever is less.
26: Professional Component: Certain procedures are a combination of professional and
technical components. When only the professional component is reported, the service is
identified by adding modifier 26 to the procedure code.
TC: Technical Component: Certain procedures are a combination of professional and
technical components. When only the technical component is reported, the service is
identified by adding modifier TC to the procedure code. In order to receive payment, a
contract with HCA is required if services are performed in a hospital setting.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
339
32: Mandated Services: For informational purposes only; no extra allowance is allowed.
47: Anesthesia by Surgeon: Not covered by HCA.
50: Bilateral Procedure: Unless otherwise identified in the listing, bilateral procedures that
are performed at the same operative session should be identified by adding this modifier
to the appropriate five-digit code describing the first procedure.
For surgical procedures typically performed on both sides of the body, payment for the
E/M service is the billed charge or HCA’s maximum allowable, whichever is less.
For surgical procedures that are typically performed on one side of the body, but
performed bilaterally in a specific case, payment is 150% of the global surgery fee for the
procedure.
51: Multiple Procedures: When multiple surgeries are performed at the same operative
session, total payment is equal to the sum of the following: 100% of the highest value
procedure; 50% of the global fee for each of the second through fifth procedures. More
than five procedures require submission of documentation and individual review to
determine the payment amount.
52: Reduced Services: Under certain circumstances, a service or procedure is partially
reduced at the physician’s discretion. Under these circumstances, the service provided
can be identified by its usual procedure number and the addition of the modifier 52,
signifying that the service is reduced. This provides a means of reporting reduced
services without disturbing the identification of the basic service. Using this modifier
does not reduce the allowance to the provider. Note: Modifier 52 may be used with
computerized tomography procedure codes for a limited study or a follow-up study.
53: Discontinued Procedure: Under certain circumstances, the physician may elect to
terminate a surgical or diagnostic procedure. Due to extenuating circumstances, or those
that threaten the well-being of the patient, it may be necessary to indicate that a surgical
or diagnostic procedure was started but discontinued.
Use of modifier 53 is allowed for all surgical procedures. Modifier 53 is a payment
modifier when used with CPT code 45378 and HCPCS codes G0105 and G0121 only. It
is information only for all other surgical procedures.
54, 55, 56 – Providers providing less than the global surgical package should use modifiers
54, 55, & 56. These modifiers are designed to ensure that the sum of all allowances for all
practitioners who furnished parts of the services included in a global surgery fee do not exceed
the total amount of the payment that would have been paid to a single practitioner under the
global fee for the procedure. The payment policy pays each physician directly for that portion of
the global surgery services provided to the client. The breakdown is as follows:

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
340
54: Surgical Care Only: When one physician performs a surgical procedure and another
provides preoperative and/or postoperative management, surgical services may be
identified by adding modifier 54 to the usual procedure number. A specific percentage of
the global surgical payment in the fee schedule is made for the surgical procedure only.
55: Postoperative Management Only: When one physician performs the postoperative
management and another physician has performed the surgical procedure, the
postoperative component may be identified by adding the modifier 55 to the usual
procedure number. A specific percentage of the global surgical payment in the fee
schedule is made for the surgical procedure only.
56: Preoperative Management Only: When one physician performs the preoperative care
and evaluation and another physician performs the surgical procedure, the preoperative
component may be identified by adding the modifier 56 to the usual procedure number. A
specific percentage of the global surgical payment in the fee schedule is made for the
surgical procedure only.
57: Decision for Surgery: An evaluation and management service that resulted in the initial
decision to perform the surgery may be identified by adding modifier 57 to the
appropriate level of E/M service.
58: Staged or Related Procedure or Service by the Same Physician During the
Postoperative Period: The physician may need to indicate that the performance of a
procedure or service during the postoperative period was: a) planned prospectively at the
time of the original procedure (staged); b) more extensive than the original procedure; or
c) for therapy following a diagnostic surgical procedure. This circumstance may be
reported by adding the modifier 58 to the staged or related procedure. Note: This
modifier is not used to report the treatment of a problem that requires a return to the
operating room. See modifier 78.
59: Distinct Procedural Service: Modifier 59 should be used only if no other more
specific modifier is appropriate. Effective January 1, 2015, use modifiers XE, XS,
XP, and XU in lieu of modifier 59 whenever possible. These modifiers were developed
by CMS to provide greater reporting specificity in situations where modifier 59 was
previously reported. The physician must indicate that a procedure or service was distinct
or separate from other services performed on the same day. This may represent a different
session or patient encounter, different procedure or surgery, different site, separate lesion,
or separate injury (or area of surgery in extensive injuries).
62: Two Surgeons: Under certain circumstances, the skills of two surgeons (usually with
different skills) may be required in the management of a specific surgical procedure. Under
such circumstances, separate services may be identified by adding modifier 62 to the
procedure code used by each surgeon for reporting his/her services. Payment for this
modifier is 125% of the global surgical fee in the fee schedule. The payment is divided
equally between the two surgeons. Clinical justification must be submitted with the claim.
No payment is made for an assistant surgeon.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
341
66: Team surgery: For informational purposes only; no extra allowance is allowed.
76: Repeat Procedure by Same Physician: The physician may need to indicate that a procedure
or service was repeated. This may be reported by adding the modifier 76 to the repeated
service.
77: Repeat Procedure by Another Physician: For informational purposes only; no extra
allowance is allowed.
78: Return to the Operating Room for a Related Procedure During the Postoperative
Period: The physician may need to indicate that another procedure was performed during the
postoperative period of the initial procedure. When this subsequent procedure is related to the
first, and requires the use of the operating room, it may be reported by adding the modifier 78
to the related procedure. When multiple procedures are performed, use modifier 78 on
EACH detail line. Payment for these procedures is the percentage of the global package for
the intra-operative services. Assistant surgeons and anesthesiologists must use modifier 99 to
indicate an additional operating room procedure.
79: Unrelated Procedure or Service by the Same Physician During the Postoperative
Period: The physician may need to indicate that the performance of a procedure or service
during the postoperative period was unrelated to the original procedure. This circumstance
may be reported by using the modifier 79.
80: Assistant Surgeon: Surgical assistant and/or physician assistant services must be
identified by adding modifier 80 to the usual procedure code(s).
81: Minimum Assistant Surgeon: Minimum surgical assistant services are identified by adding
the modifier 81 to the usual procedure number. Payment is 20% of the maximum allowance.
82: Assistant Surgeon (When Qualified Resident Surgeon Not Available): The unavailability
of a qualified resident surgeon is a prerequisite for use of modifier 82 appended to the usual
procedure code number(s). Payment is 20% of the maximum allowance.
90: Reference (Outside) Laboratory: When laboratory procedures are performed by a lab other
than the referring lab, the procedure must be identified by adding modifier 90 to the
procedure code. The reference lab NPI must be entered in the Rendering (Performing)
Provider section on the electronic professional claim. The reference lab must be CLIA-
certified.
91: Repeat Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory Test performed on the same day to obtain
subsequent report test value(s). Modifier 91 must be used when repeat tests are performed
on the same day, by the same provider to obtain reportable test values with separate
specimens taken at different times, only when it is necessary to obtain multiple results in
the course of treatment. When billing for a repeat test, use modifier 91 with the
appropriate procedure code.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
342
99: Multiple Modifiers: The ProviderOne system can read up to four modifiers on a
professional transaction. Add modifier 99 only if there are more than four modifiers to be
added to the claim line. If there are four or fewer modifiers on a claim line, do not add
modifier 99.
AS: Physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist services for assistant at
surgery.
CG Policy criteria applied
FP Family Planning: Used to identify family planning services. HCA requires this modifier
with some procedure codes for proper payment.
GB Claim being resubmitted for payment because it is no longer under a global payment
demonstration
HA Child/Adolescent program
LT Left Side: Used to identify procedures performed on the left side of the body. HCA
requires this modifier with some procedure codes for proper payment.
QP Documentation is on file showing that the lab test(s) was ordered individually or
ordered as a CPT recognized panel other than automated profile codes. This
modifier is now used FOR INFORMATION ONLY. Internal control payment
methodology for automated multi-channel test is applied. This modifier is not appropriate
to use when billing for repeat tests or to indicate not as a panel.
Q6 Physician Services: Services furnished by a locum tenens physician. For informational
purposes only; no extra allowance is allowed.
RT Right Side: Used to identify procedures performed on the right side of the body. HCA
requires this modifier with some procedure codes for proper payment.
SL State-Supplied Vaccine: This modifier must be used with procedure codes for
immunization materials obtained from the Department of Health (DOH).
ST Related to Trauma or Injury
TC: Technical Component: Certain procedures are a combination of professional and
technical components. When only the technical component is reported, the service is
identified by adding modifier TC to the procedure code. In order to receive payment, a
contract with HCA is required if services are performed in a hospital setting.
TG Complex/high level of care.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
343
TH Obstetrical treatment/services, prenatal or postpartum: Use this modifier for
unbundling maternity care for 1-3 visits. See Billing with modifiers for maternity care.
TJ Child/Adolescent Program: To be used for enhancement payment for foster care
children screening exams.
TS Follow-up service: To be used with procedures and for selected Applied Behavior
Analysis (ABA) services (see HCA’s Applied Behavioral Analysis (ABA) Billing
Guide).
UA Medicaid Care Lev 10 State Def.
UN Two patients served: To be used with CPT code R0075.
UP Three patients served: To be used with CPT code R0075.
UQ Four patients served: To be used with CPT code R0075.
UR Five patients served: To be used with CPT code R0075.
US Six or more patients served: To be used with CPT code R0075.
Use the following modifiers which were developed by CMS to provide greater reporting
specificity in situations where modifier 59 was previously reported. Use these modifiers in lieu
of modifier 59 whenever possible:
XE Separate encounter: A service that is distinct because it occurred during a separate
encounter. This modifier is used only to describe separate encounters on the same date
of service.
XS Separate structure: A service that is distinct because it was performed on a separate
organ/structure.
XP Separate practitioner: A service that is distinct because it was performed by a
different practitioner.
XU Unusual non-overlapping service: A service that is distinct because it does not
overlap usual components of the main service.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
344
Anesthesia
AA Anesthesia services personally furnished by an anesthesiologist. This includes services
provided by faculty anesthesiologists involving a physician-in-training (resident).
Payment is 100% of the allowed amount. Modifier AA must not be billed in combination
with QX.
When supervising, the physician must use one of the modifiers below. Payment for these
modifiers is 50% of the allowed amount. Modifier QX must be billed by the Certified
Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA).
AD Medical supervision by a physician for more than four concurrent anesthesia services.
QK Medical direction of two, three, or four concurrent anesthesia procedures involving
qualified individuals.
QS Monitored anesthesia services.
To bill for monitored anesthesia care services, the following applies:
If the physician personally performs the case, modifier AA must be used and payment is
100% of the allowed amount.
If the physician directs four or fewer concurrent cases and monitored care represents two
or more of the case modifiers, modifier QK must be used and payment is 50% of the
allowed amount.
QS modifier must be used in the second modifier position in conjunction with a pricing
anesthesia modifier in the first modifier position.
QX CRNA service with medical direction by a physician should be used when under the
supervision of a physician. Payment is 50% of the allowed amount. This modifier is
payable in combination with Modifiers AD or QK, which is used by the supervising
anesthesiologist. Modifier QX must not be billed in combination with AA.
QY CRNA and anesthesiologist are involved in a single procedure and the physician is
performing the medical direction. The physician must use modifier QY and the medically
directed CRNA must use modifier QX. The anesthesiologist and CRNA each receive
50% of the allowance that would have been paid had the service been provided by the
anesthesiologist or CRNA alone.
QZ CRNA service without medical direction by a physician. Must be used when practicing
independently. Payment is 100% of the allowed amount. This modifier must not be
billed in combination with any other modifier.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
345
Site-of-Service
Payment Differential
How are fees established for professional services
performed in facility and nonfacility settings?
Based on the Resource Based Relative Value Scale (RBRVS) methodology, HCA's fee schedule
amounts are established using three relative value unit (RVU) components: work, practice
expense, and malpractice expense. HCA uses two levels of practice expense components to
determine the fee schedule amounts for reimbursing professional services. This may result in two
RBRVS maximum allowable fees for a procedure code. These are:
• Facility setting maximum allowable fees (FS Fee) - Paid when the provider performs
the services in a facility setting (e.g., a hospital or ambulatory surgery center) and the cost
of the resources are the responsibility of the facility.
• Nonfacility setting maximum allowable fees (NFS Fee) - Paid when the provider
performs the service in a nonfacility setting (e.g., office or clinic) and typically bears the
cost of resources, such as labor, medical supplies, and medical equipment associated with
the service performed.
Some services, by nature of their description, are performed only in certain settings and have
only one maximum allowable fee per code. Examples of these services include:
• Evaluation and management (E/M) codes which specify the site-of-service (SOS) within
the description of the procedure codes (e.g., initial hospital care)
• Major surgical procedures that are generally performed only in hospital settings
How does the SOS payment policy affect provider
payments?
Providers billing professional services are paid at one of two maximum allowable fees,
depending on where the service is performed.
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
346
Does HCA pay providers differently for services
performed in facility and nonfacility settings?
Yes. When a provider performs a professional service in a facility setting, HCA makes two
payments - one to the performing provider and another to the facility. The payment to the
provider (FS Fee) includes the provider’s professional services only. A separate payment is
made directly to the facility where the service took place, which includes payment for necessary
resources. The FS Fee excludes the allowance for resources that are included in the payment to
the facility. Paying the lower FS Fee to the performing provider when the facility is also paid
eliminates duplicate payment for resources.
When a provider performs a professional service in a nonfacility setting, HCA makes only one
payment to the performing provider. The payment to the provider (NFS Fee) includes the
provider’s professional services and payment for necessary resources.
When are professional services paid at the facility
setting maximum allowable fee?
Providers are paid at the FS Fee when HCA also makes a payment to a facility. In most cases,
HCA follows Medicare’s determination for using the FS Fee. Professional services billed with
the following place of service codes are paid at the FS Fee:
FACILITY SETTING
Place of
Service Code
Place of Service Description
06
Indian Health Service – provider based
08
Tribal 638 – provider based
19
Off Campus-Outpatient Hospital
21
Inpatient Hospital
22
Outpatient Hospital
23
Emergency Room – Hospital
24
Ambulatory Surgery Center
25
Birthing Center
26
Military Treatment Facility
31
Skilled Nursing Facility
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
347
FACILITY SETTING (cont.)
Place of
Service Code
Place of Service Description
34
Hospice
51
Inpatient Psychiatric Facility
52
Psychiatric Facility Partial Hospitalization
53
Community Mental Health Center
56
Psychiatric Residential Treatment Center
61
Comprehensive Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility
62
Comprehensive Outpatient Rehabilitation Facility
Note: All claims submitted to HCA must include the appropriate Medicare two-
digit place of service code. HCA will deny claims with single-digit place of
service codes.
Due to Medicare’s consolidated billing requirements, HCA does not make a separate payment to
providers who perform certain services in hospitals and skilled nursing facilities. The facilities
are paid at the NFS Fee. Some therapies, such as physical therapy services are always paid at the
NFS Fee.
When are professional services paid at the
nonfacility setting maximum allowable fee?
The NFS Fee is paid when HCA does not make a separate payment to a facility, such as when
services are performed in a provider’s office or a client’s home. In most cases, HCA follows
Medicare’s determination for using the NFS Fee.
Professional services billed with the following place of service codes are paid at the NFS Fee:
NONFACILITY SETTING
Place of
Service Code
Place of Service Description
04
Homeless Shelter
05
Indian Health – Free Standing
07
Tribal 638 – Free Standing
11
Office
12
Home
13
Assisted Living Facility
14
Group Home
15
Mobile Unit
20
Urgent Care Facility
32
Nursing Facility

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
348
NONFACILITY SETTING (cont.)
Place of
Service Code
Place of Service Description
33
Custodial Care Facility
49
Independent Clinic
50
Federally Qualified Health Center
54
Intermediate Care Facility
55
Residential Substance Abuse Treatment Facility
57
Nonresident Substance Abuse Treatment Facility
60
Mass Immunization Center
65
End-Stage Renal Disease Treatment Facility
71
State or Local Public Health Clinic
72
Rural Health Clinic
81
Independent Laboratory
99
Other Place of Service
Note: All claims submitted to HCA must include the appropriate Medicare two-
digit place of service code. HCA will deny claims with single-digit place of
service codes.
Which professional services have a SOS payment
differential?
Most of the services with an SOS payment differential are from the surgery, medicine, and E/M
ranges of CPT codes. However, some HCPCS, CPT radiology, pathology, and laboratory codes
also have an SOS payment differential.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
349
Fee Schedule Information
• Maximum allowable fees for all codes, including CPT® codes and selected HCPCS
codes, are listed in the fee schedule.
• In the fee schedule, HCA identifies procedure codes that may require prior authorization.
However, this list may not be all-inclusive. Prior authorization, limitations, or
requirements detailed in HCA billing guides and Washington Administrative Code
(WAC) remain applicable.
• HCA’s fee schedules are available for on HCA’s Professional billing guides and fee
schedules webpage and the Hospital reimbursement webpage.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
350
Billing
All claims must be submitted electronically to HCA, except under limited circumstances. For
more information, see HCA’s ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide webpage and scroll
down to Paperless billing at HCA.
For providers approved to bill paper claims, visit the same webpage and scroll down to Paper
Claim Billing Resource.
What are the general billing requirements?
Providers must follow HCA ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide.
These billing requirements include, but are not limited to:
• Time limits for submitting and resubmitting claims and adjustments.
• What fee to bill HCA for eligible clients.
• When providers may bill a client.
• How to bill for services provided to primary care case management (PCCM) clients.
• Billing for clients eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid.
• Third-party liability.
• Record keeping requirements.
Billing for multiple services
If multiples of the same procedures are performed on the same day, providers must bill with the
appropriate modifier (if applicable) and must bill all the services on the same claim to be
considered for payment.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
351
Billing for outpatient hospital services in hospital-based
clinics
HCA requires clinics to bill for outpatient services in one of the following ways:
• If the Department of Health (DOH) has not designated the clinic as a hospital-based
entity, the clinic must submit to HCA an electronic professional claim containing both:
The facility and the professional fees in the Submitted Charges field.
The place of service (POS) 11 (office setting) in the Place of Service field.
Medicare and Medicaid policy prohibit the hospital from billing a facility fee in this
circumstance. HCA will reimburse the clinic the nonfacility setting fee. This single claim
comprises the total payment for the services rendered
• If DOH has designated the clinic as a hospital-based entity, for HCA to reimburse the
clinic and the associated hospital for services provided to clients eligible for Washington
Apple Health (Medicaid), the following must happen:
The clinic must submit to HCA a professional electronic claim containing both:
The professional fees in the Submitted Charges field.
POS 22 (outpatient setting) in the Place of Service field.
The hospital must submit to HCA an electronic institutional claim with the facility
fees the Total Claim Charge field.
These two billings comprise the total payment for the services rendered.
In the circumstances described above, clinics must follow instructions in this billing guide
related to office setting and outpatient services.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
352
How do I resolve issues with gender indicator
when billing for transgender clients?
For gender to procedure mismatch: for transgender female with male
genitalia
For a transgender client, providers must include a secondary diagnosis on the claim that indicates
the client is transgender (F64.0, F64.1, F64.2 and F64.9). The secondary diagnosis may be in any
diagnosis field on the claim. Use of the secondary diagnosis allows the gender-specific
procedures to be processed through HCA’s claims system. Without the secondary diagnosis
code, the claim may be denied.
Example situation:
A client self-identifies as a female but still has male specific body parts. This
client then gets a routine prostate exam. This bill would deny for a male-only
procedure being billed on a female client. However, if a diagnosis such as gender
identity disorder was listed as the secondary diagnosis, the claim would then be
processed for payment.
Providers must list the secondary diagnosis (F64.0, F64.1, F64.2 and F64.9) on the claim in these
circumstances. If a claim is denied for a gender mismatch, see How does the provider notify
HCA of a date of birth or gender mismatch?
Note: Providers should encourage transgender clients to update their gender
listed on their Washington Apple Health account by contacting HCA’s Medical
Eligibility Determination Services (MEDS) toll free 855-623-9357.
ProviderOne gender indicator does not match claim gender indicator
Such as when a client presents as a female but ProviderOne has the male gender indicator in file.
The provider should check the client’s gender in ProviderOne when verifying coverage. If a
mismatch is found, the provider should encourage the client to update the gender field to their
preferred gender. The client can do this by calling HCA’s Medical Eligibility Determination
Section toll-free 1-855-623-9357.
How does the provider notify HCA of a date of birth or gender mismatch?
If a provider finds that there is a discrepancy with a client’s date of birth or gender, send a
secured email to mmi[email protected].gov. Include the following information in the email:
• TCN #
• A comment that the client is transgender
• ProviderOne client ID
Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
353
• Client’s name
• Date of birth
• Gender at birth
• Gender identified as at the time service provided
How does a client update their gender field?
• Clients who applied through the Healthplanfinder must call HCA’s Medical Eligibility
Determination Section toll free 1-855-623-9357.
• Clients who applied through the Community Service Office (CSO) must call toll-free
1-877-501-2233 or report online at Washington Connection.
Any Washington Apple Health client can call and choose a gender. Clients should be aware other
state agencies, such as the Department of Licensing, have different requirements.
How does a client update or change their name?
Before making a name change, the client should first obtain a name change with Social Security.
If the client’s name does not match the client’s name in Social Security, the system will generate
an error and this could affect the client’s coverage.
• Clients who applied through the Healthplanfinder must call toll-free 1-855-623-9357.
• Clients who applied through the Community Service Office (CSO) must call toll-free
1-877-501-2233 or report online at Washington Connection.
If providers have any concerns or question regarding the policy with this benefit, please contact
HCA by email at tra[email protected].
How do I bill claims electronically?
Instructions on how to bill Direct Data Entry (DDE) claims can be found on HCA’s Billers,
providers, and partners webpage.
For information about billing Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) claims, see the ProviderOne 5010 companion guides on the
HIPAA Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) webpage.

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
354
Submitting professional services for Medicare crossovers
For services paid for, and/or applied to the deductible, by Medicare:
• Medicare should forward the claim to HCA. If the claim is not received by HCA, please
resolve that issue prior to resubmitting the claim.
• Mark “Yes” for the question, “Is this a Medicare Crossover Claim?” in the electronic
claim.
• See the ProviderOne Billing and Resource Guide and the Fact Sheets webpage to get
more information about submitting Medicare payment information electronically and to
find out when paper backup must be attached.
• Do not indicate any payment made by Medicare in the Other Payer Information section of
the clam. Enter only payments made by non-Medicare, third-party payers (e.g., Blue
Cross) in this section and attach the Explanation of Benefits (EOB).
Note: If Medicare allowed/paid on some services and denied other services, the
allowed/paid services must be billed on a different claim than the denied services.
Exception: When billing crossover claims for Indian Health Services, follow the
instructions in HCA’s Tribal Health Program Billing Guide.
Requirements for the provider-generated EOMB to process a crossover claim
Header level information on the EOMB must include all the following:
• Medicare as the clearly identified payer
• The Medicare claim paid or process date
• The client’s name (if not in the column level)
• Medicare Reason codes
• Text in font size 12 or greater
Column level labels on the EOMB for the CMS-1500 claim form (version 02/12) must
include all the following:
• The client’s name
• Date of service
• Number of service units (whole number) (NOS)
• Procedure Code (PROC)
• Modifiers (MODS)
• Billed amount
• Allowed amount
• Deductible

Physician-Related Services/Health Care Professional Services
CPT
® codes and descriptions only are copyright 2019 American Medical Association
355
• Amount paid by Medicare (PROV PD)
• Medicare Adjustment Reason codes and Remark codes
• Text that is font size 12
Utilization review
Utilization Review (UR) is a concurrent, prospective, and/or retrospective (including post-pay and
pre-pay) formal evaluation of a client’s documented medical care to assure that the health care
services provided are proper and necessary and are of good quality. The review considers the
appropriateness of the place of care, level of care, and the duration, frequency, or quantity of health
care services provided in relation to the condition(s) being treated.
HCA uses InterQual: Evidence-Based Clinical Criteria as a guideline in the utilization review
process.
• Concurrent UR is performed during a client’s course of care.
• Prospective UR is performed prior to the provision of health care services.
• Retrospective UR is performed following the provision of health care services and includes
both post-payment and pre-payment review.
• Post-payment retrospective UR is performed after health care services are provided and paid.
• Pre-payment retrospective UR is performed after health care services are provided but prior
to payment.
